Accuracy of Implant Casts Generated with Conventional and Digital Impressions—An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
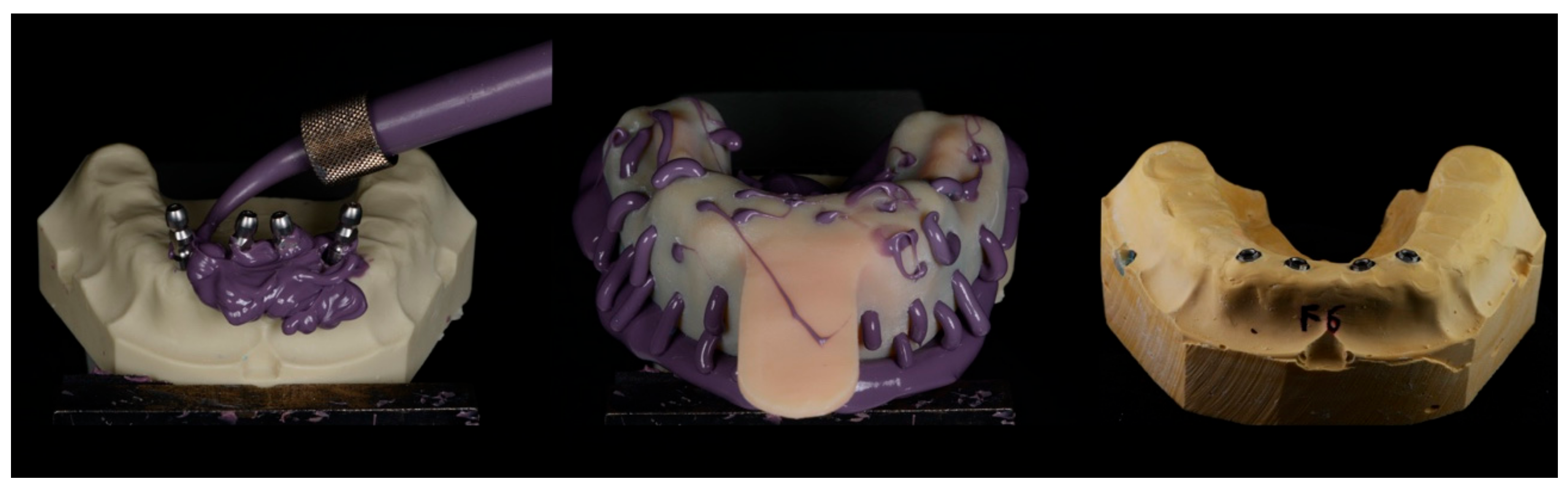
2.1. Model Preparation
2.2. Impression Procedures
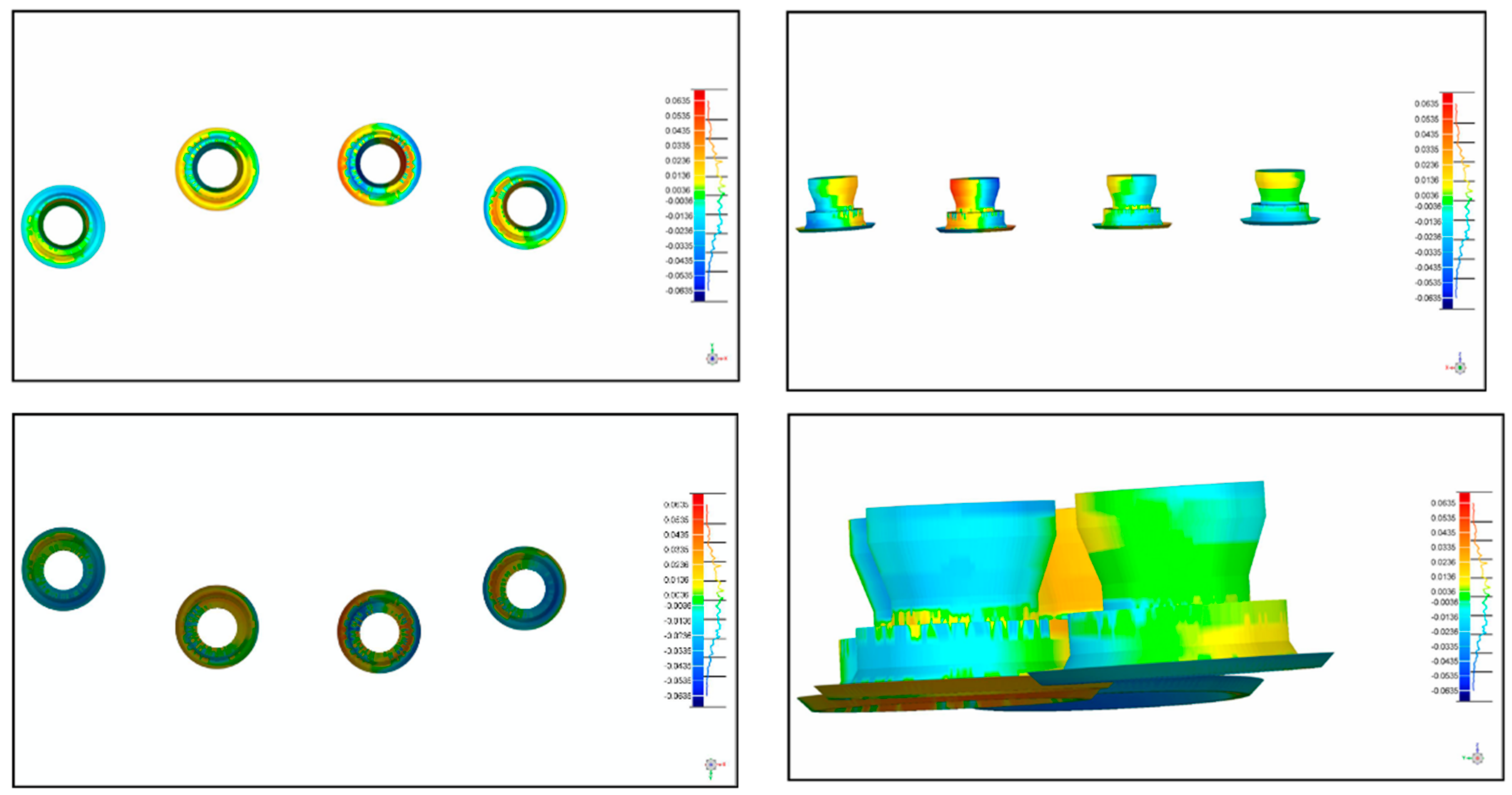
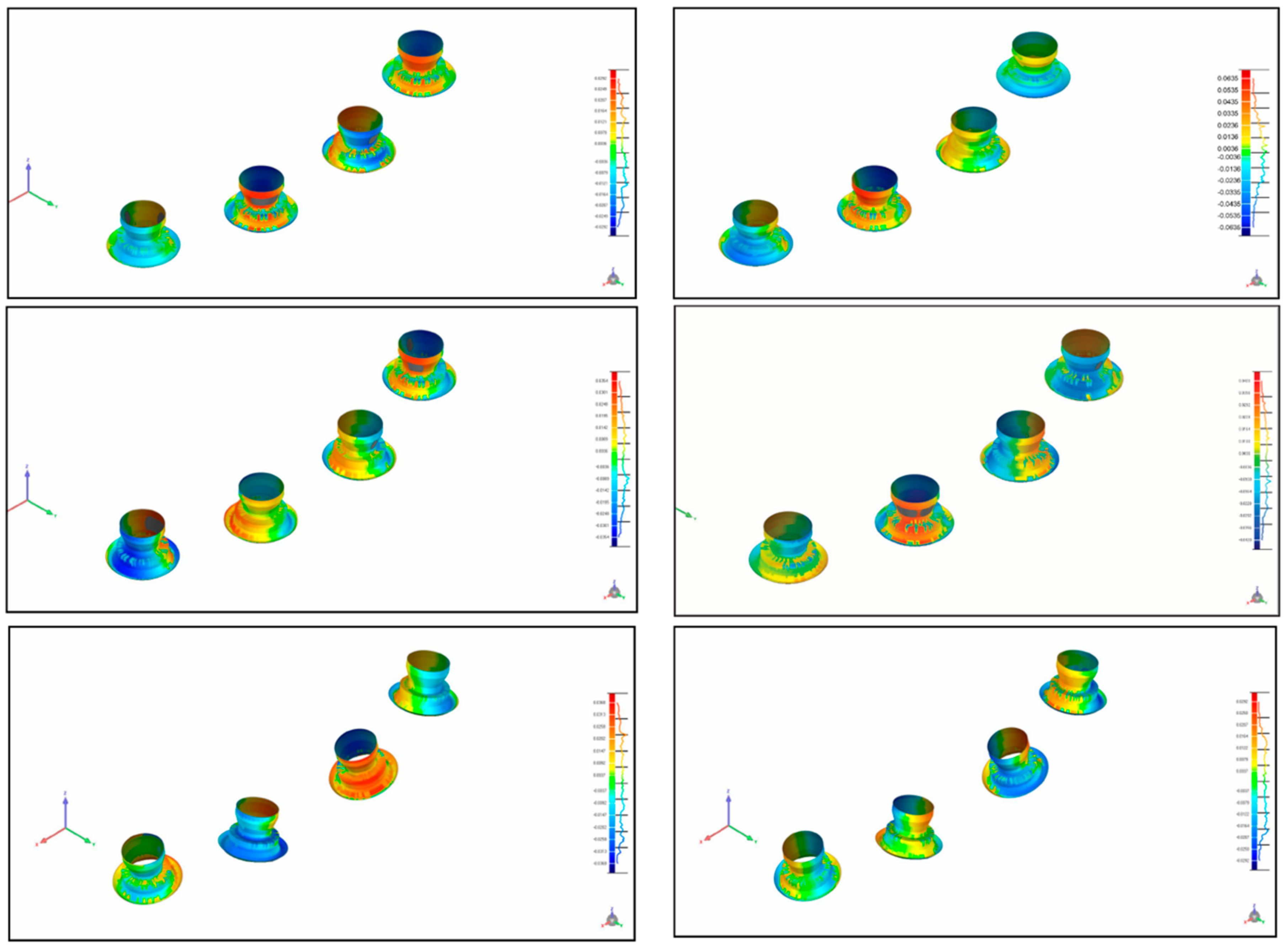
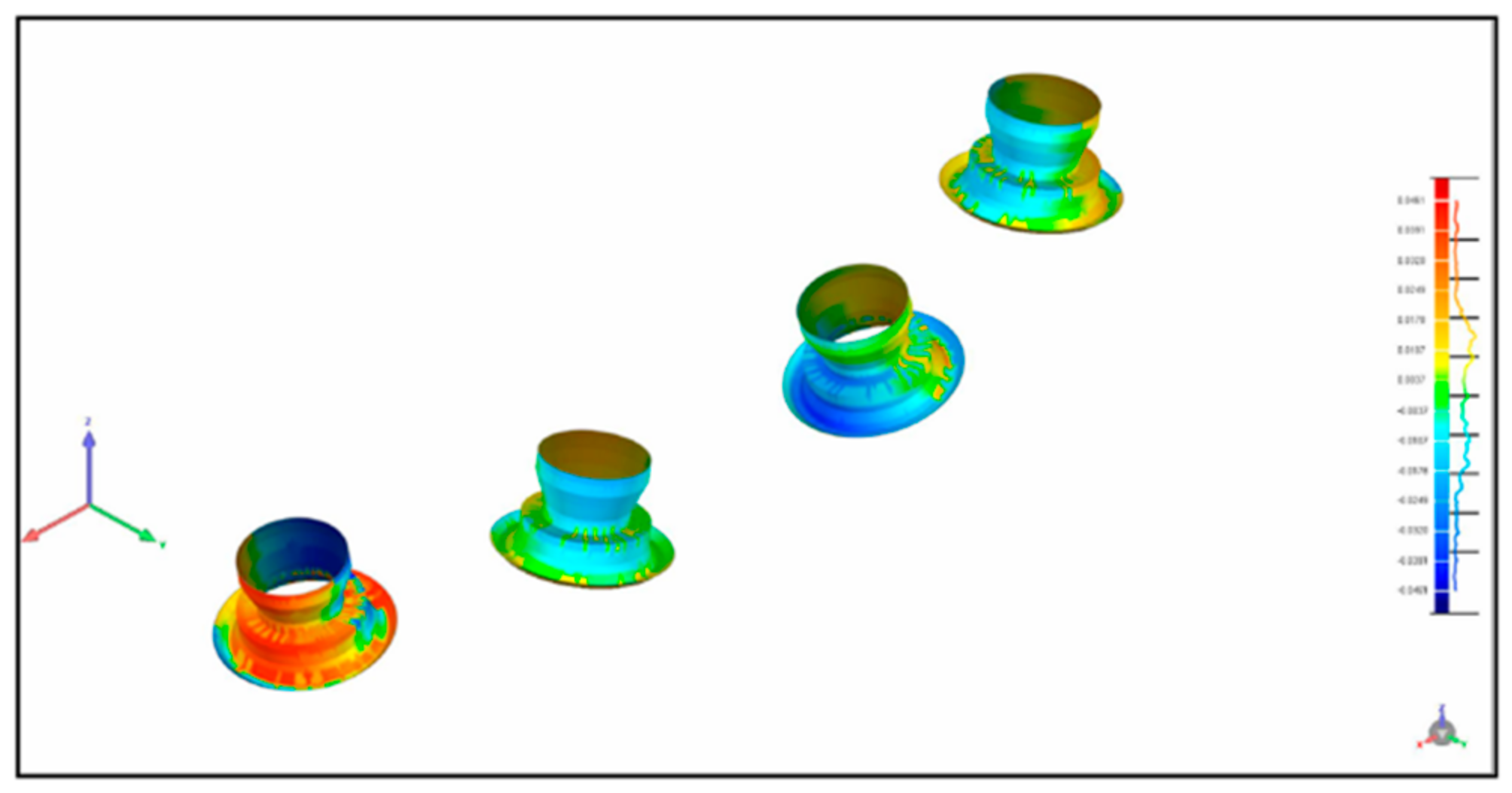
2.3. Measurement
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adell, R.; Lekholm, U.; Rockler, B.; Branemark, P.I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1981, 10, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarb, G.A.; Schmitt, A. The longitudinal clinical effectiveness of osseointegrated dental implants in anterior partially edentulous patients. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 6, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goll, G.E. Production of accurately fitting full-arch implant frameworks: Part I—Clinical procedures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 66, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangert, B.; Jemt, T.; Jorneus, L. Forces and moments on Branemark implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1989, 4, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zarb, G.A.; Schmitt, A. The longitudinal clinical effectiveness of osseointegrated dental implants: The Toronto Study. Part II: The prosthetic results. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1990, 64, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemt, T. Failures and complications in 391 consecutively inserted fixed prostheses supported by Branemark implants in edentulous jaws: A study of treatment from the time of prosthesis placement to the first annual checkup. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1991, 6, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Jemt, T. In vivo measurements of precision of fit involving implant-supported prostheses in the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1996, 11, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kallus, T.; Bessing, C. Loose gold screws frequently occur in full-arch fixed prostheses supported by osseointegrated implants after 5 years. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1994, 9, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, G.; Palmqvist, S. Complications, supplementary treatment, and maintenance in edentulous arches with implant-supported fixed prostheses. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1990, 3, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.B.; Rubenstein, J.E.; Nicholls, J.I.; Yuodelis, R.A. Three-dimensional analysis of the casting accuracy of one-piece, osseointegrated implant-retained prostheses. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 6, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Chen, C.J.; Gallucci, G.O.; Doukoudakis, A.; Weber, H.P.; Chronopoulos, V. Accuracy of implant impressions for partially and completely edentulous patients: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpel, L.J., 3rd; Quon, S.J. Adhesive abutment cylinder luting. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1993, 69, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Cho, S.B. Accuracy of five implant impression technique: Effect of splinting materials and methods. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2011, 3, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, A.; Beretta, M.; Luongo, G.; Mangano, C.; Mangano, F. Conventional Vs Digital Impressions: Acceptability, Treatment Comfort and Stress among Young Orthodontic Patients. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Benic, G.I.; Hogsett, V.L.; White, G.S.; Lal, K.; Gallucci, G.O. Accuracy of implant casts generated with splinted and non-splinted impression techniques for edentulous patients: An optical scanning study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, Y.R.; Bohner, L.; Tortamano, P.; Pigozzo, M.N.; Laganá, D.C.; Sesma, N. Patient outcomes and procedure working time for digital versus conventional impressions: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Lenherr, P.; Dedem, P.; Kovaltschuk, I.; Bragger, U.; Zitzmann, N.U. Time efficiency, difficulty, and operator’s preference comparing digital and conventional implant impressions: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.R.; Park, J.M.; Chun, Y.S.; Lee, K.N.; Kim, M. Changes in views on digital intraoral scanners among dental hygienists after training in digital impression taking. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Bragger, U. Time-efficiency analysis comparing digital and conventional workflows for implant crowns: A prospective clinical crossover trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imburgia, M.; Logozzo, S.; Hauschild, U.; Veronesi, G.; Mangano, C.; Mangano, F.G. Accuracy of four intraoral scanners in oral implantology: A comparative in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, F.; Shibli, J.A.; Fortin, T. Digital Dentistry: New Materials and Techniques. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 5261247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, F.; Gandolfi, A.; Luongo, G.; Logozzo, S. Intraoral scanners in dentistry: A review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; So, J.S.; Hochstedler, J.L.; Ercoli, C. The accuracy of implant impressions: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmelmayr, M.; Güth, J.F.; Erdelt, K.; Happe, A.; Schlee, M.; Beuer, F. Clinical study evaluating the discrepancy of two different impression techniques of four implants in an edentulous jaw. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, H.; Luthardt, R.G.; Walter, M.H. Computer-aided analysis of the influence of digitizing and surfacing on the accuracy in dental CAD/CAM technology. Comput. Biol. Med. 2007, 37, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeweghe, S.; Vervack, V.; Dierens, M.; De Bruyn, H. Accuracy of digital impressions of multiple dental implants: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosky, M.E.; Major, R.J.; DeLong, R.; Hodges, J.S. Evaluation of dental arch reproduction using three-dimensional optical digitization. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.; Mehl, A.; Mörmann, W.H.; Reich, S. Intraoral scanning systems—A current overview. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2015, 18, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Franca, D.G.; Morais, M.H.; das Neves, F.D.; Barbosa, G.A. Influence of CAD/CAM on the fit accuracy of implant-supported zirconia and cobalt-chromium fixed dental prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoulis, J.; Muller, P.; Mericske-Stern, R.; Blatz, M.B. CAD/CAM fabrication accuracy of long- vs. short-span implant-supported FDPs. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Kurtzman, G.M.; Silverstein, L.H. Improving implant framework passive fit and accuracy through the use of verification stents and casts. J. Dent. Technol. 2001, 18, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heckmann, S.M.; Karl, M.; Wichmann, M.G.; Winter, W.; Graef, F.; Taylor, T.D. Cement fixation and screw retention: Parameters of passive fit. An in vitro study of three-unit implant-supported fixed partial dentures. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syrek, A.; Reich, G.; Ranftl, D.; Klein, C.; Cerny, B.; Brodesser, J. Clinical evaluation of all-ceramic crowns fabricated from intraoral digital impressions based on the principle of active wavefront sampling. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.; Ruse, D.; Wyatt, C. A comparison of the marginal fit of crowns fabricated with digital and conventional methods. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida e Silva, J.S.; Erdelt, K.; Edelhoff, D.; Araujo, E.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Vieira, L.C.; Guth, J.F. Marginal and internal fit of four-unit zirconia fixed dental prostheses based on digital and conventional impression techniques. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, S.B.; Emmanouilidi, A.; Stampf, S.; Strub, J.R.; Att, W. Accuracy of full-arch scans using intraoral scanners. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. In-vitro evaluation of the accuracy of conventional and digital methods of obtaining full-arch dental impressions. Quintessence Int. 2015, 46, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, T.S.; Sun, J. Comparison of repeatability between intraoral digital scanner and extraoral digital scanner: An in-vitro study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2015, 59, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimenez, B.; Ozcan, M.; Martinez-Rus, F.; Pradies, G. Accuracy of a digital impression system based on active wavefront sampling technology for implants considering operator experience, implant angulation, and depth. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 1), e54–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimenez, B.; Ozcan, M.; Martinez-Rus, F.; Pradies, G. Accuracy of a digital impression system based on active triangulation technology with blue light for implants: Effect of clinically relevant parameters. Implant Dent. 2015, 24, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Gallucci, G.O. Digital vs. conventional implant impressions: Efficiency outcomes. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.S.; Harris, B.T.; Morton, D. The use of a scannable impression coping and digital impression technique to fabricate a customized anatomic abutment and zirconia restoration in the esthetic zone. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 109, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Azim, T.; Zandinejad, A.; Elathamna, E.; Lin, W.; Morton, D. The influence of digital fabrication options on the accuracy of dental implant-based single units and complete-arch frameworks. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Wittneben, J.G.; Bragger, U. Digital implant impressions with the “Individualized Scanbody Technique” for emergence profile support. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluegge, T.; Att, W.; Metzger, M.; Nelson, K. A novel method to evaluate precision of optical implant impressions with commercial scan bodies—An experimental approach. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimmelmayr, M.; Guth, J.F.; Erdelt, K.; Edelhoff, D.; Beuer, F. Digital evaluation of the reproducibility of implant scanbody fit—An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flugge, T.V.; Schlager, S.; Nelson, K.; Nahles, S.; Metzger, M.C. Precision of intraoral digital dental impressions with iTero and extraoral digitization with the iTero and a model scanner. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaruba, M.; Mehl, A. Chairside systems: A current review. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2017, 20, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prudente, M.S.; Davi, L.R.; Nabbout, K.O.; Prado, C.J.; Pereira, L.M.; Zancopé, K.; Neves, F.D. Influence of scanner, powder application, and adjustments on CAD-CAM crown misfit. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Impression System | Model 1 | Model 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Closed tray impressions with replacement abutments | A | E |
| Open tray impression groups for dragging copings, without splinting | B | F |
| Open tray impressions for ferrules | C | - |
| Using the 3M™ True Definition Scanner | D | G |
| Axis | Group | Median (P25–P75) | p | Min–Max | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | A | 20 (1–138) | b | <0.001 | 0–6579 | 758,315 |
| B | 36 (2–235) | a | 0–5165 | 914,706 | ||
| C | 33 (1–204) | a | 0–3737 | 693,878 | ||
| D | 15 (1–121) | c | 0–1791 | 507,725 | ||
| Y | A | 22 (2–113) | c | <0.001 | 0–4456 | 520,289 |
| B | 36 (2–197) | a | 0–5387 | 714,484 | ||
| C | 26 (2–104) | b | 0–1280 | 332,341 | ||
| D | 17 (1–97) | d | 0–1177 | 341,292 | ||
| Z | A | 26 (1–180) | a | <0.001 | 0–5797 | 835,738 |
| B | 21 (1–113) | b | 0–8615 | 536,301 | ||
| C | 11 (1–60) | d | 0–1982 | 239,699 | ||
| D | 15 (1–75) | c | 0–808 | 219,275 | ||
| Total | A | 194 (51–623) | b | <0.001 | 0–9909 | 2,114,342 |
| B | 242 (60–705) | a | 0–10,943 | 2,165,491 | ||
| C | 163 (43–446) | c | 0–4226 | 1,265,918 | ||
| D | 128 (32–383) | d | 0–2276 | 1,068,292 |
| Axis | Group | Median (P25–P75) | p | Min–Max | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | E | 26 (4–128) | b | <0.001 | 0–4376 | 547,692 |
| F | 17 (2–107) | c | 0–4730 | 601,235 | ||
| G | 32 (5–170) | a | 0–3277 | 781,324 | ||
| Y | E | 21 (1–121) | b | <0.001 | 0–3634 | 444,326 |
| F | 15 (1–86) | c | 0–3794 | 384,520 | ||
| G | 22 (2–90) | a | 0–1441 | 298,488 | ||
| Z | E | 24 (3–136) | b | <0.001 | 0–5755 | 668,958 |
| F | 15 (2–73) | c | 0–1969 | 272,080 | ||
| G | 32 (3–132) | a | 0–1402 | 409,517 | ||
| Total | E | 191 (51–521) | a | <0.001 | 0–7016 | 1,660,975 |
| F | 129 (32–325) | c | 0–5920 | 1,257,835 | ||
| G | 177 (53–440) | b | 0–3654 | 1,489,328 |
| Axis | Median (P25–P75) | p | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | model 1-A | 20 (1–138) | b | <0.001 | 758,315 |
| model 2-E | 26 (4–128) | a | 547,692 | ||
| Y | model 1-A | 22 (2–113) | a | <0.001 | 520,289 |
| model 2-E | 21 (1–121) | b | 444,326 | ||
| Z | model 1-A | 26 (1–180) | a | <0.001 | 835,738 |
| model 2-E | 24 (3–136) | b | 668,958 | ||
| Total | model 1-A | 194 (51–623) | a | <0.001 | 2,114,342 |
| model 2-E | 191 (51–521) | b | 1,660,975 |
| Axis | Median (P25–P75) | p | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | model 1-B | 36 (2–235) | a | <0.001 | 914,706 |
| model 2-F | 17 (2–107) | b | 601,235 | ||
| Y | model 1-B | 36 (2–197) | a | <0.001 | 714,484 |
| model 2-F | 15 (1–86) | b | 384,520 | ||
| Z | model 1-B | 21 (1–113) | a | <0.001 | 536,301 |
| model 2-F | 15 (2–73) | b | 272,080 | ||
| Total | model 1-B | 242 (60–705) | a | <0.001 | 2,165,491 |
| model 2-F | 129 (32–325) | b | 1,257,835 |
| Axis | Median (P25–P75) | p | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | model 1-D | 15 (1–121) | b | <0.001 | 507,725 |
| model 2-G | 32 (5–170) | a | 781,324 | ||
| Y | model 1-D | 17 (1–97) | b | <0.001 | 341,292 |
| model 2-G | 22 (2–90) | a | 298,488 | ||
| Z | model 1-D | 15 (1–75) | b | <0.001 | 219,275 |
| model 2-G | 32 (3–132) | a | 409,517 | ||
| Total | model 1-D | 128 (32–383) | b | <0.001 | 1,068,292 |
| model 2-G | 177 (53–440) | a | 1,489,328 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, P.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Díaz-Castro, C.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Padrós, R.; Mur, J.G.; Falcão, C. Accuracy of Implant Casts Generated with Conventional and Digital Impressions—An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081599
Ribeiro P, Herrero-Climent M, Díaz-Castro C, Ríos-Santos JV, Padrós R, Mur JG, Falcão C. Accuracy of Implant Casts Generated with Conventional and Digital Impressions—An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(8):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081599
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Paulo, Mariano Herrero-Climent, Carmen Díaz-Castro, José Vicente Ríos-Santos, Roberto Padrós, Javier Gil Mur, and Carlos Falcão. 2018. "Accuracy of Implant Casts Generated with Conventional and Digital Impressions—An In Vitro Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 8: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081599
APA StyleRibeiro, P., Herrero-Climent, M., Díaz-Castro, C., Ríos-Santos, J. V., Padrós, R., Mur, J. G., & Falcão, C. (2018). Accuracy of Implant Casts Generated with Conventional and Digital Impressions—An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(8), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081599








