From Eutrophic to Mesotrophic: Modelling Watershed Management Scenarios to Change the Trophic Status of a Reservoir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
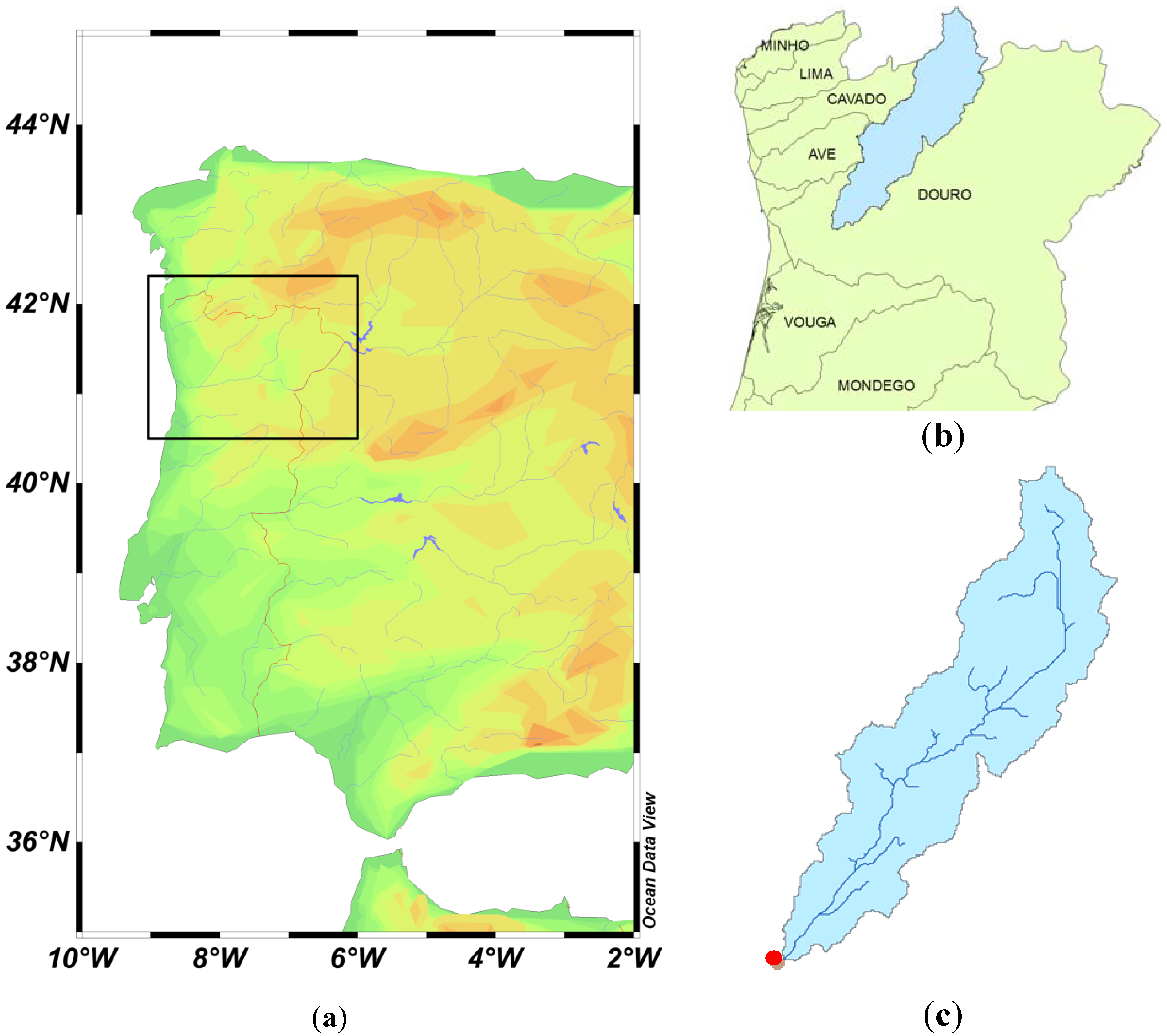
2.1. Study Area


| Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | Nitrate (mgN/L) | Ammonium (mgN/L) | Orthophosphate (mgP/L) | Chl-a (ug/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 8.7 | 0.77 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 11.5 |
| Minimum | 5.1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0 |
| Maximum | 12.5 | 2.91 | 0.47 | 0.24 | 82.9 |
2.2. Field Data
2.3. CE-QUAL-W2 (CQW2) Model
2.4. SWAT Model
3. Application of the Integrated Model System to Simulate the Tâmega River
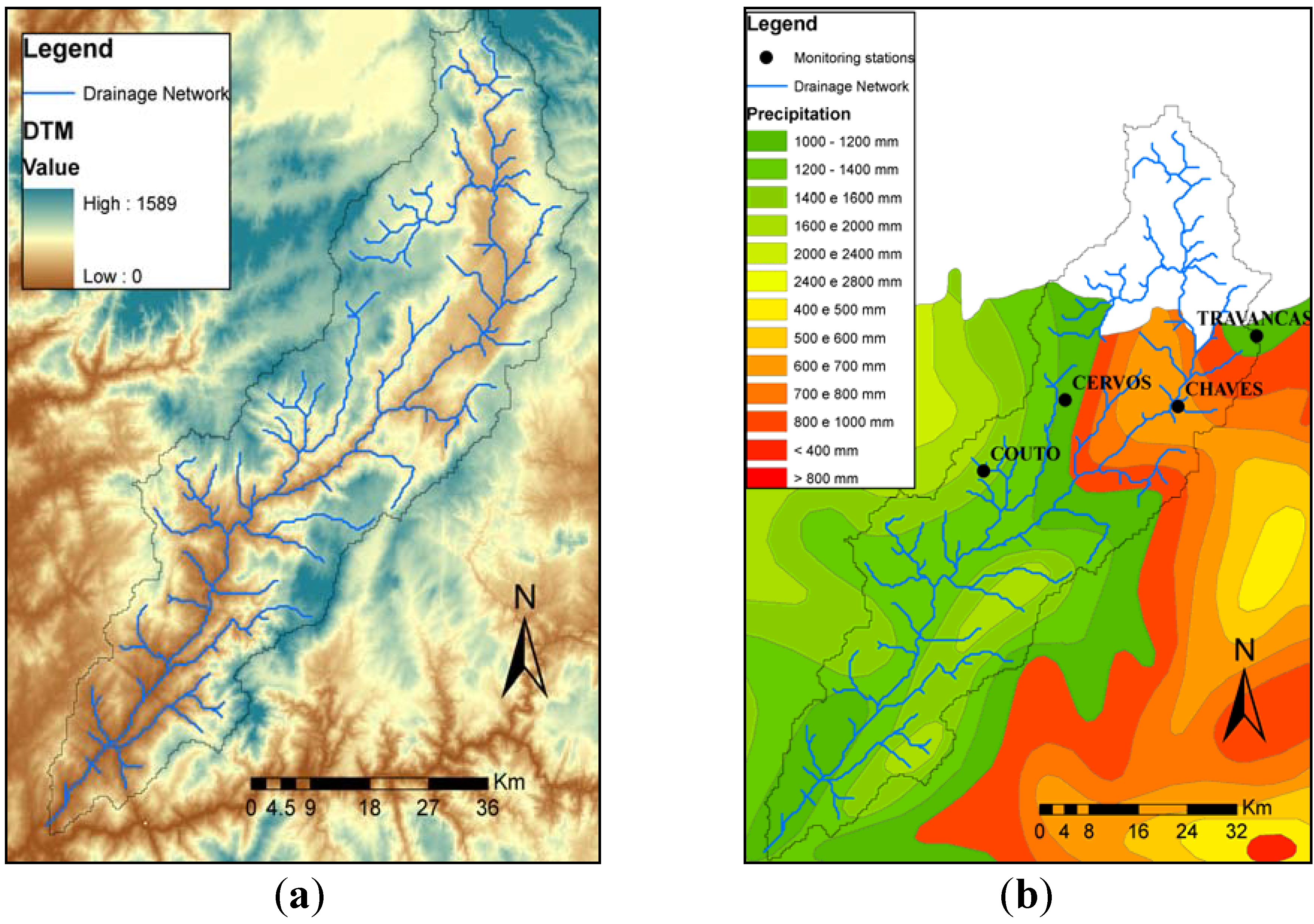
3.1. Input Data
| Stations | Mean annual Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|
| Cervos | 1,028 |
| Chaves | 576 |
| Couto | 1,422 |
| Travancas | 903 |
| Parameters | Units | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Per capita flow | L/(p.e.·day) | 100 |
| Total Suspended Solids (TSS) | mg/L | 60 |
| Ammonium | mg NH4/L | 10 |
| Nitrate | mg NO3/L | 50 |
| Total phosphorus | mg P/L | 3 * |
3.2. Implementation of the SWAT Model
3.3. Implementation of the CQW2 Model
3.4. Simulations Scenarios
4. Results and Discussion
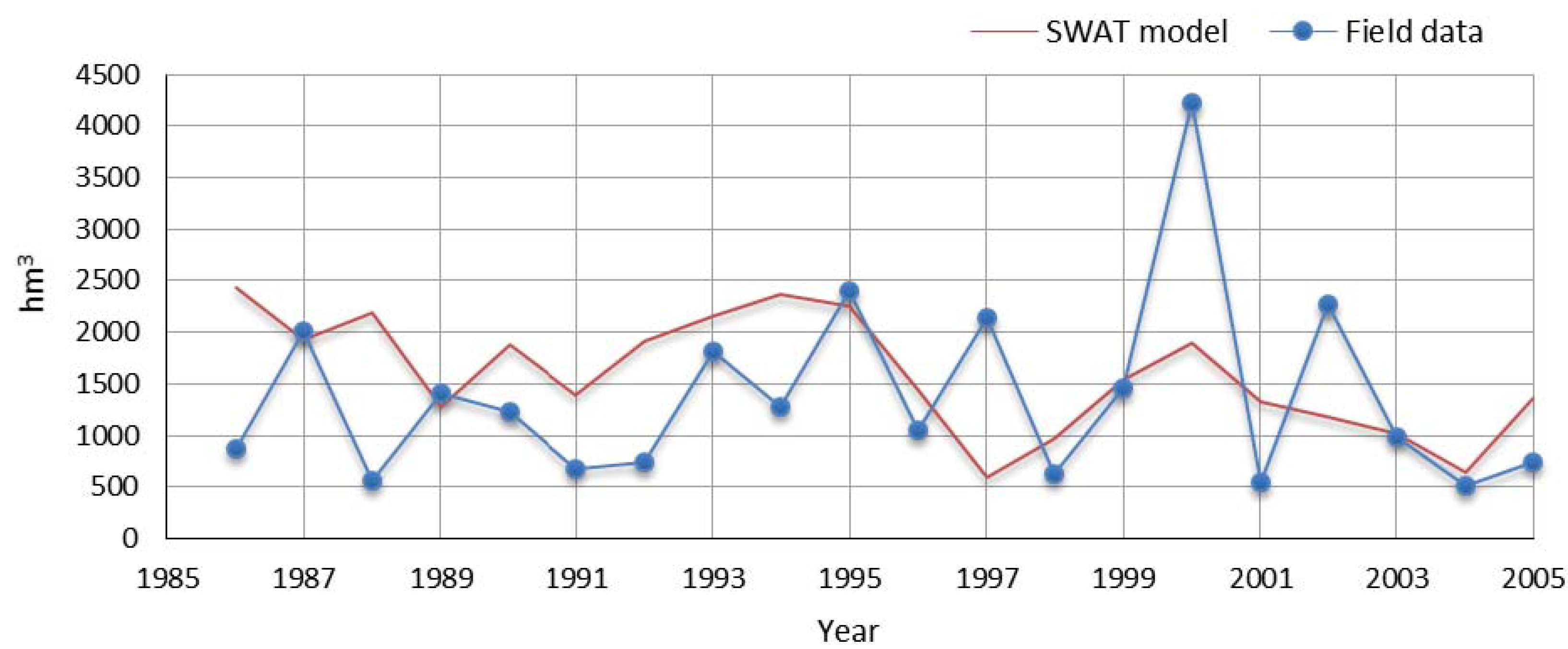
4.1. SWAT Model Validation
| Period | Mean flow (m3/s) | RMSE (m3/s) | R2 | Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Data | ||||
| 2007–2009 | 53 | 48 | 51 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
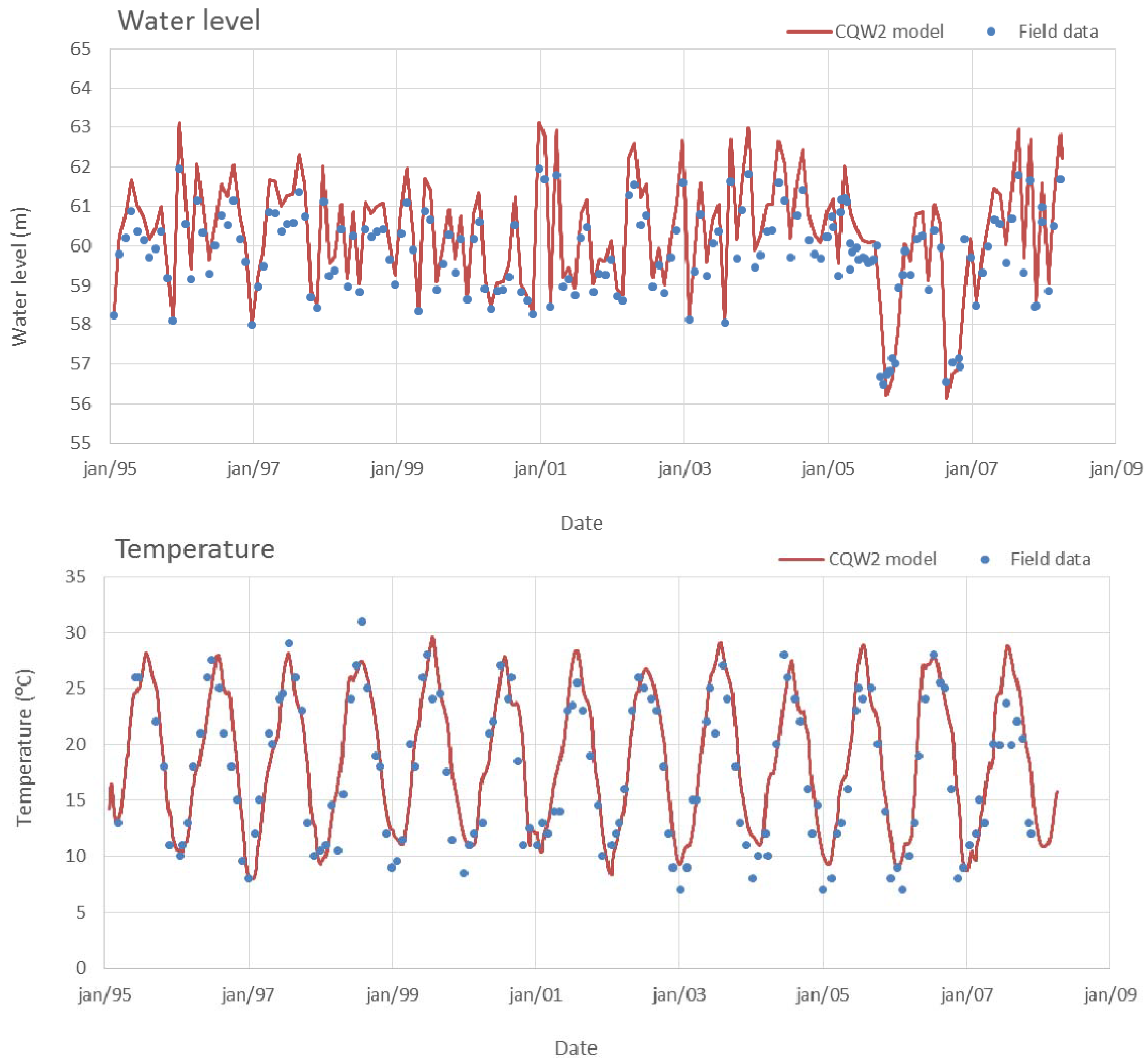
4.2. CE-QUAL-W2 Model Performance Assessment
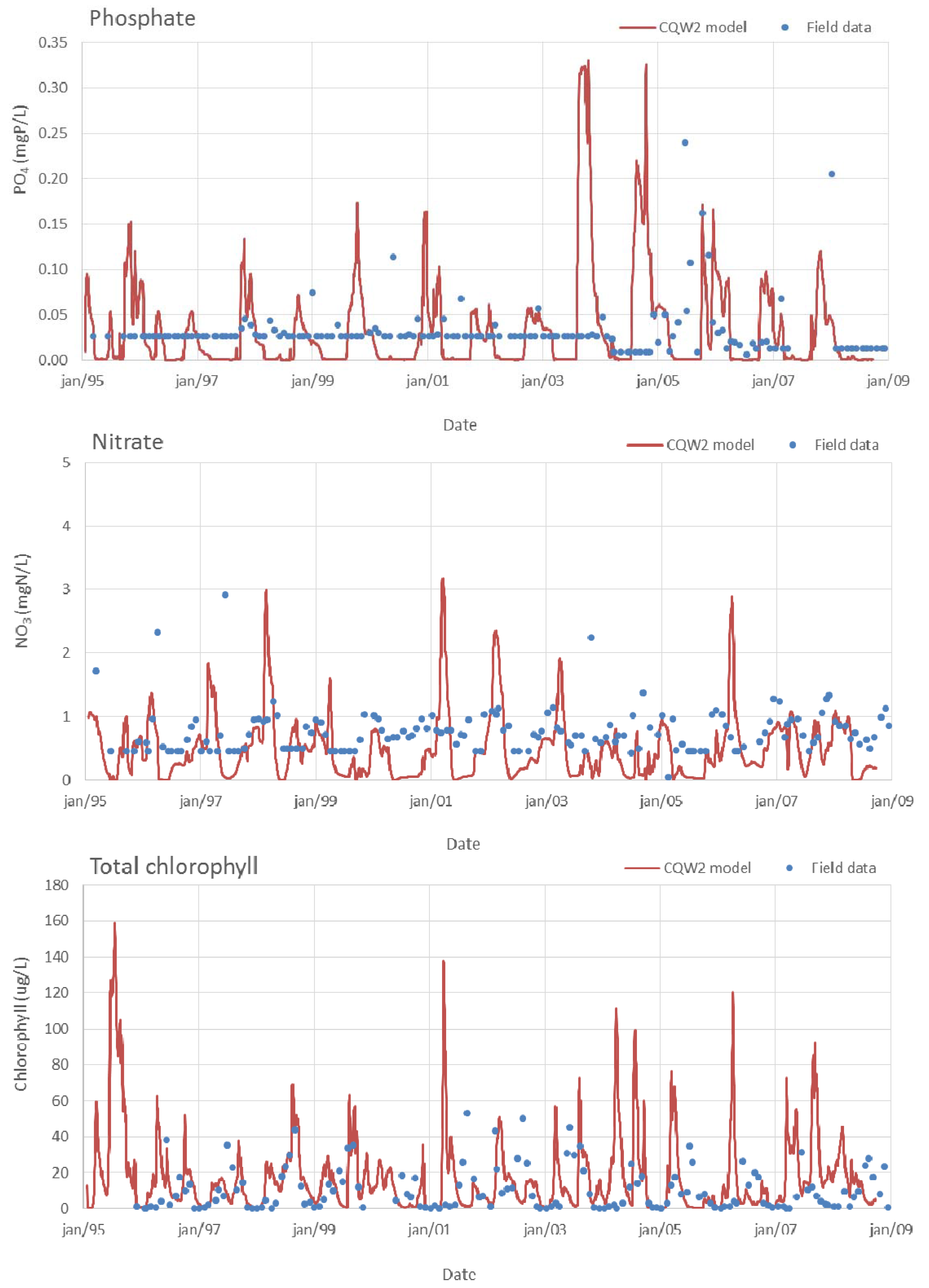
| Scenario | Trophic state |
|---|---|
| Reference scenario – field data | 10.6 (eutrophic) |
| Reference scenario – model simulation | 10.3 (eutrophic) |
| Simulation with a 10% nutrient load reduction | 9.2 (mesotrophic) |
| Simulation without point sources (WWTP) | 4.0 (mesotrophic) |
4.3. Pressures
4.4. Maximum Load to the Reservoir
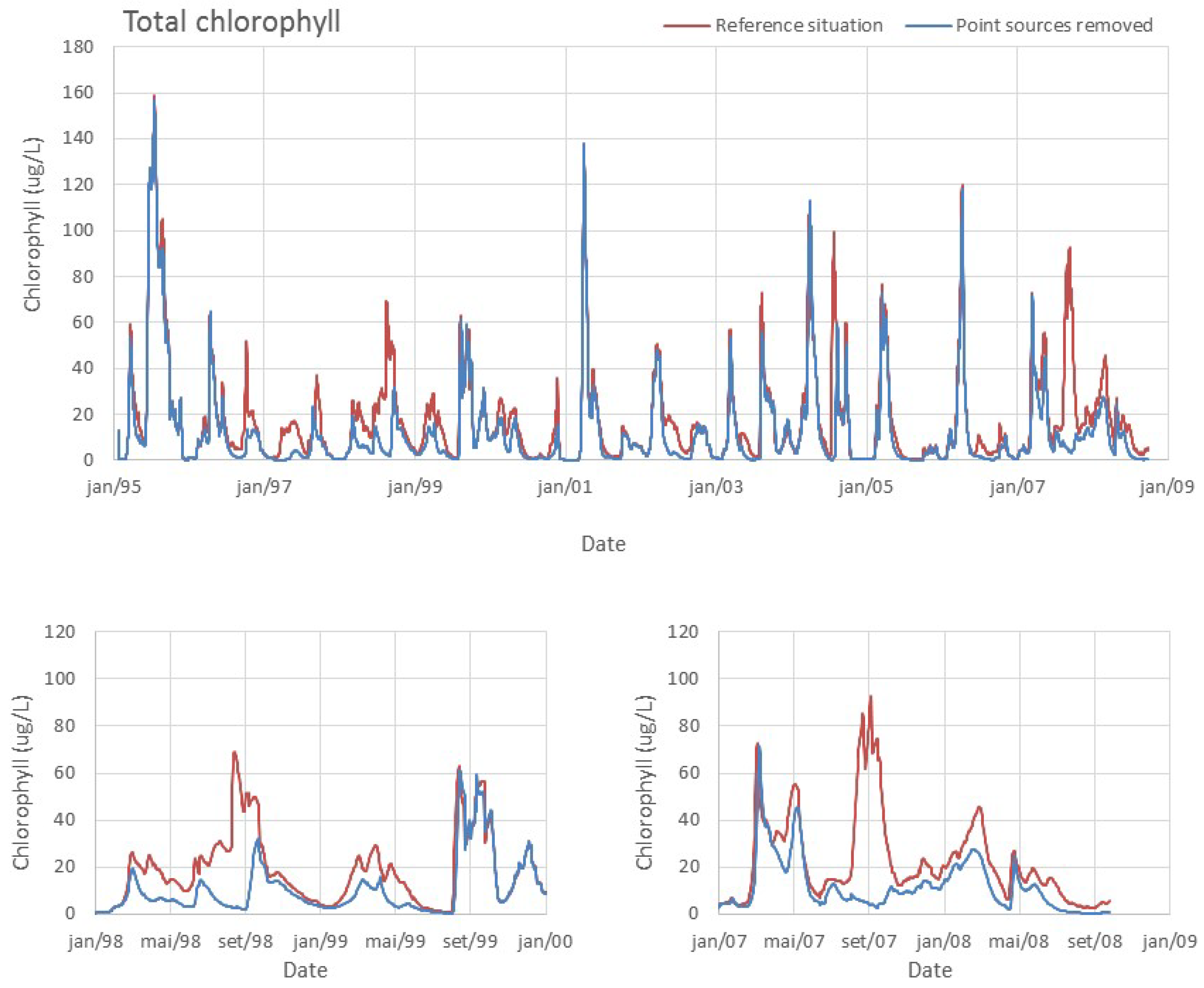

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seeboonruang, U. A statistical assessment of the impact of land uses on surface water quality indexes. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 101, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.L.; Rueda, F.J.; Hormann, G.; Fohrer, N. Implementing river water quality modelling issues in mesoscale watershed models for water policy demands—An overview on current concepts, deficits, and future tasks. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Global environmental impacts of agricultural expansion: The need for sustainable and efficient practices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5995–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Geist, H.J. Are agricultural land-use models able to predict changes in land-use intensity? Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Li, H.; Sun, D.F.; Zhou, L.D. A statistical assessment of the impact of agricultural land use intensity on regional surface water quality at multiple scales. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 4170–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, W.S.; Bai, S. A water quality for the Patuxent Estuary: Current conditions and predictions under changing land-use scenarios. Estuaries 2003, 26, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marce, R.; Moreno-Ostos, E.; Garcia-Barcina, J.M.; Armengol, J. Tailoring dam structures to water quality predictions in new reservoir projects: Assisting decision-making using numerical modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.B.; Qian, X.; Yuan, X.C.; Ye, R.; Xia, B.S.; Wang, Y.L. Simulation of water environmental capacity and pollution load reduction using qual2k for water environmental management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2012, 9, 4504–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, O.; Ikramova, M.; Bauer, M.; Froebrich, J. Applicability of adapted reservoir operation for water stress mitigation under dry year conditions. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelshtein, K.K.; Grechushnikova, M.G.; Datsenko, Y.S.; Puklakov, V.V. Diagnostic modelling of within-water processes in reservoirs. Water Resour. 2012, 39, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashghaei, M.; Bagheri, A.; Morid, S. Rainfall-runoff modeling in a watershed scale using an object oriented approach based on the concepts of system dynamics. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 5119–5141. [Google Scholar]
- Chiueh, P.T.; Shang, W.T.; Lo, S.L. An integrated risk management model for source water protection areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3724–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for the Economic Cooperation and Development. Europhication of Waters: Monitorign Assement and Control; Organization for the Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto da Água. Aplicação da Directiva Relativa Ao Tatamento Das Águas Residuais Urbanas Em Portugal; Instituto da Água: Lisboa, Portugal, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.L. Application of two-dimensional water quality model. J. Environ. Eng. ASCE 1988, 114, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, E.J.; Tobiason, E.; Hayes, M.; Wolfram, E.; Reckhow, D.A.; Male, J.W. Coliform transport in Pristine Reservoir: Modeling and field studies. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Gunduz, O.; Soyupak, S.; Yurteri, C. Development of water quality management strategies for the proposed Isikli Reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, R.G.; Hamilton, D.P.; Phillips, R.L. Comparison of two-dimensional, laterally averaged hydrodynamic model application to the Swan River Estuary. Math. Comput. Simul. 2000, 51, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.T.; Liu, W.C.; Lin, R.T.; Lung, W.S.; Yang, M.D.; Yang, C.P.; Chu, S.C. Water quality modeling for the Feitsui Reservoir in northern Taiwan. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.T.; Lung, W.S.; Yang, C.P.; Liu, W.C.; Yang, M.D.; Tang, T.S. Eutrophication modelling of reservoirs in Taiwan. Environ. Modelling Softw. 2006, 21, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A.; Shojaei, N.; Sagharjooghifarahani, M. Multiobjective calibration of reservoir water quality modeling using Multiobjective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO). Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1931–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.M.; Buchak, E. CE-QUAL-W2: A Two-Dimensional, Laterally Averaged, Hydrodynamics and Water Quality Model, Version 2.0; Tech. Report EL-95-May 1995; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.M.; Wells, S.A. Hydrodynamic Modeling with Application to CE-QUAL-W2. Workshop Notes; Portland State University: Portland, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool. User’s Manual. Version 2005; Grassland, Soil and Water Research Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service: Temple, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.K.; Rui, H.Y.; Zuo, T.H.; Li, Q.; Zheng, D.P.; Chen, A.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Xu, C.Y. Hydrological simulation by SWAT model with fixed and varied parameterization approaches under land use change. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2823–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaini, P.; Artita, K.; Nicklow, J.W. Optimizing structural best management practices using SWAT and genetic algorithm to improve water quality goals. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1827–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Bauwe, A.; Lennartz, B. Application of the SWAT model for a tile-drained lowland catchment in North-Eastern Germany on subbasin scale. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskidis, I.; Gikas, G.D.; Sylaios, G.K.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Hydrologic and water quality modeling of lower nestos river basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3023–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; He, H.M.; Zhang, S.F.; Jiang, X.H.; Xia, Z.Q.; Huang, F. Influence of reservoir operation in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River (China) on the inflow and outflow regime of the TGR-based on the improved SWAT model. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Sensitivity analysis of the penman-monteith actual evapotranspiration estimates. J. Hydrol. 1979, 44, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90m Database. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 7 March 2014).
- Saxton, K.E.; Rawls, W.J.; Romberger, J.S.; Papendick, R.I. Estimating generalized soil-water characteristics from texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorman, J.; Hone, T.; Sudman, T.; Dirksen, T.; Iles, J.; Islam, K.R. Agricultural impacts on lake and stream water quality in Grand Lake St. Marys, western Ohio. Water Air Soil Poll. 2008, 193, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, N.-G.; Boavida, M.-J. Effects of catchment development on the trophic status of a deep and a shallow reservoir in Portugal. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, M.J.; Marques, R.T. Total phosphorus as an indicator of trophic state of Portuguese reservoirs. Limnetica 1996, 12, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, S.D.; Brito, D.; Ferreira, M.T.; Neves, R.; Franco, A. Modeling water quality in reservoirs used for angling competition: Can groundbait contribute to eutrophication? Lake Reserv. Manag. 2013, 29, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.M.P.; Pinho, J.L.S.; Dias, N.; Schwanenberg, D.; van den Boogaard, H.F.P. Parameter estimation for eutrophication models in reservoirs. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mateus, M.; Almeida, C.; Brito, D.; Neves, R. From Eutrophic to Mesotrophic: Modelling Watershed Management Scenarios to Change the Trophic Status of a Reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3015-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303015
Mateus M, Almeida C, Brito D, Neves R. From Eutrophic to Mesotrophic: Modelling Watershed Management Scenarios to Change the Trophic Status of a Reservoir. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(3):3015-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303015
Chicago/Turabian StyleMateus, Marcos, Carina Almeida, David Brito, and Ramiro Neves. 2014. "From Eutrophic to Mesotrophic: Modelling Watershed Management Scenarios to Change the Trophic Status of a Reservoir" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 3: 3015-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303015
APA StyleMateus, M., Almeida, C., Brito, D., & Neves, R. (2014). From Eutrophic to Mesotrophic: Modelling Watershed Management Scenarios to Change the Trophic Status of a Reservoir. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(3), 3015-3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110303015





