A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature Assessing Health Outcomes in Populations Living near Oil and Natural Gas Operations: Study Quality and Future Recommendations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scope of Analysis
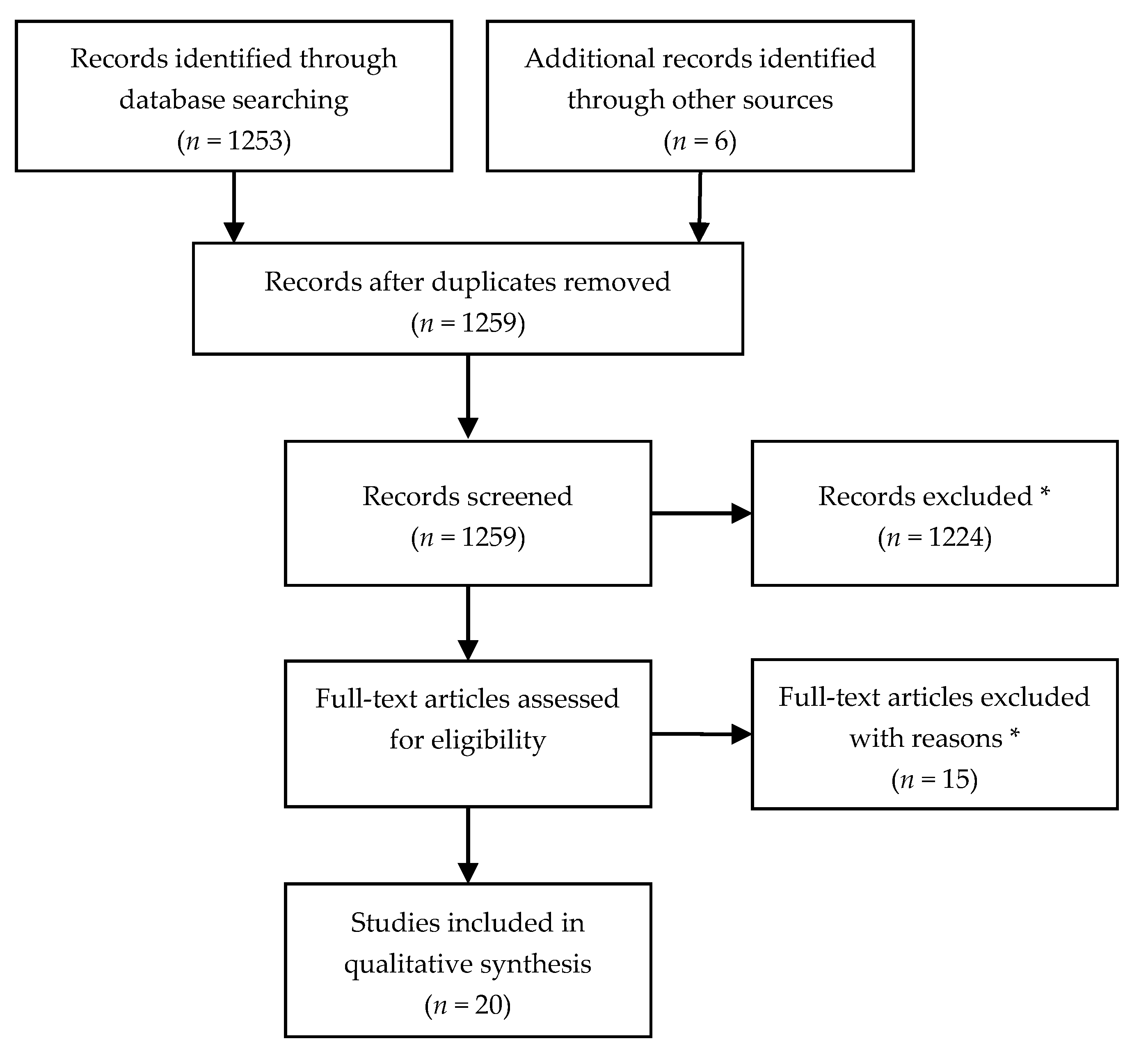
2.2. Data Search
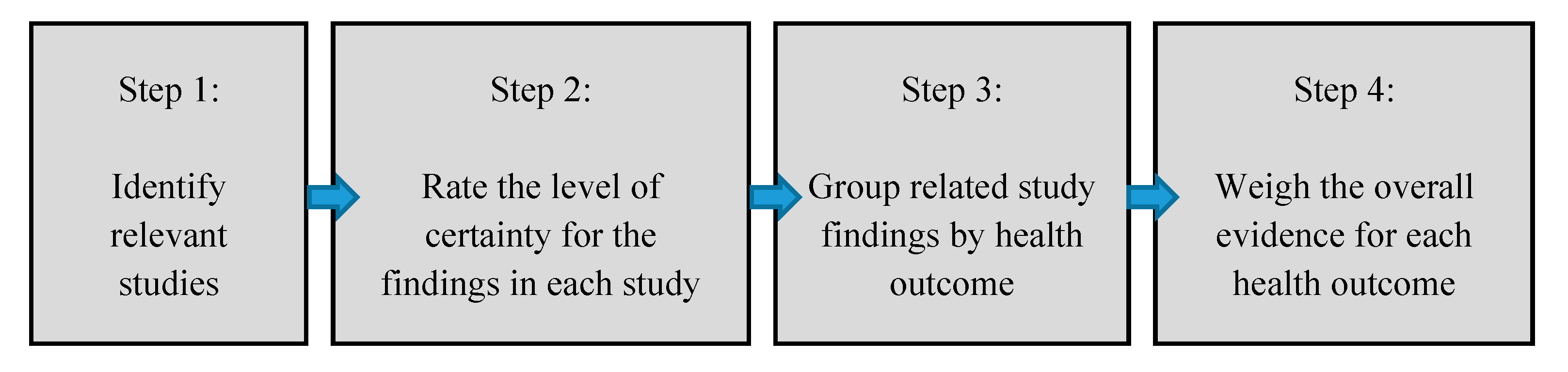
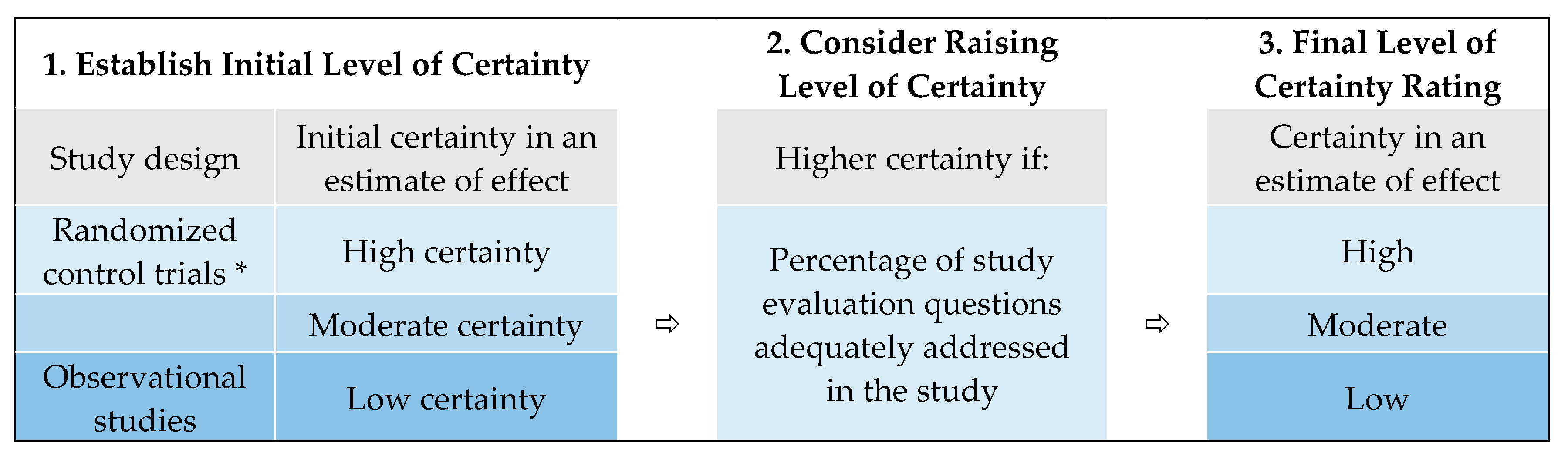
2.3. Level of Certainty Rating and Level of Evidence Conclusions for Individual Studies
3. Results
3.1. Birth Defects and Birth Outcomes
3.2. Cancer
3.3. Respiratory Health Outcomes
3.4. Neurological Health Outcomes
3.5. Other Health Outcomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. U.S. Natural Gas Production Hit A New Record High in 2018. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=38692 (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. Hydraulically Fractured Horizontal Wells Account For Most New Oil And Natural Gas Wells. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=37815 (accessed on 14 January 2019).
- Czolowski, E.D.; Santoro, R.L.; Srebotnjak, T.; Shonkoff, S.B.C. Toward consistent methodology to quantify populations in proximity to oil and gas development: A national spatial analysis and review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitka, M. Rigorous evidence slim for determining health risks from natural gas fracking. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 307, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, A.K.; Vink, S.; Watt, K.; Jagals, P. Environmental health impacts of unconventional natural gas development: A review of the current strength of evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Impact Assessment for Battlement Mesa, Garfield County, Colorado. Available online: https://www.garfield-county.com/public-health/documents/1%20%20%20Complete%20HIA%20without%20Appendix%20D.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2010).
- Ferrar, K.J.; Kriesky, J.; Christen, C.L.; Marshall, L.P.; Malone, S.L.; Sharma, R.K.; Michanowicz, D.R.; Goldstein, B.D. Assessment and longitudinal analysis of health impacts and stressors perceived to result from unconventional shale gas development in the Marcellus Shale region. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2013, 19, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, B.; Greiner, L.H.; Walleigh, L.; Brown, D. Health symptoms in residents living near shale gas activity: A retrospective record review from the Environmental Health Project. Prev. Med. Rep. 2017, 8, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.J.; Theodori, G.L. Local leaders’ perceptions of energy development in the Barnett Shale. South. Rural Sociol. 2009, 24, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Brasier, K.J.; Filteau, M.; McLaughlin, D.K.; Jacquet, J.; Stedman, R.C.; Kelsey, T.W.; Goetz, S.J. Residents’ perceptions of community and environmental impacts from development of natural gas in the Marcellus Shale: A comparison of Pennsylvania and New York cases. J. Rural Soc. Sci. 2011, 26, 32–61. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, M.; Saberi, P.; Pepino, R.; Strupp, E.; Bugos, E.; Cannuscio, C.C. Popular epidemiology and “fracking”: Citizens’ concerns regarding the economic, environmental, health and social impacts of unconventional natural gas drilling operations. J. Community Health 2015, 40, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hays, J.; Shonkoff, S.B.C. Toward an understanding of the environmental and public health impacts of unconventional natural gas development: A categorical assessment of the peer-reviewed scientific literature, 2009–2015. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacy, S.L. A review of the human health impacts of unconventional natural gas development. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2017, 4, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, P.J.; McCoy, D.; Goldstein, R.; Saunders, A.T.; Munroe, A. A review of the public health impacts of unconventional natural gas development. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, T.J.; Sutton, P. The navigation guide systematic review methodology: A rigorous and transparent method for translating environmental health science into better health outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, A.A.; Boyles, A.L.; Wolfe, M.S.; Bucher, J.R.; Thayer, K.A. Systematic review and evidence integration for literature-based environmental health science assessments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.I.; Sutton, P.; Atchley, D.S.; Koustas, E.; Lam, J.; Sen, S.; Robinson, K.A.; Axelrad, D.A.; Woodruff, T.J. The Navigation Guide—Evidence-based medicine meets environmental health: Systematic review of human evidence for PFOA effects on fetal growth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. Hydraulically Fractured Wells Provide Two-Thirds of U.S. Natural Gas Production. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=26112 (accessed on 13 February 2019).
- Hardy, K.; Kelsey, T.W. Local income related to Marcellus shale activity in Pennsylvania. Community Dev. 2015, 46, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunstall, T. Recent economic and community impact of unconventional oil and gas exploration and production on South Texas counties in the Eagle Ford Shale area. J. Reg. Anal. Policy 2015, 45, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Schünemann, H.; Hill, S.; Guyatt, G.; Akl, E.A.; Ahmed, F. The GRADE approach and Bradford Hill’s criteria for causation. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2011, 65, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Schünemann, H.J. What is “quality of evidence” and why is it important to clinicians? BMJ 2008, 336, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. Newcastle-Ottawa quality assessment scale: Case control studies. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/nosgen.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2019).
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Sterne, J. Assessing Risk of Bias in Included Studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P., Green, S., Eds.; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Balise, V.D.; Meng, C.X.; Cornelius-Green, J.N.; Kassotis, C.D.; Kennedy, R.; Nagel, S.C. Systematic review of the association between oil and natural gas extraction processes and human reproduction. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 795–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkman, N.D.; Lohr, K.N.; Ansari, M.; McDonagh, M.; Balk, E.; Whitlock, E.; Reston, J.; Bass, E.; Butler, M.; Gartlehner, G.; et al. Grading the Strength of a Body of Evidence When Assessing Health Care Interventions for the Effective Health Care Program of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: An Update. In Methods Guide for Effectiveness and Comparative Effectiveness Reviews; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2008; Chapter 15. [Google Scholar]
- Schünemann, H.J.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Higgins, J.P.; Deeks, J.; Glasziou, P.; Guyatt, G.H. Assessing the Quality of a Body of Evidence. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P., Green, S., Eds.; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011; Chapter 12.2. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, J.; Levit, L.; Berg, A.; Morton, S. Finding What Works in Health Care: Standards for Systematic Reviews; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, L.M.; Guo, R.; Witter, R.Z.; Savitz, D.A.; Newman, L.S.; Adgate, J.L. Birth outcomes and maternal residential proximity to natural gas development in rural Colorado. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Sneeringer, K.C.; Liu, L.; Kuller, L.H. Time series evaluation of birth defects in areas with and without unconventional natural gas development. J. Epidemiol. Public Heal. Rev. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, C.; Mangano, J.J. There’s a world going on underground—Infant mortality and fracking in Pennsylvania. J. Environ. Prot. (Irvine, Calif). 2017, 08, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.A.; Savitz, D.A.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Ogburn, E.L.; Pollak, J.; Mercer, D.G.; Schwartz, B.S. Unconventional natural gas development and birth outcomes in Pennsylvania, USA. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, J.; Greenstone, M.; Meckel, K. Hydraulic fracturing and infant health: New evidence from Pennsylvania. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.L. Shale gas development and infant health: Evidence from Pennsylvania. J. Health Econ. 2018, 61, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, S.L.; Brink, L.A.L.; Larkin, J.C.; Sadovsky, Y.; Goldstein, B.D.; Pitt, B.R.; Talbott, E.O. Perinatal outcomes and unconventional natural gas operations in Southwest Pennsylvania. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, K.W.; Marshall, A.K.; Symanski, E. Maternal residential proximity to unconventional gas development and perinatal outcomes among a diverse urban population in Texas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, K.W.; Marshall, A.K.; Symanski, E. Drilling and production activity related to unconventional gas development and severity of preterm birth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullin, T.S.; Bamber, A.M.; Bon, D.; Vigil, D.I.; Van Dyke, M. Exposures and Health Risks from Volatile Organic Compounds in Communities Located Near Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Activities in Colorado (U.S.A.). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inayat-Hussain, S.H.; Fukumura, M.; Muiz Aziz, A.; Jin, C.M.; Jin, L.W.; Garcia-Milian, R.; Vasiliou, V.; Deziel, N.C. Prioritization of reproductive toxicants in unconventional oil and gas operations using a multi-country regulatory data-driven hazard assessment. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Tillitt, D.E.; Davis, J.W.; Hormann, A.M.; Nagel, S.C. Estrogen and androgen receptor activities of hydraulic fracturing chemicals and surface and ground water in a drilling-dense region. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Klemp, K.C.; Vu, D.C.; Lin, C.H.; Meng, C.X.; Besch-Williford, C.L.; Pinatti, L.; Zoeller, R.T.; Drobnis, E.Z.; Balise, V.D.; et al. Endocrine-disrupting activity of hydraulic fracturing chemicals and adverse health outcomes after prenatal exposure in male mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4458–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Bromfield, J.J.; Klemp, K.C.; Meng, C.X.; Wolfe, A.; Zoeller, R.T.; Balise, V.D.; Isiguzo, C.J.; Tillitt, D.E.; Nagel, S.C. Adverse reproductive and developmental health outcomes following prenatal exposure to a hydraulic fracturing chemical mixture in female C57Bl/6 mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3469–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, M.L. Shale gas development and cancer incidence in southwest Pennsylvania. Public Health 2016, 141, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryzek, J.; Pastula, S.; Jiang, X.; Garabrant, D.H. Childhood cancer incidence in Pennsylvania counties in relation to living in counties with hydraulic fracturing sites. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 55, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, L.M.; Allshouse, W.B.; Byers, T.E.; Bedrick, E.J.; Serdar, B.; Adgate, J.L. Childhood hematologic cancer and residential proximity to oil and gas development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, P.F.; Vasey, J.J.; Moran, J.R. Long-term effects of cancer survivorship on the employment of older workers. Health Serv. Res. 2008, 43, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.D.; Malone, S. Obfuscation does not provide comfort: Response to the article by Fryzek et al. on hydraulic fracturing and childhood cancer. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 55, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adgate, J.L.; Goldstein, B.D.; McKenzie, L.M. Potential public health hazards, exposures and health effects from unconventional natural gas development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8307–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, E.G.; Ma, X.; Leaderer, B.P.; McKay, L.A.; Pedersen, C.J.; Wang, C.; Gerber, C.J.; Wright, T.J.; Sumner, A.J.; Brennan, M.; et al. A community-based evaluation of proximity to unconventional oil and gas wells, drinking water contaminants, and health symptoms in Ohio. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemielita, T.; Gerton, G.L.; Neidell, M.; Chillrud, S.; Yan, B.; Stute, M.; Howarth, M.; Saberi, P.; Fausti, N.; Penning, T.M.; et al. Unconventional gas and oil drilling is associated with increased hospital utilization rates. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Meyerhoefer, C.; Chou, S.Y. The health implications of unconventional natural gas development in Pennsylvania. Health Econ. 2018, 27, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, P.M.; Slizovskiy, I.B.; Lamers, V.; Trufan, S.J.; Holford, T.R.; Dziura, J.D.; Peduzzi, P.N.; Kane, M.J.; Reif, J.S.; Weiss, T.R.; et al. Proximity to natural gas wells and reported health status: Results of a household survey in Washington County, Pennsylvania. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.G.; Ogburn, E.L.; McCormack, M.; Casey, J.A.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Mercer, D.G.; Schwartz, B.S. Association between unconventional natural gas development in the Marcellus Shale and asthma exacerbations. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustin, A.W.; Hirsch, A.G.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Casey, J.A.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Schwartz, B.S. Associations between unconventional natural gas development and nasal and sinus, migraine headache, and fatigue symptoms in Pennsylvania. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Research on Health and Environmental Effects of Air Quality. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-research/research-health-and-environmental-effects-air-quality (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- National Library of Medicine Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Available online: https://toxtown.nlm.nih.gov/chemicals-and-contaminants/volatile-organic-compounds-vocs (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Casey, J.A.; Wilcox, H.C.; Hirsch, A.G.; Pollak, J.; Schwartz, B.S. Associations of unconventional natural gas development with depression symptoms and disordered sleep in Pennsylvania. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinzor, N.; Subra, W.; Sumi, L. Investigating links between shale gas development and health impacts through a community survey project in Pennsylvania. New Solut. 2013, 23, 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, S.; Taylor, R.; Lyle, D. A review of health effects of aircraft noise. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 1997, 21, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansfeld, S.; Haines, M.; Brown, B. Noise and health in the urban environment. Rev. Environ. Health 2000, 15, 43–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recio, A.; Linares, C.; Banegas, J.R.; Díaz, J. Road traffic noise effects on cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic health: An integrative model of biological mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, E. City Dweller Responses to Multiple Stressors Intruding into Their Homes: Noise, Light, Odour, and Vibration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3246–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooney, A.A.; Cooper, G.S.; Jahnke, G.D.; Lam, J.; Morgan, R.L.; Boyles, A.L.; Ratcliffe, J.M.; Kraft, A.D.; Schunemann, H.J.; Schwingl, P.; et al. How credible are the study results? Evaluating and applying internal validity tools to literature-based assessments of environmental health hazards. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Framework for Assessing Health Impacts of Multiple Chemicals and Other Stressors (Update). Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/interactionprofiles/ip-ga/ipga.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2019).
- Macey, G.P.; Breech, R.; Chernaik, M.; Cox, C.; Larson, D.; Thomas, D.; Carpenter, D.O. Air concentrations of volatile compounds near oil and gas production: A community-based exploratory study. Environ. Heal. 2014, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, T.M.; Breysse, P.N.; Gray, K.; Howarth, M.; Yan, B. Environmental health research recommendations from the Inter-Environmental Health Sciences Core Center Working Group on unconventional natural gas drilling operations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfmacher, K.S.; Elam, S.; Gray, K.M.; Haynes, E.; Hughes, M.H. Unconventional natural gas development and public health: Toward a community-informed research agenda. Rev. Environ. Health 2014, 29, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clough, E.; Bell, D. Just fracking: A distributive environmental justice analysis of unconventional gas development in Pennsylvania, USA. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Evaluation Questions |
|---|
| Population and Sample |
| 1. Does the control group match the exposed group? |
| 2. Is the sample generalizable to the population of interest? |
| 3. Did the study a priori quantify sample and power? |
| 4. Were missing data addressed and tested? |
| Exposure |
| 5. Was exposure directly measured and quantified? |
| 6. Was the exposure or proxy/surrogate of exposure measured from a point location? |
| 7. Does the proxy/surrogate adequately estimate exposure? |
| 8. Was there a temporal relationship between exposure and outcome? |
| Health Outcomes |
| 9. Was the health outcome determined by a medical provider? |
| 10. Was a dose-response relationship seen in any outcome? |
| Confounders |
| 11. Did the study design or analysis account for important confounding and modifying variables? |
| 12. Did the study design or analysis adjust or control for other environmental exposures that were anticipated to bias results? |
| 13. Were sensitivity analyses attempted for population, outcome, or exposure? |
| Reporting |
| 14. Did the study conclusions match the results? |
| Final level of certainty rating: Low/Moderate/High |
| Evidence Level | Definition |
|---|---|
| Substantial | Strong scientific findings that support an association between oil and gas exposure and the outcome, with no credible opposing scientific evidence. |
| Moderate | Strong scientific findings that support an association between oil and gas exposure and the outcome, but these findings have some limitations. |
| Limited | Modest scientific findings that support an association between oil and gas exposure and the outcome, but these findings have significant limitations. |
| Mixed | Both supporting and opposing scientific findings for an association between oil and gas exposure and the outcome, with neither direction dominating. |
| Failing to show an association | Body of research failing to show an association—indicates that the topic has been researched without evidence of an association; is further classified as a limited, moderate or substantial body of research failing to show an association. |
| Insufficient | The outcome has not been sufficiently studied. |
| First Author | Year | Title | Publication | State | Study Type | Health Finding Category | Positive Associations | Null Associations | Level of Certainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Busby [34] | 2017 | There’s a World Going on Underground—Infant Mortality and Fracking in Pennsylvania | Journal of Environmental Protection | Pennsylvania | Ecological | Birth outcomes | Early infant mortality | NA | Low (3) |
| Casey [35] | 2016 | Unconventional Natural Gas Development and Birth Outcomes in Pennsylvania, USA | Epidemiology | Pennsylvania | Retrospective cohort | Birth outcomes | Preterm birth and high-risk pregnancy a | Apgar score, small for gestational age, term birth weight | Moderate (9) |
| Casey [60] | 2018 | Associations of Unconventional Natural Gas Development with Depression Symptoms and Disordered Sleep in Pennsylvania | Scientific Reports | Pennsylvania | Case-control and cross-sectional | Self-reported symptoms and diagnoses | Depression symptoms (self-reported) | Disordered sleep (diagnoses) | Low (6) |
| Currie [36] | 2017 | Hydraulic Fracturing and Infant Health: New Evidence from Pennsylvania | Science Advances | Pennsylvania | Retrospective cohort | Birth outcomes | Low birth weight, decreased birth weight, decreased score on infant health index | NA | Low (5) |
| Elliott [52] | 2018 | A Community-based Evaluation of Proximity to Unconventional Oil and Gas Wells, Drinking Water Contaminants, and Health Symptoms in Ohio | Cross-sectional | Ohio | Cross-sectional | Self-reported symptoms | General symptoms (stress, fatigue, muscle or joint pain, any other self-reported health symptoms) | Respiratory, neurological b, dermal, gastrointestinal symptoms (self-reported) | Low (6) |
| Finkel [46] | 2016 | Shale Gas Development and Cancer Incidence in Southwest Pennsylvania | Public Health | Pennsylvania | Ecological | Cancer | Urinary bladder cancer | Thyroid cancer, leukemia | Low (2) |
| Fryzek [47] | 2013 | Childhood Cancer Incidence in Pennsylvania Counties in Relation to Living in Counties with Hydraulic Fracturing Sites | Journal of Environmental Medicine | Pennsylvania | Ecological | Cancer (child) | Central nervous system tumors | All childhood cancer incidence and leukemia | Low (2) |
| Hill [37] | 2018 | Unconventional Natural Gas Development and Infant Health: Evidence from Pennsylvania | Journal of Health Economics | Pennsylvania | Retrospective cohort | Birth outcomes | Low birth weight, decreased term birth weight, premature birth small for gestational age, Apgar score less than 8 | Gestation periods | Moderate (9) |
| Jemielita [53] | 2015 | Unconventional Gas and Oil Drilling is Associated with Increased Hospital Utilization Rates | PLOS ONE | Pennsylvania | Ecological | Hospitalizations | Cardiology and neurology hospitalizations | Hospitalizations for various medical categories, including pulmonary hospitalizations | Low (7) |
| Ma [33] | 2016 | Time Series Evaluation of Birth Defects in Areas with and without Unconventional Natural Gas Development | Journal of Epidemiology and Public Health Reviews | Pennsylvania | Interrupted time series | Birth defects | NA | Birth defects prevalence | Low (5) |
| McKenzie [32] | 2014 | Birth Outcomes and Maternal Residential Proximity to Natural Gas Development in Rural Colorado | Environmental Health Perspectives | Colorado | Retrospective cohort | Birth outcomes and birth defects | Congenital heart defects and neural tube defects | Oral clefts, preterm birth +, term low birth weight +, decreased term birth weight + | Low (6) |
| McKenzie [48] | 2017 | Childhood Hematologic Cancer and Residential Proximity to Oil and Gas Development | PLOS ONE | Colorado | Case-control | Cancer (child) | Childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia | Childhood non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | Low (8) |
| Peng [54] | 2018 | The Health Implications of Unconventional Natural Gas Development in Pennsylvania | Health Economics | Pennsylvania | Ecological | Hospitalizations | Pneumonia hospitalizations | Hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, upper respiratory infections | Low (6) |
| Rabinowitz [55] | 2015 | Proximity to Natural Gas Wells and Reported Health Status: Results of a Household Survey in Washington County, Pennsylvania | Environmental Health Perspectives | Pennsylvania | Cross-sectional | Self-reported symptoms | Dermal and upper respiratory symptoms (self-reported) | Lower respiratory, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, neurological symptoms (self-reported) | Low (7) |
| Rasmussen [56] | 2016 | Association Between Unconventional Natural Gas Development in the Marcellus Shale and Asthma Exacerbations | JAMA Intern Med. | Pennsylvania | Nested case-control | Respiratory diagnoses | Asthma exacerbations | NA | Moderate (8) |
| Stacy [38] | 2015 | Perinatal Outcomes and Unconventional Natural Gas Operations in Southwest Pennsylvania | PLOS ONE | Pennsylvania | Retrospective cohort | Birth outcomes | Decreased birth weight and small for gestational age | Premature birth+ | Moderate (8) |
| Steinzor [61] | 2013 | Investigating Links Between Shale Gas Development and Health Impacts Through a Community Survey Project in Pennsylvania | New Solutions | Pennsylvania | Cross-sectional | Self-reported symptoms | Throat irritation, sinus problems, nasal irritation, eye burning, persistent cough, frequent nose bleeds, loss of sense of smell, severe headaches, skin rashes, swollen painful joints symptoms (self-reported) | Joint pain, sleep disturbances, shortness of breath, forgetfulness, sleep disorders, feeling weak and tired, increased fatigue, lumbar pain, muscle aches or pain, diarrhea symptoms (self-reported) | Low (3) |
| Tustin [57] | 2016 | Associations between Unconventional Natural Gas Development and Nasal and Sinus, Migraine Headache, and Fatigue Symptoms in Pennsylvania | Environmental Health Perspectives | Pennsylvania | Cross-sectional | Self-reported symptoms | Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), migraine headache, and fatigue symptoms in combination (self-reported): CRS and fatigue, migraine headache and fatigue, and all three symptoms together | NA | Low (5) |
| Whitworth [39] | 2017 | Maternal Residential Proximity to Unconventional Gas Development and Perinatal Outcomes among a Diverse Urban Population in Texas | PLOS ONE | Texas | Retrospective cohort | Birth outcomes | Preterm birth and fetal death | Small for gestational age and term birth weight | Low (7) |
| Whitworth [40] | 2018 | Drilling and Production Activity Related to Unconventional Gas Development and Severity of Preterm Birth | Environmental Health Perspectives | Texas | Nested case-control | Birth outcomes | Preterm birth | NA | Low (9) |
| Health Outcome Categories | Total Number of Studies | Health Outcomes | Reference | Number of Studies Per Certainty Rating | Weight of Evidence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Association | Null Association | |||||||||
| High | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate | High | |||||
| Birth defects | 2 | Congenital heart defects | McKenzie [32] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||
| Oral clefts | McKenzie [32] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Neural tube defects | McKenzie [32] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Birth defects prevalence | Ma [33] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Birth outcomes | 8 | Decreased term birth weight or low birth weight | Casey [35]; Currie [36]; Hill [37]; McKenzie [32]; Stacy [38]; Whitworth [39] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | Mixed | ||
| Early infant mortality | Busby [34] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Fetal death | Whitworth [39] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Gestation period | Hill [37] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Low infant health index | Currie [36] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Low APGAR score a | Casey [35]; Hill [37] | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||||
| Preterm/premature birth | Casey [35]; Hill [37]; McKenzie [32]; Stacy [38]; Whitworth [39,40] | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||
| Small for gestational age | Casey [35]; Hill [37]; Stacy [38]; Whitworth [39] | 2 | 1 | 1 | Mixed | |||||
| Cancer | 3 | Cancer incidence (childhood) | Fryzek [47] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||
| Leukemia (childhood non-specific and acute lymphocytic leukemia) | Fryzek [47]; McKenzie [48] | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||||
| Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (childhood) | McKenzie [48] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| CNS tumorsb(child) | Fryzek [47] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Urinary bladder | Finkel [46] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Thyroid | Finkel [46] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Leukemia | Finkel [46] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Cardiovascular | 3 | Hospitalizations | Jemielita [53]; Peng [54] | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||
| Self-reported symptoms | Rabinowitz [55] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Dermal | 2 | Self-reported symptoms | Elliott [52]; Rabinowitz [55] | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||
| Gastrointestinal | 2 | Self-reported symptoms | Elliott [52]; Rabinowitz [55] | 2 | Limited- failing to show an association | |||||
| Neurological | 4 | Hospitalizations | Jemielita [53] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||
| Self-reported symptoms | Elliott [52]; Rabinowitz [55]; Tustin [57] | 3 | Limited- failing to show an association | |||||||
| Psychological | 2 | Self-reported symptoms | Casey [36]; Tustin [57] | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||
| Diagnosed sleep disturbances | Casey [36] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
| Respiratory | 6 | Self-reported symptoms | Elliott [52]; Rabinowitz [55]; Tustin [57] | 1 | 2 | Mixed | ||||
| Hospitalizations | Jemielita [53]; Peng [54] | 1 | 1 | Mixed | ||||||
| Asthma exacerbation | Rasmussen [56] | 1 | Limited | |||||||
| Other | 2 | Self-reported symptoms (multiple) | Elliott [52]; Tustin [57] | 2 | Limited | |||||
| Hospitalizations (all) | Jemielita [53] | 1 | Insufficient | |||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bamber, A.M.; Hasanali, S.H.; Nair, A.S.; Watkins, S.M.; Vigil, D.I.; Van Dyke, M.; McMullin, T.S.; Richardson, K. A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature Assessing Health Outcomes in Populations Living near Oil and Natural Gas Operations: Study Quality and Future Recommendations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122123
Bamber AM, Hasanali SH, Nair AS, Watkins SM, Vigil DI, Van Dyke M, McMullin TS, Richardson K. A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature Assessing Health Outcomes in Populations Living near Oil and Natural Gas Operations: Study Quality and Future Recommendations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(12):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122123
Chicago/Turabian StyleBamber, Alison M., Stephanie H. Hasanali, Anil S. Nair, Sharon M. Watkins, Daniel I. Vigil, Michael Van Dyke, Tami S. McMullin, and Kristy Richardson. 2019. "A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature Assessing Health Outcomes in Populations Living near Oil and Natural Gas Operations: Study Quality and Future Recommendations" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 12: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122123
APA StyleBamber, A. M., Hasanali, S. H., Nair, A. S., Watkins, S. M., Vigil, D. I., Van Dyke, M., McMullin, T. S., & Richardson, K. (2019). A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature Assessing Health Outcomes in Populations Living near Oil and Natural Gas Operations: Study Quality and Future Recommendations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122123




