Chromium Monitoring in Water by Colorimetry Using Optimised 1,5-Diphenylcarbazide Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Reagents
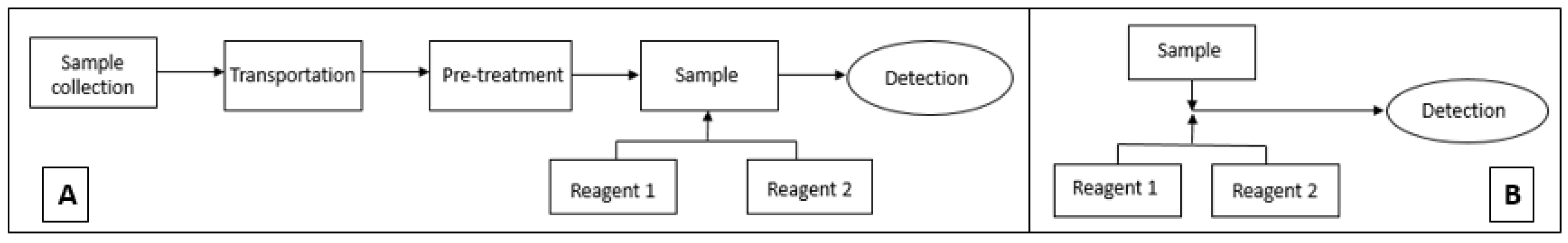
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Path Length
2.5. Sample Cell Cleaning Validation
2.6. Optimisation of Parameters
2.6.1. pH
2.6.2. Sample/Reagent Ratio
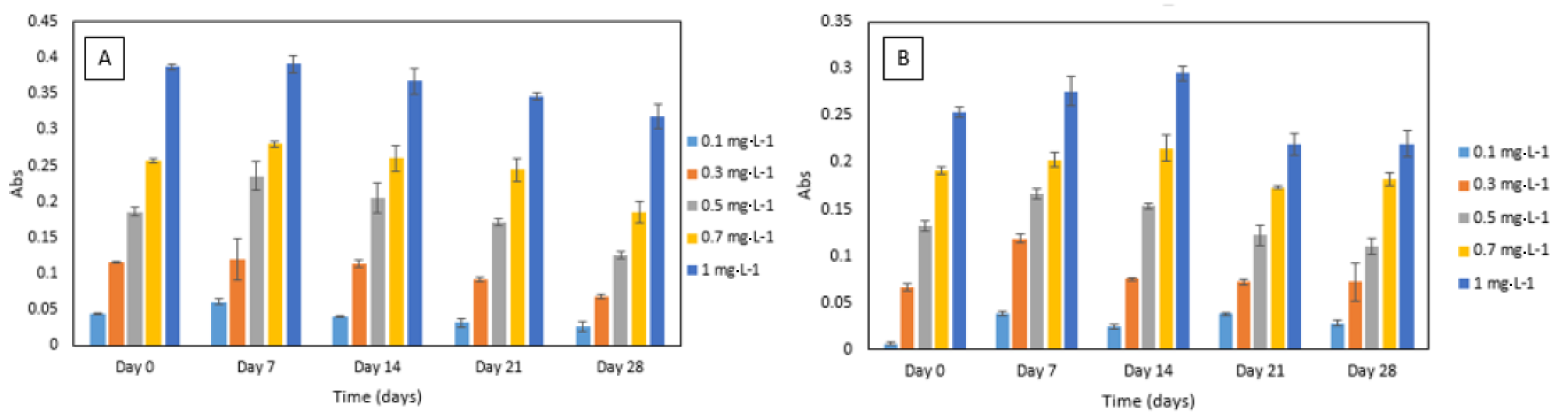
2.6.3. Reagent Stability
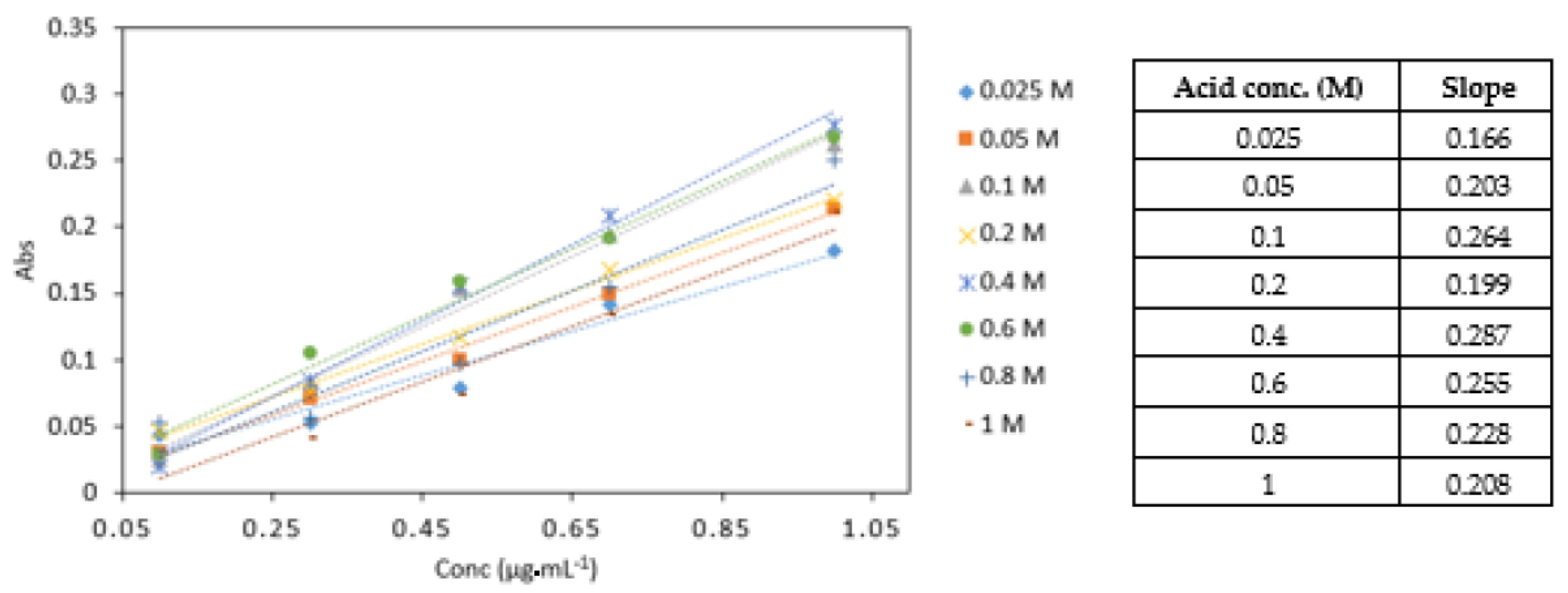
2.6.4. Effect of Different Acid Concentrations
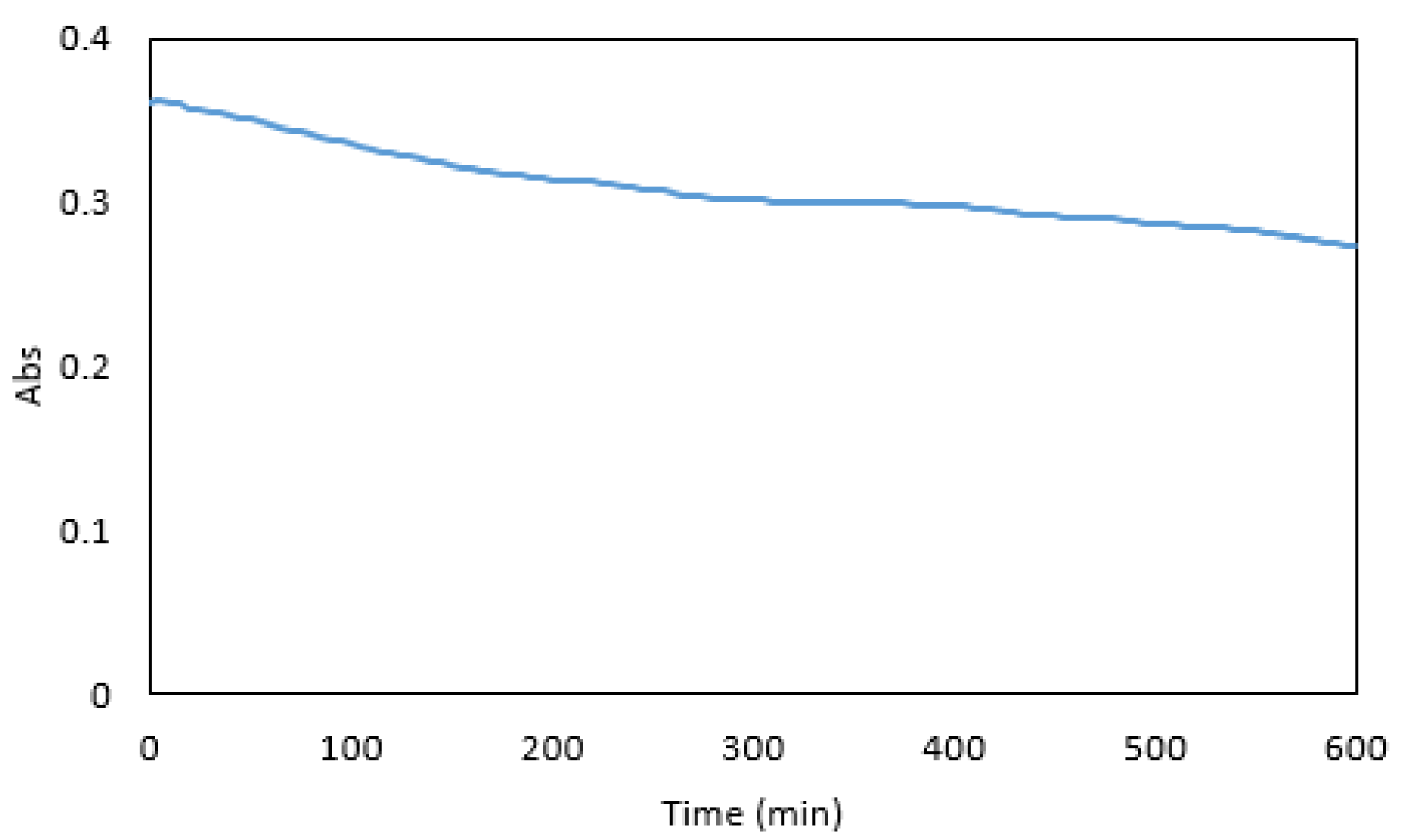
2.7. Colour Stability
2.8. Interference
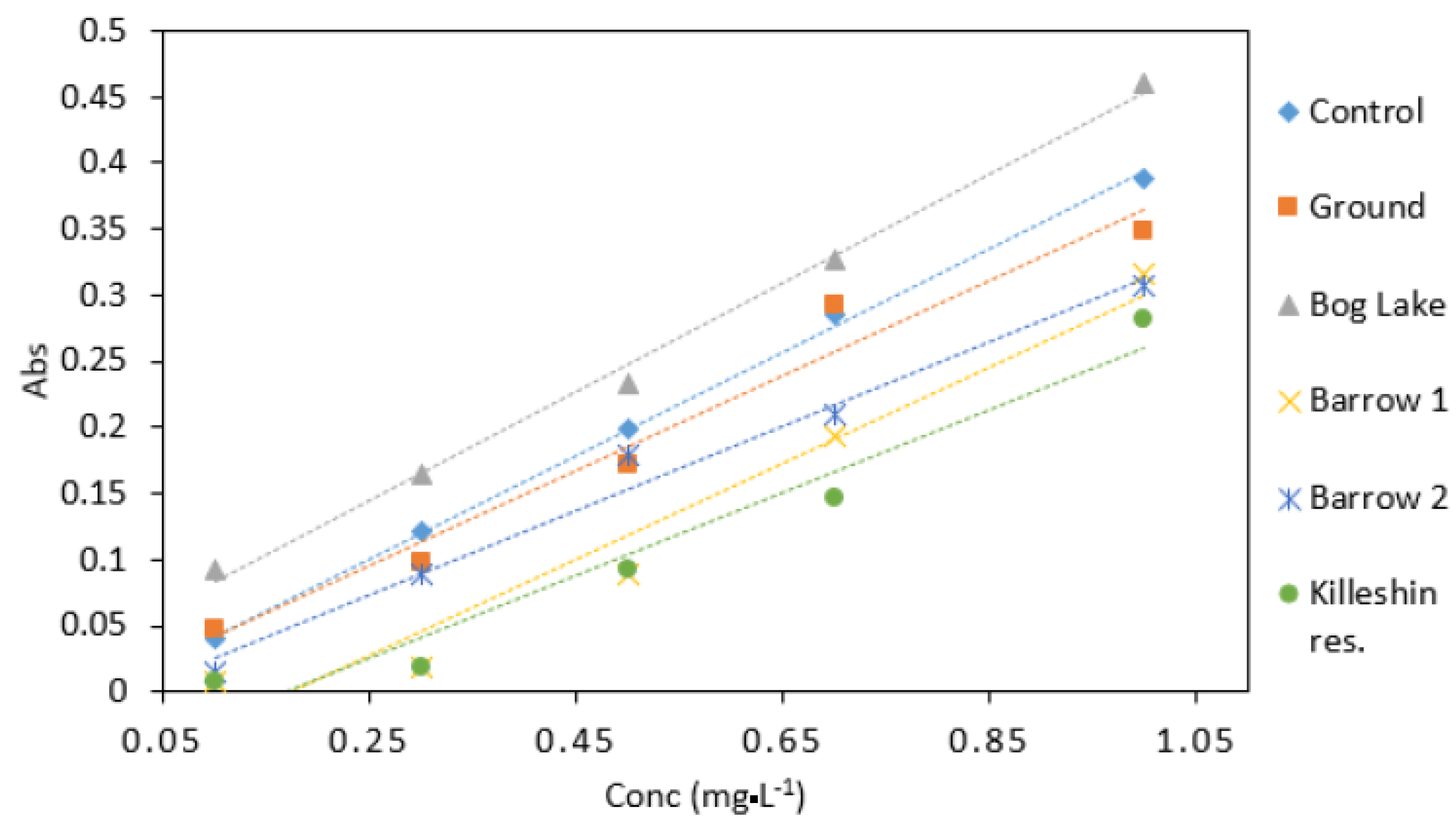
2.9. Environmental Samples
2.10. Comparison between Optimised DPC Method and ICP-MS
3. Results
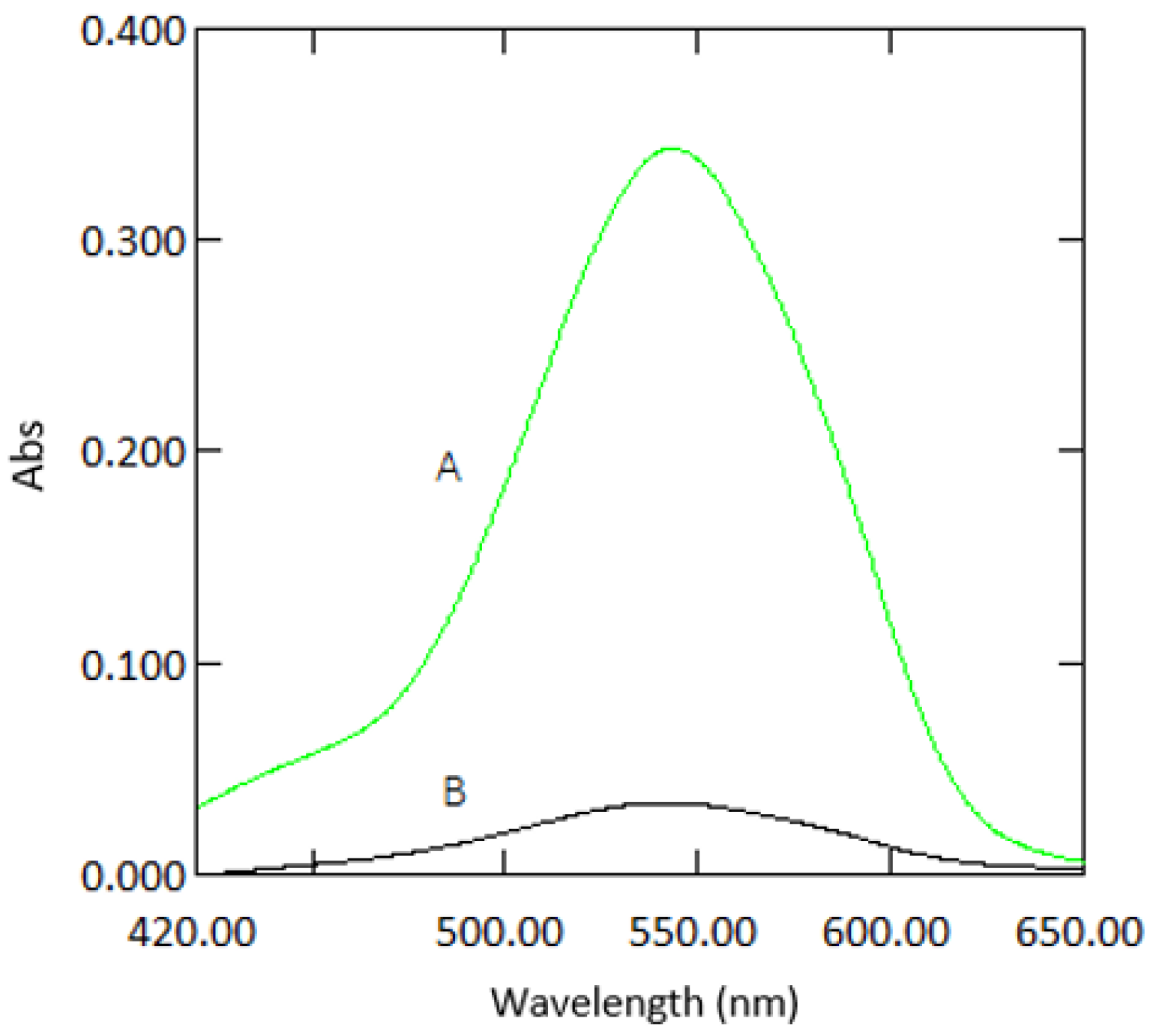
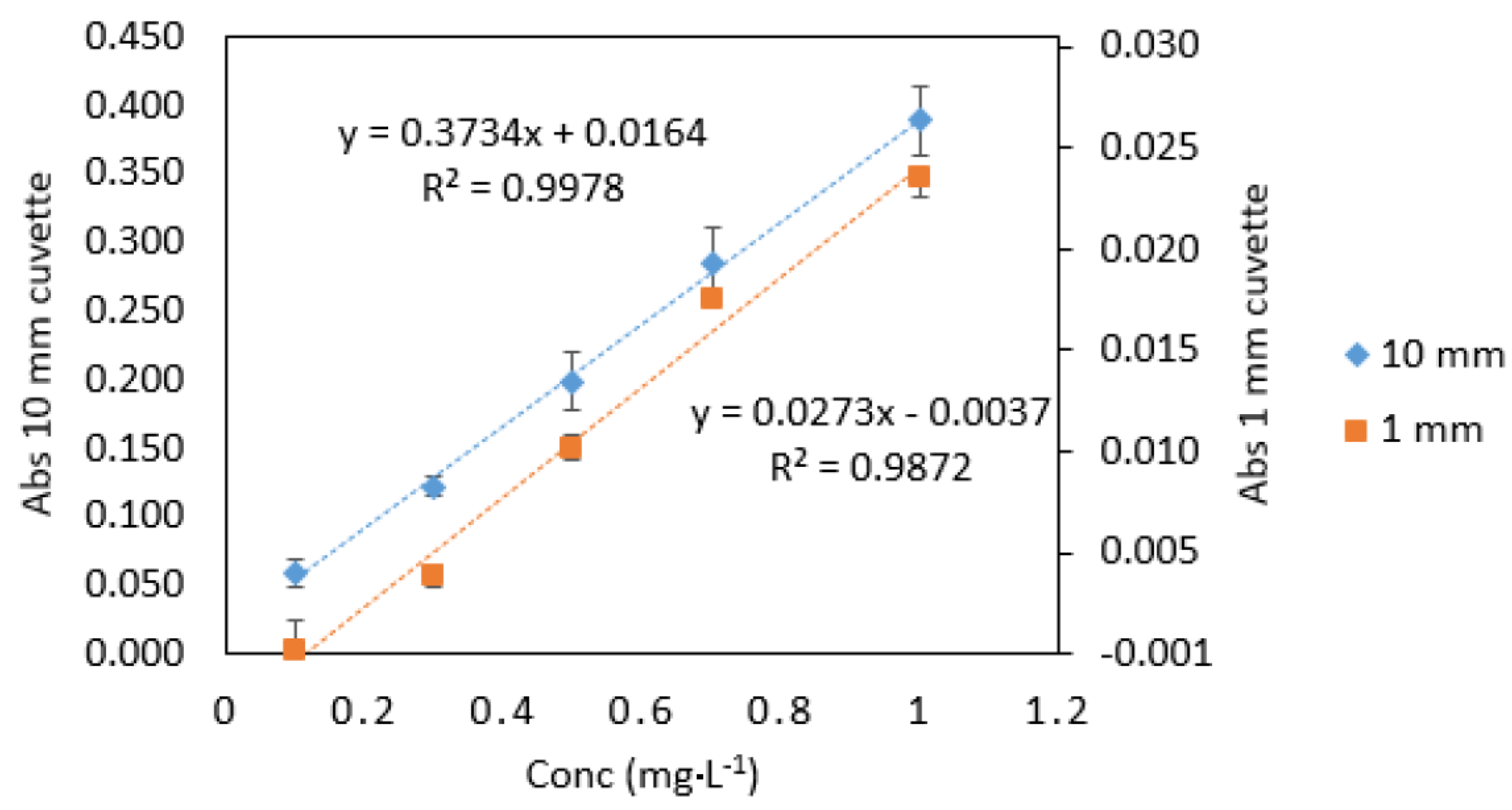
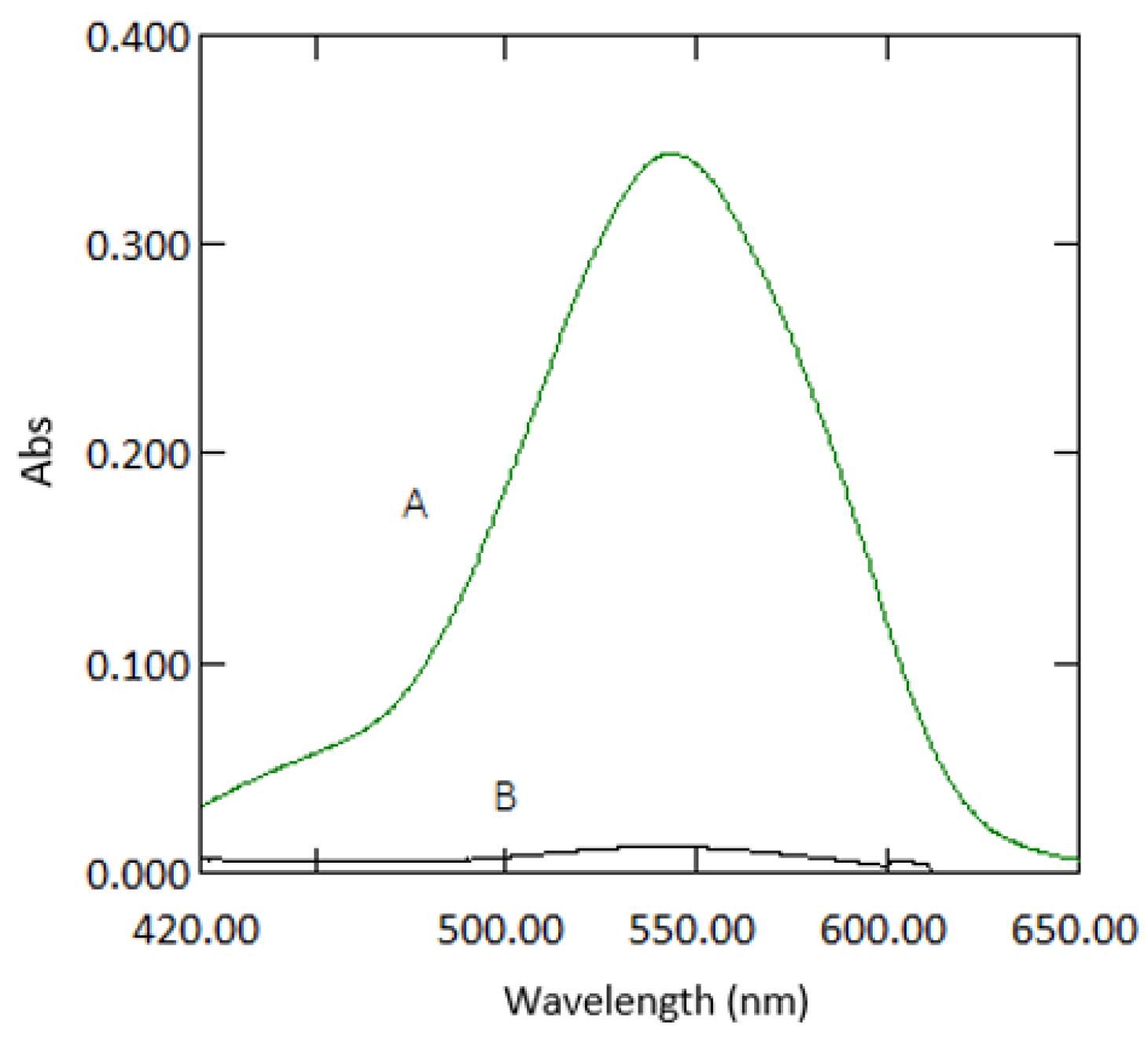
3.1. Path Length
3.2. Sample Cell Cleaning Validation
3.3. Optimisation of Parameters
3.3.1. pH
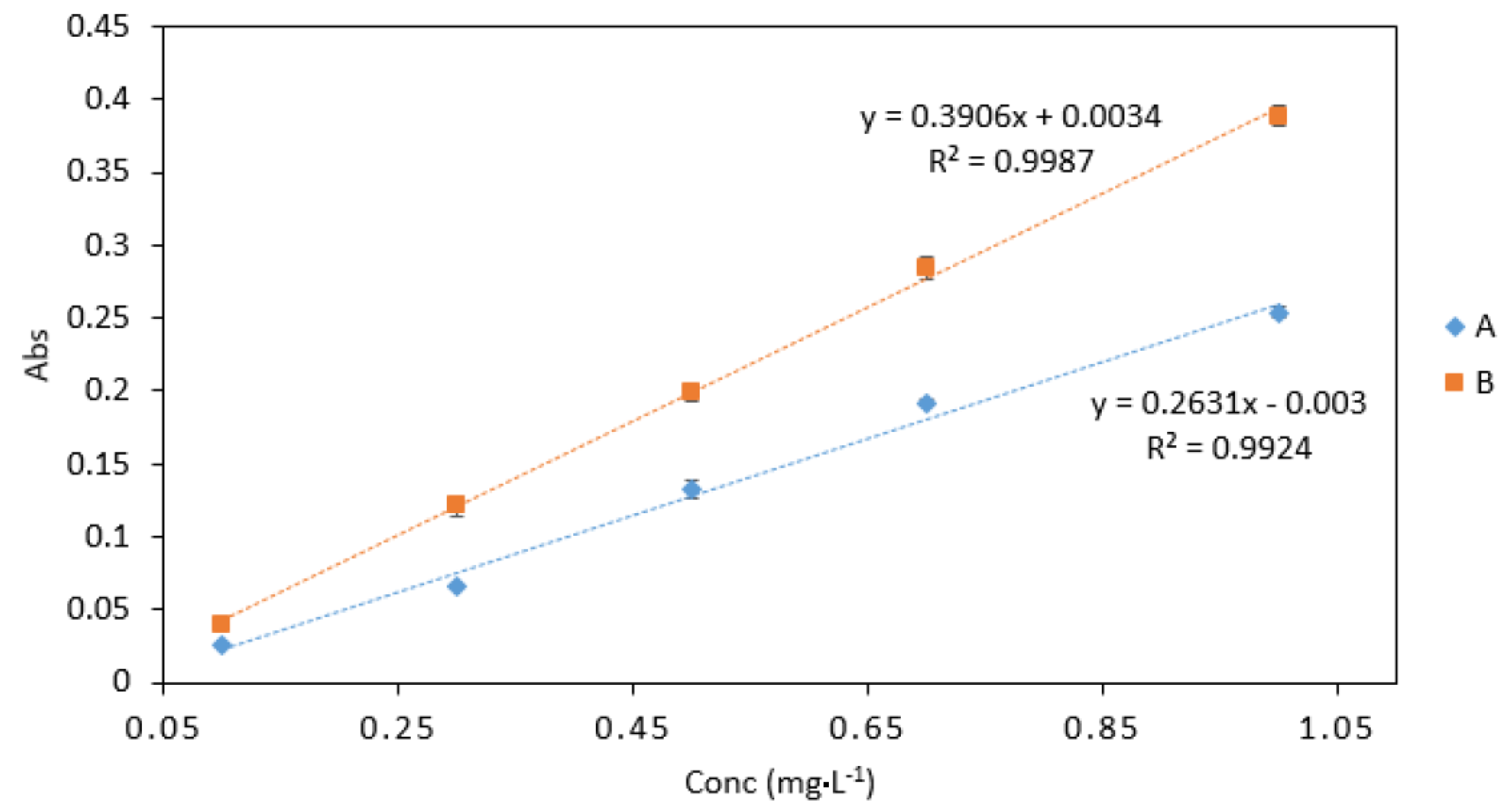
3.3.2. Sample/Reagent Ratio
3.3.3. Reagent Stability
3.3.4. Effect of Different Acid Concentrations
3.4. Colour Stability
3.5. Interference
3.6. Environmental Water Samples
3.7. Comparison between Optimised DPC Method and ICP-MS
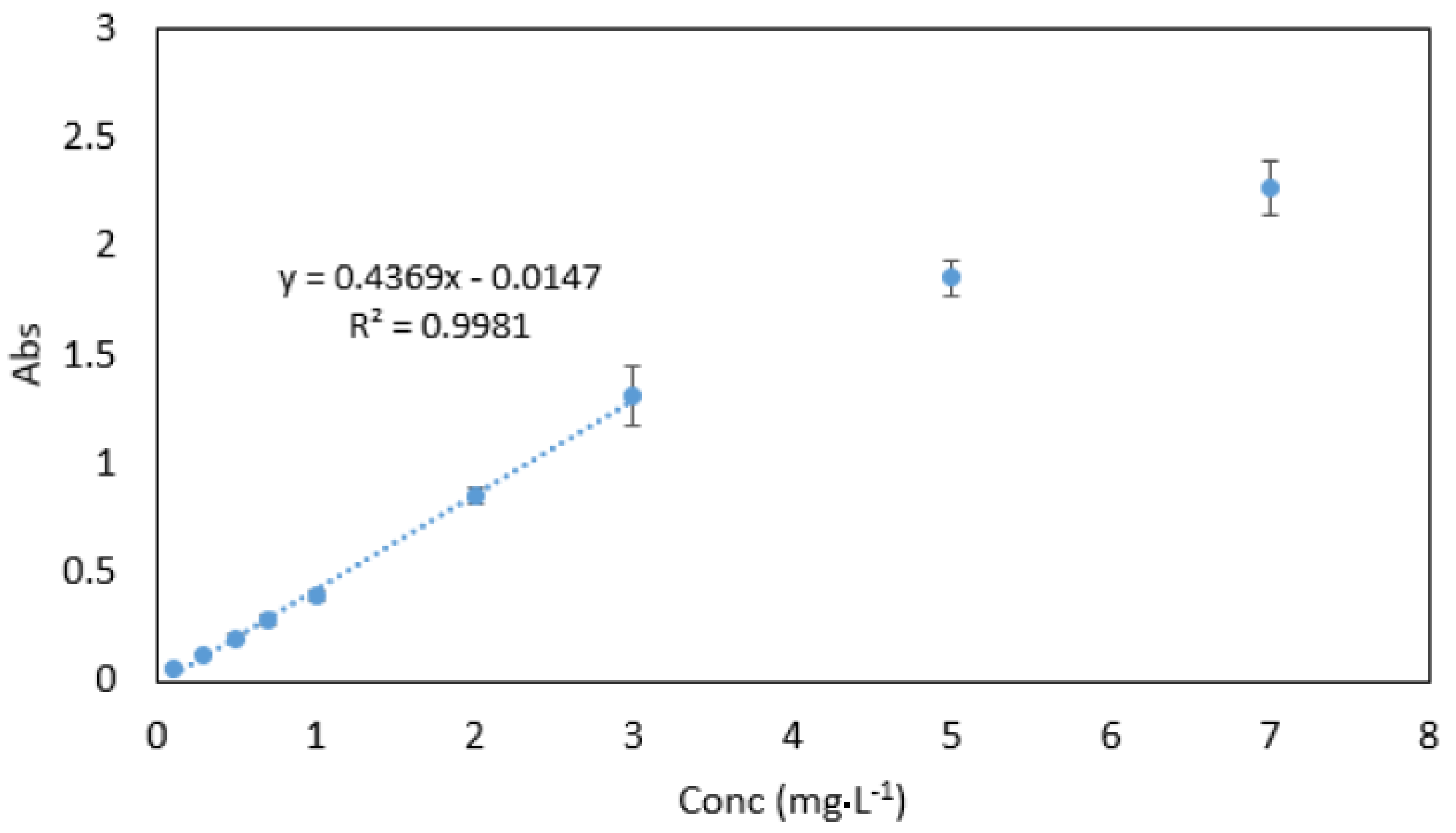
3.8. Analytical Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quantin, C.; Ettler, V.; Garnier, J.; Šebek, O. Sources and extractibility of chromium and nickel in soil profiles developed on Czech serpentinites. C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Ok, Y.S.; Murtaza, G.; Shahid, M.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Li, D.; Mahmood, T. Chromium (VI) sorption efficiency of acid-activated banana peel over organo-montmorillonite in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloof, R. Towards Healthier Water Resources Management. Waterlines 1990, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrough, D.E.; Cohen, Y.; Winer, A.M.; Creelman, L.; Mabuni, C. A Critical Assessment of Chromium in the Environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 29, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, F.C.; Bourg, A.C.M. Aqueous geochemistry of chromium: A review. Water Res. 1991, 25, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, S.; Trapp, S.; Astrup, T.F.; Christensen, T.H. Soil retention of hexavalent chromium released from construction and demolition waste in a road-base-application scenario. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Xu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, L. An effective PDMS microfluidic chip for chemiluminescence detection of cobalt (II) in water. Microsyst. Technol. 2012, 19, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xia, J. Chromium Contamination Accident in China: Viewing Environment Policy of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8605–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Chromium in Drinking-Water. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.C.; Forster, C.F. Removal of hexavalent chromium using sphagnum moss peat. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wu, G.; Chen, A. Sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of chromium (vi) based on gold nanoparticle-decorated Titania nanotube arrays. Analyst 2014, 139, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guertin, J.; Jacobs, J.A.; Avakian, C.P. Chromium (VI) Handbook, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 784. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, L.S.; McLean, J.E.; Parks, J.L.; Edwards, M.A. Hexavalent chromium review, part 2: Chemistry, occurrence, and treatment. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2012, 104, E395–E405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owlad, M.; Aroua, M.K.; Daud, W.A.W.; Baroutian, S. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Water and Wastewater: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 200, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cespón-Romero, R.M.; Yebra-Biurrun, M.C.; Bermejo-Barrera, M.P. Preconcentration and speciation of chromium by the determination of total chromium and chromium (III) in natural waters by flame atomic absorption spectrometry with a chelating ion-exchange flow injection system. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 327, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, N.; Rahman, G.M.M.; Pamuku, M.; Kingston, H.M.S. Determination of Chromium Species in Dietary Supplements Using Speciated Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry with Mass Balance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9966–9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Seo, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.H. Review of carcinogenicity of hexavalent chrome and proposal of revising approval standards for an occupational cancers in Korea. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, S.I.; Niazi, S.N.K.; Dumat, C.; Rashid, M.I. Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achmad, R.; Budiawan, B.; Auerkari, E. Effects of Chromium on Human Body. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2017, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.J. Naturally occurring Cr6+in shallow groundwaters of the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2003, 3, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becquer, T.; Quantin, C.; Sicot, M.; Boudot, J. Chromium availability in ultramafic soils from New Caledonia. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 301, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, J.J.; Sedman, R.M.; Reynolds, S.D.; Sherman, C.D.; Li, L.H.; Howd, R.A.; Sandy, M.S.; Zeise, L.; Alexeeff, G.V. Cancer mortality in a Chinese population exposed to hexavalent chromium in drinking water. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, D.; Brozzo, G.; Canepa, M.; Cipolli, F.; Marini, L.; Ottonello, G.; Zuccolini, M. Natural hexavalent chromium in groundwaters interacting with ophiolitic rocks. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, C.; Booker, S.M. Reflections on hexavalent chromium: Health hazards of an industrial heavyweight. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Sengupta, B.; Bali, R.; Shukla, B.P.; Gurunadharao, V.V.S.; Srivatstava, R. Identification and mapping of chromium (VI) plume in groundwater for remediation: A case study at Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh. J. Geol. Soc. India 2009, 74, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armienta, M.A.; Morton, O.; Rodríguez, R.; Cruz, O.; Aguayo, A.; Ceniceros, N. Chromium in a Tannery Wastewater Irrigated Area, León Valley, Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 66, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressalan, S.; Chauhan, R.S.; Goswami, A.K.; Purohit, D.N. Review of Spectrophotometric Methods for Determination of Chromium. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 69–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, J.L.; McNeill, L.; Frey, M.; Eaton, A.D.; Haghani, A.; Ramirez, L.; Edwards, M. Determination of total chromium in environmental water samples. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2827–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izbicki, J.A.; Ball, J.W.; Bullen, T.D.; Sutley, S.J. Chromium, chromium isotopes and selected trace elements, western Mojave Desert, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 1325–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wu, G.; Wang, Z.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, T.; Wu, A. Selective colorimetric detection of Cr(iii) and Cr(vi) using gallic acid capped gold nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8347–8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-F.; Lin, J.-M. Applications of microfluidic systems in environmental analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 393, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, D.; Fay, C.; Boyle, D.; Osborne, C.; Kent, N.; Cleary, J.; Diamond, D. Development of a low cost microfluidic sensor for the direct determination of nitrate using chromotropic acid in natural waters. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5396–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.; Statham, P.J.; Mowlem, M.C.; Connelly, D.P. Development and application of a microfluidic in-situ analyzer for dissolved Fe and Mn in natural waters. Talanta 2015, 136, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Colorimetric speciation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) with a gold nanoparticle probe. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provin, C.; Fukuba, T.; Okamura, K.; Fujii, T. An integrated microfluidic system for manganese anomaly detection based on chemiluminescence: Description and practical use to discover hydrothermal plumes near the Okinawa Trough. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 38, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Kumachev, A.; Martinez, A.W.; Narovlyansky, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Zoëga Andreasen, S.; Wolff, A.; Duong Bang, D. From Lab on a Chip to Point of Care Devices: The Role of Open Source Microcontrollers. Micromachines 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, J.; Maher, D.; Diamond, D. Development and Deployment of a Microfluidic Platform for Water Quality Monitoring. Smart Sen. Real-Time Water Qual. Monit. 2013, 4, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, T.N.; Muralikrishna, S.; Suresh kumar, K.; Nagaraju, G.; Ramakrishnappa, T. Electrochemical detection and photochemical detoxification of hexavalent chromium (Cr(vi)) by Ag doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3493–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. A miniaturized electrochemical system for high sensitive determination of chromium(VI) by screen-printed carbon electrode with gold nanoparticles modification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, T.K.; Takahashi, F.; Jin, J.; Zein, R.; Munaf, E. Electrochemical Determination of Chromium(VI) in River Water with Gold Nanoparticles–Graphene Nanocomposites Modified Electrodes. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, G.; Jin, L. Nafion stabilized silver nanoparticles modified electrode and its application to Cr(VI) detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 652, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.; Al-Faqheri, W.; Al-Halhouli, A. Low Cost Lab on Chip for the Colorimetric Detection of Nitrate in Mineral Water Products. Sensors 2017, 17, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xue, H. Determination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) species in natural waters by catalytic cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 448, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailapakul, O.; Korsrisakul, S.; Siangproh, W.; Grudpan, K. Fast and simultaneous detection of heavy metals using a simple and reliable microchip-electrochemistry route: An alternative approach to food analysis. Talanta 2008, 74, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.A.; Duong, C.T.; Grimley, A.; Roper, M.G. Recent advances in microfluidic detection systems. Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi Kaed Bey, S.K.; Connelly, D.P.; Legiret, F.-E.; Harris, A.J.K.; Mowlem, M.C. A high-resolution analyser for the measurement of ammonium in oligotrophic seawater. Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, L.-R.; Yang, K.-B.; Zhong, X.; Huang, R.-B.; Zheng, L.-S. p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone: A simple novel selective and sensitive fluorescent sensor for Mercury(II) in aqueous solution. Talanta 2006, 69, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogarajah, N.; Tsai, S.S.H. Detection of trace arsenic in drinking water: Challenges and opportunities for microfluidics. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Gritsenko, D.; Feng, S.; Teh, Y.C.; Lu, X.; Xu, J. Detection of heavy metal by paper-based microfluidics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, H.; Shiraishi, Y. Development of paper-based microfluidic analytical device for iron assay using photomask printed with 3D printer for fabrication of hydrophilic and hydrophobic zones on paper by photolithography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 883, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idros, N.; Chu, D. Triple-Indicator-Based Multidimensional Colorimetric Sensing Platform for Heavy Metal Ion Detections. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, B.; Qi, A.; Tian, C.; Han, J.; Shi, Y.; Chen, L. Improved assessment of accuracy and performance using a rotational paper-based device for multiplexed detection of heavy metals. Talanta 2018, 178, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, E. Selective, peroxidase substrate based “signal-on” colorimetric assay for the detection of chromium (VI). Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 630, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, A.; Rao, S.J. Photometric and fluorimetric determination of chromium(VI) using metal-oxo mediated reaction of 1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)thiourea in micellar medium. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revanasiddappa, H.D.; Kumar, T.N.K. Spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of chromium with citrazinic acid. J. of Anal. Chem. 2001, 56, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreevani, I.; Reddy, P.R.; Reddy, V.K. A rapid and simple spectrophotometric determination of traces of chromium (VI) in waste water samples and in soil samples by using 2-hydroxy, 3-methoxy benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (HMBATSC). J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 3, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onchoke, K.K.; Sasu, S.A. Determination of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)) Concentrations via Ion Chromatography and UV-Vis Spectrophotometry in Samples Collected from Nacogdoches Wastewater Treatment Plant, East Texas (USA). Adv. Environ. Chem. 2016, 2016, 3468635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurster, S.; Kratz, E.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Mildau, G. Spectrophotometric Quantification of Toxicologically Relevant Concentrations of Chromium(VI) in Cosmetic Pigments and Eyeshadow Using Synthetic Lachrymal Fluid Extraction. Int. J. Spectr. 2012, 2012, 985131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; El-Sheikh, R.; Shaltout, M.I. Utilization of 2-Amino-6-(1,3-thiazol-2yldiazenyl)phenol for Chromium Speciation in Environmental Samples Spectrophotometrically. Can. Chem. Trans. 2015, 3, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, L. Red-to-blue colorimetric detection of chromium via Cr (III)-citrate chelating based on Tween 20-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 472, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustis, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: Noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Instrumental Parameters | Scanning Parameters |
|---|---|
| Plasma flow: 15 L·min−1 | Scanning mode: Peak hopping |
| Auxiliary flow: 1.55 L·min−1 | Number of replicates: 3 |
| Nebuliser flow: 0.9 L·min−1 | Pump rate: 9 rpm |
| Sheath gas flow: 0.2 L·min−1 | Rinse time: 40 s |
| Sampling depth: 6.5·mm | Sample uptake delay: 50 s |
| Power: 1.4 kW | Internal standards: Li6, Sc45, Y89, Tb159, Ho165, Th232 |
| Solvent | Abs | Abs | Abs | Average | SD | % RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.003 | 20.830 |
| 1% HCl | 0.041 | 0.017 | 0.081 | 0.046 | 0.032 | 69.780 |
| 1% HNO3 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 57.282 |
| Methanol | 0.088 | 0.101 | 0.105 | 0.098 | 0.009 | 9.070 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.033 | 0.025 | 0.007 | 26.283 |
| Acetone | 0.085 | 0.081 | 0.086 | 0.084 | 0.003 | 3.150 |
| Tween 20 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 30.136 |
| 1% H2SO4 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 10.189 |
| Control | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 34.641 |
| Interferents | Tolerance Limit (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|
| Fe (III) | 1 |
| Cr (III), Mn, Mg, NO3 | 10 |
| PO4 | 100 |
| Sample | ICP-MS Unspiked Sample (mg·L−1) | ICP-MS (mg·L−1) | DPC Method (mg·L−1) | Percentage Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.000 | 0.883 | 1.012 | 14.607 |
| Ground | 0.002 | 0.930 | 1.000 | 7.544 |
| Killeshin res. | 0.002 | 0.959 | 1.063 | 10.805 |
| St Mullins | 0.001 | 0.987 | 1.101 | 11.595 |
| Bog Lake | 0.001 | 1.060 | 0.960 | 9.467 |
| Barrow | 0.002 | 0.907 | 1.024 | 13.249 |
| Detection Principle | ʎmax (nm) | LOD (mg·L−1) | Linear Range (mg·L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| µPDAs | 453 | 0.041 | 0.041–0.072 | 54 |
| µPDAs | 530 | 30.000 | 40.000–400.000 | 53 |
| Rotational µPDAs | 445 | 0.180 | 0.500–10.000 | 55 |
| Gold nanoparticles | 520 | 0.001 | 0.010–0.130 | 63 |
| Spectrophotometric | 503 | 0.030 | 0.010–0.400 | 62 |
| Spectrophotometric | 385 | 0.014 | 0.260–26.000 | 59 |
| Spectrophotometric | 543 | 0.023 | 0.030–3.000 | This study |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lace, A.; Ryan, D.; Bowkett, M.; Cleary, J. Chromium Monitoring in Water by Colorimetry Using Optimised 1,5-Diphenylcarbazide Method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101803
Lace A, Ryan D, Bowkett M, Cleary J. Chromium Monitoring in Water by Colorimetry Using Optimised 1,5-Diphenylcarbazide Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(10):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101803
Chicago/Turabian StyleLace, Annija, David Ryan, Mark Bowkett, and John Cleary. 2019. "Chromium Monitoring in Water by Colorimetry Using Optimised 1,5-Diphenylcarbazide Method" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 10: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101803
APA StyleLace, A., Ryan, D., Bowkett, M., & Cleary, J. (2019). Chromium Monitoring in Water by Colorimetry Using Optimised 1,5-Diphenylcarbazide Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(10), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101803





