Acute Health Impacts of the Southeast Asian Transboundary Haze Problem—A Review
Abstract
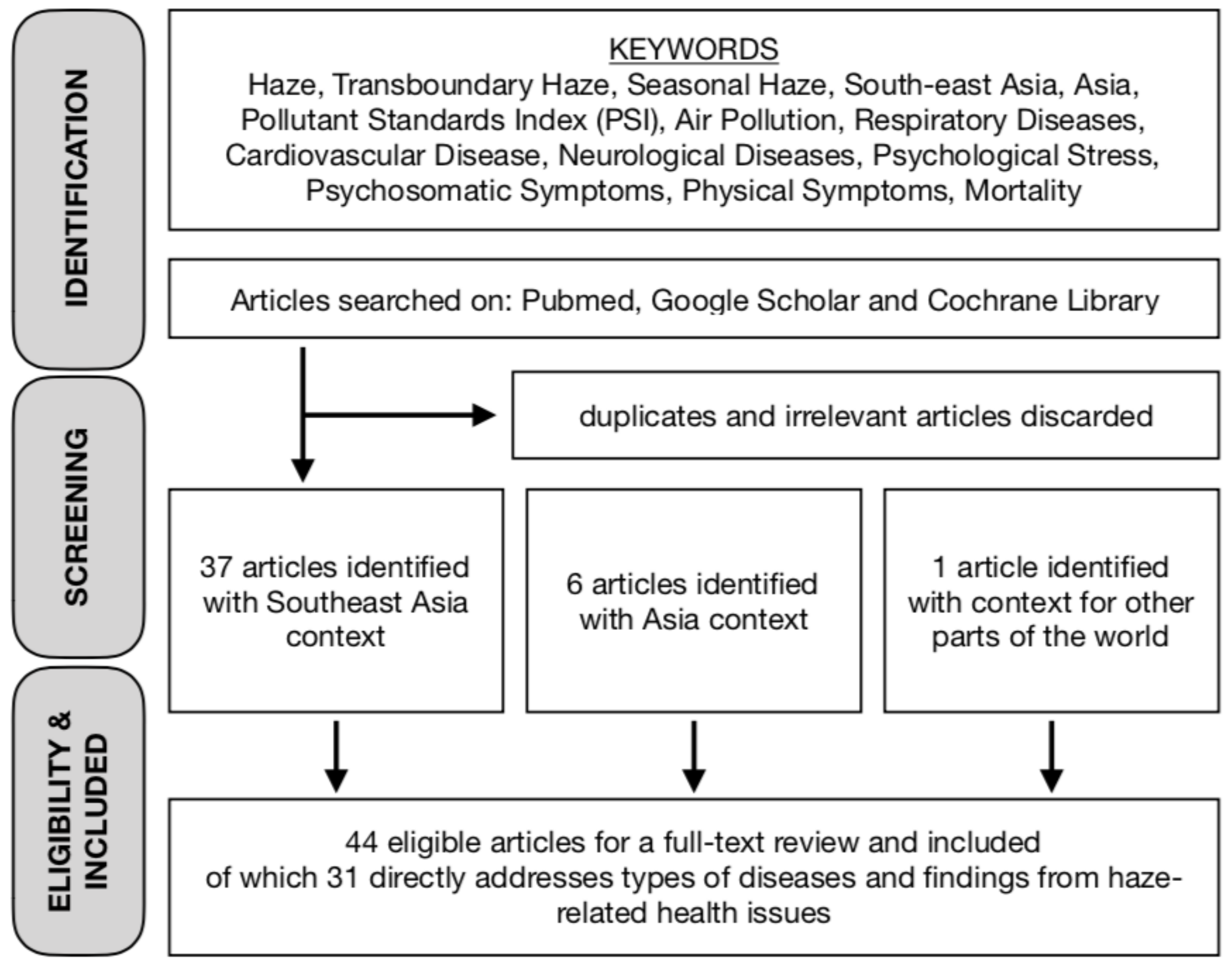
1. Introduction
2. Findings and Results
2.1. Physical Symptoms and Psychological Impact
2.2. Respiratory Disease
2.3. Neurological Diseases
2.4. Cardiovascular Diseases
2.5. Mortality
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. Air pollution and health. Available online: https://www.unece.org/environmental-policy/conventions/envlrtapwelcome/cross-sectoral-linkages/air-pollution-and-health.html. (accessed on 30 May 2019).
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; Aryee, M.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (London, England) 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Pereira, G.; Uhl, S.A.; Bravo, M.A.; Bell, M.L. A systematic review of the physical health impacts from non-occupational exposure to wildfire smoke. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Burden of disease from ambient air pollution for 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/airpollution/data/AAP_BoD_results_May2018_final.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Betha, R.; Behera, S.N.; Balasubramanian, R. 2013 Southeast Asian Smoke Haze: Fractionation of Particulate-Bound Elements and Associated Health Risk. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, N. Forest Fires, Air Pollution, and Mortality in Southeast Asia. Demography 2002, 39, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunchindah, A. Transboundary haze pollution problem in Southeast Asia: Reframing ASEAN’s response (no. DP-2015-82). Available online: http://www.eria.org/ERIA-DP-2015-82.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Marlier, M.E.; DeFries, R.S.; Voulgarakis, A.; Kinney, P.L.; Randerson, J.T.; Shindell, D.T.; Chen, Y.; Faluvegi, G. El Niño and health risks from landscape fire emissions in Southeast Asia. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odihi, J.O. Haze and Health in Brunei Darussalam: The Case of the 1997-98 Episodes. Singap. J. Trop. Geogr. 2001, 22, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddington, C.L.; Yoshioka, M.; Balasubramanian, R.; Ridley, D.; Toh, Y.Y.; Arnold, S.R.; Spracklen, D. V Contribution of vegetation and peat fires to particulate air pollution in Southeast Asia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 094006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakreshnan, L.; Aghamohammadi, N.; Fong, C.S.; Bulgiba, A.; Zaki, R.A.; Wong, L.P.; Sulaiman, N.M. Haze and health impacts in ASEAN countries: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2096–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplitz, S.N.; Mickley, L.J.; Marlier, M.E.; Buonocore, J.J.; Kim, P.S.; Liu, T.; Sulprizio, M.P.; DeFries, R.S.; Jacob, D.J.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Public health impacts of the severe haze in Equatorial Asia in September–October 2015: Demonstration of a new framework for informing fire management strategies to reduce downwind smoke exposure. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavagadhi, S.; Betha, R.; Venkatesan, S.; Balasubramanian, R.; Hande, M.P. Physicochemical and toxicological characteristics of urban aerosols during a recent Indonesian biomass burning episode. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2569–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.E. Factors Influencing the Emissions of Gases and Particulate Matter from Biomass Burning. In Fire in the Tropical Biota. Ecological Studies (Analysis and Synthesis); Goldammer, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; Volume 84, pp. 418–436. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.F.; Latif, M.T.; Saw, W.H.; Amil, N.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Sahani, M.; Tahir, N.M.; Chung, J.X. Fine particulate matter in the tropical environment: Monsoonal effects, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, E.J.; Unnikrishnan, S.; Kumar, R.; Yeole, B.; Chowdhury, Z. Fine aerosol and PAH carcinogenicity estimation in outdoor environment of Mumbai City, India. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2012, 22, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.E.; Brauer, M.; Johnston, F.H.; Jerrett, M.; Balmes, J.R.; Elliott, C.T. Critical Review of Health Impacts of Wildfire Smoke Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.; Liew, C.F.; Oon, H.H. Clinical Experience and Impact of a Community-Led Volunteer Atmospheric Haze Clinic in Singapore. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2014, 45, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- TAN, W.C.; QIU, D.; LIAM, B.L.; NG, T.P.; LEE, S.H.; van EEDEN, S.F.; D’YACHKOVA, Y.; HOGG, J.C. The Human Bone Marrow Response to Acute Air Pollution Caused by Forest Fires. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.C.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, C.S.; Pan, F.; Lu, Y.; Sharma, V.K. Impact of 2013 south Asian haze crisis: Study of physical and psychological symptoms and perceived dangerousness of pollution level. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.Y.; Leong, A.Z.; Leow, A.S.; Ngiam, N.J.; Ng, B.S.; Sharma, M.; Yeo, L.L.; Seow, P.A.; Hong, C.S.; Chee, Y.H.; et al. Psychosomatic symptoms during South East Asian haze crisis are related to changes in cerebral hemodynamics. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, S.C. Impact to lung health of haze from forest fires: The Singapore experience. Respirology 2000, 5, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg, E.; McKee, D.; Thomas, D. Health Consequences of Forest Fires in Indonesia. Demography 2005, 42, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, J.A.; Mannino, D.M.; Alverson, C.J.; Kiyu, A.; Hashim, J.; Lee, T.; Falter, K.; Redd, S.C. Cardiorespiratory hospitalizations associated with smoke exposure during the 1997 Southeast Asian forest fires. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2005, 208, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, F.T.; Ooi, B.C.; Hui, J.K.; Saharom, R.; Goh, D.Y.; Lee, B.W. Singapore’s haze and acute asthma in children. Lancet (London, England) 1995, 346, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim J., H.; Hashim, Z.; Jalaludin, J.; Lubis, S.H.; Hashim, R. Respiratory function of elementary school children exposed to the 1997 Kuala Lumpur Haze. Epidemiology 1998, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, Z.J.; Kristiansen, L.C.; Andersen, K.K.; Olsen, T.S.; Hvidberg, M.; Jensen, S.S.; Ketzel, M.; Loft, S.; Sørensen, M.; Tjønneland, A.; et al. Stroke and Long-Term Exposure to Outdoor Air Pollution from Nitrogen Dioxide. Stroke 2012, 43, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Mertz, K.J.; Arena, V.C.; Brink, L.L.; Xu, X.; Bi, Y.; Talbott, E.O. Estimation of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Stroke Hospital Admissions in Wuhan, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowicz, M.; Stieb, D.M.; Rowe, B.H. Air pollution and daily ED visits for migraine and headache in Edmonton, Canada. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowicz, M.; Kaplan, G.G.; Grafstein, E.; Rowe, B.H. Emergency department visits for migraine and headache: A multi-city study. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-S.; Yang, C.-Y. Association between Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Clinic Visits for Migraine in a Subtropical City: Taipei, Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4697–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chiu, H.-F.; Yang, C.-Y. Fine particulate air pollution and outpatient department visits for headache in Taipei, Taiwan. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. A 2015, 78, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.F.W.; Zheng, H.; De Silva, D.A.; Wah, W.; Earnest, A.; Pang, Y.H.; Xie, Z.; Pek, P.P.; Liu, N.; Ng, Y.Y.; et al. The Relationship Between Ambient Air Pollution and Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Time-Stratified Case-Crossover Study in a City-State with Seasonal Exposure to the Southeast Asian Haze Problem. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2018, 72, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongsuvivatwong, V.; Phua, K.H.; Yap, M.T.; Pocock, N.S.; Hashim, J.H.; Chhem, R.; Wilopo, S.A.; Lopez, A.D. Health and health-care systems in southeast Asia: Diversity and transitions. Lancet 2011, 377, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, X.; Chu, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J. Air particulate matter and cardiovascular disease: The epidemiological, biomedical and clinical evidence. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E8–E19. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, K.H.; Ho, A.F.W.; Zheng, H.; Earnest, A.; Pek, P.P.; Seok, J.Y.; Chan, S.K.T.; Liu, N.; Tan, J.W.C.; Wong, T.H.; et al. Significant Association between Transboundary Air Pollution and Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.F.W.; Zheng, H.; Earnest, A.; Cheong, K.H.; Pek, P.P.; Seok, J.Y.; Liu, N.; Kwan, Y.H.; Tan, J.W.C.; Wong, T.H.; et al. Time-Stratified Case Crossover Study of the Association of Outdoor Ambient Air Pollution With the Risk of Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Context of Seasonal Exposure to the Southeast Asian Haze Problem. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.; Ng, Y.; Yeo, K.K.; Sahlén, A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lee, V.; Ma, S. Particulate air pollution on cardiovascular mortality in the tropics: impact on the elderly. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Peng, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, R.; Xu, Z.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. A time-stratified case-crossover study of fine particulate matter air pollution and mortality in Guangzhou, China. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 85, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahani, M.; Zainon, N.A.; Wan Mahiyuddin, W.R.; Latif, M.T.; Hod, R.; Khan, M.F.; Tahir, N.M.; Chan, C.-C. A case-crossover analysis of forest fire haze events and mortality in Malaysia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 96, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, N.; Olivieri, O.; Girelli, D. Air particulate matter and cardiovascular disease: A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.F.W.; Bte Mohd Yazid, S.N.N.; Zheng, H.; Earnest, A.; Ng, Y.Y.; Liu, N.; Lam, S.S.W.; Ong, M.E.H.; Koh, J.M.; Cheong, K.H. Effects of Air Pollution and Other Environmental Parameters on All-Cause Mortality in Singapore. Circulation 2018, 138, A12831. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.; Goyal, P.; Upadhyay, A. Artificial intelligence based approach to forecast PM2.5 during haze episodes: A case study of Delhi, India. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogikar, P.; Tyagi, B.; Gorai, A.K. Seasonal prediction of particulate matter over the steel city of India using neural network models. Modeling Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
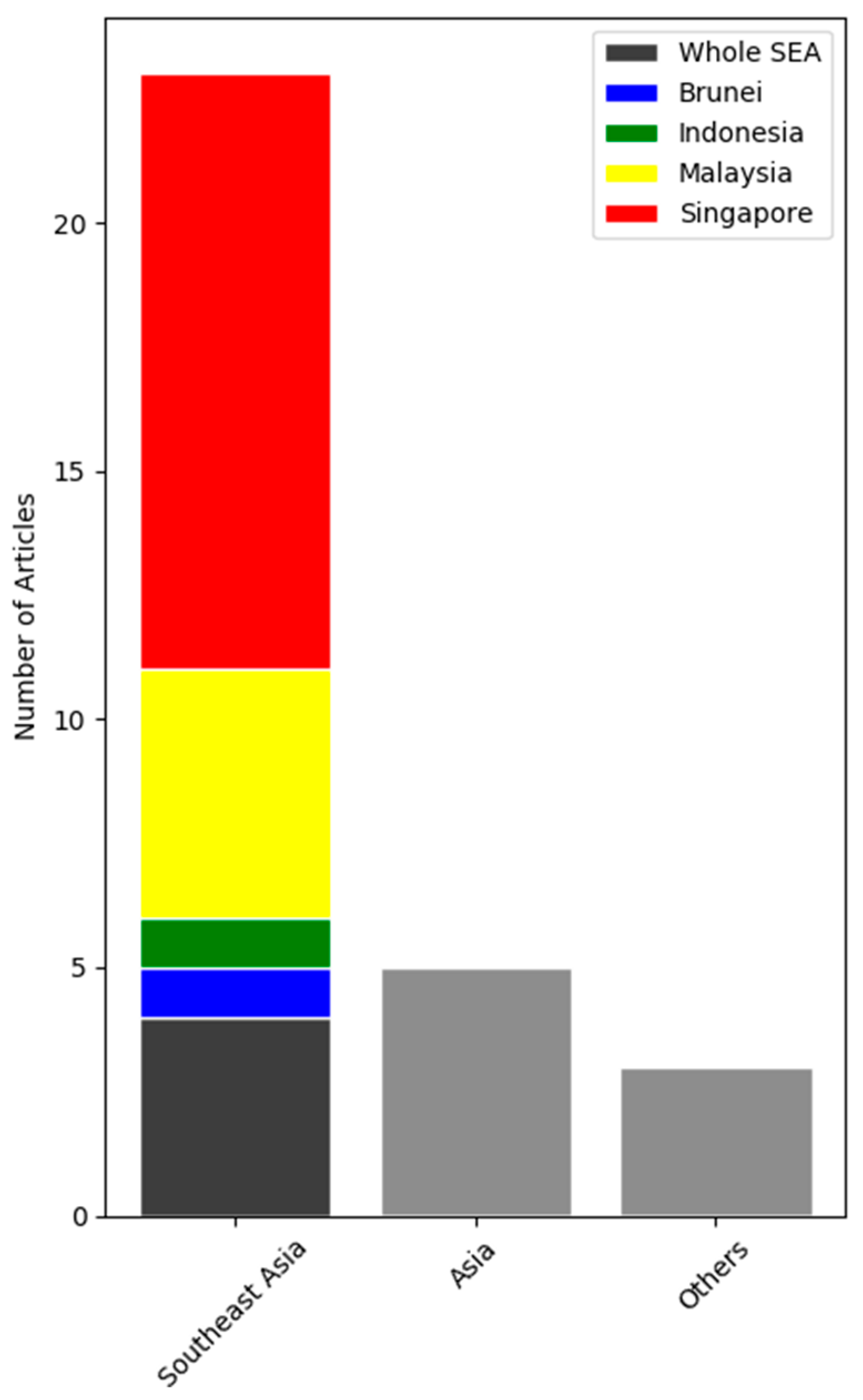
| Article | Region/Study country/Period of Study | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Chew, et al. (1995) [25] | SEA/Singapore/September to October 1994 |
|
| Hashim, et al. (1998) [26] | SEA/Malaysia/July to November 1997 |
|
| Emmanuel(2000) [22] | SEA/Singapore/data from August to November 1997 |
|
| Tan, et al. (2000) [19] | SEA/Singapore/29 September to 27 October 1997 and 21 November to 5 December 1997 |
|
| Odihi (2001) [9] | SEA/Brunei/September 1997 to September 1998 |
|
| Sastry (2002) [6] | SEA/Malaysia/April to November 1997 |
|
| Frankenberg, et al. (2005) [23] | SEA/Indonesia/1993 and 1997 |
|
| Mott, et al. (2005) [24] | SEA/Malaysia (Kuching)/ January 1995 to December 1998 |
|
| Szyszkowicz, et al. (2009) [29] | Others/Canada (Edmonton)/1992 to 2002 |
|
| Szyszkowicz, et al. (2009) [30] | Others/Canada (Edmonton, Hali- fax, Ottawa, Toronto, and Vancouver)/data from 11518 days for five cities. |
|
| Yang, et al. (2012) [39] | Asia/China (Guangzhou)/2007 to 2008 |
|
| Andersen, et al. (2012) [27] | Others/Denmark (Copenhagen and Aarhus)/data from 1971 to 2006 |
|
| Abba, et al. (2012) [16] | Asia/India (Mumbai) /2007 to 2008 |
|
| Xiang, et al. (2013) [28] | Asia/China (Wuhan)/2006 to 2008 |
|
| Marlier, et al. (2013) [8] | SEA/All/1997 to 2006 |
|
| Pavagadhi, et al. (2013) [13] | SEA/Singapore/21 to 29 October 2010 |
|
| Betha, et al. (2014) [5] | Southeast Asia (SEA)/All/June 2013 |
|
| Sahani, et al. (2014) [40] | SEA/Malaysia (Klang Valley)/data from 2000 to 2007 |
|
| Yeo, et al. (2014) [18] | SEA/Singapore/25 June to 11 July 2013 |
|
| Ho, et al. (2014) [20] | SEA/Singapore/21 June to 26 June 2013 |
|
| Reddington, et al. (2014) [10] | SEA/ Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore/2004 to 2009 |
|
| Chen, et al. (2015) [31] | Asia/Taiwan (Taipei)/data from 2006 to 2011 |
|
| Chang, et al. (2015) [32] | Asia/Taiwan (Taipei)/data from 2006 to 2011 |
|
| Koplitz, et al. (2016) [12] | SEA/ Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore/September to October 2015 compared to haze of September to October 2006 |
|
| Khan, et al. (2016) [15] | SEA/Malaysia/July to September 2013 and January to February 2014 |
|
| Ho, et al. (2018) [33] | SEA/Singapore/data from 2010 to 2015 |
|
| Yap, et al. (2019) [38] | SEA/Singapore/data from 2010 to 2015 |
|
| Ho, et al. (2018) [42] | SEA/Singapore/data from 2010 to 2015 |
|
| Tan, et al. (2019) [21] | SEA/Singapore/2015 |
|
| Ho, et al. (2019) [37] | SEA/Singapore/data from 2010 to 2015 |
|
| Groups | Incidence Rate Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Entire cohort | 1.04 (1.03–1.06) | 0.001 |
| Without overdispersion and autocorrelation | 1.04 (1.03–1.06) | 0.001 |
| Subgroups | ||
| Age | ||
| 65 y | 1.04 (1.02–1.07) | 0.001 |
| 65 y | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | 0.001 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 1.06 (1.04–1.08) | 0.001 |
| Female | 1.04 (1.01–1.06) | 0.005 |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Chinese | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | 0.001 |
| Malay | 1.05 (1.02–1.08) | 0.002 |
| Indian | 1.04 (1.01–1.08) | 0.014 |
| Subtype | ||
| STEMI | 1.00 (0.98–1.03) | 0.940 |
| NSTEMI | 1.08 (1.05–1.10) | 0.001 |
| History of MI/CABG/PCI | ||
| Yes | 1.05 (1.03–1.08) | 0.001 |
| No | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | 0.001 |
| History of diabetes mellitus | ||
| Yes | 1.06 (1.04–1.08) | 0.001 |
| No | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | 0.001 |
| History of hypertension | ||
| Yes | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | 0.001 |
| No | 1.06 (1.04–1.09) | 0.001 |
| History of hyperlipidemia | ||
| Yes | 1.05 (1.03–1.08) | 0.001 |
| No | 1.05 (1.02–1.07) | 0.001 |
| Current/former smoker | ||
| Yes | 1.04 (1.02–1.07) | 0.001 |
| No | 1.06 (1.04–1.08) | 0.001 |
| Place of MI onset | ||
| Inpatient | 1.13 (1.09–1.16) | 0.001 |
| Outpatient | 1.02 (1.00–1.04) | 0.029 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheong, K.H.; Ngiam, N.J.; Morgan, G.G.; Pek, P.P.; Tan, B.Y.-Q.; Lai, J.W.; Koh, J.M.; Ong, M.E.H.; Ho, A.F.W. Acute Health Impacts of the Southeast Asian Transboundary Haze Problem—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183286
Cheong KH, Ngiam NJ, Morgan GG, Pek PP, Tan BY-Q, Lai JW, Koh JM, Ong MEH, Ho AFW. Acute Health Impacts of the Southeast Asian Transboundary Haze Problem—A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(18):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183286
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheong, Kang Hao, Nicholas Jinghao Ngiam, Geoffrey G. Morgan, Pin Pin Pek, Benjamin Yong-Qiang Tan, Joel Weijia Lai, Jin Ming Koh, Marcus Eng Hock Ong, and Andrew Fu Wah Ho. 2019. "Acute Health Impacts of the Southeast Asian Transboundary Haze Problem—A Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 18: 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183286
APA StyleCheong, K. H., Ngiam, N. J., Morgan, G. G., Pek, P. P., Tan, B. Y.-Q., Lai, J. W., Koh, J. M., Ong, M. E. H., & Ho, A. F. W. (2019). Acute Health Impacts of the Southeast Asian Transboundary Haze Problem—A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(18), 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183286










