Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
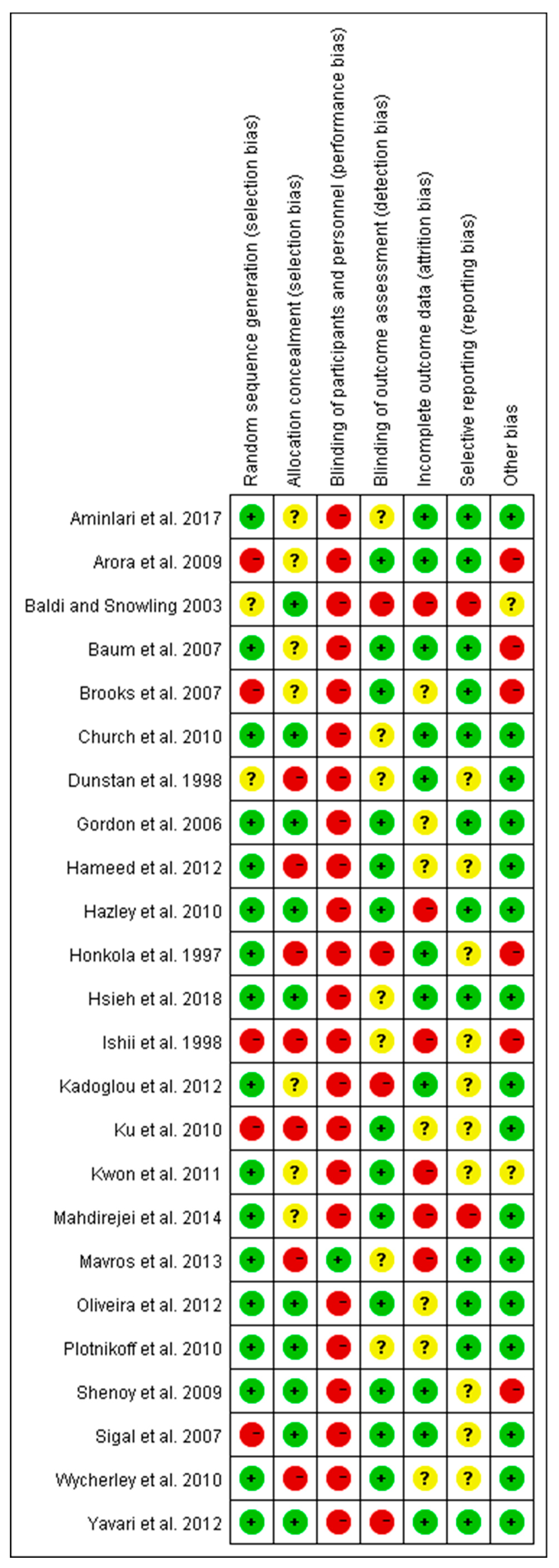
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Subgroup Division and Observed Indices
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
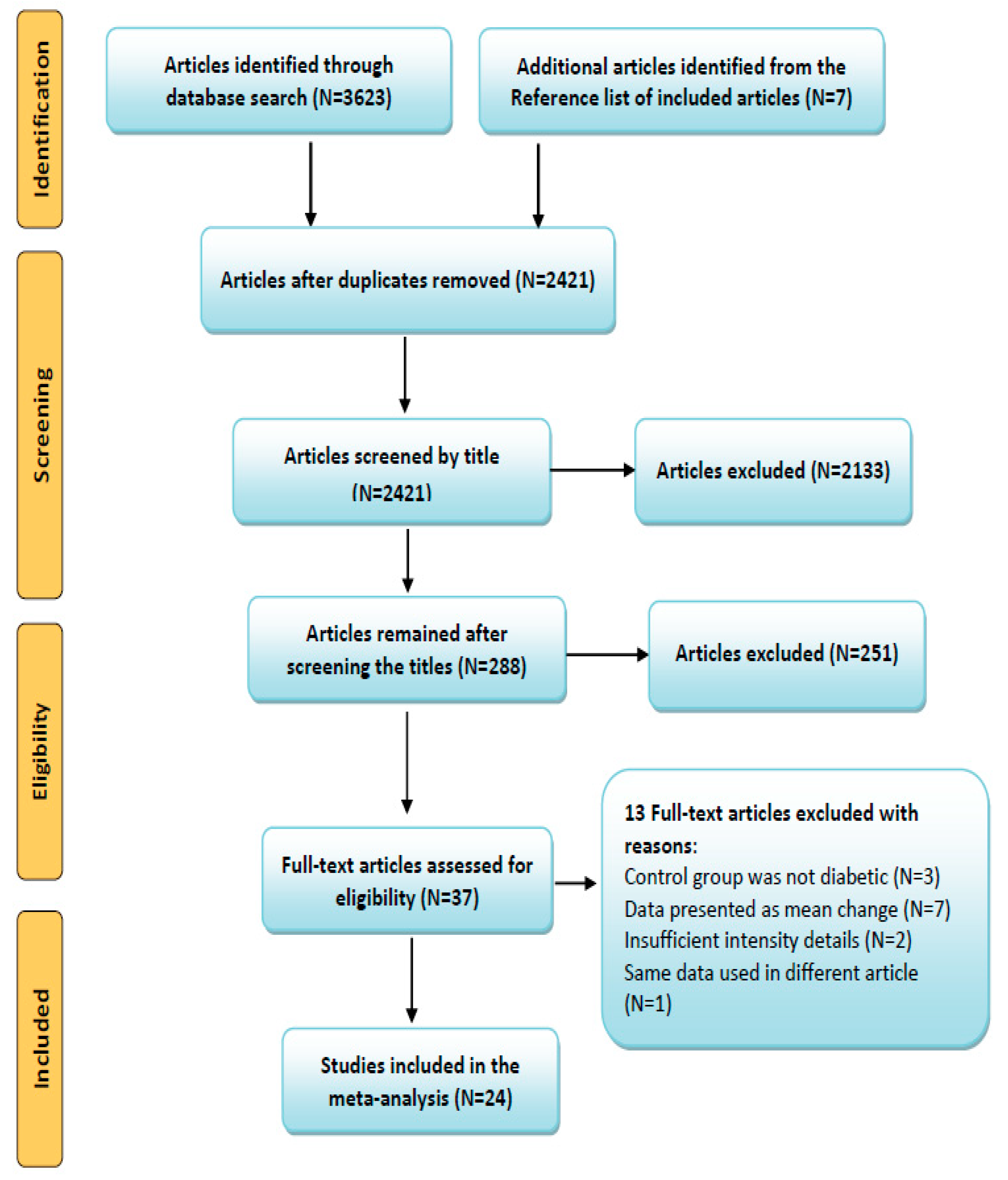
3.1. Search Results and Article Selection
3.2. Description of the Included Articles
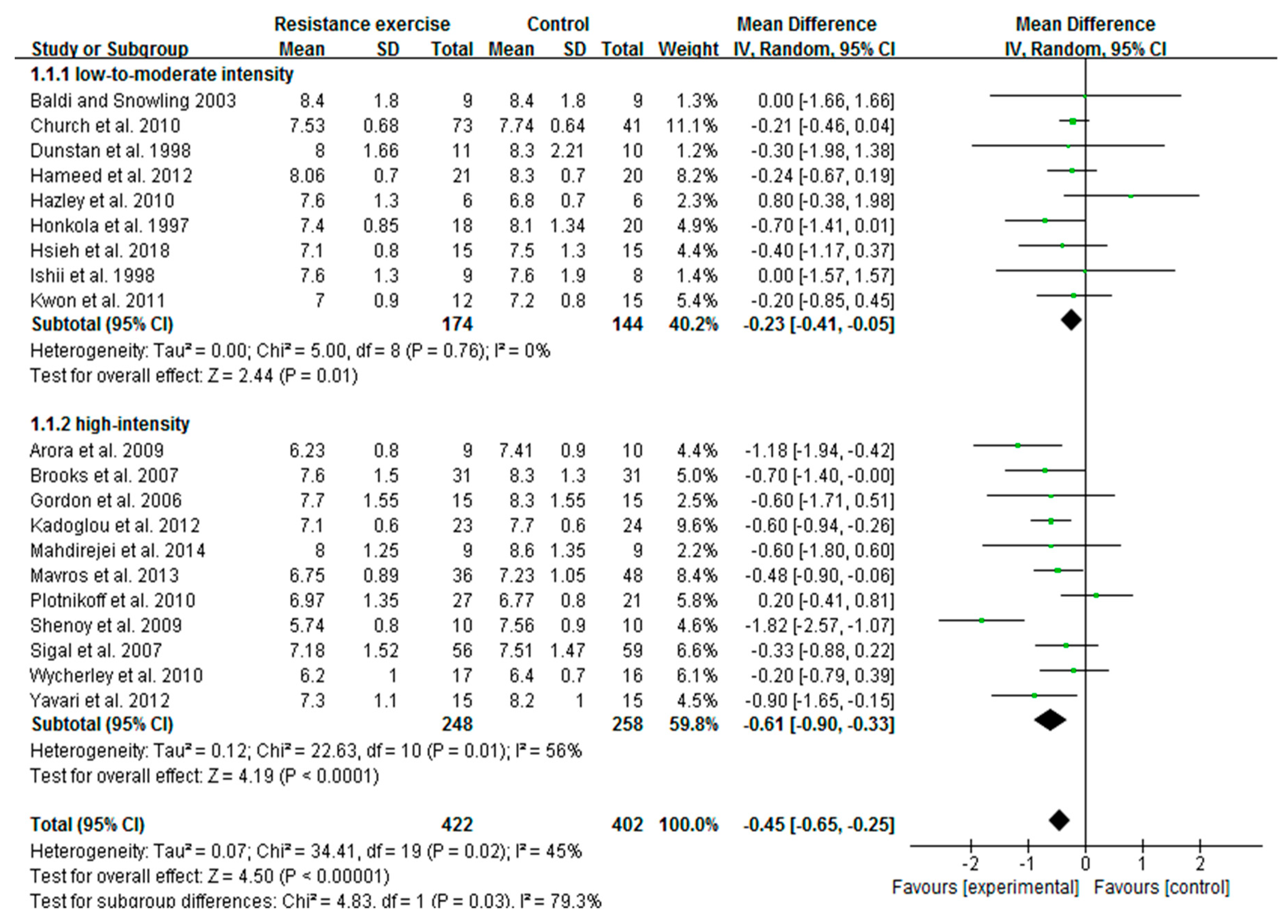
3.3. High-Intensity RE Prominently Reduces HbA1c Than Low-To-Moderate-Intensity in Patients with T2D
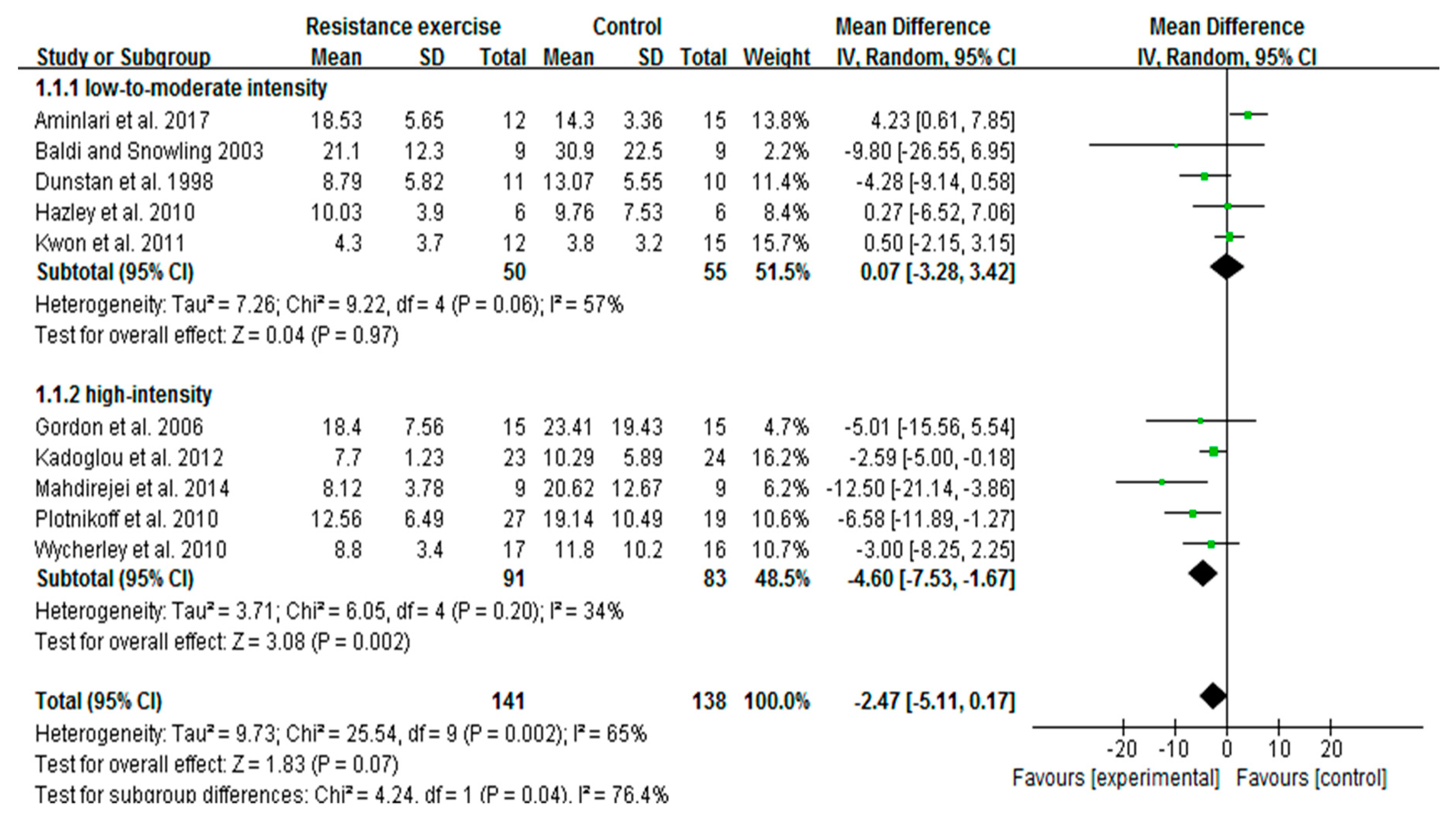
3.4. High-Intensity, Not Low-To-Moderate-Intensity RE Decreases Insulin Levels
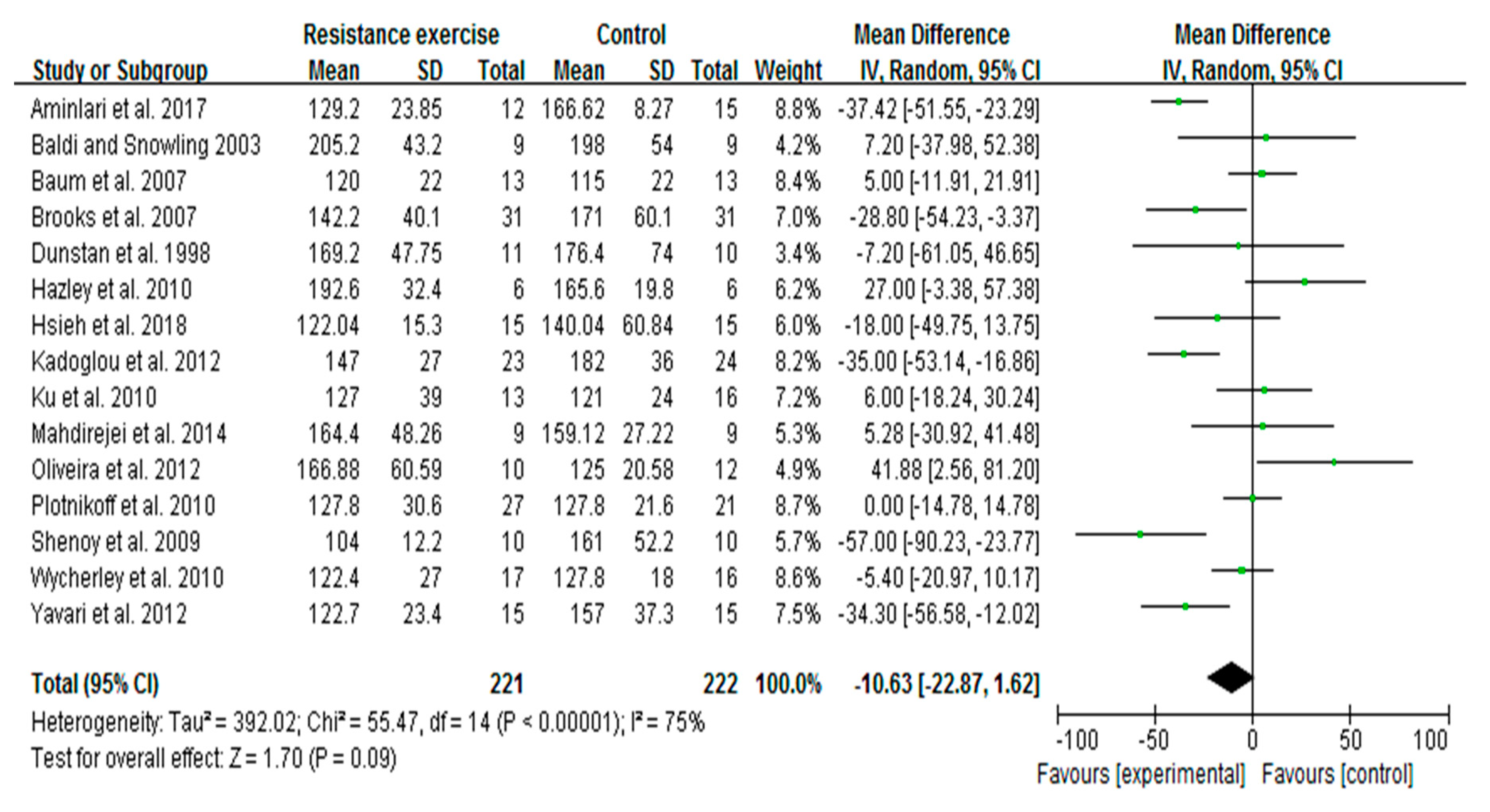
3.5. RE Trends to Decrease Blood Glucose Levels in Patients with T2D
3.6. Summary of Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
Significance of Resistance Exercise at Molecular Level
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gillies, C.L.; Abrams, K.R.; Lambert, P.C.; Cooper, N.J.; Sutton, A.J.; Hsu, R.T.; Khunti, K. Pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2007, 334, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, C. Resistance training for glycemic control, muscular strength, and lean body mass in old type 2 diabetic patients: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesta, D.H.; Goncalves, R.L.; Madiraju, A.K.; Strasser, B.; Sparks, L.M. Resistance training to improve type 2 diabetes: Working toward a prescription for the future. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, C.-S.; Wu, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chien, P.-C.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Kuo, P.-J.; Hsieh, C.-H. Mortality rate associated with admission hyperglycemia in traumatic femoral fracture patients is greater than non-diabetic normoglycemic patients but not diabetic normoglycemic patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2017, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.; Makaroff, L. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, S.H.; Hamdy, O.; Mohan, V.; Hu, F.B. Prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: Dietary components and nutritional strategies. Lancet 2014, 383, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eves, N.D.; Plotnikoff, R.C. Resistance training and type 2 diabetes. Considerations for implementation at the population level. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherwax, R.M.; Ramos, J.S.; Harris, N.K.; Kilding, A.E.; Dalleck, L.C. Changes in metabolic syndrome severity following individualized versus standardized exercise prescription: A feasibility study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Scott, C.A.; Mao, C.; Tang, J.; Farmer, A.J. Resistance exercise versus aerobic exercise for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Fernhall, B.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Blissmer, B.J.; Rubin, R.R.; Chasan-Taber, L.; Albright, A.L.; Braun, B. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: The American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association: Joint position statement executive summary. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2692–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, C.; Sigal, R.J.; Cousins, M.; Menard, M.L.; Atkinson, M.; Khandwala, F.; Kenny, G.P.; Proctor, S.; Ooi, T.C. Resistance exercise but not aerobic exercise lowers remnant-like lipoprotein particle cholesterol in type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Alappan, N.K.; Vikram, N.K.; Goel, K.; Gupta, N.; Mittal, K.; Bhatt, S.; Luthra, K. Effect of supervised progressive resistance exercise training protocol on insulin sensitivity, glycemia, lipids and body composition in Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.N.; Singh, M.A.F.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.R.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1510–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Daly, R.M.; Owen, N.; Jolley, D.; de Courten, M.; Shaw, J.; Zimmet, P. High-intensity resistance rraining improves glycemic control in older patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomgarden, Z.T. American Diabetes Association Annual Meeting, 1999: Diabetes and obesity. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, S.E.; Gallo, L.C.; Norman, G.J. Attrition and adherence rates of sustained vs. intermittent exercise interventions. Ann. Behav. Med. 2011, 42, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuff, D.J.; Meneilly, G.S.; Martin, A.; Ignaszewski, A.; Tildesley, H.D.; Frohlich, J.J. Effective exercise modality to reduce insulin resistance in women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2977–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Yamakita, T.; Sato, T.; Tanaka, S.; Fujii, S. Resistance training improves insulin sensitivity in NIDDM subjects without altering maximal oxygen uptake. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazley, L.; Ingle, L.; Tsakirides, C.; Carroll, S.; Nagi, D. Impact of a short-term, moderate intensity, lower volume circuit resistance training programme on metabolic risk factors in overweight/obese type 2 diabetics. Res. Sports Med. 2010, 18, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.; Green, S. Cochrane handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 5.1.0; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ratamess, N.A. ACSM’s Foundations of Strength Training and Conditioning; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fenicchia, L.; Kanaley, J.; Azevedo, J., Jr.; Miller, C.; Weinstock, R.; Carhart, R.; Ploutz-Snyder, L. Influence of resistance exercise training on glucose control in women with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2004, 53, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colberg, S.R.; Parson, H.K.; Nunnold, T.; Herriott, M.T.; Vinik, A.I. Effect of an 8-week resistance training program on cutaneous perfusion in type 2 diabetes. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 71, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibánez, J.; Gorostiaga, E.M.; Alonso, A.M.; Forga, L.; Argüelles, I.; Larrión, J.L.; Izquierdo, M. Lower muscle strength gains in older men with type 2 diabetes after resistance training. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2008, 22, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchi, E.; Negri, C.; Zanolin, M.E.; Milanese, C.; Faccioli, N.; Trombetta, M.; Zoppini, G.; Cevese, A.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Schena, F. Metabolic effects of aerobic training and resistance training in type 2 diabetic subjects: A randomized controlled trial (the RAED2 study). Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauza, E.; Hanusch-Enserer, U.; Strasser, B.; Ludvik, B.; Metz-Schimmerl, S.; Pacini, G.; Wagner, O.; Georg, P.; Prager, R.; Kostner, K. The relative benefits of endurance and strength training on the metabolic factors and muscle function of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.G.; Sethi, P.; Nowson, C.A.; Dunstan, D.W.; Daly, R.M. Effects of progressive resistance training and weight loss versus weight loss alone on inflammatory and endothelial biomarkers in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Daly, R.M.; Owen, N.; Jolley, D.; Vulikh, E.; Shaw, J.; Zimmet, P. Home-based resistance training is not sufficient to maintain improved glycemic control following supervised training in older individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-I.; Lee, D.H.; Hong, S.; Jo, S.-W.; Won, Y.-S.; Jeon, J.Y. Six weeks of combined aerobic and resistance exercise using outdoor exercise machines improves fitness, insulin resistance, and chemerin in the Korean elderly: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 75, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.-C.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gillham, S.; Putiri, A.; Sasagawa, M.; Bradley, R. Effects of Qigong on glucose control in type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled pilot study. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.R.; Han, K.A.; Ku, Y.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Koo, B.-K.; Kim, H.C.; Min, K.W. The effects of resistance training on muscle and body fat mass and muscle strength in type 2 diabetic women. Korean Diabetes J. 2010, 34, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wycherley, T.P.; Noakes, M.; Clifton, P.M.; Cleanthous, X.; Keogh, J.B.; Brinkworth, G.D. A high protein diet with resistance exercise training improves weight loss and body composition in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Puddey, I.B.; Beilin, L.J.; Burke, V.; Morton, A.R.; Stanton, K. Effects of a short-term circuit weight training program on glycaemic control in NIDDM. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1998, 40, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.R.; Min, K.W.; Ahn, H.J.; Seok, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Park, G.S.; Han, K.A. Effects of aerobic exercise vs. resistance training on endothelial function in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. J. 2011, 35, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, R.J.; Kenny, G.P.; Boulé, N.G.; Wells, G.A.; Prud’homme, D.; Fortier, M.; Reid, R.D.; Tulloch, H.; Coyle, D.; Phillips, P. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdirejei, H.A.; Abadei, S.F.R.; Seidi, A.A.; Gorji, N.E.; Kafshgari, H.R.; Pour, M.E.; Khalili, H.B.; Hajeizad, F.; Khayeri, M. Effects of an eight-week resistance training on plasma vaspin concentrations, metabolic parameters levels and physical fitness in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cell J. 2014, 16, 367. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, E.; Shenoy, S.; Sandhu, J. Effects of resistance training on metabolic profile of adults with type 2 diabetes. Indian J. Med. Res. 2009, 129, 515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gordon, P.; Vannier, E.; Hamada, K.; Layne, J.; Hurley, B.; Roubenoff, R.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Resistance training alters cytokine gene expression in skeletal muscle of adults with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2006, 19, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N.; Layne, J.E.; Gordon, P.L.; Roubenoff, R.; Nelson, M.E.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Strength training improves muscle quality and insulin sensitivity in Hispanic older adults with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Fotiadis, G.; Athanasiadou, Z.; Vitta, I.; Lampropoulos, S.; Vrabas, I.S. The effects of resistance training on ApoB/ApoA-I ratio, Lp (a) and inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 2012, 42, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N.; Cocreham, S.; Johannsen, N.; Johnson, W.; Kramer, K.; Mikus, C.R.; Myers, V.; Nauta, M.; Rodarte, R.Q. Effects of aerobic and resistance training on hemoglobin A1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-L.; Tseng, C.-H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Yang, W.-S. Resistance training improves muscle function and cardiometabolic risks but not quality of life in older people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 41, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, J.; Snowling, N. Resistance training improves glycaemic control in obese type 2 diabetic men. Int. J. Sports Med. 2003, 24, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- AminiLari, Z.; Fararouei, M.; Amanat, S.; Sinaei, E.; Dianatinasab, S.; AminiLari, M.; Daneshi, N.; Dianatinasab, M. The effect of 12 weeks aerobic, resistance, and combined exercises on omentin-1 levels and insulin resistance among type 2 diabetic middle-aged women. Diabetes Metab. J. 2017, 41, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavari, A.; Najafipoor, F.; Aliasgarzadeh, A.; Niafar, M.; Mobasseri, M. Effect of aerobic exercise, resistance training or combined training on glycaemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Biol. Sport 2012, 29, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.; Han, K.; Ahn, H.; Kwon, H.; Koo, B.; Kim, H.; Min, K. Resistance exercise did not alter intramuscular adipose tissue but reduced retinol-binding protein-4 concentration in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Int. Med. Res. 2010, 38, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honkola, A.; Forsen, T.; Eriksson, J. Resistance training improves the metabolic profile in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 1997, 34, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.N.D.; Bessa, A.; Jorge, M.L.M.P.; Oliveira, R.J.D.S.; de Mello, M.T.; De Agostini, G.G.; Jorge, P.T.; Espindola, F.S. The effect of different training programs on antioxidant status, oxidative stress, and metabolic control in type 2 diabetes. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 37, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, S.; Arora, E.; Jaspal, S. Effects of progressive resistance training and aerobic exercise on type 2 diabetics in Indian population. Int. J. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 17, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mavros, Y.; Kay, S.; Anderberg, K.A.; Baker, M.K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Meiklejohn, J.; Climstein, M.; O’Sullivan, A.; De Vos, N. Changes in insulin resistance and HbA1c are related to exercise-mediated changes in body composition in older adults with type 2 diabetes: Interim outcomes from the GREAT2DO trial. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2372–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, U.A.; Manzar, D.; Raza, S.; Shareef, M.Y.; Hussain, M.E. Resistance training leads to clinically meaningful improvements in control of glycemia and muscular strength in untrained middle-aged patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Plotnikoff, R.; Eves, N.; Jung, M.; Sigal, R.; Padwal, R.; Karunamuni, N. Multicomponent, home-based resistance training for obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, K.; Votteler, T.; Schiab, J. Efficiency of vibration exercise for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 4, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.; Smith, D.; Steed, L.; Hooper, R.; Carter, A.; Catto, J.; Albertsen, P.C.; Tombal, B.; Payne, H.A.; Rosario, D.J. Exercise for men with prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umpierre, D.; Ribeiro, P.; Schaan, B.; Ribeiro, J. Volume of supervised exercise training impacts glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-regression analysis. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houmard, J.A.; Tanner, C.J.; Slentz, C.A.; Duscha, B.D.; McCartney, J.S.; Kraus, W.E. Effect of the volume and intensity of exercise training on insulin sensitivity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Lim, W.Y.; Tan, C.S.; Ning, Y.; Chia, K.S.; van Dam, R.M.; Tang, W.E.; Tan, N.C.; Chen, R.; Tai, E.S.; et al. Longitudinal trends in HbA1c and associations with comorbidity and all-cause mortality in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes: A cohort study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 133, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). The Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Brinke, R.; Dekker, N.; de Groot, M.; Ikkersheim, D. Lowering HbA1c in type 2 diabetics results in reduced risk of coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality. Prim. Care Diabetes 2008, 2, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Missbach, B.; Dias, S.; König, J.; Hoffmann, G. Impact of different training modalities on glycaemic control and blood lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudyk, A.; Petrella, R.J. Effects of exercise on cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes. A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, C.; De Moraes, S.R.A.; Novaes, K.A.; Bezerra, M.A.; Silveira, P.V.D.C.; Lemos, A. Effectiveness of resistance exercise compared to aerobic exercise without insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2017, 21, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, J.; Izquierdo, M.; Argüelles, I.; Forga, L.; Larrión, J.L.; García-Unciti, M.; Idoate, F.; Gorostiaga, E.M. Twice-weekly progressive resistance training decreases abdominal fat and improves insulin sensitivity in older men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, B.; Janssen, I.; Hudson, R.; Ross, R. Effects of aerobic or resistance exercise and/or diet on glucose tolerance and plasma insulin levels in obese men. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Yokozeki, T.; Akima, H.; Funato, K. Resistance training affects GLUT-4 content in skeletal muscle of humans after 19 days of head-down bed rest. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 86, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holten, M.K.; Zacho, M.; Gaster, M.; Juel, C.; Wojtaszewski, J.F.; Dela, F. Strength training increases insulin-mediated glucose uptake, GLUT4 content, and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, H.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J.; Idris, I. Role of insulin in the regulation of human skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.A. The role of mTORC1 in regulating protein synthesis and skeletal muscle mass in response to various mechanical stimuli. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 166, 43–95. [Google Scholar]
- Fatone, C.; Guescini, M.; Balducci, S.; Battistoni, S.; Settequattrini, A.; Pippi, R.; Stocchi, L.; Mantuano, M.; Stocchi, V.; De Feo, P. Two weekly sessions of combined aerobic and resistance exercise are sufficient to provide beneficial effects in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2010, 33, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.E.; Hartman, J.W.; Phillips, S.M. Increased muscle oxidative potential following resistance training induced fibre hypertrophy in young men. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2006, 31, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, L.M.; Johannsen, N.M.; Church, T.S.; Earnest, C.P.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Moro, C.; Hesselink, M.K.; Smith, S.R.; Schrauwen, P. Nine months of combined training improves ex vivo skeletal muscle metabolism in individuals with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnopolsky, M. Mitochondrial DNA shifting in older adults following resistance exercise training. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, C.; Chung, N.; Schmidt, U.; Kreutz, T.; Lenzen, E.; Schiffer, T.; Geisler, S.; Graf, C.; Montiel-Garcia, G.; Renner, R. Training alters the skeletal muscle antioxidative capacity in non-insulin-dependent type 2 diabetic men. Scan. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2012, 22, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shultz, S.P.; Dahiya, R.; Leong, G.M.; Rowlands, D.S.; Hills, A.P.; Byrne, N.M. Muscular strength, aerobic capacity, and adipocytokines in obese youth after resistance training: A pilot study. Australas Med. J. 2015, 8, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Year, Country | Participants (M/F) | Mean Age (Y) | Diabetes Duration (Y) | Resistance Exercise Description | Intensity (% 1RM) | Repetitions | Sets | Frequency (t/wk) | Duration (wk) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise | Control | ||||||||||
| Hsieh et al. [43] | 2018, Taiwan/China | 15 (5/10) | 15 (6/9) | 71.2 ± 4.3 | RE:11 ± 7.8 C:13.9 ± 6.7 | Chest press, shoulder press, bicep curl, hip abduction, standing hip flexion, leg press, standing calf raise, and abdominal crunch | 75% | 8–12 | 3 | 3 | 12 |
| AminiLari et al. [45] | 2017, Iran | 15 (0/15) | 15 (0/15) | 45–60 | At least 2 | Leg extension, prone leg curl, abdominal crunch, biceps, triceps, and seated calf | 50–55% | 8 | 3 | 3 | 12 |
| Mahdirejei et al. [37] | 2014, Iran | 9 (9/0) | 9 (9/0) | 48.5 ± 7.7 | (nr) | Bench press, butterfly, lat pull-down, bicep curl, triceps extension, seated rowing, knee flexion, knee extension, and heel raise | 50–80% | 8–15 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| Mavros et al. [51] | 2013, Australia | 36 (nr) | 48 (nr) | ≥ 60 | RE:7 ± 5 C:9 ± 7 | Seated row, chest press, leg press, knee extension, hip flexion, hip extension, and hip abduction | 80% | 8 | 2–3 | 3 | 48 |
| Hameed et al. [52] | 2012, India | 24 (18/6) | 24 (17/7) | 45 ± 4.1 | > 0.5 | Supine bench press, leg press, lateral pull, leg extension, and seated bicep curls | 65–70% | 10 | 3 | 2–3 | 8 |
| Kadoglou et al. [41] | 2012, Greece | 23 (7/16) | 24 (5/19) | 61.3 ± 2 | RE:6 ± 2.8 C:5.6 ± 1.9 | Seated leg press, knee extension, knee flexion, chest press, lat pull-down, overhead press, bicep curl, and tricep extension | 60–80% | 6–8 | 2~3 | 3 | 12 |
| Oliveira et al. [49] | 2012, Brazil | 10 (4/6) | 12 (4/8) | 54 ± 8.9 | RE:7.7 ± 4 C:5.2 ± 3.5 | Leg press, bench press, lat pull-down, seated rowing, shoulder press, abdominal curls, and knees curls | 67–80% | 15 | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| Yavari et al. [46] | 2012, Iran | 20 (nr) | 20 (nr) | 51.5 ± 6.3 | > 1 | Bench press, seated row, shoulder press, chest press, lateral pull-down, abdominal crunches, leg press, leg extension, tricep pushdown, and seated bicep curls | 75–80% | 8–10 | 3 | 3 | 52 |
| Kwon et al. [35] | 2011, Korea | 12 (0/12) | 15 (0/15) | 57 ± 6.8 | RE:4.6 ± 2.7 C:4.9 ± 4.7 | Curls, tricep extensions, upright rows, shoulder chest press, and seated rows. Core exercises included trunk side bends, leg press, hip flexions, leg flexions, and leg extensions | 40–50% | 10–15 | 3 | 3 | 12 |
| Church et al. [42] | 2010, America | 73 (30/43) | 41 (13/28) | 55.8 ± 8.7 | RE:7.2 ± 5.5 C:7.2 ± 5.2 | 2 sets of 4 upper body exercises (bench press, seated row, shoulder press, and pulldown), 3 sets of 3 leg exercises (leg press, extension, and flexion) and 2 sets each of abdominal crunches and back extensions | 67% | 10–12 | 2–3 | 3 | 36 |
| Hazley et al. [20] | 2010, England | 6 (3/3) | 6 (4/2) | 53 ± 9 | (nr) | Leg press, chest press, leg curl, leg extension, latissimus dorsi pull-down, press up, seated row, sit up, and bicep curl | 50–60% | 15 | 1–2 | 3.5 | 8 |
| Ku et al. [47] | 2010, Korea | 13 (0/13) | 16 (0/16) | 55.7 ± 6.2 | RE:5.7 ± 4.8 C:5.8 ± 6 | Bicep curl, tricep extension, upright row, shoulder chest press, trunk side bending, seated row, leg press, hip flexion, leg flexion, and leg extension | 40–50% | 15–20 | 3 | 5 | 12 |
| Plotnikoff et al. [53] | 2010, Canada | 27 (8/19) | 21 (8/13) | 55 ± 12 | (nr) | Squats, seated row, chest press, shoulder press, lunges, lateral pull-down, standing tricep extension, standing pulley abdominal twists, bicep curl, tricep press, reverse rhomboid flies, lateral pulley deltoid raise, and pulley abdominal curls | 50–85% | 8–12 | 2–3 | 3 | 16 |
| Wycherley et al. [33] | 2010, Australia | 17 (nr) | 16 (nr) | 56 ± 7.5 | (nr) | Leg press, knee extension, chest press, shoulder press, lat pull down, seated row, tricep press, and sit-ups | 70–85% | 8–12 | 2 | 3 | 16 |
| Arora et al. [38] | 2009, India | 10 (4/6) | 10 (6/4) | 53.8 ± 8.8 | RE:5.4 ± 1.5 C:5.2 ± 3.9 | Groups-biceps, triceps, upper back, abdominals, knee flexors, and extensors | 60–100% | 10 | 3 | 2 | 8 |
| Shenoy et al. [50] | 2009, India | 10 (4/6) | 10 (6/4) | 49.6 ± 5.2 | RE:5.4 ± 1.5 C:5.2 ± 2.9 | Bicep curls, tricep curls, front lateral pull down, back lateral pull-down, knee extension exercises on quadriceps table, hamstring curls using quadriceps table and abdominal curls | 60–100% | 10 | 3 | 2 | 16 |
| Baum et al. [54] | 2007, Germany | 13 (nr) | 13 (nr) | 62.9 ± 7.3 | (nr) | Leg extension, seated leg flexion, leg press, seated calf raises, lat pulley, horizontal chest press, butterfly, and rowing | 70–80% | 10–12 | 1–3 | 3 | 12 |
| Brooks et al. [40] | 2007, America | 31 (21/10) | 31 (19/12) | 66 ± 2 | RE:8 ± 1 C:11 ± 1 | Upper back, chest press, leg press, knee extension, and flexion | 60–80% | 8 | 3 | 3 | 16 |
| Sigal et al. [36] | 2007, Canada | 64 (40/24) | 63 (41/22) | 54.7 ± 7.5 | RE:6.1 ± 4.7 C:5.0 ± 4.5 | Group A: Abdominal crunches, seated row, seated biceps curls, supine bench press, leg press, shoulder press, leg extension. Group B: abdominal crunches, lateral pulldown, triceps push-down, sitting chest press, leg press, upright row, leg curls | 80% | 7–9 | 2–3 | 3 | 26 |
| Gordon et al. [39] | 2006, America | 15 (7/8) | 15 (8/7) | 67 ± 7 | RE:9 ± 2 C:12 ± 3 | Knee extension, chest press, leg curl, upper back and leg press | 60–80% | 8 | 3 | 3 | 16 |
| Baldi and Snowling [44] | 2003, New Zealand | 9 (9/0) | 9 (9/0) | 47.9 | > 3 | Ten exercises involving major muscle groups in the upper and low body | 65–75% | 12 | 2 | 3 | 10 |
| Dunstan et al. [34] | 1998, Australia | 11 (8/3) | 10 (5/5) | 51 | RE:5.3 ± 1.4 C:5.1 ± 1.2 | Leg extension, bench press, leg curl, dumbbell bicep curls, behind neck pulldown, calf raise, dumbbell overhead press, seated rowing, forearm extension using pulley (triceps), and abdominal curls | 50–75% | 10–15 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| Ishii et al. [19] | 1998, Japan | 9 (9/0) | 8 (8/0) | 46.8 ± 8.9 | (nr) | Arm curls, military press, push-ups, squats, knee extensions, heel raises, back extensions, bent knee sit-ups, and upright rowing. Back extensions, push-ups, and bent knee sit-ups | 40–50% | 10–20 | 2 | 5 | 6 |
| Honkola et al. [48] | 1997 Finland | 18 (12/6) | 20 (5/15) | 62 ± 2 | RE:8 ± 2 C:8 ± 2 | Thigh flexors and extensors, trunk flexors and extensors, upper arm muscles | 65–67% | 12–15 | 2 | 2 | 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ye, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Korivi, M. Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010140
Liu Y, Ye W, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Kuo C-H, Korivi M. Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(1):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010140
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yubo, Weibing Ye, Qian Chen, Yong Zhang, Chia-Hua Kuo, and Mallikarjuna Korivi. 2019. "Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 1: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010140
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ye, W., Chen, Q., Zhang, Y., Kuo, C.-H., & Korivi, M. (2019). Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(1), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010140








