Hyperhidrosis, Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy, and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Cohort Study Based on the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
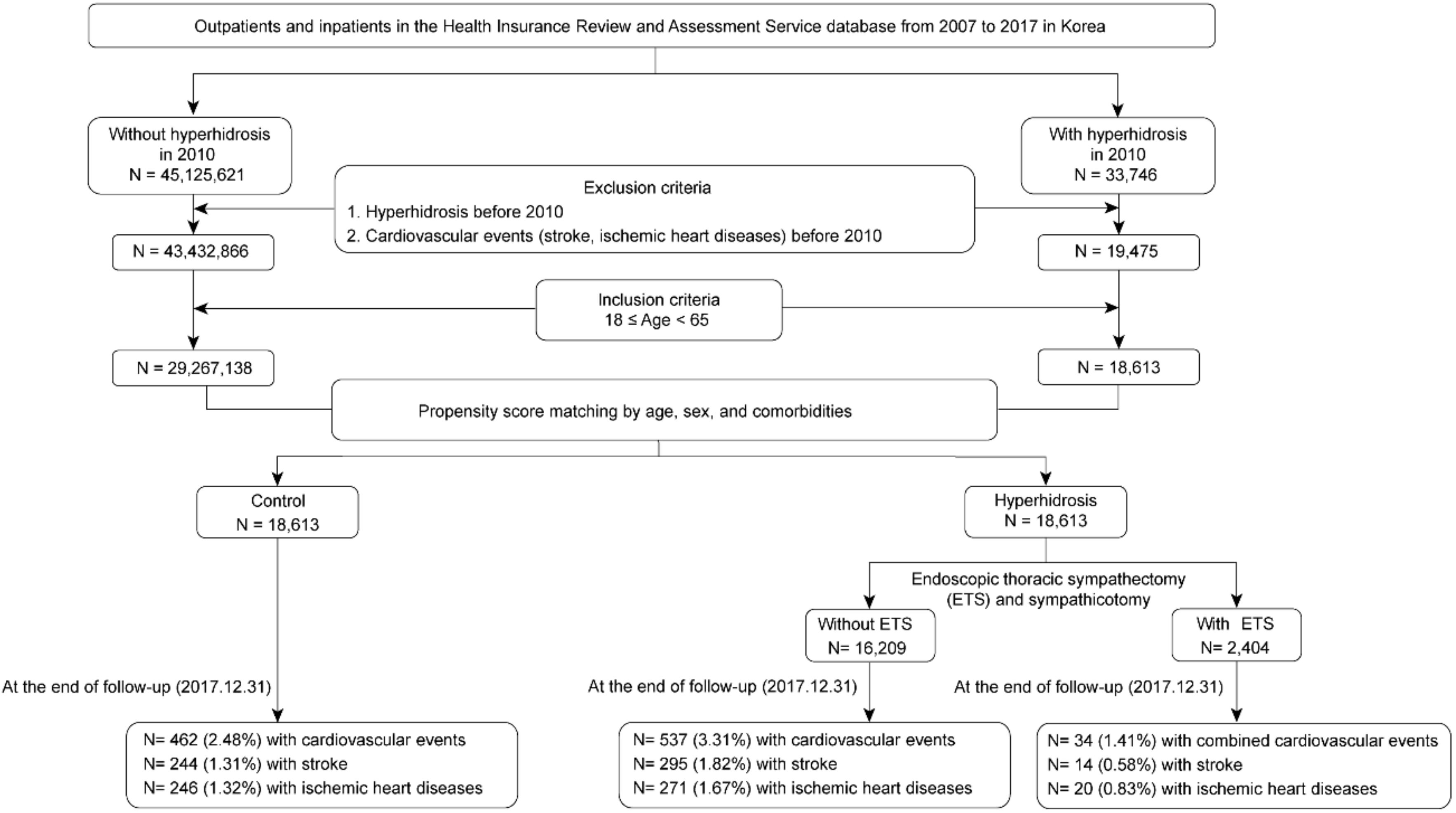
2.2. Study Population and Design
2.3. Statistical Analyses
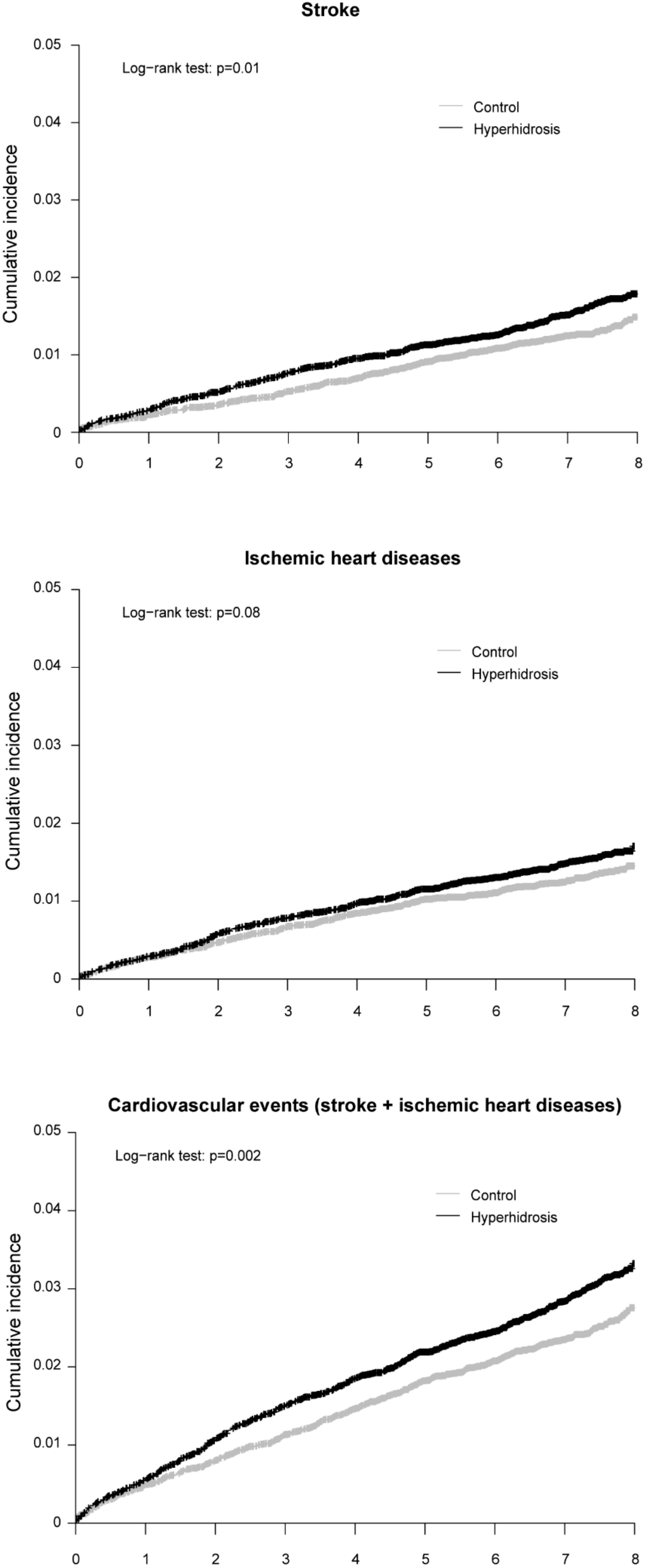
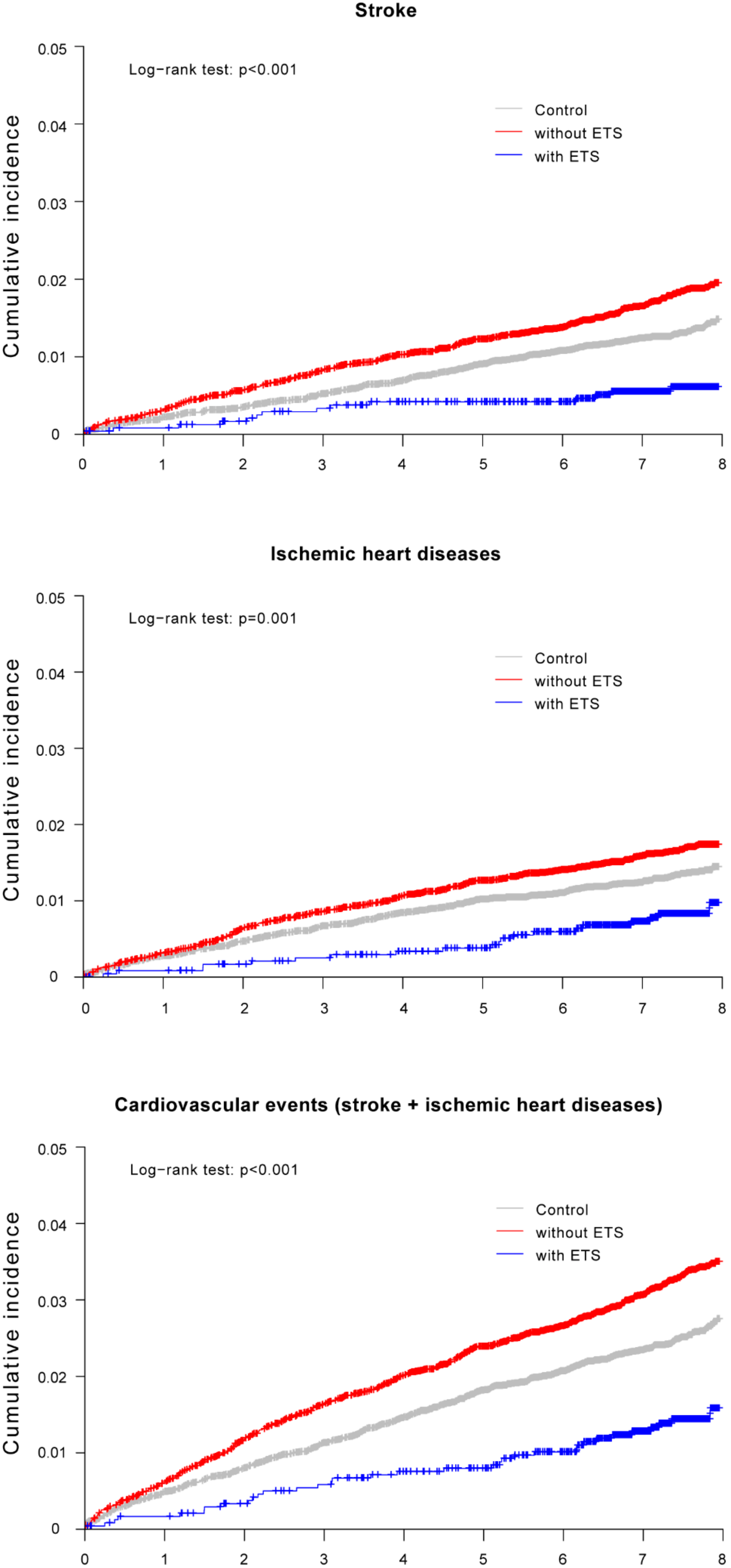
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worle, B.; Rapprich, S.; Heckmann, M. Definition and treatment of primary hyperhidrosis. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2007, 5, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strutton, D.R.; Kowalski, J.W.; Glaser, D.A.; Stang, P.E. US prevalence of hyperhidrosis and impact on individuals with axillary hyperhidrosis: Results from a national survey. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohn, D.F.; Zraik, O. Essential hyperhidrosis—Pathogenesis and treatment. Report of seven cases treated by upper thoracic sympathectomy. Clevel. Clin. Q. 1969, 36, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solish, N.; Bertucci, V.; Dansereau, A.; Hong, H.C.; Lynde, C.; Lupin, M.; Smith, K.C.; Storwick, G.; Canadian Hyperhidrosis Advisory Committee. A comprehensive approach to the recognition, diagnosis, and severity-based treatment of focal hyperhidrosis: Recommendations of the Canadian Hyperhidrosis Advisory Committee. Dermatol. Surg. 2007, 33, 908–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solish, N.; Wang, R.; Murray, C.A. Evaluating the patient presenting with hyperhidrosis. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2008, 18, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaa, A.; Mundal, H.H.; Eide, I.; Kjeldsen, S.; Rostrup, M. Sympathetic activity and cardiovascular risk factors in young men in the low, normal, and high blood pressure ranges. Hypertension 2006, 47, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Lachowska, K.; Schlaich, M. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in stress-mediated cardiovascular disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2015, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpas, S.C. Sympathetic nervous system overactivity and its role in the development of cardiovascular disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 513–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, N.; Teschemacher, A.G.; Kasparov, S.; Gourine, A.V. Glia, sympathetic activity and cardiovascular disease. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.P.; Fadel, P.J. Therapeutic strategies for targeting excessive central sympathetic activation in human hypertension. Exp. Physiol. 2010, 95, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.J.; Poulimenos, L.E.; Kallistratos, M.S.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Sympathetic overactivity in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Esler, M.D.; Jennings, G.L.; Kaye, D.M. Effect of cardiac sympathetic nervous activity on mode of death in congestive heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, D.M.; Lefkovits, J.; Jennings, G.L.; Bergin, P.; Broughton, A.; Esler, M.D. Adverse consequences of high sympathetic nervous activity in the failing human heart. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1995, 26, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, A.; Kordzadeh, A.; Lee, G.H.; Harvey, M. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis: A 16-year follow up in a single UK centre. Surgeon 2013, 11, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraites, E.; Vaughn, O.A.; Hill, S. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. Dermatol. Clin. 2014, 32, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Nagata, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kida, H.; Matsumoto, Y. Effects of endoscopic transthoracic sympathicotomy on hemodynamic and neurohumoral responses to exercise in humans. Circ. J. 2002, 66, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.A.; Cheng, C.G.; Chu, H.; Lin, H.C.; Chung, C.H.; Chiu, H.W.; Chien, W.C. Risk reduction of long-term major adverse cardiovascular events after endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy in palmar hyperhidrosis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2017, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Service. National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook 2015; National Health Insurance Service: Seoul, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, L.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, S. A guide for the utilization of health insurance review and assessment service national patient samples. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Chen, R.C.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, N.P.; Chou, P. Incidence and frequency of endoscopic sympathectomy for the treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris in Taiwan. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2010, 26, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, S.; Cha, J. The etiology, diagnosis and management of hyperhidrosis: A comprehensive review. Part I. Etiology and clinical work-up. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Sousa, J.; Oliveira, A.G.; Silva-Carvalho, L. Effects of endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis on cardiac autonomic nervous activity. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 137, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jeng, J.S.; Yip, P.K.; Huang, S.J.; Kao, M.C. Changes in hemodynamics of the carotid and middle cerebral arteries before and after endoscopic sympathectomy in patients with palmar hyperhidrosis: Preliminary results. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibasaki, M.; Crandall, C.G. Mechanisms and controllers of eccrine sweating in humans. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2010, 2, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hornberger, J.; Grimes, K.; Naumann, M.; Glaser, D.A.; Lowe, N.J.; Naver, H.; Ahn, S.; Stolman, L.P.; Multi-Specialty Working Group on the Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Primary Focal Hyperhidrosis. Recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of primary focal hyperhidrosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 274–286. [Google Scholar]
- Harker, M. Psychological sweating: A systematic review focused on aetiology and cutaneous response. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 26, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Converse, C.; Lyons, M.C.; Hsu, W.H. Neural control of sweat secretion: A review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.C.; Vekshtein, V.I.; Krantz, D.S.; Vita, J.A.; Ryan, T.J., Jr.; Ganz, P.; Selwyn, A.P. The effect of atherosclerosis on the vasomotor response of coronary arteries to mental stress. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoff, S.B.; Muldoon, M.F.; Zeigler, Z.R.; Manuck, S.B. Blood platelet responsivity to acute mental stress. Psychosom. Med. 1993, 55, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyngkaran, P.; Anavekar, N.; Majoni, W.; Thomas, M.C. The role and management of sympathetic overactivity in cardiovascular and renal complications of diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2013, 39, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.J.; Olympios, C.; Sifaki, M.; Handanis, S.; Bresnahan, M.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Suppressing sympathetic activation in congestive heart failure. A new therapeutic strategy. Hypertension 1995, 26, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, K.; Noma, T.; Fujisawa, Y.; Ishihara, Y.; Arai, Y.; Nabi, A.H.; Suzuki, F.; Nagai, Y.; Nakano, D.; Hitomi, H.; et al. Renal sympathetic denervation suppresses de novo podocyte injury and albuminuria in rats with aortic regurgitation. Circulation 2012, 125, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.L.; Fode-Thomas, N.C.; Fealey, R.D.; Eisenach, J.H.; Goerss, S.J. Endoscopic transthoracic limited sympathotomy for palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis: Outcomes and complications during a 10-year period. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.J. The effects of thoracic sympathotomy on heart rate variability in patients with palmar hyperhidrosis. Yonsei Med. J. 2012, 53, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.G.; Cheng, C.A.; Chien, W.C.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, J.T. Associated with ischemic stroke risk reduction after endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar sweating. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control | Hyperhidrosis | p-Value | Control | Hyperhidrosis | p-Value | Post Hoc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without ETS | With ETS | |||||||
| N | 18,613 | 18,613 | 18,613 | 16,209 | 2404 | |||
| Age (years) | 32.8 ± 12.2 | 32.8 ± 12.2 | 0.961 | 32.8 ± 12.2 | 33.4 ± 12.4 | 28.8 ± 9.9 | <0.001 | a, b, c |
| Sex | 0.909 | 0.041 | b, c | |||||
| Female | 9123 (49.0%) | 9134 (49.1%) | 9123 (49.0%) | 8012 (49.4%) | 1122 (46.7%) | |||
| Male | 9490 (51.0%) | 9479 (50.9%) | 9490 (51.0%) | 8197 (50.6%) | 1282 (53.3%) | |||
| Comorbidity | ||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 640 (3.4%) | 633 (3.4%) | 0.842 | 640 (3.4%) | 609 (3.8%) | 24 (1.0%) | <0.001 | b, c |
| Hypertension | 1301 (7.0%) | 1292 (7.0%) | 0.855 | 1301 (7.0%) | 1204 (7.4%) | 88 (3.7%) | <0.001 | b, c |
| Atrial fibrillation | 47 (0.3%) | 37 (0.2%) | 0.275 | 47 (0.3%) | 34 (0.2%) | 3 (0.1%) | 0.394 | — |
| Dyslipidemia | 1185 (6.4%) | 1202 (6.5%) | 0.719 | 1185 (6.4%) | 1096 (6.8%) | 106 (4.4%) | <0.001 | b, c |
| Congestive heart failure | 22 (0.1%) | 22 (0.1%) | >0.999 | 22 (0.1%) | 21 (0.1%) | 1 (0.1%) | 0.504 | — |
| Mood disorder | 862 (4.6%) | 853 (4.6%) | 0.824 | 862 (4.6%) | 785 (4.8%) | 68 (2.8%) | <0.001 | b, c |
| Anxiety disorder | 809 (4.4%) | 809 (4.4%) | >0.999 | 809 (4.4%) | 733 (4.5%) | 76 (3.2%) | 0.009 | b, c |
| Renal disease | 46 (0.2%) | 31 (0.2%) | 0.087 | 46 (0.2%) | 30 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | 0.081 | — |
| Malignant neoplasm | 243 (1.3%) | 225 (1.2%) | 0.402 | 243 (1.3%) | 210 (1.3%) | 15 (0.6%) | 0.016 | b, c |
| Control | Hyperhidrosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke | ||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.24 (1.05–1.47) |
| Adjusted HR 1 (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.28 (1.08–1.51) |
| Ischemic heart diseases | ||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.16 (0.98–1.38) |
| Adjusted HR 1 (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.17 (0.99–1.39) |
| Combined cardiovascular events | ||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.22 (1.08–1.37) |
| Adjusted HR 1 (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.24 (1.10–1.41) |
| Control | Hyperhidrosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Without ETS | With ETS | ||
| Stroke | |||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.36 (1.15–1.61) | 0.44 (0.26–0.75) |
| Adjusted HR 1 (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.32 (1.12–1.57) | 0.72 (0.42–1.24) |
| Ischemic heart diseases | |||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.24 (1.05–1.48) | 0.62 (0.39–0.98) |
| Adjusted HR 1 (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.19 (1.01–1.41) | 0.97 (0.61–1.53) |
| Combined cardiovascular events | |||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.31 (1.16–1.49) | 0.56 (0.40–0.79) |
| Adjusted HR 1 (95% CI) | 1 (reference) | 1.28 (1.13–1.45) | 0.89 (0.63–1.26) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.-M.; Moon, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, J.-y.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, S. Hyperhidrosis, Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy, and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Cohort Study Based on the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203925
Park J-M, Moon DH, Lee HS, Park J-y, Lee J-W, Lee S. Hyperhidrosis, Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy, and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Cohort Study Based on the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203925
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jae-Min, Duk Hwan Moon, Hye Sun Lee, Ju-young Park, Ji-Won Lee, and Sungsoo Lee. 2019. "Hyperhidrosis, Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy, and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Cohort Study Based on the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203925
APA StylePark, J.-M., Moon, D. H., Lee, H. S., Park, J.-y., Lee, J.-W., & Lee, S. (2019). Hyperhidrosis, Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy, and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Cohort Study Based on the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203925





