Mechanisms of Phosphorus Removal by Recycled Crushed Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sorption Studies
2.2. Desorption of P
2.3. Fractionation of Inorganic Phosphorus
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sorption Studies
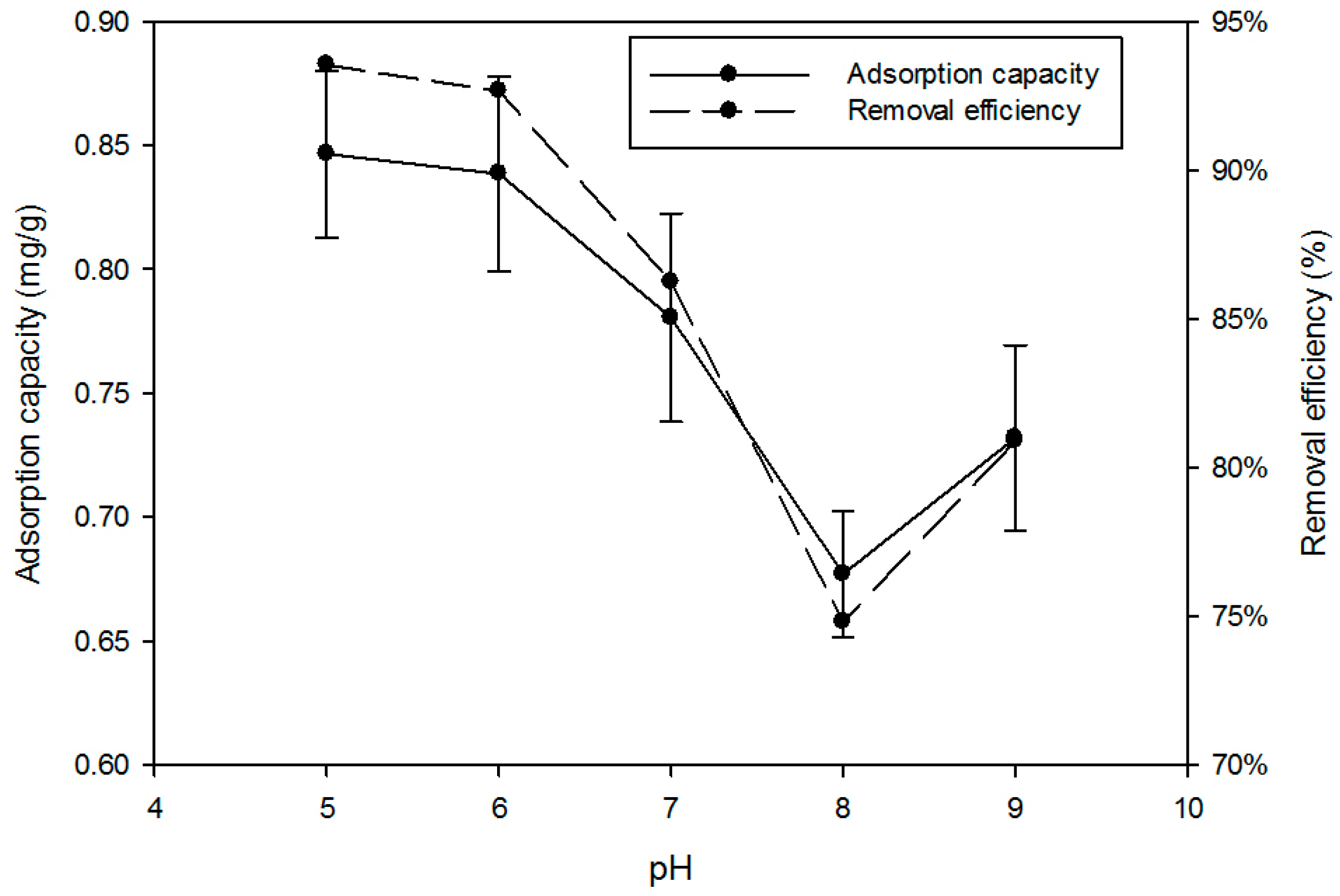
3.1.1. Effect of pH of Solution on Sorption
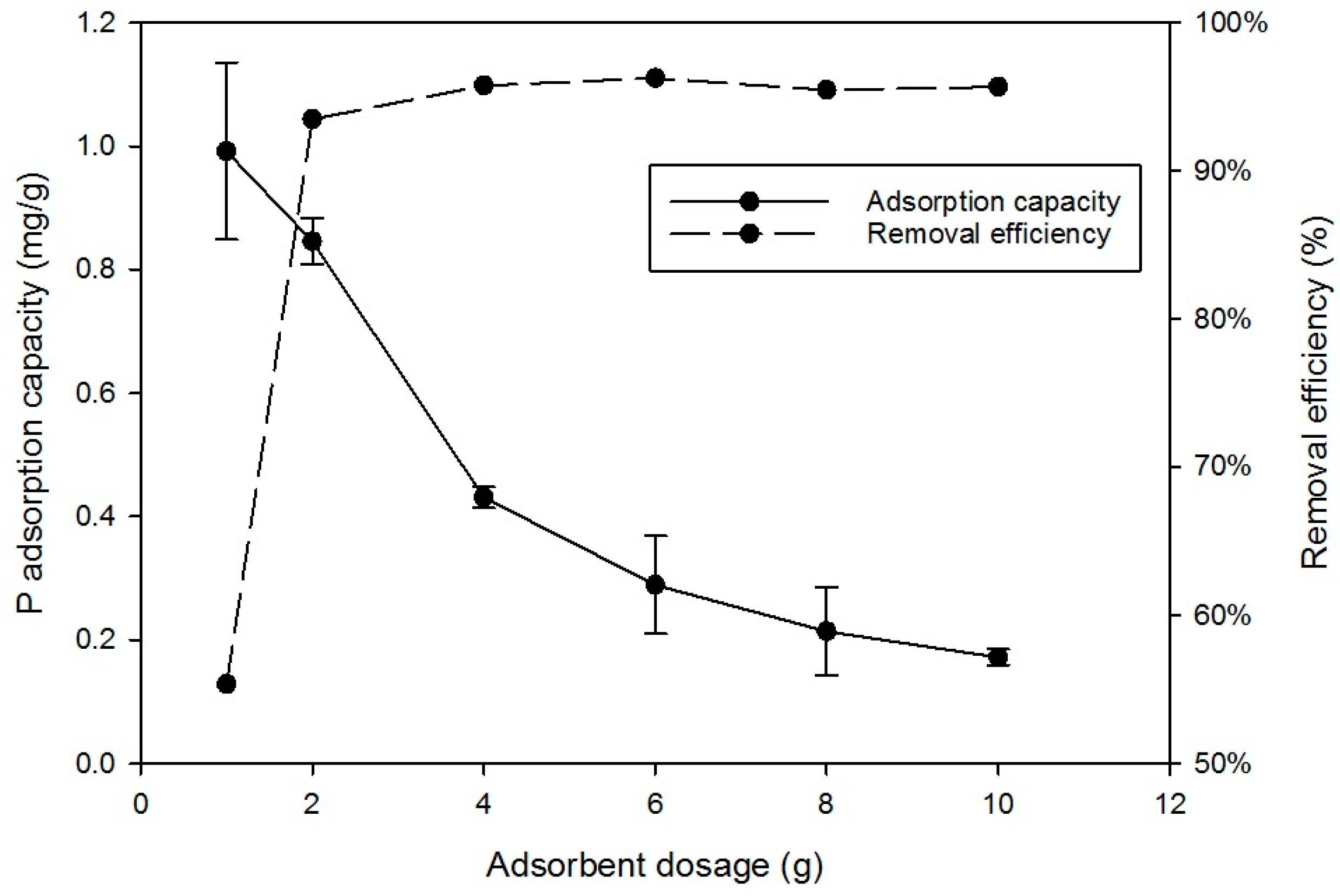
3.1.2. Effect of Dose of Sorbent on Phosphorus Sorption
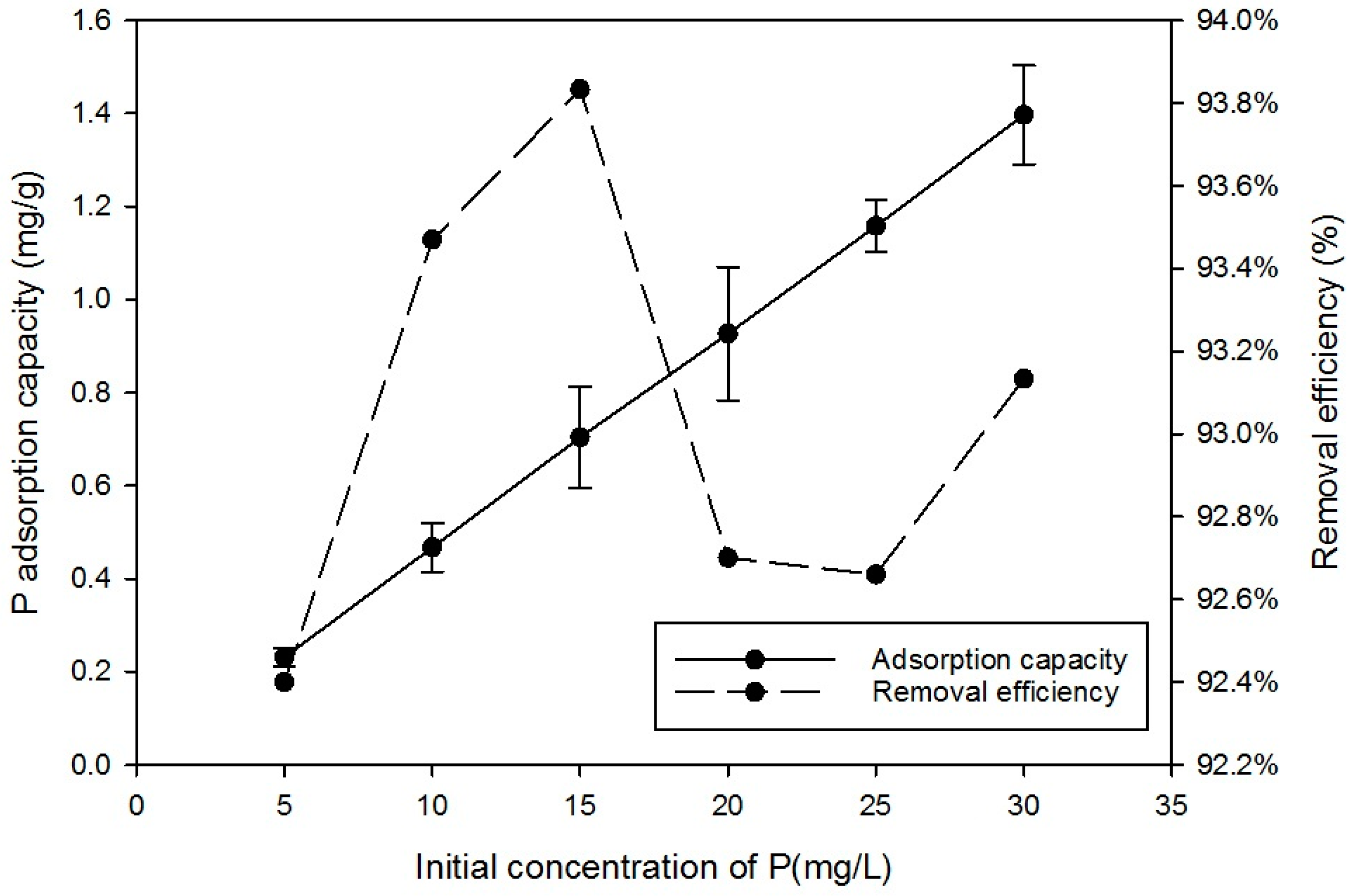
3.1.3. Effect of Initial Phosphorus Concentration
3.1.4. Equilibrium Studies
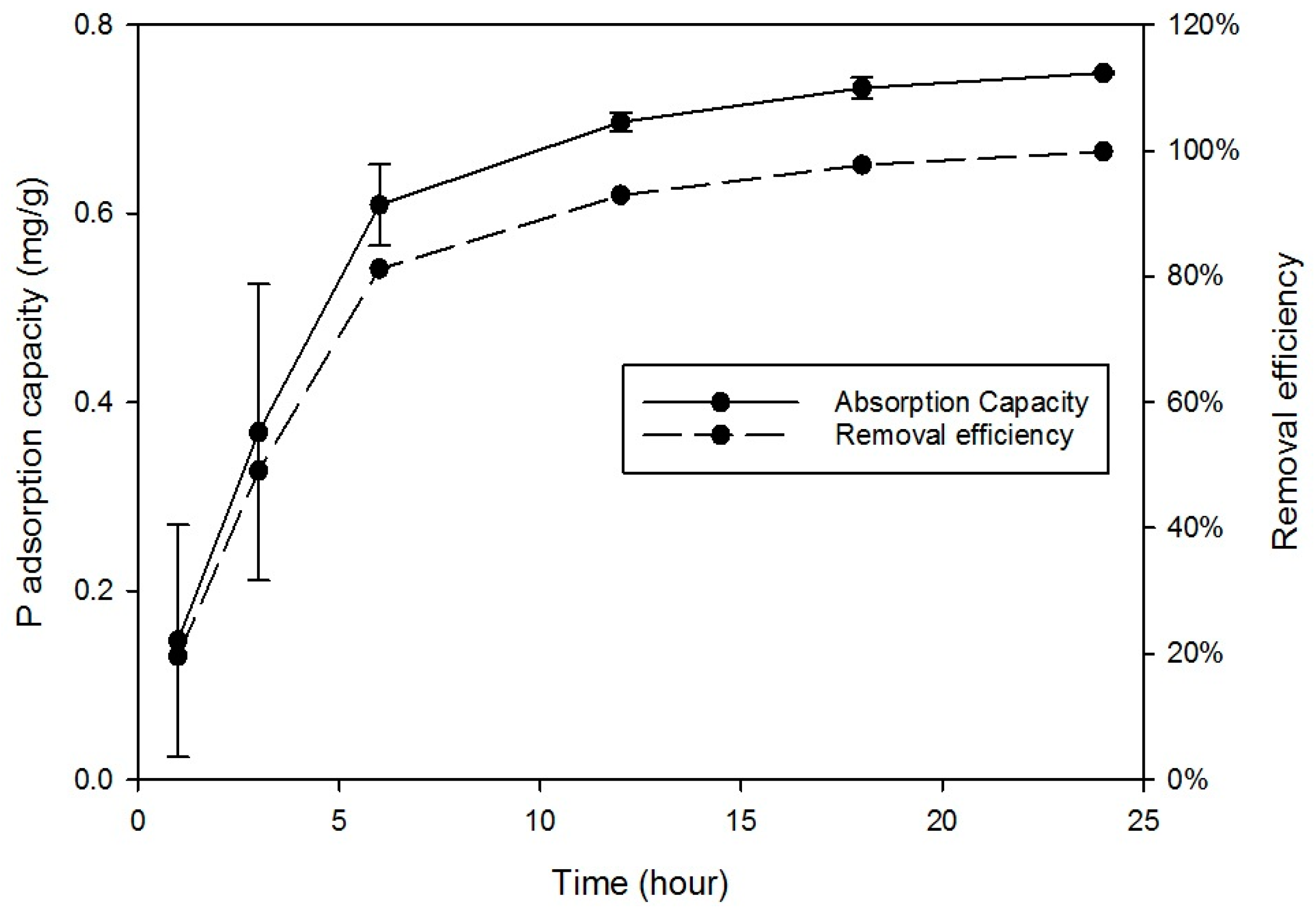
3.1.5. Kinetic Analysis
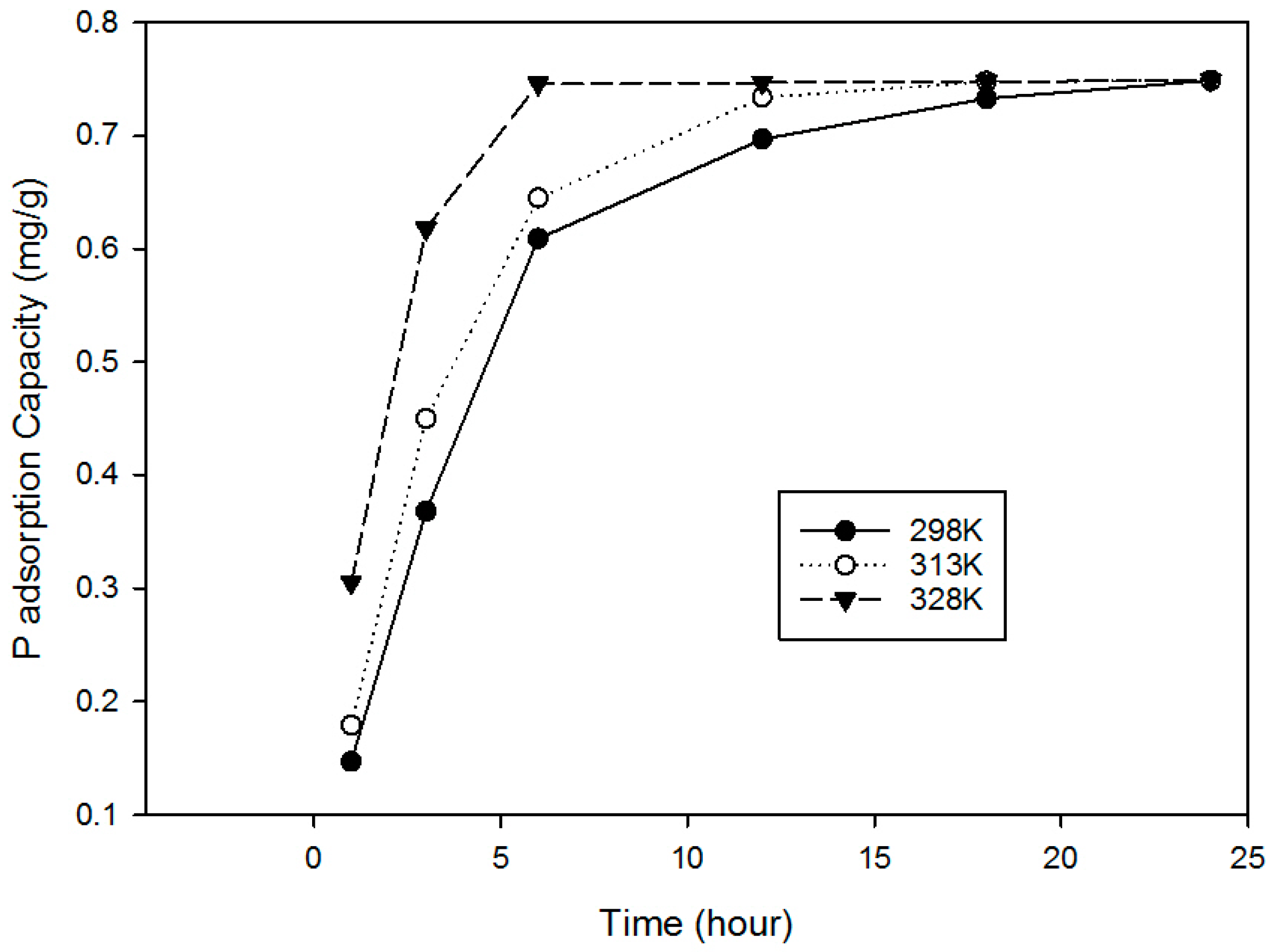
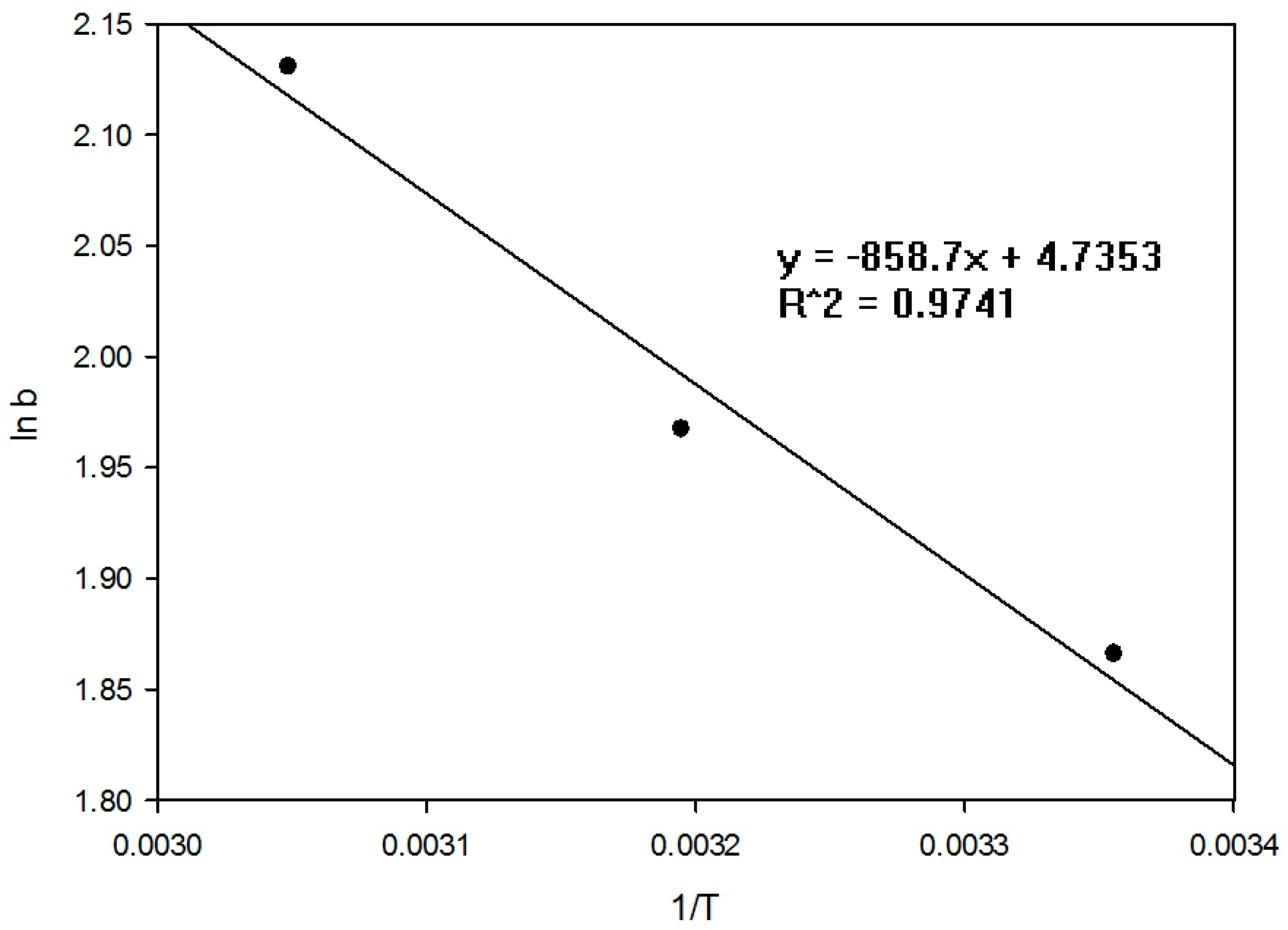
3.1.6. Effect of Temperature on Sorption
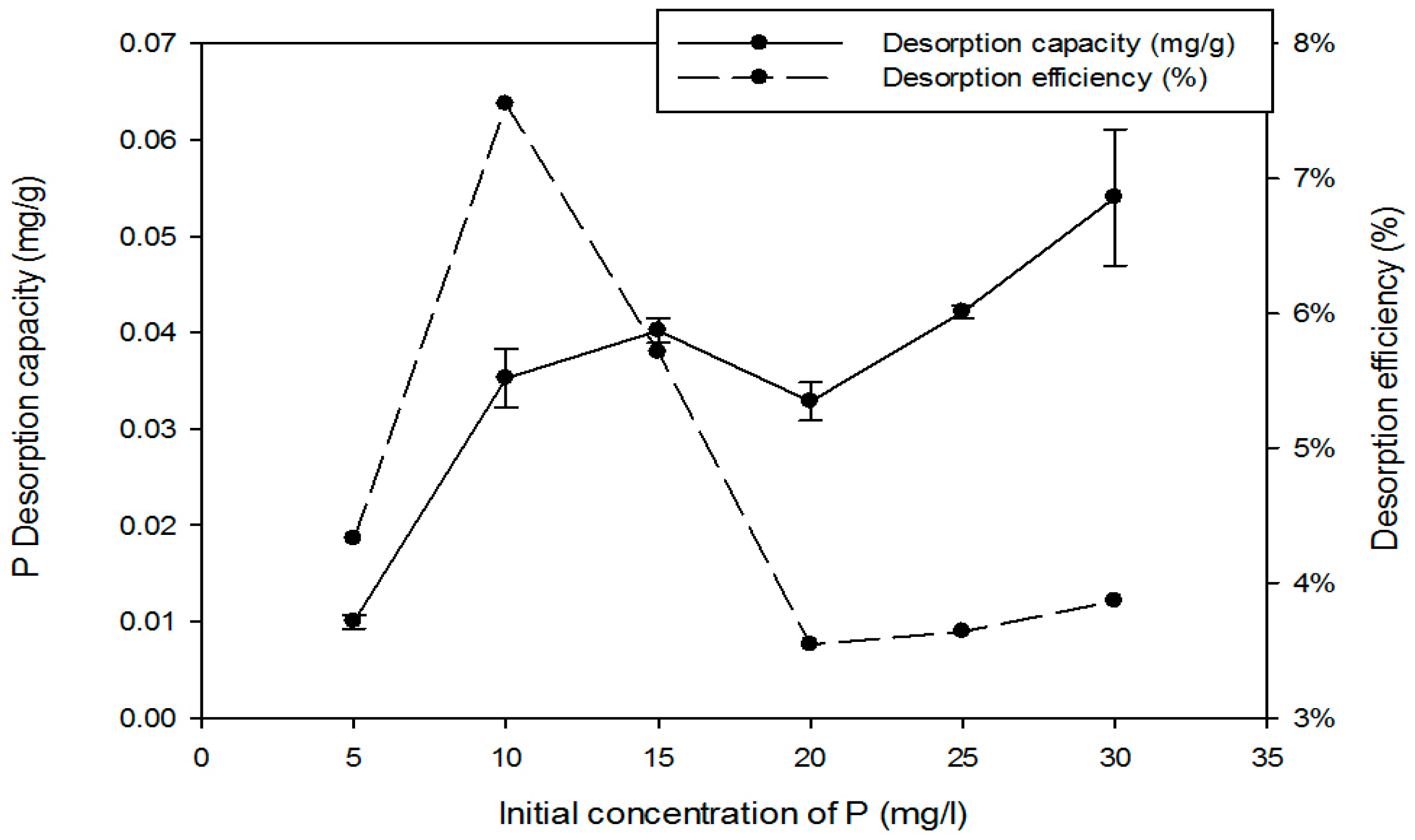
3.2. Desorption of Phosphorus
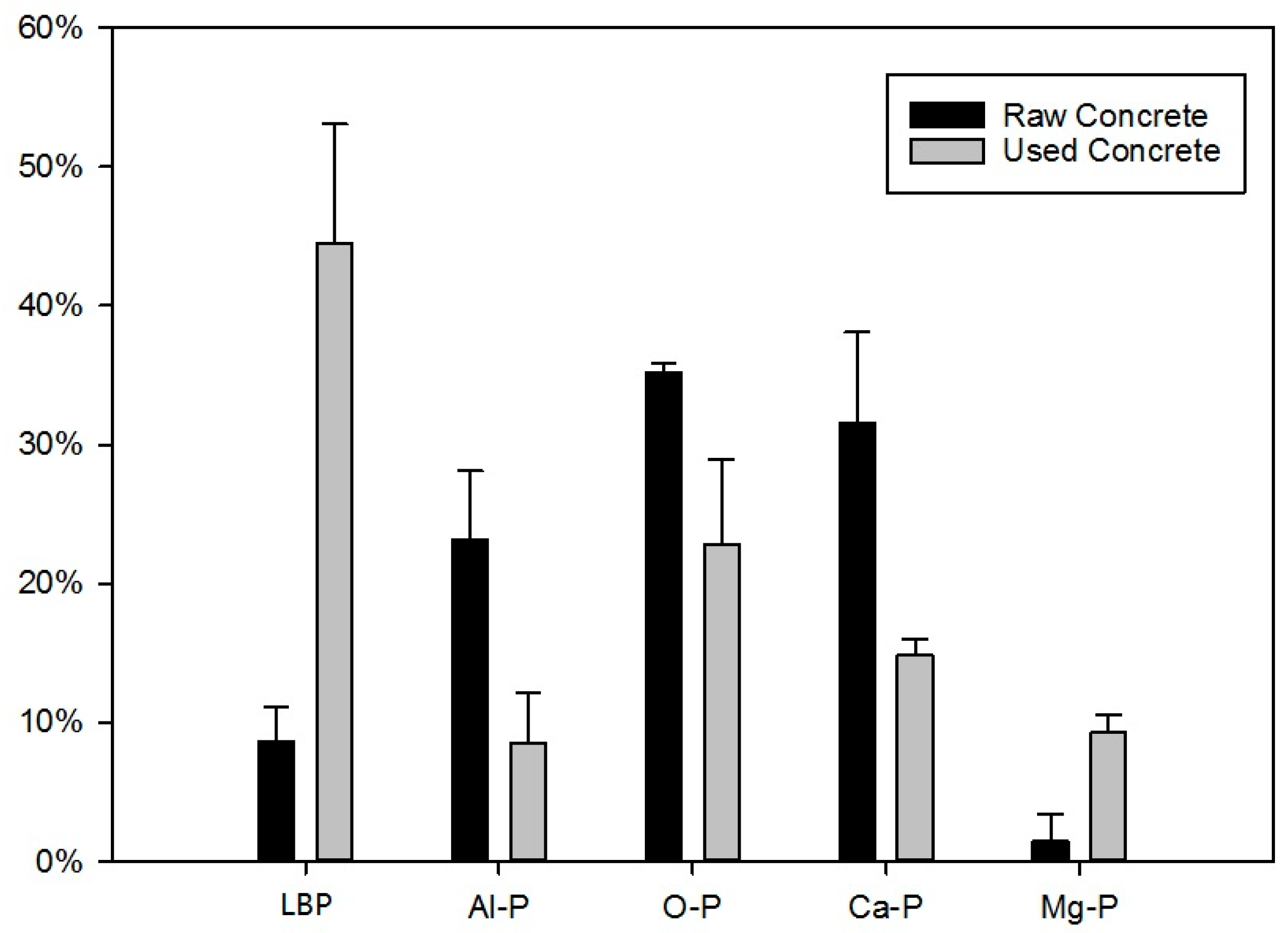
3.3. Fractionation of Inorganic Phosphorus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oikonomou, N.D. Recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. The Annual Report on Comprehensive Utilization of Resources of China; National Development and Reform Commission: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, S. The Research of the Biologic Padding of Fly Ash Applied in the Sewage Transaction. Modem Sci. Instrum. 2007, 4, 63–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, K.; Yang, L.; Qin, X.; Du, J.; Wang, S. Study on pollutants removal performance of some biological carrier in wastewater land treatment system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 22, 33–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y. Substrate screening for phosphorus removal in low concentration phosphorus-containing water body. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2013, 33, 3227–3233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Reijnders, L. Phosphorus resources, their depletion and conservation, a review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 93, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wheatley, A. Wastewater treatment in Chinese rural areas. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2016, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Yoshikawa, E.; Mizuguchi, H.; Endo, M. The Improvement of water quality in an acidic river environment using waste concrete aggregates. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2013, 11, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, T. The Application of Wasted Architecture Walling Materials Used as a constructed wetland media. In Water Infrastructure for Sustainable Communities China and the World, 1st ed.; Hao, X., Novotny, V., Nelson, V., Eds.; International Water Association: London, UK, 2010; pp. 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z. Technology of Using Eco-concrete for Sewage Treatment. J. Build. Mater. 2001, 4, 60–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Jin, L.; Zou, C.; Wan, Y.; Liu, H.; Lan, Y. Microorganisms and effectiveness of a low cost concrete biofilm reactor for sewage treatment. Environ. Pollut. Control 2006, 28, 568–571. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tamai, M.; Okinaka, T. Present and future views of environmentally-friendly concrete. In Concrete Technology for a Sustainable Development in the 21st Century, 1st ed.; Gjorv, O.E., Sakai, K., Eds.; E&FN: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 264–273. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, L.A. An attempted fractionation of the soil phosphorus. J. Agric. Sci. 1938, 28, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Jackson, M.L. Frationation of soil phosphorus. Soil Sci. 1957, 84, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leader, J.W.; Dunn, E.J.; Reddy, K.R. Phosphorus Sorbing Materials: Sorption Dynamics and Physicochemical Characteristics. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; Wang, Y.; DeBusk, W.F.; Fisher, M.M.; Newman, S. Forms of Soil Phosphorus in Selected Hydrologic Units of the Florida Everglades. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.A.; Taylor, M.D.; Albano, J.P.; Whitwell, T.; Klaine, S.J. Phosphorus retention in lab and field-scale subsurface-flow wetlands treating plant nursery runoff. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartikainen, H. Phosphorus and its reactions in terrestrial soils and lake sediments. J. Sci. Agric. Soc. Finl. 1979, 51, 537–624. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, J.; Liu, L.; Li, P.; Zheng, J. Screening of phosphate-removing filter media for use in constructed wetlands and their phosphorus removal capacities. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 227–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Agyeia, N.M.; Strydomb, C.A.; Potgieter, J.H. The removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution by fly ash, slag, ordinary Portland cement and related blends. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burianek, P.; Skalicky, M.; Grunwald, A. Phosphates adsorption from water by recycled concrete. GeoSci. Eng. 2014, LX, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, P.; Lienard, A.; Grasmick, A.; Lwema, A. Phosphorus retention in subsurface constructed wetlands: Investigations focused on calcareous materials and their chemical reactions. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cucarella, V.; Renman, G. Phosphorus sorption capacity of filter materials used for on-site wastewater treatment determined in batch experiments–a comparative study. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 3, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.G.; King, K.W.; Fischer, E.N.; Woner, D.N. PO4 3- removal by and permeability of industrial byproducts and minerals: Granulated blast furnace slag, cement kiln dust, coconut shell activated carbon, silica sand, and zeolite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 219, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawodu, F.A.; Akpomie, K.G. Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption of Cadmium (II) Ions using “Aloji Kaolinite” Mineral. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 15, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; DADA, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Tosun, İ. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Clinoptilolite Determination of Isotherm and Thermodynamic Parameters and Comparison of Kinetics by the Double Exponential Model and Conventional Kinetic Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; He, H.; Zeng, G.; Zhao, K.; Yan, Z. Biosorption of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Waste Biomass from Biotrickling Filters: Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamics. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 142, C4015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Zhu, X.; Vongsay, T.; Huang, M.; Song, L.; He, Y. phosphorus and Nitrogen removal using novel porous bricks incorporated with wastes and minerals. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Tewaria, N.; Vasudevana, P.; Guhab, B.K. Study on biosorption of Cr(VI) by Mucor hiemalis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 23, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, B.; Meng, G. Preparation of Porous Hardened Cement Paste Synthetic Filter Material and Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption. J. Civ. Archit. Environ. Eng. 2013, 35, 115–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Renman, G.; Renman, A. Sustainable use of crushed autoclaved aerated concrete (CAAC) as a filter medium in wastewater purification. In WASCON; Arm, M., Ed.; ISCOWA and SGI: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Egemose, S.; Sønderup, M.J.; Beinthin, M.V.; Reitzel, K.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Flindt, M.R. Crushed concrete as a phosphate binding material: A potential new management tool. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zha, X.; Cheng, T.; Ding, Z.; Zha, X.; Cheng, T. Phosphorus Adsorption Characteristics of Different Substrates in Constructed Wetland. China Water Wastewater 2009, 25, 80–82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Liu, P. Study on the effect of red mud in improving the phosphorus removal ability of eco-concrete. Concrete 2014, 293, 151–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, E.; Gurses, A.; Yalcin, M. Removal of phosphate from waste waters by adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 148, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Clayton, W.R. Application of Elovich Equation to the Kinetics of Phosphate Release and Sorption in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerente, C.; Lee, V.K.C.; Cloirec, P.L.; McKay, G. Application of chitosan for the removal of metals from wastewaters by adsorption—mechanisms and models review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 41–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Application of kinetic models to the sorption of copper (II) on to peat. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sudha, S.; Chand, S.; Srivastava, V.C. Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Coir-Pith Activated Carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S. Adsorption characteristics of Fe(III) and Fe(III)–NTA complex on granular activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 106, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Nie, E.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Equilibrium and kinetics of adsorption of phosphate onto iron-doped activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewská, E.; Hodossyová, R.; Bujdoš, M. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies for Phosphate Removal Using Natural Adsorption Materials. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Xia, W.; An, J.; Yin, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies on the Phosphate Adsorption Removal by Dolomite Mineral. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezenner, N.Y.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetics and thermodynamic study of phosphate adsorption on iron hydroxide-eggshell waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, F. Phosphate adsorption and desorption characteristic of several fly ashes. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 16, 1756–1760. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Berg, U.; Donnert, D.; Ehbrecht, A.; Bumiller, W.; Kusche, I.; Weidler, P.G.; Nüesch, R. “Active filtration” for the elimination and recovery of phosphorus from waste water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 265, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josan, M.S.; Nair, V.D.; Harris, W.G.; Herrera, D. Associated release of magnesium and phosphorus from active and abandoned dairy soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.; Zhou, Q.; Chan, Y.; Yu, F. Structure and Property Characterization of Oyster Shell Cementing Material. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2012, 31, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, E.; Karapinar, N.; Donat, R. The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q. A research on ammonia treated by zeolite from landfill leachate. Water Wastewater Eng. 2003, 29, 6–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Petrus, R.; Warchol, J.K. Heavy metal removal by clinoptilolite. An equilibrium study in multi-component systems. Multi-Compon. Syst. 2005, 39, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkusuz, E.A.; Beklioglub, M.; Demirer, G.N. Use of blast furnace granulated slag as a substrate in vertical flow reed beds Field application. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, P.D.; Krogstad, T.; Paruch, A.M.; Mæhlum, T.; Adam, K.; Arias, C.A.; Heistad, A.; Jonsson, L.; Hellström, D.; Brix, H.; et al. Filter bed systems treating domestic wastewater in the Nordic countries—Performance and reuse of filter media. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Bryant, R.B.; Callahan, M.P.; McGrath, J.M. Use of Industrial By-products to Sorb and Retain Phosphorus. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drizo, A.; Cummings, J.; Weber, D.; Twohig, E.; Druschel, G.; Bourke, B. New Evidence for Rejuvenation of Phosphorus Retention Capacity in EAF Steel Slag. Eviron. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6191–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylander, L.D.; Johansson, L.; Renman, G.; Ridderstolpe, P.; Siman, G. Phosphorus recycling from waste water by filter media used as fertilisers. Nordisk Jordbrugsforsking 1999, 81, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Grobbelaar, J.U.; House, W.A. Phosphorus as a limiting resource in inland waters; interactions with nitrogen. In Phosphorus in the Global Environment-Transfers, Cycles and Management; Tiessen, H., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 55–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hillbricht-Ilkowska, A.; Ryszkowski, L.; Sharpley, A.N. Phosphorus Transfers and Landscape Structure: Riparian Sites and Diversified Land Use Patterns. In Phosphorus in the Global Environment-Transfers, Cycles and Management; Tiessen, H., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 201–228. [Google Scholar]
- Frossard, E.; Brossard, M.; Hedley, M.J.; Metherell, A. Reactions Controlling the Cycling of P in Soils. In Phosphorus in the Global Environment-Transfers Cycles and Management; Tiessen, H., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 107–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.P.; Rekha, P.D.; Arun, A.B.; Shen, F.T.; Lai, W.-A.; Young, C.C. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2006, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.S.D.; Gutiérrez, P.A. Study on the influence of attached mortar content on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Construct. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagoe-Crentsil, K.K.; Taylor, T.B. Performance of concrete made with commercially produced coarse recycled concrete aggregate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Study | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Effect of pH of solution on sorption | The pH of the solution was varied between 6.0 and 8.0. Dose of media 2 g; initial P concentration 20 mg/L; contact time 24 h; agitator 180-rpm |
| 2 | Effect of dose of sorbent on phosphorus sorption | RCA was varied in the range 1–10 g, 20 mg/L P solution; contact time 24 h; agitator 180-rpm; pH-5 |
| 3 | Effect of initial phosphorus concentration | Phosphate concentrations in the range 5–30 mg/L. Dose of media 2 g contact time 24 h; agitator 180-rpm; pH-5; |
| 4 | Equilibrium studies | Evaluation of maximum adsorption by isotherm models |
| 5 | Kinetic analysis | Initial P concentration 15 mg/L with 2 g of RCA, contact time 24 h at 298 K, agitator 180-rpm, pH 5 |
| 6 | Effect of temperature on sorption | Initial P concentration 15 mg/L with 2 g of RCA and contact time 24 h at 298, 318 and 328 °C, pH 5 |
| Step | Inorganic P | Extraction Reagents | Concentration | Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | LBP | NH4Cl | 1 mol/L | 50 mL, shaking 0.5 h |
| II | Al-P | NH4F (pH 8) | 0.5 mol/L | 50 mL, shaking 1 h |
| III | Fe-P | NaOH | 0.1 mol/L | 50 mL, shaking 2 h |
| IV | O-P | CDB (pH 7.6) | - | 45 mL, shaking 0.5 h |
| V | Ca-P | H2SO4 | 0.5 mol/L | 50 mL, shaking 1 h |
| VI | Mg-Ca-P | HCl | 0.5 mol/L | 50 mL, shaking 1 h |
| Isotherm Models | Linear Expression | Associated Equations | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | K and n are empirical constants | Kf (L/mg) = Langmuir equilibrium constant; n = dimensionless correction factor; qe = adsorption capacity (mg/g) | |
| Langmuir | KL = Isotherm constant (L/mg); CO = initial concentration; qm=mainxmum adsorption capacity (mg/g) | ||
| Tempkin | - | = Tempkin isotherm equilibrium binding constant (L/g); B = constant related to heat of sorption (J/mol) | |
| D-R | qs = theoretical isotherm saturation capacity (mg/g), Kad = Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm constant (mol2/kJ2) and ε = Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm constant | ||
| Frumkin | - | = fractional surface coverage; = lateral interaction coefficient; Kfr (L/g) = Frumkin equilibrium constant, | |
| BET | - | Ce = equilibrium concentration (mg/L); Cs = adsorbate monolayer saturation concentration (mg/L); CBET = BET adsorption isotherm relating to the energy of surface interaction (L/mg) |
| Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm | Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm | ||||||||
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | RL | R2 | n | Kf | R2 | |||
| 6.88 | 0.089 | 0.281 | 0.984 | 0.996 | 0.669 | 0.983 | |||
| Tempkin Adsorption Isotherm | Dubinin-Radushkevich Isotherm | ||||||||
| AT (L/mg) | At | B | R2 | qs (mg/g) | Kad (mol2/kJ2) | ε (kJ/mol) | R2 | ||
| 0.195 | 134.9 | 0.649 | 0.958 | 1.4 | 2 × 10−7 | 2.24 | 0.968 | ||
| Frumkin Adsorption Isotherm | BET Adsorption Isotherm | ||||||||
| α | Kfr | R2 | CBET | qs | R2 | ||||
| 2.959 | 0.00342 | 0.669 | −0.798 | 0.553 | 0.898 | ||||
| Types | Media | Size (mm) | Time | Qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical | Ordinary Portland cement | 0.045–0.300 | 16 h | 19.90 | [21] |
| Empirical | Recycled Crushed Concrete | 0.125–0.250 | 1 h | 0.134 | [22] |
| Empirical | Crushed concrete | 0.125 | 40 days | 19.6 | [34] |
| Theoretical | Cement | 0.425–0.85 | 24 h | 1.185 | [35] |
| Empirical | Cement | 0.85 | 28 days | 16.16 | [36] |
| Empirical | Gas concrete | 0.063–2 | 1 h | 11.5 | [37] |
| Theoretical | Recycled crushed concrete | 0.3–2.3 | 24 h | 6.1 | [23] |
| Empirical | Crushed autoclaved aerated concrete | 2–4 | 24 h | 70.9 | [33] |
| Theoretical | Recycled concrete | 2–5 | 24 h | 6.88 | Present study |
| Theoretical | Cement | 3–5 | 32 h | 4.98 | [32] |
| Kinetic Study | Linear Expression | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| The pseudo-first-order | Q = the amount of adsorption time (min) (mg/g); k1 = the rate, constant of pseudo first-order sorption (L/min); Qe = adsorption capacities at equilibrium, Qt = adsorption capacities at time t(min) | |
| The pseudo second-order | k2 = the rate constant of the second-order equation | |
| Elovich model equation | are constants | |
| Fractional power model | qt = the amount of adsorbate sorbed by adsorbent at a time t; and b = constants with b < 1 |
| The Pseudo-First-Order | The Pseudo Second-Order | ||||
| k1 | Qe | R2 | k2 | Qe | R2 |
| 0.211 | 0.657 | 0.9876 | 0.279 | 0.893 | 0.9916 |
| Elovich Model Equation | Fractional Power Model | ||||
| R2 | a | b | R2 | ||
| 0.476 | 5.061 | 0.9599 | 0.184 | 0.5 | 0.8986 |
| Thermodynamic Parameters | Temperature (K) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 313 | 328 | |
| b | 6.460 | 7.150 | 8.418 |
| ΔG° (kJ/mol) | −4.623 | −5.119 | −5.808 |
| ΔH° (kJ/mol) | 7.139 | - | - |
| ΔS° (J/mol) | 39.336 | - | - |
| Adsorbent | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinoptilolite rich tuff | 20.8 | 100 | [44] |
| Coir-pith activated carbon | 3.88 | 21.88 | [41] |
| Dolomite | −5.85 | −10.17 | [45] |
| Granulated ferric hydroxide | 15.1 | 80 | [44] |
| Iron hydroxide-eggshell waste | 81.84 | - | [46] |
| Bentonite | −5.3 | 10 | [44] |
| RCA | 7.139 | 39.336 | Present study |
| Slovakite | 104.9 | 300 | [44] |
| Sequence | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 |
| Media | Total (mg/g) | Soluble P (mg/g) | Al-P (mg/g) | Fe-P (mg/g) | O-P (mg/g) | Ca-P (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blast furnace granulated slag | 0.086 | 0.042 | - | 0.007 | - | 0.037 | [54] |
| 49% | - | 8% | - | 43% | |||
| Zeolite | 0.448 | 0.024 | 0.352 | 0.041 | 0.016 | 0.0131 | [20] |
| 5.4% | 78.6% | 9.2% | 3.6% | 2.9% | |||
| Volcanic rock | 0.516 | 0.066 | 0.311 | 0.027 | 0.054 | 0.058 | [20] |
| 12.8% | 60.3% | 5.2% | 10.5% | 11.2% | |||
| Crushed Bricks | 0.956 | 0.068 | 0.498 | 0.277 | 0.024 | 0.089 | [20] |
| 7.1% | 52.1% | 29.0% | 2.5% | 9.3% | |||
| RCA | 1.298 | 0.577 | 0.110 | 0 | 0.297 | 0.193 | Present study |
| 44.42% | 8.50% | 0% | 22.86% | 14.86% | |||
| Oyster shell | 3.596 | 0.363 | 0.08 | 0.014 | 0.589 | 2.55 | [20] |
| 10.1% | 2.2% | 0.4% | 16.4% | 70.9% | |||
| Light-weight expanded clay | 6.527 | 0.053 | 1.641 | 0.022 | - | 4.811 | [55] |
| 1% | 25% | <1% | - | 74% | |||
| Gas desulfurization products | 8.607 | 2.544 | 1.452 | 0.008 | 0.9 | 3.703 | [56] |
| 30% | 17% | 0% | 10% | 43% | |||
| Bauxite residual | 19.487 | 0.568 | 14.31 | 2.203 | 1.21 | 1.196 | [56] |
| 3% | 73% | 11% | 6% | 6% | |||
| Fly ash | 28.074 | 9.131 | 16.631 | 0.147 | 1.316 | 0.849 | [56] |
| 33% | 59% | 1% | 5% | 3% | |||
| Drinking Water treatment residual | 30.031 | 0.367 | 20.726 | 4.66 | 1.755 | 2.523 | [56] |
| 1% | 69% | 16% | 6% | 8% | |||
| Electric arc fumace steel slag | - | - | - | - | - | - | [57] |
| 0.63% | 3.05% | 13.67% | - | 82.65% | |||
| Iron melter slag | - | - | - | - | - | - | [57] |
| 2.41% | 22.88% | 12.69% | - | 62% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Y.; Wheatley, A. Mechanisms of Phosphorus Removal by Recycled Crushed Concrete. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020357
Deng Y, Wheatley A. Mechanisms of Phosphorus Removal by Recycled Crushed Concrete. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(2):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020357
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Yihuan, and Andrew Wheatley. 2018. "Mechanisms of Phosphorus Removal by Recycled Crushed Concrete" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 2: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020357
APA StyleDeng, Y., & Wheatley, A. (2018). Mechanisms of Phosphorus Removal by Recycled Crushed Concrete. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(2), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020357





