Comparison between the Physiological Responses and Subjective Ratings of a Group of Male Students to Three Backpack Designs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
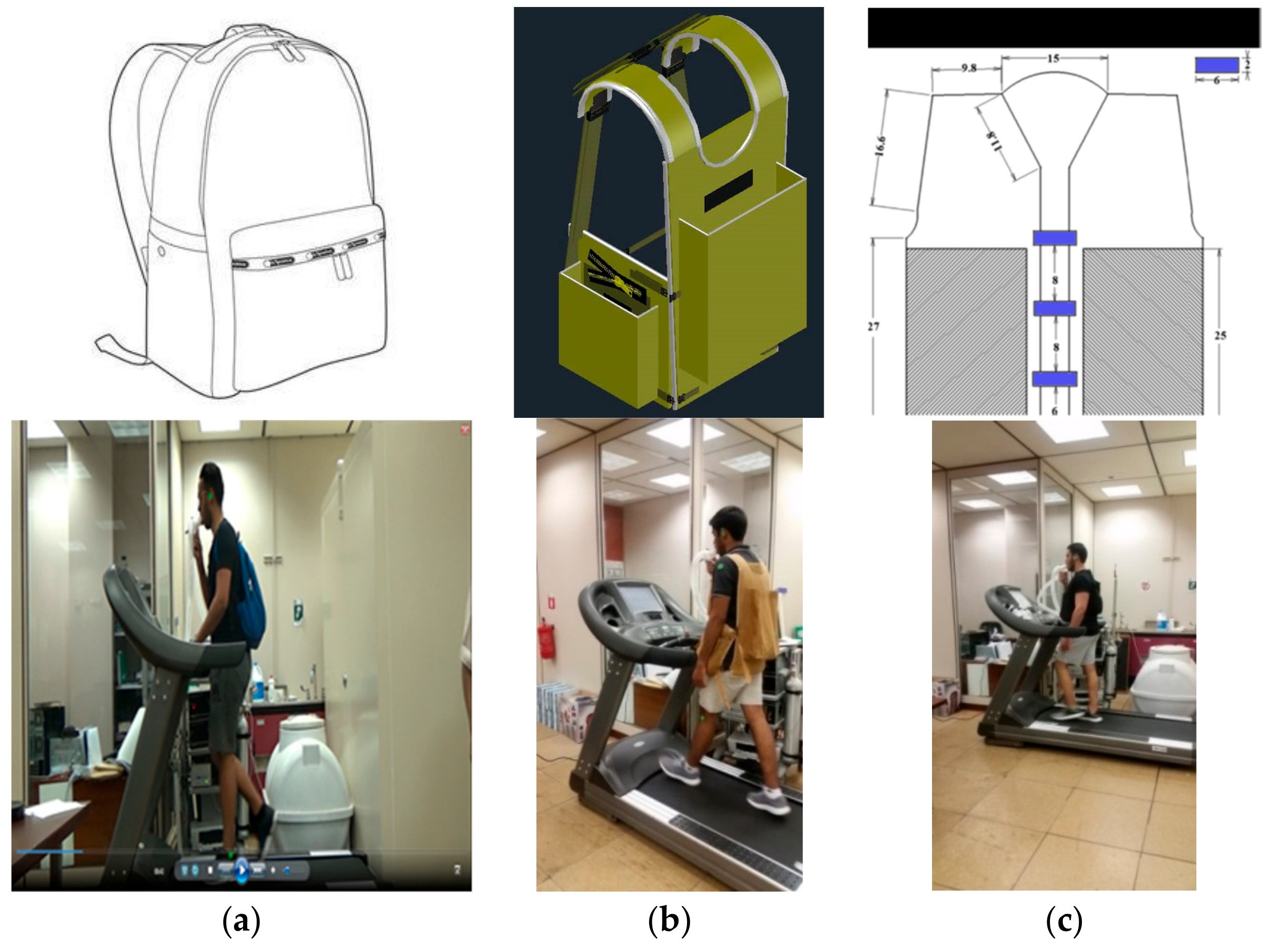
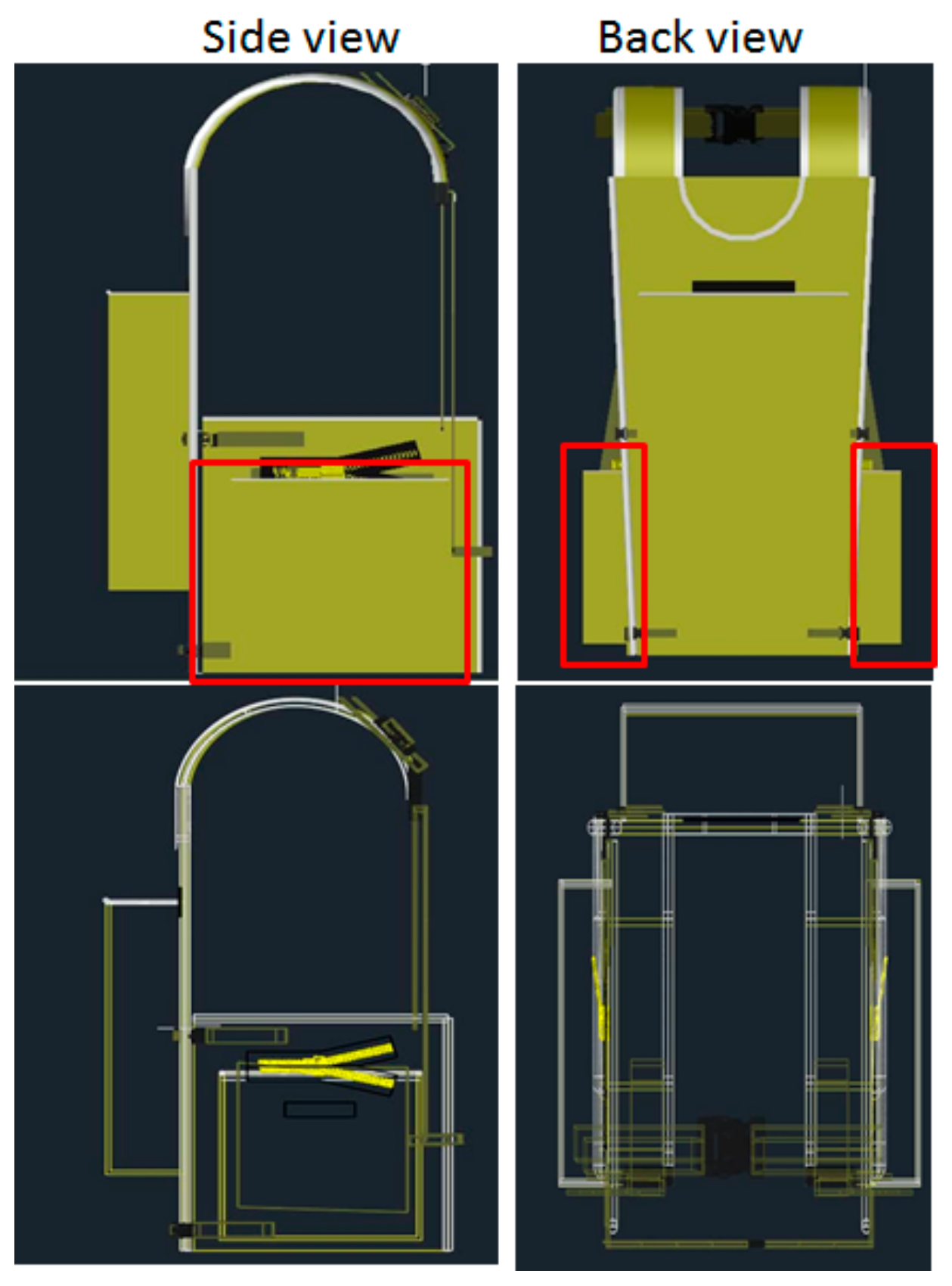
2.2. Backpacks
2.3. Equipment
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Experimental Protocol
3. Results
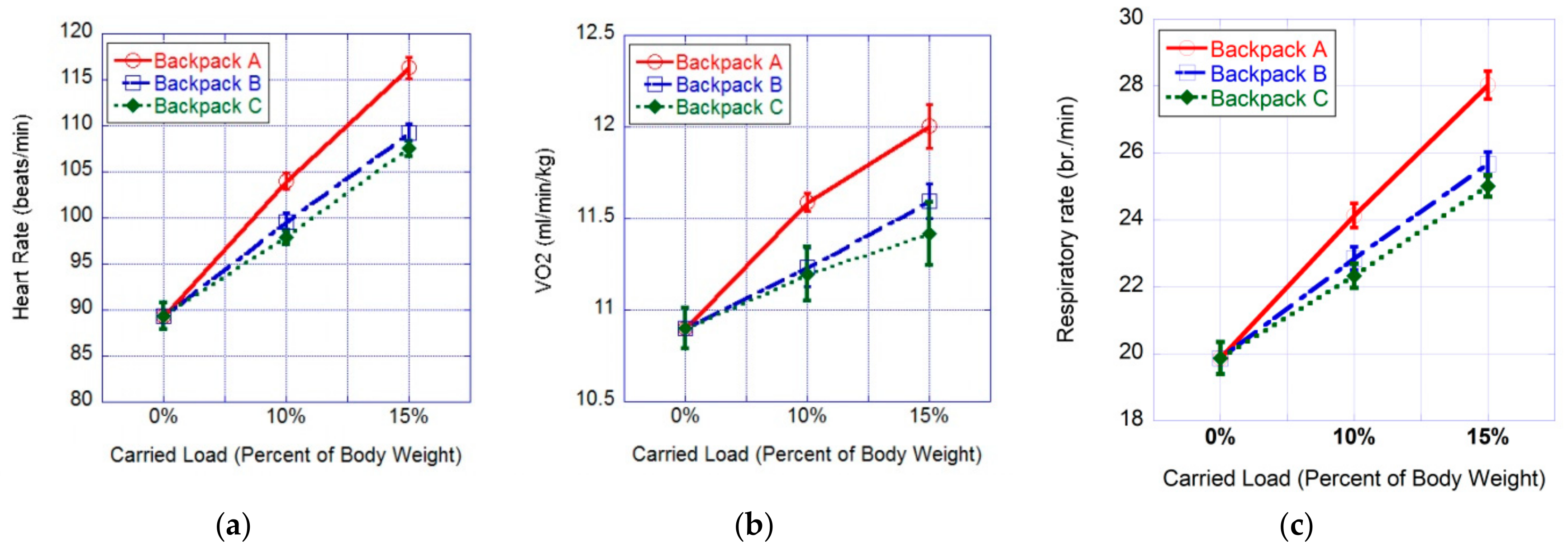
3.1. Heart Rate
3.2. VO2·kg−1
3.3. Respiratory Rate
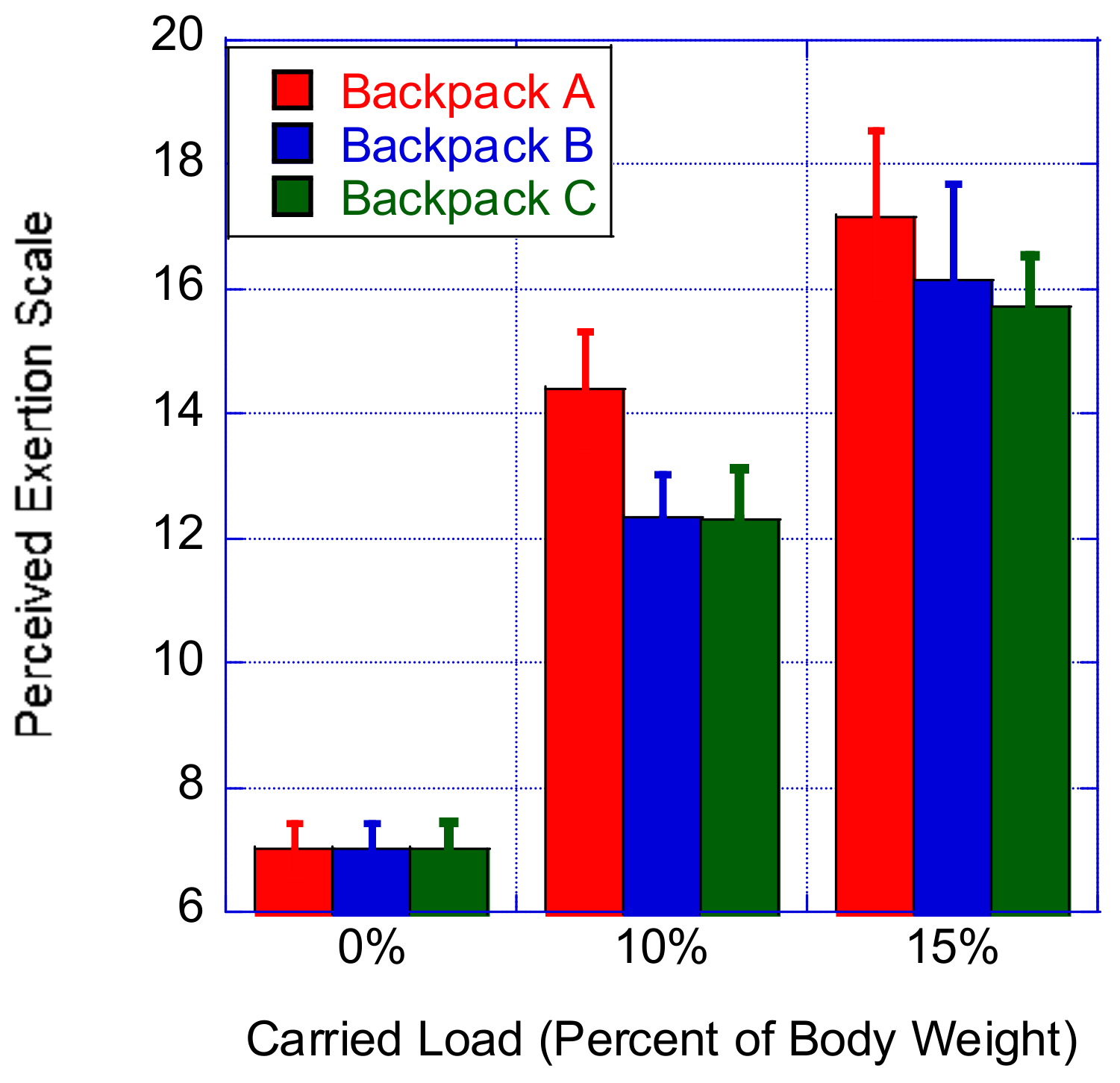
3.4. Perceived Exertion Rating
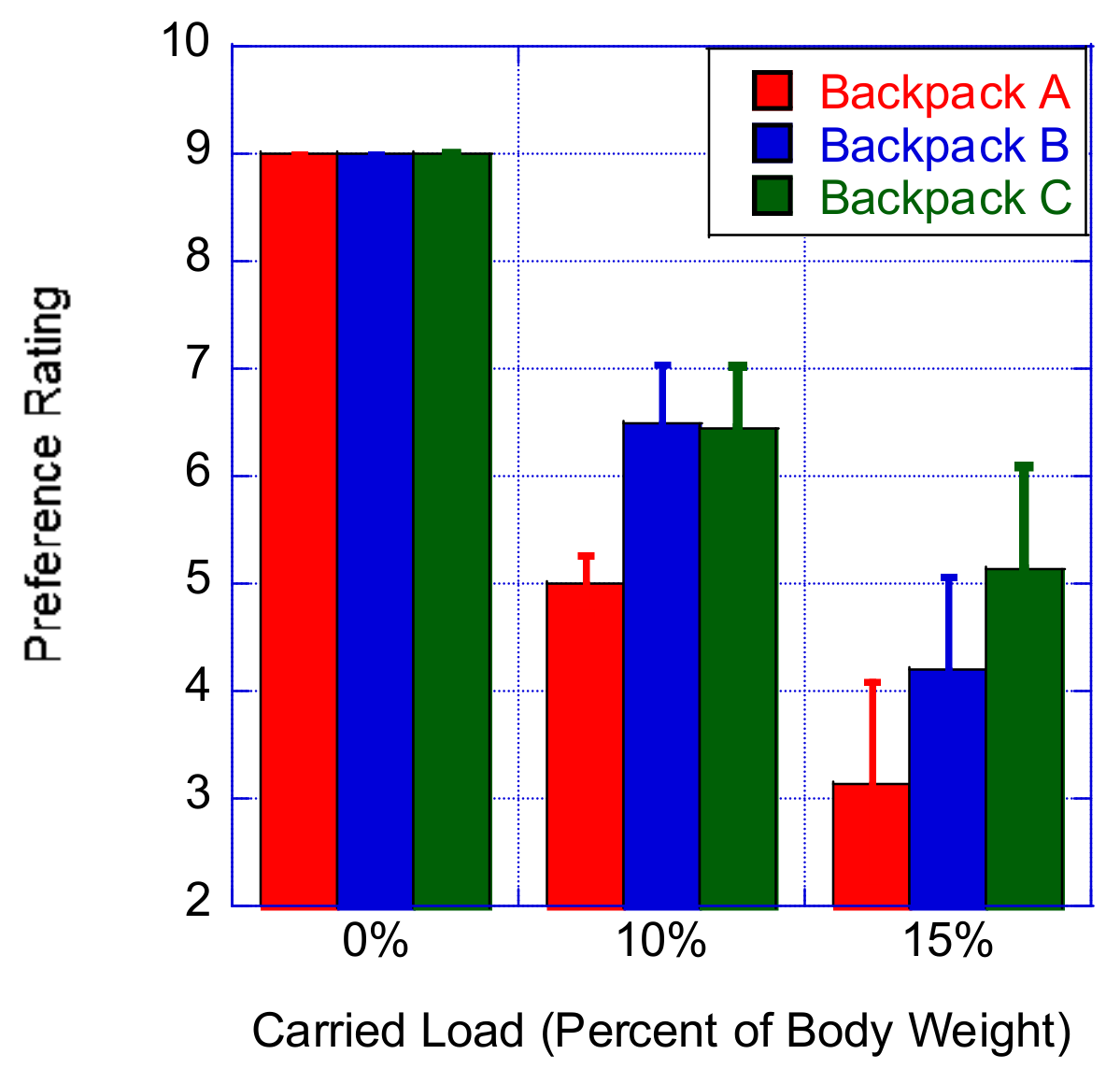
3.5. Backpack Preference Rating
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiat, W.Y.; Abidin, E.Z.; Rasdi, I.; Ismail, N.H. Association between schoolbag weight with back pain and perceived load among primary schoolchildren in Selangor. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 6, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, R.B.; Coelho-e-Silva, M.J.; Sousa, N.F.; Valente-dos-Santosa, J.; Machado-Rodrigues, A.M.; Cumming, S.P.; Lima, A.V.; Gonalves, R.S.; Martins, R.A. Quality of life, school backpack weight, and nonspecific low back pain in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2015, 91, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.E.; Shrier, I.; Rossignol, M.; Abenhaim, L. Risk factors for the development of low back pain in adolescence. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 154, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, L.J.; Frasure, H.E.; White, P.; White, B.; White, M.J. Weight of backpacks carried by elementary school children: Students or sherpas? Acad. Emerg. Med. 2000, 7, 1168. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Soto, A.E.; Jaworski, R.; Jensen, A.; Niederberger, B.; Hargens, A.R.; Frank, L.R.; Kelly, K.R.; Ward, S.R. Effect of load carriage on lumbar spine kinematics. Spine 2013, 38, E783–E791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.D.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Jones, G.T.; Taylor, S.; Symmons, D.P.; Silman, A.J.; Macfarlane, G.J. Low back pain in schoolchildren: Occurrence and characteristics. Pain 2002, 97, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Neuschwander, T.B.; Macias, B.R.; Bachman, L.; Hargens, A.R. Upper extremity hemodynamics and sensation with backpack loads. Appl. Ergon. 2014, 45, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, H. Effects of Educational Efficiency on National Competitiveness Based on Cross-National Data. Educ. Sci. 2017, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, L.J.; Milanese, S.F.; Grimmer-Somers, K.A. Epidemiology of adolescent spinal pain: A systematic overview of the research literature. Spine 2007, 32, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, F.; Dudler, J.; Nordin, M. Low-back pain in children. Lancet 2003, 361, 1403–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, A.J.; Rohani, J.M.; MatRebi, A.R. Back pain arising from schoolbag usage among primary schoolchildren. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2014, 44, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, A.J.F.; Silva, J.C.P.; Paschoarelli, L.C.; Fuji, J.B. Backpacks and school children’s obesity: Challenges for public health and ergonomics. Work 2012, 41 (Suppl. 1), 900–906. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, M.Z.; Al-Shayea, A.M. A modified backpack design for male school children. Int. J. Indus. Ergon. 2013, 43, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, B.R.; Murthy, G.; Chambers, H.; Hargens, A.R. High contact pressure beneath backpack straps of children contributes to pain. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2005, 159, 1186–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, B.R.; Murthy, G.; Chambers, H.; Hargens, A.R. Asymmetric loads and pain associated with backpack carrying by children. J. Pediatr. Orthoped. 2008, 28, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, J.P.; Ramstad, R.; Mattila, V.; Pihlajamaki, H. Brachial plexus lesions after backpack carriage in young adults. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 452, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, D.H.; Kwok, M.L.; Au-Yang, A.C.; Holmes, A.D.; Cheng, J.C.; Yao, F.Y.; Wong, M.S. The effect of backpack load on the gait of normal adolescent girls. Ergonomics 2005, 48, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Li, J.X.; Fong, D.T.P. Effect of prolonged walking with backpack loads on trunk muscle activity and fatigue in children. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rahman, S.A.S.; Rambely, A.S.; Ahmad, R.R. Preliminary studies on the effects of varying backpack loads on trunk inclination during level walking. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 28, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Safikhani, H.; Fadilah, T.; Kamalden, T.; Amri, S.B.; Ahmad, M. The effect of different backpack loading systems on trunk forward lean angle during walking among college students. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2012, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshmandi, H.; Rahmani-Nia, F.; Hosseini, S.H. Effect of carrying school backpacks on cardio-respiratory changes in adolescent students. Sport Sci. Health 2008, 4, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander, T.; Cutrone, B.M.; Cutrone, S.; Murthy, G.; Chambers, H.; Hargens, A. Typical school backpack loads significantly compress lumbar discs in children. Proceedings of the NASS 23rd Annual Meeting. Spine 2008, 8, S69. [Google Scholar]
- Pau, M.; Corona, F.; Leban, B.; Pau, M. Effects of backpack carriage on foot ground relationship in children during upright stance. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proffitt, D.R.; Stefanucci, J.; Banton, T.; Epstein, W. The role of effort in perceiving distance. Psycholog. Sci. 2003, 14, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pau, M.; Mandaresu, S.; Leban, B.; Nussbaum, M.A. Short-term effects of backpack carriage on plantar pressure and gait in schoolchildren. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 25, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, S.; Rebai, H.; Ghroubi, S.; Yahia, A.; Guermazi, M.; Elleuch, M.H. The effects of backpack load and carrying method on the balance of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjects. Spine 2013, 13, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K. An ergonomics evaluation of the vibration backpack harness system in walking. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2014, 44, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southard, S.A.; Mirka, G.A. An evaluation of backpack harness systems in non-natural torso postures. Appl. Ergon. 2007, 38, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafiandra, M.; Harman, E. The distribution of forces between the upper and lower back during load carriage. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holewijn, M. Physiological strain due to load carrying. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occupat. Physiol. 1990, 61, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.; Stevenson, J.; Whiteside, R. Biomechanical assessment of lateral stiffness elements in the suspension system of a backpack. Ergonomics 2004, 47, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, K.D.; Wang, H.; Popp, J.K.; Dickin, D.C. Load distribution and postural changes in young adults when wearing a traditional backpack versus the BackTpack. Gait Posture 2016, 45, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OAC297-OLYMPIA Treadmill. Available online: http://www.olympiafitnessplanet.com/commercial-treadmill.html (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Borg, G. Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1970, 2, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stamford, B.A. Validity and Reliability of Subjective Ratings of Perceived Exertion during Work. Ergonomics 1976, 191, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, J.E.; Roemmich, J.N. Validity of a pediatric RPE scale when different exercise intensities are completed on separate days. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2011, 9, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, T.A.; Bishop, N.C.; Leicht, C.A.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Perceived Exertion as a Tool to Self-Regulate Exercise in Individuals with Tetraplegia. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, L.B.; Pender, N.J.; Ronis, D.L.; Kazanis, A.S.; Pis, M.B. Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy, and Perceived Exertion among Adolescents. Res. Nurs. Health 2004, 27, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.Z.; Alkahtani, M. Development of a device to reduce the risk of injury in handling unstable loads. Work 2017, 58, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.B.; Ehnes, C.M.; Stickland, M.K.; Petersen, S.R. Ventilatory responses in males and females during graded exercise with and without thoracic load carriage. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.N.; Barbosa, T.M. The effects of backpack carriage on gait kinematics and kinetics of schoolchildren. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, S.J.; Perko, L.; Campbell, P. Subjective perceptual methods for comparing backpacks. Ergonomics 1997, 40, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legg, S.; Cruz, C.; Chaikumarn, M.; Kumar, R. Efficacy of Subjective Perceptual Methods in Comparing Between Single and Double Strap Student Backpack. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Cyberspace Conference on Ergonomics, Lulea, Sweden, September–October 2002; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Yang, L. Influence of the Increasing Weight of the Backpack on the Balance of Movement to Primary School Students. Rev. Piel. Incaltaminte 2018, 18, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable of Interest | Min | Mean | Max | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 20 | 25.9 | 30 | 2.69 |
| Body mass (kg) | 62 | 75.1 | 94 | 8.35 |
| Height (m) | 1.56 | 1.68 | 1.80 | 0.05 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 18.4 | 25.1 | 32.53 | 3.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramadan, M.Z.; Al-Tayyar, S.N. Comparison between the Physiological Responses and Subjective Ratings of a Group of Male Students to Three Backpack Designs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214104
Ramadan MZ, Al-Tayyar SN. Comparison between the Physiological Responses and Subjective Ratings of a Group of Male Students to Three Backpack Designs. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(21):4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214104
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadan, Mohamed Z., and Sultan N. Al-Tayyar. 2019. "Comparison between the Physiological Responses and Subjective Ratings of a Group of Male Students to Three Backpack Designs" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 21: 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214104
APA StyleRamadan, M. Z., & Al-Tayyar, S. N. (2019). Comparison between the Physiological Responses and Subjective Ratings of a Group of Male Students to Three Backpack Designs. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(21), 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214104





