Air Pollution Exposure and Cognitive Function in Taiwanese Older Adults: A Repeated Measurement Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Cognitive Function Measurement
2.3. Exposure Assessment
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Distributions of PM10 and O3 Concentrations for Different Exposure Windows
3.3. Relations of Exposure to PM10 and O3 Levels and Cognitive Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Neurological Disorders: Public Health Challenges. 2006. Available online: http://www.who.int/mental_health/neurology/chapter1_neuro_disorders_public_h_challenges.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 22 January 2019).
- WHO. Mental Health of Older Adults. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-of-older-adults (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- National Development Council, Important Issue. Available online: https://www.ndc.gov.tw/cp.aspx?n=4AE5506551531B06 (accessed on 26 January 2019).
- Wortmann, M. Dementia: A global health priority-highlights from an ADI and World Health Organization report. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2012, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Croze, M.L.; Zimmer, L. Ozone Atmospheric Pollution and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Epidemiological Facts to Molecular Mechanisms. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Vazquez-Sandoval, R.; Gonzalez-Kladiano, D.; Schneider-Rivas, S.; Lechuga-Guerrero, A. Effects of Ozone Exposure in Rats on Memory and Levels of Brain and Pulmonary Superoxide Dismutase. Environ. Res. 1998, 76, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirivelu, M.P.; MohanKumar, S.M.J.; Wagner, J.G.; Harkema, J.R.; MohanKumar, P.S. Activation of the Stress Axis and Neurochemical Alterations in Specific Brain Areas by Concentrated Ambient Particle Exposure with Concomitant Allergic Airway Disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorace, A.; Acetis, L.D.; Alleva, E.; Santucci, D. Prolonged exposure to low doses of ozone: Short- and long-term changes in behavioral performance in mice. Environ. Res. 2001, 85, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Mora-Tiscareño, A.; Ontiveros, E.; Gómez-Garza, G.; Barragán-Mejía, G.; Broadway, J.; Chapman, S.; Valencia-Salazar, G.; Jewells, V.; Maronpot, R.R.; et al. Air pollution, cognitive deficits and brain abnormalities: A pilot study with children and dogs. Brain Cogn. 2008, 68, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Solt, A.C.; Henriquez-Roldan, C.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Nuse, B.; Herritt, L.; Villarreal-Calderon, R.; Osnaya, N.; Stone, I.; Garcia, R.; et al. Long-term air pollution exposure is associated with neuroinflammation, an altered innate immune response, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, ultrafine particulate deposition, and accumulation of amyloid beta-42 and alpha-synuclein in children and young adults. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colicino, E.; Wilson, A.; Frisardi, M.C.; Prada, D.; Power, M.C.; Hoxha, M.; Dioni, L.; Spiro, A.; Vokonas, P.S.; Weisskopf, M.G.; et al. Telomere Length, Long-Term Black Carbon Exposure, and Cognitive Function in a Cohort of Older Men: The VA Normative Aging Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Power, M.C.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Alexeeff, S.E.; Coull, B.A.; Spiro, A., 3rd; Schwartz, J. Traffic-related air pollution and cognitive function in a cohort of older men. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallon, L.A.; Manjourides, J.; Pun, V.C.; Salhi, C.; Suh, H. Cognitive impacts of ambient air pollution in the National Social Health and Aging Project (NSHAP) cohort. Environ. Int. 2017, 104, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weuve, J.; Puett, R.C.; Schwartz, J.; Yanosky, J.D.; Laden, F.; Grodstein, F. Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution and Cognitive Decline in Older Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gatto, N.M.; Henderson, V.W.; Hodis, H.N.; St John, J.A.; Lurmann, F.; Chen, J.C.; Mack, W.J. Components of air pollution and cognitive function in middle-aged and older adults in Los Angeles. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranft, U.; Schikowski, T.; Sugiri, D.; Krutmann, J.; Kramer, U. Long-term exposure to traffic-related particulate matter impairs cognitive function in the elderly. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzivian, L.; Jokisch, M.; Winkler, A.; Weimar, C.; Hennig, F.; Sugiri, D.; Soppa, V.J.; Dragano, N.; Erbel, R.; Jockel, K.H.; et al. Associations of long-term exposure to air pollution and road traffic noise with cognitive function-An analysis of effect measure modification. Environ. Int. 2017, 103, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare. Taiwan Longitudinal Study on Aging (TLSA). Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/EngPages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1077&pid=6197 (accessed on 3 August 2019).
- Pun, V.C.; Manjourides, J.; Suh, H. Association of Ambient Air Pollution with Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Older Adults: Results from the NSHAP Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katzman, R.; Zhang, M.; Qu, O.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.T.; Yu, E.; Wong, S.-C.; Salmon, D.P.; Grant, I. A Chinese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination; impact of illiteracy in a Shanghai dementia survey. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Chang, H.Y. Developmental Patterns of Cognitive Function and Associated Factors among the Elderly in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, A.R.; Wallace, R.B. Measures of cognitive functioning in the AHEAD Study. J. Gerontol B. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 1997, 52, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofstedal, M.B.; Zimmer, Z.S.; Lin, H.-S. A comparison of correlates of cognitive functioning in older persons in Taiwan and the United States. J. Gerontol B. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 1999, 54, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwan Environmental Protection. Available online: https://taqm.epa.gov.tw/taqm/tw/YearlyDataDownload.aspx (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Chang, K.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Muo, C.H.; Wu, T.N.; Chen, C.Y.; Kao, C.H. Increased risk of dementia in patients exposed to nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide: A population-based retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklo, M.; Nieto, F.J. Epidemiology: Beyond the Basics; Jones & Bartlett Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, K.J.; Greenland, S.; Lash, T.L. Modern Epidemiology; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tonne, C.; Elbaz, A.; Beevers, S.; Singh-Manoux, A. Traffic-related air pollution in relation to cognitive function in older adults. Epidemiology 2014, 25, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzivian, L.; Dlugaj, M.; Winkler, A.; Weinmayr, G.; Hennig, F.; Fuks, K.B.; Vossoughi, M.; Schikowski, T.; Weimar, C.; Erbel, R.; et al. Long-Term Air Pollution and Traffic Noise Exposures and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.C.; Schwartz, J. Neurobehavioral effects of ambient air pollution on cognitive performance in US adults. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleary, E.G.; Cifuentes, M.; Grinstein, G.; Brugge, D.; Shea, T.B. Association of Low-Level Ozone with Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X. The impact of exposure to air pollution on cognitive performance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9193–9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, C.R.; Lin, Y.T.; Hwang, B.F. Ozone, particulate matter, and newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 44, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zanobetti, A.; Wang, Y.; Koutrakis, P.; Choirat, C.; Dominici, F.; Schwartz, J.D. Air Pollution and Mortality in the Medicare Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Utell, M.J. Ultrafine particles in the urban air to the respiratory. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, A440–A441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Veronesi, B.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Gehr, P.; Chen, L.C.; Geiser, M.; Reed, W.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Schurch, S.; Schulz, H. Translocation and potential neurological effects of fine and ultrafine particles a critical update. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado-Martínez, C.; Paredes-Carbajal, C.; Mascher, D.; Borgonio-Pérez, G.; Rivas-arancibia, S. Effects of Different Ozone Doses on Memory, Motor Activity and Lipid Peroxidation Levels, in Rats. Int. J. Neurosci. 2001, 108, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, M.C.; Adar, S.D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Weuve, J. Exposure to air pollution as a potential contributor to cognitive function, cognitive decline, brain imaging, and dementia: A systematic review of epidemiologic research. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashford, J.W.; Kolm, P.; Colliver, J.A.; Bekian, C.; Hsu, L.-N. Alzheimer patient evaluation and the mini-mental state: Item characteristic curve analysis. Int. J. Gerontol. 1989, 44, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
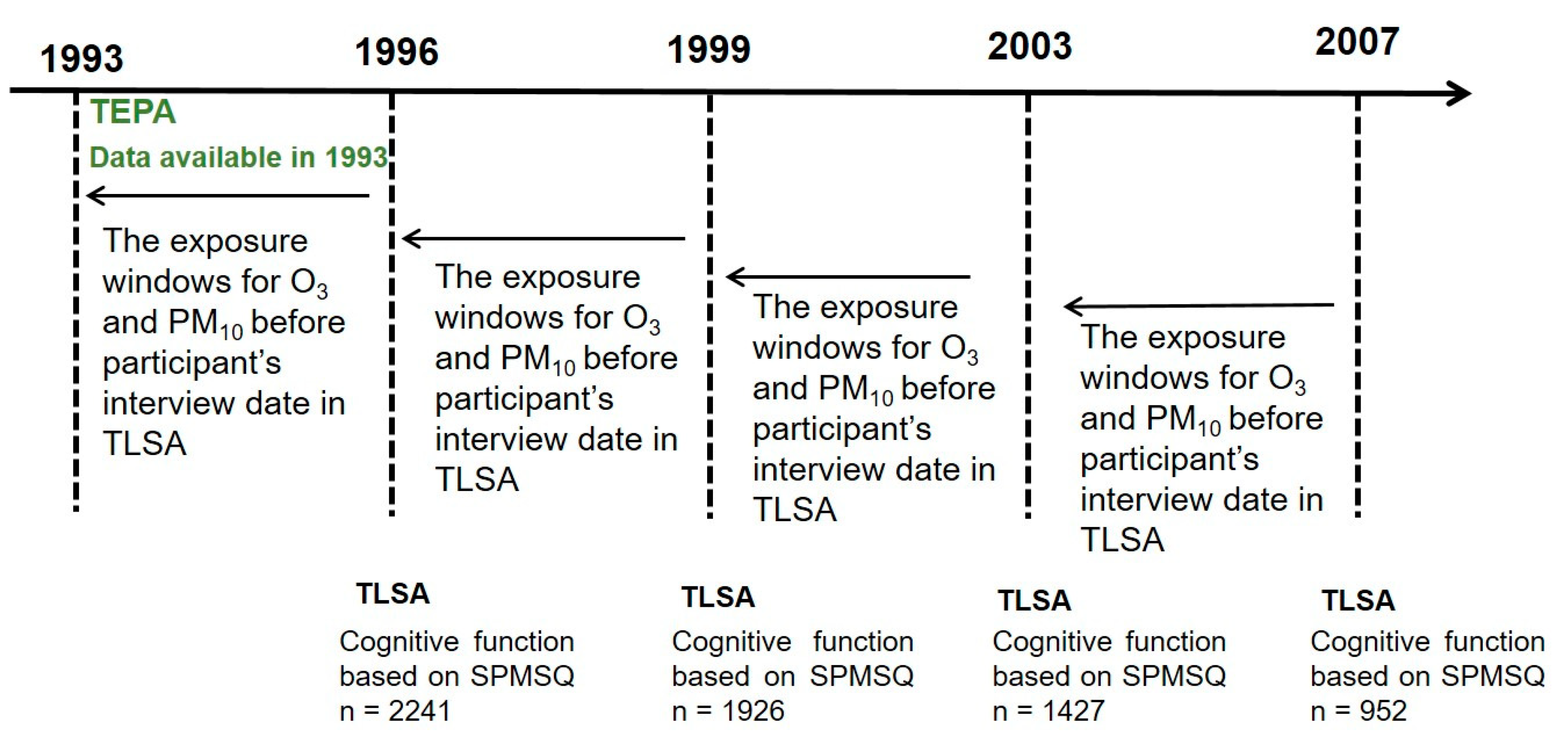
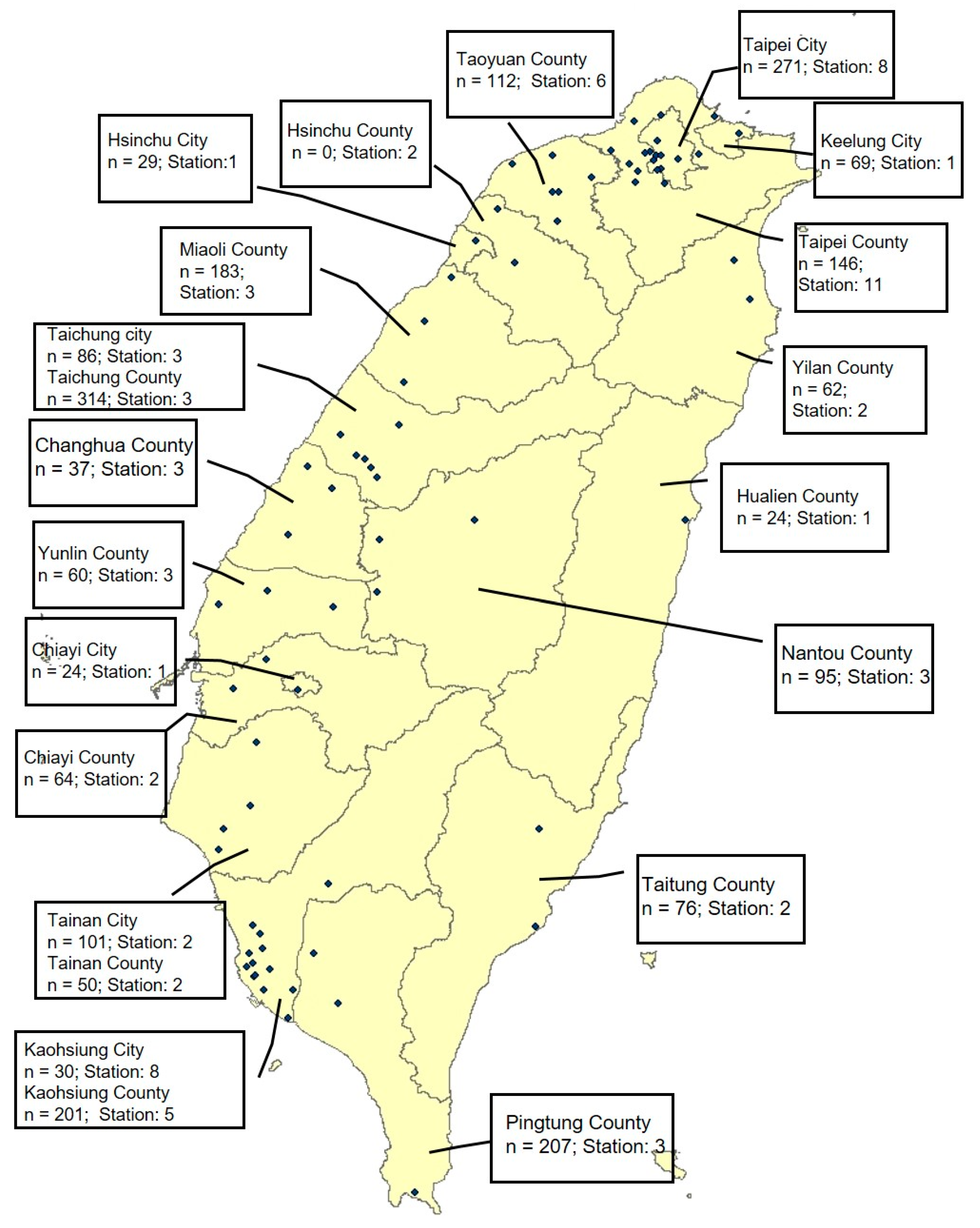

| Variables | Year 1996 (n = 2241) | Year 1999 (n = 1926) | Year 2003 (n = 1427) | Year 2007 (n = 952) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 1289 (57.5) | 1088 (56.5) | 797 (55.9) | 498 (52.3) |
| Age, y, mean ± SD | 73.62 ± 4.94 | 76.28 ± 4.73 | 78.79 ± 4.09 | 82.28 ± 3.76 |
| Spouse, yes, n (%) | 1362 (60.8) | 1091 (56.6) | 730 (51.2) | 434 (45.6) |
| Personal education, n (%) | ||||
| Illiterate | 805 (35.9) | 672 (34.9) | 463 (32.4) | 311 (32.7) |
| Primary and secondary school | 1162 (51.9) | 1017 (52.8) | 766 (53.7) | 503 (52.8) |
| High school and above | 274 (12.2) | 237 (12.3) | 198 (13.9) | 138 (14.5) |
| Self-reported financial status, n (%) | ||||
| Very satisfied | 178 (7.90) | 140 (7.30) | 83 (5.80) | 52 (5.50) |
| Satisfied | 757 (33.8) | 628 (32.6) | 594 (41.6) | 396 (41.6) |
| Fair | 965 (43.1) | 775 (40.2) | 479 (33.6) | 340 (35.7) |
| Dissatisfied | 278 (12.4) | 289 (15.0) | 207 (14.5) | 122 (12.8) |
| Very dissatisfied | 63 (2.80) | 94 (4.90) | 64 (4.50) | 42 (4.40) |
| Physical activity, n (%) | 913 (40.7) | 1246 (64.7) | 962 (67.4) | 638 (67.0) |
| Smoking status, n (%) | 586 (26.1) | 436 (22.6) | 247 (17.3) | 114 (12.0) |
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | 421 (18.8) | 410 (21.3) | 283 (19.8) | 179 (18.8) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 596 (26.6) | 722 (37.5) | 631 (44.2) | 449 (47.2) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 228 (10.2) | 294 (15.3) | 243 (17.0) | 135 (14.2) |
| Heart disease, n (%) | 352 (15.7) | 444 (23.1) | 378 (26.5) | 240 (25.2) |
| SPMSQ (0−5), (n (%), mean ± SD) | 4.49 ± 0.89 | 4.45 ± 0.91 | 4.20 ± 1.03 | 3.74 ± 1.32 |
| ≥3 | 2124 (94.8) | 1817 (94.3) | 1313 (92.0) | 776 (81.5) |
| <3 | 117 (5.20) | 109 (5.7) | 114 (8.00) | 179 (18.5) |
| IADL (0−18), mean ± SD | 1.91 ± 3.62 | 2.37 ± 3.95 | 3.31 ± 4.54 | 4.22 ± 5.06 |
| PM10 (µg/m3) Moving Averages | SPMSQ < 3 | p-Value | SPMSQ < 3 | p-Value |
| OR (95%CI) AD | OR (95%CI) BD | |||
| 7 days | 1.020 (0.980, 1.062) | 0.390 | 1.030 (0.990, 1.083) | 0.218 |
| 14 days | 1.010 (0.961, 1.062) | 0.691 | 1.000 (0.961, 1.062) | 0.731 |
| 21days | 1.020 (0.980, 1.073) | 0.331 | 1.010 (0.970, 1.062) | 0.526 |
| 30 days | 1.030 (0.990, 1.083) | 0.212 | 1.020 (0.980, 1.073) | 0.337 |
| 60 days | 1.030 (0.990, 1.083) | 0.173 | 1.020 (0.980, 1.073) | 0.331 |
| 90 days | 1.030 (1.000, 1.083) | 0.102 | 1.030 (0.990, 1.073) | 0.218 |
| 180 days | 1.041 (1.000, 1.094) | 0.032 | 1.041 (1.000, 1.083) | 0.063 |
| 1 year | 1.083 (1.000, 1.174) | 0.035 | 1.083 (1.000, 1.174) | 0.039 |
| 3 years | 1.116 (1.041, 1.197) | 0.001 | 1.094 (1.020, 1.174) | 0.007 |
| O3 (ppb) Moving Averages | SPMSQ < 3 | p-Value | SPMSQ < 3 | p-Value |
| OR (95%CI) AD | OR (95%CI) CD | |||
| 7 days | 0.961 (0.827, 1.094) | 0.510 | 0.923 (0.787, 1.062) | 0.272 |
| 14 days | 1.010 (0.869, 1.197) | 0.828 | 1.000 (0.852, 1.197) | 0.926 |
| 21days | 1.150 (0.980, 1.363) | 0.101 | 1.127 (0.961, 1.350) | 0.143 |
| 30 days | 1.221 (1.030, 1.448) | 0.017 | 1.209 (1.020, 1.433) | 0.024 |
| 60 days | 1.419 (1.162, 1.733) | <0.001 | 1.405 (1.150, 1.716) | <0.001 |
| 90 days | 1.682 (1.350, 2.096) | <0.001 | 1.649 (1.323, 2.054) | <0.001 |
| 180 days | 1.751 (1.350, 2.248) | <0.001 | 1.716 (1.323, 2.203) | <0.001 |
| 1 year | 1.974 (1.448, 2.691) | <0.001 | 1.954 (1.448, 2.664) | <0.001 |
| 3 years | 1.954 (1.433, 2.664) | <0.001 | 1.878 (1.363, 2.560) | <0.001 |
| Variables | n | SPMSQ < 3 | p-Value B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR A,C | 95%CI | |||
| O3 and PM10 1 year moving averages | <0.001 | |||
| O3 ≤ 25 (ppb) and PM10 ≤ 60 (µg/m3) | 2099 | Reference | ||
| O3 ≤ 25 (ppb) and PM10 > 60 (µg/m3) | 1568 | 1.510 | (1.087, 2.098) | |
| O3 > 25 (ppb) and PM10 ≤ 60 (µg/m3) | 1654 | 1.852 | (1.381, 2.479) | |
| O3 > 25 (ppb) and PM10 > 60 (µg/m3) | 1225 | 2.012 | (1.473, 2.746) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lo, Y.-T.C.; Lu, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Kao, S.; Huang, H.-B. Air Pollution Exposure and Cognitive Function in Taiwanese Older Adults: A Repeated Measurement Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162976
Lo Y-TC, Lu Y-C, Chang Y-H, Kao S, Huang H-B. Air Pollution Exposure and Cognitive Function in Taiwanese Older Adults: A Repeated Measurement Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(16):2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162976
Chicago/Turabian StyleLo, Yuan-Ting C., Ya-Chi Lu, Yu-Hung Chang, Senyeong Kao, and Han-Bin Huang. 2019. "Air Pollution Exposure and Cognitive Function in Taiwanese Older Adults: A Repeated Measurement Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 16: 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162976
APA StyleLo, Y.-T. C., Lu, Y.-C., Chang, Y.-H., Kao, S., & Huang, H.-B. (2019). Air Pollution Exposure and Cognitive Function in Taiwanese Older Adults: A Repeated Measurement Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(16), 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162976





