Risk of Dementia in Patients with Leptospirosis: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Statistical Analysis
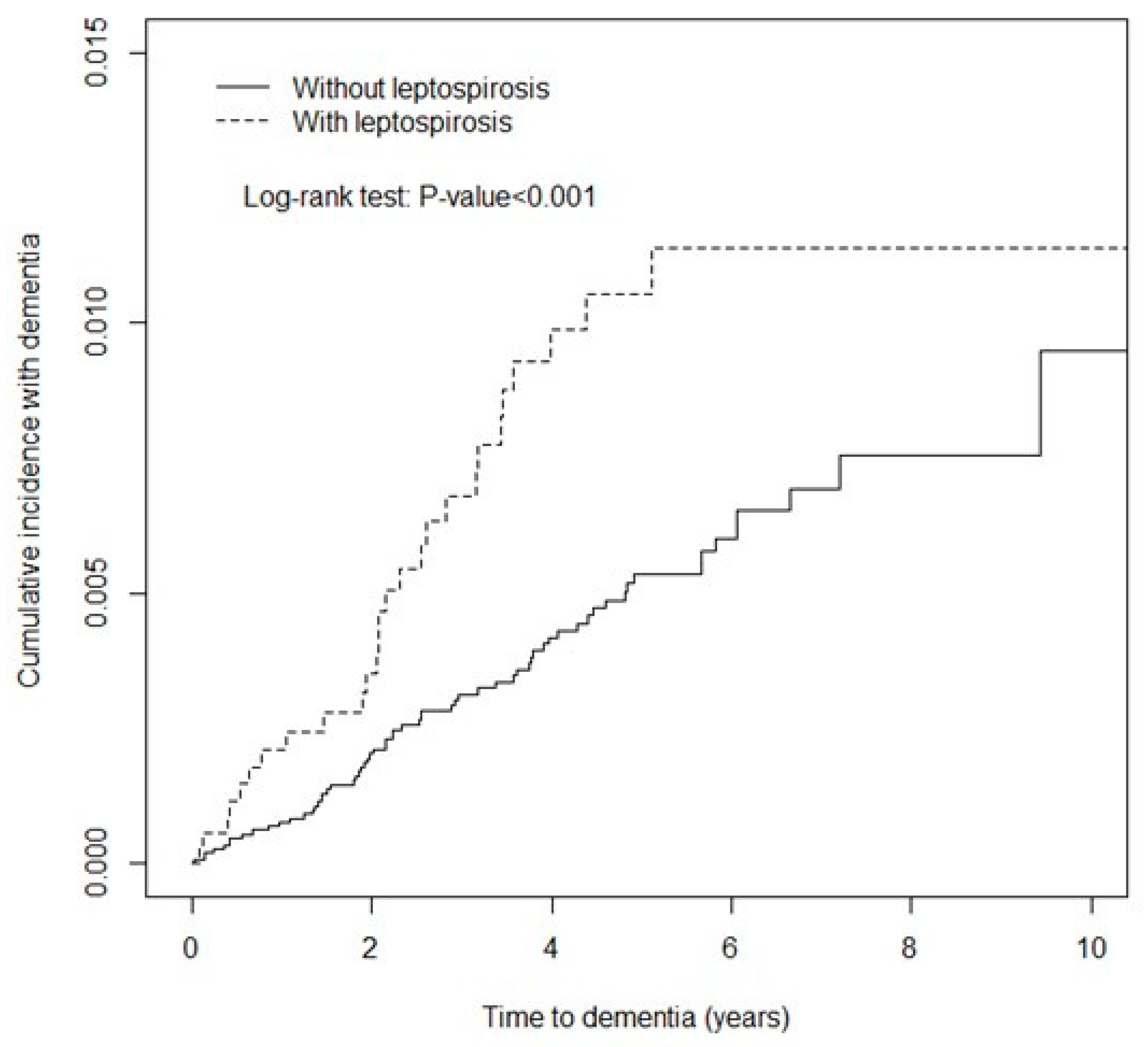
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| NHI | National Health Insurance |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database |
| ICD-9-CM | Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification |
| HRs | hazard ratios |
| CIs | confidence intervals |
References
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.I.; Reis, M.G.; Dourado, C.M.; Johnson, W.D., Jr.; Riley, L.W.; Salvador Leptospirosis Study Group. Urban epidemic of severe leptospirosis in Brazil. Lancet 1999, 354, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.R.; Ansdell, V.E.; Effler, P.V.; Middleton, C.R.; Sasaki, D.M. Assessment of the clinical presentation and treatment of 353 cases of laboratory-confirmed leptospirosis in Hawaii, 1974–1998. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faine, S.; Adler, B.; Bolin, C.; Perolat, P. Leptospira and Leptospirosis, 2nd ed.; Melbourne Vic: Melbourne, Australia, 1999; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2013 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 208–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorm, A.F.; Jolley, D. The incidence of dementia: A meta-analysis. Neurology 1998, 51, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.A.; Lochner, K.A.; Thambisetty, M.; Wingo, T.S.; Posner, S.F.; Ling, S.M. Prevalence of dementia subtypes in United States Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries, 2011–2013. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Grant, M.M.; Aldred, S. Oxidative stress in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: A common pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2009, 17, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, P.B.; Scuteri, A.; Black, S.E.; DeCarli, C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Iadecola, C.; Launer, L.J.; Laurent, S.; Lopez, O.L.; Nyenhuis, D.; et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: A statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2011, 42, 2672–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; He, G.; Qing, H.; Zhou, W.; Dobie, F.; Cai, F.; Staufenbiel, M.; Huang, L.E.; Song, W. Hypoxia facilitates Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis by up-regulating BACE1 gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18727–18732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.S.; Chu, Y.H.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, C.H. Increased risk of acute coronary syndrome among leptospirosis patients: A nationwide cohort analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Database N.H.I.R. Available online: http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html (accessed on 18 April 2018).
- Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, H.Y.; Wu, J.C.; Haschler, I.; Chen, T.J.; Wetter, T. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: Administrative health care database as study object in bibliometrics. Scientometrics 2011, 86, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.W.; Yu, M.C.; Lin, C.L.; Yu, T.M.; Shu, K.H.; Huang, S.T.; Kao, C.H. Risk of peripheral arterial occlusive disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A nationwide population-based cohort study. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Chang, C.T.; Lin, C.L.; Huang, B.R.; Kao, C.H. Spinal cord injury is associated with an increased risk of atrial fibrillation: A population-based cohort study. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.Y.; Hsu, P.Y.; Pan, M.J.; Wu, M.S.; Lee, C.H.; Yu, C.C.; Hung, C.C.; Yang, C.W. Clinical distinction and evaluation of leptospirosis in Taiwan—A case-control study. J. Nephrol. 2005, 18, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Baghestani, A.R.; Vahedi, M. How to control confounding effects by statistical analysis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2012, 5, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jansen, A.; Stark, K.; Schneider, T.; Schöneberg, I. Sex differences in clinical leptospirosis in Germany: 1997–2005. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, e69–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagliero, J.; Villanueva, S.; Matsui, M. Leptospirosis Pathophysiology: Into the Storm of Cytokines. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barage, S.H.; Sonawane, K.D. Amyloid cascade hypothesis: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropeptides 2015, 52, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.M.; Robinson, S.R. The amyloid hypothesis: Let sleeping dogmas lie? Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, J.C. Alzheimer disease as a vascular disorder: Nosological evidence. Stroke 2002, 33, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, R.D.; Lathe, R.; Tanzi, R.E. The antimicrobial protection hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.G.; Schmitt, F.A.; Wekstein, D.R.; Markesbery, W.R. Alzheimer neuropathologic alterations in aged cognitively normal subjects. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 58, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, R.D.; Masliah, E.; Salmon, D.P.; Butters, N.; DeTeresa, R.; Hill, R.; Hansen, L.A.; Katzman, R. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: Synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 30, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, S.; Aisen, P.S.; Ferris, S.H.; Saumier, D.; Duong, A.; Haine, D.; Garceau, D.; Suhy, J.; Oh, J.; Lau, W.; et al. Effect of tramiprosate in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease: Exploratory analyses of the MRI sub-group of the Alphase study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbimbo, B.P.; Giardina, G.A. gamma-secretase inhibitors and modulators for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Disappointments and hopes. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1555–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, V.T. Alzheimer’s dementia begins as a disease of small blood vessels, damaged by oxidative-induced inflammation and dysregulated amyloid metabolism: Implications for early detection and therapy. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, E.N.; Bicca, M.A.; Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. The Amyloid-beta Oligomer Hypothesis: Beginning of the Third Decade. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, S567–S610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Distefano, D.A.; Parlascino, P.; Fresta, C.G.; Lazzarino, G.; Lunte, S.M.; Nicoletti, V.G. Receptor-mediated toxicity of human amylin fragment aggregated by short- and long-term incubations with copper ions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 425, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, C.; Tomberlin, C.; Roberts, C.M.; Akram, A.; Stein, G.H.; Silverman, M.A.; Link, C.D. In vivo induction of membrane damage by beta-amyloid peptide oligomers. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, S.A.; Geraci, F.; Tropea, M.R.; Grasso, M.; Caruso, G.; Fidilio, A.; Musso, N.; Sanfilippo, G.; Tascedda, F.; Palmeri, A.; et al. Fluoxetine and Vortioxetine Reverse Depressive-Like Phenotype and Memory Deficits Induced by Abeta1–42 Oligomers in Mice: A Key Role of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratiglioni, L.; Winblad, B.; von Strauss, E. Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. Major findings from the Kungsholmen Project. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launer, L.J.; Ross, G.W.; Petrovitch, H.; Masaki, K.; Foley, D.; White, L.R.; Havlik, R.J. Midlife blood pressure and dementia: The Honolulu-Asia aging study. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, A.; Ott, A.; Breteler, M.M.; Bots, M.L.; Slooter, A.J.; van Harskamp, F.; van Duijn, C.N.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; Grobbee, D.E. Atherosclerosis, apolipoprotein E, and prevalence of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in the Rotterdam Study. Lancet 1997, 349, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N. A Systematic Review of the Mortality from Untreated Leptospirosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limmathurotsakul, D.; Turner, E.L.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Thaipadungpanit, J.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Chierakul, W.; Smythe, L.D.; Day, N.P.; Cooper, B.; Peacock, S.J. Fool’s gold: Why imperfect reference tests are undermining the evaluation of novel diagnostics: A reevaluation of 5 diagnostic tests for leptospirosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reller, M.E.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Miles, J.J.; Flom, J.E.; Mayorga, O.; Woods, C.W.; Ko, A.I.; Dumler, J.S.; Matute, A.J. Unsuspected leptospirosis is a cause of acute febrile illness in Nicaragua. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monahan, A.M.; Miller, I.S.; Nally, J.E. Leptospirosis: Risks during recreational activities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.C.; Tsan, Y.T.; Tsai, S.L.; Chang, C.J.; Wang, J.D.; Chen, P.C.; Health Data Analysis in Taiwan (hDATa) Research Group. Hepatitis C viral infection and the risk of dementia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1068-e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.S.; Yang, T.Y.; Shen, W.C.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, M.C.; Kao, C.H. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and dementia. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, L.L.; Capuano, A.W.; Aiello, A.E.; Turner, A.D.; Yolken, R.H.; Torrey, E.F.; Bennett, D.A. Cytomegalovirus infection and risk of Alzheimer disease in older black and white individuals. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H.; Huang, W.S.; Muo, C.H.; Kao, C.H. Increased risk of dementia among chronic osteomyelitis patients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, L.T.; Sheu, J.J.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, M.C.; Chung, S.D. Association between sepsis and dementia. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 1430–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklossy, J. Alzheimer’s disease—A neurospirochetosis. Analysis of the evidence following Koch’s and Hill’s criteria. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzhaki, R.F. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: Increasing evidence for a major role of the virus. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, N.S.; Chung, C.H.; Lin, F.H.; Chiang, C.P.; Yeh, C.B.; Huang, S.Y.; Lu, R.B.; Chang, H.A.; Kao, Y.C.; Yeh, H.W.; et al. Anti-herpetic Medications and Reduced Risk of Dementia in Patients with Herpes Simplex Virus Infections—A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarinejad, H.; Moghoofei, M.; Mostafaei, S.; Salimian, J.; Jamalkandi, S.A.; Ahmadi, A. Worldwide prevalence of viral infection in AECOPD patients: A meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, S. Diabetes and infection: Is there a link?—A mini-review. Gerontology 2013, 59, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.T.; Hsieh, M.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Tsai, C.S.; Chen, V.C.; Gossop, M. Association between depression and enterovirus infection: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Medicine 2017, 96, e5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Leptospirosis (n = 3766) | Control (n = 15,064) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 1185 (31.5) | 4740 (31.5) | 0.99 | |
| Male | 2581 (68.5) | 10,324 (68.5) | ||
| Age, mean | Mean (SD) | 52.4 (16.3) | 52.0 (16.5) | 0.20 |
| Age groups (years) | ≤49 | 1127 (45.2) | 6804 (45.2) | 0.99 |
| 50–64 | 1127 (29.9) | 4508 (29.9) | ||
| ≥65 | 938 (24.9) | 3752 (24.9) | ||
| Comorbidity | ||||
| Diabetes | 570 (15.1) | 827 (5.5) | <0.001 | |
| Hypertension | 824 (21.9) | 1444 (9.6) | <0.001 | |
| Head injury | 236 (6.3) | 503 (3.3) | <0.001 | |
| Depression | 70 (1.9) | 88 (0.6) | <0.001 | |
| Stroke | 301 (8.0) | 596 (4.0) | <0.001 | |
| COPD | 206 (5.5) | 393 (2.6) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Leptospirosis | Control | Crude HR* (95% CI) | Adjusted HR† (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of dementia | PY | Rate# | No. of dementia | PY | Rate# | |||
| All | 27 | 13,989 | 1.93 | 65 | 64,400 | 1.01 | 1.91 (1.71, 2.13) | 1.89 (1.72, 2.08) |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 12 | 4447 | 2.70 | 22 | 20,138 | 1.09 | 2.47 (2.06, 2.96) | 2.69 (2.29, 3.15) |
| Male | 15 | 9542 | 1.57 | 43 | 44,262 | 0.97 | 1.62 (1.41, 1.86) | 1.54 (1.36, 1.74) |
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| ≤65 | 3 | 11,074 | 0.27 | 5 | 48,961 | 0.10 | 2.65 (2.32, 3.03) | 1.53 (1.34, 1.73) |
| >65 | 24 | 2915 | 8.23 | 60 | 15,439 | 3.89 | 2.12 (1.74, 2.58) | 1.73 (1.42, 2.10) |
| Comorbidity‡ | ||||||||
| No | 4 | 9145 | 0.44 | 29 | 55,001 | 0.53 | 0.84 (0.29, 2.38) | 1.23 (1.06, 1.43) |
| Yes | 23 | 4844 | 4.75 | 36 | 9399 | 3.83 | 1.23 (0.73, 2.07) | 2.06 (1.70, 2.50) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Lee, F.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, K.-H. Risk of Dementia in Patients with Leptospirosis: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16173168
Chiu C-H, Chen P-C, Wang Y-C, Lin C-L, Lee F-Y, Wu C-C, Chang K-H. Risk of Dementia in Patients with Leptospirosis: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(17):3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16173168
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Chun-Hsiang, Po-Chung Chen, Ying-Chuan Wang, Cheng-Li Lin, Feng-You Lee, Chia-Chang Wu, and Kuang-Hsi Chang. 2019. "Risk of Dementia in Patients with Leptospirosis: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 17: 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16173168
APA StyleChiu, C.-H., Chen, P.-C., Wang, Y.-C., Lin, C.-L., Lee, F.-Y., Wu, C.-C., & Chang, K.-H. (2019). Risk of Dementia in Patients with Leptospirosis: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(17), 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16173168





