Evolution of Landscape Ecological Risk at the Optimal Scale: A Case Study of the Open Coastal Wetlands in Jiangsu, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets and Processing
2.3. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Landscape Classification and Landscape Pattern Mapping
3.2. Landscape Pattern Analysis Using an Optinal Scale
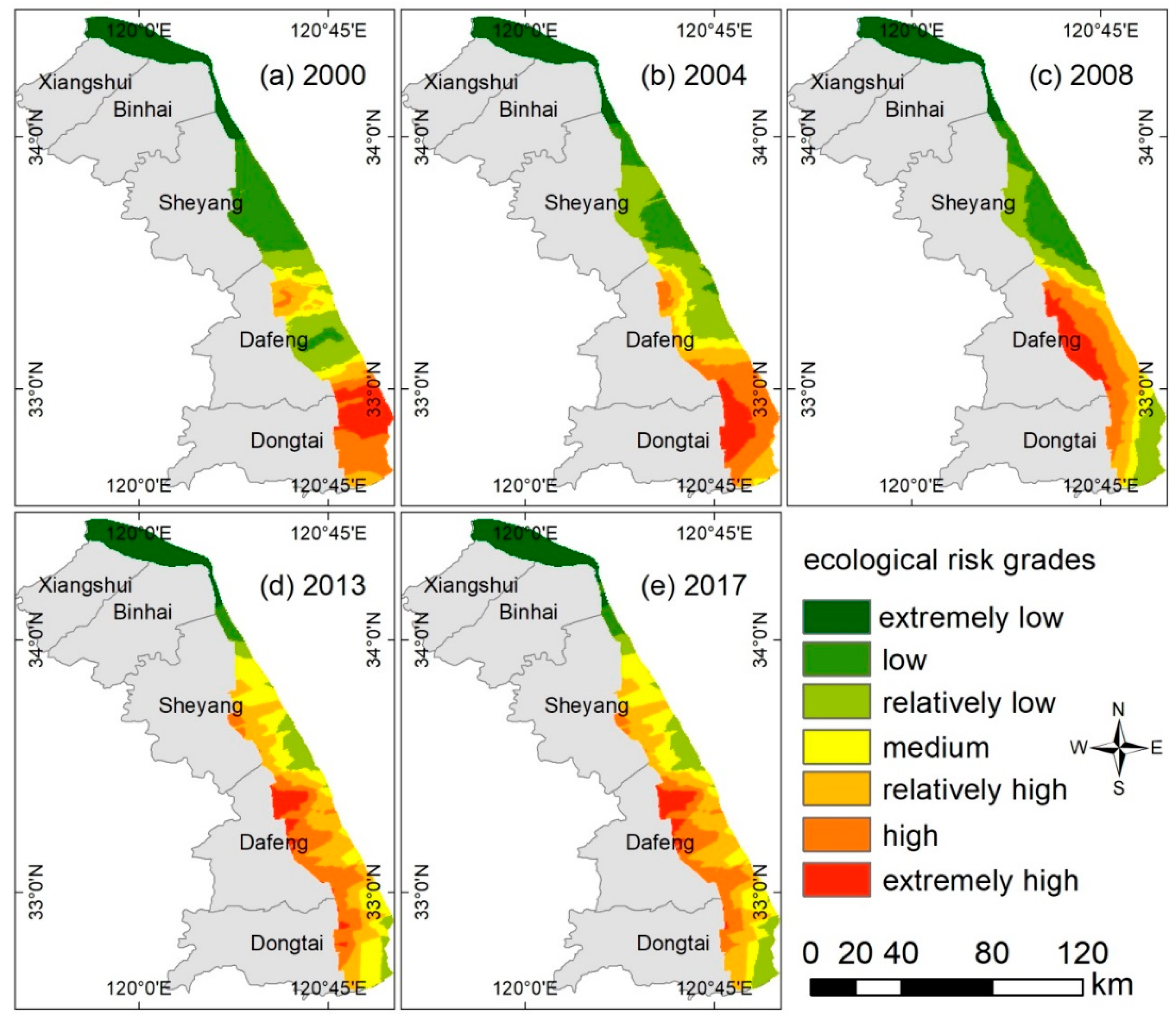
3.3. Spatiotemporal Differences in Landscape Ecological Risk Patterns
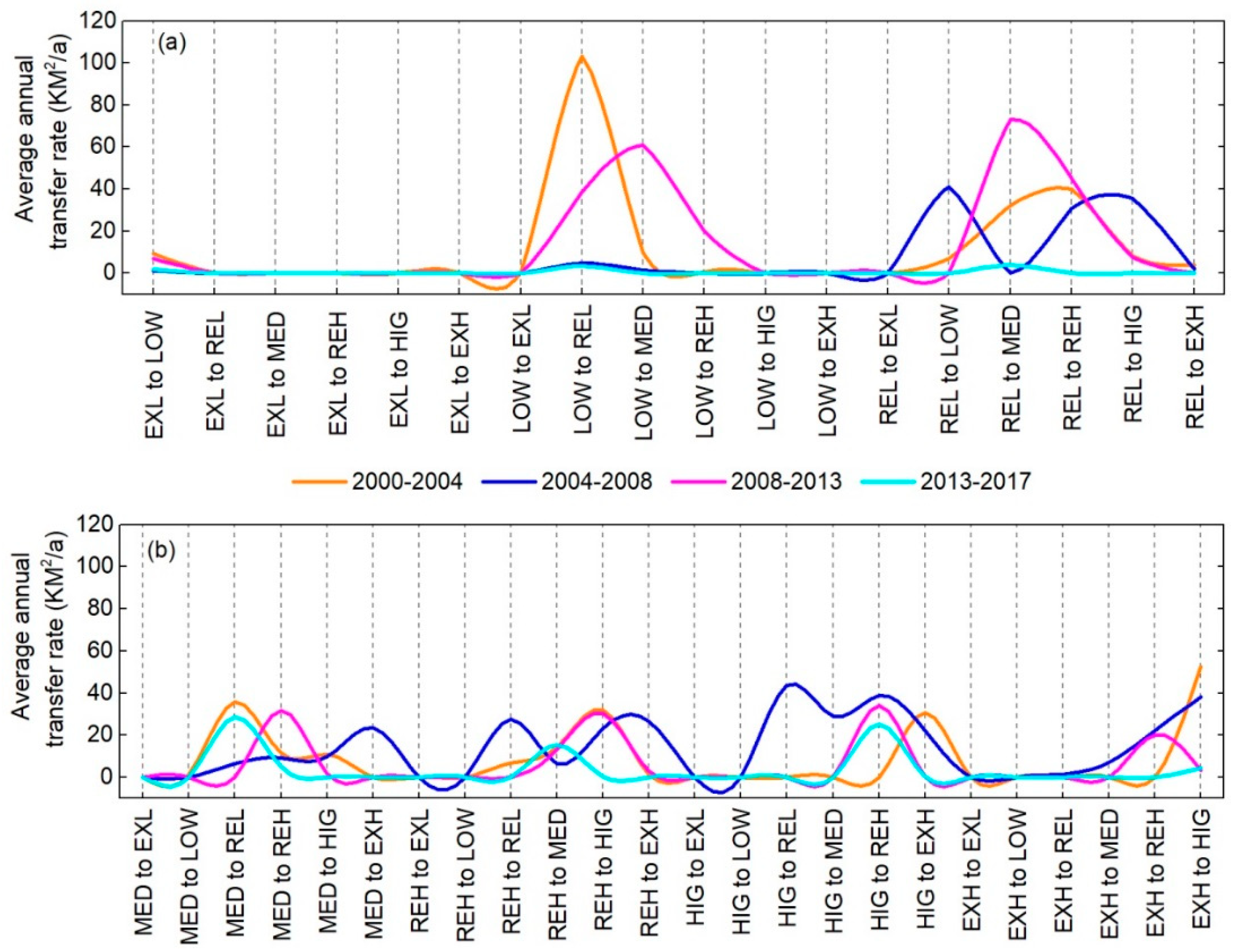
3.4. Landscape Ecological Risk Transfer Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inkoom, J.N.; Frank, S.; Greve, K.; Walz, U.; Fürst, C. Suitability of different landscape metrics for the assessments of patchy landscapes in West Africa. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.J.R.; De Pablo, C.L.; De Agar, P.M. Landscape changes over time: Comparison of land uses, boundaries and mosaics. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Landscape sustainability science: Ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, A.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Li, W. Research on landscape ecology and sustainable land use. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2004, 40, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Landscape Ecology Pattern, Process, Scale and Hierarchy; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pickett, S.T.A.; Cadenasso, M.L. Landscape ecology—Spatial heterogeneity in ecological-systems. Science 1995, 269, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, P.; Huang, H. Ecological risk assessment of land use change in the Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, S.; Fang, S.; Liu, X.; Pu, M. Gradient analysis of dry valley of minjiang river landscape pattern, based on moving window method. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 3276–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galpern, P.; Manseau, M. Finding the functional grain: Comparing methods for scaling resistance surfaces. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J. Geology of mankind. Nature 2002, 415, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.; Stoermer, E. The “anthropocene”. IGBP Newsl. 2000, 41, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Pu, R.; Liu, Y. A review on anthropogenic geomorphology. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Jia, Y.; Shan, H.; Tang, C.; Ma, W. Gis-based coastal area suitability assessment of geo-environmental factors in laoshan district, Qingdao. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of coastal plumes and ocean fronts: Overview and case study. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Goward, S.N. Landsat’s role in ecological applications of remote sensing. Bioscience 2004, 54, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, W.R., Jr. Assessing risks to wildlife populations from multiple stressors: Overview of the problem and research needs. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zong, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Assessing landscape ecological risk in a mining city: A case study in Liaoyuan city, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8312–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, R. Ecological risk assessment of urbanization processes—A case study. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1998, 18, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, S. Managing industrial risk—Having a tested and proven system to prevent and assess risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 130, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pu, R.; Gong, H.; Luo, X.; Ye, M.; Feng, B. Evolution characteristics of landscape ecological risk patterns in coastal zones in Zhejiang province, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, K.F.; Porter, D.E.; Dyer, S.A.; Wein, G.R.; Pinder, J.E.; Brisbin, I.L. Using wildlife as receptor species: A landscape approach to ecological risk assessment. Environ. Manag. 2004, 34, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenbaum, L.V. Detoxifying ecological risk assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2005, 11, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cao, K.; Li, M.; Xu, Z. Coastal ecological risk assessment: Its research progress and prospect. Adv. Earth Sci. 2016, 31, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhang, M.; Zuo, T.; Lu, J. Land use and ecosystems services value changes and ecological land management in coastal Jiangsu, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, F. Landscape effects of environmental impact on bay-area wetlands under rapid urban expansion and development policy: A case study of Lianyungang, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 94, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cao, H.; Yu, T. Coastal wetland loss and environmental change due to rapid urban expansion in Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, X. Ecological security and ecosystem services in response to land use change in the coastal area of Jiangsu, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boongaling, C.G.K.; Faustino-Eslava, D.V.; Lansigan, F.P. Modeling land use change impacts on hydrology and the use of landscape metrics as tools for watershed management: The case of an ungauged catchment in the philippines. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, P.B.; Sutherland, R.W.; Baldwin, R.F.; Fedak, D.A.; Carnes, R.G.; Montgomery, A.P. Landscape connectivity losses due to sea level rise and land use change. Anim. Conserv. 2017, 20, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, K.; Hong, Y.; Qi, J. Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Valle, M.D.; Harvey, N.; Marcomini, A. Assessing coastal vulnerability to climate change: Comparing segmentation at global and regional scales. Sustain. Sci. 2008, 3, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Mitra, D.; Dewan, A.; Akhter, S.H. Coastal multi-hazard vulnerability assessment along the ganges deltaic coast of bangladesh—A geospatial approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 127, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, K.A. Assessing coastal vulnerability index to climate change: The case of Accra-Ghana. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, G.; Dang, L. Identifying ecological red lines: A case study of the coast in Liaoning province. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9461–9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Bertness, M.D.; Bruno, J.F.; Li, B.; Chen, G.; Coverdale, T.C.; Altieri, A.H.; Bai, J.; Sun, T.; Pennings, S.C.; et al. Economic development and coastal ecosystem change in China. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Groenewold, N. Reducing regional disparities in china: An evaluation of alternative policies. J. Comp. Econ. 2010, 38, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, W. Spatially explicit landscape-level ecological risks induced by land use and land cover change in a national ecologically representative region in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 14192–14215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ives, A.R.; Carpenter, S.R. Stability and diversity of ecosystems. Science 2007, 317, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; De Fries, R.S.; Díaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Oteng-Yeboah, A.; Pereira, H.M. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the millennium ecosystem assessment. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y. Sustainability associated coastal eco-environmental problems and coastal science development in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2016, 31, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Mao, L.; Cheng, L.; Chen, K. Seasonal pattern of tidal-flat topography along the Jiangsu middle coast, China, using HJ-1 optical images. Wetlands 2013, 33, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Sun, J. Saltmarshes response to human activities on a prograding coast revealed by a dual-scale time-series strategy. Estuar. Coasts 2017, 40, 522–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Goldstein, N.C.; Clarke, K.C. The spatiotemporal form of urban growth: Measurement, analysis and modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C. Make earth observations open access. Nature 2014, 513, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Andrefouet, S.; Cohen, W.B.; Gomez, C.; Griffiths, P.; Hais, M.; Healey, S.P.; Helmer, E.H.; Hostert, P.; Lyons, M.B.; et al. Bringing an ecological view of change to landsat-based remote sensing. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiang, W.; Zhao, J. Urban ecology in China: Historical developments and future directions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Myint, S. A comparison of spatial autocorrelation indices and landscape metrics in measuring urban landscape fragmentation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 121, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesterowicz, J.; Stepinski, T.F. On using landscape metrics for landscape similarity search. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Shao, G. Assessment of regional ecosystem health—A case study of the golden triangle of southern Fujian province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarigal, K. Fragstats Help. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/documents/fragstats.help.4.2.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Zhao, W.; Fu, B.; Chen, L. The effects of grain change on landscape indices. Quat. Sci. 2003, 23, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y. A review on the accuracy analysis of spatial scaling data. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Leuven, R.; Poudevigne, I. Riverine landscape dynamics and ecological risk assessment. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 845–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J. The research progress and prospect of watershed ecological risk assessment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; You, N.; Meng, J. Dynamic ecological risk assessment and management of land use in the middle reaches of the Heihe river based on landscape patterns and spatial statistics. Sustainability 2016, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Land use/land cover change analysis using object-based classification approach in munessa-shashemene landscape of the ethiopian highlands. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2411–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lou, Q.; Huang, H.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Z. Landscape ecological security assessment based on projection pursuit in Pearl River Delta. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Z.; Zou, X.; Zuo, P.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Impact of landscape patterns on ecological vulnerability and ecosystem service values: An empirical analysis of yancheng nature reserve in China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, C.A.; Borsuk, M.E.; Stanley, D.W. Long-term changes in watershed nutrient inputs and riverine exports in the Neuse river, North Carolina. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, P.; Dang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zong, M.; Hu, X. Review on landscape ecological risk assessment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 664–677. [Google Scholar]
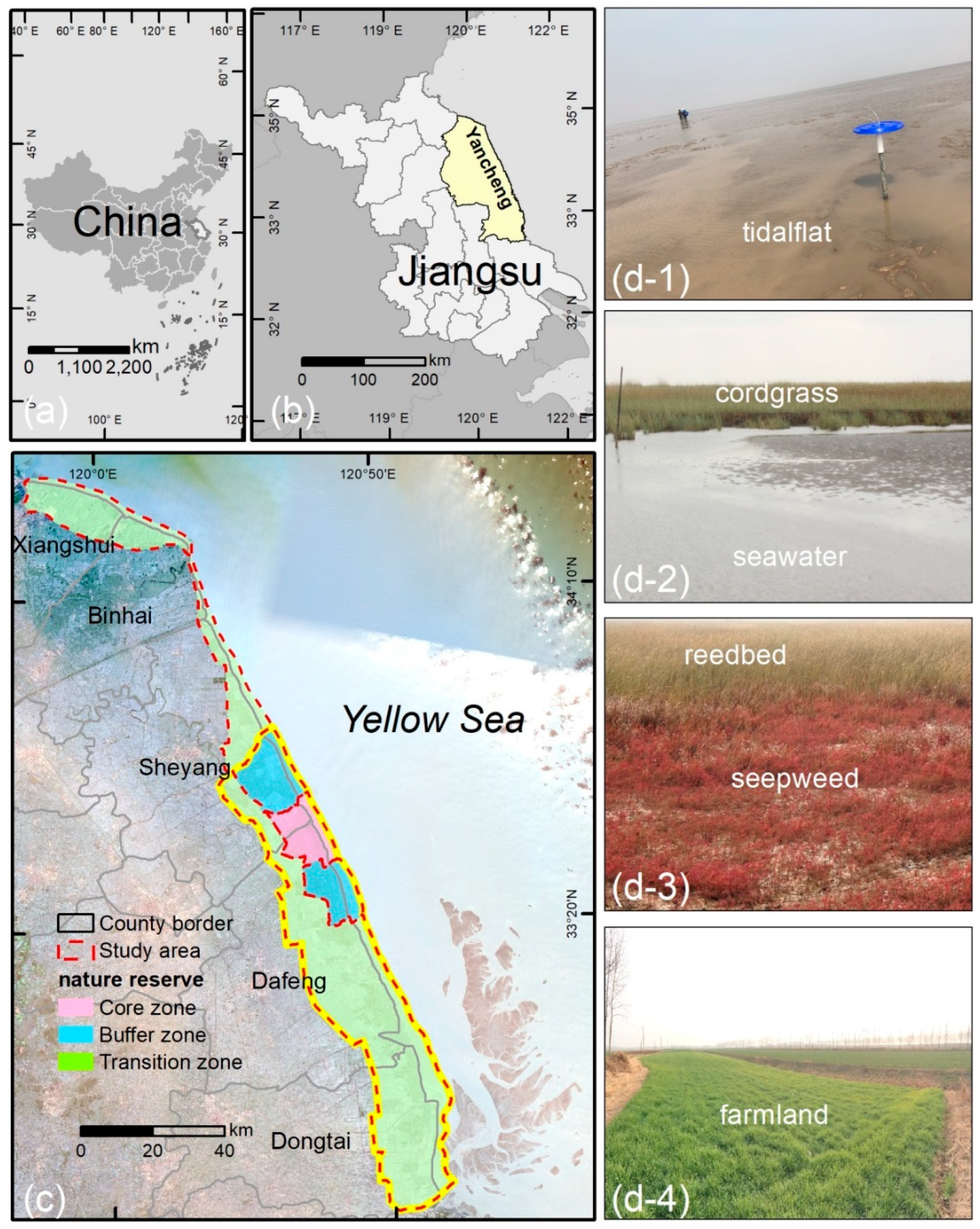
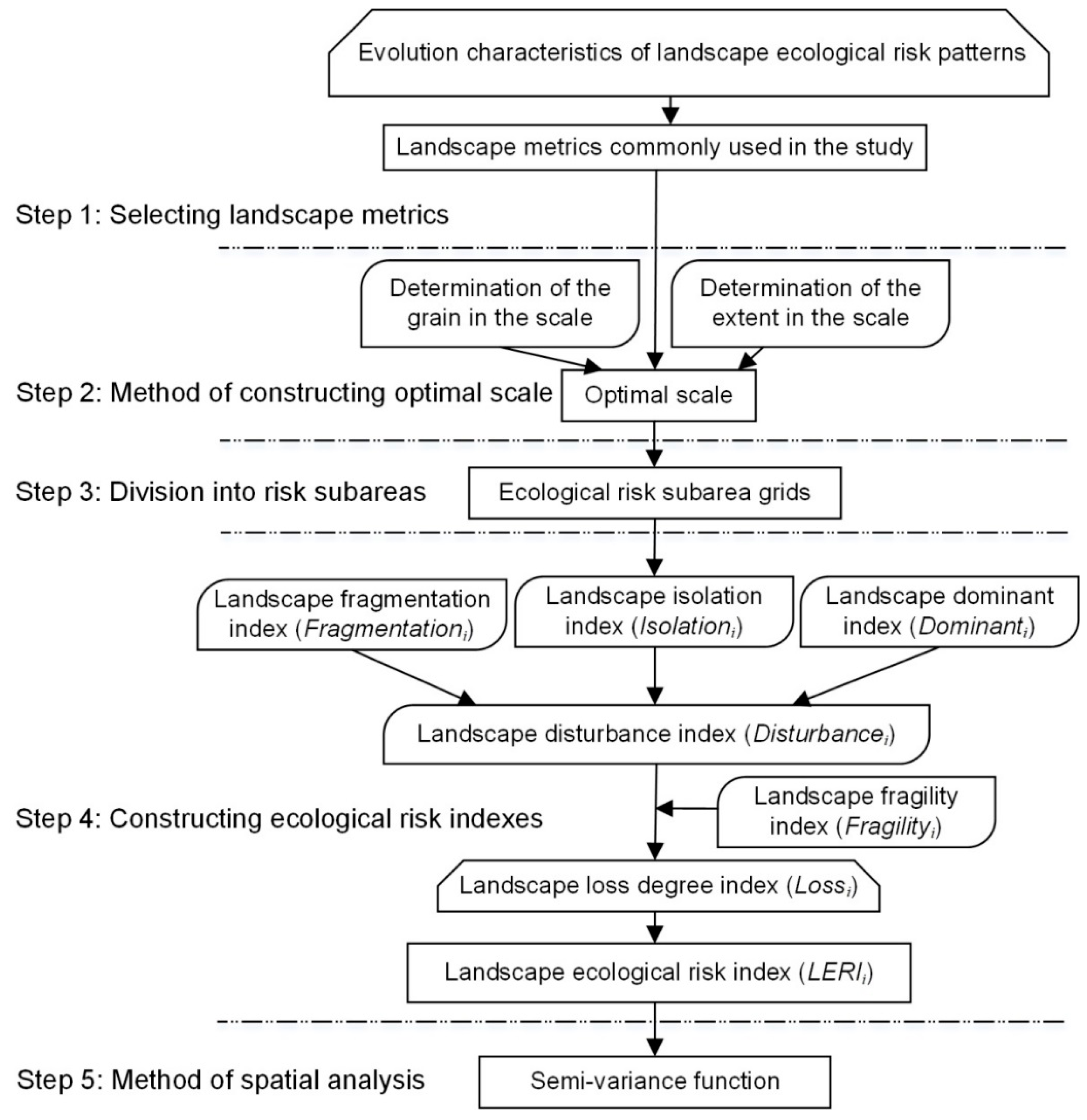
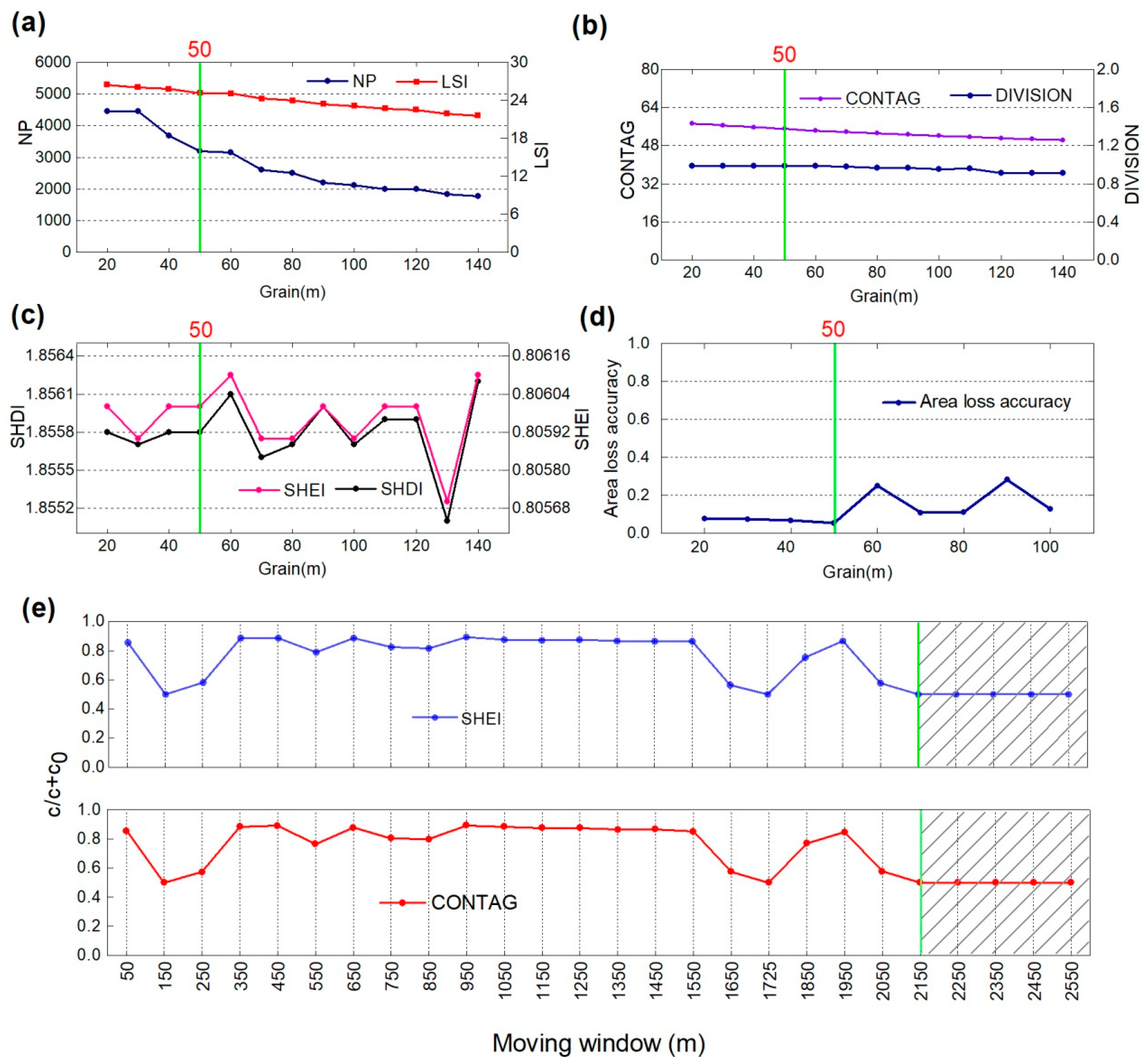
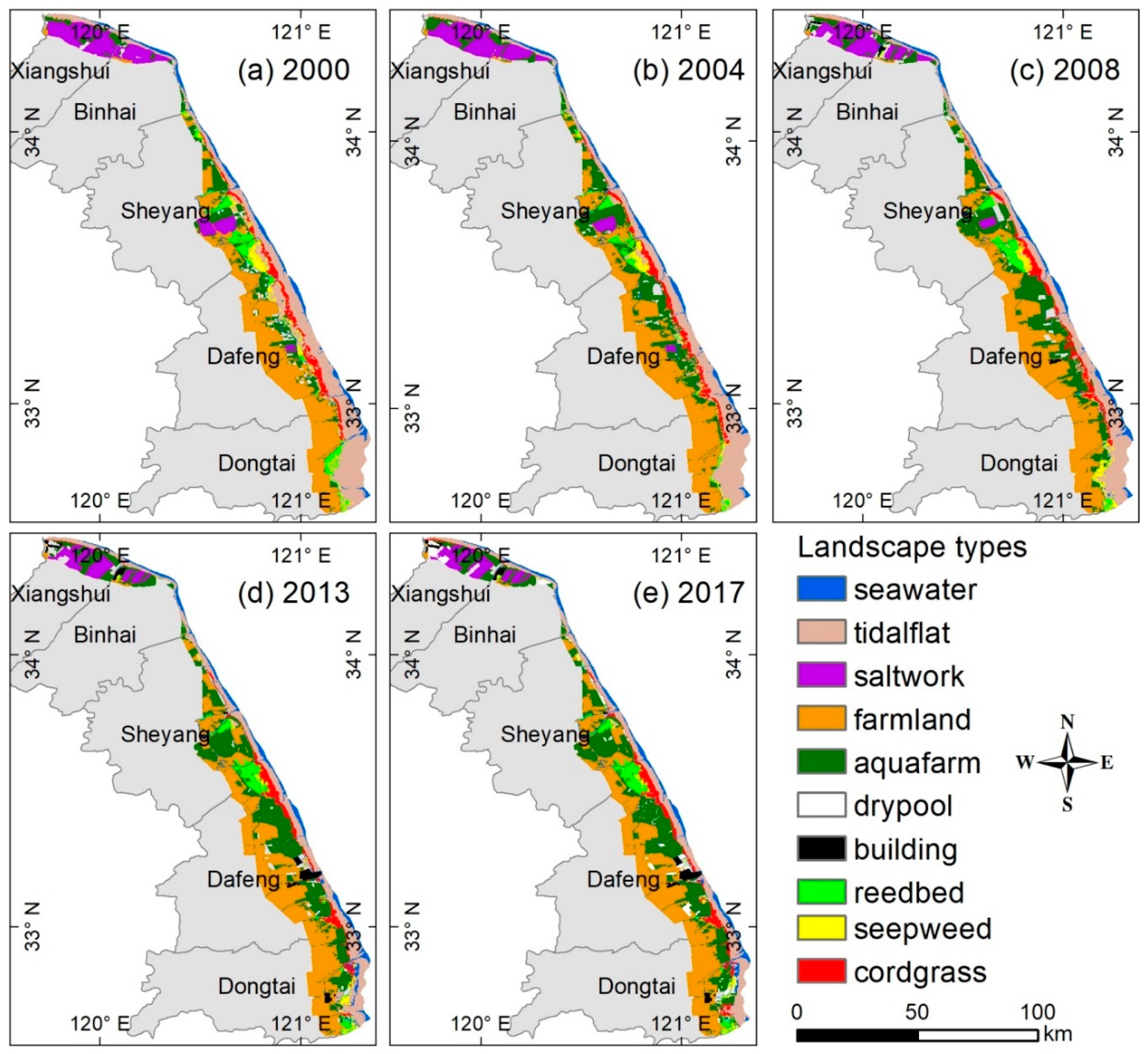
| Satellite | Sensors | Path/Row | Date | Satellite | Sensors | Path/Row | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 | TM | 120/36 | 13 December 2000 | Landsat 5 | TM | 119/37 | 06 December 2000 |
| Landsat 5 | TM | 120/36 | 08 December 2004 | Landsat 5 | TM | 119/37 | 15 November 2004 |
| Landsat 5 | TM | 120/36 | 19 December 2008 | Landsat 5 | TM | 119/37 | 13 January 2009 |
| Landsat 8 | OLI | 120/36 | 01 December 2013 | Landsat 8 | OLI | 119/37 | 10 December 2013 |
| Landsat 8 | OLI | 120/36 | 06 December 2017 | Landsat 8 | OLI | 119/37 | 22 December 2017 |
| Level | Landscape Metric | Significance/Description | Themes/Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Number of patches (NP) | Total number of patches in the landscape | a Measure of configuration/standard method |
| Landscape shape index (LSI) | Landscape boundary and total edge within the landscape divided by the total area | a/b Measure of configuration/standard method | |
| Landscape division index (DIVISION) | Degree of plaque fragmentation in the landscape, describing the complexity of the landscape | a Diversity assessment/standard method | |
| Shannon’s diversity index (SHDI) | Heterogeneity of the landscape: the higher the landscape heterogeneity, the higher the diversity index | a Diversity assessment/standard method | |
| Percentage of the landscape (PLAND) | Percentage of the landscape comprising of the corresponding patch type | b Measure of configuration/standard method | |
| Patch density (PD) | Configuration metrics patch density | b Spatial differentiation/standard method | |
| Total Area (CA) | Sum of the areas of all patches belonging to a given class | b Measure of configuration/standard method | |
| Largest patch index (LPI) | Percentage of the landscape comprised by the largest patch of the corresponding patch type | b Measure of configuration/standard method | |
| Edge Density (ED) | Amount of edge relative to the landscape area | b Spatial differentiation/standard method | |
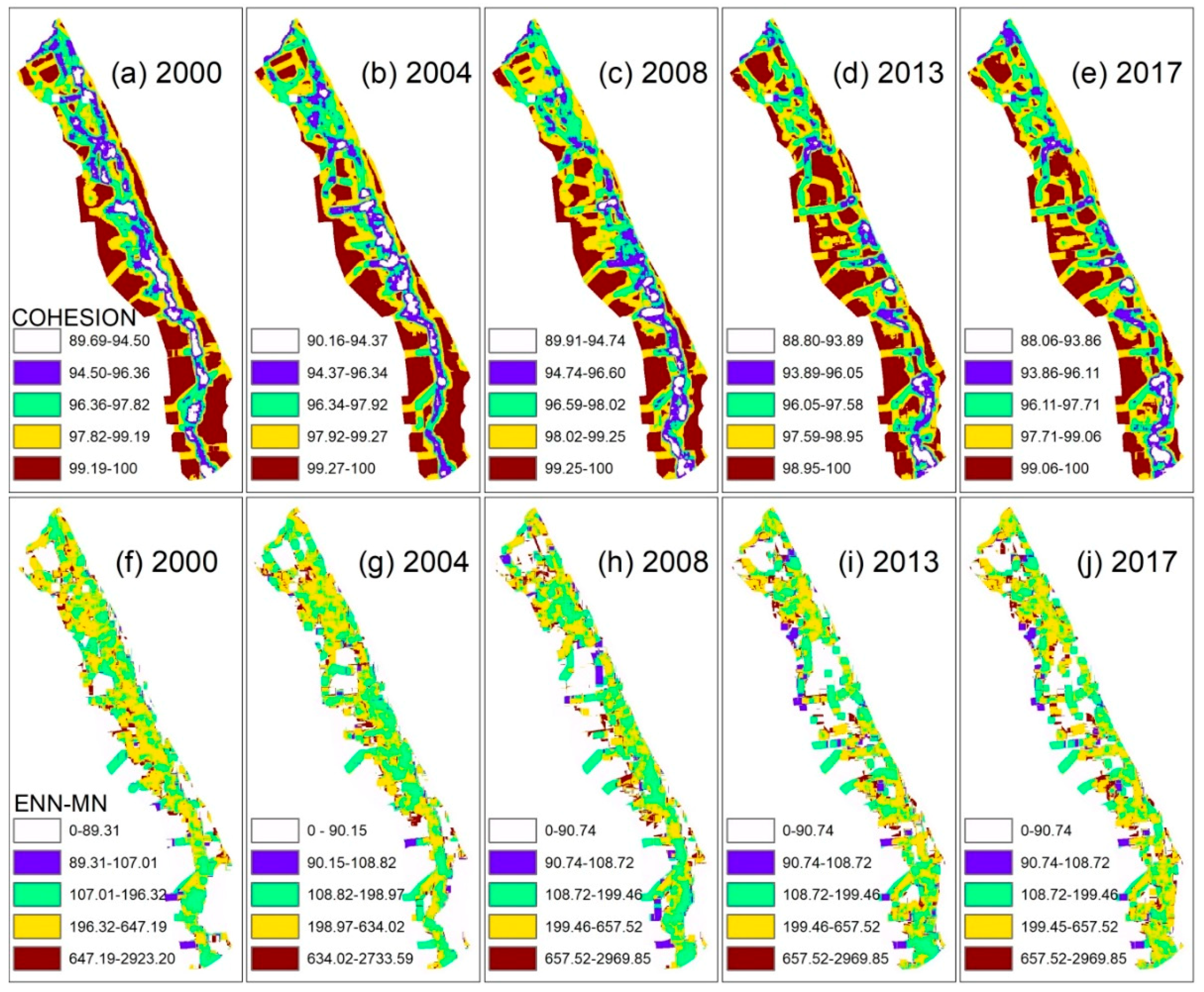
| landscape | Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION) | Measures the physical connectedness of the corresponding patch type | d Measure of configuration/moving window |
| Euclidean nearest neighbor distance mean index (ENN–MN) | Distance to the nearest neighboring patch of the same type, based on shortest edge-to-edge distance | d Measure of configuration /moving window | |
| Class/landscape | Shannon’s evenness index (SHEI) | Expresses the uniformity of distribution at different landscape levels | a/c Measure of configuration/standard method and moving window |
| Contagion index (CONTAG) | Measures the extent to which patch types are aggregated or clumped | a/c Measure of configuration/moving window |
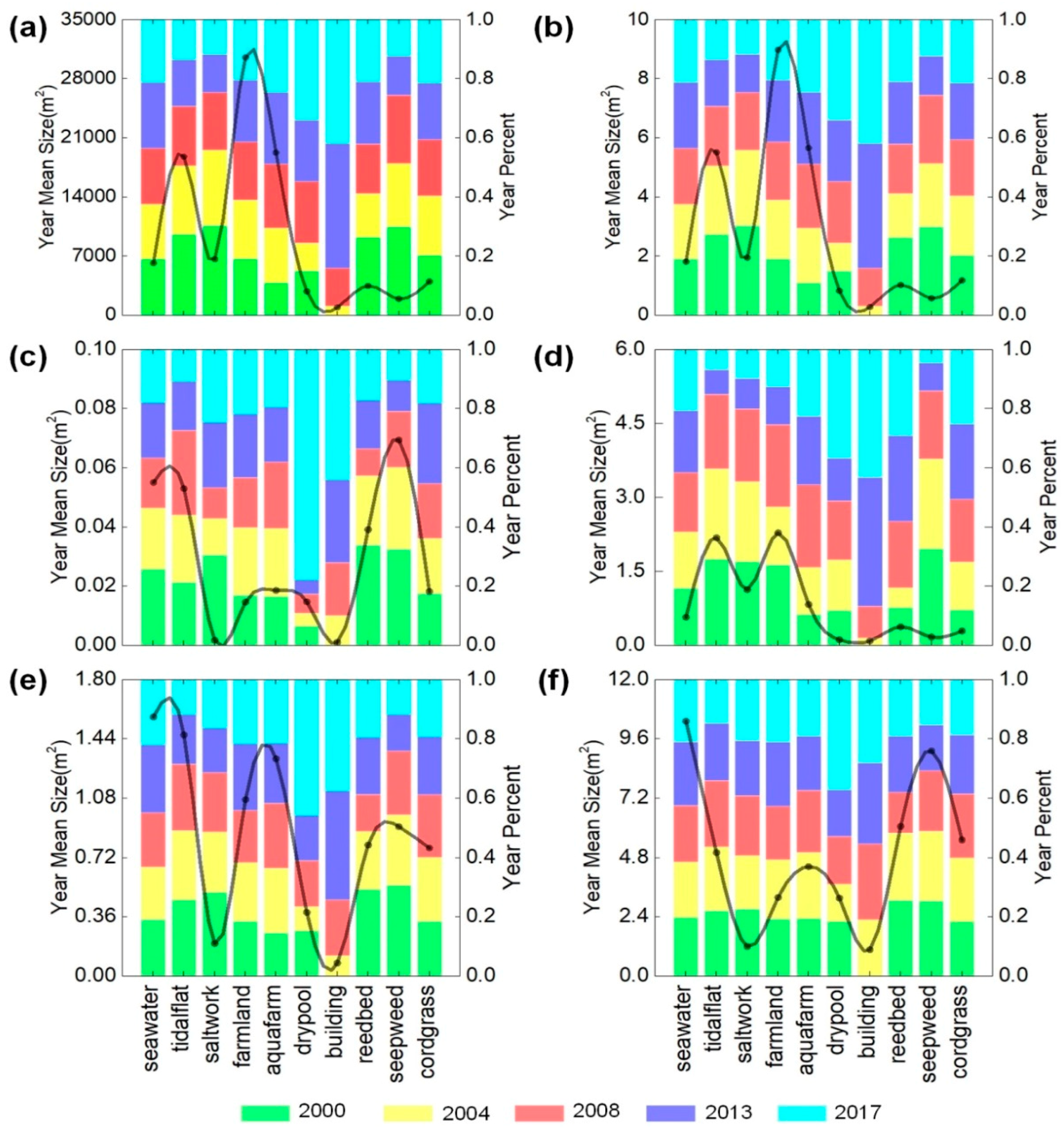
| Year | Types | SEA | TID | SAL | FAR | AQU | DRY | BUI | REE | SEE | COR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Fragmentationi | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.01 |
| Isolationi | 0.41 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 1.04 | 0.28 | |
| Dominanti | 2.13 | 8.37 | 3.28 | 9.40 | 3.50 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 1.62 | 1.12 | 1.39 | |
| Disturbancei | 0.57 | 1.70 | 0.67 | 1.89 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 0.37 | |
| Lossi | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 2004 | Fragmentationi | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| Isolationi | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.38 | 1.41 | 0.74 | 1.35 | 0.29 | |
| Dominanti | 2.08 | 7.19 | 2.75 | 9.91 | 5.87 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 1.39 | |
| Disturbancei | 0.55 | 1.47 | 0.56 | 2.00 | 1.20 | 0.22 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.66 | 0.37 | |
| Lossi | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | |
| 2008 | Fragmentationi | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.02 |
| Isolationi | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 1.03 | 0.30 | |
| Dominanti | 2.12 | 6.28 | 2.12 | 9.71 | 6.87 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 1.01 | 0.88 | 1.33 | |
| Disturbancei | 0.54 | 1.30 | 0.44 | 1.95 | 1.39 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 0.53 | 0.36 | |
| Lossi | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 2013 | Fragmentationi | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 |
| Isolationi | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.44 | 1.34 | 0.37 | |
| Dominanti | 2.47 | 4.90 | 1.39 | 10.34 | 7.61 | 1.03 | 0.67 | 1.27 | 0.52 | 1.35 | |
| Disturbancei | 0.60 | 1.02 | 0.31 | 2.08 | 1.54 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 0.55 | 0.39 | |
| Lossi | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 2017 | Fragmentationi | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.01 |
| Isolationi | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.22 | 0.45 | 1.42 | 0.27 | |
| Dominanti | 2.37 | 4.26 | 1.28 | 10.23 | 7.81 | 1.74 | 0.67 | 1.31 | 0.52 | 1.51 | |
| Disturbancei | 0.58 | 0.89 | 0.29 | 2.06 | 1.58 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.39 | |
| Lossi | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
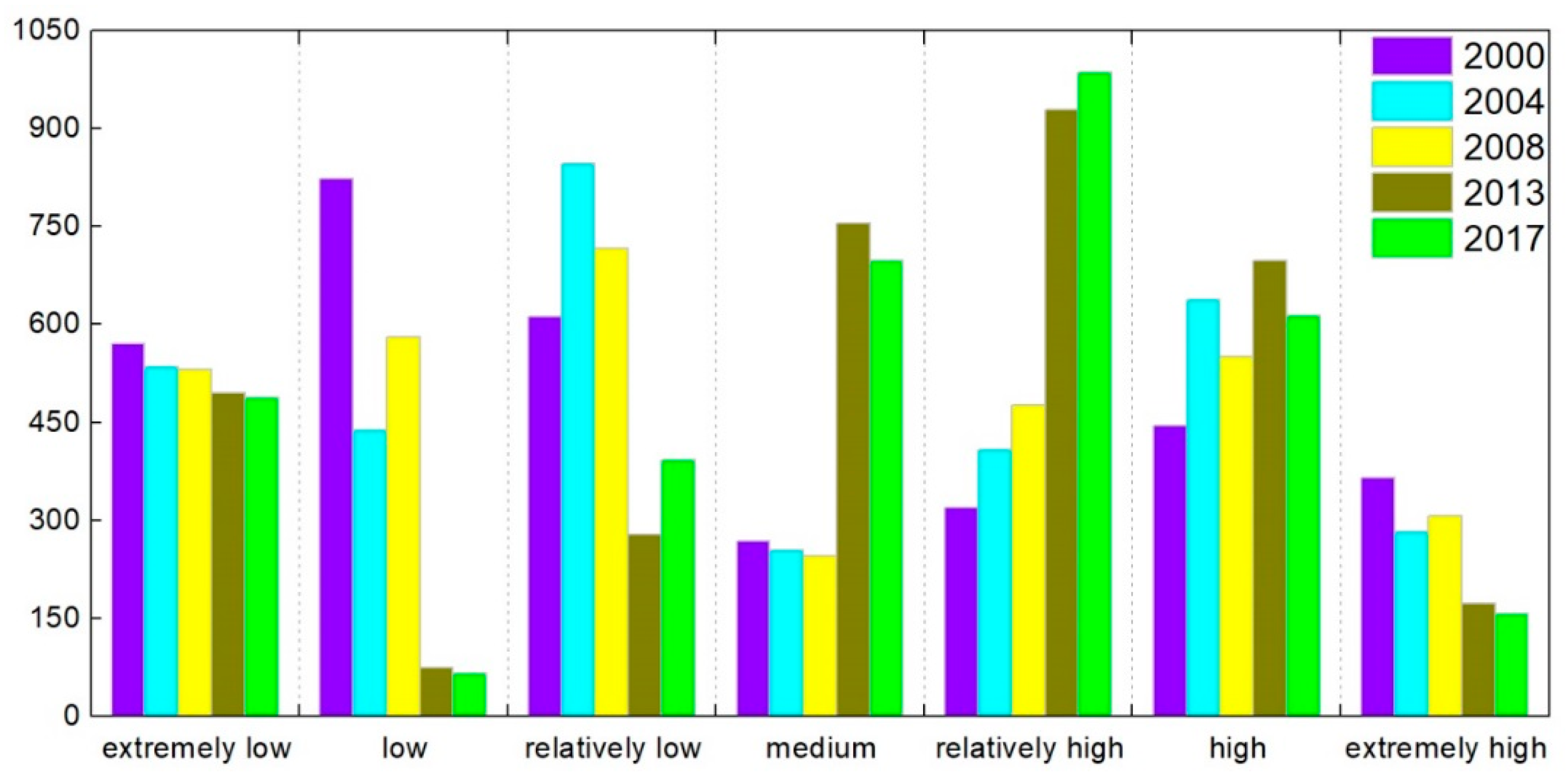
| Year 2017 | EXL | LOW | REL | MED | REH | HIG | EXH | TOT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 2000 | |||||||||
| EXL | 483.71 | 66.12 | 17.59 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 567.42 | |
| LOW | 1.63 | 6.98 | 124.74 | 331.74 | 273.45 | 88.15 | 0 | 826.68 | |
| REL | 0 | 0 | 70.72 | 108.82 | 262.80 | 144.20 | 23.22 | 609.75 | |
| MED | 0 | 0 | 1.56 | 36.99 | 119.01 | 99.83 | 10.03 | 267.42 | |
| REH | 0 | 0 | 26.05 | 18.48 | 59.85 | 121.29 | 92.01 | 317.68 | |
| HIG | 0 | 0 | 112.13 | 67.17 | 164.55 | 71.02 | 27.72 | 442.60 | |
| EXH | 0 | 0 | 37.74 | 132.85 | 103.64 | 86.44 | 2.78 | 363.44 | |
| TOT | 485.34 | 73.10 | 390.52 | 696.05 | 983.29 | 610.93 | 155.76 | 3394.98 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Wei, X.; Sun, C. Evolution of Landscape Ecological Risk at the Optimal Scale: A Case Study of the Open Coastal Wetlands in Jiangsu, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081691
Liu Y, Liu Y, Li J, Lu W, Wei X, Sun C. Evolution of Landscape Ecological Risk at the Optimal Scale: A Case Study of the Open Coastal Wetlands in Jiangsu, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(8):1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081691
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yongchao, Yongxue Liu, Jialin Li, Wanyun Lu, Xianglin Wei, and Chao Sun. 2018. "Evolution of Landscape Ecological Risk at the Optimal Scale: A Case Study of the Open Coastal Wetlands in Jiangsu, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 8: 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081691
APA StyleLiu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, J., Lu, W., Wei, X., & Sun, C. (2018). Evolution of Landscape Ecological Risk at the Optimal Scale: A Case Study of the Open Coastal Wetlands in Jiangsu, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(8), 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081691






