Bacterial Community Shifts Driven by Nitrogen Pollution in River Sediments of a Highly Urbanized City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Samples Collection
2.2. Analysis of Bottom Water and Sediment Characteristics
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification and 16S rRNA Gene-Based Pyrosequencing
2.4. Processing of Sequence Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characteristics of Overlying Water and Sediment
3.2. Bacterial Richness and Diversity Indexes
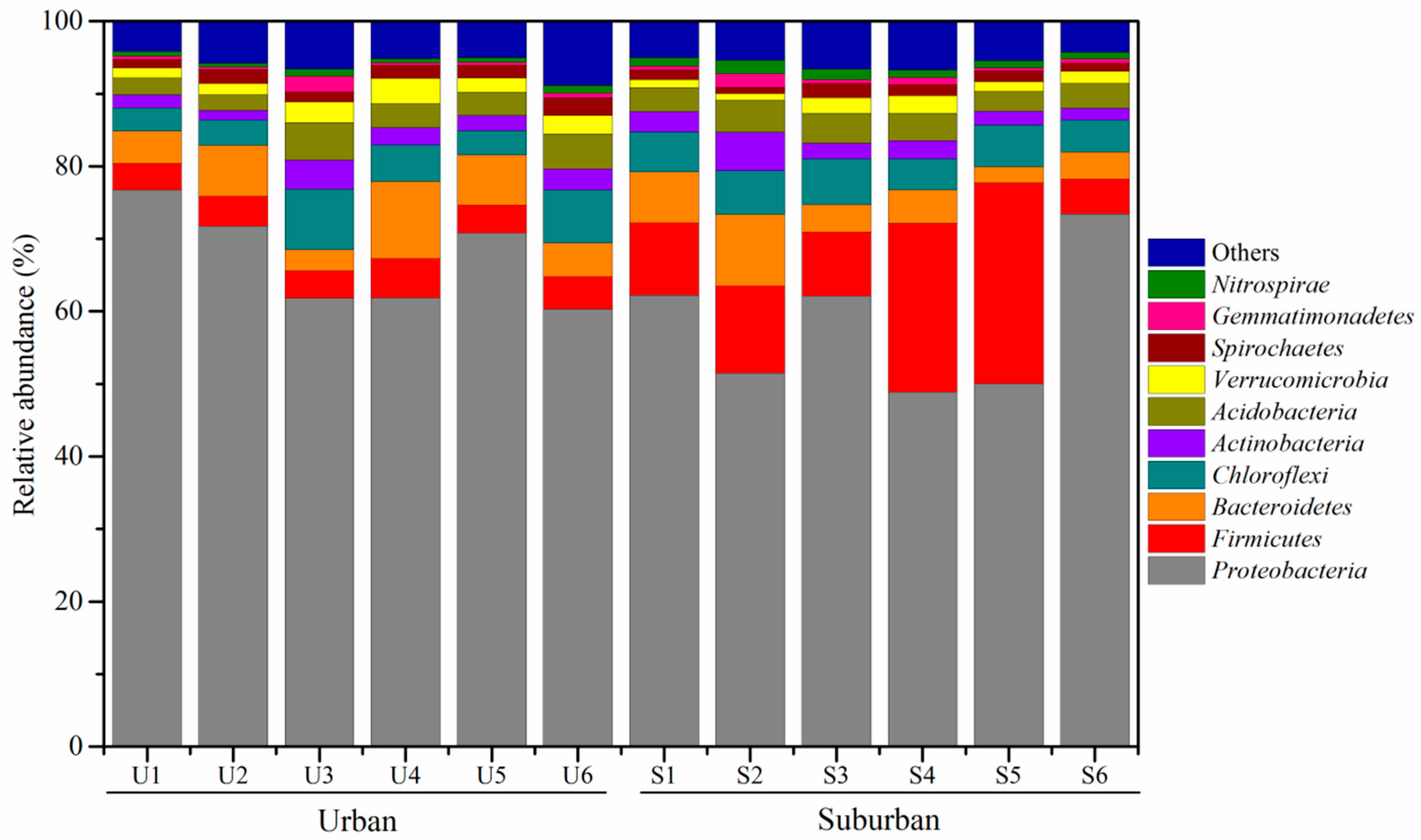
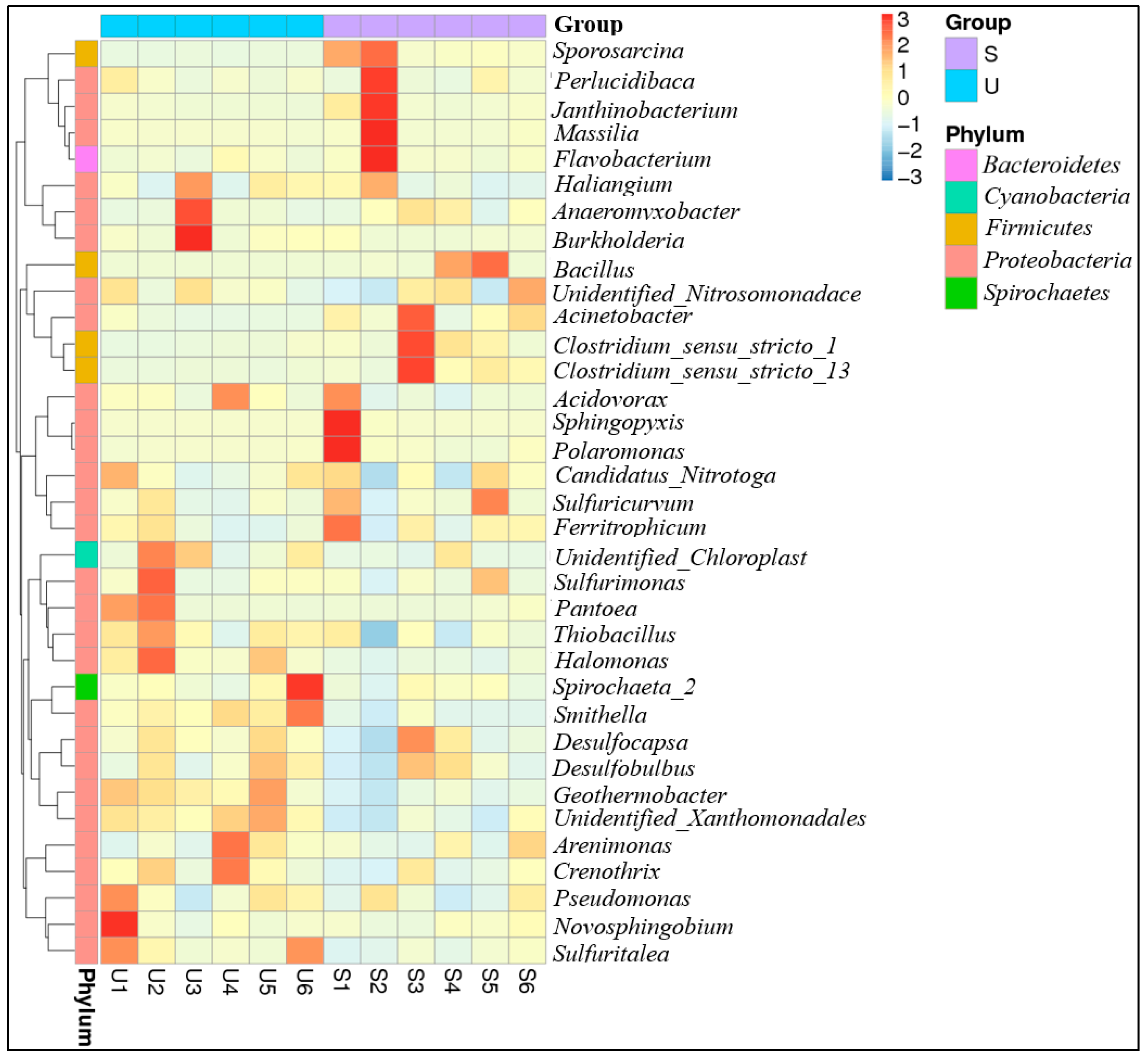
3.3. Phylogenetic Affiliation of 16S rRNA Gene Sequences
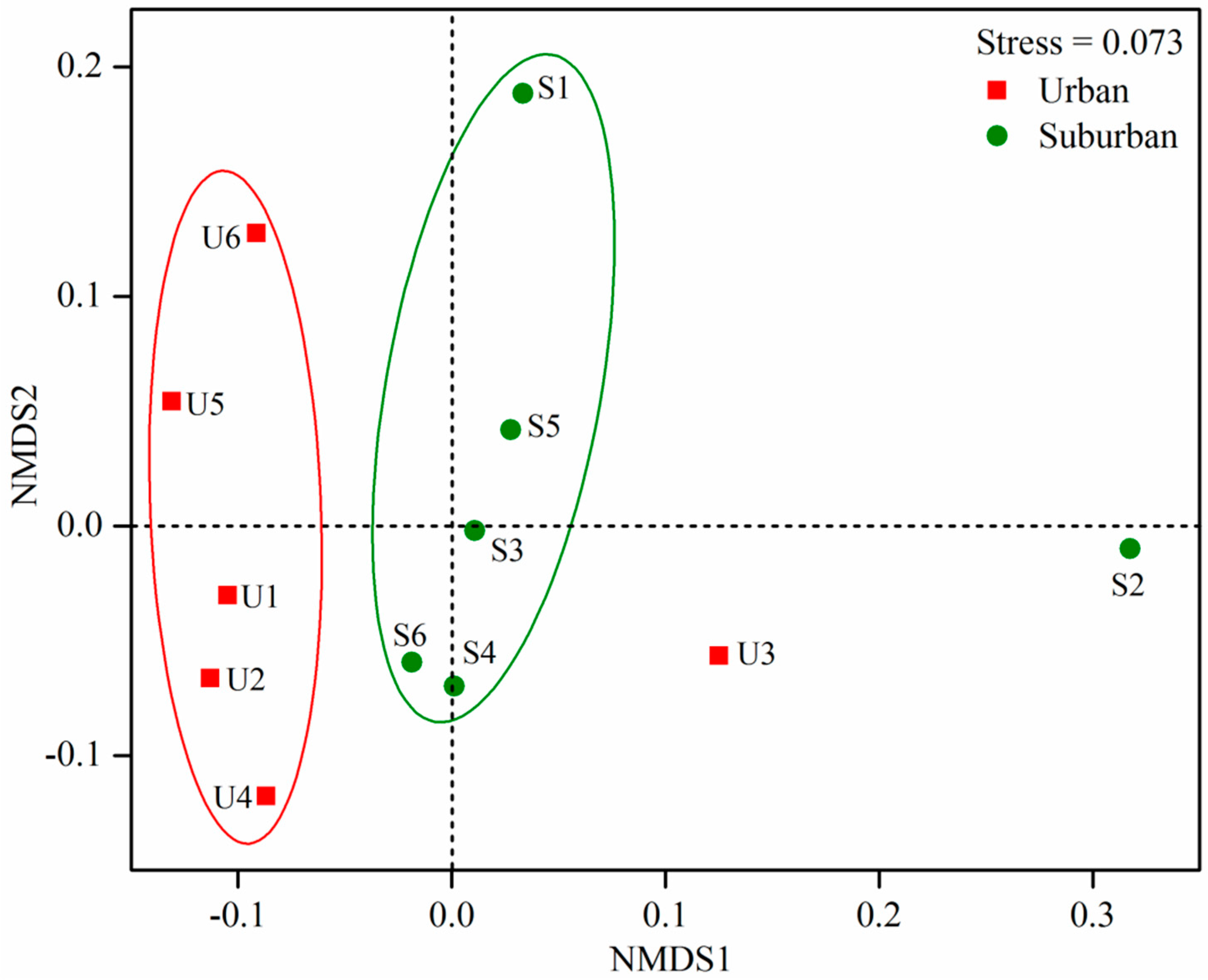
3.4. Factors Shaping Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity
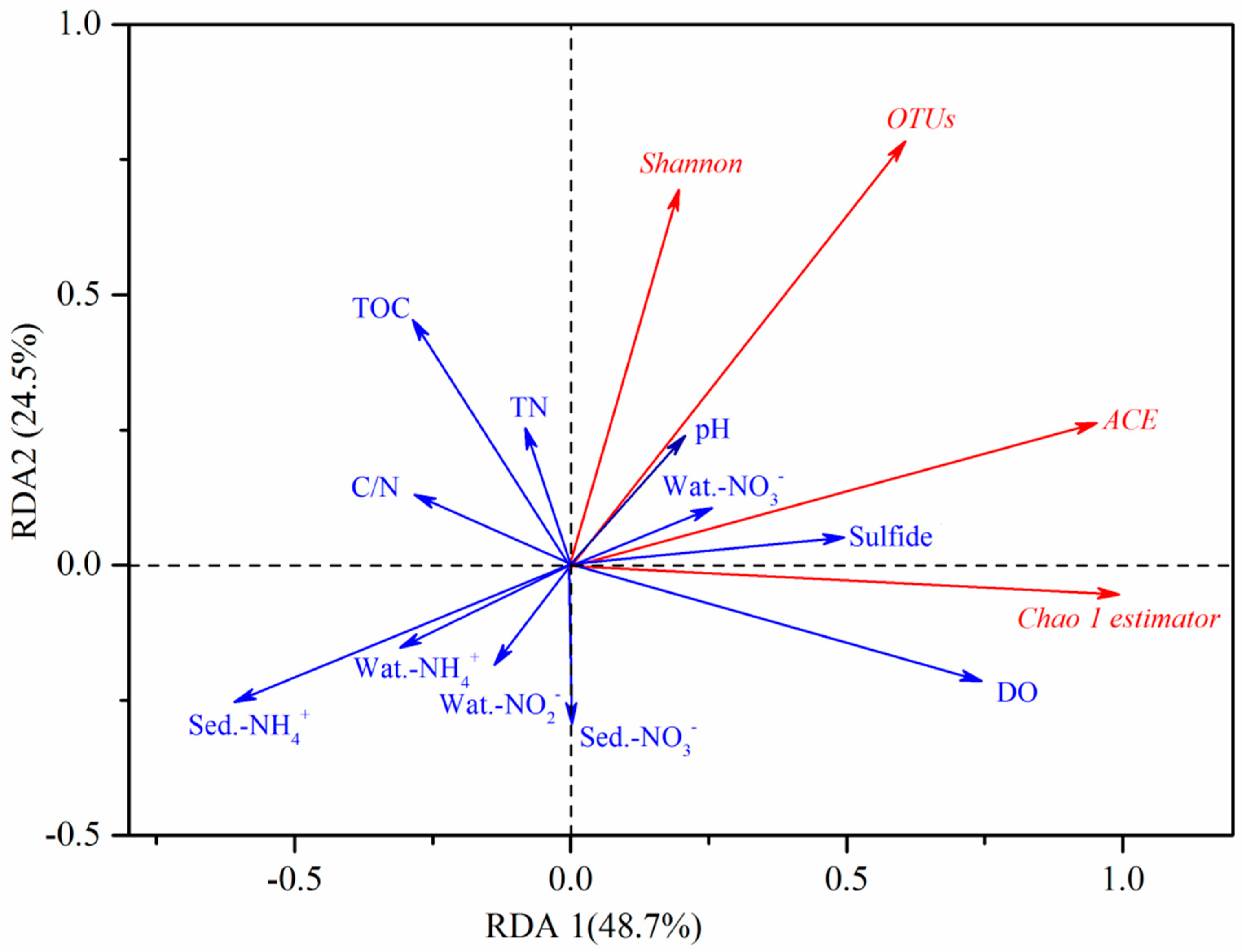
3.5. Redundancy Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. On the fate of anthropogenic nitrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, N.B.; Foster, D.; Groffman, P.; Grove, J.M.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Pataki, D.E.; Peters, D.P. The changing landscape: Ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.J.; Deng, H.G.; Wang, D.Q.; Ye, M.W.; Tan, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Xu, S.Y. Nitrous oxide emissions in the Shanghai river network: Implications for the effects of urban sewage and IPCC methodology. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, B.; Rosi-Marshall, E.; Kelly, J.J. Wastewater treatment effluent reduces the abundance and diversity of benthic bacterial communities in urban and suburban rivers. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2013, 79, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, L.Q.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.X.; Qian, G.R. Influences of land use on water quality in a reticular river network area: A case study in Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 137, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J.; Murinda, S.E. Bacterial community composition and structure in an urban river impacted by different pollutant sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Gu, B.J. Urban rivers as hotspots of regional nitrogen pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriya, J.; Shekar, M.C.; Nathani, N.M.; Suganya, T.; Bharathiraja, S.; Krishnan, M. Assessment of bacterial community composition in response to uranium levels in sediment samples of sacred Cauvery River. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2017, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.J.; Dong, X.L.; Peng, C.H.; Luo, W.D.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y. The long-term impact of urbanization on nitrogen patterns and dynamics in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 171, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, D.; Stief, P.; Amann, R.; De Beer, D.; Schramm, A. In situ distribution and activity of nitrifying bacteria in freshwater sediment. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhao, Z.F.; Chen, S.N.; Kang, P.L.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J.; Jia, J.Y.; Yan, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. Paracoccus versutus KS293 adaptation to aerobic and anaerobic denitrification: Insights from nitrogen removal, functional gene abundance, and proteomic profiling analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.N.; Zhao, Z.F.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Lu, K.Y.; Jia, J.Y. Water bacterial and fungal community compositions associated with urban lakes, Xi’an, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, C.S.; Eiler, A.; Herfort, L.; Needoba, J.A.; Peterson, T.D.; Crump, B.C. Determining indicator taxa across spatial and seasonal gradients in the Columbia River coastal margin. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.H.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.L.; Wang, P.F.; Zhang, W.L.; Wang, C.; Cai, W.; Wang, L.Q. Ignored fungal community in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants: Diversity and altitudinal characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, X.F.; Lin, X.B.; Hou, L.J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.T. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in sediments of urban river networks: Spatiotemporal variations and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.B.; Li, X.F.; Gao, D.Z.; Liu, M.; Cheng, L. Ammonium production and removal in the sediments of Shanghai River networks: Spatiotemporal variations, controlling factors, and environmental implications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2461–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, S.A.; Colloff, M.J.; Kookana, R.S. Effect of wastewater treatment plant effluent on microbial function and community structure in the sediment of a freshwater stream with variable seasonal flow. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Y.; Zhuang, M.F.; Geng, Y.; Wu, F.; Dong, H.J. Emergy-based ecological footprint analysis for a mega-city: The dynamic changes of Shanghai. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 210, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Liu, M.; Gong, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Yin, G.Y.; You, L. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacterial diversity, abundance, and activity in marsh sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J. Rapid assay for microbially reducible ferric iron in aquatic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1987, 53, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication, ACMSIG Mobile: Mobile Computing and Communications Review. Sci. Res. 2001, 5, 3–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, M.A.; Covich, A.P.; Lake, S.; Biro, P.; Brooks, J.J.; Cole, J.; Dahm, C.; Gibert, J.; Goedkoop, W.; Martens, K. Linkages between aquatic sediment biota and life above sediments as potential drivers of biodiversity and ecological processes: A disruption or intensification of the direct and indirect chemical, physical, or biological interactions between aquatic sediment biota and biota living above the sediments may accelerate biodiversity loss and contribute to the degradation of aquatic and riparian habitats. BioScience 2000, 50, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Perryman, S.E.; Rees, G.N.; Walsh, C.J. Analysis of denitrifying communities in streams from an urban and non-urban catchment. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Zhang, W.G.; Di, P.P.; Yi, N.; Chen, C.R. Vertical and horizontal assemblage patterns of bacterial communities in a eutrophic river receiving domestic wastewater in southeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.X.; Wang, M.C.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Z.; Hashidoko, Y.; Shen, W.J. Ammonium nitrogen content is a dominant predictor of bacterial community composition in an acidic forest soil with exogenous nitrogen enrichment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, C.; Gould, T.J.; Wang, P.; Phillips, J.; Cotner, J.B.; Sadowsky, M.J. Species sorting and seasonal dynamics primarily shape bacterial communities in the Upper Mississippi River. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.M.; Steinman, A.D.; Tang, X.M.; Xue, Q.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xie, L.Q. Response of bacterial communities to cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.G.; Bai, X.M.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wang, F.H.; Zhang, W.F.; Ma, W.Q.; Velthof, G.; Qin, W.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F.S. Environmental assessment of management options for nutrient flows in the food chain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7260–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, A.; Larsen, L.H.; Revsbech, N.P.; Amann, R. Structure and function of a nitrifying biofilm as determined by microelectrodes and fluorescent oligonucleotede probes. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, Q.; Long, X.E.; Li, Z.L.; Liu, D.X.; Ye, D.H.; He, C.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Kristiina, V.; Chen, X.P. Anthropogenic activities drive the microbial community and its function in urban river sediment. J. Soil Sediments 2016, 16, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G. Diversity and vertical distributions of sediment bacteria in an urban river contaminated by nutrients and heavy metals. Front. Env. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margot, J.; Rossi, L.; Barry, D.A.; Holliger, C. A review of the fate of micropollutants in wastewater treatment plants. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.G.; Dai, T.J.; Tang, Y.S.; Tao, Y.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.L.; Wen, D.H. Sediment bacterial community structures and their predicted functions implied the impacts from natural processes and anthropogenic activities in coastal area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N. Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, X.J.; Song, L.; Lin, X.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Shen, C.C.; Chu, H.Y. Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 92, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Kim, M.; Singh, D.; Lee-Cruz, L.; Lai-Hoe, A.; Ainuddin, A.; Go, R.; Rahim, R.A.; Husni, M.; Chun, J. Tropical soil bacterial communities in Malaysia: pH dominates in the equatorial tropics too. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, T.C.; Khardenavis, A.A.; Kapley, A. Shifts in microbial community in response to dissolved oxygen levels in activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, K.; Alleman, J.E.; Barnard, J.L.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Impacts of reduced sulfur components on active and resting ammonia oxidizers. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2004, 31, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Armisen, T.; İnceoğlu, Ö.; Ouattara, N.K.; Anzil, A.; Verbanck, M.A.; Brion, N.; Servais, P. Seasonal variations and resilience of bacterial communities in a sewage polluted urban river. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ye, X.S.; Chen, H.P.; Zhao, Q.F.; Hu, C.J.; He, J.Y.; Qian, Y.X.; Xiong, J.B.; Zhu, J.L.; Zhang, D.M. Bacterial biogeography in the coastal waters of northern Zhejiang, East China Sea is highly controlled by spatially structured environmental gradients. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3898–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
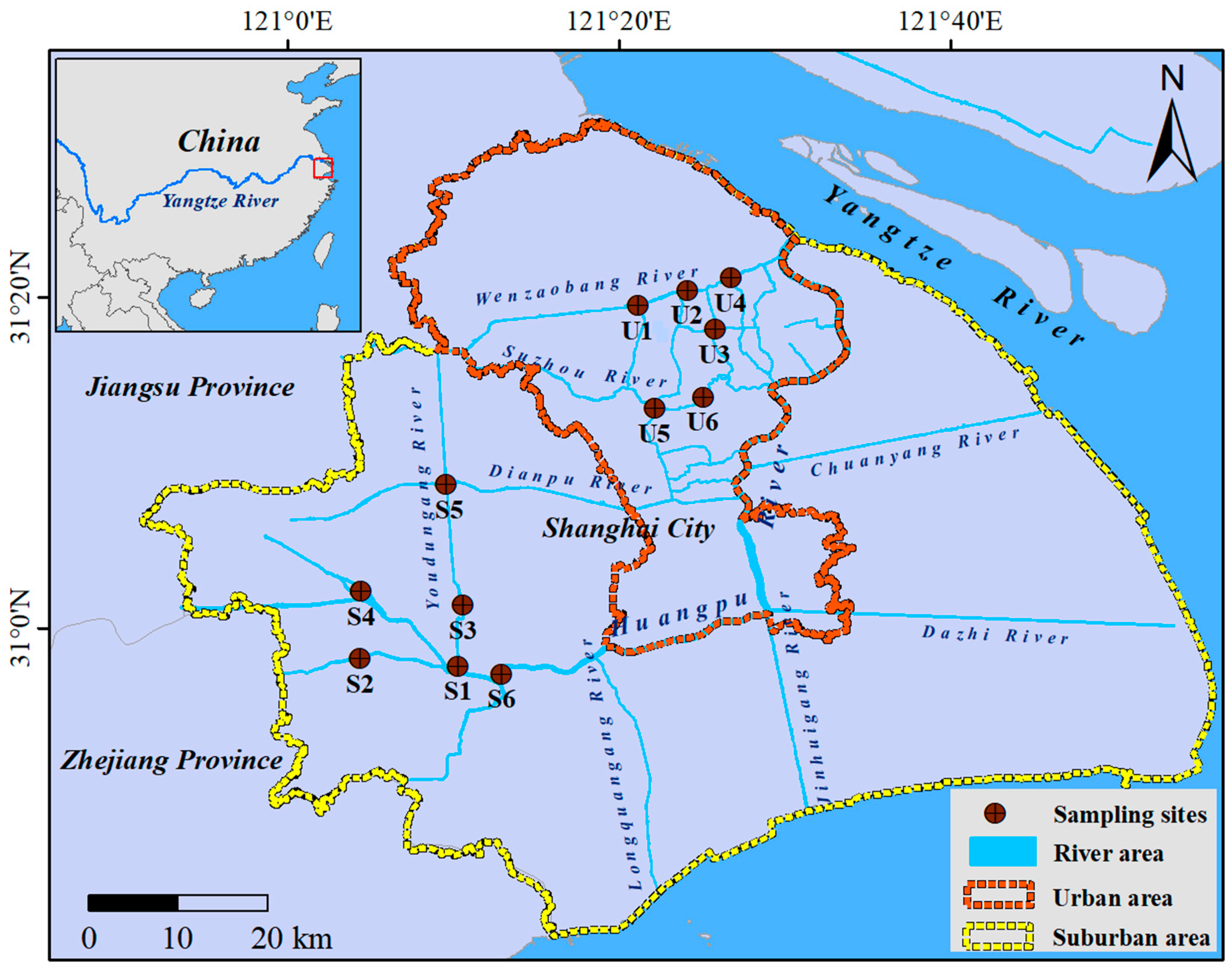
| Sites | Overlying Water | Sediment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | DO (mg L–1) | DOC (mg C L–1) | NO3– (mg N L–1) | NH4+ (mg N L–1) | NO2– (μg N L–1) | Sulfide (μg S g–1) | TOC (mg C g–1) | TN (mg N g–1) | C/N | NO3– (μg N g–1) | NH4+ (μg N g–1) | Fe(II) (mg Fe g–1) | |
| U1 | 6.9 | 2.89 | 21.8 | 3.81 | 15.4 | 8.03 | 158 | 10.8 | 1.51 | 7.17 | 2.25 | 188 | 9.87 |
| U2 | 6.9 | 2.58 | 11.6 | 2.80 | 11.9 | 1.89 | 216 | 18.5 | 1.35 | 13.7 | 3.11 | 234 | 15.4 |
| U3 | 7.0 | 2.68 | 14.4 | 3.39 | 13.7 | 89.5 | 152 | 33.2 | 3.15 | 10.5 | 2.93 | 147 | 7.89 |
| U4 | 7.1 | 1.24 | 18.9 | 2.64 | 10.7 | 197 | 130 | 17.9 | 3.26 | 5.48 | 2.07 | 140 | 8.47 |
| U5 | 6.8 | 2.01 | 13.6 | 9.06 | 6.43 | 12.1 | 4.15 | 22.1 | 2.43 | 9.12 | 3.25 | 240 | 9.83 |
| U6 | 7.0 | 1.15 | 7.2 | 5.10 | 8.90 | 8.03 | 32.5 | 18.3 | 2.46 | 7.47 | 0.79 | 135 | 8.69 |
| S1 | 7.3 | 2.65 | 19.6 | 3.29 | 0.24 | 5.47 | 515 | 15.3 | 1.06 | 14.4 | 0.32 | 38.8 | 9.01 |
| S2 | 7.2 | 4.92 | 6.3 | 5.78 | 0.04 | 15.2 | 669 | 12.5 | 1.87 | 6.70 | 1.87 | 4.79 | 0.43 |
| S3 | 7.3 | 1.31 | 5.8 | 2.77 | 0.02 | 12.1 | 274 | 22.8 | 3.11 | 7.34 | 1.35 | 52.5 | 9.68 |
| S4 | 7.5 | 3.11 | 8.7 | 5.68 | 0.01 | 7.52 | 815 | 26.7 | 2.08 | 12.8 | 0.57 | 154 | 9.39 |
| S5 | 7.2 | 2.01 | 7.7 | 4.15 | 0.02 | 17.3 | 172 | 26.4 | 2.03 | 13.0 | 0.38 | 115 | 8.66 |
| S6 | 7.3 | 2.17 | 10.4 | 3.69 | 0.04 | 2.40 | 248 | 19.2 | 1.62 | 11.8 | 0.63 | 132 | 25.1 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.83 | <0.001 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.007 | 0.01 | 0.92 |
| Sites | OTUs a | ACE b | Chao 1 c | Shannon d | Simpson e | Coverage f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 3881 | 4799 | 4664 | 8.4 | 0.98 | 98.5 |
| U2 | 3883 | 4624 | 4515 | 8.7 | 0.99 | 98.7 |
| U3 | 4599 | 5423 | 5247 | 9.5 | 0.99 | 98.5 |
| U4 | 3870 | 4545 | 4422 | 8.9 | 0.99 | 98.8 |
| U5 | 4215 | 4987 | 4899 | 9.1 | 0.99 | 98.6 |
| U6 | 4762 | 5455 | 5308 | 9.8 | 1.00 | 98.6 |
| S1 | 4522 | 5288 | 5176 | 9.3 | 0.99 | 98.6 |
| S2 | 4756 | 7021 | 11,205 | 9.0 | 0.99 | 97.4 |
| S3 | 4468 | 5208 | 5121 | 9.2 | 0.99 | 98.6 |
| S4 | 4398 | 5270 | 5126 | 8.7 | 0.97 | 98.5 |
| S5 | 4137 | 4947 | 4787 | 8.0 | 0.95 | 98.5 |
| S6 | 4014 | 4741 | 4644 | 8.3 | 0.97 | 98.7 |
| Environmental Parameters | OTUs | ACE | Chao | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.21 | −0.17 | −0.43 |
| DO | 0.26 | 0.69 * | 0.76 * | −0.16 | −0.08 |
| NO3− a | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.11 | −0.02 |
| NH4+ a | −0.34 | −0.35 | −0.32 | 0.20 | 0.46 |
| NO2− | −0.23 | −0.21 | −0.14 | 0.14 | 0.25 |
| Fe(II) | −0.55 | −0.66 * | −0.59 * | −0.39 | −0.34 |
| Sulfide | 0.34 | 0.53 | 0.51 | −0.10 | −0.20 |
| TOC | 0.18 | −0.15 | −0.32 | 0.09 | −0.25 |
| TN | 0.18 | −0.02 | −0.09 | 0.40 | 0.28 |
| C/N | −0.10 | −0.24 | −0.31 | −0.29 | −0.46 |
| NO3− b | −0.26 | −0.08 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.49 |
| NH4+ b | −0.60 * | −0.65 * | −0.60 * | −0.19 | −0.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Gao, D.; Lu, K.; Li, X. Bacterial Community Shifts Driven by Nitrogen Pollution in River Sediments of a Highly Urbanized City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203794
Lin X, Gao D, Lu K, Li X. Bacterial Community Shifts Driven by Nitrogen Pollution in River Sediments of a Highly Urbanized City. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203794
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xianbiao, Dengzhou Gao, Kaijun Lu, and Xiaofei Li. 2019. "Bacterial Community Shifts Driven by Nitrogen Pollution in River Sediments of a Highly Urbanized City" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203794
APA StyleLin, X., Gao, D., Lu, K., & Li, X. (2019). Bacterial Community Shifts Driven by Nitrogen Pollution in River Sediments of a Highly Urbanized City. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203794





