Angry Drivers Take Risky Decisions: Evidence from Neurophysiological Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experiment Design
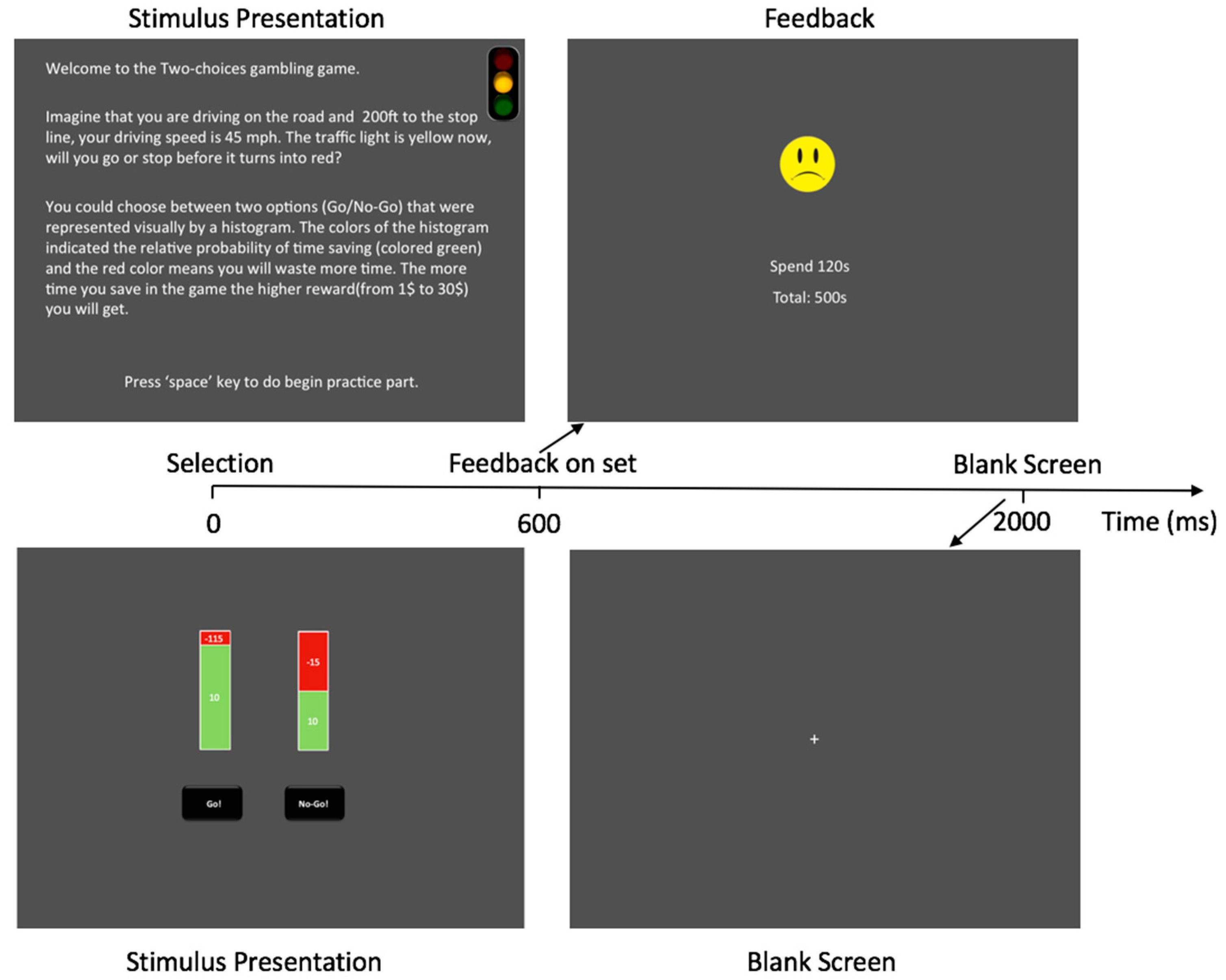
2.3. Experiment Procedure
2.4. Task EEG Recording
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
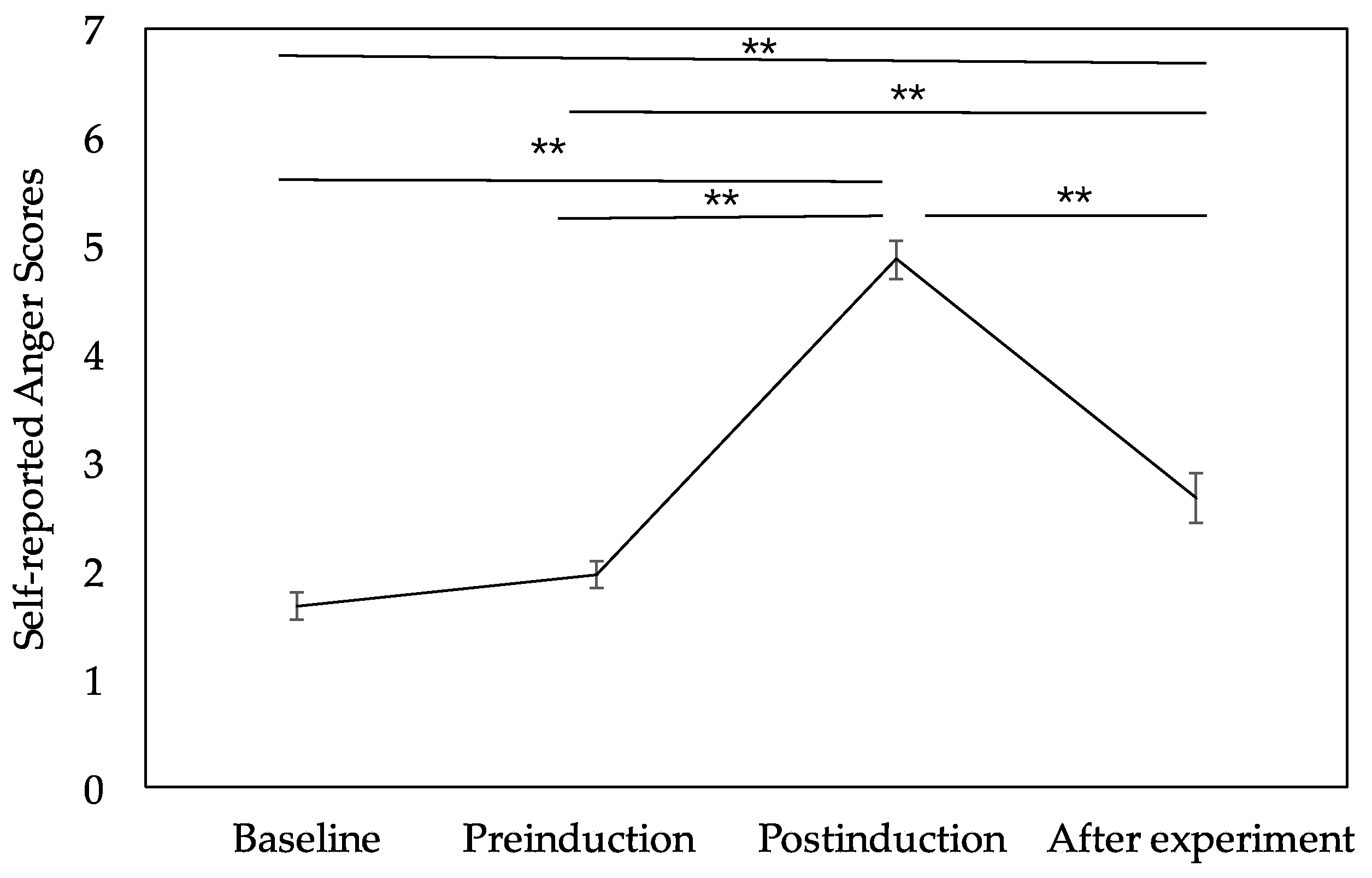
3.1. Emotion Manipulation
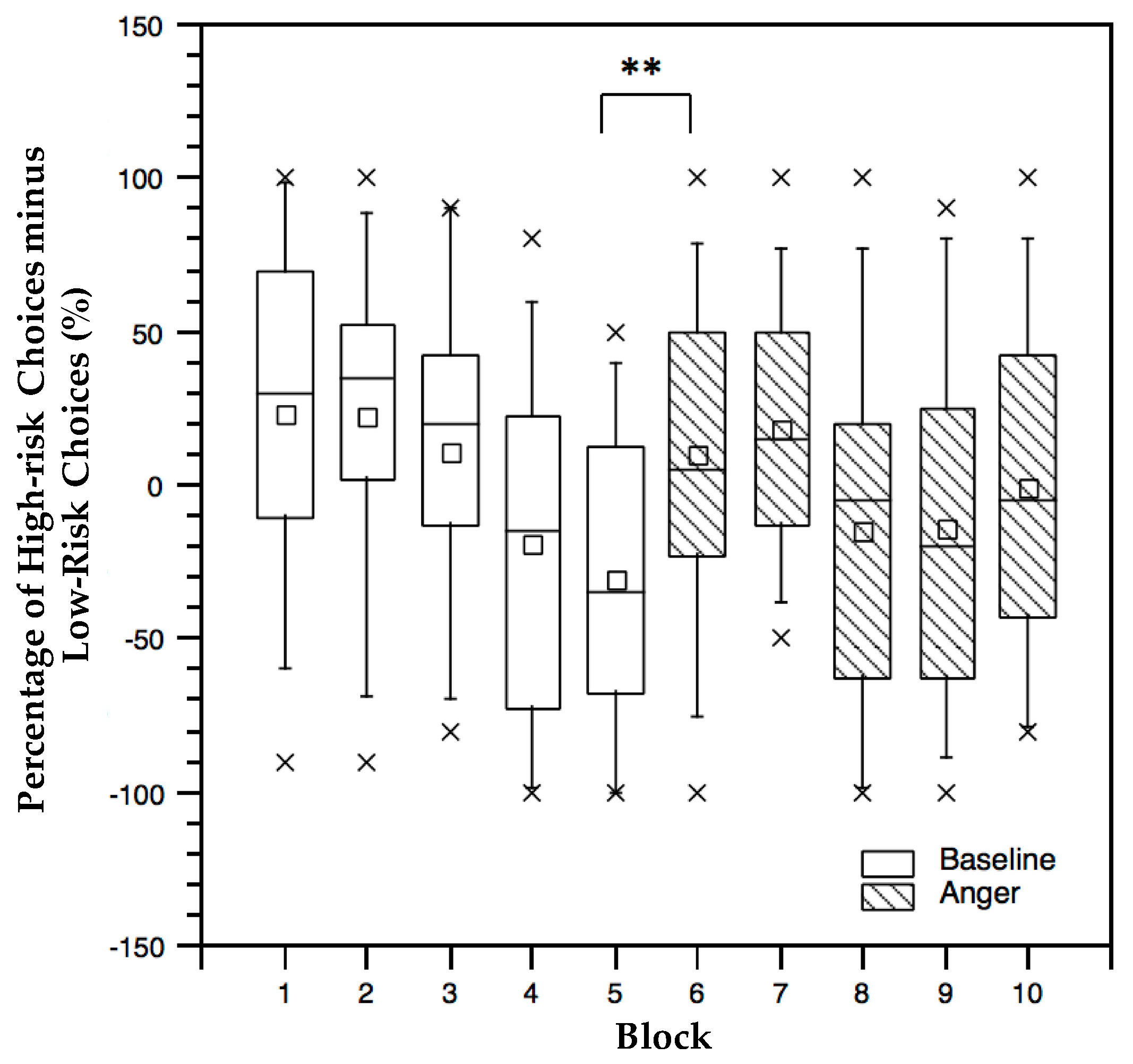
3.2. Performance Data
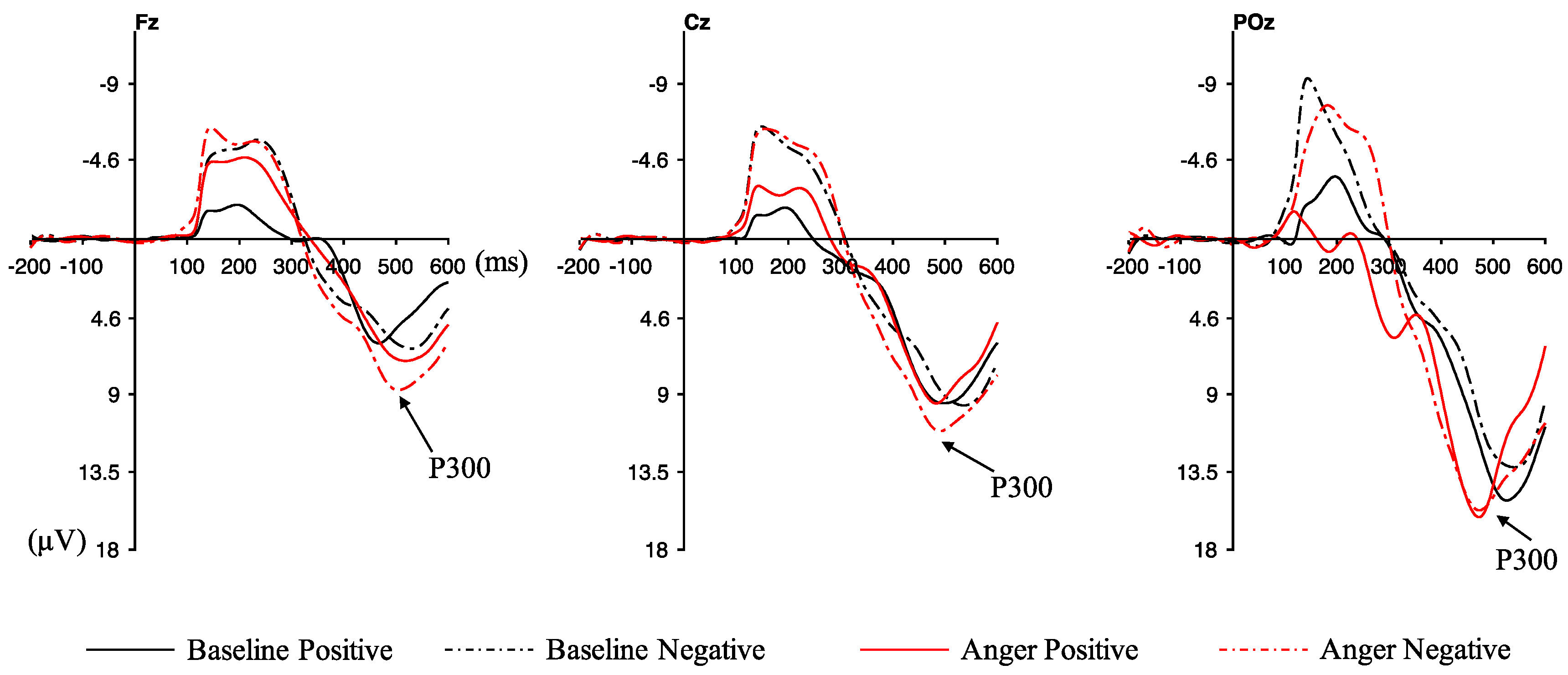
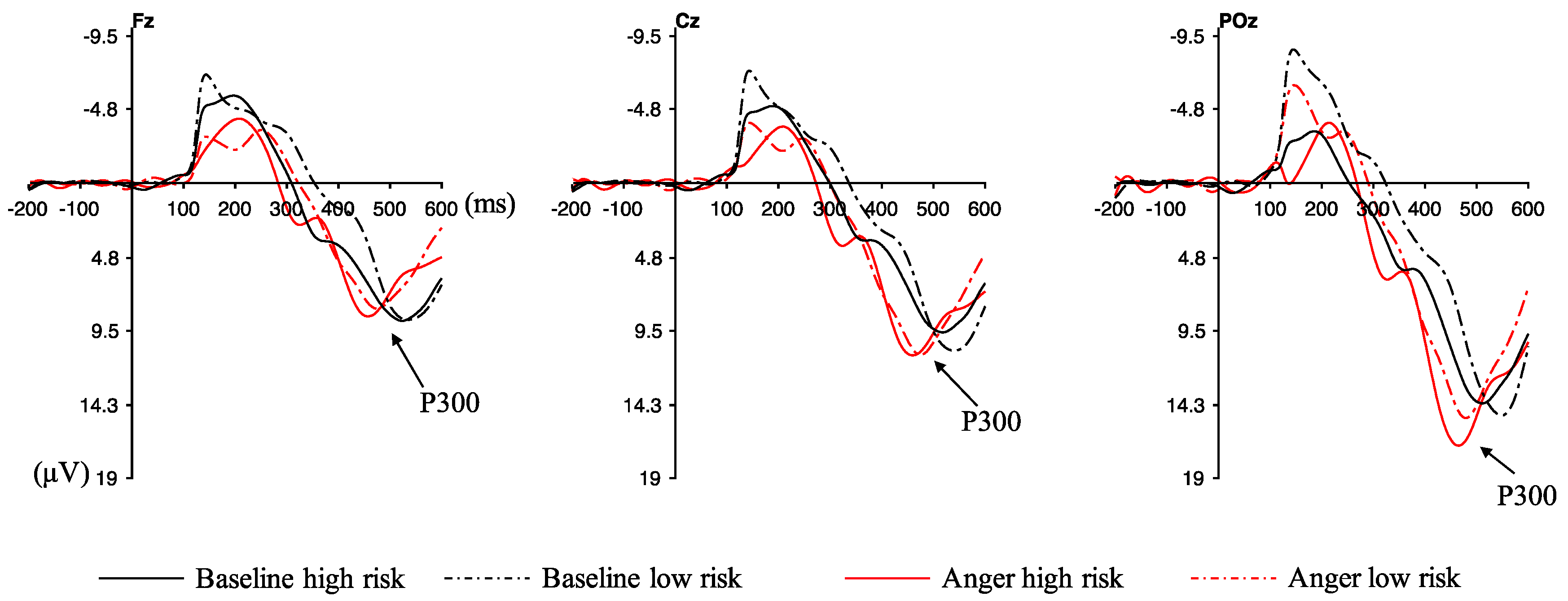
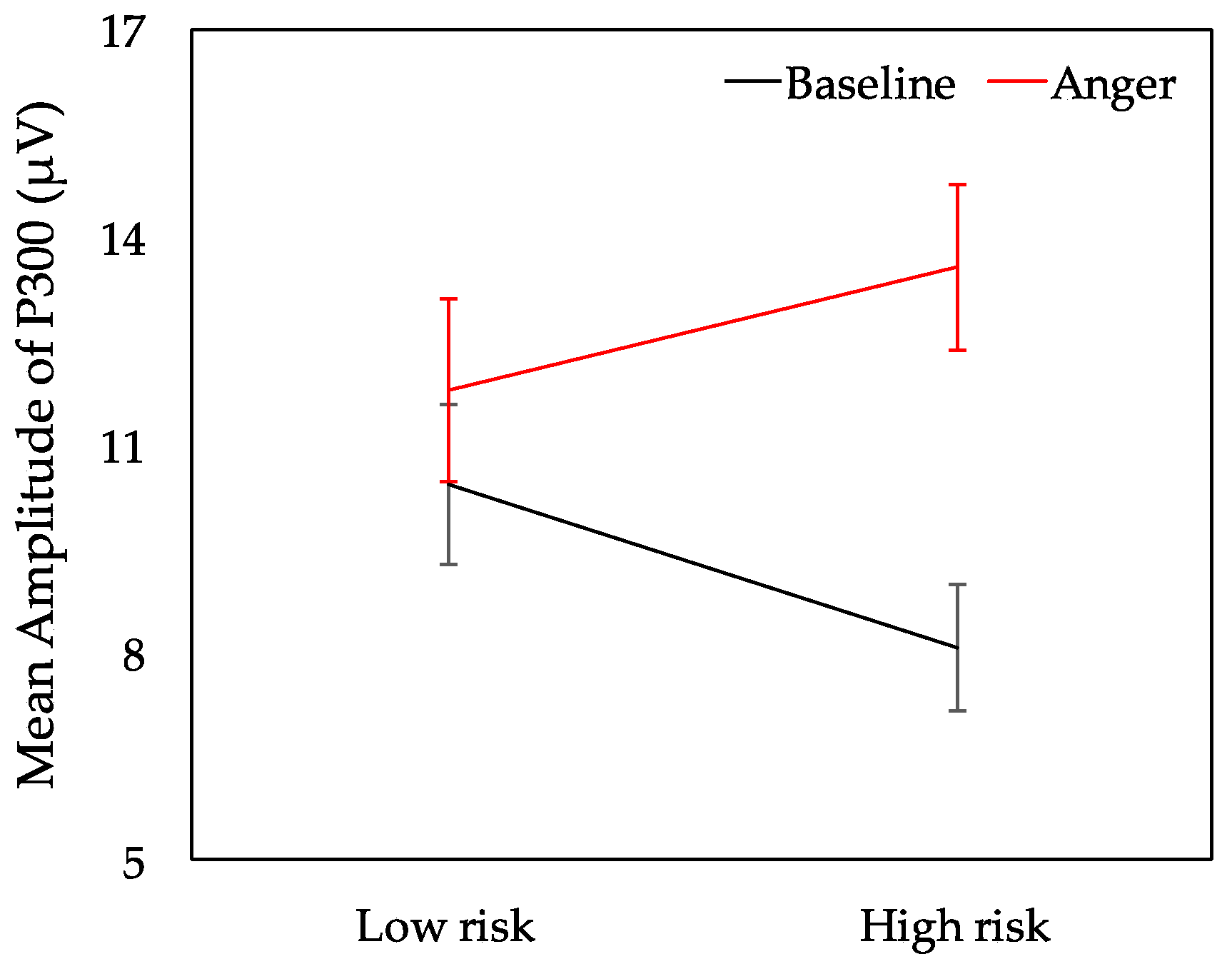
3.3. ERP Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galovski, T.E.; Blanchard, E.B. Road rage: A domain for psychological intervention? Aggress. Violent Behav. 2004, 9, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAA Foundation. Prevalence of Self-Reported Aggressive Driving Behavior: United States, 2014; AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, D.; Lajunen, T.; Summala, H. Anger and aggression among drivers in three European countries. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2002, 34, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullman, M.J.M.; Gras, M.E.; Cunill, M.; Planes, M.; Font-Mayolas, S. Driving anger in Spain. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2007, 42, 701–713. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y. Driving anger in China: Psychometric properties of the Driving Anger Scale (DAS) and its relationship with aggressive driving. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2014, 68, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLinton, S.S.; Dollard, M.F. Work stress and driving anger in Japan. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2010, 42, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, H.G. Anger and Irritability. Br. J. Psychiatry 1992, 161, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill, J.R. Studies on anger and aggression: Implications for theories of emotion. Am. Psychol. 1983, 38, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, P.A. Some Pitfalls in the Promises of Automated and Autonomous Vehicles. Ergonomics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chan, A.H.S.; Ba, Y.; Zhang, W. Situational driving anger, driving performance and allocation of visual attention. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2016, 42, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, P.A.; Scallen, S.F. The Driving Question. Transp. Hum. Factors 1999, 1, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chan, A.H.S.; Xue, H.; Zhang, X.; Tao, D. Driving Anger, Aberrant Driving Behaviors, and Road Crash Risk: Testing of a Mediated Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, H.; Rundmo, T. Personality, risky driving and accident involvement among Norwegian drivers. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2002, 33, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlen, E.R.; White, R.P. The Big Five factors, sensation seeking, and driving anger in the prediction of unsafe driving. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 41, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffenbacher, J.L.; Deffenbacher, D.M.; Lynch, R.S.; Richards, T.L. Anger, aggression, and risky behavior: A comparison of high and low anger drivers. Behav. Res. Ther. 2003, 41, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, L.; Useche, S.; Alonso, F.; Cendales, B. Work Environment, Stress, and Driving Anger: A Structural Equation Model for Predicting Traffic Sanctions of Public Transport Drivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, B.; Özkan, T.; Lajunen, T. Professional and non-professional drivers’ stress reactions and risky driving. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2010, 13, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.-Y.; Xie, X.; Li, J. Negative or positive? The effect of emotion and mood on risky driving. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2013, 16, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, R. Focusing on appraisals: How and why anger and fear influence driving risk perception. J. Saf. Res. 2013, 45, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Singhal, A. Emotion matters: Implications for distracted driving. Saf. Sci. 2015, 72, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Q.; Salvendy, G.; Crundall, D. Risk-taking on the road and in the mind: Behavioural and neural patterns of decision making between risky and safe drivers. Ergonomics 2016, 59, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techer, F.; Jallais, C.; Corson, Y.; Moreau, F.; Ndiaye, D.; Piechnick, B.; Fort, A. Attention and driving performance modulations due to anger state: Contribution of electroencephalographic data. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 636, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euser, A.S.; van Meel, C.S.; Snelleman, M.; Franken, I.H.A. Acute effects of alcohol on feedback processing and outcome evaluation during risky decision-making: An ERP study. Psychopharmacology 2011, 217, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bacigalupo, F.; Luck, S.J. Event-related potential components as measures of aversive conditioning in humans. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.J. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-262-32406-9. [Google Scholar]
- Miltner, W.H.R.; Braun, C.H.; Coles, M.G.H. Event-related brain potentials following incorrect feedback in a time-estimation task: Evidence for a “Generic” Neural System for Error Detection. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.Z.; Cottone, L.A.; Jia, Z.; Maloney, T.; Volkow, N.D.; Squires, N.K. The effect of graded monetary reward on cognitive event-related potentials and behavior in young healthy adults. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 62, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, W.S. Psychophysiology of P300. Psychol. Bull. 1981, 89, 506–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, X. The P300 and reward valence, magnitude, and expectancy in outcome evaluation. Brain Res. 2009, 1286, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, S.; Gilzenrat, M.S.; Holmes, B.D.; Cohen, J.D. The Role of the Locus Coeruleus in Mediating the Attentional Blink: A Neurocomputational Theory. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2005, 134, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, B.; Endrass, T.; Kathmann, N. Neural correlates of feedback processing in decision-making under risk. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, N.; Sanfey, A.G. Independent Coding of Reward Magnitude and Valence in the Human Brain. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6258–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polezzi, D.; Sartori, G.; Rumiati, R.; Vidotto, G.; Daum, I. Brain correlates of risky decision-making. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, E.R.A.; Mars, R.B.; Hulstijn, W. “It wasn’t me… or was it?” How false feedback effects performance. In Errors, Conflicts, and the Brain. Current Opinions on Performance Monitoring; Ullsperger, M., Falkenstein, M., Eds.; Leipzig: MPI Cognitive Neuroscience: Leipzig, Germany, 2004; pp. 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.R.; Damasio, H.; Anderson, S.W. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 1994, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, A.R. Deciding Advantageously Before Knowing the Advantageous Strategy. Science 1997, 275, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R. Emotion, Decision Making and the Orbitofrontal Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Q. The neural basis of risky decision-making in a blackjack task. Neuroreport 2007, 18, 1507–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sawyer, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Hancock, P. Anger Leads to Risk Insensitivity in Gambling and Driving. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Newhagen, J.E. TV news images that induce anger, fear, and disgust: Effects on approach-avoidance and memory. J. Broadcast. Electron. Media 1998, 42, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, J.W. PsychoPy—Psychophysics software in Python. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 162, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, W.J.; Willoughby, A.R. The Medial Frontal Cortex and the Rapid Processing of Monetary Gains and Losses. Science 2002, 295, 2279–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, T. Aggression differentially modulates brain responses to fearful and angry faces: An exploratory study. NeuroReport 2015, 26, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.T.E. Eta squared and partial eta squared as measures of effect size in educational research. Educ. Res. Rev. 2011, 6, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Y.; Tang, P.; Gu, R.; Luo, Y. Differentiating the influence of incidental anger and fear on risk decision-making. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 184, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deffenbacher, J.L.; Lynch, R.S.; Filetti, L.B.; Dahlen, E.R.; Oetting, E.R. Anger, aggression, risky behavior, and crash-related outcomes in three groups of drivers. Behav. Res. Ther. 2003, 41, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullman, M.J.M. Anger amongst New Zealand drivers. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.J.; Woroch, B.S.; Curran, T. Error-Related Negativity Predicts Reinforcement Learning and Conflict Biases. Neuron 2005, 47, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, B.; Kathmann, N.; Stiglmayr, C.; Renneberg, B.; Endrass, T. Impaired decision making and feedback evaluation in borderline personality disorder. Psychol. Med. 2011, 41, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balconi, M.; Crivelli, D. FRN and P300 ERP effect modulation in response to feedback sensitivity: The contribution of punishment-reward system (BIS/BAS) and Behaviour Identification of action. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellebaum, C.; Daum, I. Learning-related changes in reward expectancy are reflected in the feedback-related negativity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Yasuda, A.; Ohira, H.; Miyawaki, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Kumano, H.; Kuboki, T. Effects of value and reward magnitude on feedback negativity and P300. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlen, E.R.; Martin, R.C.; Ragan, K.; Kuhlman, M.M. Driving anger, sensation seeking, impulsiveness, and boredom proneness in the prediction of unsafe driving. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2005, 37, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutnik, L.A.; Hakimzada, A.F.; Yoskowitz, N.A.; Patel, V.L. The role of emotion in decision-making: A cognitive neuroeconomic approach towards understanding sexual risk behavior. J. Biomed. Inform. 2006, 39, 720–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, B.; Fong, G.W.; Adams, C.M.; Varner, J.L.; Hommer, D. Dissociation of reward anticipation and outcome with event-related fMRI. NeuroRep. Rapid Commun. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 12, 3683–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijda, N.H. The laws of emotion. Am. Psychol. 1988, 43, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, P.J. The emotion probe: Studies of motivation and attention. Am. Psychol. 1995, 50, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacham, S. A Shortened Version of the Profile of Mood States. J. Personal. Assess. 1983, 47, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, M.; Roberts, J.; Raman, P.; Yim, J.-B.; Walker, B.N. Participatory Design Process for an In-vehicle Affect Detection and Regulation System for Various Drivers. In Proceedings of the 13th International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility, Dundee, UK, 24–26 October 2011; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 271–272. [Google Scholar]
| Probability and Value | Go/No-Go Gambling Task | Anger Elicitation Gambling Task | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Go Choices (A) | Go Choices (B) | No-Go Choices (C) | Go Choices (D) | M | N | |
| Time saved | +10 | +10 | +5 | +5 | 25 | 30 |
| Time wasted | −15 | −115 | 0 | −20 | −15 | −25 |
| Probability of time saved | 50% | 90% | 50% | 90% | 0% | 0% |
| Probability of time wasted | 50% | 10% | 50% | 10% | 100% | 100% |
| Expected value | −2.5 | −2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | ||
| Standard deviation | 12.5 | 37.5 | 2.5 | 7.5 | ||
| Choice type | Low risks with negative expected values | High risks with negative expected values | Low risks with positive expected values | High risks with positive expected values | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Sawyer, B.D.; Zhang, W.; Hancock, P.A. Angry Drivers Take Risky Decisions: Evidence from Neurophysiological Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101701
Li S, Zhang T, Sawyer BD, Zhang W, Hancock PA. Angry Drivers Take Risky Decisions: Evidence from Neurophysiological Assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(10):1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuling, Tingru Zhang, Ben D. Sawyer, Wei Zhang, and Peter A. Hancock. 2019. "Angry Drivers Take Risky Decisions: Evidence from Neurophysiological Assessment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 10: 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101701
APA StyleLi, S., Zhang, T., Sawyer, B. D., Zhang, W., & Hancock, P. A. (2019). Angry Drivers Take Risky Decisions: Evidence from Neurophysiological Assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(10), 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101701






