Water Quality in Surface Water: A Preliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of the Mashavera River, Georgia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation and Instrumental Analysis
2.4. Analytical Methods
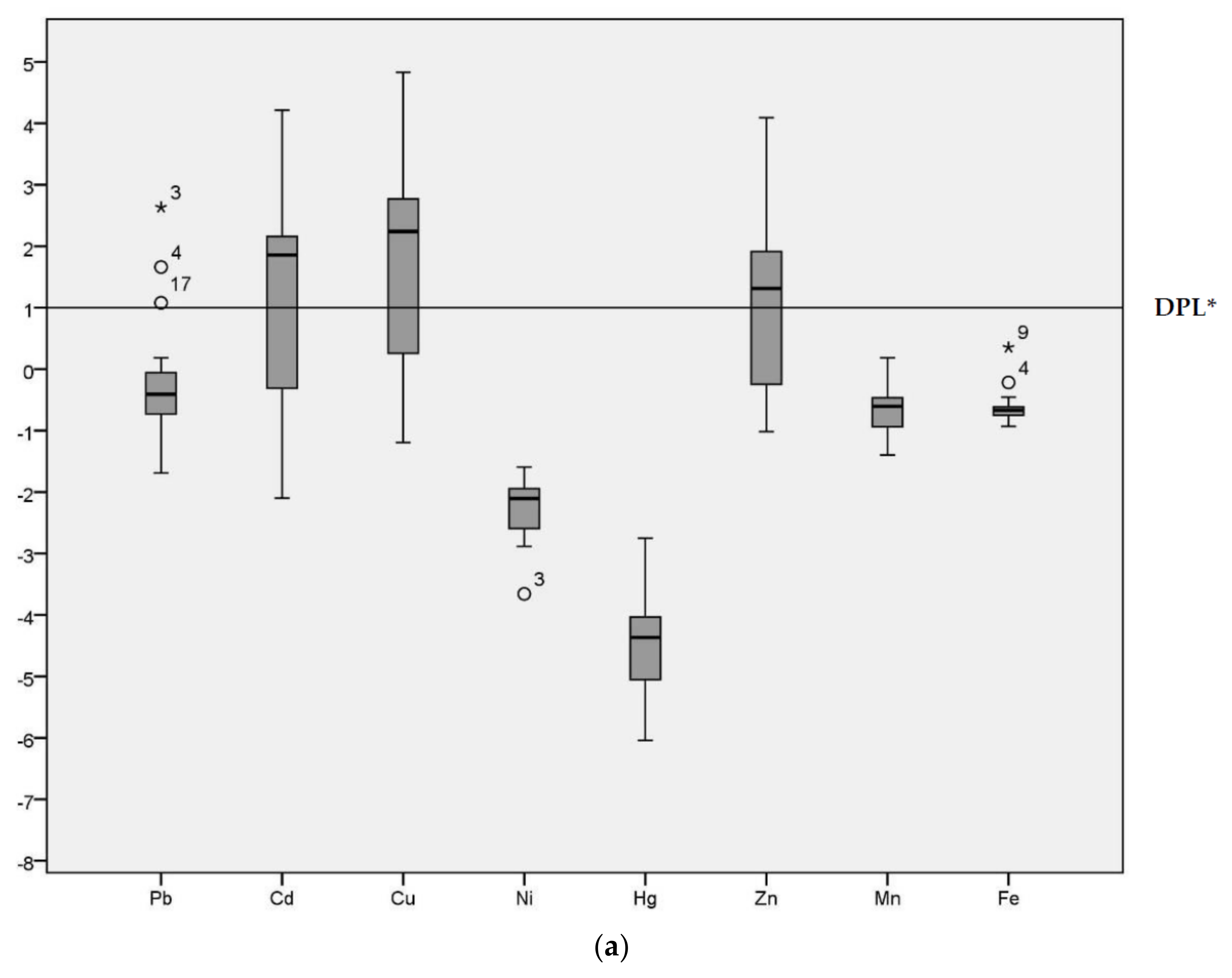
2.4.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
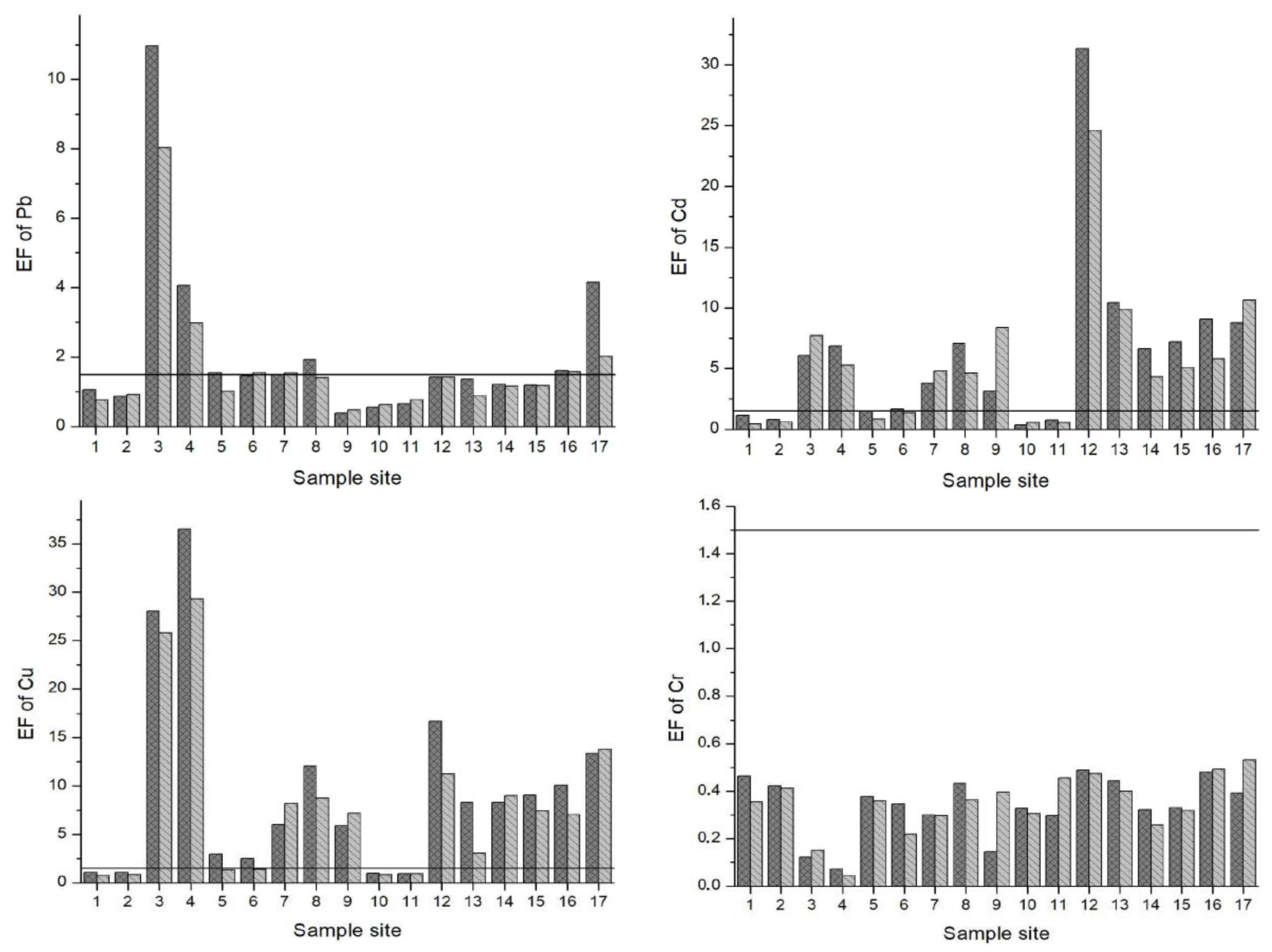
2.4.2. Enrichment Factor (EF)
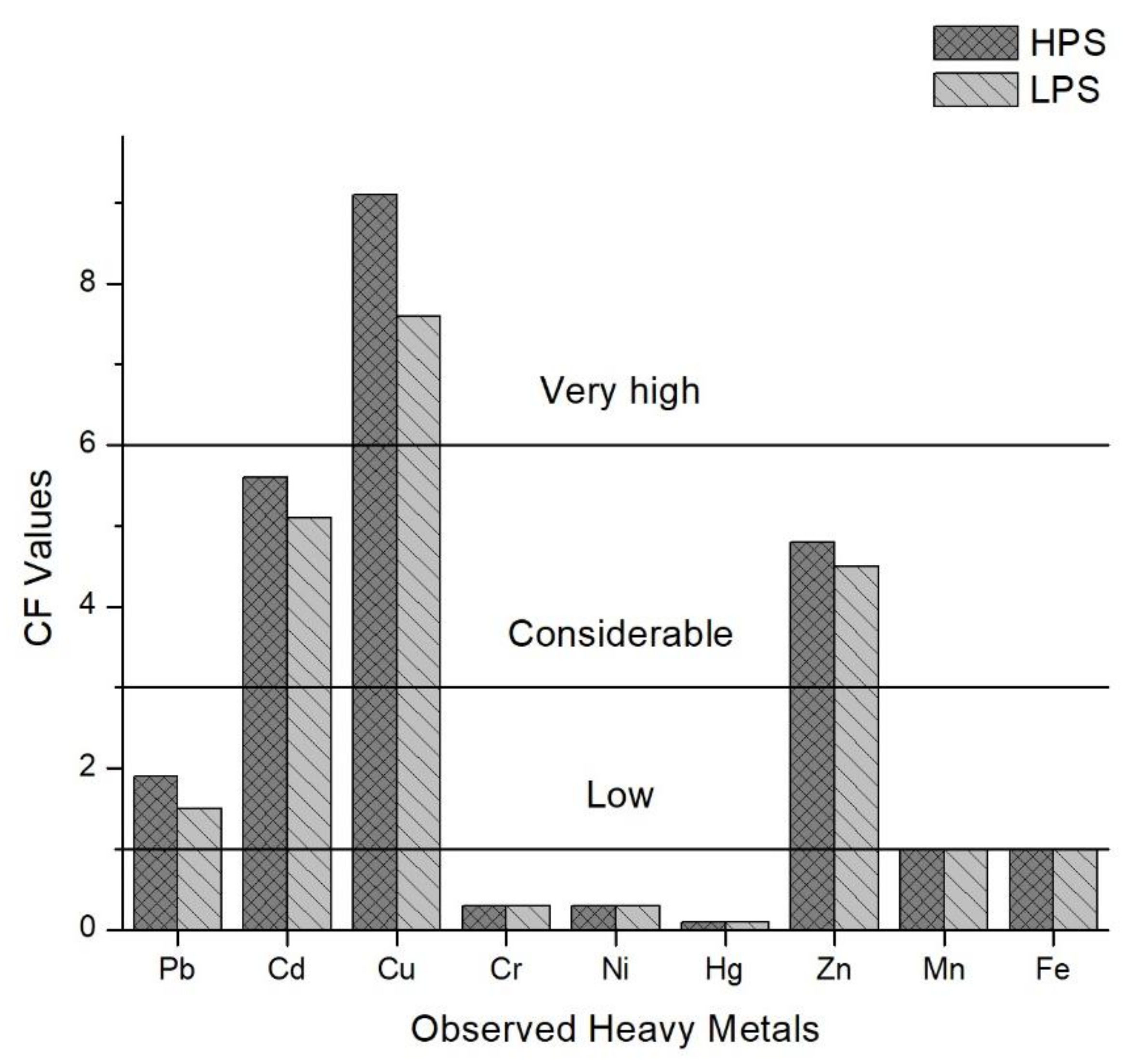
2.4.3. Contamination Factor (CF) and Pollution Load Index (PLI)
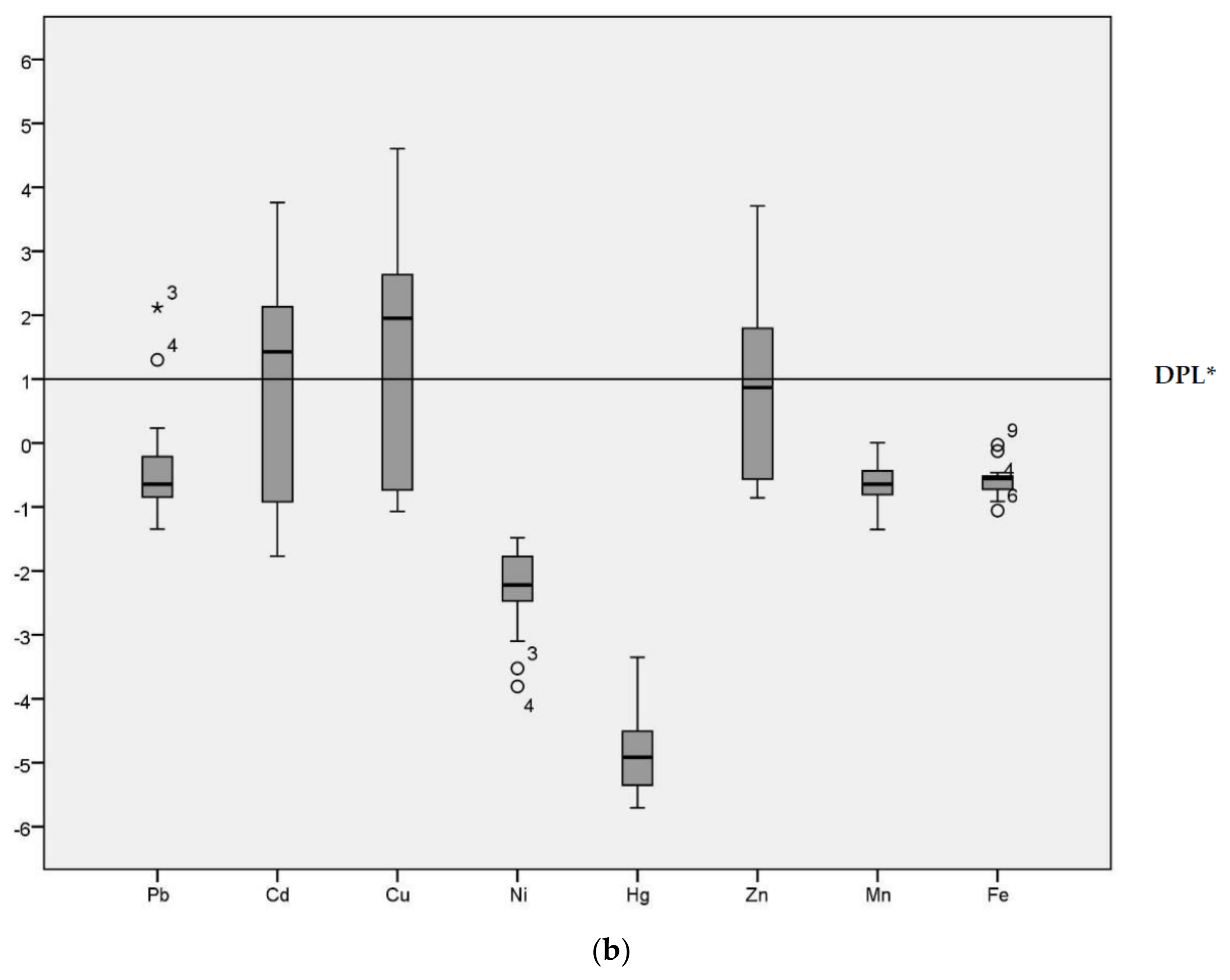
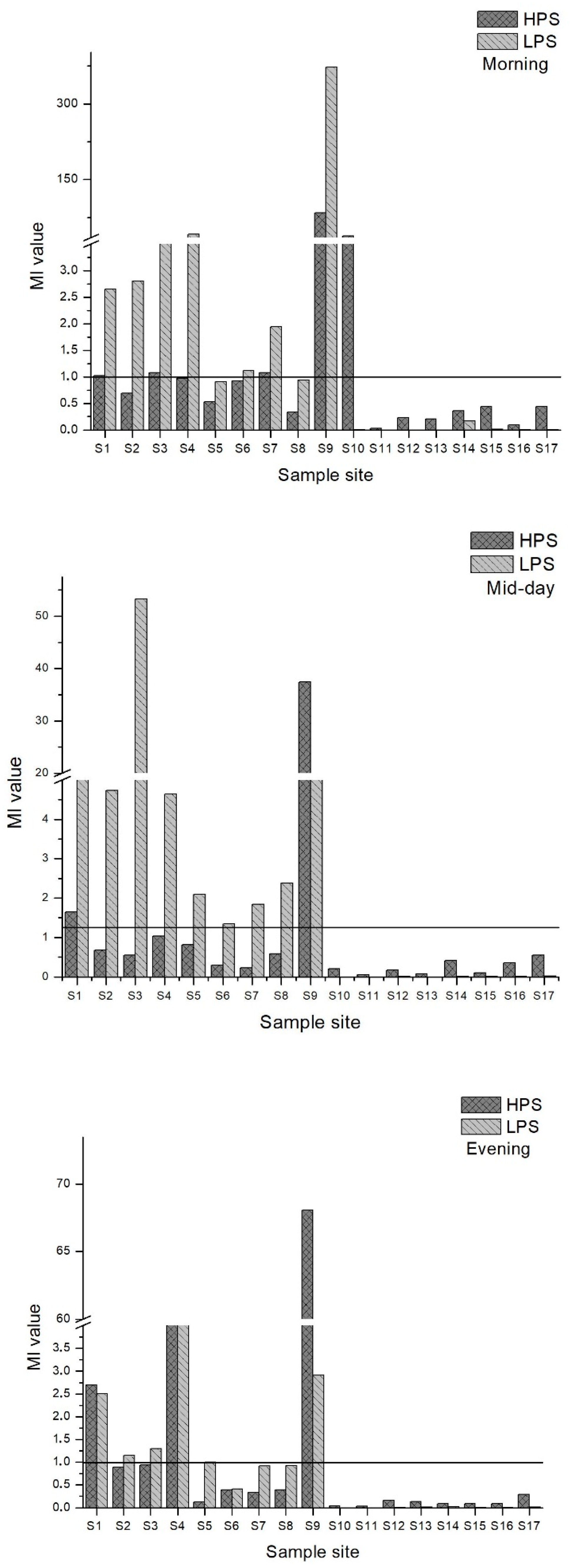
2.4.4. Metal Index
2.5. Statistical and Graphical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Properties
3.2. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Sediments
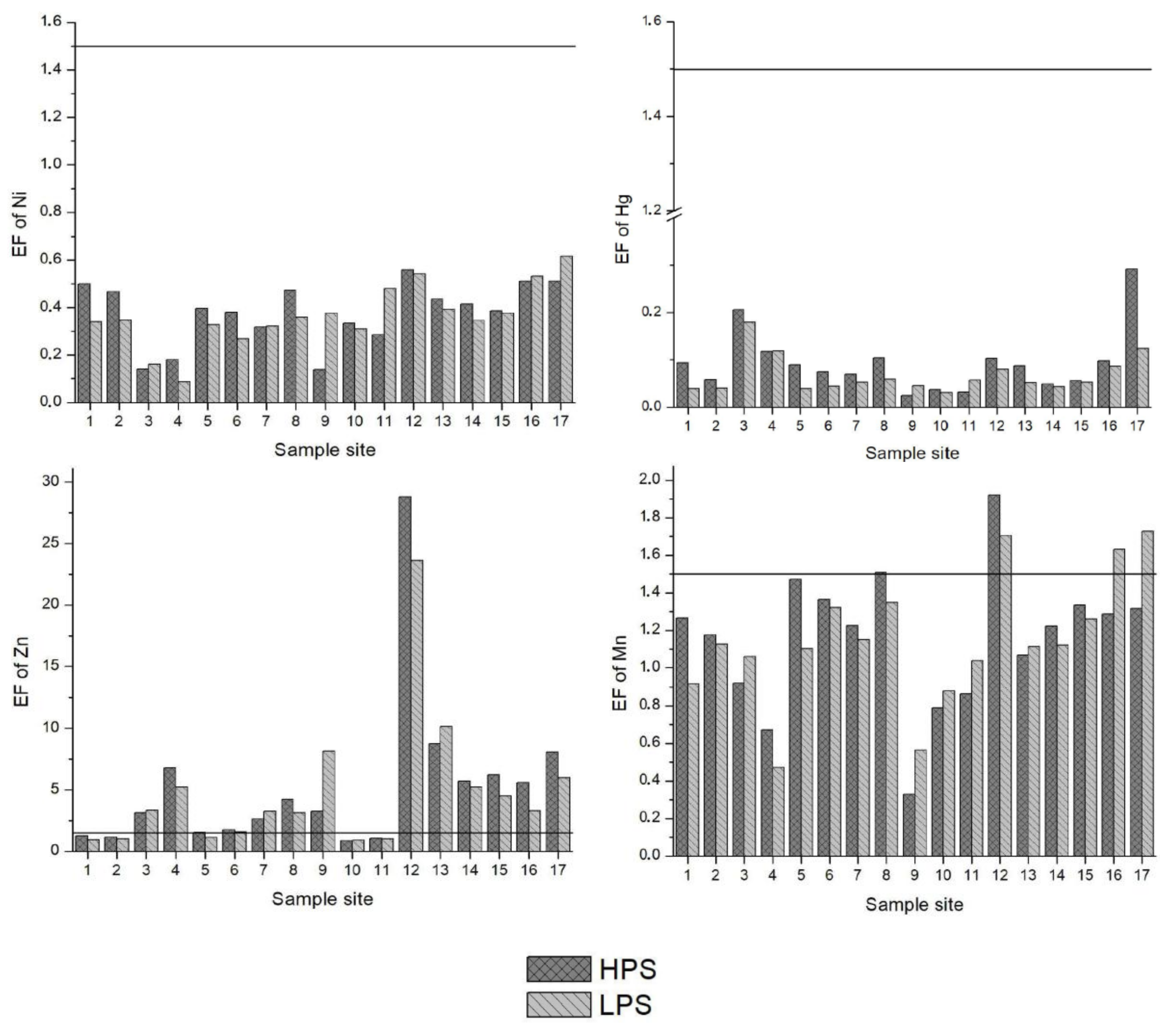
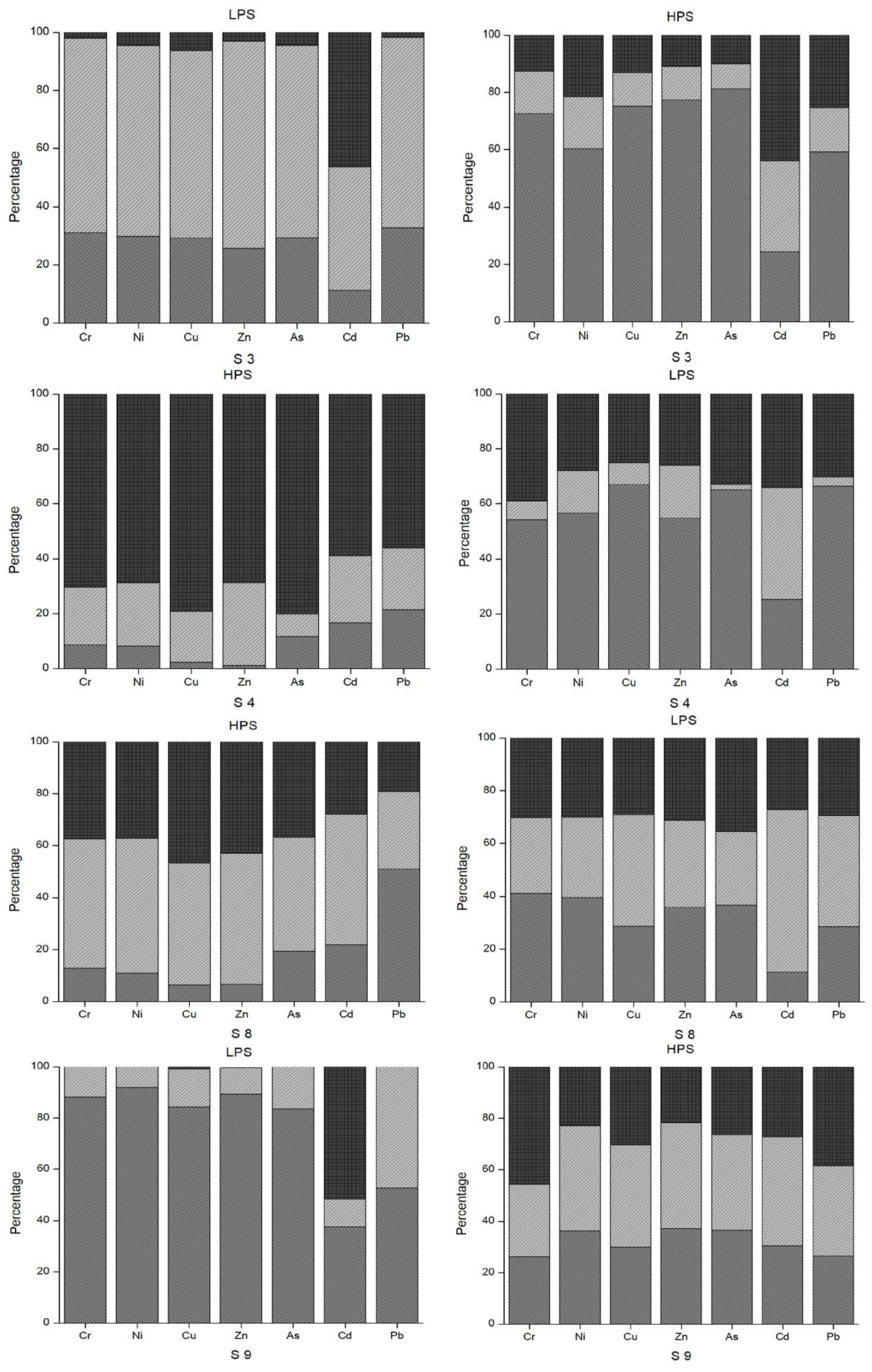
3.3. Index Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments
3.4. Correlation among Individual Heavy Metals and PLI in the Sediment Samples
3.5. Heavy Metal Concentrations in the Water
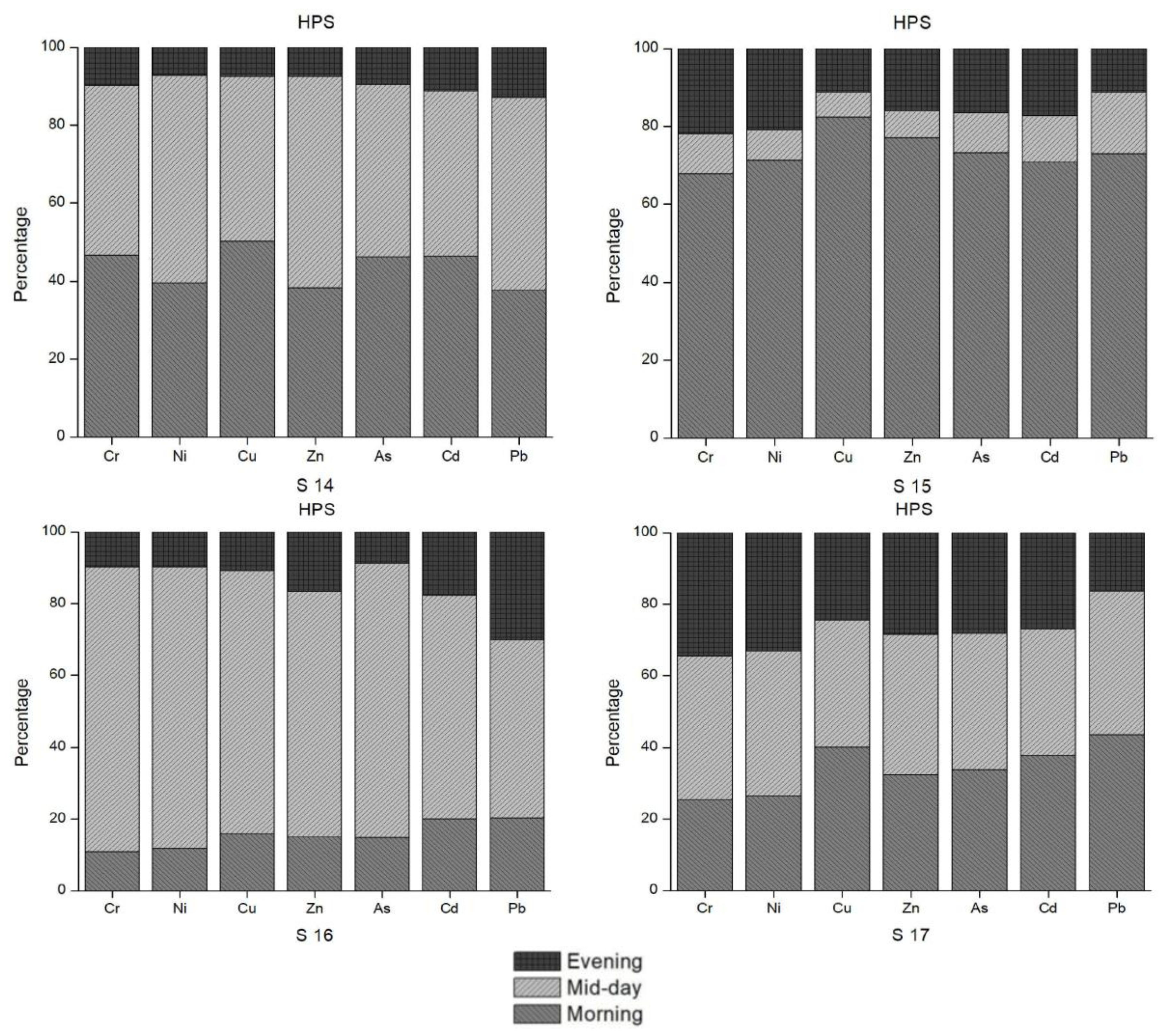
3.6. Index Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution in Water
3.7. Previous Studies and the Overall Current Status
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nation. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2017; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hassing, J.; Ipsen, N.; Clausen, T.J.; Larsen, H.; Lindgaard-Jørgensen, P. Integrated Water Resources Management in Action; DHI Water Policy and the UNEP-DHI Centre for Water and Environment: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch, O.; Adelle, C.; Benson, D. The EU Water Initiative at 15: Origins, processes and assessment. Water Int. 2017, 42, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Nithila, P.; Reddy, S.J. Estimation of heavy metals in drinking water and development of heavy metal pollution index. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 1996, 31, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbehzadeh, S.; Vahid Dastjerdi, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Kiyanizadeh, T. Heavy metals in water and sediment: A case study of Tembi River. J. Environ. Public Health 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihampa, C. Heavy metal contamination in water and sediment downstream of municipal wastewater treatment plants, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 1407. [Google Scholar]
- Lomsadze, Z.; Makharadze, K.; Pirtskhalava, R. The ecological problems of rivers of Georgia (the Caspian Sea basin). Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2016, 14, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yan, X.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, M.; Shrestha, S.; Devkota, L.P.; Yao, T. Influence of traffic activity on heavy metal concentrations of roadside farmland soil in mountainous areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 1715–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix-Henningsen, P.; Urushadze, T.F.; Narimannidze, E.I.; Wichmann, L.; Steffens, D.; Kalandadze, B. Heavy metal pollution of soils and food crops due to mining wastes in an irrigation district south of Tbilisi, eastern Georgia. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2007, 5, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Matchavariani, L.; Kalandadze, B. Pollution of Soils by Heavy Metals from Irrigation near Mining Region of Georgia. Forum Geogr. 2012, 11, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avkopashvili, G.; Avkopashvili, M.; Gongadze, A.; Tsulukidze, M.; Shengelia, E. Determination of Cu, Zn and Cd in soil, water and food products in the vicinity of RMG gold and copper mine, Kazreti, Georgia. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenda—Mining Resumes at Controversial Sakdrisi Gold Mine. 2014. Available online: http://agenda.ge/news/26482/eng (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Georgian Mining Corporation (GEO). Drilling Update from KB Gold Zone 2 and New Gold Discovery. Available online: http://intel.rscmme.com/report/Georgian_Mining_Corp_Zone_2_24-10-2017 (accessed on 5 January 2018).
- Enhancing Capacity for Low Emission Development Strategies (EC-LEDS)/Clean Energy Program and the Bolnisi Municipality. Available online: http://remissia.ge/SEAP-Bolnisi-ENG.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2018).
- Ministry of Agriculture of Georgia (MOA). Georgian Agro-Food Sector—For Your Investment. 2016. Available online: https://www.rvo.nl/sites/default/files/2016/01/Agro%20Guide%20Georgie.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Melikadze, G.; Chelidze, T.; Leveinen, J. Modeling of heavy metal contamination within an irrigated area. In Groundwater and Ecosystems; Baba, A., Howard, K.W., Gunduz, O., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 70, pp. 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Tsivtsivadze, N.; Matchavariani, L.; Lagidze, L.; Paichadze, N.; Motsonelidze, N. Problem of Surface Water Ecology in Georgia. In Environment and Ecology in the Mediterranean Region II; Efe, R., Ozturk, M., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Schadstoffe in Sedimenten—Sedimente als Schadstoffe. Available online: http://www2.uibk.ac.at/downloads/oegg/Band_79_107_126.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2017).
- Withanachchi, S.S.; Ghambashidze, G.; Kunchulia, I.; Urushadze, T.; Ploeger, A. A Paradigm Shift in Water Quality Governance in a Transitional Context: A Critical Study about the Empowerment of Local Governance in Georgia. Water 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgia Environmental and Climate Change Policy Brief. Department of Economics, Sweden; University of Gothenburg, 2009. Available online: http://sidaenvironmenthelpdesk.se/wordpress3/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Georgia-EnvCC-Policy-Brief-Draft-090130.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2017).
- Meladze, G.; Meladze, M. Agroclimatic Resources of Eastern Georgia; Publishing House Universal: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2010; pp. 152–160. (In Georgian) [Google Scholar]
- Tsikaridze, N.; Avkopashvili, G.; Kazaishvili, K.H.; Avkopashvili, M.; Gognadze, A.; Samkharadze, Z. Kvemo Kartli Manufacturing Mining Pollution Analysis in Green Politics Context; Green Policy Public Platform: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2017. (In Georgian) [Google Scholar]
- GDAM (Global Administrative Areas) Data Set. Available online: http://gadm.org/download (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Planet OSM. 2017. Available online: https://planet.osm.org (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Simpson, S.L.; Batley, G.E.; Chariton, A.A.; Stauber, J.L.; King, C.K.; Chapman, J.C.; Hyne, R.V.; Gale, S.A.; Roach, A.C.; Maher, W.A. Handbook for Sediment Quality Assessment. 2005. Available online: http://www.clw.csiro.au/publications/cecr/handbook_sediment_quality_assessment.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2018).
- Singare, P.U.; Mishra, R.M.; Trivedi, M.P. Sediment contamination due to toxic heavy metals in Mithi River of Mumbai. Adv. Anal. Chem. 2012, 2, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourg, A.C.; Bertin, C. Diurnal variations in the water chemistry of a river contaminated by heavy metals: Natural biological cycling and anthropic influence. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 86, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimick, D.A.; Gammons, C.H.; Cleasby, T.E.; Madison, J.P.; Skaar, D.; Brick, C.M. Diel cycles in dissolved metal concentrations in streams: Occurrence and possible causes. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudall, S.; Jarvis, A.P. Diurnal fluctuation of zinc concentration in metal polluted rivers and its potential impact on water quality and flux estimates. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimick, D.A. Diurnal Variation in Trace-Metal Concentrations in Streams (No. 086-03). 2003. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs08603/pdf/fs08603.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2018).
- Nowrouzi, M.; Pourkhabbaz, A. Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factor for assessing metal contamination in the sediments of Hara Biosphere Reserve, Iran. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2014, 26, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štrbac, S.; Grubin, M.K.; Vasić, N. Importance of background values in assessing the impact of heavy metals in river ecosystems: Case study of Tisza River, Serbia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the Elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geol Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqin, J.I.; Yinchang, F.E.N.G.; Jianhui, W.U.; Tan, Z.H.U.; Zhipeng, B.A.I.; Chiqing, D.U.A.N. Using geoaccumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S.; Singh, V.K.; Murthy, R.C. Estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in sediments of Gomti River (India) using principal component analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 166, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments from the Yanghe River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 12441–12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, J.; Singh, R. Heavy metals in sediments of Ganga River: Up-and downstream urban influences. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, M.E.; Farhat, H.I.; Abdo, M.H.; Salem, S.G. Metal pollution assessment in the surface sediment of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Zhao, J.Z.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Söderlund, L.; Liu, G.H. Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.A.; Barreto, M.S.; Passos, E.A.; Alves, J.D.P.H. Regional geochemical baselines and controlling factors for trace metals in sediments from the Poxim River, Northeast Brazil. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, P.; Zimmermann, S.; Luster, J.; Shoty, K.W. Critical Examination of Trace Element Enrichment and Depletions in Soils; As, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in Swiss Forest Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvalchrelidze, A.G. Mineral resource base of Georgia in the XXI century. In Mineral Resource Base of the Southern Caucasus and Systems for its Management in the XXI Century; Tvalchrelidze, A.G., Morizot, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 19–70. [Google Scholar]
- Buat-Menard, P.; Chesselet, R. Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Martens, W.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 1980, 33, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, K.M.; Zakir, H.M.; Otomo, K.; Sharmin, S.; Shikazono, N. Geochemical distribution of trace metal pollutants in water and sediments of downstream of an urban river. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojekunle, O.Z.; Ojekunle, O.V.; Adeyemi, A.A.; Taiwo, A.G.; Sangowusi, O.R.; Taiwo, A.M.; Adekitan, A.A. Evaluation of surface water quality indices and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in scrap yard neighbourhood. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goher, M.E.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-Moniem, I.A.; Fahmy, A.H.; El-sayed, S.M. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal indices of Ismailia Canal, Nile River, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakan, G.; Özkoç, H.B.; Tülek, S.; Cüce, H. Integrated environmental quality assessment of the Kızılırmak River and its coastal environment. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 10, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnam, Z.; Sarikhani, R.; Ahmadnejad, Z. Evaluation of Water Quality Using Heavy Metal Index and Multivariate Statistical Analysis in Lorestan Province, Iran. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tamasi, G.; Cini, R. Heavy metals in drinking waters from Mount Amiata (Tuscany, Italy). Possible risks from arsenic for public health in the Province of Siena. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 327, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondriest Fundamentals of Environmental Measurements. Conductivity, Salinity & Total Dissolved Solids. 2016. Available online: http://www.fondriest.com/environmental-measurements/parameters/water-quality/conductivity-salinity-tds/ (accessed on 19 January 2017).
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Aquatic Toxicity Reference Values (TRVs) in Surface Water. Available online: https://clu-in.org/download/contaminantfocus/dnapl/Toxicology/DOE_SW_tox_valuep 76.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2017).
- Georgian Mining Corporation. Building the Next Georgian Copper-Gold Producer. Available online: http://www.georgianmining.com/cms/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/GEO-Presentation-July-2017-UK.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- Çevik, F.; Göksu, M.Z.L.; Derici, O.B.; Fındık, Ö. An assessment of metal pollution in surface sediments of Seyhan dam by using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index and statistical analyses. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 152, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, A.; Tarnawski, M.; Koniarz, T. Spatial distribution of trace elements and ecotoxicity of bottom sediments in Rybnik reservoir, Silesian-Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17255–17268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, G.; Sutharsan, P.; Ramasamy, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klake, R.K.; Nartey, V.K.; Doamekpor, L.K.; Edor, K.A. Correlation between heavy metals in fish and sediment in Sakumo and Kpeshie Lagoons, Ghana. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 3, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muohi, A.W.; Onyari, J.M.; Omondi, J.G.; Mavuti, K.M. Heavy metal distribution in surface sediments from Mtwapa and Shirazi creeks, Kenyan coast. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 70, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Labour, Health, and Social Affairs of Georgia. Order of Minister of Labour, Health, and Social Affairs of Georgia—On Approval of the Norms of the Quality of Environment 297/N; Update 2012; Ministry of Labour, Health, and Social Affairs of Georgia: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- European Council. European Council Directive 98/83/EC—The Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; European Council: Brussels, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality (Electronic Resource): Incorporating 1st and 2nd Addenda, Volume 1, Recommendations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.L.H.; So, M.K.; Connell, D.W.; Fung, C.N.; Lam, M.H.W.; Nicholson, S.; Richardson, B.J.; Lam, P.K. A preliminary risk assessment of trace elements accumulated in fish to the Indo-Pacific Humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis) in the Northwestern waters of Hong Kong. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, P.C.T.; Sundarabarathy, T.V.; Sivananthawerl, T.; Kodithuwakku, S.P.; Edirisinghe, U. Arsenic and Cadmium Contamination in Water, Sediments and Fish is a Consequence of Paddy Cultivation: Evidence of River Pollution in Sri Lanka. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Sengupta, M. Lead toxicity on non-specific immune mechanisms of freshwater fish Channa punctatus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanauer, T.; Felix-Henningsen, P.; Steffens, D.; Kalandadze, B.; Navrozashvili, L.; Urushadze, T. In situ stabilization of metals (Cu, Cd, and Zn) in contaminated soils in the region of Bolnisi, Georgia. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanauer, T.; Jung, S.; Felix-Henningsen, P.; Schnell, S.; Steffens, D. Suitability of inorganic and organic amendments for in situ immobilization of Cd, Cu, and Zn in a strongly contaminated Kastanozem of the Mashavera valley, SE Georgia. I. Effect of amendments on metal mobility and microbial activity in soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikadze, G. Monitoring and spatial-time modelling of groundwater on territories of Georgia for solving ecological and seismic problems (in Georgian). Ph.D. Dissertation, Tbilisi State University, Tbilisi, Georgia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- National Environmental Agency. Personal communication, National Environmental Agency: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2016.
- Luinnik, P.M.; Zubenko, I.B. Role of Bottom Sediments in the Secondary Pollution of Aquatic Environment by Heavy Metal Compounds. Lakes Reser. Res. Manag. 2000, 5, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temitope, A.E.; Ebeniro, L.A.; Oyediran, A.G.; C-Oluwatosin, T.J. An Assessment of Some Heavy Metals in Sediment of Otamiri River, Imo State, South-Eastern Nigeria. OALib J. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjavidze, T. National Nutrition Study in Georgia. 2016. Available online: http://foodsecuritysc.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Nutrition-Research-short-version-English-Final.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2017).
- Hanauer, T.; Navrozashvili, L.; Schnell, S.; Kalandadze, B.; Urushadze, T.; Felix-Henningsen, P. Soil Pollution with Cu, Zn and Cd by Non-Ferrous Metal Mining Affects Soil-Microbial Activity of Kastanozems in the Mashavera Valley. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2011, 9, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- National Environmental Agency of Georgia (NEA). Water Quality Assessment Reports 2013, 2014, 2015. Available online: http://www.moe.gov.ge/ka/%E1%83%97%E1%83%94%E1%83%9B%E1%83%94%E1%83%91%E1%83%98/wyali/wylis-monitoringi (accessed on 28 January 2017).
- Mie, A.; Andersen, H.R.; Gunnarsson, S.; Kahl, J.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Quaglio, G.; Grandjean, P. Human health implications of organic food and organic agriculture: A comprehensive review. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubiński, J. Sustainable development of mining mineral resources. J. Sustain. Min. 2013, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
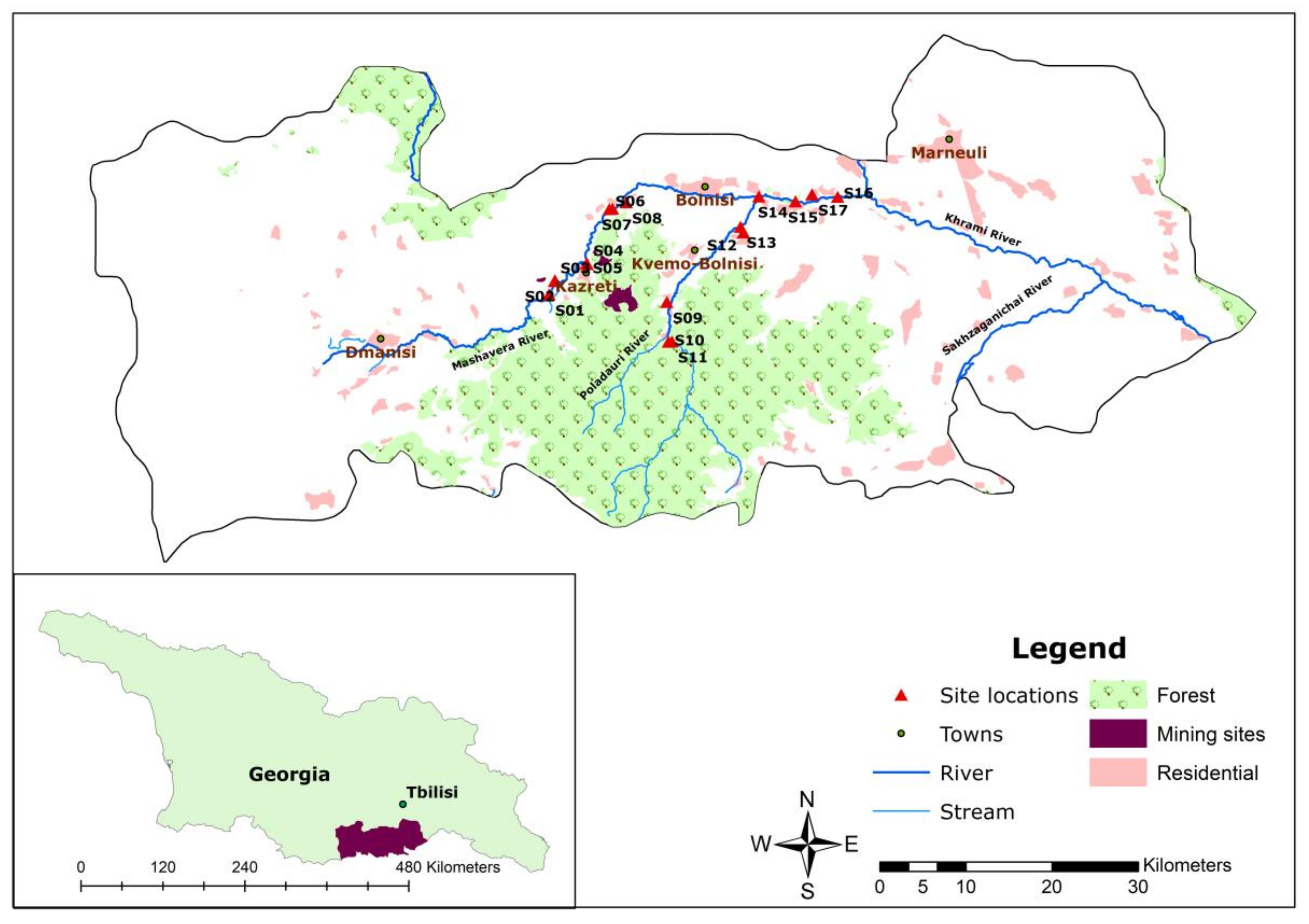
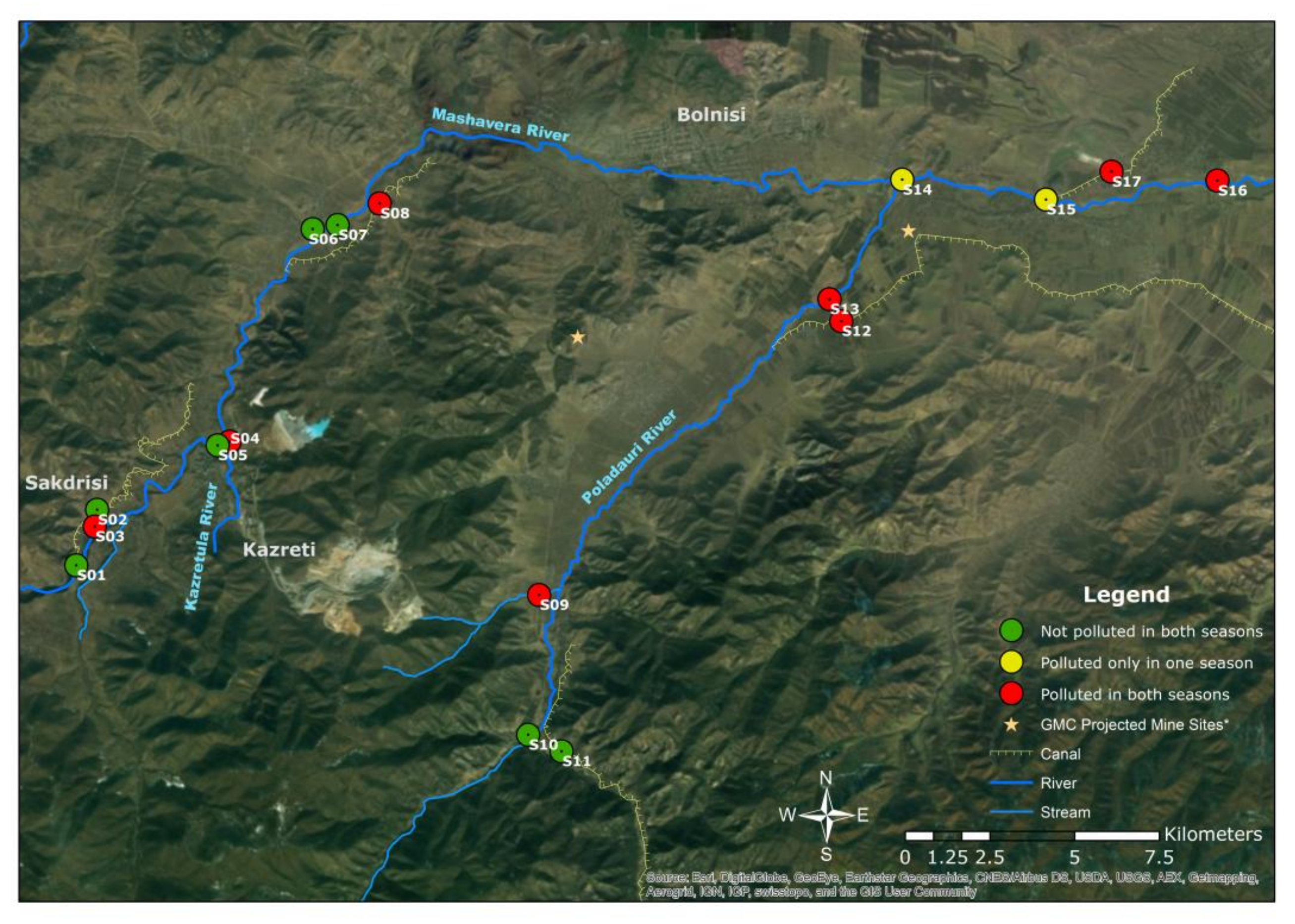
| Sample Sites | Explanation |
|---|---|
| S1 | Mashavera River, upstream at starting point of one irrigation canal |
| S2 | Upstream irrigation canal |
| S3 | Tributary coming from the Sakdrisi mine sites |
| S4 | Kazretula River |
| S5 | Mashavera River, before confluence of Kazretula River |
| S6 | Javshaniani-Kveshi village tributary |
| S7 | Mashavera River at Javshaniani-Kveshi |
| S8 | Irrigation canal at Nakaduli village |
| S9 | Tributary from Madneuli highland |
| S10 | Poladauri River, upstream |
| S11 | Irrigation canal in Poladauri village |
| S12 | Irrigation canal in Vanati village |
| S13 | Poladauri River, downstream |
| S14 | After confluence of Poladauri River and Mashavera River at Rachisubani village |
| S15 | Starting point of one irrigation canal off the Mashavera River |
| S16 | Mashavera River, downstream at Khidiskuri village |
| S17 | Irrigation canal at Tashtikulari village |
| Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo) 1 | Enrichment Factor (EF) 2 | Contamination Factor (CF) 3 | Pollution Load Index (PLI) 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Igeo Class | Sediment quality | EF Value | Nature of enrichment | CF Value | Pollution level | PLI | Indication |
| >0 | 0 | Not polluted | EF < 2 | Deficiency to mineral enrichment * | CF < 1 | Low | 0 | Perfection |
| >0–1 | 1 | Not polluted to moderately polluted | EF = 2–5 | Moderate enrichment | 1 ≤ CF ≥ 3 | Moderate | <1 | Baseline level |
| >1–2 | 2 | Moderately polluted | EF = 5–20 | Significant enrichment | 3 ≤ CF ≥ 6 | Considerable | >1 | Polluted |
| >2–3 | 3 | Moderately polluted to strongly polluted | EF = 20–40 | Very high enrichment | CF > 6 | Very high | ||
| >3–4 | 4 | Strongly polluted | EF > 40 | Extremely high enrichment | ||||
| >4–5 | 5 | Strongly polluted to extremely polluted | ||||||
| >5 | 6 | Extremely polluted | ||||||
| MI | Class | Nature of Water Quality |
|---|---|---|
| <0.3 | I | Very pure |
| 0.3–1.0 | II | Pure |
| 1.0–2.0 | III | Slightly affected |
| 2.0–4.0 | IV | Moderately affected |
| 4.0–6.0 | V | Strongly affected |
| >6.0 | VI | Seriously affected |
| Site | Water Analysis (In Situ) * | Sediment Analysis (Laboratory) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | |||||
| pH | EC (µS/cm) | pH | EC (µS/cm) | pH | EC (µS/cm) | pH | EC (µS/cm) | |
| S1 | 8.46 | 109 | 8.45 | 194 | 7.62 | 500 | 7.78 | 267 |
| S2 | 7.96 | 115 | 8.43 | 194 | 7.96 | 340 | 7.76 | 268 |
| S3 | 7.76 | 320 | 8.48 | 594 | 8.06 | 280 | 8.32 | 272 |
| S4 | 7.55 | 580 | 7.89 | 885 | 7.57 | 580 | 3.83 | 779 |
| S5 | 8.12 | 127 | 8.33 | 275 | 7.54 | 590 | 7.71 | 269 |
| S6 | 8.43 | 415 | 8.49 | 656 | 7.62 | 720 | 7.89 | 356 |
| S7 | 8.13 | 164 | 8.34 | 6809 | 7.67 | 650 | 7.74 | 326 |
| S8 | 7.81 | 142 | 8.41 | 279 | 7.64 | 470 | 7.59 | 455 |
| S9 | 4.24 | 29,952 | 3.18 | 11,115 | 3.35 | 1440 | 2.98 | 2440 |
| S10 | 8.91 | 1704 | 8.41 | 325 | 7.96 | 260 | 7.88 | 207 |
| S11 | 8.73 | 166 | 8.44 | 297 | 7.95 | 160 | 7.86 | 315 |
| S12 | 8.54 | 218 | 8.30 | 524 | 7.73 | 330 | 7.54 | 577 |
| S13 | 8.70 | 237 | 8.01 | 542 | 7.52 | 560 | 7.74 | 330 |
| S14 | 8.37 | 279 | 7.98 | 964 | 7.84 | 430 | 7.90 | 235 |
| S15 | 8.24 | 301 | 8.28 | 586 | 7.85 | 570 | 7.63 | 610 |
| S16 | 8.45 | 328 | 8.28 | 562 | 7.59 | 1070 | 7.63 | 775 |
| S17 | 8.45 | 265 | 8.35 | 505 | 7.96 | 320 | 7.70 | 841 |
| Sample Site | Pb | Cd | Cu | Cr | Ni | Hg | Zn | Mn | Fe | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | |
| S1 | 18.1 | 14.3 | 0.292 | 0.132 | 41.3 | 32.2 | 35.8 | 30.3 | 29.2 | 21.9 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 102 | 84.4 | 923 | 738 | 40,500 | 44,700 |
| S2 | 14.4 | 18.1 | 0.196 | 0.173 | 38.5 | 36.3 | 31.8 | 36.6 | 26.4 | 23.3 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 91.8 | 92.9 | 832 | 943 | 39,300 | 46,500 |
| S3 | 186 | 130 | 1.55 | 1.88 | 1070 | 940 | 9.38 | 11.1 | 8.08 | 8.86 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 251 | 257 | 663 | 729 | 40,000 | 38,200 |
| S4 | 94.9 | 73.9 | 2.4 | 1.97 | 1920 | 1640 | 7.44 | 4.93 | 14.4 | 7.29 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 752 | 614 | 667 | 499 | 55,100 | 58,700 |
| S5 | 27.4 | 19.2 | 0.398 | 0.238 | 118 | 57 | 29.9 | 30.5 | 23.7 | 21.1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 129 | 99.4 | 1100 | 888 | 41,500 | 44,700 |
| S6 | 21 | 20.2 | 0.363 | 0.264 | 80.8 | 40.6 | 22.6 | 12.8 | 18.7 | 11.9 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 120 | 96.4 | 838 | 733 | 34,100 | 30,800 |
| S7 | 23.2 | 25.9 | 0.89 | 1.21 | 212 | 311 | 21.1 | 22.4 | 16.9 | 18.4 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 196 | 260 | 814 | 820 | 36,900 | 39,600 |
| S8 | 34.1 | 26.2 | 1.87 | 1.3 | 479 | 368 | 34.3 | 30.6 | 28.3 | 22.8 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 354 | 279 | 1130 | 1070 | 41,600 | 44,100 |
| S9 | 13.4 | 12.7 | 1.63 | 3.35 | 460 | 430 | 22.4 | 47.4 | 16.3 | 34.1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 537 | 1030 | 484 | 637 | 81,800 | 62,800 |
| S10 | 11.1 | 11.8 | 0.105 | 0.155 | 43.2 | 34.6 | 29.2 | 25.8 | 22.5 | 19.8 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 80.8 | 78.7 | 664 | 701 | 46,700 | 44,300 |
| S11 | 9.29 | 14.3 | 0.159 | 0.156 | 29.5 | 37.1 | 19 | 37.9 | 13.8 | 30.2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 70.4 | 86.6 | 524 | 816 | 33,600 | 43,600 |
| S12 | 25.2 | 23.5 | 8.35 | 6.11 | 666 | 419 | 39 | 35.4 | 33.8 | 30.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 2430 | 1860 | 1450 | 1200 | 41,900 | 39,100 |
| S13 | 22.6 | 17 | 2.59 | 2.86 | 310 | 134 | 33.1 | 34.7 | 24.6 | 25.8 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 687 | 929 | 752 | 911 | 39,100 | 45,500 |
| S14 | 20.8 | 16.7 | 1.7 | 0.936 | 319 | 292 | 24.8 | 16.7 | 24.1 | 16.9 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 461 | 355 | 888 | 687 | 40,300 | 34,000 |
| S15 | 19.2 | 17.8 | 1.74 | 1.15 | 330 | 253 | 24 | 21.5 | 21.2 | 19.3 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 479 | 321 | 917 | 806 | 38,100 | 35,500 |
| S16 | 28.8 | 25.9 | 2.44 | 1.43 | 406 | 261 | 38.7 | 36.4 | 31.1 | 29.8 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 476 | 258 | 977 | 1140 | 42,200 | 38,800 |
| S17 | 63.4 | 35.3 | 2.01 | 2.78 | 458 | 541 | 27 | 41.8 | 26.5 | 36.5 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 584 | 494 | 853 | 1280 | 36,000 | 41,100 |
| Mean | 37.2 | 29.6 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 410.7 | 342.8 | 26.4 | 28.0 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 458.9 | 423.3 | 851.5 | 858.7 | 42,864.7 | 43,058.8 |
| SD± | 43.8 | 29.6 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 474.4 | 411.3 | 9.1 | 11.7 | 6.9 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 556.1 | 468.7 | 234.9 | 211.3 | 11,181.8 | 7996.7 |
| STRV | 46.7 | 1.2 | 34 | 81 | 20.9 | 0.15 | 150 | N.S | N.S | |||||||||
| Variable | Pb | Cd | Cu | Cr | Ni | Hg | Zn | Mn | Fe | PLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Cd | 0.620 ** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Cu | 0.733 ** | 0.765 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Cr | −0.012 | 0.277 | −0.113 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.108 | 0.380 | −0.012 | 0.951 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| Hg | 0.903 ** | 0.569 * | 0.652 ** | 0.179 | 0.298 | 1.000 | ||||
| Zn | 0.529 * | 0.939 ** | 0.806 ** | 0.096 | 0.211 | 0.495 * | 1.000 | |||
| Mn | 0.324 | 0.375 | 0.113 | 0.735 ** | 0.792 ** | 0.370 | 0.199 | 1.000 | ||
| Fe | 0.118 | 0.248 | 0.453 | 0.248 | 0.189 | 0.145 | 0.306 | 0.091 | 1.000 | |
| PLI | 0.789 ** | 0.926 ** | 0.895 ** | 0.174 | 0.321 | 0.754 ** | 0.885 ** | 0.363 | 0.328 | 1.000 |
| Variable | Pb | Cd | Cu | Cr | Ni | Hg | Zn | Mn | Fe | PLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Cd | 0.461 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Cu | 0.679 ** | 0.826 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Cr | −0.275 | 0.186 | −0.100 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Ni | −0.242 | 0.294 | −0.037 | 0.968 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| Hg | 0.645 ** | 0.732 ** | 0.792 ** | 0.216 | 0.265 | 1.000 | ||||
| Zn | 0.280 | 0.909 ** | 0.750 ** | 0.132 | 0.245 | 0.537 * | 1.000 | |||
| Mn | 0.328 | 0.203 | −0.029 | 0.561 * | 0.613 ** | 0.222 | 0.108 | 1.000 | ||
| Fe | −0.244 | 0.052 | −0.063 | 0.386 | 0.300 | 0.163 | 0.064 | −0.101 | 1.000 | |
| PLI | 0.514 * | 0.939 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.248 | 0.348 | 0.843 ** | 0.838 ** | 0.260 | 0.104 | 1.000 |
| Sample Site | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | HPS | LPS | |
| S1 | 0.7 | 50.5 | 0.9 | 46.4 | 1.0 | 47.3 | 3.1 | 109.6 | 0.4 | 28.2 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 15.8 | 11.1 |
| S2 | 0.7 | 44.8 | 0.9 | 35.5 | 1.0 | 43.3 | 3.4 | 111.9 | 0.3 | 28.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.1 | 9.3 |
| S3 | 0.3 | 28.1 | 0.5 | 34.0 | 40.5 | 2570.8 | 14.5 | 737.5 | 4.7 | 178.8 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 4.9 | 69.6 |
| S4 | 0.5 | 24.2 | 1.5 | 41.7 | 260.4 | 7905.7 | 153.4 | 5380.1 | 4.2 | 307.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 6.0 | 62.8 |
| S5 | 1.0 | 14.1 | 0.8 | 10.5 | 3.7 | 31.4 | 3.1 | 32.7 | 0.6 | 14.8 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 5.7 |
| S6 | 0.8 | 5.9 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 10.0 | 3.5 | 24.2 | 0.8 | 9.9 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 |
| S7 | 2.3 | 8.3 | 2.2 | 4.5 | 22.9 | 22.3 | 21.9 | 33.4 | 1.7 | 12.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 5.4 |
| S8 | 1.7 | 14.0 | 1.4 | 11.8 | 21.5 | 107.6 | 18.2 | 121.8 | 1.3 | 16.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 2.3 | 5.5 |
| S9 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 22.8 | 180.3 | 2603.7 | 13,157.6 | 21,912.2 | 125,057.1 | 0.6 | 5.4 | 62.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.9 |
| S10 | 0.2 | BD | 2.6 | BD | 503.8 | 3.0 | 2342.7 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 10.1 | BD | 0.6 | BD |
| S11 | 0.1 | BD | 0.0 | BD | 0.7 | 3.0 | 1.1 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 0.0 | BD | 0.2 | BD |
| S12 | 0.1 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 8.2 | 0.8 | 19.5 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| S13 | 0.1 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 8.4 | 3.3 | 20.3 | 7.7 | 0.1 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| S14 | 1.0 | BD | 0.7 | BD | 22.9 | 8.9 | 18.6 | 30.0 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| S15 | 0.5 | BD | 0.3 | BD | 21.4 | 4.1 | 8.5 | BD | 0.4 | BD | 0.1 | BD | 1.6 | 0.1 |
| S16 | 1.1 | BD | 0.6 | BD | 15.5 | 3.5 | 9.1 | BD | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | BD | 0.9 | 0.1 |
| S17 | 2.0 | BD | 1.3 | BD | 34.5 | 3.1 | 18.3 | BD | 1.0 | BD | 0.2 | BD | 2.6 | 0.2 |
| Mean | 0.8 | 21.3 | 2.2 | 40.8 | 210.2 | 1407.4 | 1445.4 | 11,967.8 | 1.0 | 54.7 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 2.8 | 11.5 |
| SD± | 0.7 | 17.1 | 5.4 | 54.9 | 630.2 | 3610.6 | 5304.1 | 37,541.0 | 1.4 | 98.0 | 15.1 | 0.3 | 3.7 | 22.5 |
| MAC | 500 | 100 | 1000 | 1000 | 50 | 1 | 30 | |||||||
| EU | 50 | 20 | 2000 | N.S | 10 | 5 | 10 | |||||||
| WHO | 5 | 70 | 2000 | 3000 | 10 | 3 | 10 | |||||||
| SWTRV | 117.32 | 87.71 | 6.54 | 120 | 120 | 0.66 | 1.32 | |||||||
| Reference | Sample Sites | Sample Type and Unit | Pb | Cd | Cu | Cr | Ni | Hg | Zn | Mn | As | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other Studies | This Study | ||||||||||||
| Avkopashvili et al. [12] | N1 | S5 | Sediment (mg/kg) | N.S | 0.004 | 0.01 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 0.04 | N.S | N.S | 0.12 |
| N2 | S4 | N.S | 13.2 | 1.4 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 510.2 | N.S | N.S | 1.1 | ||
| N5 | S14 | N.S | 0.3 | 1.6 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 26.6 | N.S | N.S | 18.2 | ||
| N6 | S16 | N.S | 0.05 | 0.3 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 1.7 | N.S | N.S | 0.6 | ||
| Hanauer et al. [79] | Top soil (0–20 cm) in Mashavera valley, irrigated contaminated | C.T | Topsoil (mg/kg) | N.S | 1.73 | 314.99 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 343.68 | N.S | N.S | N.S |
| Melikadze [74] | N1 | S4 | Water (mg/L) | 0.34 | 21.6 | 2334.7 | N.S | N.S | N.S | N.S | 71.7 | N.S | 1552.0 |
| N3 | S9 | 0.5 | 10 | 1680 | N.S | 0.14 | N.S | 372 | 101 | N.S | 1152.0 | ||
| N6 | S5 | 0.2 | 0.14 | 32 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 9.84 | 1.96 | N.S | 9.6 | ||
| N7 | S7 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 16 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 7.08 | 0.98 | N.S | 6.4 | ||
| N10 | S14 | N.S | N.S | 8.1 | N.S | N.S | N.S | 5.10 | 1.0 | N.S | 2.4 | ||
| NEA 2013 [80] | Lower Mashavera | C.T | Water (mg/L) | N.S | N.S | 1.2 | N.S | N.S | N.S | N.S | 0.12 | N.S | 1.31 |
| NEA 2014 [80] | Lower Mashavera | C.T | Water (mg/L) | 0.0536 | N.S | N.S | N.S | N.S | N.S | N.S | 1.04 | N.S | 1.73 |
| NEA 2015 [80] | Upper Mashavera | C.T | Water (mg/L) | 0.0412 | 0.0083 | N.S | N.S | 0.1057 | N.S | N.S | 0.2817 | N.S | 0.6783 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Withanachchi, S.S.; Ghambashidze, G.; Kunchulia, I.; Urushadze, T.; Ploeger, A. Water Quality in Surface Water: A Preliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of the Mashavera River, Georgia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040621
Withanachchi SS, Ghambashidze G, Kunchulia I, Urushadze T, Ploeger A. Water Quality in Surface Water: A Preliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of the Mashavera River, Georgia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(4):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040621
Chicago/Turabian StyleWithanachchi, Sisira S., Giorgi Ghambashidze, Ilia Kunchulia, Teo Urushadze, and Angelika Ploeger. 2018. "Water Quality in Surface Water: A Preliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of the Mashavera River, Georgia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 4: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040621
APA StyleWithanachchi, S. S., Ghambashidze, G., Kunchulia, I., Urushadze, T., & Ploeger, A. (2018). Water Quality in Surface Water: A Preliminary Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of the Mashavera River, Georgia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(4), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040621






