Improving Biomethanation of Chicken Manure by Co-Digestion with Ethanol Plant Effluent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Inoculum
2.2. Reactor Start-Up and Operation
2.3. Specific Methanogenic Activity Test
2.4. Analytical Methods
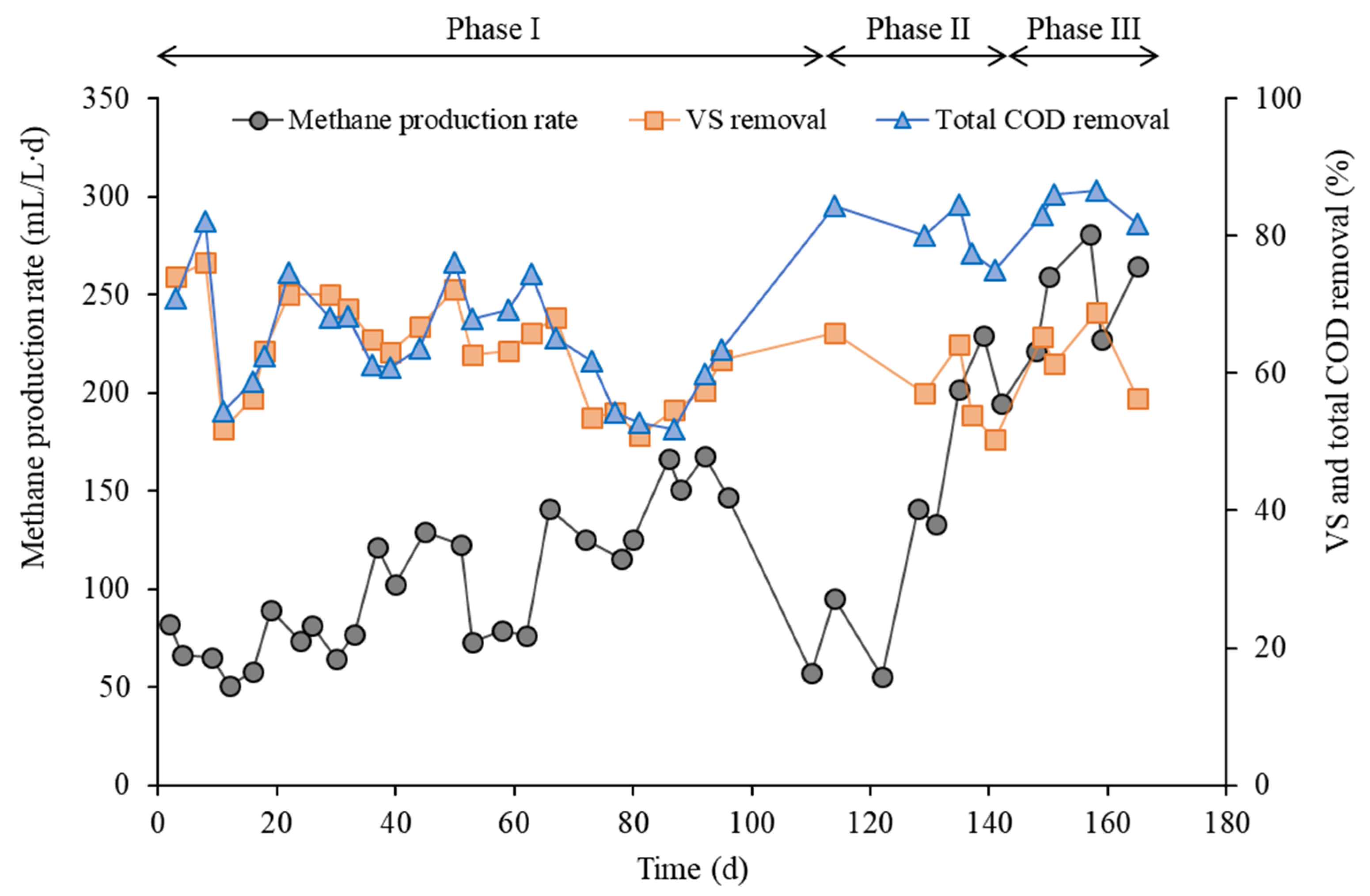
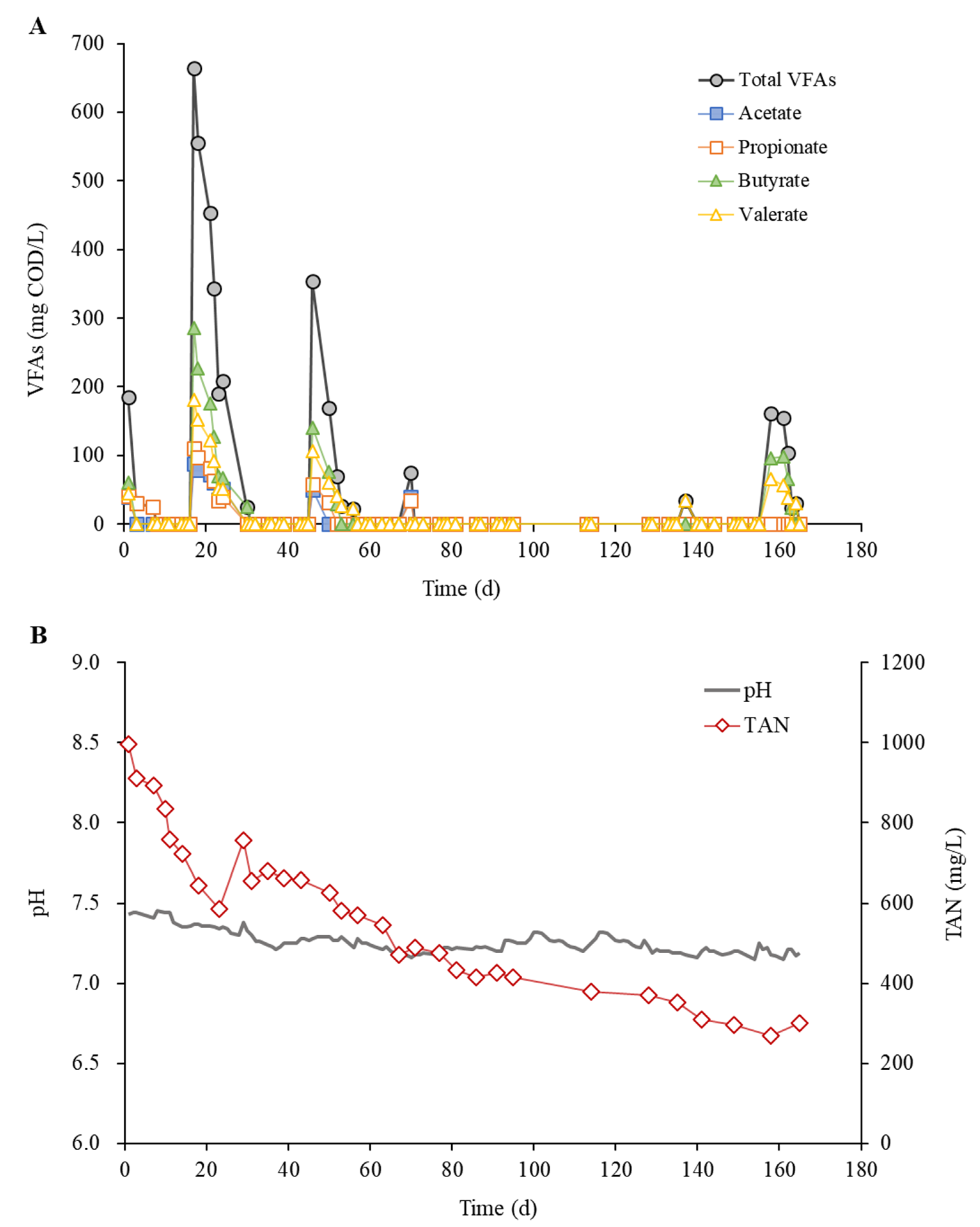
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakar, S.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Kocak, E. Anaerobic digestion technology in poultry and livestock waste treatment—A literature review. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Pei, M.; Qiu, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qiang, H. Performance of anaerobic digestion of chicken manure under gradually elevated organic loading rates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2239. [Google Scholar]
- Bolan, N.S.; Szogi, A.A.; Chuasavathi, T.; Seshadri, B.; Rothrock, M.J.; Panneerselvam, P. Uses and management of poultry litter. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2010, 66, 673–698. [Google Scholar]
- Billen, P.; Costa, J.; Van der Aa, L.; Van Caneghem, J.; Vandecasteele, C. Electricity from poultry manure: A cleaner alternative to direct land application. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 96, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Mamphweli, S.N.; Meyer, E.L.; Okoh, A.I.; Makaka, G.; Simon, M. Microbial anaerobic digestion (bio-digesters) as an approach to the decontamination of animal wastes in pollution control and the generation of renewable energy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4390–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Massé, D.I. Start-up of dry anaerobic digestion system for processing solid poultry litter using adapted liquid inoculum. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Ran, X.; Li, R.; Kougias, P.G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Liu, H. Performance evaluation of mesophilic anaerobic digestion of chicken manure with algal digestate. Energies 2018, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioro, V.; Steinmetz, R.L.R.; do Amaral, A.C.; Gaspareto, T.C.; Treichel, H.; Kunz, A. Poultry litter solid state anaerobic digestion: Effect of digestate recirculation intervals and substrate/inoculum ratios on process efficiency. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Molaey, R.; Bayrakdar, A.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Çalli, B. Anaerobic digestion of chicken manure: Mitigating process inhibition at high ammonia concentrations by selenium supplementation. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speece, R.E. Anaerobic Biotechnology for Industrial Wastewaters; Archae Press: Nashville, TN, USA, 1996; p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Fonoll, X.; Astals, S.; Dosta, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and fruit wastes: Evaluation of the transitory states when the co-substrate is changed. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Frunzo, L.; Giordano, A.; Liotta, F.; Panico, A.; Pirozzi, F. Anaerobic co-digestion of organic wastes. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J.; Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Fonoll, X.; Peces, M.; Astals, S. A critical review on anaerobic co-digestion achievements between 2010 and 2013. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Higgins, M.J.; Bustamante, H.; Galway, B.; Nghiem, L.D. Current status and perspectives on anaerobic co-digestion and associated downstream processes. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Koch, K.; Bolzonella, D.; Drewes, J.E. Full scale co-digestion of wastewater sludge and food waste: Bottlenecks and possibilities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.J.; Milligan, E.; Carver, J.; Roy, E.D. Integrating anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure and food waste with cultivation of edible mushrooms for nutrient recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Energy production from different organic wastes by anaerobic co-digestion: Maximizing methane yield versus maximizing synergistic effect. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Biogas production from co-digestion of corn stover and chicken manure under anaerobic wet, hemi-solid, and solid state conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cao, W.; Banks, C.J.; Heaven, S.; Liu, R. Biogas production from undiluted chicken manure and maize silage: A study of ammonia inhibition in high solids anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Umar, M.; Ding, W.; Mehryar, E.; Zhao, C. Methane enhancement through co-digestion of chicken manure and oxidative cleaved wheat straw: Stability performance and kinetic modeling perspectives. Energy 2017, 141, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, R.; Cui, S.; Yu, Q.; Ma, R. Anaerobic co-digestion of animal manures with corn stover or apple pulp for enhanced biogas production. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Li, P.; Yin, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zheng, G. A novel alternate feeding mode for semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with chicken manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelegenis, J.; Georgakakis, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Mavris, V. Optimization of biogas production by co-digesting whey with diluted poultry manure. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, D.P.; Hirl, P.J.; Belia, E. Methane production from ethanol co-products in anaerobic SBRs. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, W.; Magnus, B.S.; Guimarães, L.B.; Gottardo, M.; Belli Filho, P. Feasibility of thermophilic anaerobic processes for treating waste activated sludge under low HRT and intermittent mixing. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 201, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.; Méndez, R.; Lema, J. Methanogenic and non-methanogenic activity tests. Theoretical basis and experimental set up. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1361–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.; Jacobi, H.F.; Strach, K.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Liebetrau, J. Mono-fermentation of chicken manure: Ammonia inhibition and recirculation of the digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachaiyasit, S.; Stuckey, D.C. The effect of shock loads on the performance of an anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR). 2. Step and transient hydraulic shocks at constant feed strength. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, D.-Y.; Hansen, C.L. Effect of feeding strategy on the stability of anaerobic sequencing batch reactor responses to organic loading conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5058–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Qiao, W.; Qiang, H.; Hojo, T.; Li, Y.-Y. Mesophilic methane fermentation of chicken manure at a wide range of ammonia concentration: Stability, inhibition and recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, J.; Hwang, K.; Lee, C. A comparative study of single- and two-phase anaerobic digestion of food waste under uncontrolled pH conditions. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.B.; Uellendahl, H.; Ahring, B.K. Regulation and optimization of the biogas process: Propionate as a key parameter. Biomass Bioenergy 2007, 31, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Chicken Manure | BPE a |
|---|---|---|
| Total solids (g/L) | 13.2–28.9 | 26.4 |
| Volatile solids (g/L) | 5.5–9.1 | 7.5 |
| Total carbon (g/L) | 39 (<1.0) b | − c |
| Total nitrogen (g/L) | 4 (<1.0) | − |
| C/N ratio | 9.75 (<1.0) | − |
| pH | 6.9–7.4 | 5.3–5.4 |
| Total chemical oxygen demand (g/L) | 8.7–13.0 | 111.8 |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand (g/L) | 3.2–9.7 | 110.3 |
| Total ammonia nitrogen (mg/L) | 150–360 | − |
| Total volatile fatty acids (mg COD/L) | 100–500 | 2541 |
| Acetate (mg/L) | 60–300 | 2264 |
| Propionate (mg/L) | 25–140 | 30 |
| n-Butyrate (mg/L) | 20–50 | 40 |
| n-Valerate (mg/L) | 20–60 | not detected |
| Lactate (mg/L) | 3–20 | 184 |
| Phosphorous (mg/L) | 81 (<1.0) | − |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 206 (<1.0) | − |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 547 (<1.0) | − |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 271 (<1.0) | − |
| Parameter a | Mono-Digestion | Co-Digestion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I | Phase II | Phase III | |
| Period (d) | 0–112 | 112–143 | 143–165 |
| CM feeding rate (L/d) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| BPE feeding rate (L/d) | – b | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| CM feeding frequency (times/d) | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| BPE feeding frequency (times/d) | – | 2 | 2 |
| Hydraulic retention time (d) | 19.5 | 17.7 | 16.3 |
| Organic loading rate (g tCOD/L/d) | 0.65 | 1.13 | 1.80 |
| Organic loading rate (g VS/L/d) | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.47 |
| Parameter | Mono-Digestion | Co-Digestion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I | Phase II | Phase III | |
| Data acquisition period (d) | 88–96 | 135–142 | 157–165 |
| Total COD removal (%) | 54.4 | 79.0 | 83.2 |
| Volatile solids removal (%) | 58.0 | 56.2 | 61.5 |
| Methane production rate (mL/L/d) | 155 | 208 | 258 |
| Methane yield (mL/g VS fed) | 396 | 478 | 540 |
| Methane yield (mL/g VS removed) | 672 | 821 | 958 |
| Substrate a | Mono-Digestion Sludge (Phase I) | Co-Digestion Sludge (Phase III) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rm b (mL/d) | SMA c (mL/g VS/d) | Rm (mL/d) | SMA (mL/g VS/d) | |
| Glucose | 4.20 | 2.17 | 5.17 | 3.66 |
| HAc | 8.18 | 4.23 | 7.44 | 5.27 |
| HPr | 8.16 | 4.22 | 8.72 | 6.18 |
| HBu | 6.98 | 3.61 | 7.56 | 5.35 |
| HAc:HPr (2:1) | 6.72 | 3.48 | 8.09 | 5.73 |
| HAc:HPr:HBu (2:1:1) | 7.49 | 3.88 | 7.85 | 5.56 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheong, D.-Y.; Harvey, J.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Improving Biomethanation of Chicken Manure by Co-Digestion with Ethanol Plant Effluent. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245023
Cheong D-Y, Harvey JT, Kim J, Lee C. Improving Biomethanation of Chicken Manure by Co-Digestion with Ethanol Plant Effluent. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(24):5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245023
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheong, Dae-Yeol, Jeffrey Todd Harvey, Jinsu Kim, and Changsoo Lee. 2019. "Improving Biomethanation of Chicken Manure by Co-Digestion with Ethanol Plant Effluent" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 24: 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245023
APA StyleCheong, D.-Y., Harvey, J. T., Kim, J., & Lee, C. (2019). Improving Biomethanation of Chicken Manure by Co-Digestion with Ethanol Plant Effluent. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(24), 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245023





