Correlations between Forgetfulness and Social Participation: Community Diagnosing Indicators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Forgetfulness as a Risk of Dementia
2.2. Social Factors and Dementia
2.3. Community Diagnosis
3. Study Methods
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Variables Used in the Analysis
3.3. Analytical Methods
3.3.1. Age Adjustment
3.3.2. Statistical Method
3.4. Ethical Considerations
4. Results
4.1. Inter-Municipality Differences
4.1.1. Ratio of People with Forgetfulness
4.1.2. Ratio of Social Participation, Social Contact, and Social Support
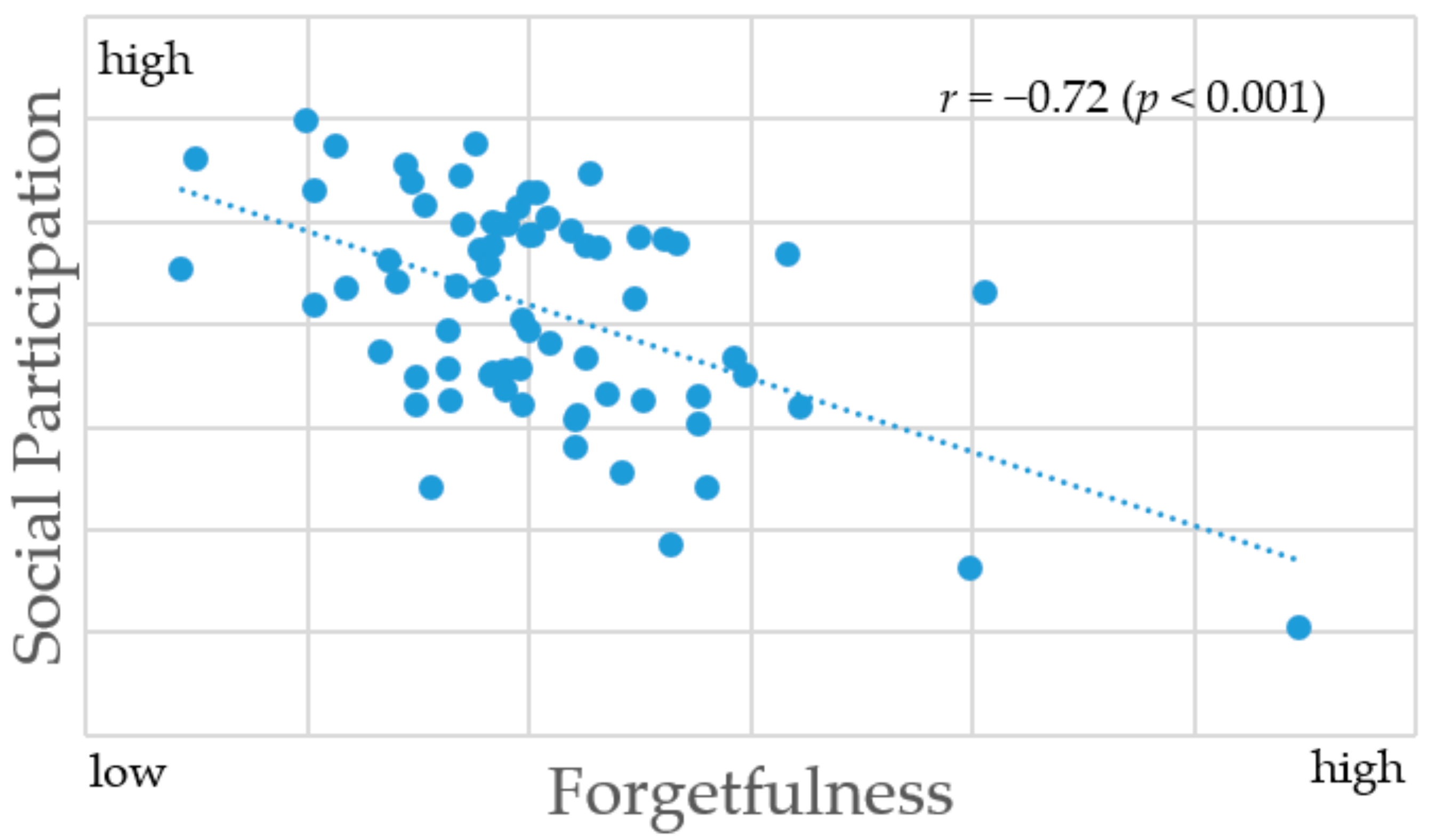
4.2. Partial Correlation Analysis between the Ratio of People with Forgetfulness and Social Participation by Municipality
5. Discussion
5.1. High Ratio of Social Participation in Regions with a Small Ratio of People with Forgetfulness
5.2. Appropriateness as a Community Diagnosing Indicator
5.3. Significance and Limitations of the Study and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Urban-HEART (Urban-Health Equity Assessment and Response Tool). Available online: https://www.who.int/topics/urban_health/en/ (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- WHO. Age Friendly City Indicators. Available online: http://www.who.int/ageing/projects/age_friendly_cities_network/en/ (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare. Health Japan 21 (the Second Term). Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/kenkou/kenkounippon21.html (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Ohara, T.; Hata, J.; Yoshida, D.; Mukai, N.; Nagata, M.; Iwaki, T.; Kitazono, T.; Kanba, S.; Kiyohara, Y.; Ninomiya, T. Trends in dementia prevalence, incidence, and survival rate in a Japanese community. Neurology 2017, 88, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teraoka, S.; Konishi, M.; Kamata, K. A study of associations between the daily-social activity of elderly people living at home and symptoms of forgetfulness; screening for dementia risk. Jpn. J. Public Health 2005, 52, 853–864. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, T.; Kondo, K.; Hirai, H. Psychosocial risk factors involved in progressive dementia-associated senility among the elderly residing at home; AGES Project-Three year cohort longitudinal study. Jpn. J. Public Health 2010, 57, 1054–1065. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, C.P.; Prince, M.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Fratiglioni, L.; Ganguli, M.; Hall, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Hendrie, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. DiseaseInternational as: Global prevalence of dementia: A Delphi consensus study. Lancet 2005, 366, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, K.; Tadaka, E.; Kanagawa, K.; Miyashita, H.; Tachiura, K.; Amatsu, E.; Matsudaira, Y.; Dai, Y.; Kawahara, C.; Taguchi, R.; et al. Characteristics of the Participants and Non-participants in Prevention of Long−term Care among a Rural Community−dwelling Elderly People. J. Jpn. Acad. Community Health Nurs. 2011, 13, 16–22. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.; Bebbington, P.; Lindesay, J.; Meltzer, H.; McManus, S.; Jenkins, R.; Livingston, G. The meaning of reporting forgetfulness: A cross-sectional study of adults in the English 2007 Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, L.; Tan, K.; Diener, E.; Gonzalez, E. Social relations, health behaviors, and health outcomes: A survey and synthesis. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 2013, 5, 28–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, B.N. Social support and health: A review of physiological processes potentially underlying links to disease outcomes. J. Behav. Med. 2006, 29, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Matsumoto, D.; Hayashi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kondo, K. Is it possible to make a town less Fall? AGES Project. J. Health Welf. Stat. 2012, 59, 1–7. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Katsunori, K. JAGES Project. Visualization of Health Inequalities and Social Determinants of Health-Jagaes 2010–11 Proj. Iryo Shakai 2014, 24, 5–20. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T.; Kondo, K.; Yamada, M.; Matsumoto, D. Is it possible to make a town less fall? Analysis of region. AGES Project. J. Health Welf. Stat. 2014, 61, 1–7. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T.; Kondo, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, M.; Matsumoto, D. Factors associated with falls in community-dwelling older people with focus on participation in sport organizations: The Japan Gerontological Evaluation Study Project. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 537614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, D.; Kondo, K. The relationship between the rate of Certification of Needed Support or Long Term Care and Community Organization participation rate as an Index of Social Capital. Jpn. J. Soc. Welf. 2013, 54, 56–69. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori, S.; Kai, Y.; Aida, J.; Kondo, K.; Kawachi, I.; Hirai, H.; Shirai, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Suzuki, K.; JAGES Group. Social participation and the prevention of functional disability in older Japanese: The JAGES cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörman, D.E.; Rönnlund, M.; Sundström, A.; Adolfsson, R.; Nilsson, L.G. Social relationships and risk of dementia: A population-based study. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2015, 27, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A.; Tang, Y.; Arnold, S.E.; Wilson, R.S. The effect of social networks on the relation between Alzheimer’s disease pathology and level of cognitive function in old people: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, V.C.; Lubben, J.; Petitti, D.B.; Little, D.; Chiu, V. Social network, cognitive function, and dementia incidence among elderly women. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratiglioni, L.; Wang, H.X.; Ericsson, K.; Maytan, M.; Winblad, B. Influence of social network on occurrence of dementia: A community-based longitudinal study. Lancet 2000, 355, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, L.C.; Anstey, K.J.; Walker, R.B.; Luszcz, M.A. Social networks and memory over 15 Years of followup in a cohort of older Australians: Results from the Australian longitudinal study of ageing. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwerda, T.J.; Deeg, D.J.; Beekman, A.T.; van Tilburg, T.G.; Stek, M.L.; Jonker, C.; Schoevers, R.A. Feelings of loneliness, but not social isolation, predict dementia onset: Results from the Amsterdam study of the elderly (AMSTEL). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 85, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt-Lunstad, J.; Smith, T.B.; Layton, J.B. Social relationships and mortality risk: A meta-analytic review. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Reitz, C.; Honig, L.S.; Tang, M.X.; Shea, S.; Mayeux, R. Aggregation of vascular risk factors and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2005, 65, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarmeas, N.; Levy, G.; Tang, M.X.; Manly, J.; Stern, Y. Influence of leisure activity on the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 2001, 57, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, S. How to Proceed for Community Diagnosis; Igakushoin: Tokyo, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- The Community-Based Integrated Care: Visualization System. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/05-Shingikai-12301000-Roukenkyoku-Soumuka/0000138621.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Haseda, M.; Kondo, N.; Ashida, T.; Tani, Y.; Takagi, D.; Kondo, K. Community Social Capital, Built Environment, and Income-Based Inequality in Depressive Symptoms among Older People in Japan: An Ecological Study From the JAGES Project. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Kondo, N.; Aida, J.; Kawachi, I.; Koyama, S.; Ojima, T.; Kondo, K. Development of an instrument for community-level health related social capital among Japanese older people: The JAGES Project. J. Epodemiol. 2017, 27, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, H.; Nofuji, Y.; Matsuo, E.; Nishi, M.; Taniguchi, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shinkai, S. Are neighborhood bonding and bridging social capital protective against depressive mood in old age? A multilevel analysis in Japan. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 124, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, D.; Kondo, K.; Kondo, N.; Cable, N.; Ikeda, K.I.; Kawachi, I. Social disorganization/social fragmentation and risk of depression among older people in Japan: Multilevel investigation of indices of social distance. Soc. Sci. Med. 2013, 83, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Aida, J.; Saito, M.; Kondo, N.; Sato, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Tani, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Kondo, K.; Ojima, T.; et al. Community social capital and tooth loss in Japanese older people: A longitudinal cohort study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Aida, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Ohtsuka, R.; Nakade, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kondo, K.; Osaka, K. Individual-and community-level social gradients of edentulousness. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kondo, K.; Aida, J.; Suzuki, K.; Misawa, J.; Nakade, M.; Fuchida, S.; Hirata, Y. Social determinants of denture/bridge use: Japan gerontological evaluation study project cross-sectional study in older Japanese. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, J.; Hanibuchi, T.; Nakade, M.; Hirai, H.; Osaka, K.; Kondo, K. The different effects of vertical social capital and horizontal social capital on dental status: A multilevel analysis. Soc. Sci. Med. 2009, 69, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, H.; Yoshie, S.; Sugawara, I.; Wakui, T.; Arami, R. Contextual effect of neighborhood environment on homebound elderly in a Japanese community. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 54, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. JAGES HEART. Available online: http://sdh.umin.jp/heart/ (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- The Questionnaire of the Survey of Needs in Spheres of Daily Life for Elderly by Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/seisakunitsuite/bunya/hukushi_kaigo/kaigo_koureisha/osirase/hokenjigyou/06/dl/s1-1.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- JAGES Home Page. For the 6th Survey of Needs in Spheres of Daily Life. Available online: https://www.jages.net/renkei/300bm/ (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Takeda, T.; Kondo, K.; Hirai, H.; Murata, C. Psychosocial factors as predictors of dementia among community-dwelling older people. J. Jpn. Occup. Ther. Assoc. 2007, 26, 55–65. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare. About Age-Adjusted Mortality Rate. Available online: http://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/jinkou/other/05sibou/01.html (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Leung, G.T.; Fung, A.W.; Tam, C.W.; Lui, V.W.; Chiu, H.F.; Chan, W.M.; Lam, L.C. Examining the association between late-life leisure activity participation and global cognitive decline in community-dwelling elderly Chinese in Hong Kong. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jean Yeung, W.J. Gender matters: Productive social engagement and the subsequent cognitive changes among older adults. Soc. Sci. Med. 2019, 229, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, K.; Jeong, S.; Murayama, H.; Miyaguni, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Ojima, T.; Kondo, K. Community diagnosis indices for care prevention in Japan Review of the literatures and evaluation quantitative indices using six criteria. Sogo Rehabil. 2018, 46, 1205–1216. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ashihara, H.; Jeong, S.; Kondo, K.; Suzuki, K.; Fukushima, S. Relationship between suicide and social capital of elderly. Suicide Prev. Crisis Interv. 2014, 34, 31–40. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Age-Adjusted (n = 105 Municipalities) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | A Few Times a Year or More% (Range) | Once per Month or More% (Range) | Once per Week or More% (Range) | |
| Forgetfulness | Those who are deemed forgetful | 19.0 (7.1–35.6) | ||
| Social Participation | Neighborhood or residents’ association | 45.3 (14.3–75.1) | 2.5 (0.5–7.1) | 2.4 (0.5–5.4) |
| Interest club or groups | 38.5 (24.2–49.2) | 28.9 (12.4–40.8) | 21.5 (9.8–30.7) | |
| Community living environment improvement activities | 33.7 (9.8–59.8) | 4.9 (1.5–11.9) | 1.6 (0.5–4.3) | |
| Sports club or groups | 28.8 (14.5–42.4) | 22.1 (6.2-34.0) | 16.6 (1.9-26.8) | |
| Paid work | 27.4 (13.9–43.1) | 22.6 (12.3–35.5) | 19.5 (11.4–31.9) | |
| Volunteer club or groups | 25.3 (7.7–45.5) | 13.2 (3.5–21.0) | 6.1 (1.8–10.4) | |
| Senior citizens’ club | 24.0 (6.0–49.6) | 9.9 (3.7–19.2) | 3.5 (0.6–10.3) | |
| Study or cultural groups | 16.9 (8.5–30.1) | 9.0 (1.8–26.2) | 3.6 (0.313.8) | |
| Support for older adults requiring protection | 10.1 (4.5–31.7) | 5.3 (2.2–14.6) | 2.8 (1.0–9.5) | |
| Support for older adults requiring nursing care | 7.2 (3.9–19.9) | 3.2 (1.2–6.8) | 2.1 (0.9–4.5) | |
| Support for parents raising children | 7.5 (3.8–13.1) | 3.7 (1.2–8.0) | 2.3 (0.4–6.1) | |
| Participate in any group above | 75.0 (47.3–89.1) | 55.2 (32.7–69.6) | 41.6 (22.3–54.3) | |
| Social Contact | Contact with friends and/or acquaintances | 90.5 (72.5–96.4) | 72.1 (52.2–86.3) | 49.5 (30.8–69.5) |
| Social Support | Providing or receiving emotional support | 96.7 (90.6–98.8) | ||
| Providing or receiving instrumental support | 96.1 (90.0–98.0) | |||
| Receiving emotional or instrumental support | 98.2 (90.6–99.4) | |||
| Providing emotional or instrumental support | 95.0 (88.5–97.5) | |||
| Regional Variables | Ratio of older adults living alone 1 | 10.1% (5.0%–28.3%) | ||
| Population density of the inhabitable land area 1 | 1749.3 people (3.4–18,253.7 people) | |||
| The ratio of older adults educated for less than 9 years 1 | 46.6% (11.4%–84.0%) | |||
| Taxable income 2 (Yen) | 290,075.1 (536.0–6,817,509) | |||
| Variables | Correlation Coefficient (r) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | A few Times a Year or More | Once per Month or More | Once per Week or More | |
| Experiences Forgetfulness | ||||
| Social Participation | Neighborhood or residents’ association | −0.55 ** | −0.21 | −0.20 |
| Interest groups | −0.51 ** | −0.38 * | −0.37 * | |
| Community living environment improvement activities | −0.54 ** | −0.20 | −0.04 | |
| Sports groups | −0.48 ** | −0.39 ** | −0.26 | |
| Paid work | −0.25 | −0.21 | −0.15 | |
| Volunteer groups | −0.43 ** | −0.40 ** | −0.31 | |
| Senior citizens’ club | −0.27 | −0.14 | 0.10 | |
| Study or cultural groups | −0.46 ** | −0.29 | −0.29 | |
| Support for older adults requiring protection | −0.22 | −0.04 | −0.07 | |
| Support for older adults requiring nursing care | −0.23 | −0.11 | −0.19 | |
| Support for parents raising children | −0.24 | −0.20 | −0.13 | |
| Participate in any group above | −0.72 ** | −0.68 ** | −0.64 ** | |
| Social Contact | Contact with friends and/or acquaintances | −0.66 ** | −0.36 ** | −0.17 |
| Social Support | Providing or receiving emotional support | −0.45 ** | ||
| Providing or receiving instrumental support | −0.38 * | |||
| Receiving emotional or instrumental support | −0.23 | |||
| Providing emotional or instrumental support | −0.13 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.; Inoue, Y.; Kondo, K.; Ide, K.; Miyaguni, Y.; Okada, E.; Takeda, T.; Ojima, T. Correlations between Forgetfulness and Social Participation: Community Diagnosing Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132426
Jeong S, Inoue Y, Kondo K, Ide K, Miyaguni Y, Okada E, Takeda T, Ojima T. Correlations between Forgetfulness and Social Participation: Community Diagnosing Indicators. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(13):2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132426
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Seungwon, Yusuke Inoue, Katsunori Kondo, Kazushige Ide, Yasuhiro Miyaguni, Eisaku Okada, Tokunori Takeda, and Toshiyuki Ojima. 2019. "Correlations between Forgetfulness and Social Participation: Community Diagnosing Indicators" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 13: 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132426
APA StyleJeong, S., Inoue, Y., Kondo, K., Ide, K., Miyaguni, Y., Okada, E., Takeda, T., & Ojima, T. (2019). Correlations between Forgetfulness and Social Participation: Community Diagnosing Indicators. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(13), 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132426







