Optimization of the Use of His6-OPH-Based Enzymatic Biocatalysts for the Destruction of Chlorpyrifos in Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation for Analysis of Enzyme Samples and Enzyme Polyelectrolyte Complexes
2.3. Immobilization Technique Processing of Mineral Carrier with Non-Equilibrium Low Temperature Plasma
2.4. Preparation of Soil and Its Treatment with Enzymatic Preprationss
2.5. Determination of Chlorpyrifos Decomposition in Soil Samples
2.6. Assessment of Soil Samples Toxicity Using Photobacteria
2.7. Statistical Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. The Choice of Conditions and Sequence of Operations to Increase the Efficiency of Applying His6-OPH-Based Enzyme Biocatalysts for Chlorpyrifos Degradation in Soil
3.2. Choice of the Form of the His6-OPH-Based Biocatalysts for Introduction into Soils for Destroying Chlorpyrifos
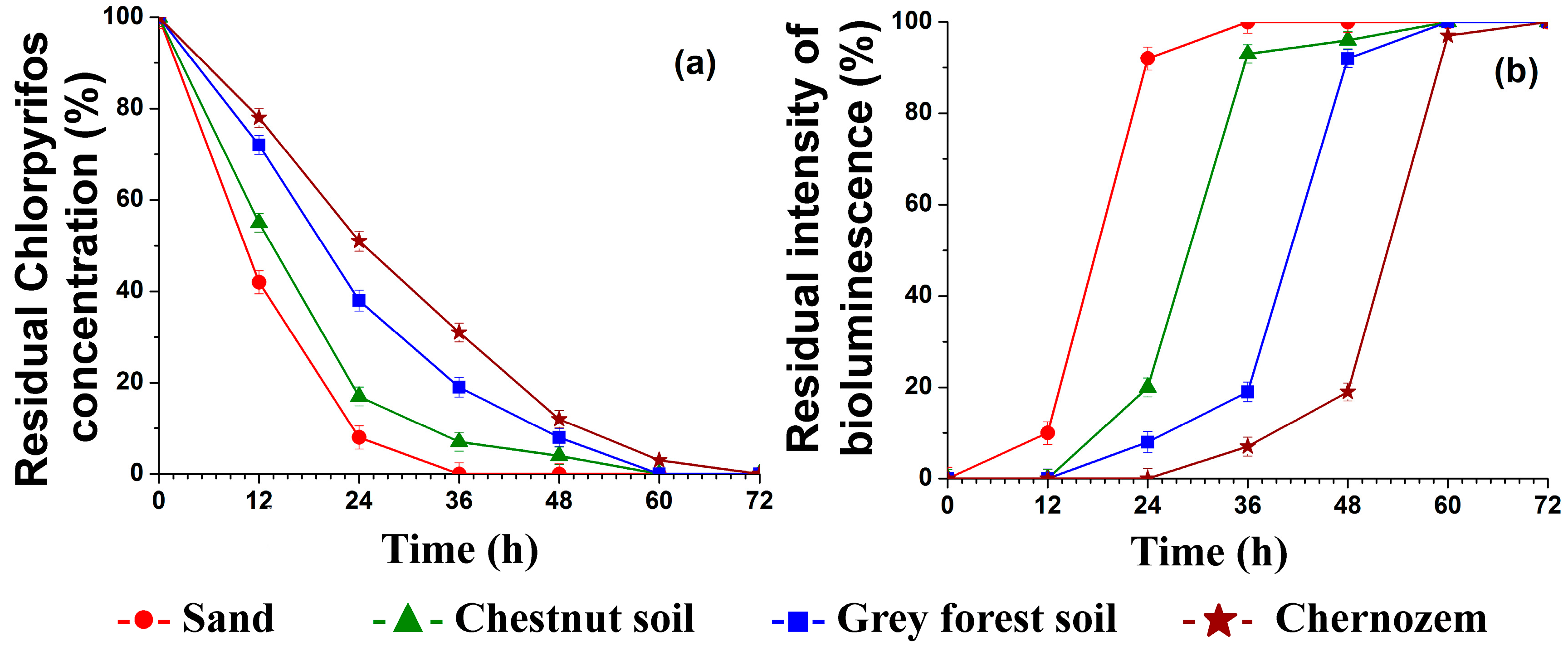
3.3. The Chlorpyrifos Hydrolysis in Different Types of Soil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomlinson, I. Doubling food production to feed the 9 billion: A critical perspective on a key discourse of food security in the UK. J. Rural Stud. 2013, 29, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, J. Food security in the face of salinity, drought, climate change, and population growth. In Halophytes for Food Security in Dry Lands; Khan, M.A., Ozturk, M., Eds.; Academic Press, Amazon Digital Services LLC: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Zhou, X.; Wan, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, W. Land use changes to cash crop plantations: Crop types, multilevel determinants and policy implications. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, K.M.; Curran, L.M.; Ratnasari, D.; Pittman, A.M.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Asner, G.P.; Trigg, S.N.; Gaveau, D.A.; Lawrence, D.; Rodrigues, H.O. Committed carbon emissions, deforestation, and community land conversion from oil palm plantation expansion in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7559–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrends, A.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Ziegler, A.D.; Fox, J.M.; Chen, H.; Su, Y.; Xu, J. Current trends of rubber plantation expansion may threaten biodiversity and livelihoods. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 34, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, T.; Wang, C. Loss of labile organic carbon from subsoil due to land-use changes in subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engindeniz, S.; Cosar, G.O. An economic comparison of pesticide applications for processing and table tomatoes: A case study for Turkey. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2013, 53, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uqab, B.; Mudasir, S.; Nazir, R. Review on bioremediation of pesticides. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2016, 7, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Antle, J.M. Pesticide Policy, Production Risk, and Producer Welfare: An Econometric Approach to Applied Welfare Economics; RFF Press, Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, S.E.; Lei, Z.; Zilberman, D. The economics of pesticides and pest control. IRERE 2007, 1, 271–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.; Shaike, J. Chlorpyrifos: Pollution and remediation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.R.; Williams, W.M.; Mackay, D.; Purdy, J.; Giddings, J.M.; Giesy, J.P. Properties and uses of chlorpyrifos in the United States. In Ecological Risk Assessment for Chlorpyrifos in Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems in the United States; Giesy, J., Solomon, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, E. The Current Status of the Date Palm Sector in the Gaza Strip, Palestine; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2017; p. 156. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, B.S.; Halimah, M.; Tan, Y.A.; Tayeb, M.A. Dissipation of chlorpyrifos in a Malaysian agricultural soil: A comparison between a field experiment and simulation by the VARLEACH and PERSIST models. Sains Malays. 2017, 46, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Xu, P.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J. Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: Applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medo, J.; Maková, J.; Kovácsová, S.; Majerčíková, K.; Javoreková, S. Effect of Dursban 480 EC (chlorpyrifos) and Talstar 10 EC (bifenthrin) on the physiological and genetic diversity of microorganisms in soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2015, 50, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Notario, D.P.J.; Capowiez, Y.; Mazzia, C.; Rault, M. Soil enzyme dynamics in chlorpyrifos-treated soils under the influence of earthworms. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 612, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, J.; Harsh, N.S.K.; Palni, L.M.S.; Pande, V. Effect of repeated application of chlorpyrifos on fungal population of pine forest soil. Indian For. 2016, 142, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Jallow, M.F.; Awadh, D.G.; Albaho, M.S.; Devi, V.Y.; Ahmad, N. Monitoring of pesticide residues in commonly used fruits and vegetables in Kuwait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinasi, L.; Leon, M.E. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma and occupational exposure to agricultural pesticide chemical groups and active ingredients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4449–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z. Health risk characterization of maximum legal exposures for persistent organic pollutant (POP) pesticides in residential soil: An analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, A.A.; Li, Z. Scope of the worldwide effort to regulate pesticide contamination in surface soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 420–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafalou, S.; Abdollahi, M. Pesticides and human chronic diseases: Evidences, mechanisms, and perspectives. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 268, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, J.F.; Geraghty, E.M.; Tancredi, D.J.; Delwiche, L.D.; Schmidt, R.J.; Ritz, B.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Neurodevelopmental disorders and prenatal residential proximity to agricultural pesticides: The Charge study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Ou, C.; Huang, C. Effect of micro-remediation on enzymes activity and available nutrients in chlorpyrifos-polluted soils. Agric. For. Fish. 2017, 6, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Orts, A.; Cabrera, S.; Gómez, I.; Parrado, J.; Rodriguez-Morgado, B.; Tejada, M. Use of okara in the bioremediation of chlorpyrifos in soil: Effects on soil biochemical properties. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 121, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Walker, A.; Morgan, J.A.W.; Wright, D.J. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by Enterobacter strain B-14 and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4855–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, K.; Joshi, N. Effect of chlorpyrifos on soil microbial health. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Castelo-Grande, T.; Augusto, P.A.; Monteiro, P.; Estevez, A.M.; Barbosa, D. Remediation of soils contaminated with pesticides: A review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 438–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, E.; Villaverde, J. Advanced technologies for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 576–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, N.; Peñuela, G. Simultaneous degradation of the pesticides methyl parathion and chlorpyrifos by an isolated bacterial consortium from a contaminated site. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailan, S.; Gupta, D.; Apte, S.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Saha, P. Degradation of organophosphate insecticide by a novel Bacillus aryabhattai strain SanPS1, isolated from soil of agricultural field in Burdwan, West Bengal, India. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 103, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceno, G.; Schalchli, H.; Mutis, A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Palma, G.; Tortella, G.R.; Diez, M.C. Use of pure and mixed culture of diazinon-degrading Streptomyces to remove other organophosphorus pesticides. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 114, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, K.L.; Belden, J.B.; Zhao, S.; Coats, J.R. Phytoremediation of pesticide wastes in soil. Z. Naturforsch. C 2006, 61, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bert, V.; Seuntjens, P.; Dejonghe, W.; Lacherez, S.; Thuy, H.T.T.; Vandecasteele, B. Phytoremediation as a management option for contaminated sediments in tidal marshes, flood control areas and dredged sediment landfill sites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.; Pradhan, S.; Saha, M.; Sanyal, N. Impact of pesticides on soil microbiological parameters and possible bioremediation strategies. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanekar, P.P.; Bhadbhade, B.J.; Deshpande, N.M.; Sarnaik, S.S. Biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2004, B70, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, V.; Lovatelli, A. Aquaculture in Desert and Arid Lands: Development Constraints and Opportunities; FAO Technical Workshop (Hermosillo, Mexico, 2010); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Svintsov, I.P. Development of sandy and stony deserts. In Agricultural Land Improvement: Ameloration and Reclamation; Maslov, B.S., Ed.; EOLSS: Paris, France, 2009; Volume 1, p. 448. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Dong, J.; Ai, S.; Qiu, Y.; Han, R. Electro-enzymatic degradation of chlorpyrifos by immobilized hemoglobin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, B.; Ge, S.; Hu, M. Assessment of the ecological security of immobilized enzyme remediation process with biological indicators of soil health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5773–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirotkina, M.; Lyagin, I.; Efremenko, E. Hydrolysis of organophosphorus pesticides in soil: New opportunities with ecocompatible immobilized His6-OPH. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 68, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslova, O.V.; Stepanov, N.A.; Grigoryeva, A.I.; Bruyako, M.G.; Efremenko, E.N. New effective His6-OPH-containing mineral carriers pretreated by low-temperature plasma for destruction of organophosphates in different types of soil. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 8, 27317–27333. [Google Scholar]
- Eibes, G.; Arca-Ramos, A.; Feijoo, G.; Lema, J.M.; Moreira, M.T. Enzymatic technologies for remediation of hydrophobic organic pollutants in soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8815–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyagin, I.V.; Andrianova, M.S.; Efremenko, E.N. Extensive hydrolysis of phosphonates as unexpected behavior of the known His6-organophosphorus hydrolase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5829–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremenko, E.; Lyagin, I.; Gudkov, D.; Varfolomeyev, S. Immobilized biocatalysts for detoxification of neurotoxic organophosphorous compounds. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2007, 25, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votchitseva, Y.A.; Efremenko, E.N.; Aliev, T.K.; Varfolomeyev, S.D. Properties of hexahistidine-tagged organophosphate hydrolase. Biochemistry 2006, 71, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyagin, I.V.; Efremenko, E.N.; Kabanov, A.V. Catalytic characteristics of enzyme-polyelectrolyte complexes based on hexahistidine-containing organophosphorus hydrolase. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 2014, 69, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.N.; Lyagin, I.V.; Klyachko, N.L.; Bronich, T.; Zavyalova, N.V.; Jiang, Y.; Kabanov, A.V. A simple and highly effective catalytic nanozyme scavenger for organophosphorus neurotoxins. J. Control. Release 2017, 247, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyagin, I.V.; Efremenko, E.N. Biomolecular engineering of biocatalysts hydrolyzing neurotoxic organophosphates. Biochimie 2018, 144, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremenko, E.N.; Votchitseva, J.A.; Aliev, T.K.; Varfolomeev, S.D. Recombinant Plasmid DNA pTES-His-OPH and Producer of Oligohistidine Containing Organophosphate Hydrolase. Russia Patent 2,255,975, 10 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Efremenko, E.; Votchitseva, Y.; Plieva, F.; Galaev, I.; Mattiasson, B. Purification of His6-Organophosphate hydrolase using monolithic supermacroporous polyacrylamide cryogels developed for immobilized metal affinity chromatography. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 70, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pevgov, V.G. Method of Plasmachemical Treatment of Raw Stock of Organic or Vegetable Origin and Device to This End. Russia Patent 2,448,768 C2, 27 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Efremenko, E.N.; Sirotkina, M.S.; Lyagin, I.V. Method for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Organophosphorus Soil Compounds. Russia Patent 2,451,077, 20 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Skoog, D.A.; West, D.M.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, 9th ed.; Brooks/Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2014; p. 1090. [Google Scholar]
- Frische, T.; Höper, H. Soil microbial parameters and luminescent bacteria assays as indicators for in situ bioremediation of TNT-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.N.; Maslova, O.V.; Kholstov, A.V.; Senko, O.V.; Ismailov, A.D. Biosensitive element in the form of immobilized luminescent photobacteria for detecting ecotoxicants in aqueous flow-through systems. Luminescence 2016, 31, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangira, C.; Loeppert, R.H.; Moore, T.J.; Hons, F.M.; Shahandeh, H. Relative effectiveness of CaCO3 and Ca(OH)2 in minimizing metals solubility in contaminated sediment. J. Soils Sediment 2017, 17, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, B.K.; Lambricht, P.; Laurent, G.; Maldague, P.; Wagner, R.; Tulkens, P.M. Mechanism of protection afforded by polyaspartic acid against gentamicin-induced phospholipidosis. II. Comparative in vitro and in vivo studies with poly-l-aspartic, poly-l-glutamic and poly-d-glutamic acids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 255, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neumann, G.; Bott, S.; Ohler, M.A.; Mock, H.P.; Lippmann, R.; Grosch, R.; Smalla, K. Root exudation and root development of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. cv. Tizian) as affected by different soils. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, G.W. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 131, p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Mansee, A.H.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A. Detoxification of the organophosphate nerve agent coumaphosusing organophosphorus hydrolase immobilized on cellulose materials. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 32, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Tarkalson, D.D.; Lehrsch, G.A. Zeolite soil application method affects inorganic nitrogen, moisture, and corn growth. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dercová, K.; Sejáková, Z.; Skokanová, M.; Barančíková, G.; Makovníková, J. Potential use of organomineral complex (OMC) for bioremediation of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2006, 58, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, D.; Li, G. Porous biocarrier-enhanced biodegradation of crude oil contaminated soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyako, M.G.; Glukhoedov, V.A.; Kravtsova, D.; Smirnov, V.A.; Ushkov, V.A. Plasma processing in industry of building materials. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1040, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyako, M.; Grigorieva, L.; Grigorieva, A.; Ivanova, I. Treatment of natural zeolites for increasing the sorption capacity. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 871, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Vissokov, G.P.; Jang, B.W.L. Catalyst preparation using plasma technologies. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, N.; Guo, X.; Qiao, C. Cloning of mpd gene from a chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium and use of this strain in bioremediation of contaminated soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 265, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, C.V.; Kumar, M.; Khanna, S. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos in soil by enriched cultures. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipnis, E.; Sawa, T.; Wiener-Kronish, J. Targeting mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2006, 36, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hota, S.; Hirji, Z.; Stockton, K.; Lemieux, C.; Dedier, H.; Wolfaardt, G.; Gardam, M.A. Outbreak of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization and infection secondary to imperfect intensive care unit room design. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Hafeez, F.; Ali, A.; Farooq, M.; Latif, M.; Saleem, M.; Ghaffar, A. Date palm white scale (Parlatoria blanchardii T): A new threat to date industry in Pakistan. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2014, 2, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
| pH Controlling Agent | Dose Introduced into Soil (g/kg soil) | Soil pH after Introduction of Agent | Residual Activity of the Enzyme upon Introduction into the Soil (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In 15 min | In 48 h | In 1 h | In 48 h | ||
| Control (no agent) | - | 7.4 ± 0.02 | 7.4 ± 0.03 | 84 ± 2 | 51 ± 2 |
| Hydrated calcitic lime | 22 ± 1 | 8.4 ± 0.03 | 8.0 ± 0.03 | 93 ± 2 | 60 ± 2 |
| Dolomite powder | 64 ± 1 | 8.2 ± 0.05 | 8.1 ± 0.03 | 91 ± 2 | 50 ± 2 |
| Birch ash | 120 ± 3 | 8.1 ± 0.02 | 8.0 ± 0.02 | 91 ± 2 | 45 ± 2 |
| Group | Form of the Enzymatic Biocatalysts | Initial Dose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 U/kg soil | 600 U/kg soil | 1000 U/kg soil | ||
| 1 | His6-OPH | 74 ± 4 | 61 ± 3 | 48 ± 3 |
| 2 | His6-OPH/PLD50 | 48 ± 2 | 27 ± 1 | 13 ± 0.5 |
| 3 | His6-OPH/PLE50 | 43 ± 2 | 29 ± 1 | 8 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | His6-OPH/PLD50 on zeolite | 27 ± 1 | 19 ± 0.5 | 0 |
| 5 | His6-OPH/PLE50 on zeolite | 29 ± 1 | 17 ± 0.5 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senko, O.; Maslova, O.; Efremenko, E. Optimization of the Use of His6-OPH-Based Enzymatic Biocatalysts for the Destruction of Chlorpyrifos in Soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121438
Senko O, Maslova O, Efremenko E. Optimization of the Use of His6-OPH-Based Enzymatic Biocatalysts for the Destruction of Chlorpyrifos in Soil. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(12):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121438
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenko, Olga, Olga Maslova, and Elena Efremenko. 2017. "Optimization of the Use of His6-OPH-Based Enzymatic Biocatalysts for the Destruction of Chlorpyrifos in Soil" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 12: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121438
APA StyleSenko, O., Maslova, O., & Efremenko, E. (2017). Optimization of the Use of His6-OPH-Based Enzymatic Biocatalysts for the Destruction of Chlorpyrifos in Soil. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(12), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121438






