Modeling the Effect of Physical Activity on Obesity in China: Evidence from the Longitudinal China Health and Nutrition Study 1989–2011
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Results of Granger Causality Test for Children
3.2. Results of Longitudinal Regressions for Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarma, S.; Zaric, G.S.; Campbell, M.K.; Gilliland, J. The effect of physical activity on adult obesity: Evidence from the Canadian NPHS panel. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2014, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littman, A.J.; Kristal, A.R.; White, E. Effects of physical activity intensity, frequency, and activity type on 10-y weight change in middle-aged men and women. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon-Larsen, P.; Hou, N.; Sidney, S.; Sternfeld, B.; Lewis, C.E.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Popkin, B.M. Fifteen-year longitudinal trends in walking patterns and their impact on weight change. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankinson, A.L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Bouchard, C.; Carnethon, M.; Lewis, C.E.; Schreiner, P.J.; Liu, K.; Sidney, S. Maintaining a high physical activity level over 20 years and weight gain. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2010, 304, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekelund, U.; Besson, H.; Luan, J.; May, A.M.; Sharp, S.J.; Brage, S.; Travier, N.; Agudo, A.; Slimani, N.; Rinaldi, S. Physical activity and gain in abdominal adiposity and body weight: Prospective cohort study in 288,498 men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.T. Maintaining vigorous activity attenuates 7-yr weight gain in 8340 runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Summerbell, C.D.; Douthwaite, W.; Whittaker, V.; Ells, L.J.; Hillier, F.; Smith, S.; Kelly, S.; Edmunds, L.D.; Macdonald, I. The association between diet and physical activity and subsequent excess weight gain and obesity assessed at 5 years of age or older: A systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, S1–S92. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Z.; Baker, D.W. Changes in weight among a nationally representative cohort of adults aged 51–61, 1992–2000. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2004, 27, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, L.; Schnohr, P.; Sørensen, T.I.A. Longitudinal study of the long-term relation between physical activity and obesity in adults. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 28, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dencker, M.; Thorsson, O.; Karlsson, M.K.; Lindén, C.; Eiberg, S.; Wollmer, P.; Andersen, L.B. Daily physical activity related to body fat in children aged 8–11 years. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ness, A.R.; Leary, S.D.; Mattocks, C.; Blair, S.N.; Reilly, J.J.; Wells, J.; Ingle, S.; Tilling, K.; Smith, G.D.; Riddoch, C. Objectively measured physical activity and fat mass in a large cohort of children. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Colley, R.C.; Saunders, T.J.; Healy, G.N.; Owen, N. Physiological and health implications of a sedentary lifestyle. Appl. Phys. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 35, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Pavon, D.; Kelly, J.; Reilly, J.J. Associations between objectively measured habitual physical activity and adiposity in children and adolescents: Systematic review. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010, 5, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komlos, J.; Smith, P.K.; Bogin, B. Obesity and the rate of time preference: Is there a connection? J. Biosoc. Sci. 2004, 36, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.K.; Bogin, B.; Bishai, D. Are time preference and body mass index associated? Evidence from the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2005, 3, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.F. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults—Study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2002, 15, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.-Y.; Grossman, M.; Saffer, H. An economic analysis of adult obesity: Results from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. J. Health Econ. 2004, 23, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T. Socioeconomic determinants of obesity and hypertension at the county level in China. Math. Popul. Stud. 2016, 23, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J.M. Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nickell, S. Biases in dynamic models with fixed effects. Econometrica 1981, 49, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, M.; Bond, S. Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1991, 58, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, M.; Bover, O. Another look at the instrumental variable estimation of error-components models. J. Econom. 1995, 68, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltagi, B.H. Econometric Analysis of Panel Data; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-Spectral Methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, E.-I.; Hurlin, C. Testing for Granger Non-causality in Heterogeneous Panels. Econ. Model. 2012, 29, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godley, J.; McLaren, L. Socioeconomic status and body mass index in Canada: Exploring measures and mechanisms. Can. Rev. Sociol. 2010, 47, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, L.; Auld, M.C.; Godley, J.; Still, D.; Gauvin, L. Examining the association between socioeconomic position and body mass index in 1978 and 2005 among Canadian working-age women and men. Int. J. Public Health 2010, 55, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, H.; Delhumeau, C.; Beer-Borst, S.; Golay, A.; Costanza, M.C.; Morabia, A. Converging prevalences of obesity across educational groups in Switzerland. Obesity 2006, 14, 2080–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, A.M.; Mellecker, R.R. Physical activity and obese children. J. Sport Health Sci. 2012, 1, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareham, N.J.; van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Ekelund, U. Physical activity and obesity prevention: A review of the current evidence. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
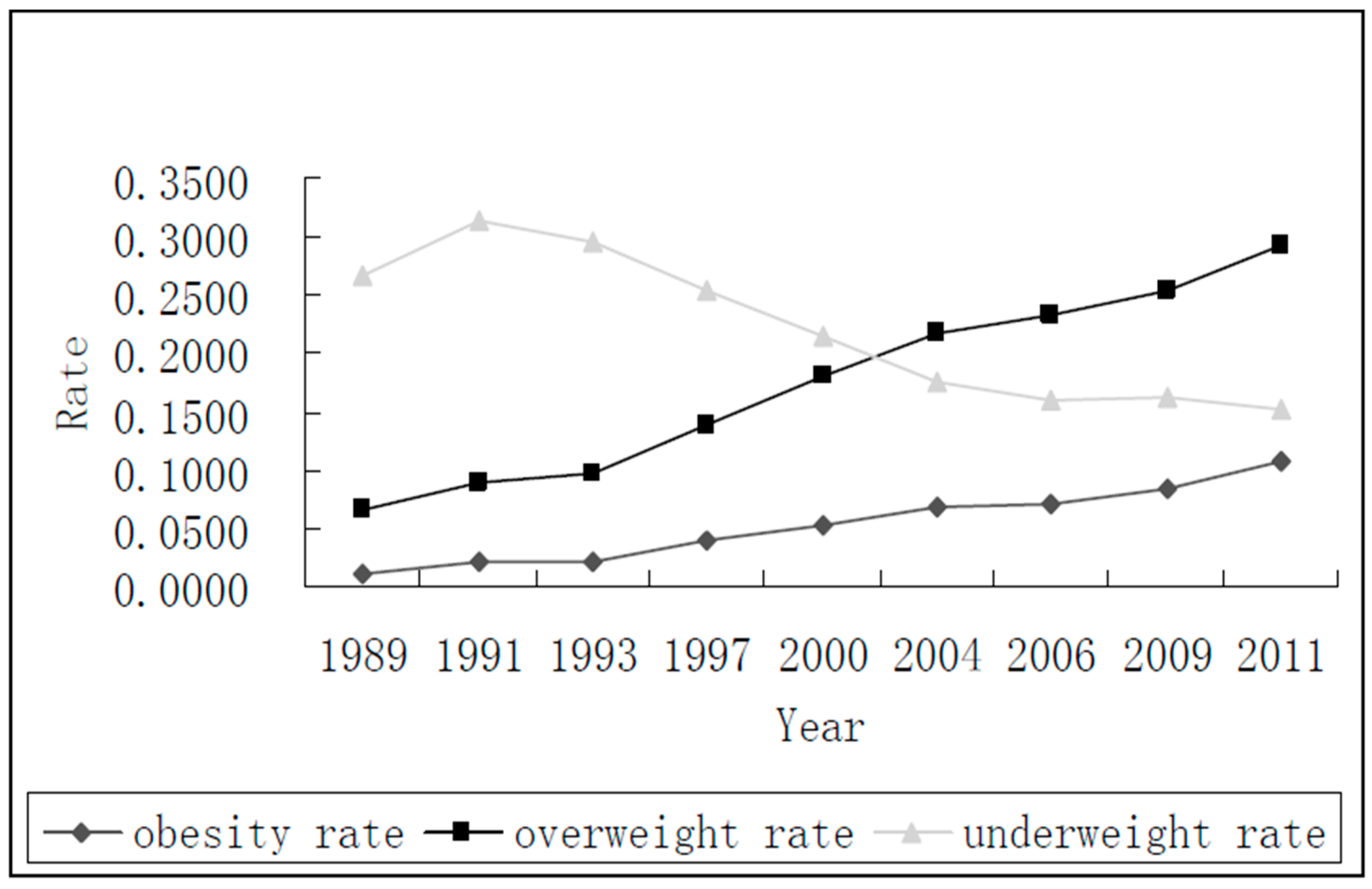
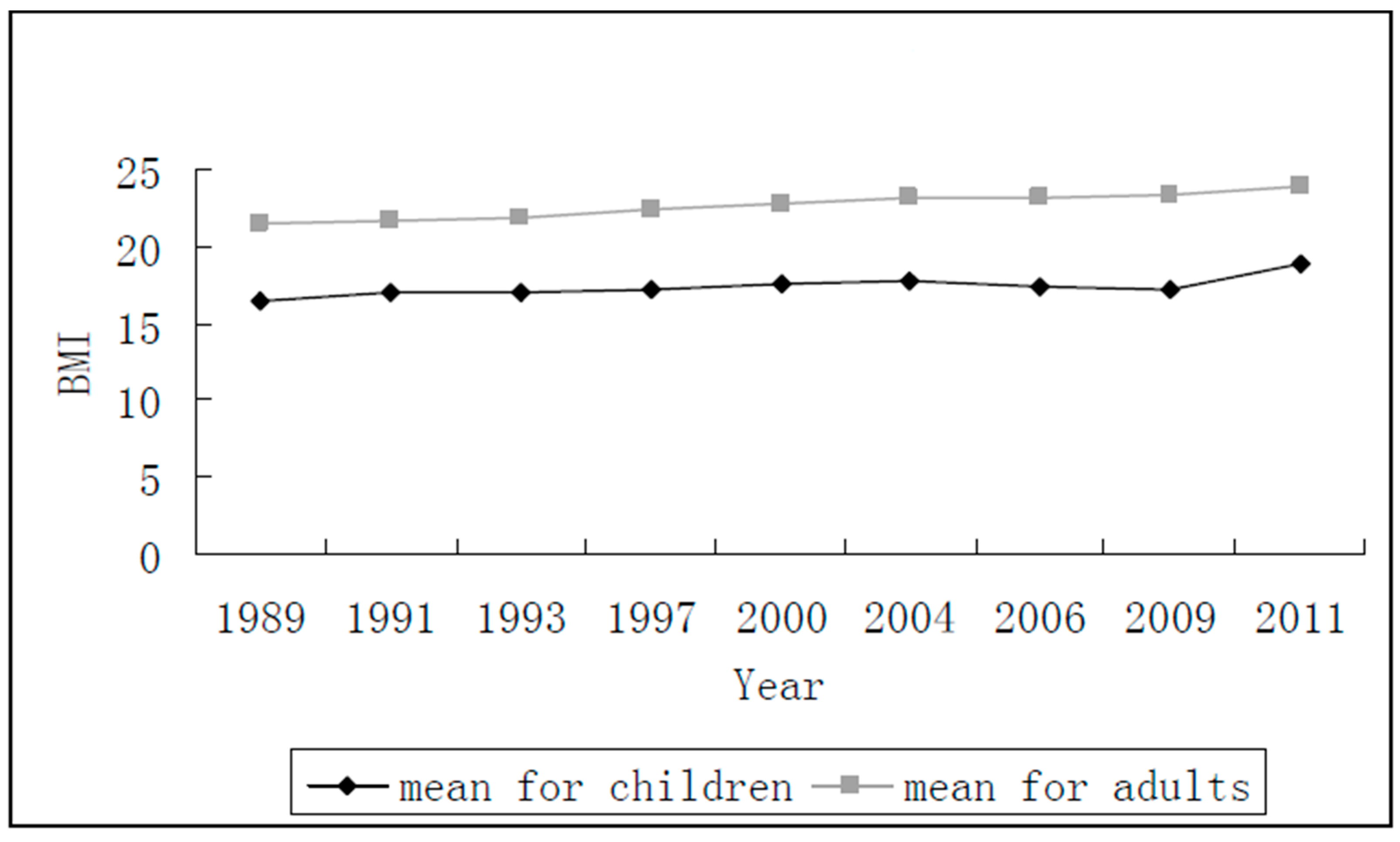
| Year | Walking (min) | PA in School (h) | Participating in PA (0/1) | PA Before or after School (min) | Watching TV (min) | Reading or Writing (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | 30.02 | 3.75 | 0.07 | 405.55 | 451.07 | |
| 2000 | 27.17 | 3.04 | 0.34 | 387.41 | 210.38 | |
| 2004 | 37.60 | 3.76 | 0.35 | 54.85 | ||
| 2006 | 39.09 | 5.97 | 0.34 | 50.81 | ||
| 2009 | 37.72 | 5.53 | 0.37 | 52.22 | ||
| 2011 | 40.86 | 6.43 | 0.34 | 58.20 |
| Year | Education | Household Income | PA | Age | Urban/Rural | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 6.81 | 4243.57 | 31.46 | 0.69 | 0.51 | |
| 1991 | 5.22 | 4411.37 | 41.18 | 0.67 | 0.51 | |
| 1993 | 6.03 | 6174.58 | 42.09 | 0.69 | 0.51 | |
| 1997 | 6.23 | 11,754.65 | 890.99 | 43.58 | 0.65 | 0.50 |
| 2000 | 7.54 | 14,180.95 | 811.01 | 44.99 | 0.66 | 0.51 |
| 2004 | 8.71 | 18,288.92 | 1050.15 | 48.02 | 0.65 | 0.51 |
| 2006 | 8.58 | 21,801.42 | 996.72 | 49.27 | 0.66 | 0.52 |
| 2009 | 8.85 | 35,466.88 | 932.12 | 50.01 | 0.67 | 0.51 |
| 2011 | 9.09 | 44,186.12 | 939.48 | 51.68 | 0.66 | 0.52 |
| Null Hypothesis: | F-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|
| ‘Participating in PA’ does not cause BMI | 8.5446 *** | 0.0035 |
| BMI does not cause ‘Participating in PA’ | 1.9653 | 0.161 |
| ‘PA in school’ does not cause BMI | 2.1007 | 0.1473 |
| BMI does not cause ‘PA in school’ | 0.1818 | 0.6699 |
| ‘PA before or after school’ does not cause BMI | 9.7411 *** | 0.002 |
| BMI does not cause ‘PA before or after school’ | 2.4027 | 0.1225 |
| ‘Reading or writing’ does not cause BMI | 0.9261 | 0.3363 |
| BMI does not cause ‘Reading or writing’ | 0.1201 | 0.7291 |
| ‘Watching TV’ does not cause BMI | 0.4782 | 0.4894 |
| BMI does not cause ‘Watching TV’ | 7.9869 *** | 0.0048 |
| ‘Walking from home to school’ does not cause BMI | 3.5197 ** | 0.0298 |
| BMI does not cause ‘Walking from home to school’ | 0.1766 | 0.8382 |
| Static Fixed Effects Regression | Static Random Effects Regression | Dynamic Panel Regression without the Lagged PA | Dynamic Panel Regression with Equation (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban/Rural | −0.01633 | −0.06740 | 4.27214 *** | 5.40653 *** |
| Gender | 0.12796 | 0.06986 | 10.44104 *** | 9.94068 *** |
| Education | 0.00498 | 0.04019 *** | 0.00034 | −0.00976 |
| Household income (1000 Yuan) | 0.00057 | 0.00466 *** | 0.00032 | 0.00198 ** |
| Age | 0.10589 *** | 0.05322 *** | 0.03818 *** | 0.03493 *** |
| PA | −0.00002 | −0.00005 *** | −0.00006 *** | −0.00018 ** |
| BMI(t−1) | 0.46047 *** | 0.38019 *** | ||
| PA(t−1) | −0.00034 ** | |||
| PA(t−2) | 0.00005 | |||
| Constant | 18.160 *** | 19.710 *** | −12.149 *** | −10.930 ** |
| Sigma_u | 3.437 | 2.815 | ||
| Sigma_e | 2.001 | 2.001 | ||
| Test of individual effects | F = 5.77 *** | χ2 = 15,806.56 *** | ||
| Wald test for all variables | F = 305.96 *** | χ2 = 1218.46 *** | χ2 = 853.72 *** | χ2 = 734.79 *** |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T. Modeling the Effect of Physical Activity on Obesity in China: Evidence from the Longitudinal China Health and Nutrition Study 1989–2011. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080844
Zhang T. Modeling the Effect of Physical Activity on Obesity in China: Evidence from the Longitudinal China Health and Nutrition Study 1989–2011. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(8):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080844
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao. 2017. "Modeling the Effect of Physical Activity on Obesity in China: Evidence from the Longitudinal China Health and Nutrition Study 1989–2011" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 8: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080844
APA StyleZhang, T. (2017). Modeling the Effect of Physical Activity on Obesity in China: Evidence from the Longitudinal China Health and Nutrition Study 1989–2011. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080844





