Evaluation of HBV-Like Circulation in Wild and Farm Animals from Brazil and Uruguay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
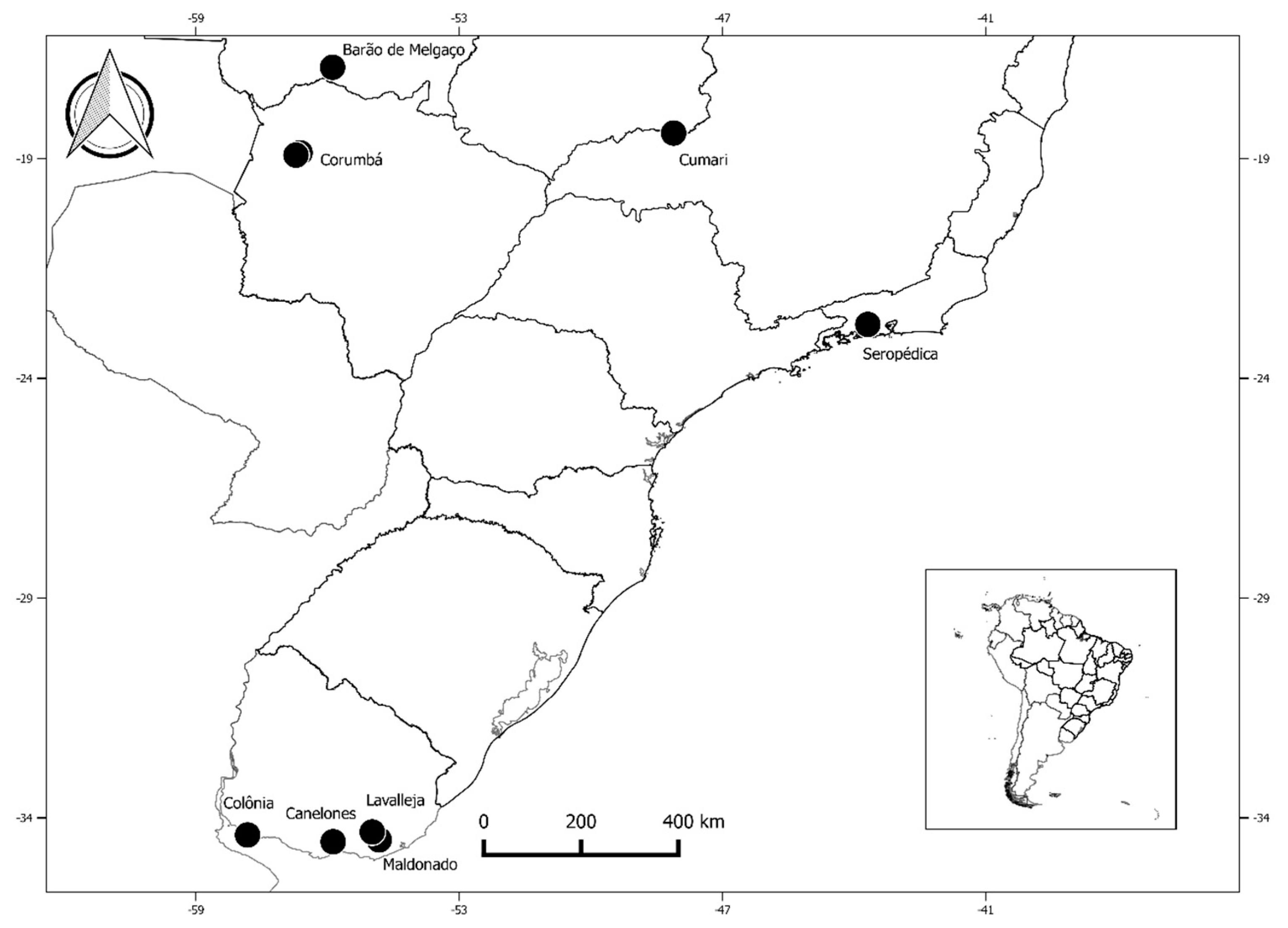
2.1. Ethics Committee, Study Group, and Sample Collection
2.2. Evaluation of Serological Markers
2.3. Reactivity to HBsAg Marker Analysis
2.4. Molecular Tests
2.5. Detection and Characterization of Hepadnavirus DNA
2.6. Phylogenetic Analyses and Recombination Detection
3. Results
3.1. Serological Tests
3.2. Molecular Tests
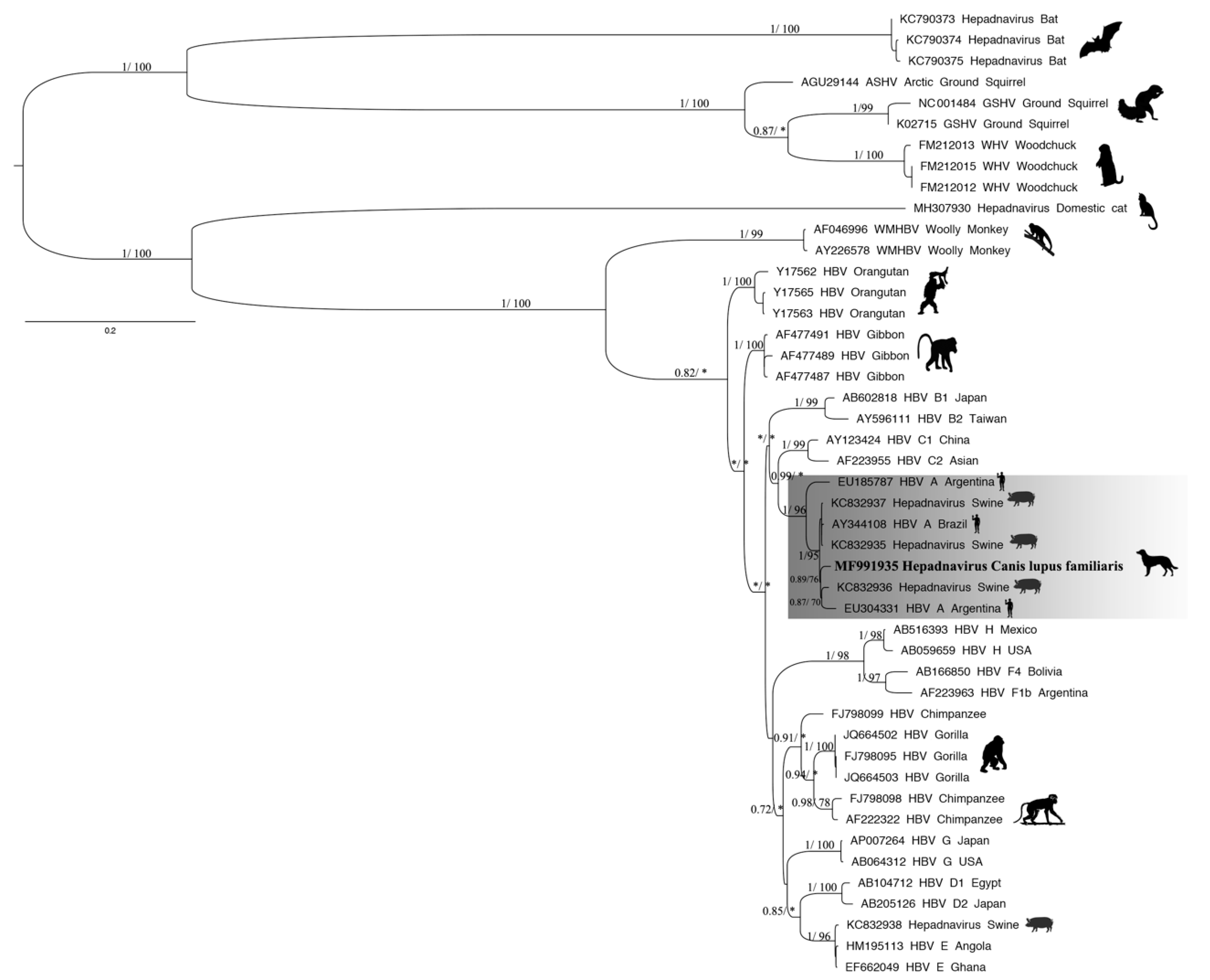
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree and Recombination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiollais, P.; Pourcel, C.; Dejean, A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature 1985, 317, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandart, E.; Kay, A.; Galibert, F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: Comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J. Virol. 1984, 49, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R.E.; Chavez, D.; Brasky, K.M.; Burns, R.B.; Rico-Hesse, R. Isolation of a hepadnavirus from the woolly monkey, a New World primate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5757–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, K.S.; Heeney, J.L.; Swan, R.A.; Heriyanto; Verschoor, E.J. A new group of hepadnaviruses naturally infecting orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus). J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7860–7865. [Google Scholar]
- Grethe, S.; Heckel, J.O.; Rietschel, W.; Hufert, F.T. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis B virus variants in nonhuman primates. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5377–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Margolis, H.S.; Purcell, R.H.; Ebert, J.; Robertson, B.H. Identification of hepatitis B virus indigenous to chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.M.; Holmes, E.C.; Lewis, J.C.; Simmonds, P. Detection of hepatitis B virus infection in wild-born chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus): Phylogenetic relationships with human and other primate genotypes. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4253–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Smolec, J.M.; Snyder, R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4533–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, P.L.; Oshiro, L.S.; Regnery, D.C.; Scullard, G.H.; Robinson, W.S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 2941–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueba, D.; Phelan, M.; Nelson, J.; Beck, F.; Pecha, B.S.; Brown, R.J.; Varmus, H.E.; Ganem, D. Transmission of ground squirrel hepatitis virus to homologous and heterologous hosts. Hepatology 1985, 5, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Geipel, A.; Konig, A.; Corman, V.M.; van Riel, D.; Leijten, L.M.; Bremer, C.M.; Rasche, A.; Cottontail, V.M.; Maganga, G.D.; et al. Bats carry pathogenic hepadnaviruses antigenically related to hepatitis B virus and capable of infecting human hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16151–16156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Aldrich, C.; Summers, J.; Taylor, J.M. Asymmetric replication of duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver cells: Free minus-strand DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 3997–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilbert, A.R.R.; Freiman, J.S.S.; Gowans, E.J.J.; Holmes, M.; Cossart, Y.E.E.; Burrell, C.J.J. Duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver, spleen, and pancreas: Analysis by in situ and southern blot hybridization. Virology 1987, 158, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprengel, R.; Kaleta, E.F.; Will, H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 3832–3839. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.F.; Netter, H.J.; Bruns, M.; Schneider, R.; Frölich, K.; Will, H. A new avian hepadnavirus infecting snow geese (Anser caerulescens) produces a significant fraction of virions containing single-stranded DNA. Virology 1999, 262, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pult, I.; Netter, H.J.; Bruns, M.; Prassolov, A.; Sirma, H.; Hohenberg, H.; Chang, S.F.; Frölich, K.; Krone, O.; Kaleta, E.F.; et al. Identification and analysis of a new hepadnavirus in white storks. Virology 2001, 289, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triyatni, M.; Ey, P.; Tran, T.; Le Mire, M.; Qiao, M.; Burrell, C.; Jilbert, A. Sequence comparison of an Australian duck hepatitis B virus strain with other avian hepadnaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 76, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Mason, W.S.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.R.; Miller, D.S.; Jilbert, A.R.; Newbold, J.E. Identification and characterization of avihepadnaviruses isolated from exotic anseriformes maintained in captivity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2729–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; She, R.; Liu, L.; You, H.; Yin, J. Prevalence of a virus similar to human hepatitis B virus in swine. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, Y.R.; Silva, M.F.; Santos, D.R.; Vieira, A.A.; Ciacci-Zanella, J.R.; Barquero, G.; do Lago, B.V.; Gomes, S.A.; Pinto, M.A.; De Paula, V.S. Serological and molecular evidence of hepadnavirus infection in swine. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. Ann. Agric. Env. Med. 2015, 22, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Xia, K.; She, R.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Yin, J. Detection of hepatitis B virus in serum and liver of chickens. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, A.; Weber, C.C.; Kehlmaier, C.; Braun, E.L.; Green, R.E.; Fritz, U.; Ray, D.A.; Ellegren, H. Early Mesozoic coexistence of Amniotes and hepadnaviridae. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, C.; Meik, J.M.; Dashevsky, D.; Card, D.C.; Castoe, T.A.; Schaack, S. Endogenous hepadnaviruses, bornaviruses and circoviruses in snakes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.M.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Cornman, R.S.; Conway, C.M.; Winton, J.R.; Blazer, V.S. Characterization of a novel hepadnavirus in the White Sucker (Catostomus commersonii) from the great lakes region of the United States. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11801–11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevis, D.; Angelis, K.; Magiorkinis, G.; Kostaki, E.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Hatzakis, A. Dating the origin of hepatitis B virus reveals higher substitution rate and adaptation on the branch leading to F/H genotypes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 93, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, H. Hepatitis B virus: Where do we stand and what is the next step for eradication? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8998–9016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/topics/hepatitis/en/ (accessed on 4 June 2016).
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuwa, M.; Souquière, S.; Clifford, S.L.; Mouinga-Ondeme, A.; Bawe-Johnson, M.; Wickings, E.J.; Latour, S.; Simon, F.; Roques, P. Identification of hepatitis B virus genome in faecal sample from wild living chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) in Gabon. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, S83–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvicino, C.R.; Moreira, M.A.; Soares, M.A. Hepatitis B virus lineages in mammalian hosts: Potential for bidirectional cross-species transmission. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7665–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, A.M.; Barnes, A.N.; Gray, G.C. Reverse zoonotic disease transmission (Zooanthroponosis): A systematic review of seldom-documented human biological threats to animals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, Y.R.; dos Santos, D.R.L.; Portilho, M.M.; Velloso, C.E.P.; Arissawa, M.; Villar, L.M.; Pinto, M.A.; de Paula, V.S. Hepadnavirus detected in bile and liver samples from domestic pigs of commercial abattoirs. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Portilho, M.M. Desenvolvimento de Testes de Detecção e Quantificação do Vírus da Hepatite B em Amostras de Soro e Fluido Oral; Instituto Oswaldo Cruz: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Niel, C.; Moraes, M.T.; Gaspar, A.M.; Yoshida, C.F.; Gomes, S.A. Genetic diversity of hepatitis B virus strains isolated in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Med. Virol 1994, 44, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta-Castro, A.R.C.; Martins, R.M.B.; Yoshida, C.F.T.; Teles, S.A.; Paniago, A.M.; Lima, K.M.B.; Gomes, S.A. Hepatitis B virus infection in isolated Afro-Brazilian communities. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 77, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum-likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mrbayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O.; Sullivan, J. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z. Emerging human infectious diseases: Anthroponoses, zoonoses, and sapronoses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guterres, A.; de Lemos, E.R.S. Hantaviruses and a neglected environmental determinant. One Heal. 2018, 5, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, D.R.L.; Vitral, C.L.; de Paula, V.S.; Marchevsky, R.S.; Lopes, J.F.; Gaspar, A.M.C.; Saddi, T.M.; Júnior, N.C.D.M.; Guimarães, F.D.R.; Júnior, J.G.C.; et al. Serological and molecular evidence of hepatitis E virus in swine in Brazil. Vet. J. 2009, 182, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, A.S.; Lampe, E.; do Espírito-Santo, M.P.; do Amaral Mello, F.C.; de Almeida, F.Q.; de Lemos, E.R.S.; Godoi, T.L.O.S.; Dimache, L.A.G.; dos Santos, D.R.L.; Villar, L.M. Identification of two phylogenetic lineages of equine hepacivirus and high prevalence in Brazil. Vet. J. 2015, 206, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xi, Q.; Deng, R.; Wang, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, X. Identification of interspecies recombination among hepadnaviruses infecting cross-species hosts. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borer, E.T.; Mitchell, C.E.; Power, A.G.; Seabloom, E.W. Consumers indirectly increase infection risk in grassland food webs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.D.; Roy, M. Predation can increase the prevalence of infectious disease. Am. Nat. 2007, 169, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, G.; Dushoff, J.; Yee, S.H. The combined effects of pathogens and predators on insect outbreaks. Nature 2004, 430, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, C.; Holt, R.D.; Hudson, P.J.; Lafferty, K.D.; Dobson, A.P. Keeping the herds healthy and alert: Implications of predator control for infectious disease. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.R.; Duffy, M.A.; Cáceres, C.E. Selective predation and productivity jointly drive complex behavior in host-parasite systems. Am. Nat. 2005, 165, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H. Medical virology of hepatitis B: How it began and where we are now. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HBV/index.htm (accessed on 4 June 2016).
- Houareau, C.; Offergeld, R. Anti-HBc screening— Is it worth the effort? Results of a 10-year surveillance programme covering more than 30 million donations in Germany. Vox Sang. 2019, 114, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouval, D.; Roggendorf, H.; Roggendorf, M. Enhanced immune response to hepatitis B vaccination through immunization with a Pre-S1/Pre-S2/S vaccine. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Ganem, D. The pre-S domain of the large viral envelope protein determines host range in avian hepatitis B viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6259–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouteau, P.; Le Seyec, J.; Cannie, I.; Nassal, M.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Gripon, P. A short N-proximal region in the large envelope protein harbors a determinant that contributes to the species specificity of human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11565–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebe, D.; Urban, S. Viral and cellular determinants involved in hepadnaviral entry. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagins, A.R.; Opriessnig, T.; Huang, Y.W.; Halbur, P.G.; Meng, X.J. Cross-species infection of specific-pathogen-free pigs by a genotype 4 strain of human hepatitis E virus. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Groups | Common Name | Species | Country | Municipality | Total Specimens n (%) | Reactive Total Anti-HBc n (%) | Reactive HBsAg n (%) | Detected Hepadnavirus-DNA n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A—Domestic raised in semi-extensive farms or confined | Domestic pig | Sus scrofa | Uruguay | Canelones/Lavalleja/Colonia | 75 (37.50) | 15 (20.00) | 2 (2.67) | 1 (1.34) |
| Horse | Equus ferus caballus | Brazil | Seropédica | 125 (62.50) | 4 (3.20) | 4 (3.20) | 3 (2.40) | |
| Total | 200 (100) | 19 (9.50) | 6 (3.00) | 4 (2.00) | ||||
| B—Domestic raised wildly or free | Domestic dog | Canis lupus familiaris | Brazil | Corumbá/Cumari | 189 (100) | 19 (10.05) | 11 (5.82) | 19 (10.05) |
| Total | ||||||||
| C—Free-roaming exotic and wild mammals | Wild boar | Sus scrofa | Uruguay | Maldonado | 11 (11.22) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wild pig | Sus scrofa | Brazil | Barão de Melgaço/Corumbá | 61 (62.24) | 6 (9.84) | 15 (24.59) | 7 (11.48) | |
| Jaguar | Panthera onca | Brazil | Barão de Melgaço | 1 (1.02) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0 | |
| Crab-eating fox | Cerdocyon thous | Brazil | Cumari | 19 (19.39) | 0 | 0 | 2 (10.53) | |
| Maned wolf | Chrysocyon brachyurus | Brazil | Cumari | 4 (4.08) | 1 (25.00) | 0 | 0 | |
| Crab-eating raccoon | Procyon cancrivorus | Brazil | Cumari | 1 (1.02) | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | |
| Hoary fox | Lycalopex vetulus | Brazil | Cumari | 1 (1.02) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 98 (100) | 8 (8.16) | 16 (16.33) | 9 (9.18) | ||||
| Total | 487 (100) | 46 (9.45) | 33 (6.78) | 32 (6.57) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, Y.R.; Portilho, M.M.; Oliveira, F.F.; Guterres, A.; dos Santos, D.R.L.; Villar, L.M.; Mirazo, S.; Arbiza, J.; Dimache, L.A.G.; Almeida, F.Q.; et al. Evaluation of HBV-Like Circulation in Wild and Farm Animals from Brazil and Uruguay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152679
Vieira YR, Portilho MM, Oliveira FF, Guterres A, dos Santos DRL, Villar LM, Mirazo S, Arbiza J, Dimache LAG, Almeida FQ, et al. Evaluation of HBV-Like Circulation in Wild and Farm Animals from Brazil and Uruguay. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(15):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152679
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Yasmine R., Moyra M. Portilho, Flávia F. Oliveira, Alexandro Guterres, Débora Regina L dos Santos, Lívia M. Villar, Santiago Mirazo, Juan Arbiza, Luana A.G. Dimache, Fernando Q. Almeida, and et al. 2019. "Evaluation of HBV-Like Circulation in Wild and Farm Animals from Brazil and Uruguay" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 15: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152679
APA StyleVieira, Y. R., Portilho, M. M., Oliveira, F. F., Guterres, A., dos Santos, D. R. L., Villar, L. M., Mirazo, S., Arbiza, J., Dimache, L. A. G., Almeida, F. Q., Brandão, M. L., Cordeiro, J. L. P., Rocha, F. L., Azevedo, F. C., Lemos, F. G., Campos, J. B. V., Macedo, G. C., Herrera, H. M., Péres, I. A. S., ... Pinto, M. A. (2019). Evaluation of HBV-Like Circulation in Wild and Farm Animals from Brazil and Uruguay. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(15), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152679






