Radioactivity of Drinking-Water in the Vicinity of Nuclear Power Plants in China Based on a Large-Scale Monitoring Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Area
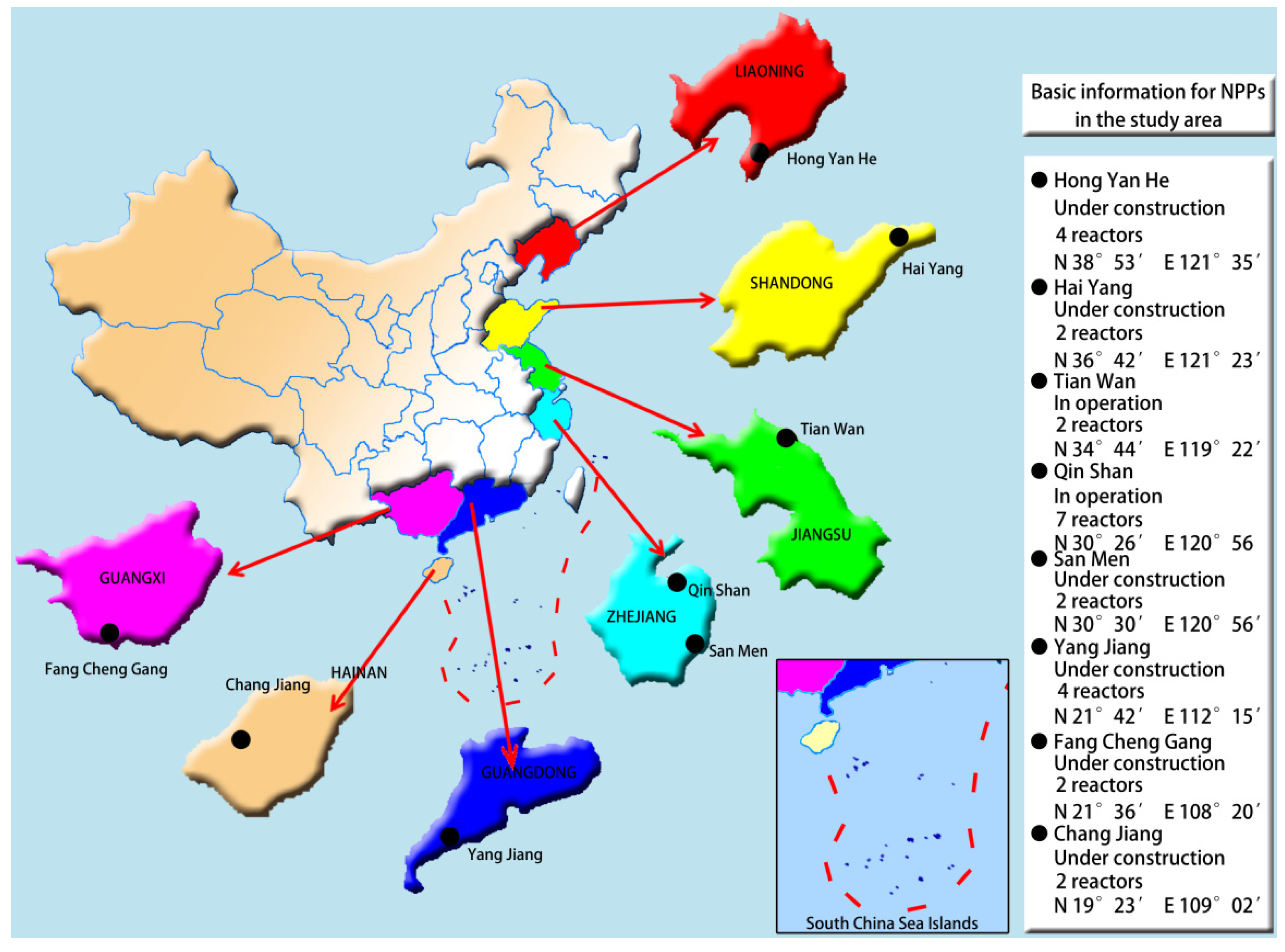
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Sample Analysis
| Number | Province | Instrument Model | Source for α Calibration | Source for β Calibration | Active Area Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liaoning | BH-1216 | 241Am/Uranium | 40K | 20 |
| 2 | Jiangsu | MPC-9604 | 241Am | 90Sr/90Y | 30.25 |
| 3 | Zhejiang | BH-1216 | 241Am/Uranium | 40K | 25 |
| 4 | Shandong | BH-1216II | 241Am | 40K | 20 |
| 5 | Guangdong | MPC-9604 | 241Am | 90Sr/90Y | 20 |
| 6 | Guangxi | MPC-9604 | 241Am | 40K | 29 |
| 7 | Hainan | LB-2008 | 239Pu | 90Sr/90Y | 25 |
2.4. Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gross α and Gross β Activity of Drinking-Water for Each Monitoring Province in Dry and Wet Season
| Liaoning | Jiangsu | Zhejiang | Shandong | Guangdong | Guangxi | Hainan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry season | Gross α | n | 5 | 10 | 11 | 5 | 14 | 15 | 23 |
| Range | 0.020–0.220 | ND–0.110 | ND–0.053 | ND–0.289 | ND–0.100 | ND–0.027 | ND–0.334 | ||
| Mean | 0.074 | 0.078 | 0.041 | 0.200 | 0.053 | 0.009 | 0.109 | ||
| S.D | 0.083 | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.127 | 0.029 | 0.008 | 0.131 | ||
| Gross β | n | 5 | 10 | 11 | 5 | 14 | 15 | 23 | |
| Range | 0.040–0.150 | ND–0.140 | 0.06–0.256 | 0.045–0.859 | 0.070–0.420 | 0.003–0.280 | 0.012–0.236 | ||
| Mean | 0.080 | 0.114 | 0.137 | 0.320 | 0.144 | 0.067 | 0.067 | ||
| S.D | 0.045 | 0.023 | 0.072 | 0.317 | 0.084 | 0.065 | 0.068 | ||
| Wet season | Gross α | n | 5 | 10 | 10 | 6 | * | 15 | 24 |
| Range | 0.050–0.280 | 0.050–0.120 | ND–0.027 | 0.048–0.412 | * | ND–0.005 | ND–0.012 | ||
| Mean | 0.124 | 0.076 | 0.024 | 0.175 | * | 0.013 | 0.002 | ||
| S.D | 0.090 | 0.024 | 0.004 | 0.127 | * | 0.010 | 0.004 | ||
| Gross β | n | 5 | 10 | 10 | 6 | * | 15 | 24 | |
| Range | 0.070–0.770 | 0.050–0.140 | 0.076–0.328 | ND–0.630 | * | 0.014–0.220 | 0.031–0.232 | ||
| Mean | 0.334 | 0.100 | 0.144 | 0.257 | * | 0.070 | 0.060 | ||
| S.D | 0.273 | 0.028 | 0.100 | 0.227 | * | 0.076 | 0.041 |
3.2. Gross α and Gross β Activity of Drinking-Water for Different Water Types in Each Monitoring Province
| Liaoning | Jiangsu | Zhejiang | Shandong | Guangdong | Guangxi | Hainan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | Gross α | n | 1 | 14 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 24 | 29 |
| Range | * | ND–0.110 | ND–0.053 | ND–0.412 | ND–0.100 | ND–0.027 | ND–0.045 | ||
| Mean | 0.040 | 0.075 | 0.048 | 0.169 | 0.063 | 0.010 | 0.012 | ||
| S.D | * | 0.019 | 0.005 | 0.131 | 0.033 | 0.007 | 0.018 | ||
| Gross β | n | 1 | 14 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 24 | 29 | |
| Range | * | ND–0.140 | 0.060–0.328 | ND–0.859 | 0.070–0.420 | 0.023–0.064 | 0.012–0.221 | ||
| Mean | 0.150 | 0.101 | 0.168 | 0.327 | 0.154 | 0.045 | 0.050 | ||
| S.D | * | 0.028 | 0.093 | 0.276 | 0.105 | 0.013 | 0.036 | ||
| Well water | Gross α | n | 9 | 2 | 2 | * | * | 6 | 14 |
| Range | 0.020–0.280 | 0.050–0.070 | ND–0.027 | * | * | ND–0.041 | ND–0.112 | ||
| Mean | 0.106 | 0.060 | 0.027 | * | * | 0.022 | 0.024 | ||
| S.D | 0.088 | 0.014 | * | * | * | 0.016 | 0.044 | ||
| Gross β | n | 9 | 2 | 2 | * | * | 6 | 14 | |
| Range | 0.040–0.770 | 0.090–0.120 | 0.069–0.081 | * | * | 0.014–0.280 | 0.031–0.236 | ||
| Mean | 0.213 | 0.105 | 0.075 | * | * | 0.133 | 0.066 | ||
| S.D | 0.241 | 0.021 | 0.008 | * | * | 0.106 | 0.052 | ||
| Others | Gross α | n | * | 4 | 8 | * | 5 | * | 2 |
| Range | * | ND–0.120 | ND–0.021 | * | 0.020–0.090 | * | 0.012–0.334 | ||
| Mean | * | 0.097 | 0.020 | * | 0.046 | * | 0.173 | ||
| S.D | * | 0.021 | 0.001 | * | 0.027 | * | 0.228 | ||
| Gross β | n | * | 4 | 8 | * | 5 | * | 2 | |
| Range | * | ND–0.140 | 0.061–0.275 | * | 0.110–0.140 | * | 0.232–0.235 | ||
| Mean | * | 0.127 | 0.127 | * | 0.124 | * | 0.234 | ||
| S.D | * | 0.015 | 0.073 | * | 0.015 | * | 0.002 |
3.3. Radiation Exposure through Ingestion of Different Types of Drinking-Water in Each Monitoring Province
| Liaoning | Jiangsu | Zhejiang | Shandong | Guangdong | Guangxi | Hainan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 0.021 | 0.039 | 0.025 | 0.088 | 0.033 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| Well water | 0.055 | 0.031 | 0.014 | * | * | 0.012 | 0.013 |
| Others | * | 0.051 | 0.010 | * | 0.024 | * | 0.090 |
3.4. Comparison This Work with Others on the Gross α and Gross β Activity of Different Types of Drinking-Water in Different Places
| Place and Country | Type of water | Gross α (Bq/L) | Gross β (Bq/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seven provinces, China | Tap water | 0.010–0.169 | 0.045–0.327 | This work |
| Well water | 0.022–0.106 | 0.066–0.213 | ||
| Spring/stream etc. | 0.020–0.173 | 0.124–0.234 | ||
| Milano, Italy | Tap water | <0.0077–0.349 | <0.025–0.273 | Rusconi, 2004 [20] |
| Dhaka city, Bangladesh | Tap water | 0.0019–0.0082 | 0.0293–0.1157 | Fedous, 2012 [21] |
| Eastern Black Sea Region, Turkey | Tap water | 0.0002–0.015 | 0.0252–0.2644 | Damla, 2006 [22] |
| Amman, Jordan | Tap water | <0.05–0.2495 | <0.1879–0.3270 | Sajedah Al-Amir, 2009 [23] |
| Katsina State, Nigeria | Well water | 0.080–2.300 | 0.120–4.970 | Muhammad, 2010 [18] |
| Nevşehir province, Turkey | Well water | 0.080–0.380 | 0.120–3.470 | Turhan, 2013 [24] |
| Balaton Upland region, Hungary | Spring water | 0.026–1.749 | 0.033–2.015 | Jobbαgy, 2013 [19] |
| Zacatecas and Guadaluoe, Mexico | Mineral water | <0.011–0.415 | <0.026–0.695 | Davila Rangel, 2001 [25] |
| Greece | Bottled water | 0.008–0.094 | 0.071–0.350 | Karamanis, 2007 [26] |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Decade for Action ‘Water for Life’ 2005–2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/background.shtml (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- Onda, K.; LoBuglio, J.; Bartram, J. Global access to safe water: Accounting for water quality and the resulting impact on MDG progress. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2012, 9, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinking Water Contaminants: List of Contaminants and their Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs). Available online: http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/index.cfm#List (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- Fawell, J.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Contaminants in drinking water environmental pollution and health. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Exposures from Natural Radiation Sources. Available online: http://www.unscear.org/docs/reports/annexb.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- World Nuclear Power Reactors and Uranium Requirements. Available online: http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Facts-and-Figures/World-Nuclear-Power-Reactors-and-Uranium-Requirements/ (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- Su, X.; Sun, Q.-F. Health response to Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant accident in Japan. Chin. J. Radiol. Med. Prot. 2012, 32, 113–115. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-Q.; Yin, L.-L; Tian, Q.; Yue, B.-R.; Su, X. Radioactivity analyses of food and drinking water in China following the Fukushima nuclear accident. Chin. J. Radiol. Med. Prot. 2012, 32, 125–128. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Standards. GBT 5750.2–2006. In Standard Examination Methods for Drinking Water—Collection and Preservation of Water Samples; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Chinese Standards. GB/T 5750.13–2006. In Standard Examination Methods for Drinking Water—Radiological Parameters; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Krieger, H.L. Interim Radiochemical Methodology for Drinking Water; Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Cowart, J.B.; Burnett, W.C. The distribution of Uranium and Thorium decay-series radionuclides in the environment—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbaniang, D.G. Radioactivity (Gross-A and Gross-B) studies of surface water collected from domiasiat area, West Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya, India. Int. J. Environ. Prot. 2011, 1, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Limiting Values of the Radionuclide Intake and Air Concentration and Dose Conversion Factors for Inhalation, Submersion and Ingestion: Federal Guidance Reprot No. 11. Available online: http://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/6294233 (accessed on 2 December 2013).
- Fernandez, F.; Lozano, J.C.; Gomez, J.M.G. Natural radionuclides in ground water in western Spain. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1992, 45, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
- Radon: Is My Private Water Well at Risk? Available online: http://wellowner.org/water-quality/radon/. (accessed on 8 November 2013).
- Muhammad, B.G.; Jaafar, M.S.; Akpa, T.C. A survey of gross alpha and beta activity concentrations in groundwater from Katsina area of Northern Nigeria. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2010, 141, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, V.; Kávási, N.; Somlai, J.; Dombovári, P.; Gyöngyösi, C.; Kovács, T. Gross alpha and beta activity concentrations in spring waters in Balaton Upland, Hungary. Radiat. Meas. 2011, 46, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, R.; Forte, M.; Badalamenti, P.; Bellinzona, S.; Gallini, R.; Maltese, S.; Romeo, C.; Sgorbati, G. The monitoring of tap waters in Milano: Planning, methods and results. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2004, 111, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, J.; Rahman, M.; Begum, A. Gross alpha and gross beta activities of tap water samples from different locations of Dhaka City. Sri Lankan J. Physic. 2012, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Damla, N.; Cevik, U.; Karahan, G.; Kobya, A.I. Gross α and β activities in tap waters in Eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amir, M.S.; Al-Hamarneh, F.I.; Al-Abed, T. A Study of Natural Radioactivity in Drinking Water in Amman, Jordan. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Nuclear Energy, Al-Balqa’ Applied University, Salt, Jordan, 26–28 October 2009.
- Turhan, Ş.; Özçıtak, E.; Taşkın, H.; Varinlioğlu, A. Determination of natural radioactivity by gross alpha and beta measurements in ground water samples. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3103–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila Rangel, J.I.; López del Río, H.; Rodríguez, B.L.; Solache-Ríos, B.M. Gross alpha and gross beta radioactivity in drinking water from Zacatecas and Guadalupe cities, Mexico. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2001, 247, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanis, D.; Stamoulis, K.; Loannides, K.G. Natural radionuclides and heavy metals in bottled water in Greece. Desalination 2007, 213, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, X.-X.; Ji, Y.-Q.; Shao, X.-Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q.-F.; Su, X. Radioactivity of Drinking-Water in the Vicinity of Nuclear Power Plants in China Based on a Large-Scale Monitoring Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6863-6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10126863
Miao X-X, Ji Y-Q, Shao X-Z, Wang H, Sun Q-F, Su X. Radioactivity of Drinking-Water in the Vicinity of Nuclear Power Plants in China Based on a Large-Scale Monitoring Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013; 10(12):6863-6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10126863
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Xiao-Xiang, Yan-Qin Ji, Xian-Zhang Shao, Huan Wang, Quan-Fu Sun, and Xu Su. 2013. "Radioactivity of Drinking-Water in the Vicinity of Nuclear Power Plants in China Based on a Large-Scale Monitoring Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, no. 12: 6863-6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10126863
APA StyleMiao, X.-X., Ji, Y.-Q., Shao, X.-Z., Wang, H., Sun, Q.-F., & Su, X. (2013). Radioactivity of Drinking-Water in the Vicinity of Nuclear Power Plants in China Based on a Large-Scale Monitoring Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(12), 6863-6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10126863




