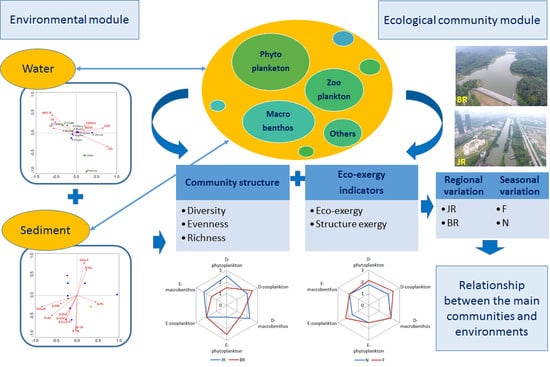
Relationship between the Main Communities and Environments of an Urban River and Reservoir: Considering Integrated Structural and Functional Assessments of Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
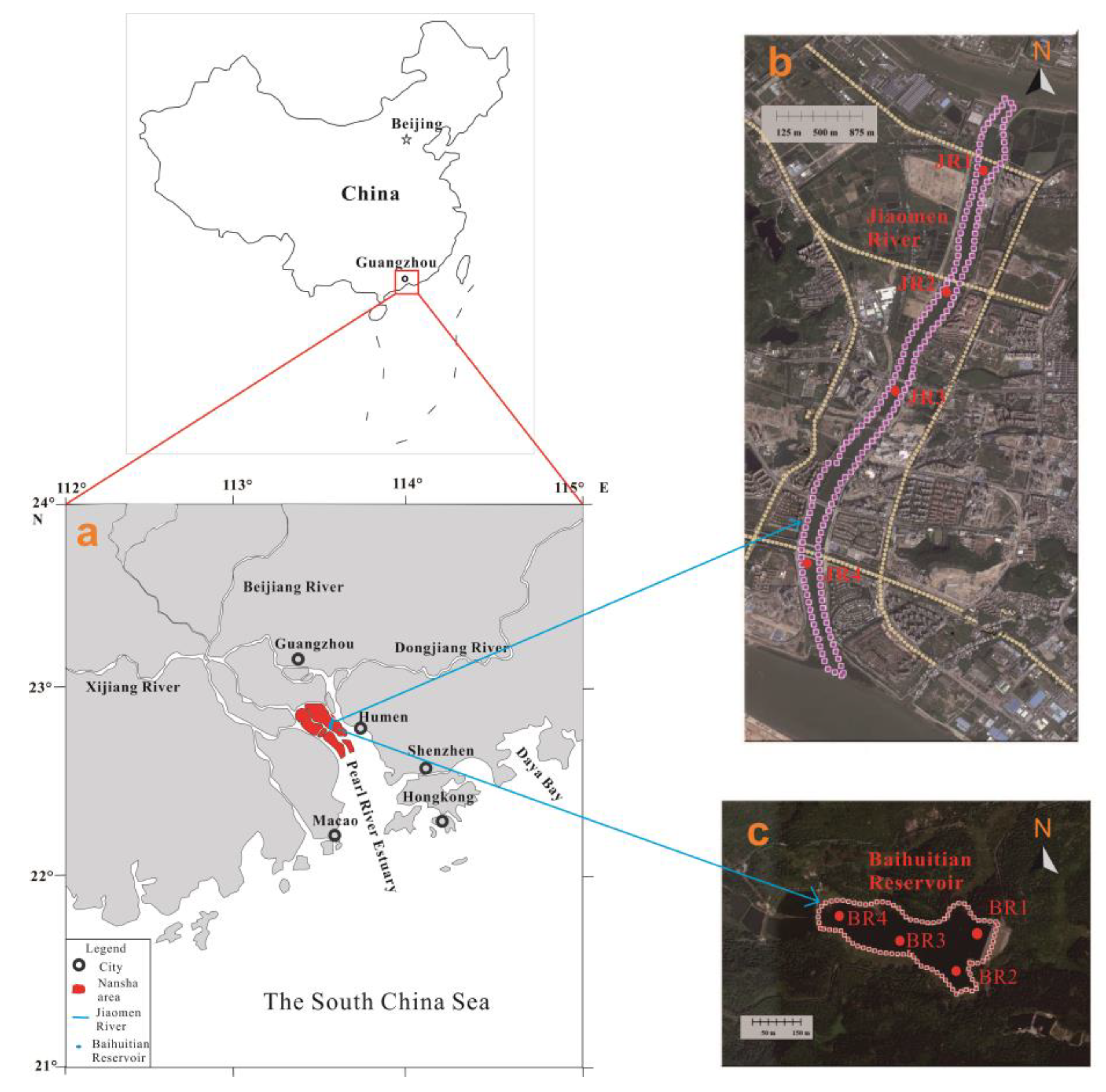
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
2.2. Environmental Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Biological Sampling Collection
2.4. Calculation of Indicators
2.4.1. Calculation of Biodiversity Indicators
2.4.2. Calculation of Exergy-Based Indicators
2.4.3. Data Analysis
2.5. Conceptual Model
3. Results
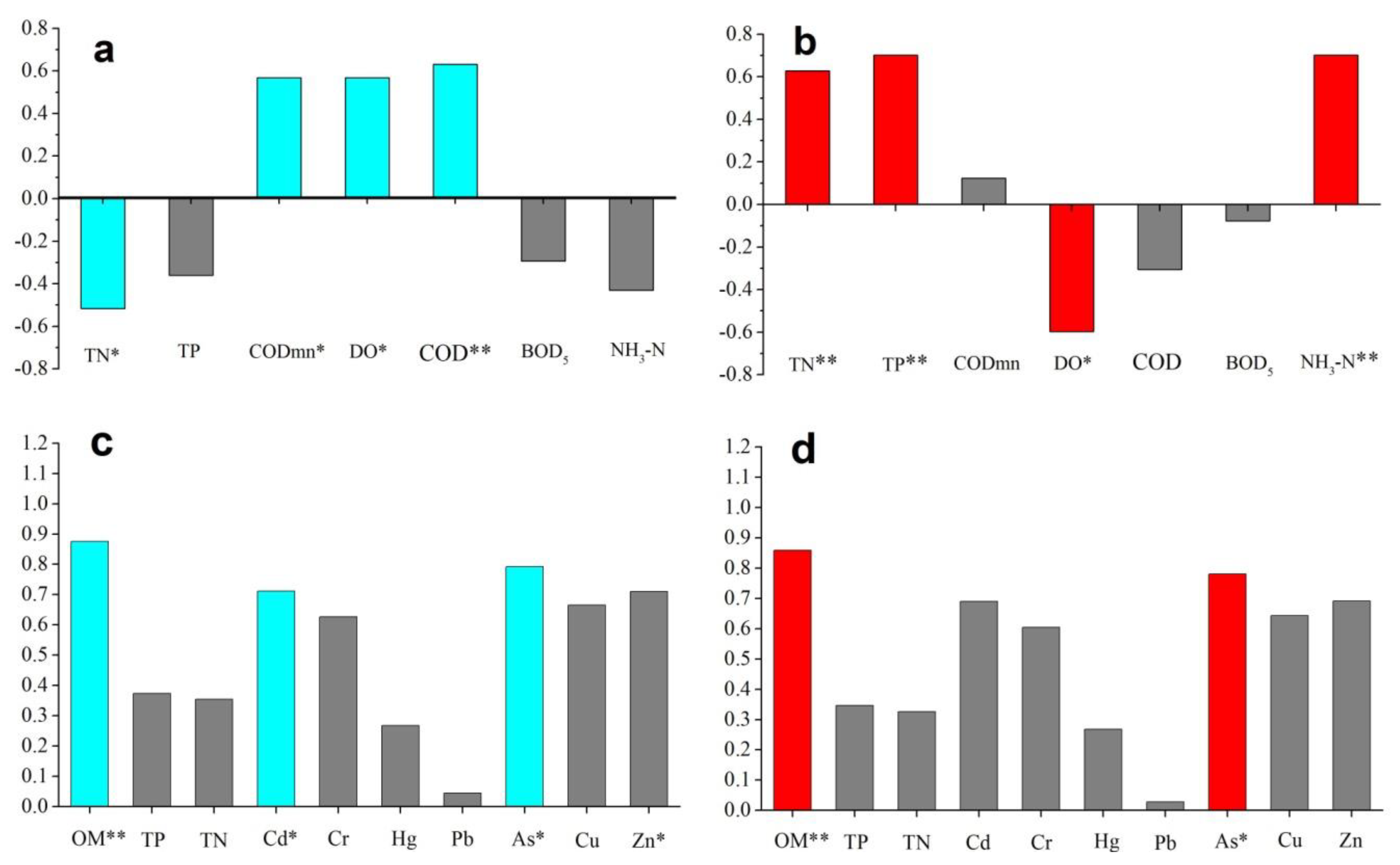
3.1. Environmental Module and Quality Standards
3.1.1. Surface Water
3.1.2. Sediment
3.2. Ecological Community Module
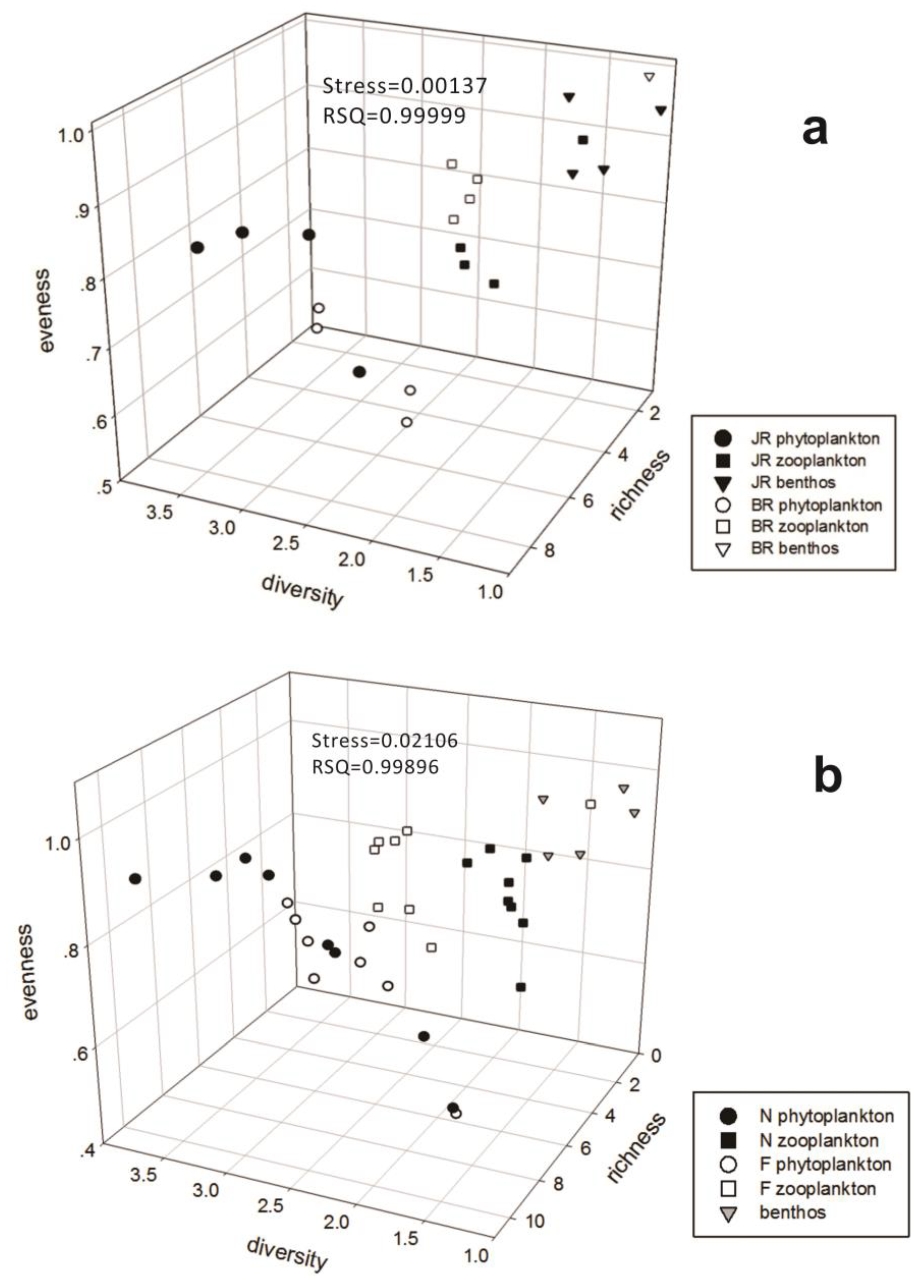
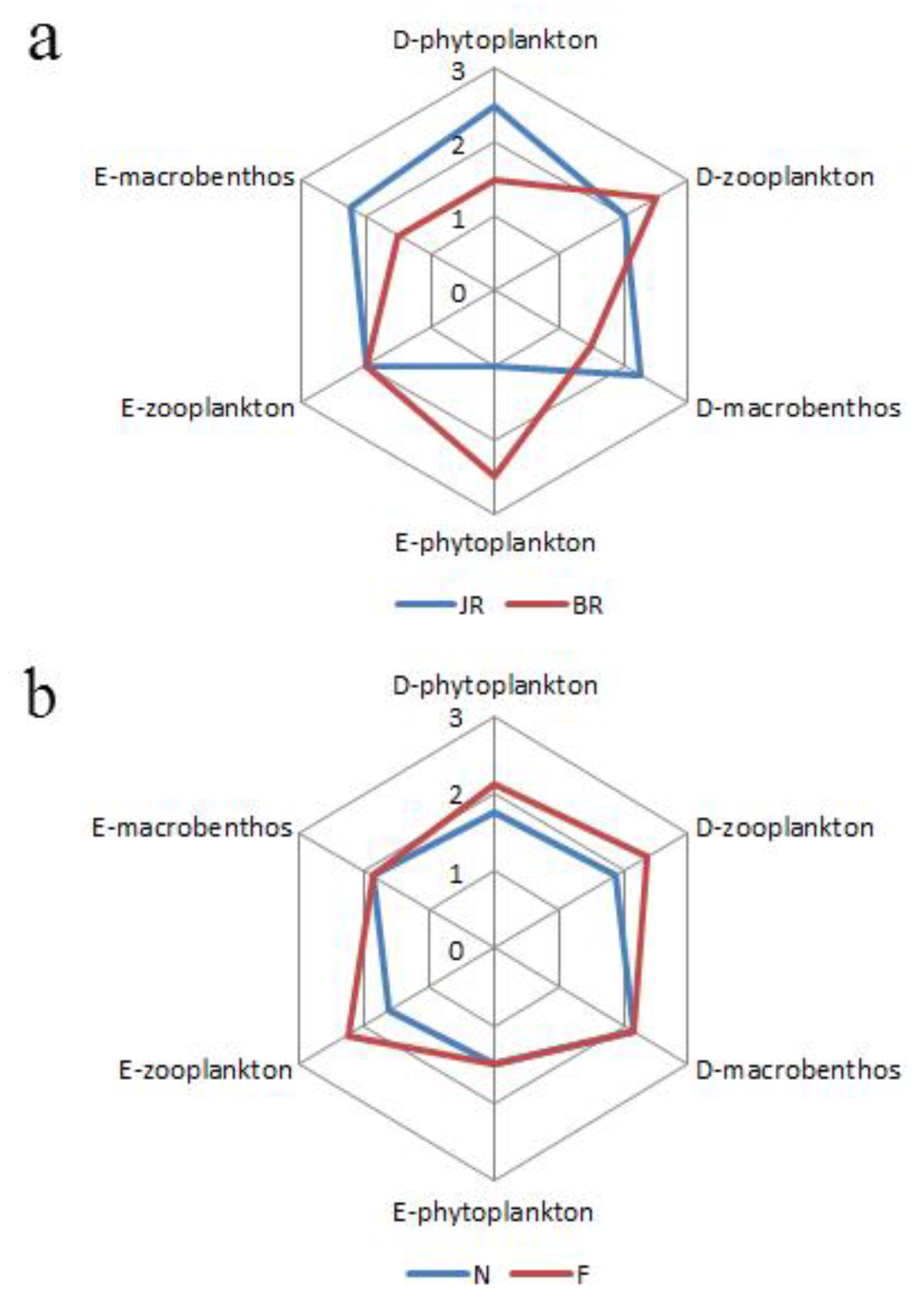
3.2.1. Community Structure and Assessment Results
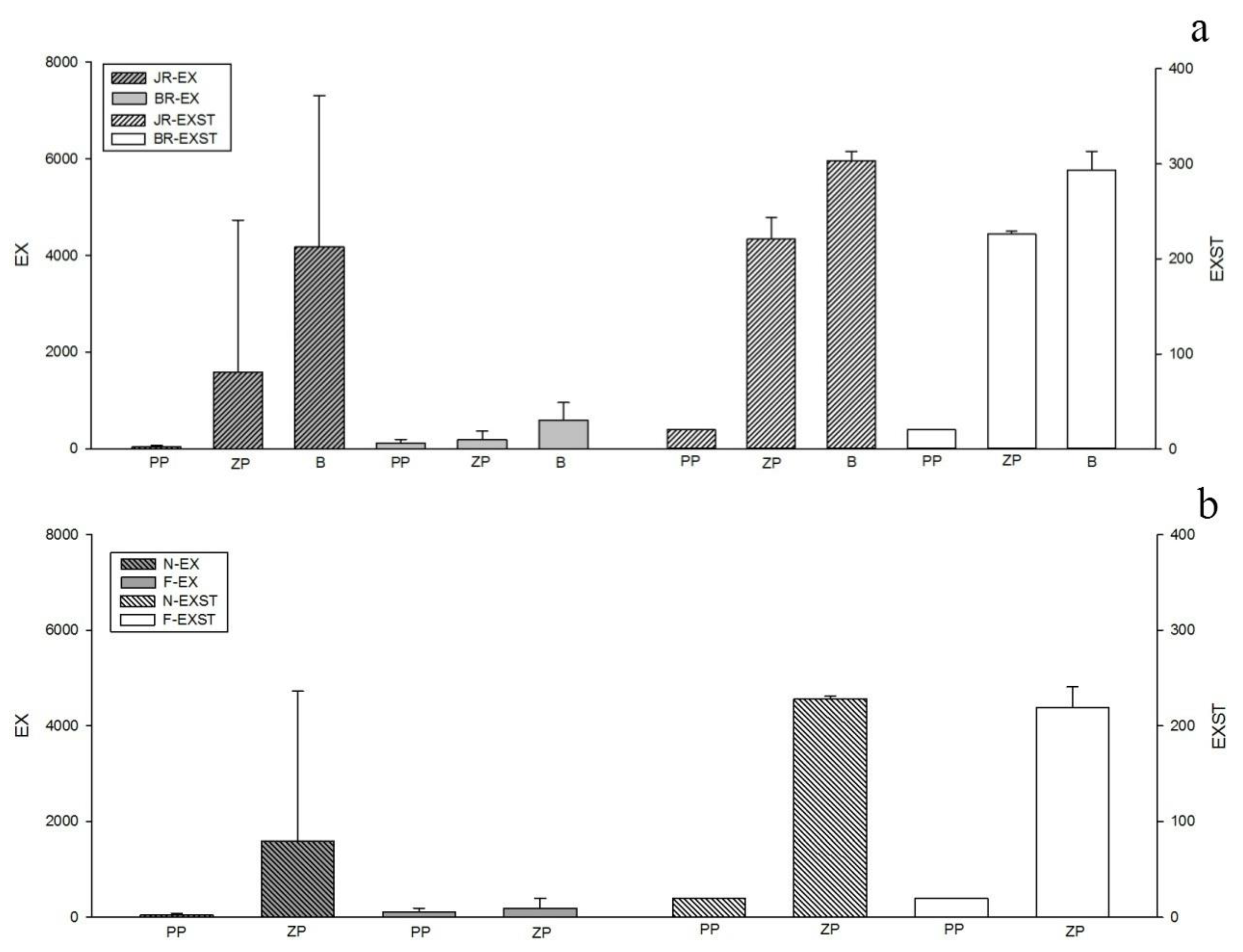
3.2.2. Thermodynamic Structure and Assessment Results
4. Discussion
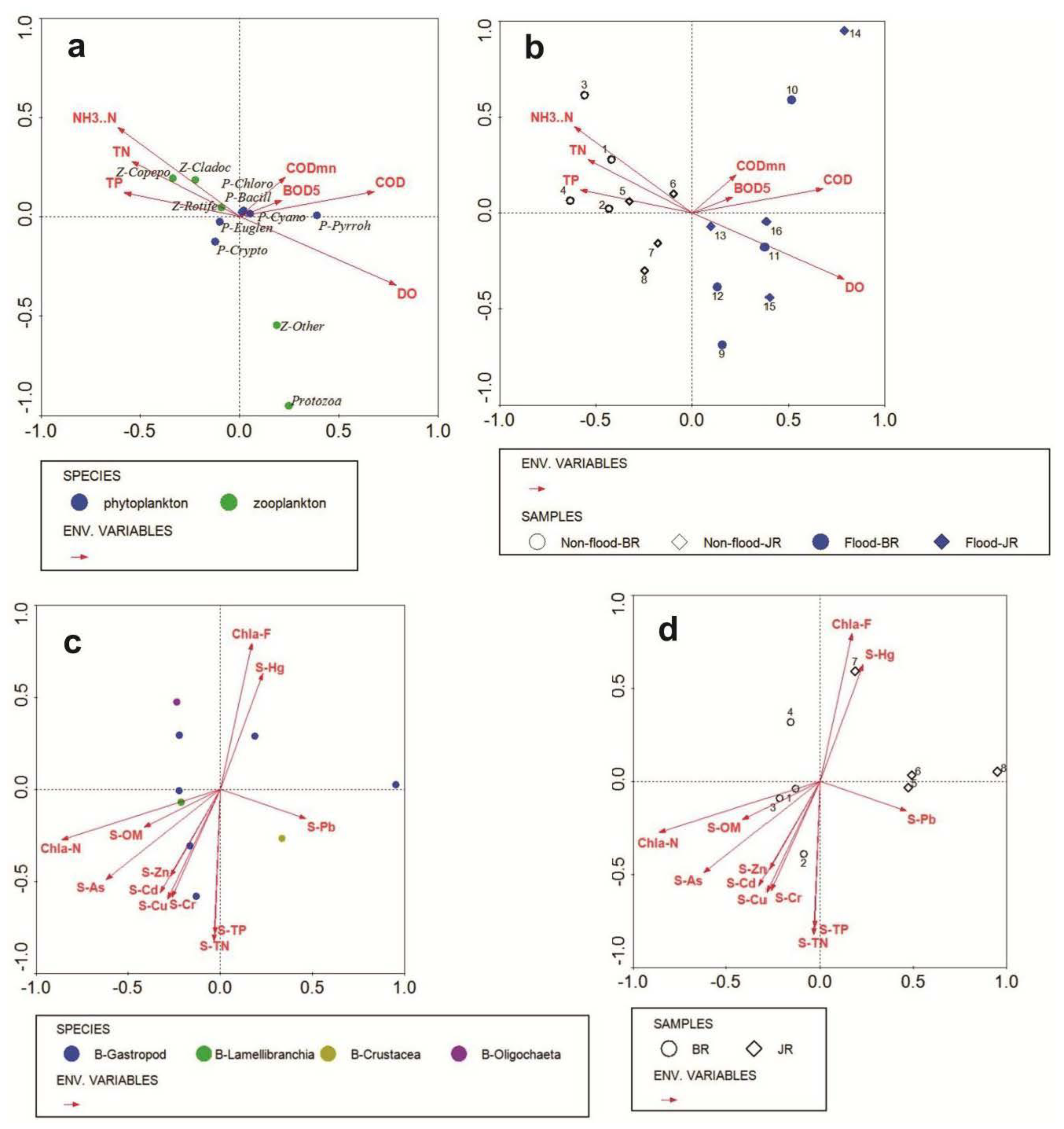
4.1. Relationship between the Environmental Module and the Ecological Community Module
4.2. Integrated Assessment Results for Spatiotemporal Changes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomson, J.R.; Taylor, M.P.; Fryirs, K.A.; Brierley, G.J. A geomorphological framework for river characterization and habitat assessment. Aquat. Conserv. 2001, 11, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Paavola, R.; Kwandrans, J.; Muotka, T. Diatoms: Unicellular surrogates for macroalgal community structure in streams? Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bere, T.; Mangadze, T.; Mwedzi, T. Variation partitioning of diatom species data matrices: Understanding the influence of multiple factors on benthic diatom communities in tropical streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidlerová, D.; Hlúbiková, D. Relationships between benthic diatom assemblages’ structure and selected environmental parameters in Slovak water reservoirs (Slovakia, Europe). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2016, 417, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, L.K.; Soininen, J. Temporal variation in community–environment relationships and stream classifications in benthic diatoms: Implications for bioassessment. Limnologica 2016, 58, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.gzepb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 7 June 2017).
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Huo, S.; Qian, W.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, J. Using multiple combined analytical techniques to characterize water extractable organic nitrogen from Lake Erhai sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.J.; Pan, C.G.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.S.; Windfeld, R.; Salvito, D.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Ying, G.G. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of emerging organic chemicals in urban rivers: Guangzhou as a case study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.guangzhou.gov.cn/ (accessed on 31 December 2015).
- Noorhosseini, S.A.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A.; Moghaddam, S.S. Public environmental awareness of water pollution from urban growth: The case of Zarjub and Goharrud Rivers in Rasht, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.C. Physicochemical conditions and properties of particles in urban runoff and rivers: Implications for runoff pollution. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, C.E.; Allan, J.D. Chapter 5—Ecology: The structure and function of riverine ecosystems. Streams 2001, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.J.; Hofmann, E.E.; Watkins, J.L.; Johnston, N.M.; Piñones, A.; Ballerini, T.; Hill, S.L.; Trathan, P.N.; Tarling, G.A.; Cavanagh, R.A.; et al. Comparison of the structure and function of Southern Ocean regional ecosystems: The Antarctic Peninsula and South Georgia. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 109–110, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Elliot, M.; Andersen, J.H.; Berg, T.; Cartsensen, J.; Halpern, B.S.; Heiskanen, A.; Korpinen, S.; Lowndes, J.S.S.; Martin, G.; et al. Overview of integrative assessment of marine systems: The ecosystem approach in practice. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, R.C.; Anthwall, A. Monitoring phytoplankton diversity in the hill stream chandrabhaga of Garhwal Himalaya. Life Sci. J. 2007, 4, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J.; Magoro, M.L.; Mwedzi, T.; Froneman, P.W.; Weyl, O.W. Variation partitioning of benthic diatom community matrices: Effects of multiple variables on benthic diatom communities in an austral temperate river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Changes in the soil microbial phospholipid fatty acid profile with depth in three soil types of paddy fields in China. Geoderma 2017, 290, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, R.; Szpakowska, B.; Świerk, D.; Domek, P.; Buxakowski, J.; Dondajewska, R.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Sajnóg, A. Influence of stormwater runoff on macroinvertebrates in a small urban river and a reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Han, L.; Gao, B.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Wan, X. Distribution, bioavailability, and potential risk assessment of the metals in tributary sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir: The impact of water impoundment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, H.; Verdelhos, T.; Baeta, A.; Linden, P.V.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Marques, J.C. Comparison of thermodynamic-oriented indicators and trait-based indices ability to track environmental changes: Response of benthic macroinvertebrates to management in a temperate estuary. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 73, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.; Chan, K.M.A.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M.; et al. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Güneralp, B.; Kreuter, U.P.; Güneralp, İ.; Filippi, A.M. Spatial and temporal changes in biodiversity and ecosystem services in the San Antonio River Basin, Texas, from 1984 to 2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 619, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.A.; Berry, P.M.; Simpson, G.; Haslett, J.R.; Blicharska, M.; Bucur, M.; Dunford, R.; Egoh, B.; Garciallorente, M.; Geamănă, N. Linkages between biodiversity attributes and ecosystem services: A systematic review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 9, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittensor, D.P.; Mora, C.; Jetz, W.; Lotze, H.K.; Ricard, D.; Berghe, E.V.; Worm, B. Global patterns and predictors of marine biodiversity across taxa. Nature 2010, 466, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Yu, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, M. Application of excel in calculation of biodiversity indices. Mar. Sci. 2012, 36, 57–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- May, R.M. Will a large complex system be stable. Nature 1972, 238, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B. Conserving biological diversity through ecosystem resilience. Conserv. Biol. 1995, 9, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U.; Iii, F.S.C.; Ewel, J.J.; Hector, A.; Inchausti, P.; Lavorel, S.; Lawton, J.H.; Lodge, D.M.; Loreau, M.; Naeem, S. Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecol. Monogr. 2005, 75, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.H.; Zou, X.Q.; Liu, X.J. The difference between exergy and biodiversity in ecosystem health assessment: A case study of Jiangsu coastal zone. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 1240–1250, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaelli, D.G.; Friedlander, A.M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: An ecosystem-level approach. In Marine Biodiversity Futures and Ecosystem Functioning: Frameworks, Methodologies and Integration; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Zou, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Zhamangulova, N.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y. Integrated ecosystem health assessment based on eco-exergy theory: A case study of the Jiangsu coastal area. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Marceau, D. Modeling complex ecological systems: An introduction. Ecol. Model. 2002, 153, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E.; Marques, J.C.; Nielsen, S.N. Integrated Environmental Management: A Transdisciplinary Approach; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 369. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, S.E. The application of ecological indicators to assess the ecological condition of a lake. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1995, 1, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyjol, Y.; Argillier, C.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Buijse, A.D.; Cardoso, A.C.; Daufresne, M.; Kernan, M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Poikane, S. Assessing the ecological status in the context of the European water framework directive: Where do we go now? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R.; Norton, B.G.; Haskell, B.D. (Eds.) Ecosystem Health: New Goals for Environmental Management; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 237–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanowicz, R.E.; Goerner, S.J.; Lietaer, B.; Gomez, R. Quantifying sustainability: Resilience, efficiency and the return of information theory. Ecol. Complex. 2009, 6, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, B.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, H. Heavy metals in water, soils and plants in riparian wetlands in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, J. Measuring biological diversity. J. Limnol. Soc. S. Afr. 2010, 29, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Liu, X.; Zou, X. An improved method for integrated ecosystem health assessments based on the structure and function of coastal ecosystems: A case study of the Jiangsu coastal area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB3838-2002. The Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, K.; Lu, W.; Cui, K. Bottom-up versus top-down effects on ciliate community composition in four eutrophic Lakes (China). Eur. J. Protistol. 2016, 53, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Ni, Z.; Xi, H.; Liao, J.; Zhu, C. Characteristics of phosphorus species identified by 31 P NMR in different trophic lake sediments from the eastern plain, China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, B. An Atlas of British Diatoms; Biopress Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 1996; p. 601. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of biodiversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Information theory in ecology. Gen. Syst. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E. Integration of Ecosystem Theories: A Pattern; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ludovisi, A.; Poletti, A. Use of thermodynamic indices as ecological indicators of the development state of lake ecosystems: 2. Exergy and specific exergy indices. Ecol. Model. 2003, 159, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E.; Ladegaard, N.; Debeljak, M.; Marques, J.C. Calculations of exergy for organisms. Ecol. Model. 2005, 185, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TerBraak, C.J.F. Canonical correspondence analysis: A new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 1986, 67, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TerBraak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a non-metric hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, V.; Caputo, L.; Ordóñez, J.; Marcé, R.; Armengol, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Huszar, V.L.M. Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean Reservoir. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, O.A.; Tippett, R.; Murphy, K.J. Seasonal changes in phytoplankton community structure in relation to physico-chemical factors in Loch Lomond, Scotland. Hydrobiologia 1997, 350, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, W.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Jin, P.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Ao, D. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kentzer, A.; Dembowska, E.; GizinSki, A.; Napiórkowski, P. Influence of the włocławek reservoir on hydrochemistry and plankton of a large, lowland river (the Lower Vistula River, Poland). Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Macrobenthic community structure and species composition in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in Jellyfish bloom. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, V.D.; Summers, J.K. Latitudinal gradients in benthic community composition in Western Atlantic Estuaries. J. Biogeogr. 1999, 26, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibler, E.E.; Ciocco, N.F. Distribution of macroinvertebrate assemblages along a saline wetland in harsh environmental conditions from Central-West Argentina. Limnologica 2011, 41, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.L.; Jin, S.F.; Tang, F.H.; Dong, J.B. Does invasion of spartinaalterniflora alter microhabitats and benthic communities of salt marshes in Yangtze River estuary? Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sui, J.; Yang, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Variation in the macrofaunal community over large temporal and spatial scales in the southern Yellow Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 173, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrabsky, J.E.; Hrbek, T.; Hand, S.C. Physical and chemical characteristics of ephemeral pond habitats in the Maracaibo Basin and llanos region of Venezuela. Hydrobiologia 1997, 362, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, A.K.; Williams, D.D. The roles of natural temporal and spatial variation versus biotic influences in shaping the physicochemical environment of intermittent ponds: A case study. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2006, 165, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, S.; Jabłońska, E. Aquatic and swamp plant communities as indicators of habitat properties of astatic water bodies in north-eastern Poland. Limnologica 2009, 39, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparecida, L.S.M.; Eduardo, R.C. Behavior of selected micro and trace elements and organic matter in sediments of a freshwater system in South-East Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 292, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Q.; Song, J.M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Li, X.G.; Zhang, Y. The distribution, enrichment and source of potential harmful elements in surface sediments of Bohai Bay, North China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.P. Metals in exposed-lawn soils from 18 urban parks and its human health implications in southern China’s largest city, Guangzhou. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, J.; Gan, H.; Guo, Y. Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in urban soils of Guangzhou, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, G.D.; Vos, R.D.; Vandecasteele, B.; Lesage, E.; Tack, F.M.G.; Verloo, M.G. Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf 2008, 77, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, G. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in wetland soils under different land uses along a 100-year chronosequence of reclamation in a Chinese estuary. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. River ecosystem assessment and application in ecological restorations: A mathematical approach based on evaluating its structure and function. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 76, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bark, R.H.; Colloff, M.J.; Macdonald, D.H.; Pollino, C.A.; Jackson, S.; Crossman, N.D. Integrated valuation of ecosystem services obtained from restoring water to the environment in a major regulated river basin. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Chakrabarty, M.; Rakshit, N.; Mukherjee, J.; Ray, S. Indicators and assessment of ecosystem health of Bakreswar Reservoir, India: An approach through network analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgen, S.; Sarıkaya, İ. Exergy for environment, ecology and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1115–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E. A New Ecology: Systems Perspective. A New Ecology: Systems Perspective; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, M.S.; Callisto, M.; Marques, J.C. Compliance of secondary production and eco-exergy as indicators of benthic macroinvertebrates assemblages’ response to canopy cover conditions in neotropical headwater streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molozzi, J.; Salas, F.; Callisto, M.; Marques, J.C. Thermodynamic oriented ecological indicators: Application of eco-exergy and specific eco-exergy in capturing environmental changes between disturbed and non-disturbed tropical reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austoni, M.; Giordani, G.; Viaroli, P.; Zaldívar, J.M. Application of specific exergy to macrophytes as an integrated index of environmental quality for coastal lagoons. Ecol. Indic. 2007, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovisi, A.; Jørgensen, S.E. Comparison of exergy found by a classical thermodynamic approach and by the use of the information stored in the genome. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1897–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabwe, A.; Yang, J.R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Community assembly processes underlying phytoplankton and bacterioplankton across a hydrologic change in a human-impacted River. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, B.J. Global dispersal of free-living microbial eukaryote species. Science 2002, 296, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowe, A.E.F.; Pahlow, M.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Follows, M.; Oschlies, A. Top-down control of marine phytoplankton diversity in a global ecosystem model. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 101, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Biodiversity | Indexes | Calculation Formulas | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance | Species abundance | S | S = Number of species in the community |
| Diversity | Shannon Wiener Index (base e) | = | N = Number of individuals in the community |
| Simpson Index | , | ||
| Richness | Margalef Index | ||
| Evenness | Pielou’s Index | J = H_/lnS |
| Investigation Station and Value | JR1 | JR2 | JR3 | JR4 | BR1 | BR2 | BR3 | BR4 | Average Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM (g/kg) | 5.00 | 43.80 | 6.50 | 33.80 | 10.20 | 10.10 | 6.20 | 5.50 | 15.1 |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.36 | 0.91 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.62 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.44 |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.34 | 1.05 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.43 |
| Species | Species Number | Abundance | Dominant Species | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Mean | Non-Flood | Flood | Non-Flood | Flood | ||
| Phytoplankton | 185 | 7.53–566.70 × 105 ind./L | 129.82 × 105 ind./L | Low | High | chlorophyta | cyanobacteria |
| Zooplankton | 66 | 0.90–377.60 ind./L | 42.64 ind./L | High | low | Rotifer | Rotifer |
| Benthos | 11 | 3.33–96.67 ind./m2 | 33.00 ind./m2 | -- | gastropods | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yin, K. Relationship between the Main Communities and Environments of an Urban River and Reservoir: Considering Integrated Structural and Functional Assessments of Ecosystems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102302
Tang D, Liu X, Wang X, Yin K. Relationship between the Main Communities and Environments of an Urban River and Reservoir: Considering Integrated Structural and Functional Assessments of Ecosystems. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(10):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102302
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Dehao, Xingjian Liu, Xutao Wang, and Kedong Yin. 2018. "Relationship between the Main Communities and Environments of an Urban River and Reservoir: Considering Integrated Structural and Functional Assessments of Ecosystems" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 10: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102302
APA StyleTang, D., Liu, X., Wang, X., & Yin, K. (2018). Relationship between the Main Communities and Environments of an Urban River and Reservoir: Considering Integrated Structural and Functional Assessments of Ecosystems. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102302