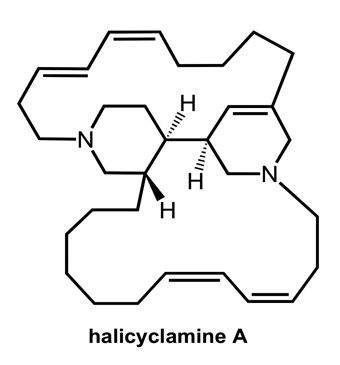
DedA Protein Relates to Action-Mechanism of Halicyclamine A, a Marine Spongean Macrocyclic Alkaloid, as an Anti-dormant Mycobacterial Substance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
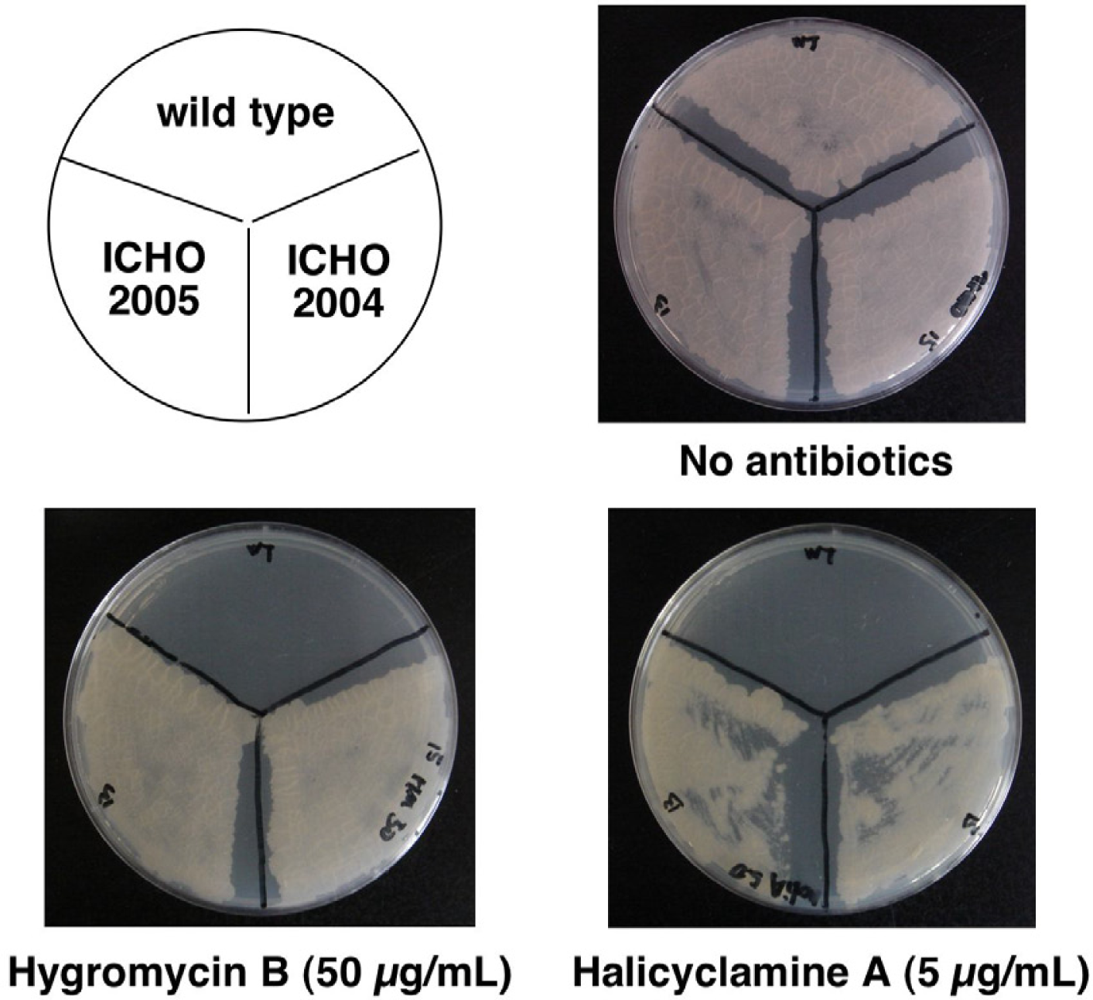
2.1. Isolation of the Halicyclamine A-Resistant Clones from the Transformants of M. smegmatis with Genomic DNA Library
2.2. Second Selection of the Transformants of M. smegmatis Expressing the Candidate Region Showing Resistance to Halicyclamine A
2.3. Identification of the Gene Causing Resistance to Halicyclamine A
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Bacterial Culture
3.3. Construction of Gnomic DNA Library and Transformation of M. smegmatis mc2155
3.4. Isolation of Halicyclamine A-Resistant Clones from the Transformants of M. smegmatis with Genomic DNA Library and End Sequencing of Cosmids
3.5. Preparation of the Transformants of M. smegmatis Over-Expressing the Candidate-Genes for Giving Resistance to Halicyclamine A
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Idemyor, V. HIV and tuberculosis coinfection: inextricably linked liaison. J Natl Med Assoc 2007, 99, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Global Tuberculosis Control: Epidemiology, Strategy, Financing; WHO report 2009. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2009/en/index.html (accessed on 25 May 2011).
- Wayne, LG; Hayes, LG. An in vitro model for sequential study of shiftdown of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through two stages of nonreplicating persistence. Infect Immun 1996, 64, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A; Eleuterio, M; Hutter, B; Murugasu-Oei, B; Dick, T. Oxygen depletion-induced dormancy in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Bacteriol 1999, 181, 2252–2256. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, T; Lee, BH; Murugasu-Oei, B. Oxygen depletion induced dormancy in Mycobacterium smegmatis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1998, 163, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, M; Sobou, M; Vilchèze, C; Baughn, A; Hashizume, H; Pruksakorn, P; Ishida, S; Matsumoto, M; Jacobs, WR, Jr; Kobayashi, M. Halicyclamine A, a marine spongean alkaloid as a lead for anti-tuberculosis agent. Bioorg Med Chem 2008, 16, 6732–6736. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, M; Ishida, S; Setiawan, A; Kobayashi, M. Haliclonacyclamines, tetracyclic alkylpiperidine alkaloids, as anti-dormant mycobacterial substances from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Chem Pharm Bull 2009, 57, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Pruksakorn, P; Arai, M; Kotoku, N; Vilchèze, C; Baughn, AD; Moodley, P; Jacobs, WR, Jr; Kobayashi, M. Trichoderins, novel aminolipopeptides from a marine sponge-derived Trichoderma sp., are active against dormant mycobacteria. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2010, 20, 3658–3663. [Google Scholar]
- Jaspars, M; Pasupathy, V; Crews, P. A tetracyclic diamine alkaloid, halicyclamine A, from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. J Org Chem 1994, 59, 3253–3255. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A; Dubnau, E; Quemard, A; Balasubramanian, V; Um, KS; Wilson, T; Collins, D; de Lisle, G; Jacobs, WR, Jr. inhA, a gene encoding a target for isoniazid and ethionamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 1994, 263, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Telenti, A; Philipp, WJ; Sreevatsan, S; Bernasconi, C; Stockbauer, KE; Wieles, B; Musser, JM; Jacobs, WR, Jr. The emb operon, a gene cluster of Mycobacterium tuberculosis involved in resistance to ethambutol. Nature Med 1997, 3, 567–570. [Google Scholar]
- Biehle, JR; Cavalieri, SJ; Saubolle, MA; Getsinger, LJ. Evaluation of Etest for susceptibility testing of rapidly growing mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol 1995, 33, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Ledgham, F; Quest, B; Vallaeys, T; Mergeay, M; Covès, J. A probable link between the DedA protein and resistance to selenite. Res Microbiol 2005, 156, 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Thompkins, K; Chattopadhyay, B; Xiao, Y; Henk, MC; Doerrler, WT. Temperature sensitivity and cell division defects in an Escherichia coli strain with mutations in yghB and yqjA, encoding related and conserved inner membrane proteins. J Bacteriol 2008, 190, 4489–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, S; Miyata, Y; van Soest, RWM; Fusetani, N. Tetradehydrohalicyclamine A and 22-hydroxyhalicyclamine A, new cytotoxic bis-piperidine alkaloids from a marine sponge Amphimedon sp. J Nat Prod 2004, 67, 1758–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, ND. Mycobacterium: isolation, maintenance, transformation, and mutant selection. Methods Cell Biol 1994, 45, 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, V; Pavelka, MS, Jr; Bardarov, SS; Martin, J; Weisbrod, TR; McAdam, RA; Bloom, BR; Jacobs, WR, Jr. Allelic exchange in Mycobacterium tuberculosis with long linear recombination substrates. J Bacteriol 1996, 178, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
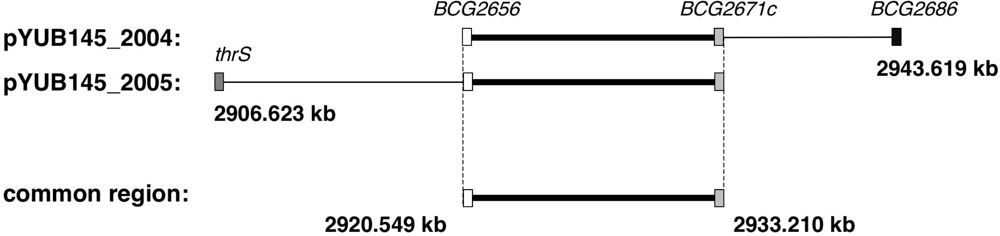
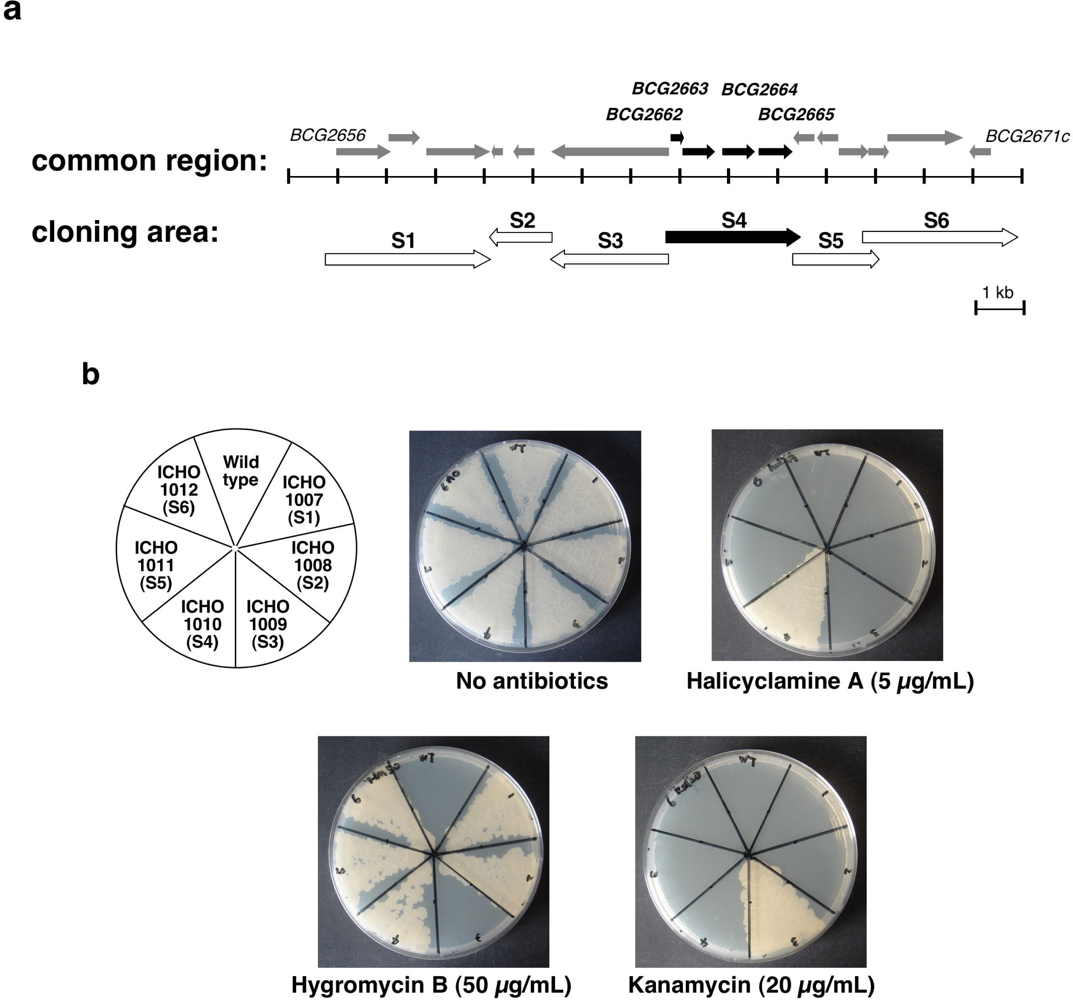
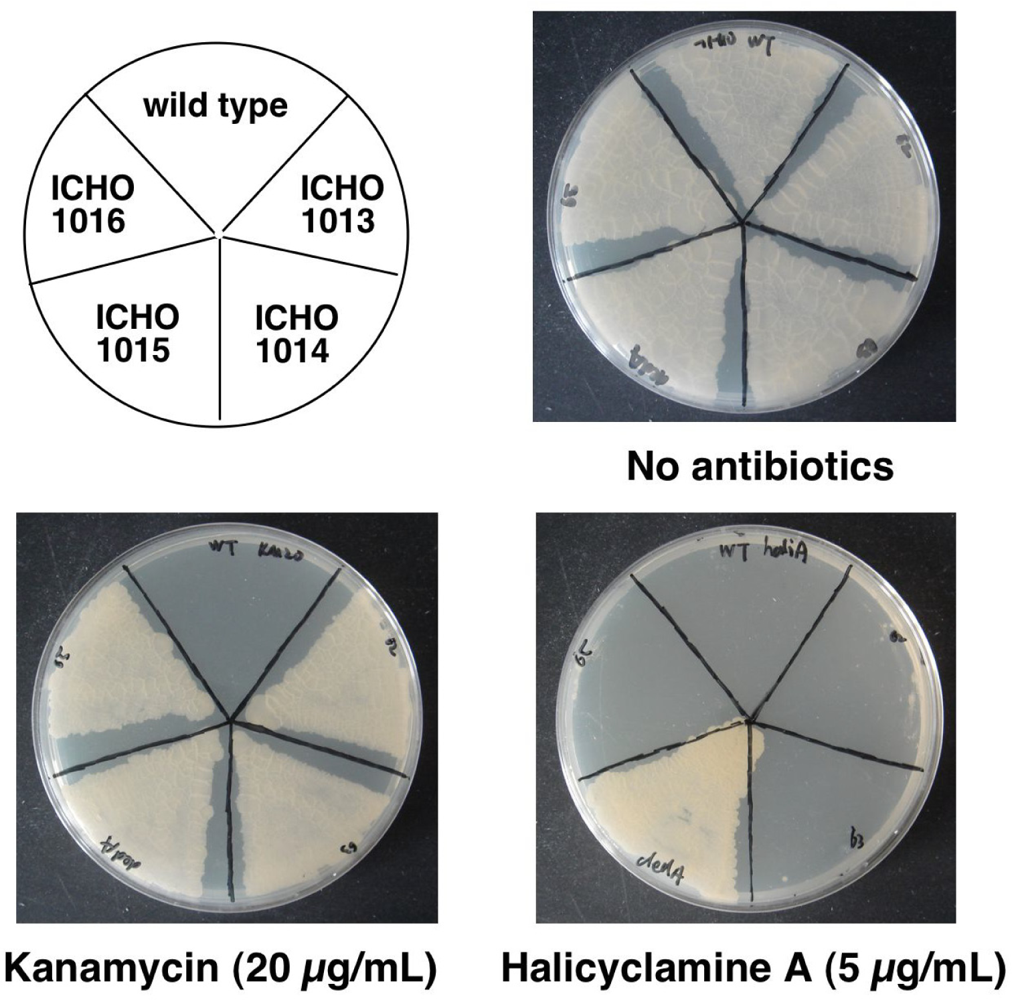
| Strains | Plasmids | Description of plasmids | Sequence of primers (5’ to 3’) F; Forward primer, R; Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICHO1007 | pMV206 | Cloned S1 area# (2919991–2923343 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F:TCTAGAGCCACACCCTGATAGCATTG R: AAGCTTTCGCGACGGCTGGAATG |
| ICHO1008 | pMV206 | Cloned S2 area # (2924490–2923316 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F:GGATCCAACTGTTTCCGCACGAGGAG R:CTGCAGTCAACGGCGAACATTCCAGC |
| ICHO1009 | pMV261 | Cloned S3 area # (2926966–2924589 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F:GGATCCATCCAGGAGGTCGCAGATGTC R: GAATTCGTGATGTTCGCGCCTAACGG |
| ICHO1010 | pMV206 | Cloned S4 area # (2926766–2929363 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F:CAGCTGATAGCTCTGCGCGTACGAC R: TTCGAAGATCAGCAACGGGCTGGAC |
| ICHO1011 | pMV206 | Cloned S5 area # (2929454–2931112 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F: GGATCCTGCGGTATCGCTTGCCTTG R: AAGCTTGCGCGACTACGCAGCTC |
| ICHO1012 | pMV206 | Cloned S6 area # (2930898–2933532 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F:GGATCCAAGCGGCTAACTGTAGGCCTG R: AAGCTTTCAGCCCGGTGGTGTTGG |
| ICHO1013 | pMV261 | Cloned BCG2662 gene (2926980–2927222 bp of M. bovis BCGgenome)* | F:GAATTCAGGACAACCCGCATGGTCG R: AAGCTTTATCACTCAGCGCCGGTACG |
| ICHO1014 | pMV261 | Cloned BCG2663 gene (2927223–2927900 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F: GAATTCCCGGTCAGGCATTCTTTACCC R:AAGCTTGAAAGTTCCAGTTGCGCACGAC |
| ICHO1015 | pMV261 | Cloned BCG2664 gene(2928096–2928752 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F: GAATTCCCGGTCAGGCATTCTTTACCC R: AAGCTTCAAGCCGGTCGGTCACG |
| ICHO1016 | pMV261 | Cloned BCG2665 gene(2928915–2929361 bp of M. bovis BCG genome)* | F: GGATCCATGCACCATGGGCCTGATCAC R: GAATTCTACGGCCGGGATCAGCAAC |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Arai, M.; Liu, L.; Fujimoto, T.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. DedA Protein Relates to Action-Mechanism of Halicyclamine A, a Marine Spongean Macrocyclic Alkaloid, as an Anti-dormant Mycobacterial Substance. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 984-993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060984
Arai M, Liu L, Fujimoto T, Setiawan A, Kobayashi M. DedA Protein Relates to Action-Mechanism of Halicyclamine A, a Marine Spongean Macrocyclic Alkaloid, as an Anti-dormant Mycobacterial Substance. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(6):984-993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060984
Chicago/Turabian StyleArai, Masayoshi, Liu Liu, Takao Fujimoto, Andi Setiawan, and Motomasa Kobayashi. 2011. "DedA Protein Relates to Action-Mechanism of Halicyclamine A, a Marine Spongean Macrocyclic Alkaloid, as an Anti-dormant Mycobacterial Substance" Marine Drugs 9, no. 6: 984-993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060984
APA StyleArai, M., Liu, L., Fujimoto, T., Setiawan, A., & Kobayashi, M. (2011). DedA Protein Relates to Action-Mechanism of Halicyclamine A, a Marine Spongean Macrocyclic Alkaloid, as an Anti-dormant Mycobacterial Substance. Marine Drugs, 9(6), 984-993. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060984