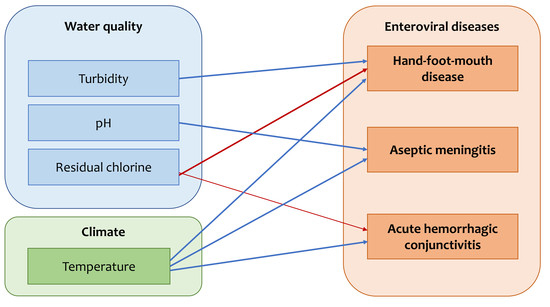
Impact of Drinking Water Quality on the Development of Enteroviral Diseases in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
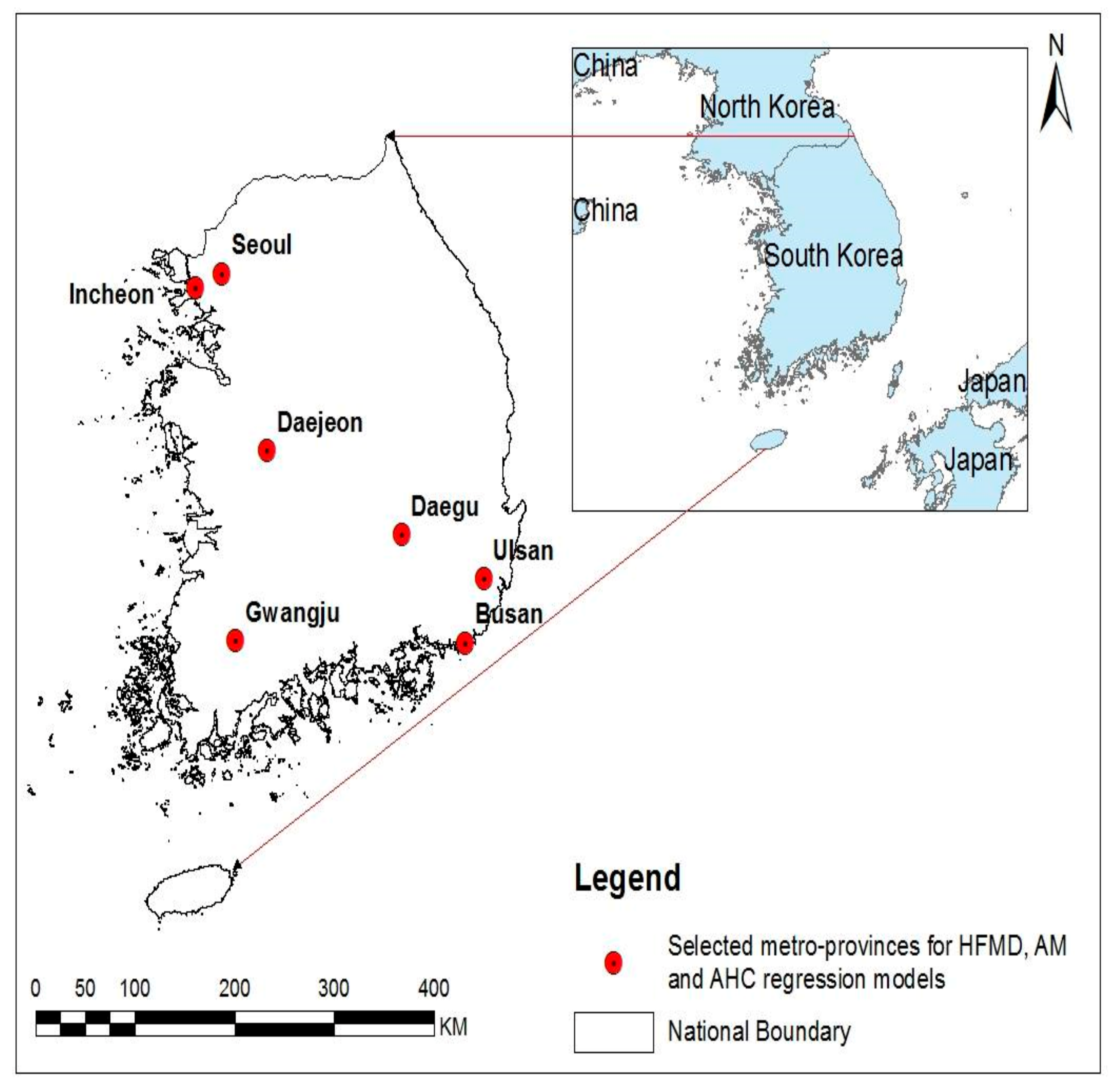
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. GLM Analysis
2.3.2. Meta-Analysis in the Seven Metropolitan Provinces
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
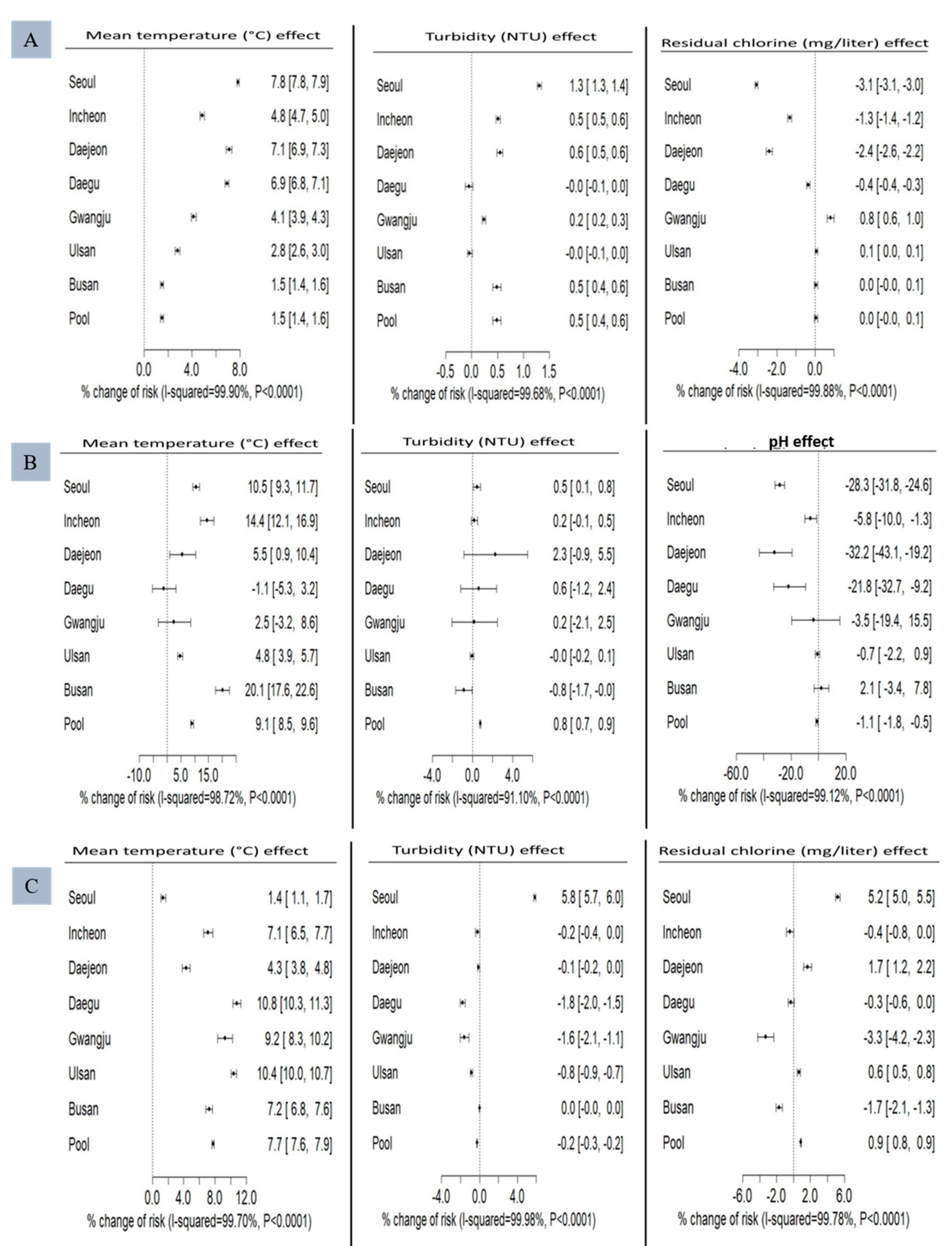
3.2. Generalized Linear Model
3.3. Meta-Analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHC | acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| AM | aseptic meningitis |
| GLM | generalized linear model |
| HFMD | hand-foot-mouth disease |
| HIRA | Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Korea |
| NTU | nephelometric turbidity unit |
| NWIS | National Waterworks Information Service, Korea |
| REML | restricted maximum likelihood |
| VIF | variance inflation factor |
References
- Pallanch, M.A.; Ross, R.P. Enteroviruses: Polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses and newer enteroviruses. In Fields Virology, 4th ed.; Howley, K.D., Ed.; Williams and Wilkins Publishers: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 723–775. [Google Scholar]
- Kocwa-Haluch, R. Waterborne enteroviruses as a hazard for human health. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2001, 10, 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Maitreyi, R.S.; Dar, L.; Vajpayee, M.M.; Xess, I.; Vajpayee, P.; Seth, P.; Broor, S. Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis due to enterovirus 70 in India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Tsai, H.P.; Huang, S.W.; Kuo, P.H.; Kiang, D.; Liu, C.C. Laboratory diagnosis and genetic analysis of an echovirus 30-associated outbreak of aseptic meningitis in Taiwan in 2001. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4439–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Yeo, S.; Lee, S.; Cheon, D.S.; Choi, W.; Ahn, J.; Kim, S.; Jee, Y. Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis epidemic caused by coxsackievirus A24 variants in Korea during 2002–2003. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, H.K.; Park, S.K.; Ki, M.; Lee, K. Six year national trend of childhood aseptic meningitis incidence in Korea, 1996–2001. Korean J. Epidemiol. 2008, 30, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozuka, D.; Hashizume, M. The influence of temperature and humidity on the incidence of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.I.; Ki, H.; Park, S.; Cho, E.; Chun, B.C. Effect of climatic factors on hand, foot, and mouth disease in South Korea, 2010–2013. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, F.X.; Pinto, R.M.; Bosch, A. Survival of enteric viruses on environmental fomites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3704–3710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilgen, M.; Wegmüller, B.; Burkhalter, P.; Bühler, H.P.; Müller, U.; Lüthy, J.; Candrian, U. Reverse transcription PCR to detect enteroviruses in surface water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.; Yeo, S.; Lee, B.; Park, K.S.; Song, J.H.; Yu, J.S.; Rheem, I.S.; Kim, J.K.; Hwang, S.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; et al. Epidemics of enterovirus infection in Chungnam Korea, 2008 and 2009. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kang, B.; Hwang, S.; Hong, J.; Kim, K.; Cheon, D.S. Epidemics of viral meningitis caused by echovirus 6 and 30 in Korea in 2008. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.J. Detection of infectious enteroviruses and adenoviruses in tap water in urban areas in Korea. Water Res. 2002, 36, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, C.; Lee, K.W.; Cho, H.B.; Kim, S.J. The simultaneous detection of both enteroviruses and adenoviruses in environmental water samples including tap water with an integrated cell culture-multiplex-nested PCR procedure. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Park, B.; Ki, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Jung, C.; Sohn, Y.M.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Transmission of seasonal outbreak of childhood enteroviral aseptic meningitis and hand-foot-mouth disease. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, T.T.; Lipp, E.K. Enteric viruses of humans and animals in aquatic environments: Health risks, detection, and potential water quality assessment tools. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.B.; Epstein, P.R.; Lipp, E.K.; Sherman, B.H.; Bernard, S.M.; Patz, J.A. Climate variability and change in the United States: Potential impacts on water and food borne diseases caused by microbiologic agents. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.L.; Chio, C.P.; Su, H.J.; Liao, C.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Shau, W.Y.; Chi, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chou, Y.L.; Li, C.Y.; et al. The association between enterovirus 71 infections and meteorological parameters in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2002, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, Y.P.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.; Cheong, H.K. Associations between meteorological factors and aseptic meningitis in six metropolitan provinces of Republic of Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, e1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzezutka, A.; Cook, N. Survival of human enteric viruses in the environment and food. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keswick, B.H.; Gerba, C.P.; Goyal, S.M. Occurrence of enteroviruses in community swimming pools. Am. J. Public Health 1981, 71, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, R.S.; Yoneyama, B.S. Sunlight inactivation of human enteric viruses and fecal bacteria. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Statistical Information Service. Republic of Korea. Available online: http://kosis.kr/eng/ (accessed on 14 February 2016).
- Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service. Healthcare Bigdata Hub. Available online: http://opendata.hira.or.kr/home.do/ (accessed on 8 February 2016).
- Korean Meteorological Agency (KMA). Republic of Korea. Available online: http://data.kma.go.kr/ (accessed on 10 January 2016).
- National Waterworks Information System (NWIS). Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Available online: http://waternow.go.kr/ (accessed on 28 March 2016).
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; García, M.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Münkemüller, T.; et al. Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 2012, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, J.; Demtrio, C.G.B. Overdispersion: Models and estimation. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 1998, 27, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.J. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br. Med. J. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbeil, R.R.; Searle, S.R. Restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimation of variance components in the mixed model. Technometrics 1976, 18, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2015).
- Ang, L.W.; Koh, B.K.W.; Chan, P.K.; Chua, T.L.; James, L.; Goh, K.T. Epidemiology and control of hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore, 2001–2007. Ann. Acad. Med. 2009, 38, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fisman, D. Seasonality of viral infection: Mechanisms and unknowns. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 2012, 18, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebruegge, M.; Curtis, N. Enterovirus infections in neonates. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009, 14, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwachuku, N.; Greba, C.P. Health risks of enteric viral infections in children. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 186, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.C.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Jia, J.; Han, Y.L.; Hao, B.; Cao, G.W. Meteorological factors affect the hand, foot, and mouth disease epidemic in Qingdao, China, 2007–2014. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 2354–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbithi, J.N.; Springthorpe, V.S.; Sattar, S.A. Effect of relative humidity and air temperature on survival of hepatitis-A virus on environmental surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jean, J.S.; Guo, H.R.; Chen, S.H.; Liu, C.C.; Chang, W.T.; Yang, Y.J.; Huang, M.C. The association between rainfall rate and occurrence of an enterovirus epidemic due to a contaminated well. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keswick, B.H.; Gerba, C.P.; Dupont, H.L.; Rose, J.B. Detection of Enteric Viruses in treated drinking water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fenner, F. The nature and classification of viruses of man. Pharmacol. Ther. 1979, 4, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, R.J.; Cliver, D.O. Effect of acid pH, salts, and temperature on the infectivity and physical integrity of enteroviruses. Arch. Virol. 1976, 52, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variables | No. of Cases | Incidence (/100,000/year) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFMD | AM | AHC | HFMD | AM | AHC | ||
| Year | 2010 | 185,560 | 3050 | 56,878 | 375.6 | 6.2 | 115.1 |
| 2011 | 380,111 | 3499 | 42,710 | 763.6 | 7.0 | 85.8 | |
| 2012 | 226,650 | 4344 | 18,491 | 453.3 | 8.7 | 37.0 | |
| 2013 | 305,536 | 4287 | 12,692 | 608.4 | 8.5 | 25.3 | |
| 2014 | 411,191 | 3493 | 4976 | 815.5 | 6.9 | 9.9 | |
| 2015 | 213,815 | 6263 | 4181 | 422.4 | 12.4 | 8.3 | |
| Metropolitan provinces * | Seoul | 278,144 | 2601 | 37,572 | 465.5 | 4.4 | 62.9 |
| Busan | 107,852 | 1117 | 12,609 | 523.6 | 5.4 | 61.2 | |
| Daegu | 100,515 | 130 | 6146 | 679.4 | 0.9 | 41.5 | |
| Incheon | 74,639 | 595 | 2981 | 443.9 | 3.5 | 17.7 | |
| Gwangju | 68,518 | 77 | 1365 | 757.3 | 0.9 | 15.1 | |
| Daejeon | 50,437 | 210 | 5620 | 548.9 | 2.3 | 61.2 | |
| Ulsan | 61,632 | 3195 | 11,223 | 916.5 | 47.5 | 166.9 | |
| Gyeonggi | 453,361 | 4511 | 25,022 | 628.3 | 6.3 | 34.7 | |
| Gangwon | 51,675 | 105 | 1569 | 575.1 | 1.2 | 17.5 | |
| Nonmetropolitan provinces | Chungbuk | 56,101 | 210 | 1823 | 604.8 | 2.3 | 19.7 |
| Chungnam | 73,130 | 689 | 3746 | 562.2 | 5.3 | 28.8 | |
| Jeonbuk | 66,476 | 150 | 6742 | 616.2 | 1.4 | 62.5 | |
| Jeonnam | 52,582 | 100 | 1930 | 496.5 | 0.9 | 18.2 | |
| Gyeongbuk | 81,073 | 30 | 5285 | 512.3 | 0.2 | 33.4 | |
| Gyeongnam | 129,494 | 11,201 | 14,937 | 664.1 | 57.4 | 76.6 | |
| Jeju | 17,234 | 15 | 1358 | 507.3 | 0.4 | 40.0 | |
| Total | 1,722,863 | 24,936 | 139,928 | 573.4 | 8.3 | 46.6 | |
| Variables | Seoul | Incheon | Daegu | Gwangju | Daejeon | Busan | Ulsan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFMD | 3863.1 ± 5165.9 | 1036.7 ± 1366.4 | 1396.0 ± 1810.6 | 951.6 ± 920.1 | 700.5 ± 855.0 | 1497.9 ± 1809 | 856 ± 883.4 |
| AM | 36.1 ± 50.6 | 10.8 ± 21.7 | 2.1 ± 2.0 | 2.1 ± 1.5 | 6.2 ± 9.2 | 19.3 ± 26.8 | 44.4 ± 33.9 |
| AHC | 521.8 ± 1619.0 | 41.4 ± 46.1 | 85.4 ± 169.2 | 19.2 ± 37.5 | 78.1 ± 110.0 | 175.1 ± 334.4 | 155.9 ± 213.8 |
| Population density † | 16,433.8 ± 120.0 | 2904.1 ± 63.6 | 2783.0 ± 7.5 | 3010.0 ± 19.1 | 2836.3 ± 21.6 | 4516.7 ± 30.9 | 1061.3 ± 16.7 |
| Mean temperature ‡ | 13.52 ± 9.25 | 13 ± 8.95 | 14.64 ± 9.28 | 14.21 ± 9.17 | 13.55 ± 9.31 | 14.99 ± 8.05 | 14.38 ± 8.53 |
| Turbidity ¶ | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.02 |
| Residual chlorine § | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.78 ± 0.07 | 0.55 ± 0.06 | 0.62 ± 0.04 | 0.72 ± 0.06 | 0.58 ± 0.06 | 0.76 ± 0.15 |
| pH § | 7.13 ± 0.09 | 7.36 ± 0.47 | 7.10 ± 0.17 | 6.77 ± 0.12 | 7.08 ± 0.10 | 6.84 ± 0.14 | 7.12 ± 0.19 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joshi, Y.P.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Cheong, H.-K. Impact of Drinking Water Quality on the Development of Enteroviral Diseases in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112551
Joshi YP, Kim J-H, Kim H, Cheong H-K. Impact of Drinking Water Quality on the Development of Enteroviral Diseases in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(11):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112551
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoshi, Yadav P., Jong-Hun Kim, Ho Kim, and Hae-Kwan Cheong. 2018. "Impact of Drinking Water Quality on the Development of Enteroviral Diseases in Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 11: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112551
APA StyleJoshi, Y. P., Kim, J.-H., Kim, H., & Cheong, H.-K. (2018). Impact of Drinking Water Quality on the Development of Enteroviral Diseases in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(11), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112551