Effects of Sludge Retention Times on Nutrient Removal and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Biological Nutrient Removal Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Treatment Systems and Their Operation
2.2. Sludge Activity at Different SRTs
2.3. N2O Emission at Different SRTs
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Nutrient Removal at Different SRTs
| Parameter | Unit | Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRT | d | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | |
| CODin | mg/L | 399.3 ± 20.6 | ||||
| NH4-Nin | mg/L | 40.6 ± 1.4 | ||||
| PO4-Pin | mg/L | 8.4 ± 0.8 | ||||
| CODeff | mg/L | 20.1 ± 3.4 | 17.5 ± 3.5 | 13.6 ± 2.6 | 18.5 ± 4.7 | |
| TNeff | mg/L | 9.2 ± 1.8 | 11.3 ± 1.6 | 11.2 ± 1.7 | 11.7 ± 0.6 | |
| TPeff | mg/L | 3.6 ± 1.5 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | |
| NH4-Neff | mg/L | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0 | |
| NO3-Neff | mg/L | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 6.7 ± 1.6 | 6.8 ± 0.7 | 8.9 ± 0.9 | |
| NO2-Neff | mg/L | 2.6 ± 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| PO4-Peff | mg/L | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | |
| SS | mg/L | 20.3 ± 4.3 | 19.3 ± 6.7 | 17.6 ± 5.4 | 19.1 ± 4.9 | |
| SMP | TOC | mg/L | 7.8 ± 0.6 | 13.3 ± 1.8 | 12 ± 3.7 | 9 ± 1.7 |
| Protein | mg/L | 5.44 | 6.44 | 4.19 | 4.19 | |
| UVA254 | 1/cm | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |

3.2. Dynamics of Nutrients in SBR Cycles at Different SRTs
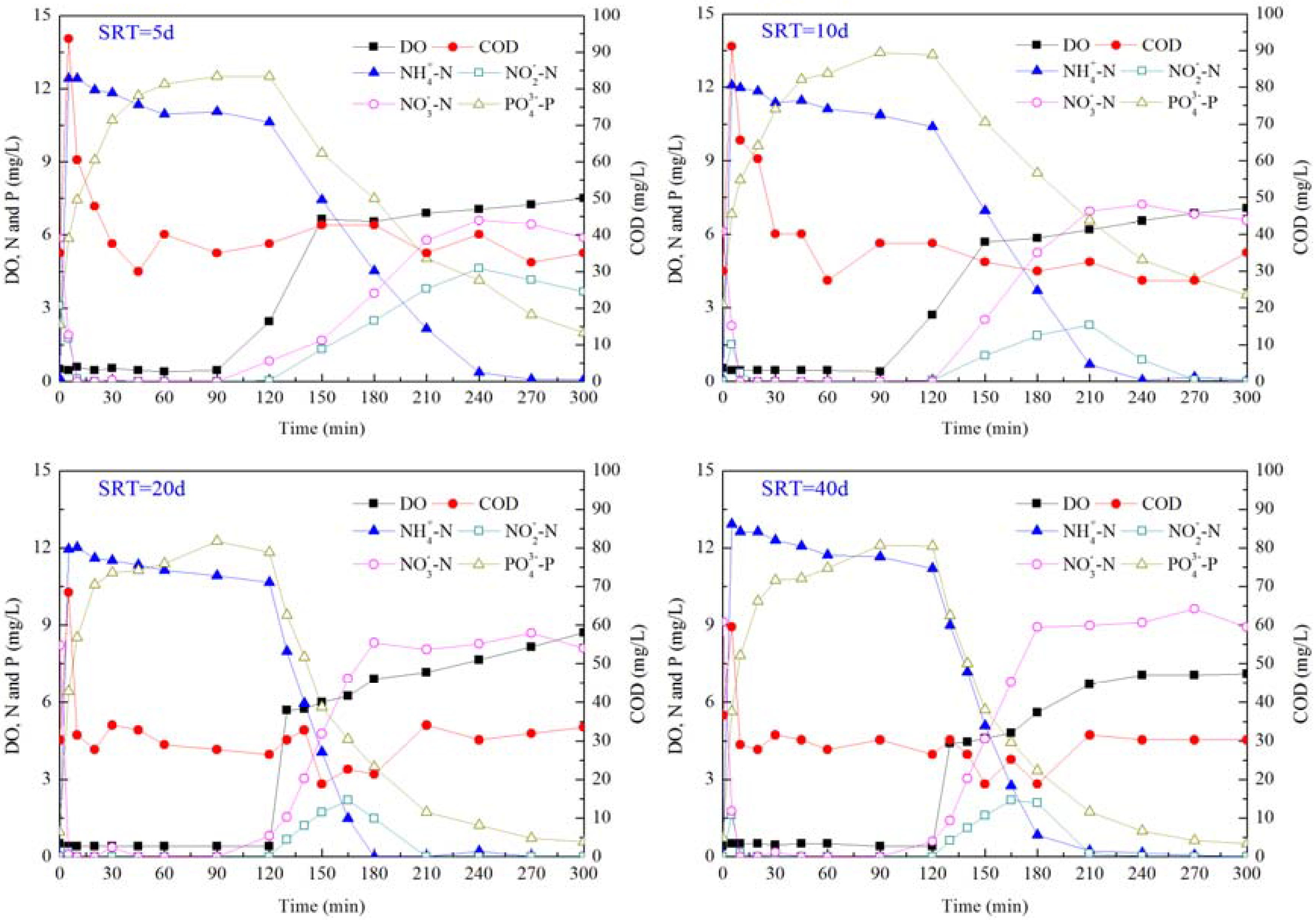
3.3. Sludge Characteristics at Different SRTs

| Parameter | Unit | Sludge Retention Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRT | d | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | |
| SS | mg/L | 1,103 ± 80 | 1,449 ± 67 | 3,165 ± 130 | 5,127 ± 600 | |
| VSS | mg/L | 1,041 ± 100 | 1,324 ± 104 | 2,682 ± 170 | 3,900 ± 350 | |
| SVI | mL/g | 49 ± 18 | 23 ± 5 | 69 ± 5 | 108 ± 14 | |
| EPS | Total | mg/g VSS | 157 ± 12 | 145 ± 19 | 111 ± 10 | 95 ± 10 |
| Protein | mg/g VSS | 82.3 ± 12.4 | 78.6 ± 10.8 | 73 ± 4.4 | 60.7 ± 6.3 | |
| Carbohydrate | mg/g VSS | 74.3 ± 7.5 | 66.3 ± 9.8 | 37.8 ± 6.2 | 33.9 ± 6.8 | |
| Nitrification rate | 1st step | mg/(g VSS·h) | 5.4 | 3.9 | 3 | 2.4 |
| 2nd step | mg/(g VSS·h) | 1.3 | 2.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | |
| Denitrification rate | 1st step | mg/(g VSS·h) | 15.6 | 10.6 | 13.8 | 9.4 |
| 2nd step | mg/(g VSS·h) | 7.6 | 6.5 | 8.8 | 2.9 | |
3.4. N2O Emission in SBR Cycles at Different SRTs

3.5. N2O Emission in Batch Experiments under Different Conditions
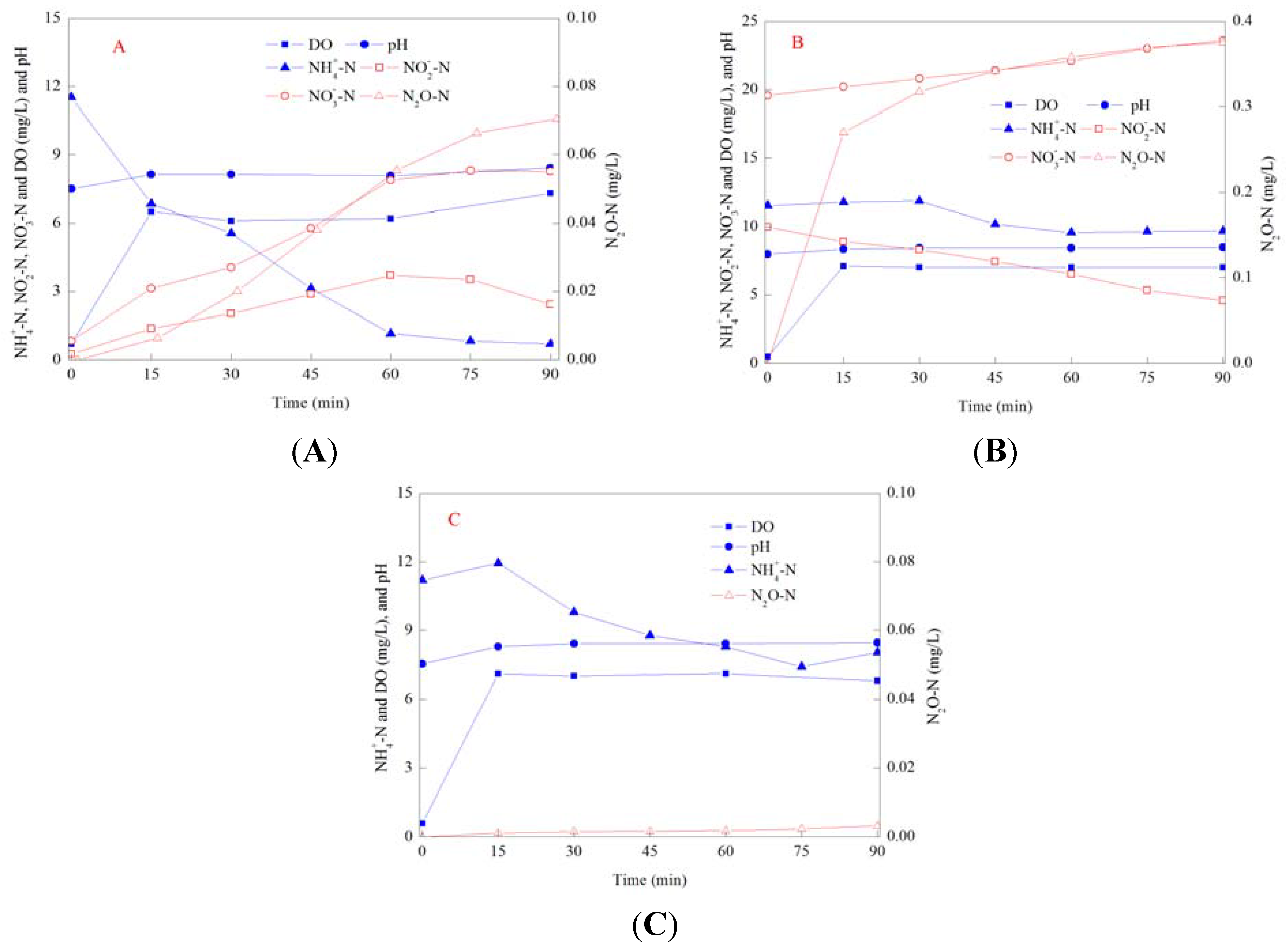
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pai, T.Y.; Wan, T.J.; Tsai, Y.P.; Tzeng, C.J.; Chu, H.H.; Tsai, Y.S.; Lin, C.Y. Effect of sludge retention time on nitrifiers’ biomass and kinetics in an anaerobic/oxic process. Clean Soil Air Water 2010, 38, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, F.; Uygur, A. Nutrient removal performance of a sequencing batch reactor as a function of the sludge age. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 31, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. United States Environmental Protection Agency: Design Manual, Phosphorus Removal; EPA/625/1–87/001; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Wentzel, M.C.; Ekama, G.A.; Marais, G.R. Kinetics of nitrification denitrification biological excess phosphorus removal systems—A review. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 23, 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Kim, M.; Chung, J. Relationship between solid retention time and phosphorus removal in anaerobic-intermittent aeration process. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2007, 103, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Stuckey, D.C. A review of soluble microbial products (SMP) in wastewater treatment systems. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3063–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Nam, S.N.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Krasner, S.W.; Amy, G. Fate of effluent organic matter and DBP precursors in an effluent-dominated river: A case study of wastewater impact on downstream water quality. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, J.R.; Shang, H.L.; Tang, X.G.; Peng, Y.Z. Characterization of the dissolved organic matter in the sewage of an SBR. Acta Sci. Cirumstantiae 2011, 31, 20–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, K.; Naruse, T.; Watanabe, Y. Changes in characteristics of soluble microbial products in membrane bioreactors associated with different solid retention times: relation to membrane fouling. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, A.; Pareilleux, A.; Rols, J.; Goma, G.; Huyard, A. Decreased sludge production strategy for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Gui, P.; Qian, Y. Effect of sludge retention time on microbial behaviour in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Process. Biochem. 2001, 36, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbain, V.; Block, J.C.; Manem, J. Bioflocculation in activated sludge: An analytic approach. Water Res. 1993, 27, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.Q.; Allen, D.G.; Droppo, I.G.; Leppard, G.G.; Liss, S.N. Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res. 2001, 35, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halbouni, D.; Traber, J.; Lyko, S.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T.; Tacke, D.; Hollender, J. Correlation of EPS content in activated sludge at different sludge retention times with membrane fouling phenomena. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Song, K.; Yun, H.; Ahn, K.; Kim, J.; Chung, T.H. Quantitative analysis of biological effect on membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, J.A.S.; Forster, C.F. A further examination into the composition of activated sludge surfaces in relation to their settlement characteristics. Water Res. 1985, 19, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Kang, H.S.; Nam, S.Y. Effect of carbohydrate and protein in the EPS on sludge settling characteristics. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Desloover, J.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Clauwaert, P.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Strategies to mitigate N2O emissions from biological nitrogen removal systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassamee, V.; Sattayatewa, C.; Pagilla, K.; Chandran, K. Effect of oxic and anoxic conditions on nitrous oxide emissions from nitrification and denitrification processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cartmell, E.; Stephenson, T. Nitrous oxide emissions for early warning of biological nitrification failure in activated sludge. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poughon, L.; Dussap, C.G.; Gros, J.B. Energy model and metabolic flux analysis for autotrophic nitrifiers. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 72, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Chandran, K. Factors promoting emissions of nitrous oxide and nitric oxide from denitrifying sequencing batch reactors operated with methanol and ethanol as electron donors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 106, 390–398. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.L.; Zeng, R.J.; Giugliano, V.; Blackall, L.L. Challenges for simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in microbial aggregates: Mass transfer limitation and nitrous oxide production. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 52, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlin, P.; Mohn, J.; Joss, A.; Emmenegger, L.; Siegrist, H. Mechanisms of N2O production in biological wastewater treatment under nitrifying and denitrifying conditions. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, N.; Kaneko, N.; Mikami, M.; Kimochi, Y.; Tsuneda, S.; Hirata, A.; Inamori, Y. Effects of SRT and DO on N2O reductase activity in an anoxic-oxic activated sludge system. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 48, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, H.L.; Peng, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.R.; Wang, S.Y. Effects of SRT on N2O production during nitrification and denitrification. Acta Sci. Circumstanite 2009, 29, 754–758. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Smolders, G.J.F.; van der Meij, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process: Stoichiometry and pH influence. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 43, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.; Aiken, G.; O’Loughlin, E. Molecular weight, polydispersity and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaar, J.L.; Aiken, G.R.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Fram, M.S.; Fujii, R.; Mopper, K. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4702–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Fang, H.H. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 95, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.H.; Cabaniss, S.E.; Maurice, P.A. Considerations in the use of high-pressure size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) for determining molecular weights of aquatic humic substances. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3505–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollice, A.; Tandoi, V.; Lestingi, C. Influence of aeration and sludge retention time on ammonium oxidation to nitrite and nitrate. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Effect of SRT on nutrient removal in SBR system. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 1999, 3, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, H.K.; Vigneswaran, S.; Snyder, S.A. Effluent organic matter (EfOM) in wastewater: Constituents, effects, and treatment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 327–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarusutthirak, C.; Amy, G. Understanding soluble microbial products (SMP) as a component of effluent organic matter (EfOM). Water Res. 2007, 41, 2787–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Soto, M.; Fox, P.; Westerhoff, P. Transformation of molecular weight distributions of dissolved organic carbon and UV-absorbing compounds at full-scale wastewater-treatment plants. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.H.; Ouyang, C.F.; Wang, Y.B. Kinetic competition between phosphorus release and denitrification on sludge under anoxic condition. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, A.W.; McCarty, P.L. Unified basis for biological treatment design and operation. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1970, 96, 757–778. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Malack, M.H. Determination of biokinetic coefficients of an immersed membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Lee, J.; Inamori, Y.; Mizuochi, M.; Ahn, K. Effects of fill modes on N2O emission from the SBR treating domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Colliver, B.B.; Stephenson, T. Production of nitrogen oxide and dinitrogen oxide by autotrophic nitrifiers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.; Felgate, H.; Watmough, N.; Thomson, A.; Baggs, E. Mitigating release of the potent greenhouse gas N2O from the nitrogen cycle-could enzymic regulation hold the key? Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Wu, G. Effects of Sludge Retention Times on Nutrient Removal and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Biological Nutrient Removal Processes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3553-3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403553
Li B, Wu G. Effects of Sludge Retention Times on Nutrient Removal and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Biological Nutrient Removal Processes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(4):3553-3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403553
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, and Guangxue Wu. 2014. "Effects of Sludge Retention Times on Nutrient Removal and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Biological Nutrient Removal Processes" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 4: 3553-3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403553
APA StyleLi, B., & Wu, G. (2014). Effects of Sludge Retention Times on Nutrient Removal and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Biological Nutrient Removal Processes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(4), 3553-3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403553




