Enhanced Arsenate Removal Performance in Aqueous Solution by Yttrium-Based Adsorbents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Yttrium-Based Adsorbents
2.2. Adsorbent Characterization
2.3. Adsorption, Effect of Coexisting Anionic Species, Desorption and Regeneration Tests
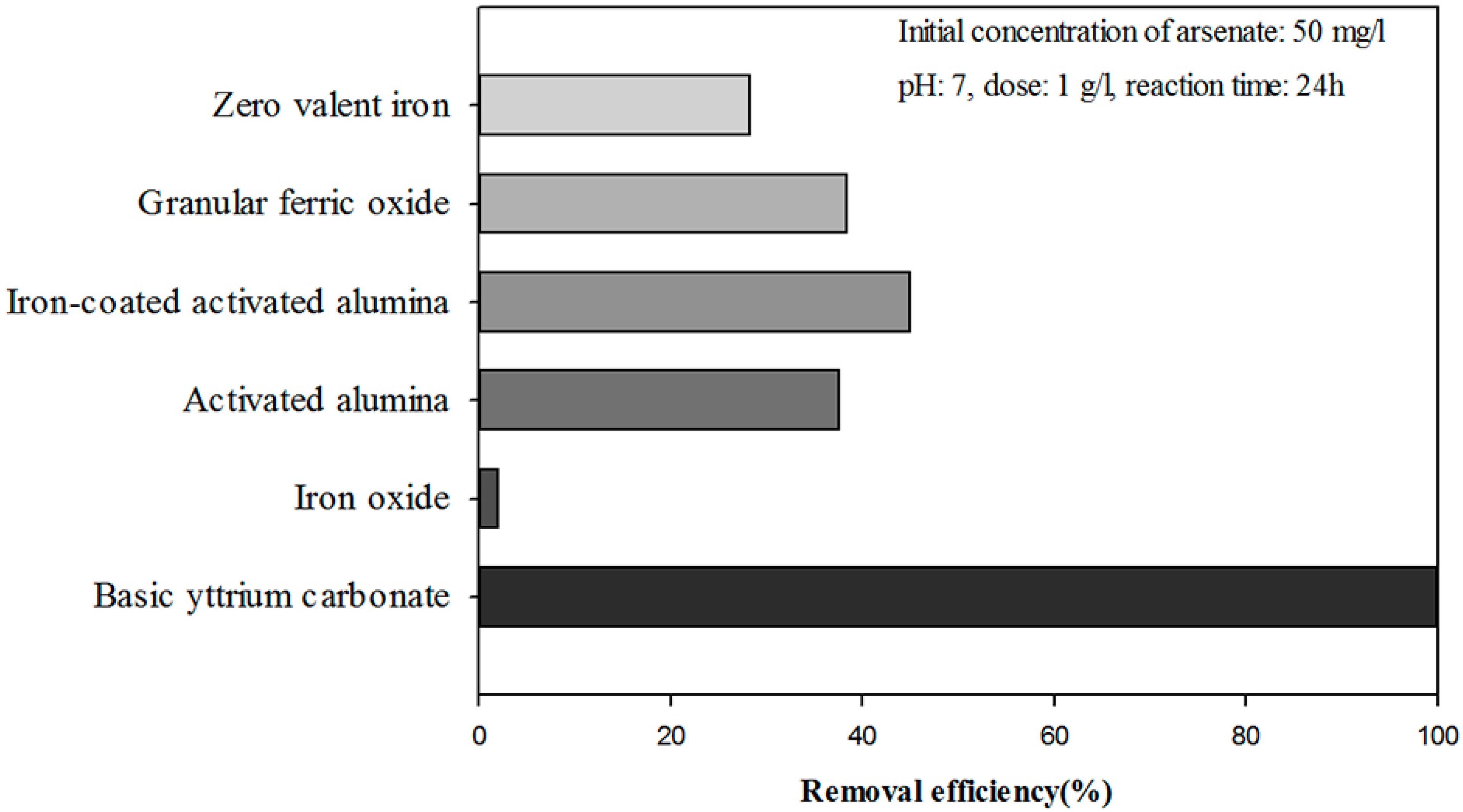
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Ti-loaded BYC
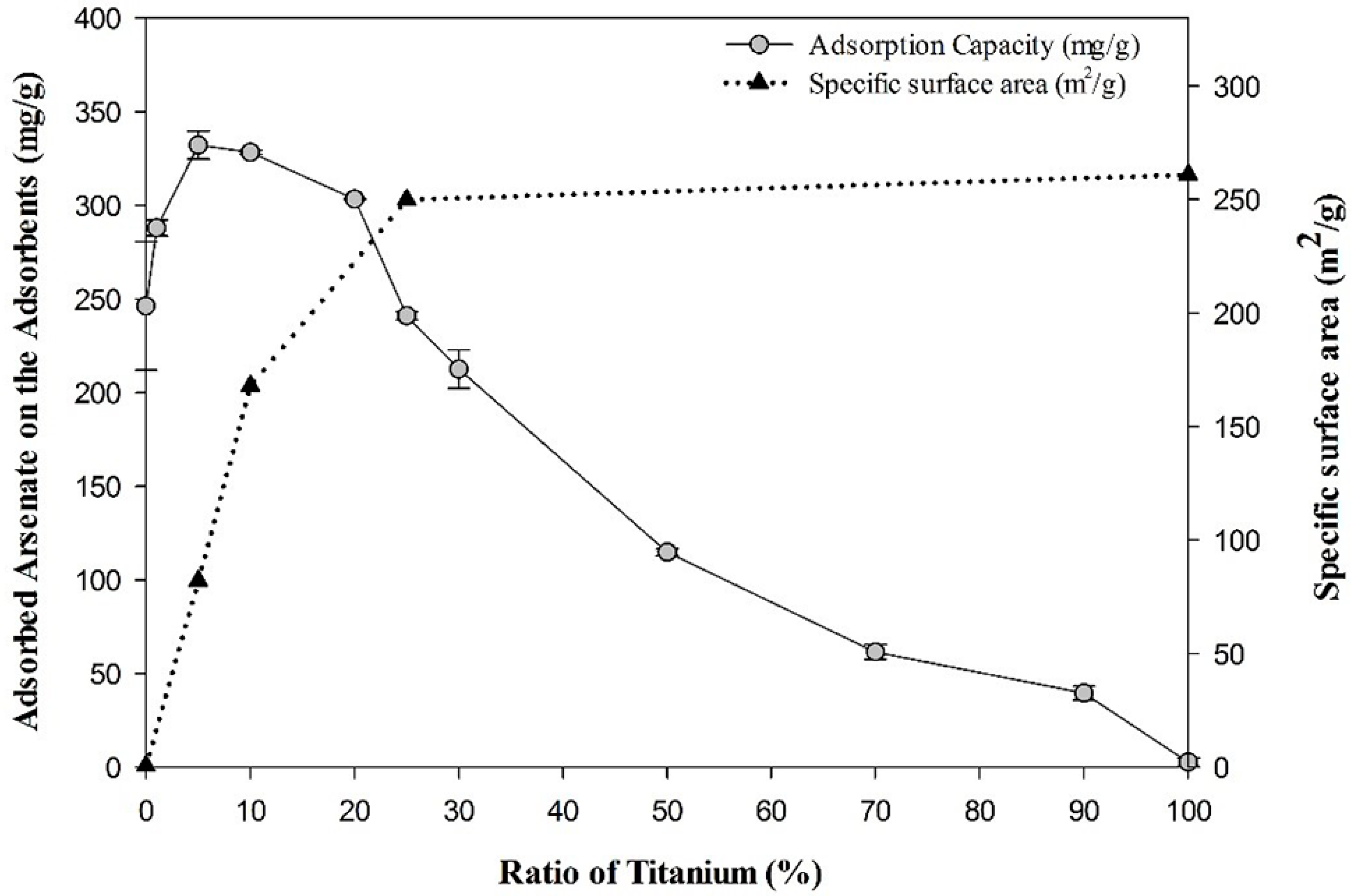
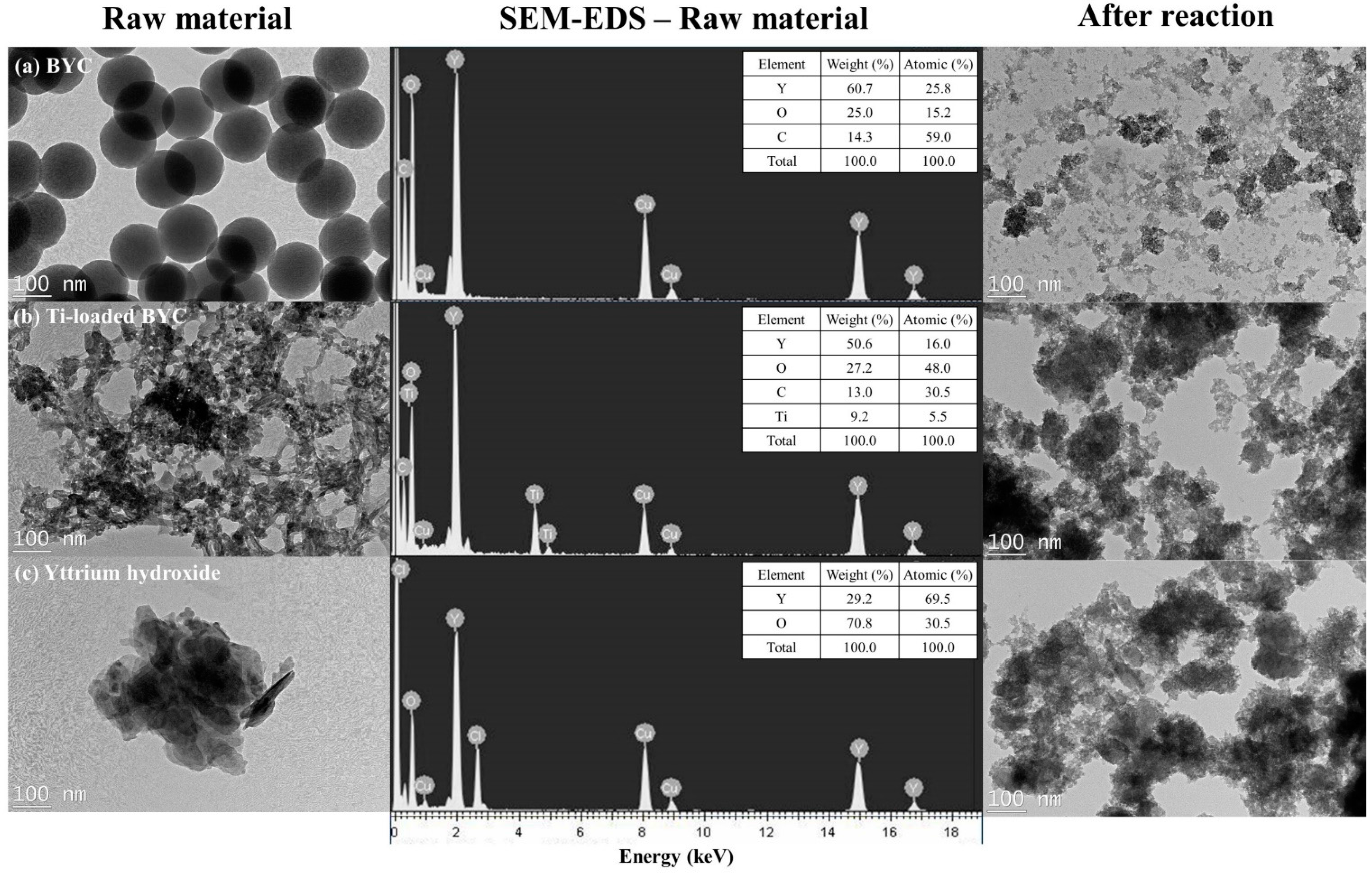
3.2. Determination of Surface Characteristics in Yttrium-based Adsorbents
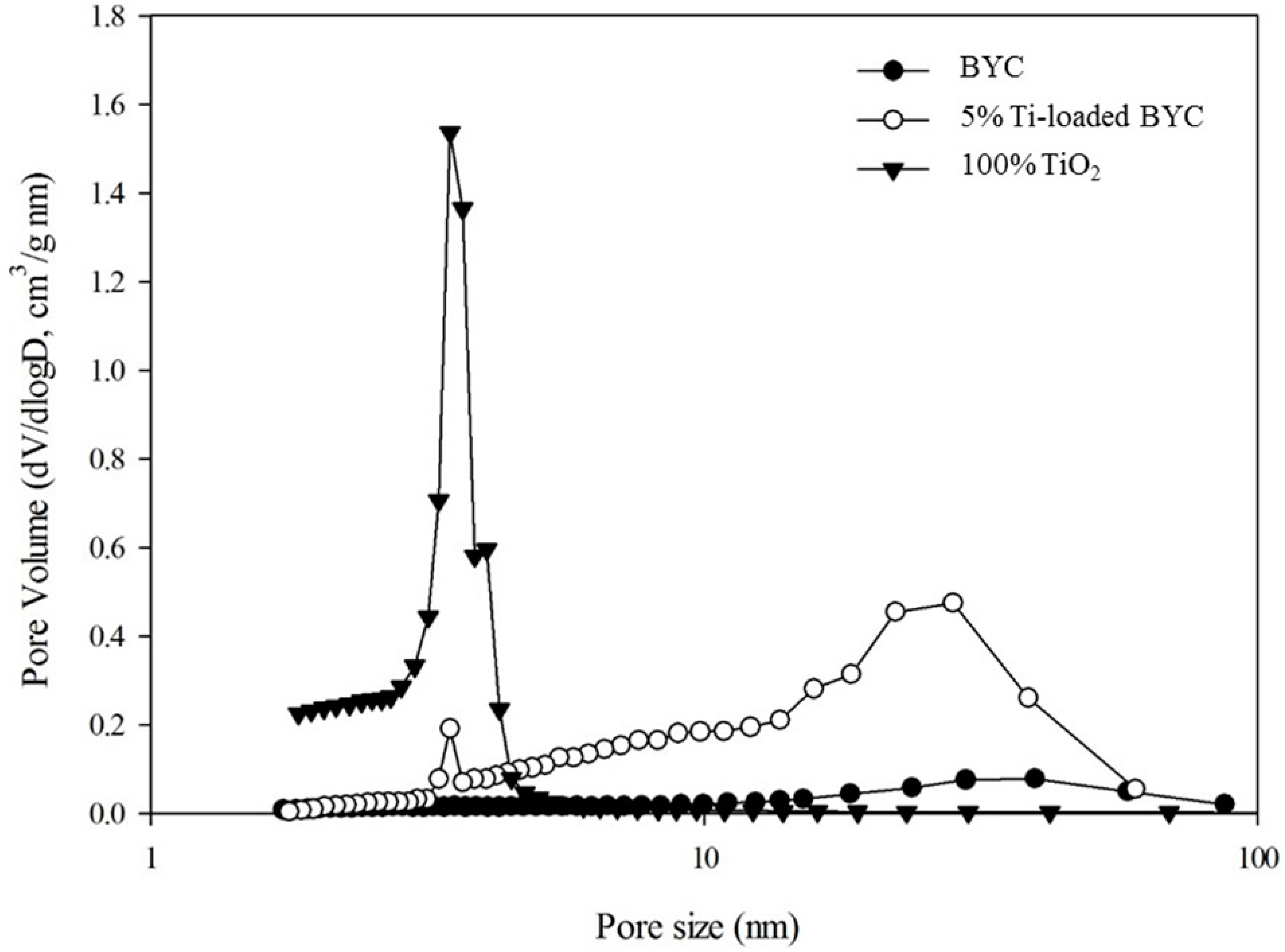
| Adsorbent | PZC * | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | pH | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BYC | 7.9 | <1 | 7.0 | 289.6 | This study |
| Ti-loaded BYC | 8.4 | 82 | 7.0 | 348.5 | This study |
| Yttrium hydroxide | 10.3 | <1 | 7.0 | 206.5 | This study |
| Magnetite | - | 179 | 7.0 | 16.6 | [37] |
| Akaganeite | - | 111 | - | 29.0 | [38] |
| Goethite | 6.7 | 39 | - | 4.0 | [19] |
| Fe-Cu binary oxide | 7.9 | 282 | 7 | 82.7 | [39] |
| CuO nanoparticles | 9.4 | 21 | 8 | 22.6 | [40] |
| Mesoporous alumina | - | 312 | 6.6 | 36.6 | [41] |
| Nano TiO2 | 5.8 | 329 | 7.0 | 37.5 | [42] |
| CeO2-ZrO2 | - | 29 | 6.9 | 145.4 | [28] |
| Y-Mn binary composite | 7.1 | - | 7.0 | 279.9 | [29] |
| Zr nanoparticles | 2.9 | - | 3.0 | 256.4 | [27] |
3.3. FT-IR Study for the Measurement of the Functional Groups
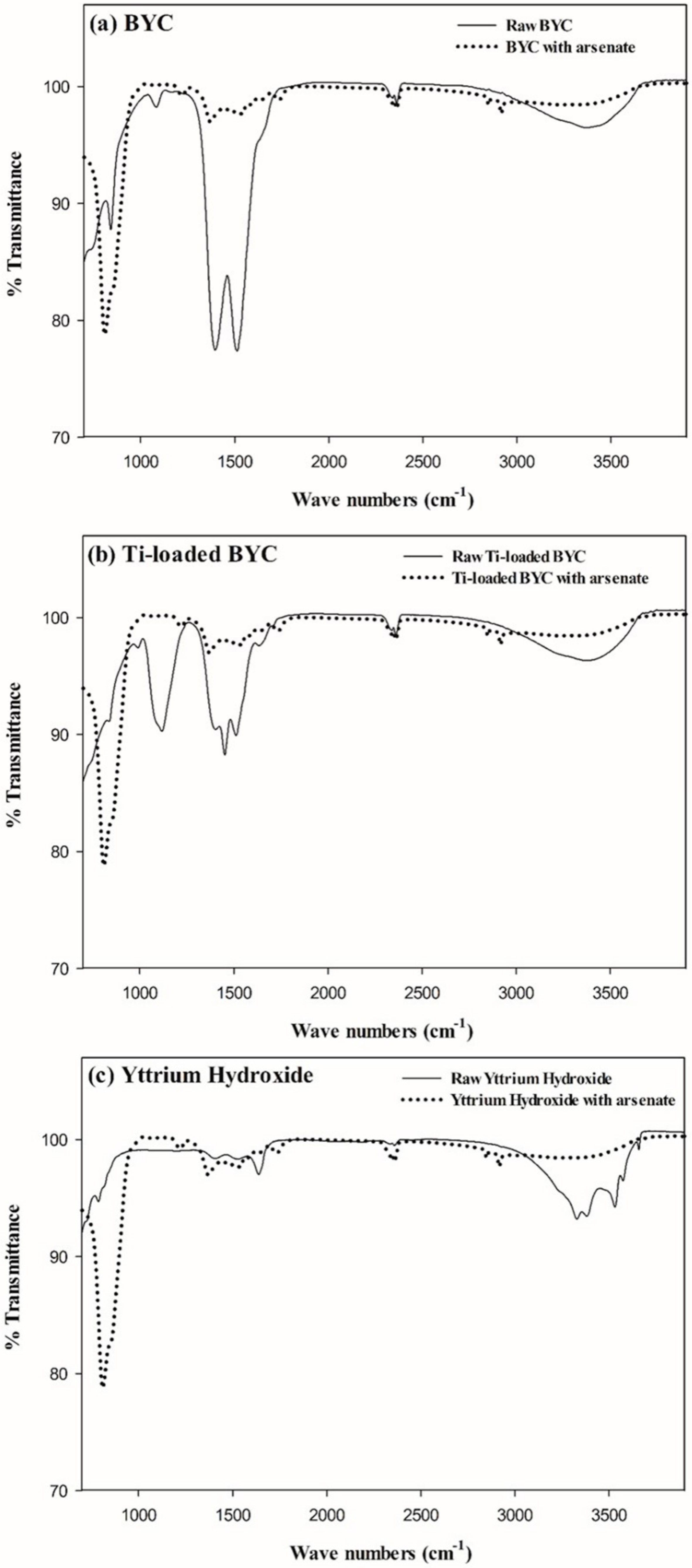
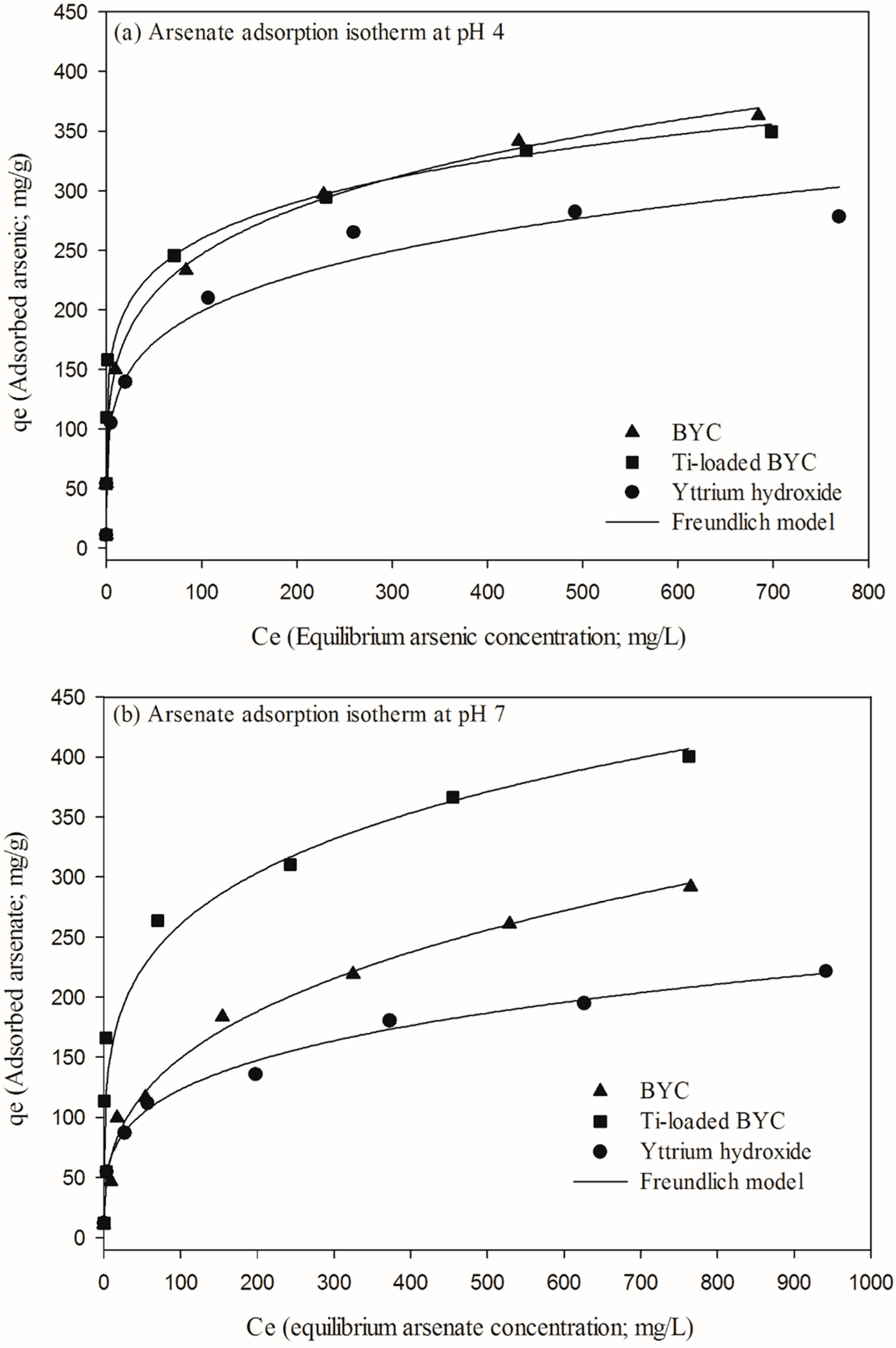
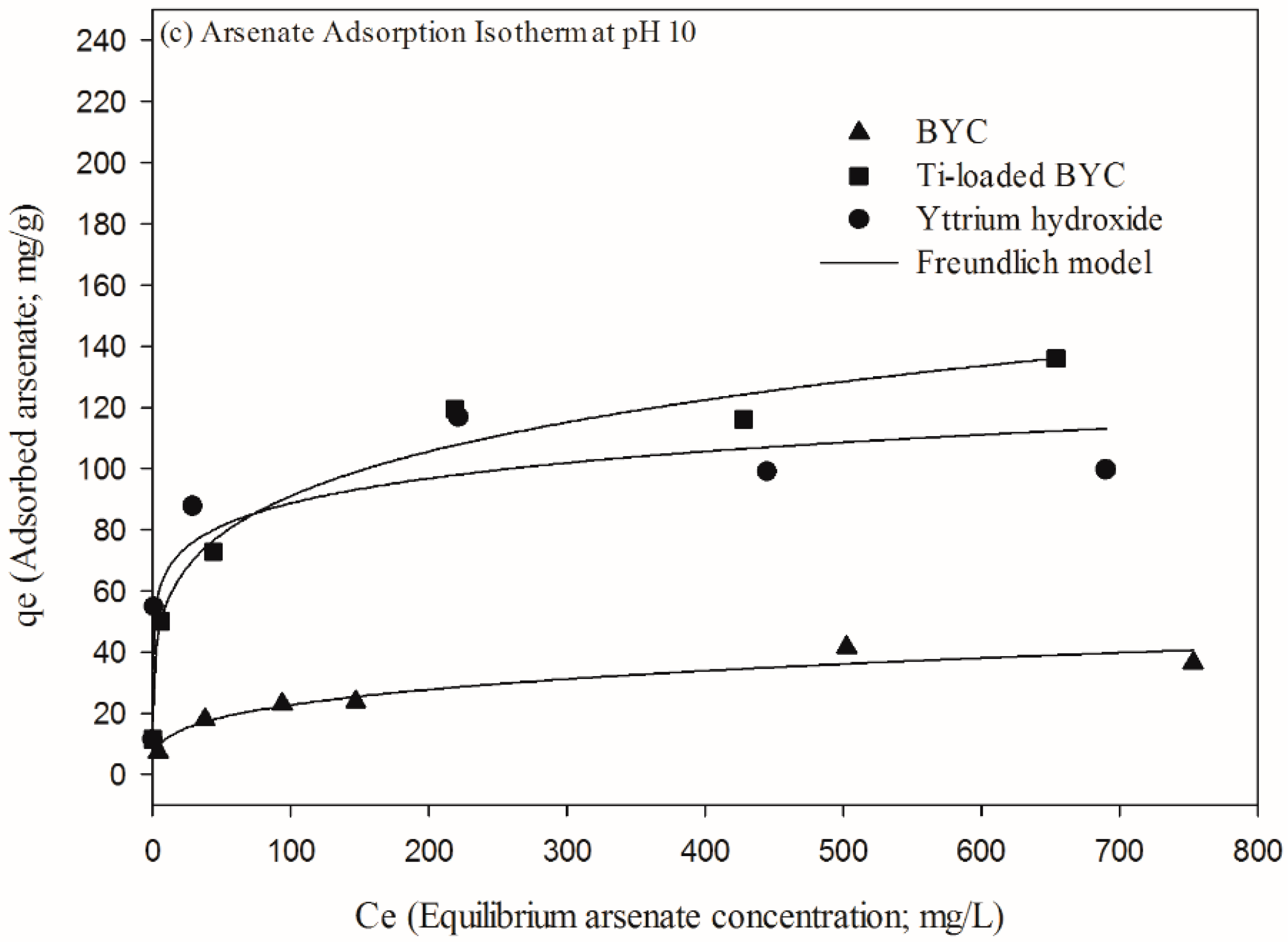
3.4. Arsenate Removal by the Yttrium-based Adsorbents and Adsorption Isotherm
| Adsorbents | Pseudo First Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo Second Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe, cal (mg/g) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | qe, cal (mg/g) | K2 (g/mg·min) | R2 | |
| BYC | 97.67 | 0.151 | 0.993 | 58.41 | 0.085 | 0.978 |
| Ti-loaded BYC | 98.04 | 0.304 | 0.992 | 78.63 | 0.382 | 0.996 |
| Yttrium hydroxide | 95.24 | 0.197 | 0.986 | 62.52 | 0.072 | 0.993 |
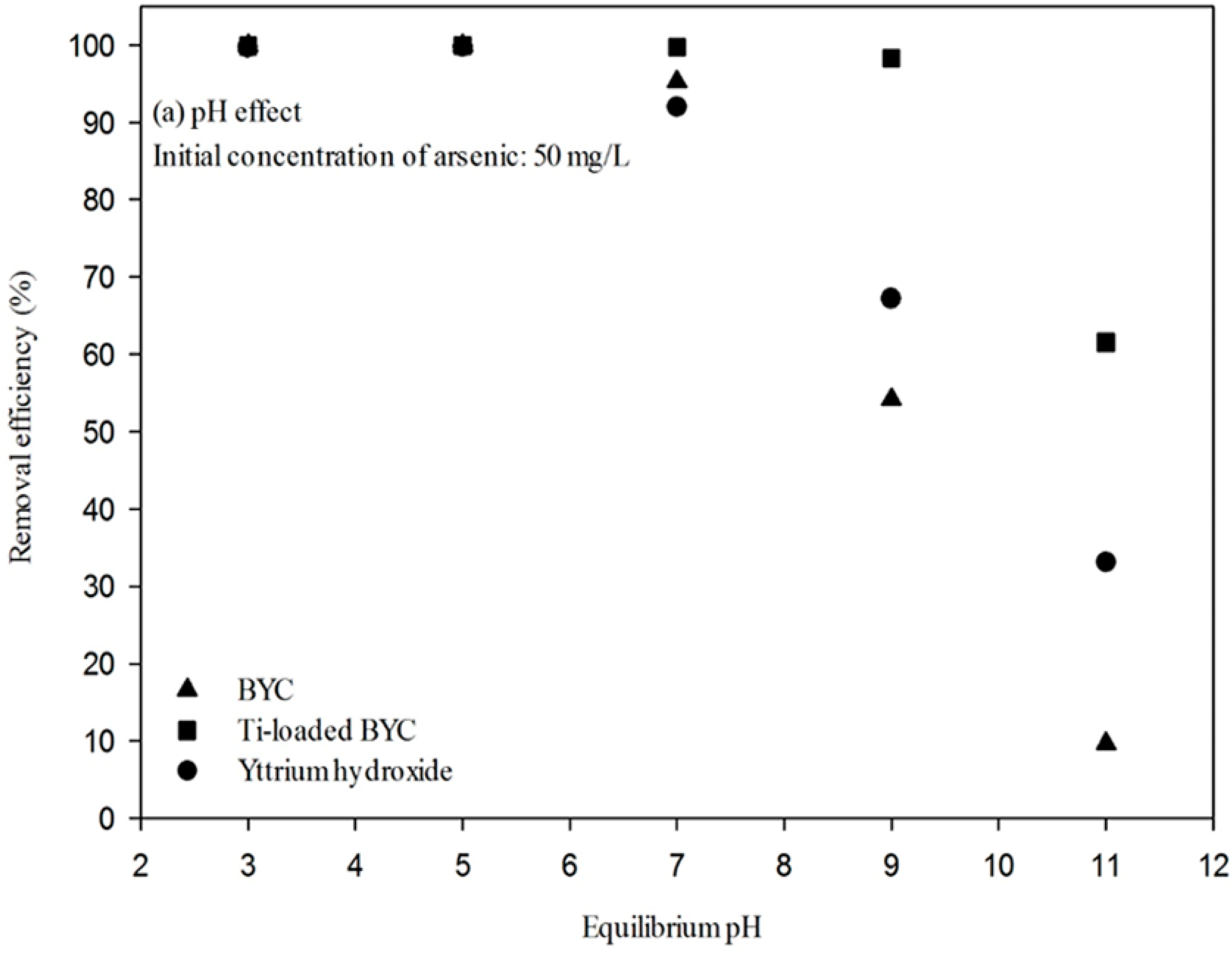
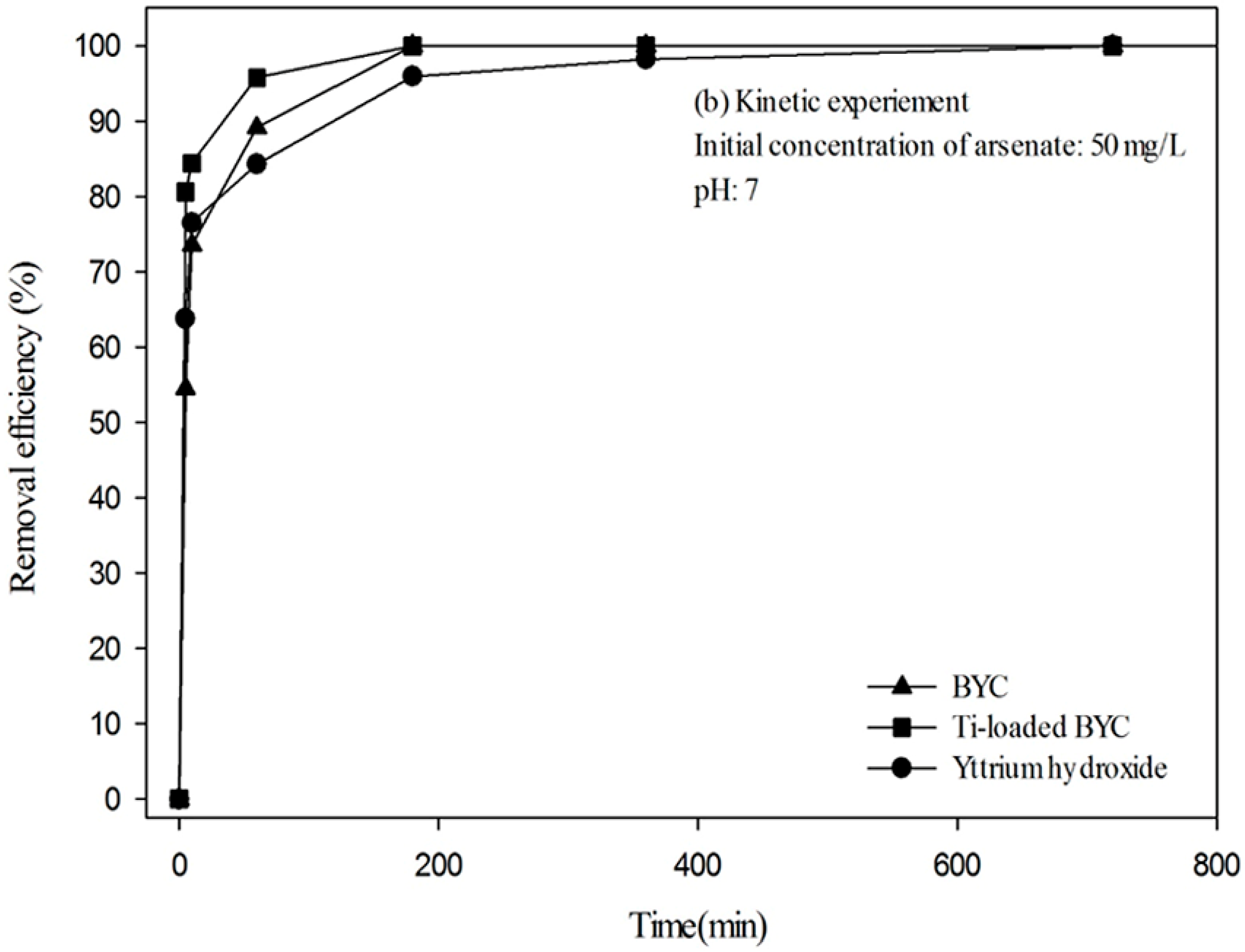
| Adsorbents | pH Condition | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | K (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg/g) | 1/N | R2 | ||
| BYC | pH4 | 326.1 | 0.099 | 0.884 | 93.78 | 0.209 | 0.986 |
| pH 7 | 289.6 | 0.014 | 0.951 | 31.81 | 0.335 | 0.987 | |
| pH 10 | 41.76 | 0.014 | 0.893 | 6.031 | 0.287 | 0.931 | |
| Ti-loaded BYC | pH4 | 303.5 | 1.451 | 0.886 | 123.1 | 0.162 | 0.964 |
| pH 7 | 348.5 | 0.152 | 0.841 | 94.77 | 0.219 | 0.938 | |
| pH 10 | 128.6 | 0.031 | 0.836 | 30.44 | 0.229 | 0.957 | |
| Yttrium hydroxide | pH4 | 274.5 | 0.068 | 0.923 | 76.72 | 0.206 | 0.966 |
| pH 7 | 206.5 | 0.022 | 0.904 | 37.41 | 0.258 | 0.993 | |
| pH 10 | 96.98 | 1.480 | 0.886 | 48.26 | 0.128 | 0.829 | |
3.5. Effect of Coexisting Anionic Species and Desorption
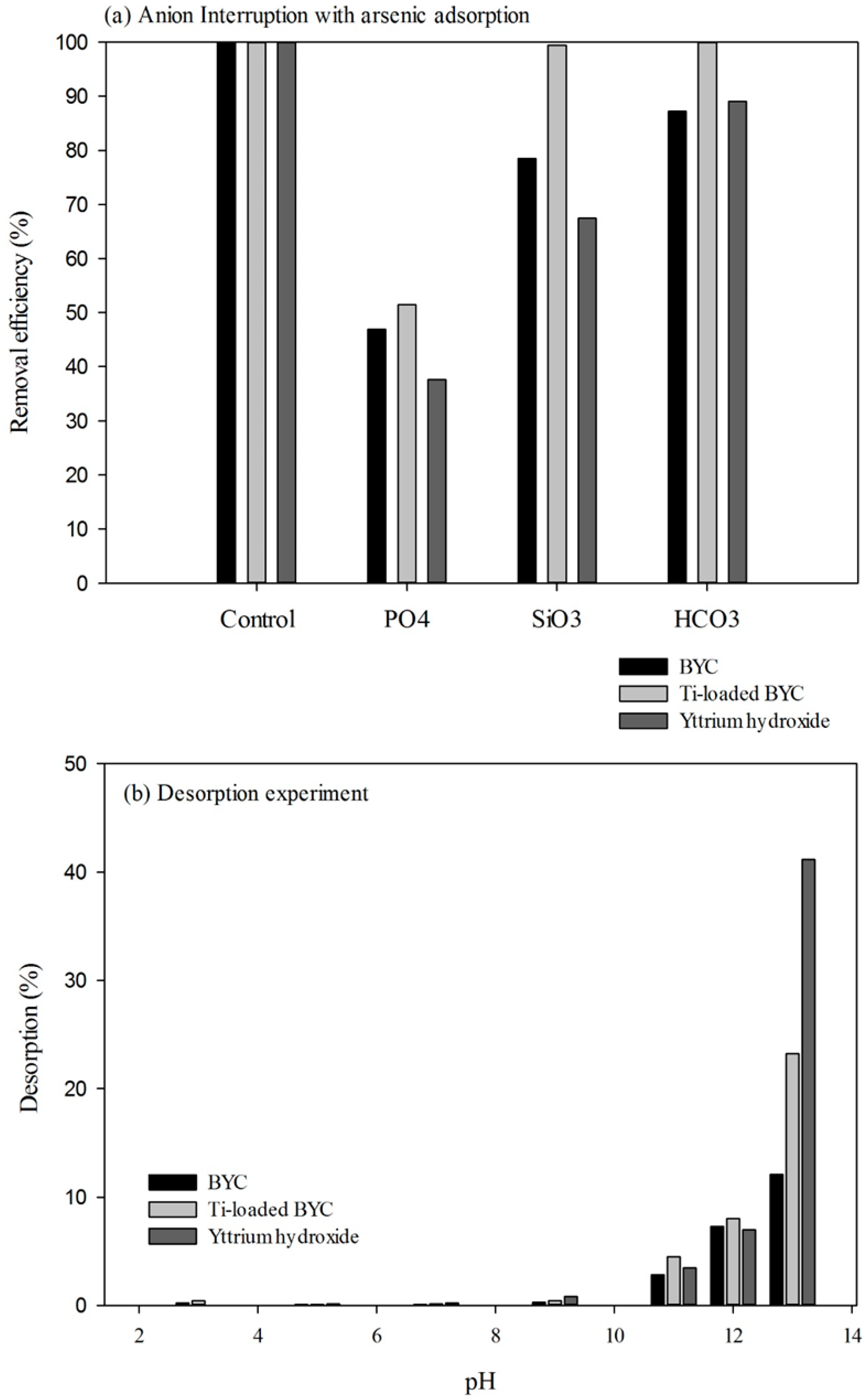
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, J.F.; Gavis, J. A review of the arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Res. 1972, 6, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanel, S.R.; Manning, B.; Charlet, L.; Choi, H. Removal of Arsenic (III) from Groundwater by Nanoscale Zero–Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, K.M.; Hanh, H.T.; Kim, K.-W. Arsenic geochemistry and human health in South East Asia. Rev. Environ. Health 2011, 26, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagas, M.R.; Le, C.X.; Morris, S.; Blum, J.; Lu, X.; Spate, V.; Carey, M.; Stannard, V.; Klaue, B.; Tosteson, T.D. Markers of low level arsenic exposure for evaluating human cancer risks in a US population. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2001, 14, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agusa, T.; Kunito, T.; Fujihara, J.; Kubota, R.; Minh, T.B.; Kim Trang, P.T.; Iwata, H.; Subramanian, A.; Viet, P.H.; Tanabe, S. Contamination by arsenic and other trace elements in tube-well water and its risk assessment to humans in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanpiwat, P.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Cho, K. H.; Kim, K.-W.; San, V.; Suvanthong, B.; Vongthavady, C. Contamination by arsenic and other trace elements of tube-well water along the Mekong River in Lao PDR. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, K.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Kim, K.-W.; Wong, M.H.; Sao, V.; Hashim, J.H.; Mohamed Yasin, M. S.; Aljunid, S.M. Health risk assessment of inorganic arsenic intake of Cambodia residents through groundwater drinking pathway. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5777–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proposed Revision to Arsenic Drinking Water Standard. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/lawsregs/rulesregs/sdwa/arsenic/regulations_pro-factsheet.cfm (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- Arsenic in Drinking Water. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/arsenic.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- Proposed Arsenic in Drinking Water Rule Regulatory Impact Analysis. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/drink/info/arsenic/upload/2005_11_10_arsenic_prop_ria.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- Awual, M.R.; El-Safty, S.A.; Jyo, A. Removal of trace arsenic(V) and phosphate from water by a highly selective ligand exchange adsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.-H.; Wang, J.; Chusuei, C.C. Removal of arsenic from water using granular ferric hydroxide: macroscopic and microscopic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Ohki, A. Adsorption and removal of arsenic(V) from drinking water by aluminum-loaded Shirasu-zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, A.G.; Pigna, M.; Azam, S.M.G.G.; Sommella, A.; Rao, M.A.; Violante, A. Effect of competing ligands on the sorption/desorption of arsenite on/from Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides (Mg–Fe-LDH). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W.; Marques, M.; Sillanpää, M. Interaction of anionic pollutants with Al-based adsorbents in aqueous media—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 241, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, M.; Wu, F. Photooxidation of arsenite by natural goethite in suspended solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Day, P.A. Chemistry and Mineralogy of Arsenic. Elements 2006, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Muñiz, K.; Jia, F.; Song, S. Adsorption of AsV in aqueous solutions on porous hematite prepared by thermal modification of a siderite-goethite concentrate. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lam, K.F.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, B.; Arruebo, M.; Yeung, K.L. Synthesis of highly selective magnetic mesoporous adsorbent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 9804–9813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Han, M.-J.; Wang, C.; Meng, X. Enhanced removal of arsenite from water by a mesoporous hybrid material—Thiol-functionalized silica coated activated alumina. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 124, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, U.C. Synthesis and characterization of nanostructure hydrous iron-titanium binary mixed oxide for arsenic sorption. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Dou, X.-M.; He, H.; Wang, D.-S. Arsenate Adsorption on an Fe–Ce Bimetal Oxide Adsorbent: Role of Surface Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7246–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.-W.; Choi, H.; Takahashi, Y. Simultaneous photooxidation and sorptive removal of As(III) by TiO2 supported layered double hydroxide. J. Environ. Manage. 2015, 161, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awual, M.R.; Jyo, A.; Ihara, T.; Seko, N.; Tamada, M.; Lim, K.T. Enhanced trace phosphate removal from water by zirconium(IV) loaded fibrous adsorbent. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4592–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.; Samal, A. Synthesis, characterisation and rehydration behaviour of titanium(IV) containing hydrotalcite like compounds. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 72, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, J.P. A zirconium based nanoparticle for significantly enhanced adsorption of arsenate: Synthesis, characterization and performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Sheng, G.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, X.-J. Enhanced arsenic removal from water by hierarchically porous CeO2–ZrO2 nanospheres: role of surface- and structure-dependent properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.P. Introduction of an Yttrium–Manganese Binary Composite That Has Extremely High Adsorption Capacity for Arsenate Uptake in Different Water Conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Household Electrical Appliances Perforamnce Hardwater for Testing. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/17551 (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- Wasay, S.A.; Haron, M.J.; Uchiumi, A.; Tokunaga, S. Removal of arsenite and arsenate ions from aqueous solution by basic yttrium carbonate. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Ghosh, U.C. Arsenic removal using hydrous nanostructure iron(III)-titanium(IV) binary mixed oxide from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Langford, C.H. Photoactivity of titanium dioxide supported on MCM41, zeolite X, and zeolite Y. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 3115–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-H.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.-K. Preparation and characterization of nanosized TiO2 powders from aqueous TiCl4 solution. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordelet, D.; Akinc, M. Preparation of spherical, monosized Y2O3 precursor particles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1988, 122, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, M.J.; Wasay, S.A.; Tokunaga, S. Preparation of basic yttrium carbonate for phosphate removal. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Cao, M.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, C. Superparamagnetic high-surface-area Fe3O4 nanoparticles as adsorbents for arsenic removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Jia, Y. A facile solution approach for the synthesis of akaganéite (β-FeOOH) nanorods and their ion-exchange mechanism toward As(V) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Nanostructured iron(III)-copper(II) binary oxide: A novel adsorbent for enhanced arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4022–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinson, C.A.; Reddy, K.J. Adsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) by cupric oxide nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2009, 336, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Li, H.; Pu, H.; Yu, H.; Deng, L.; Huang, S.; Luo, Y. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous alumina and their performances for removing arsenic(V). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, M.; Meng, X.; Korfiatis, G.P.; Jing, C. Adsorption mechanism of arsenic on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.; Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R. Microwave assisted synthesis of polycinnamamide Mg/Al mixed oxide nanocomposite and its application towards the removal of arsenate from aqueous medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, A.; Strydom, C.A. DTA and FT-IR analysis of the rehydration of basic magnesium carbonate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 71, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Hu, X.; Qu, J.; Yang, M. Characterization and adsorption performance of Zr-doped akaganéite for efficient arsenic removal. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partey, F.; Norman, D.I.; Ndur, S.; Nartey, R. Mechanism of arsenic sorption onto laterite iron concretions. Colloid. Surface. A 2009, 337, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-F.; Wu, J.-K. Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate within activated alumina grains: Equilibrium and kinetics. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, X. Arsenic(V) removal with a Ce(IV)–doped iron oxide adsorbent. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Pigna, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Caporale, A.G.; Violante, A. Sorption of arsenite and arsenate on ferrihydrite: Effect of organic and inorganic ligands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendtner, K.; Kolitsch, U. CsGa(H1.5AsO4)2(H2AsO4) and isotypic CsCr(H1.5AsO4)2(H2AsO4): Decorated kröhnkite-like chains in two unusual hydrogen arsenates. Acta Crystallogr. C 2005, 61, i90–i93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Zhang, T.; Bu, X. Arsenate zeolite analogues with 11 topological types. J. Am. Chem. 2001, 123, 8608–8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.-W.; Lee, B.-T.; Bang, S.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Jang, A. Enhanced Arsenate Removal Performance in Aqueous Solution by Yttrium-Based Adsorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13523-13541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121013523
Lee S-H, Kim K-W, Lee B-T, Bang S, Kim H, Kang H, Jang A. Enhanced Arsenate Removal Performance in Aqueous Solution by Yttrium-Based Adsorbents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015; 12(10):13523-13541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121013523
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang-Ho, Kyoung-Woong Kim, Byung-Tae Lee, Sunbaek Bang, Hyunseok Kim, Hyorang Kang, and Am Jang. 2015. "Enhanced Arsenate Removal Performance in Aqueous Solution by Yttrium-Based Adsorbents" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 12, no. 10: 13523-13541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121013523
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Kim, K.-W., Lee, B.-T., Bang, S., Kim, H., Kang, H., & Jang, A. (2015). Enhanced Arsenate Removal Performance in Aqueous Solution by Yttrium-Based Adsorbents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(10), 13523-13541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121013523






