Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Toxin | Producer | Mechanism of action | LD50(i.p.) µg kg−1 (a) | Detoxication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcystins (MCs) | Microcystis | Inhibition protein phosphatase (PP1 and PP2A) | 50→1000 (b) | GST |
| Anabaena | ||||
| Plankthotrix | ||||
| Nodularin (NOD) | Nodularia | Inhibition protein phosphatase (PP1 and PP2A) | 50 | GST |
| Saxitoxins (STXs) | Dinoflagellates: | Binding and blocking the sodium channels in neural cells | 8–10 | GST |
| Protogonyaulux | ||||
| Alexandrium | ||||
| Gymnodinium | ||||
| Pyrodinium | ||||
| Cyanobacteria: | ||||
| Anabaena | ||||
| Aphanizomenon | ||||
| Cylindrospermopsis | ||||
| Lyngbya | ||||
| Anatoxins (ANTX-a) | Anabaena | Binding irreversibly to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors | 20–250 | Cytochrome P450 |
| Aphanizomenon | GST | |||
| Cylindrospermopsis | ||||
| Plankthotrix | ||||
| Oscillatoria | ||||
| Microcystis | ||||
| Anatoxin-a(s) (ANTX-a(s)) | Anabaena | Inhibition of Ach-esterase activity | 20 | Cytochrome P450 |
| GST | ||||
| Cylindrospermopsin (CYN) | Cylindrospermopsis | Inhibitor of protein biosynthesis cytogenetic damage on DNA | 2100 (24 h) | Cytochrome P450 |
| Aphanizomenon | 200 (5–6 days) | |||
| Umezakia | ||||
| Raphidiopsis | ||||
| Anabaena | ||||
| Lipopolysaccarides (LPS) | Cyanobacteria in general | Irritant; causes inflammation in exposed tissues | unknown | Deacylation via lysossomal pathway |
2. Accumulation of Cyanotoxins and Their Effects on Aquatic Invertebrates
2.1. Accumulation and Effects of Hepatotoxins on Invertebrates
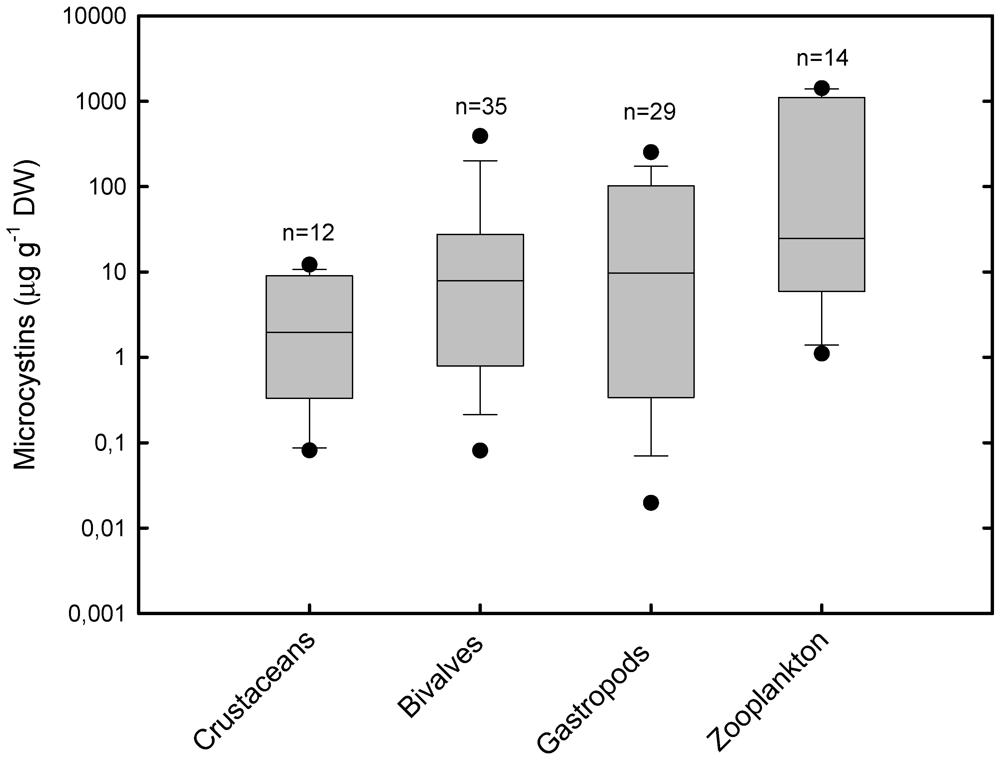
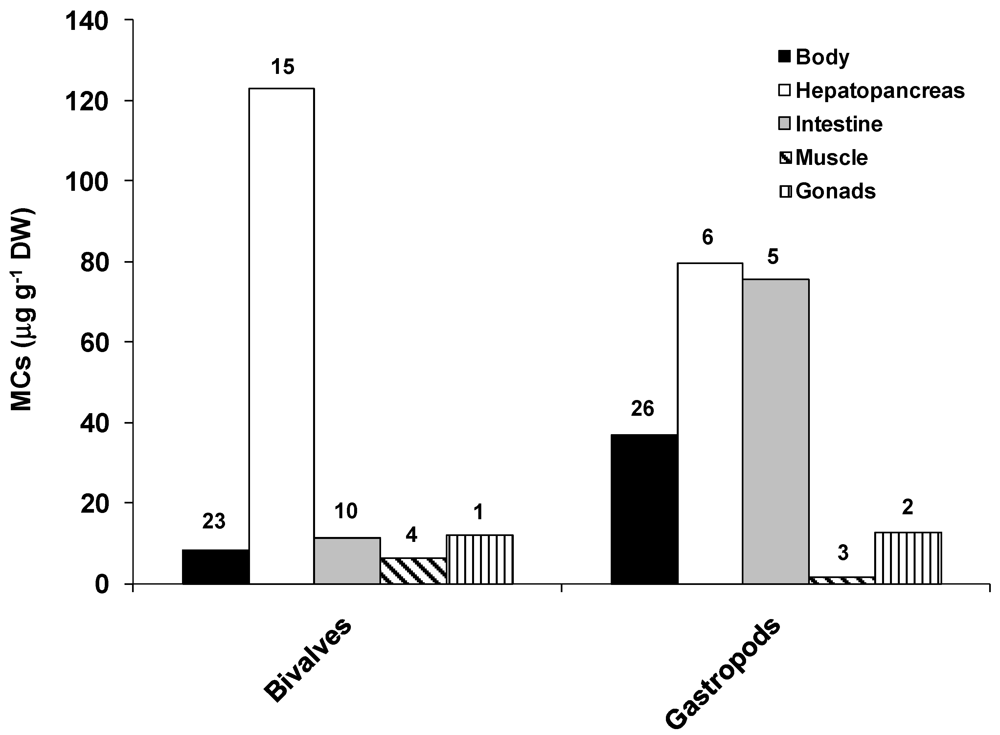
2.2. Accumulation and Effects of Cylindrospermopsin on Invertebrates
2.3. Accumulation and Effects of Neurotoxins on Invertebrates
3. Accumulation of Cyanotoxins and Their Effects on Aquatic Vertebrates
3.1. Accumulation and Effects of Hepatotoxins on Fish
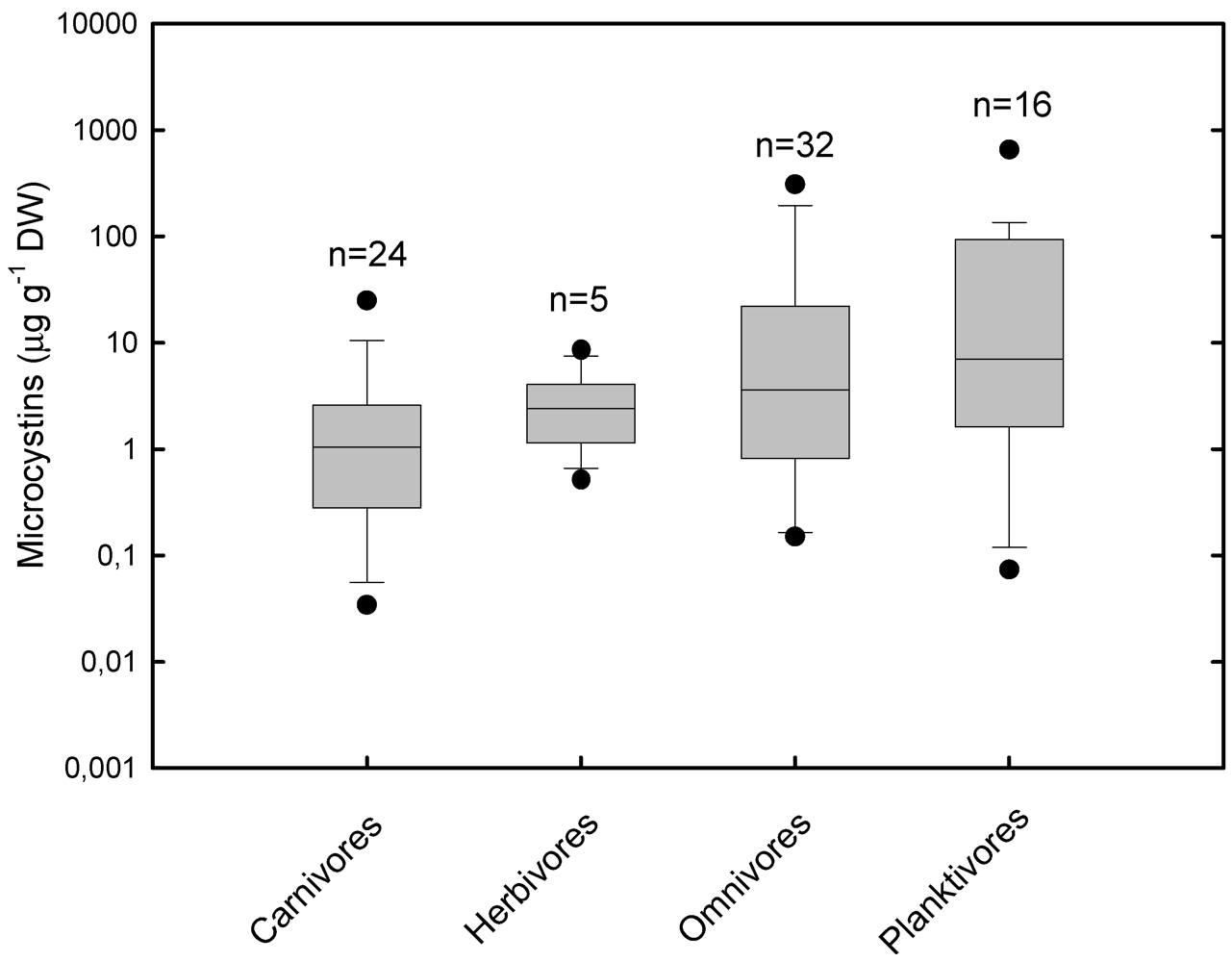
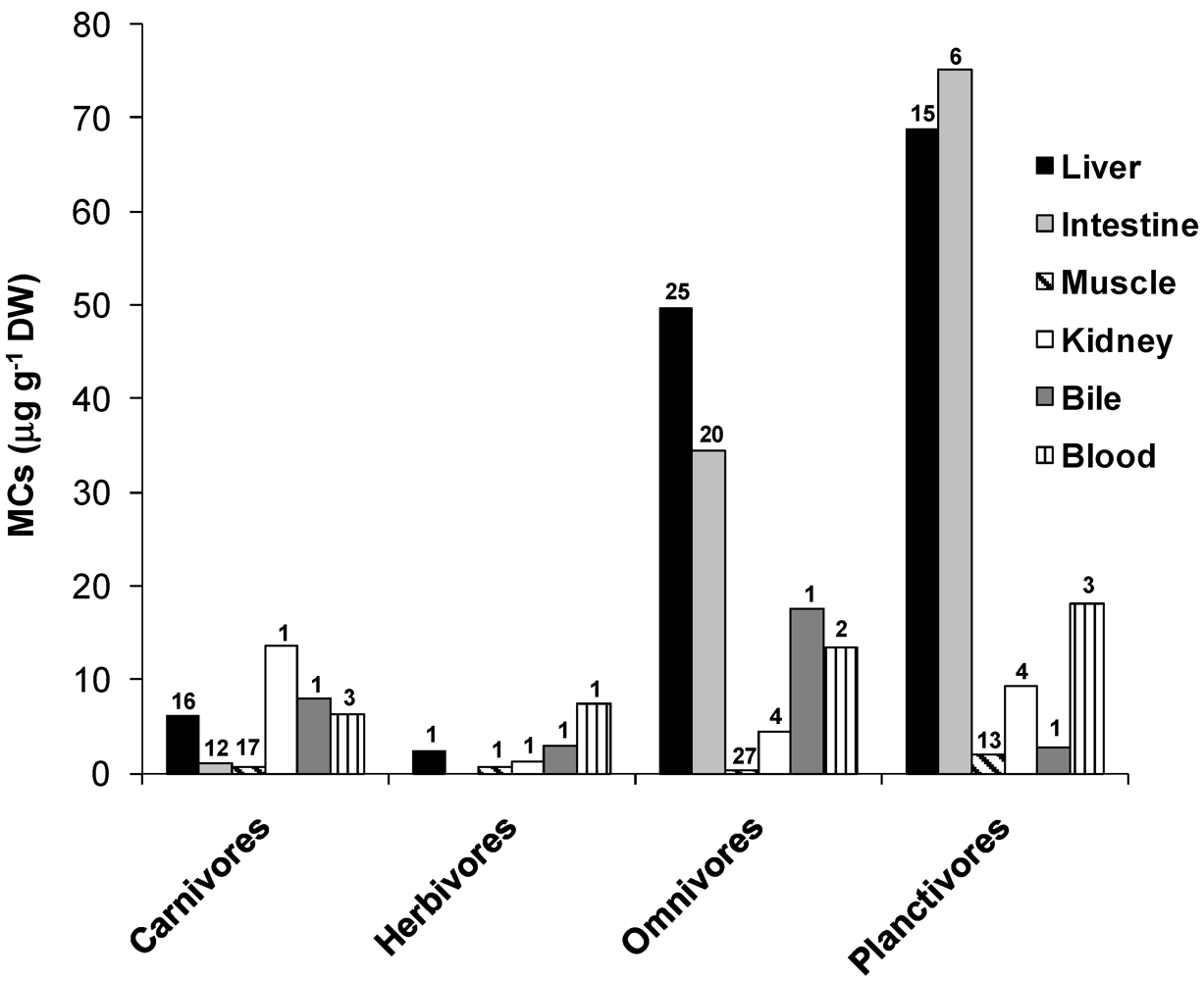
3.2. Accumulation and Effects of Cylindrospermopsin on Fish
3.3. Accumulation and Effects of Neurotoxins on Fish
3.4. Effects of Cyanotoxins on Other Aquatic Vertebrates
4. Exposure Mode and Experimental Conditions
5. Tolerance/Resistance to Cyanotoxins
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
Supplementary Files
References
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. Introduction to the Cyanobacteria. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria, Their Diversity in Time and Space, 1st; Whitton, B.A., Potts, M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Plublishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, W.W. Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites: The cyanotoxins. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 72, 445–459. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, 1st; Chorus, I., Bartran, J., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; Bell, S.G.; Kaya, K.; Ward, C.J.; Beattie, K.A.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins, exposure routes and human health. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 405–415. [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen, K. Cyanobacterial toxins and toxin production. Phycologia 1996, 190, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M. Red tides. Sci. Am. 1994, 271, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.Y. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning. In Toxins in Seafood and Drinking Water; Falconer, I.R., Ed.; Algal Academic Press: London, UK, 1993; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.W. Recurrence of kills of Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus harengus) caused by dinoflagellate toxins transferred through herbivorous zooplankton. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 2262–2265. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Elder, N.E.; Hershberger, P.K.; Trainer, V.L.; Stehr, C.M.; Scholz, N.L. Dissolved saxitoxin causes transient inhibition of sensorimotor function in larval Pacific herring (Clupea harengus pallasi). Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Costa, S.M.; Ribeiro, M.G.L.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Effects of a saxitoxin-producer strain of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) on the swimming movements of cladocerans. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, J.H. Toxins and Harmful Mechanisms. In The Effect of Harmful Algal Blooms on Aquatic Organisms; Stickney, R.R., Ed.; CCR Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; Volume 10, pp. 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Havens, K.; Codd, G.A.; Dyble, J.; Landsberg, J.; Coveney, M.; Fournie, J.W.; Hilborn, E.D. Ecosystem Effects Group. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 619, Chapter 31, pp. 656–674. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, A.; Schelske, C. Recent appearance of Cylindrospermopsis (Cyanobacteria) in five hypereutrophic Florida lakes. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- St Amand, A. Cylindrospermopsis: An invasive toxic algae. Lakeline 2002, 22, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gugger, M.; Molica, R.; Le Berre, B.; Dufour, P.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.-F. Genetic diversity of Cylindrospermopsis strains (Cyanobacteria) isolated from four continents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, J.D.; Quinlan, E.L.; Kane, D.D.; Culver, D.A. Cylindrospermopsis in Lake Erie: Testing its association with other cyanobacterial genera and major limnological parameters. J. Great Lakes Res. 2007, 33, 519–535. [Google Scholar]
- Huszar, V.L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Marinho, M.M.; Domingos, P.; Sant’Anna, C. Cyanoprokaryote assemblages in eight productive tropical Brazilian waters. Hydrobiologia 2000, 424, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yunes, J.S.; Cunha, N.T.; Barros, L.P.; Proença, L.A.O.; Monserrat, J.M. Cyanobacterial neurotoxins from southern Brazilian freshwaters. Comments Toxicol. 2003, 9, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Molica, R.J.R.; Oliveira, E.J.A.; Carvalho, P.V.V.C.; Costa, A.N.S.F.; Cunha, M.C.C.; Melo, J.L.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermospsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae) isolated from Tabocas reservoir in Caruaru, Brazil, including demonstration of a new saxitoxin analogue. Phycology 2002, 41, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Molica, R.J.R.; Oliveira, E.J.A.; Carvalho, P.V.V.C.; Costa, A.N.S.F.; Cunha, M.C.C.; Melo, J.L.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Occurrence of saxitoxins and an anatoxin-a(s)-like anticholinesterase in a Brazilian drinking water supply. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 743–753. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; Magalhães, V.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Biomonitoring of cyanotoxins in two tropical reservoirs by cladoceran toxicity bioassays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.; Chapman, A.; Williams, C.; Flewelling, L.; Carmichael, W.; Pawlowicz, M. Cyanotoxic Blooms in Florida’s (USA) Lakes, Rivers and Tidal River Estuaries: The Recent Invasion of Toxigenic Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Consequences for Florida’s Drinking Water Supplies. In Proceedings of the IX Conference on Harmful Algal Blooms, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 7–11 February 2000.
- Griffiths, D.J.; Saker, M.L. The Palm island mystery disease 20 years on: A review of research on the cyanotoxin cylindrospermopsin. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Brittain, S.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Shaw, G.R.; Mahakhant, A.; Noparatnaraporn, N.; Yongmanitchai, W.; Kaya, K.; Watanabe, W.W. Isolation and identification of the cyanotoxin cylindrospermopsin and deoxy-cylindrospermopsin from a Thailand strain of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). Toxicon 2001, 39, 973–980. [Google Scholar]
- Lagos, N.; Onodera, H.; Zagatto, P.A.; Andrinolo, D.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Oshima, Y. The first evidence of paralytic shelfish toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, isolated from Brazil. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, P.A.; Banack, S.A.; Murch, S.J.; Rasmussen, U.; Tien, G.; Bidigare, R.R.; Metcalf, J.S.; Morrison, L.F.; Codd, G.A.; Bergman, B. Diverse taxa of cyanobacteria produce beta-N-methylamino-l-alanine, a neurotoxic amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5074–5078. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, P.A.; Banack, S.A.; Murch, S.J. Biomagnification of cyanobacterial neurotoxins and neurodegenerative disease among the Chamorro people of Guam. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13380–13383. [Google Scholar]
- Charmichael, W.W.; Gorham, P.R. Freshwater Cyanophyte Toxins: Types and Their Effectes on the Use of Microalgae Biomass. In Algae Biomass: Production and Use; Shelef, G., Soeder, C.J., Eds.; Elsevier, North Holand Biomedical Press: Amsterdan, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Spoof, L. Microcystins and Nodularins. In Toxic Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; Meriluoto, J., Codd, G.A., Eds.; Åbo Akademi University Press: Pargas, Finland, 2005; Volume 65. [Google Scholar]
- Apeldoorn, M.E.; Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Bakker, G.J.I. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I.; Seawright, A.A.; Shaw, G.R. Cyanobacterial Poisoning in Livestock, Wild Mammals and Birds—An Overview. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 619, Chapter 28, pp. 613–637. [Google Scholar]
- Jochimsen, E.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; An, J.; Cardo, D.M.; Cookson, S.T.; Holmes, C.E.M.; Antunes, B.C.; Filho, D.A.M.; Lyra, T.M.; Barreto, V.S.T.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Jarvis, W.R. Liver failure and death after exposure to mycrocystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 873–878. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Na, J.S.; Molica, R.J.R.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Lau, S.; Rinehart, K.I.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: Chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 663–668. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, I.R. Tumor promotion and liver injury caused by oral consumption of cyanobacteria. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1991, 6, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, C.; Pflugmacher, S. Ecotoxicological effects of selected cyanobacterial secondary metabolites: A short review. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Leflaive, J.; Ten-Hage, L. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: A comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 199–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. Toxicity of blue-green Microcystis aeruginosa: Effective defense mechanism against grazing pressure by Daphnia. Verh. Intern. Verein Limnol. 1981, 21, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, K.L.; Gilbert, J.J. Variation in herbivore response to chemical defenses: Zooplankton foraging on toxic cyanobacteria. Ecology 1992, 73, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.E.; Sarnelle, O.; Tillmanns, A.R. Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplâncton: Meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.E.; Hay, M.E. A direct test of cyanobacterial chemical defense: Variable effects of microcystin-treated food on two Daphnia pulicaria clones. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmanns, A.; Wilson, A.E.; Pick, F.R.; Sarnelle, O. Meta-analysis of cyanobacterial effects on zooplankton population growth rate: Species-specific responses. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2008, 171, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.-H.; Ha, K.; Joo, G.-J.; Takamura, N. Toxin production of cyanobacteria is increased by exposure to zooplankton. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.-H.; Jung, J.-M.; Takamura, N. Changes in microcystin production in cyanobacteria exposed to zooplankton at different population densities and infochemical concentrations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, K.G.; Orcutt, J.D. Nutritional adequacy, manageability and toxicity as factors that determine the food quality of green and blue-green algae for Daphnia. In Evolution and Ecology of Zooplankton Communities; Kerfoot, W.C., Ed.; University Press of New England: Hanover, NH, USA, 1980; pp. 268–281. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R.; Müller-Navarra, D.C. The importance of highly unsaturated fatty acids in zooplâncton nutrition: Evidence from experiments with Daphnia, a cyanobacterium and lipid emulsions. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 38, 649–664. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T.; Henning, M.; Kohl, J.-G. Mechanisms of the inhibitory effect of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on Daphnia galeata’s ingestion rate. J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Von Elert, E.; Wolffrom, T. Supplementation of cyanobacterial food with polyunsaturated fatty acids does not improve growth of Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Infante, A.; Abella, S.E.B. Inhibition of Daphnia by Oscilatoria in Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1985, 30, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Hazanato, T.; Yasuno, M. Evaluation of Microcystis as food for zooplankton in an eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 1987, 144, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Matveev, V.F.; Balseiro, E.G. Contrasting responses of two cladocerans in the nutritional value of nanoplankton. Freshw. Biol. 1990, 23, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lundsted, L.; Brett, M.T. Differential growth rates of three cladoceran species in response to mono- and mixed-algal cultures. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlgren, G.; Lundsted, L.; Brett, M.; Fosberg, C. Lipid composition and food quality of some freshwater phytoplankton for cladoceran zooplankters. J. Plankton Res. 1990, 12, 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Gladyshev, M.I.; Sushchik, N.N.; Makhutova, O.N.; Dubovskaya, O.P.; Kravchuk, E.S.; Kalachova, G.S.; Khromechek, E.B. Correlations between fatty acid composition of seston and zooplankton and effects of environmental parameters in a eutrophic Siberian reservoir. Limnologica 2010, 40, 343–357. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, C.W.; Xu, Z. Calanoid copepods feeding on algae and filamentous cyanobacteria: Retes of ingestion, defecation and effects on tricome length. J. Plankton Res. 1990, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Gliwicz, Z.M.; Lampert, W. Food thresholds in Daphnia species in the absence and presence of blue-green filaments. Ecology 1990, 71, 691–702. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, R.S.; Jones, C. Growth and reproductive responses of Daphnia to cyanobacterial blooms on the Potomac River. Int. Revue Ges. Hydrobiol. 1991, 76, 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Koski, M.; Schmidt, K.; Engström-Ost, J.; Vitasalo, M.; Jónasdóttir, S.; Repka, S.; Sivonen, K. Calanoid copepods feed and produce eggs in the presence of toxic cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 878–885. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Karjalainen, M.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Engström-Ost, J.; Koski, M.; Carlsson, P. Feeding, reproduction and toxin accumulation by the copepods Acartia bifilosa and Eurytemora affinis in the presence of the toxic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 249, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, R.S.; Pearl, H.W. Toxic and inhibitory effects of the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa on herbivorous zooplankton. J. Plankton Res. 1987, 9, 837–855. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R.; Moxter, F. Foraging cyanobacteria by copepods: Responses to chemical defenses and resource abundance. Ecology 1991, 72, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, J.A.; Pearl, H.W. Zooplankton community structure, micro-zooplankton grazing impact, and seston energy content in the St. Johns river system, Florida as influenced by the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Hydrobiologia 2005, 537, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, L.; Gustafsoson, S.; Rengefors, K.; Bomark, L. Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, S.; Hansson, L.-A. Development of tolerance against toxic cyanobacteria in Daphnia. Aquat. Ecol. 2004, 38, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, S.; Rengefors, K.; Hansson, L.-A. Increased consumer fitness following transfer of toxin tolerance to offspring via maternal effects. Ecology 2005, 86, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, N.; Xie, P. Development of tolerance against toxic Microcystis aeruginosa in three cladocerans and the ecological implications. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T.; Dittmann, E.; Henning, M.; Börner, T.; Kohl, J.-G. Role of mycrocystins in poisoning and food ingestion inhibition of Daphnia galeata caused by the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 737–739. [Google Scholar]
- Kaebernick, M.; Rohrlack, T.; Christoffersen, K.; Neilan, B.A. A spontaneous mutant of microcystin biosynthesis: Genetic characterization and effect on Daphnia. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Lürling, M. Daphnia growth on microcystin-producing and microcystin-free Microcystis aeruginosa in different mixtures with the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T.; Christoffersen, K.; Dittmann, E.; Nogueira, I.; Vasconcelos, V.; Börner, T. Ingestion of microcystins by Daphnia: Intestinal uptake and toxic effects. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Christoffersen, K. Ecological implications of cyanobacterial toxins in aquatic food webs. Phycologia 1996, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R.; Zhang, Q.X.; Carmichael, W.W. Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on the survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; DeMott, W.R. Effects of toxic and nontoxic cyanobacteria on the life history of tropical and temperate cladocerans. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 43, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.M.; Kaya, K.; Takamura, N.J. Fate of the toxic cyclic hepatopeptides, the microcystins, from blooms of Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) in a hypereutrophic lake. Phycology 1992, 28, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Kotak, B.G.; Zurawell, R.W.; Prepas, E.E.; Holmes, C.F.B. Microcystin-LR concentrations in aquatic food web compartments from lakes of varying trophic status. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Accumulation of microcystins by a tropical zooplankton community. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 59, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Bruning, K.; Jonge, J.; Wolfstein, K.; Dionisio, L.M.; Postma, J.; Burger, T. Distribuition of microcystins in a lake foodweb: No evidence for biomagnification. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 487–500. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, P.W.; Boyer, G.; Satchwell, M.; Waller, S. The influence of environmental conditions on the seasonal variation of Microcystis cell density and microcystins concentration in San Francisco Estuary. Hydrobiologia 2008, 600, 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, P.W.; Teh, S.J.; Boyer, G.; Nobriga, M.L.; Bass, E.; Hogle, C. Initial impacts of Microcystis aeruginosa blooms on the aquatic food web in the San Francisco Estuary. Hydrobiologia 2010, 637, 229–248. [Google Scholar]
- Thorstrup, L.; Christoffersen, K. Accumulation of microcystin in Daphnia magna feeding on toxic Microcystis. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1999, 145, 447–467. [Google Scholar]
- Laurén-Määttä, C.; Hietala, J.M.; Reinikainen, M.; Walls, M. Do Microcystis aeruginosa toxins accumulate in the food web? A laboratory study. Hydrobiologia 1995, 304, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaus, L.; Gélinas, M.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Ghadouani, A.; Humbert, J.-F. Grazing of two toxic Planktothrix species by Daphnia pulicaria: Potential for bloom control and transfer of microcystins. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 827–838. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, K.; Yokoyama, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Kumagai, K.; Watanabe, M.F.; Park, H.D. Accumulation and depuration of microcystin produced by the cyanobacterium Microcystis in a freshwater snail. Limnology 2003, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, A.; Park, H.-D. Depuration kinetics and persistence of the cyanobacterial toxin, microcystins-LR, in the freshwater bivalve Unio douglasiae. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P. Tissue distributions and seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins-LR and -RR in two freshwater shrimps, Palaemon modestus and Macrobrachium nipponensis, from a large shallow, eutrophic lake of the subtropical China. Toxicon 2005, 45, 615–625. [Google Scholar]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Havens, K.E. Cyanobacterial Toxins: A Qualitative Meta-Analysis of Concentrations, Dosage and Effects in Freshwater, Estuarine and Marine Biota. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 619, Chapter 32, pp. 675–732. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Wilson, A.; Ferrão-Filho, A.S. Biomagnification or biodilution of microcystins in aquatic food webs? Meta-analyses of laboratory and field studies. Harmful Algae 2011. submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Yokoyama, A.; Nakamura, K.; Park, H. Accumulation of microcystins in various organs of the freshwater snail Sinotaia histrica and three fishes in a temperate lake, the eutrophic Lake Suwa, Japan. Toxicon 2007, 49, 646–652. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, V. Uptake and depuration of the heptapeptide toxin microcystin-LR in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 1995, 32, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Dynamics of microcystins in the mussel Mylilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, A.; Park, H.-D. Mechanism and prediction for contamination of freshwater bivalve (Unionidae) with the cyanobacterial toxin, microcystin, in the hypereutrophic Lake Suwa, Japan. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 424–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Zheng, L.; NI, L. Tissue distributions and seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins-LR and -RR in in a freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) from a large shallow, eutrophic lake of the subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Engström-öst, J.; Lehtinienmi, M.; Green, S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Viitassalo, M. Does cyanobacterial toxin accumulate in mysid shrimps and fish via copepods? J. Exp. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 276, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, M.; Reinikainen, M.; Lindvall, F.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J.A.O. Uptake and accumulation of dissolved radiolabeled nodularin in Baltic Sea zooplankton. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtiniemi, M.; Engström-Ost, J.; Karjalainen, M.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Vitasalo, M. Fate of cyanobacterial toxins in the pelagic food web: Transfer to copepods or to faecal pellets? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 241, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Svensen, C.; Strogyloudi, E.; Wexels Riser, C.; Dahlmann, J.; Legrand, C.; Wassmann, P.; Granéli, E.; Pagou, K. Reduction of cyanobacterial toxins through coprophagy in Mytilus edulis. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Strogyloudi, E.; Giannakourou, A.; Legrand, C.; Ruehl, A.; Granéli, E. Estimating the accumulation and transfer of Nodularia spumigena toxins by the blue mussel Mytilus edulis: An appraisal from culture and mesocosm experiments. Toxicon 2006, 48, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Sopanen, S.; Uronen, P.; Kuuppo, P.; Svensen, C.; Rühl, A.; Tamminen, T.; Granéli, E.; Legrand, C. Transfer of nodularin to the copepod Eurytemora affinis through the microbial food web. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 55, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen, K.K.; Kankaanpää, H.; Leiniö, S.; Sipiä, V.O.; Pflugmacher, S.; Sandberg-Kilpi, E. Accumulation of nodularin-like compounds from the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena and changes in acetylcholinesterase activity in the clam Macoma balthica during short-term laboratory exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 64, 461–476. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, M.; Reinikainen, M.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J.A.O.; Sivonen, K.; Vitasalo, M. Trophic transfer of cyanobacterial toxins from zooplankton to planktivores: Consequences for pike larvae and mysid shrimps. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 354–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kankaanpää, H.T.; Holliday, J.; Schröder, H.; Goddard, T.J.; von Fister, R.; Carmichael, W.W. Cyanobacteria and prawn farming in northern New South Wales, Australia—A case study on cyanobacteria diversity and hepatotoxin bioaccumulation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Korpinen, S.; Karjalainen, M.; Viitasalo, M. Effects of cyanobacteria on survival and reproduction of the littoral crustacean Gammarus zaddachi (Amphipoda). Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Sipiä, V.; Kankaanpää, H.T.; Pflugmacher, S.; Flinkman, J.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Bioaccumulation and detoxification of nodularin in tissues of flounder (Platichthus flesus), mussels (Mytilus edulis, Dreissena polymorpha), and clams (Macoma balthica) from the northern Baltic Sea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 53, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Kankaanpää, H.; Leiniö, S.; Olin, M.; Sjövall, O.; Meriluoto, J.; Lehtonen, K.K. Accumulation and depuration of cyanobacterial toxin nodularin and biomarker responses in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, M.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Engström-Öst, J.; Kankaanpää, H.; Viitasalo, M. Nodularin accumulation during cyanobacterial blooms and experimental depuration in zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 2006, 148, 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann, D.; Benndorf, J. Toxicity to Daphnia of a compound extracted from laboratory and natural Microcystis spp., and the role of microcystins. Freshw. Biol. 1994, 32, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T.; Dittmann, E.; Börner, T.; Christoffersen, K. Effects of cell-bound microcystins on survival and feeding of Daphnia spp. Appl.Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Beattie, K.A.; Ressler, J.; Wiegand, C.; Krause, E.; Codd, G.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Pflugmacher, S. Comparative effects and metabolism of two microcystins and nodularin in the brine shrimp Artemia salina. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadouani, A.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Plath, K.; Codd, G.A.; Lampert, W. Effects of Microcystis aeruginosa and purified microcystin-LR on the feeding behavior of Daphnia pulicaria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 666–679. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.D.; Gilbert, J.J. Relative susceptibilities of rotifers and cladocerans to Microcystis aeruginosa. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1995, 132, 309–336. [Google Scholar]
- Nandini, S. Responses of rotifers and cladocerans to Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanophyceae): A demographic study. Aquat. Ecol. 2000, 34, 227–242. [Google Scholar]
- Reinikainen, M.; Lindvall, F.; Meriluoto, J.A.O.; Repka, S.; Sivonen, K.; Spoof, L.; Wahlsten, M. Effects of dissolved cyanobacterial toxins on the survival and egg hatching of estuarine calanoid copepods. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Kiviranta, J.; Sivonen, K.; Niemela, S.I. Detection of toxicity of cyanobacteria by Artemia salina bioassay. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1991, 6, 423–436. [Google Scholar]
- Kiviranta, J.; Andel-Hameed, A. Toxicity of the blue-green alga Oscillatoria agardhii to the mosquito Aedes aegypti and the shrimp Artemia salina. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 10, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Saario, E.; Abbel-Hamed, A.; Kivranta, J. Larvicidal microcystin toxins of cyanobacteria affect midgut epithelial cells of Aedes aegipty mosquitoes. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1994, 8, 398–400. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Song, L.; Ou, D.; Gan, N. Chronic toxicity and responses of several important enzymes in Daphnia magna on exposure to sublethal microcystin-LR. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R.; Dhawale, S. Inhibition of in vitro protein phosphatase activity in three zooplâncton species by microcystin-LR, a toxin from cyanobacteria. Arch. Hydorbiol. 1995, 134, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, M.K.; Bagchi, D.; Bagchi, S.N. Acute inhibition of protease and suppression of growth in zooplankter, Moina macrocopa, by Microcystis blooms collected in Central India. Hydrobiologia 2001, 464, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, M.K.; Zitt, A.; Bagchi, D.; Weckersser, J.; Bagchi, S.N.; Von Elert, E. Characterization of proteases in guts of Daphnia magna and their inhibition by Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, C.; Peuthert, A.; Pflugmacher, S.; Carmeli, S. Effects of microcyn SF608 and microcystin-LR, two cyanobacterial compounds produced by Microcystis sp., on aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, P.A.G. Efeitos tóxicos de Cianobactérias em Cladóceros. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Törökné, A.K.; László, E.; Chorus, I.; Sivonen, K.; Barbosa, F.A.R. Cyanobacterial toxins detected by Thamnotoxkit: A double blind experiment. Environ. Toxicol. 2000, 15, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Tarczynska, M.; Nalecz-Jawecki, G.; Romanowska-Duda, Z.; Sawicki, J.; Beattie, K.; Codd, G.A.; Zalewski, M. Tests for the toxicity assessment of cyanobacterial bloom samples. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Drobniewska, A.; Tarczynska, M.; Mankiewicz, J.; Jurczak, T.; Zalewski, M. Increase of crustacean sensitivity to purified hepatotoxic cyanobacterial extracts by manipulation of experimental conditions. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 416–420. [Google Scholar]
- Maršálek, B.; Bláha, L. Comparison of 17 biotests for detection of cyanobacterial toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, J.F.; Robinson, J.A.; Jüttner, F. High grazer toxicity of [D-Asp3, (E)-Dhb7]microcystin-RR of Planktothrix rubescens as compared to different microcystins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, V.; Oliveira, S.; Teles, F.O. Impact of a toxic and a non-toxic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa on the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Montagnolli, W.; Zamboni, A.; Luvizotto-Santos, R.J.; Yunes, J.S. Acute effects of Microcystis aeruginosa from the Patos Lagoon estuary, Southern Brazil, on the microcrustacean Kalliapseudes schubartii (Crustacea: Tanaidacea). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, G.L.L.; Moura da Rosa, C.; Maciel, F.E.; Bianchini, A.; Yunes, J.S.; Proença, L.A.O.; Monserrat, J.M. Antioxidant responses and oxidative stress after microcystin exposure in the hepatopancreas of an estuarine crab species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, G.L.L.; Moura da Rosa, C.; Maciel, F.E.; Bianchini, A.; Yunes, J.S.; Proença, L.A.O.; Monserrat, J.M. Antioxidant responses after microcystin exposure in gills of an estuarine crab species pre-treated with vitamin E. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Dewes, L.J.; Sandrini, J.Z.; Monserrat, J.M.; Yunes, J.M. Biochemical and physiological responses after exposure to microcystins in the crab Chasmagnathus granulatus (Decapoda, Brachyura). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 65, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, J.R.; Hargraves, P.E.; O’Connell, S.M. Effect of selected marine and freshwater microalgae on development and survival of the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Aquatic Ecology. 2009, 43, 987–997. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, C.; Brient, L.; Rouzic, B.L. Variation in the response of juvenile and adult gastropods (Lymnaea stagnalis) to cyanobacterial toxin (microcystin-LR). Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Juhel, G.; Davenport, J.; O’Halloran, J.; Culloty, S.C.; O’Riordan, R.M.; James, K.F.; Furey, A.; Allis, O. Impacts of microcystins on the feeding behaviour and energy balance of zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha: A bioenergetics approach. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Juhel, G.; Davenport, J.; O’Halloran, J.; Culloty, S.C.; Ramsay, R.M.; James, K.J.; Furey, A.; Allis, O. Pseudodiarrhoea in zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas), exposed to microcystins. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, M.; Engström-Öst, J.; Korpinen, S.; Peltonen, H.; Pääkkönen, J.-P.; Rönkkönen, S.; Suikkanen, S.; Viitasalo, M. Ecosystem consequences of cyanobacteria in the northen Baltic Sea. Ambio 2007, 36, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, F.J.A.; Karlson, A.M.L.; Elmgren, R. Settling blooms of filamentous cyanobacteria as food for meiofauna assemblages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2636–2643. [Google Scholar]
- Karlson, A.M.L.; Nascimento, F.J.A.; Elmgren, R. Incorporation and burial of carbon from settling cyanobacteria blooms by deposit-feeding macrofauna. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2754–2758. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnear, S. Cylindrospermopsin: A decade of progress on bioaccumulation research. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 542–564. [Google Scholar]
- Saker, M.L.; Eaglesham, G.K. The accumulation of cylindrospermopsin from the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in tissues of the Redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Saker, M.L.; Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Accumulation and depuration of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin in the freshwater mussel Anodonta cygnea. Toxicon 2004, 43, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, I.C.G.; Saker, M.L.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Toxicity of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii to Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, I.C.G.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Effects of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (cyanobacteria) ingestion on Daphnia magna midgut and associated diverticula epithelium. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.H.; Duivenvoorden, L.J.; Fabbro, L.D.; Eaglesham, G.K. Influence of intracellular toxin concentrations on cylindrospermopsin bioaccumulation in a freshwater gastropod (Melanoides tuberculata). Toxicon 2006, 47, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.P.; Lind, O. First evidence of “paralytic shellfish toxins” and cylindrospermopsin in a Mexican freshwater system, Lago Catemaco, and apparent bioaccumulation of the toxins in “tegogolo” snails (Pomacea patula catemacensis). Toxicon 2010, 55, 930–938. [Google Scholar]
- Sasner, J.J.; Ikawa, M.; Foxall, T.L. Studies on Aphanizomenon and Microcystis Toxins. In Seafood Toxins; Ragelis, E.P., Ed.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 391–406. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, A.P.; Jones, G.J. Bioaccumulation of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins from the cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis by the freshwater mussels Alathrya condola. Toxicon 1995, 33, 667–678. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, I.C.G.; Pereira, P.; Dias, E.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Franca, S.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Accumulation of paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) from the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon issatschenkoi by cladoceran Daphnia magna. Toxicon 2004, 44, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.; Dias, E.; Franca, S.; Pereira, E.; Carolino, M.; Vasconcelos, V. Accumulation and depuration of cyanobacterial paralytic shellfish toxins by the freshwater mussel Anodonta cygnea. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Haney, J.F.; Sasner, J.J.; Ikawa, M. Effects of products released by Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and purified saxitoxin on the movements of Daphnia carinata feeding appendages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.M. Efeitos de Saxitoxinas Produzidas por Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii e de Outras Cianotoxinas sobre Cladóceros (Branchiopoda). 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Lürling, M.; Panosso, R.; Huszar, V. Effects of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii on feeding and life-history characteristics of the grazer Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Cunha, R.; Magalhães, V.F.; Soares, M.C.S.; Baptista, D.F. Evaluation of sub-lethal toxicity of cyanobacteria on the swimming activity of aquatic organisms by image analysis. J. Braz. Soc. Ecotoxicol. 2007, 2, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; Magalhães, V.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. A rapid bioassay for detecting saxitoxins using a Daphnia acute toxicity test. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.J. Succeptibility of planktonic rotifers to a toxic strain of Anabaena floes-aquae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, L.E.; Pablo, J.; Compton, A.; Hammerschlag, N.; Mash, D.C. Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 620–635. [Google Scholar]
- Dvořáková, D.; Dvořáková, K.; Bláha, L.; Maršálek, B.; Knotková, Z. Effects of Cyanobacterial biomass and purified microcystins on malformations in Xenopus laevis: Teratogenesis assay (FETAX). Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
- Burýšková, B.; Hilscherová, K.; Babica, P.; Vršková, D.; Maršálek, B.; Bláha, L. Toxicity of complex cyanobacterial samples and their fractions in Xenopus laevis embryos and the role of microcystins. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.H.; Duivenvoorden, L.J.; Fabbro, L.D.; Eaglesham, G.K. Mortality and toxin bioaccumulation in Bufo marinus following exposure to Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii cell extracts and live cultures. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, H.; El Herryb, S.; Bouaïcha, N. First reported case of turtle deaths during a toxic Microcystis spp. bloom in Lake Oubeira, Algeria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 535–544. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z. Simultaneous determination of microcystin contaminations in various vertebrates (fish, turtle, duck and water bird) from a large eutrophic Chinese lake, Lake Taihu, with toxic Microcystis blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen, P.; Carmichael, W.W.; Na, J.; Moestrup, O. Detection of an anatoxin-a(s)-like anticholinesterase in natural blooms and cultures of cyanobacteria/blue-green algae from Danish lakes and in the stomach contents of poisoned birds. Toxicon 1997, 35, 901–913. [Google Scholar]
- Krienitz, L.; Ballot, A.; Kotut, K.; Wiegand, C.; Pütz, S.; Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A.; Pflugmacher, S. Contribution of hot spring cyanobacteria to the mysterious deaths of Lesser Flamingos at Lake Bogoria, Kenya. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 43, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pašková, V.; Adamovský, O.; Pikula, J.; Skočovská, B.; Band’ouchová, H.; Horáková, J.; Babica, P.; Maršálek, B.; Hilscherová, K. Detoxification and oxidative stress responses along with microcystins accumulation in Japanese quail exposed to cyanobacterial biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 398, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sipiä, V.O.; Karlsson, K.A.; Meriluoto, J.A.O.; Kankaanpää, H.T. Eiders (Somateria mollissima) obtain nodularin, a cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, in Baltic Sea food web. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 23, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Sipiä, V.; Sjövall, O.; Valtonen, T.; Barnaby, D.L.; Codd, G.A.; Metcalf, J.S.; Kilpi, M.; Mustonen, O.; Meriluoto, J.A.O. Analysis of nodularin-r in eider (Somateria mollissima), roach (Rutilus rutilus) and flounder (Platichthus flesus) liver and muscle samples from the Western Gulf of Finland, northern Baltic Sea. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar]
- Sipiä, V.; Neffling, M.R.; Metcalf, J.; Nybom, S.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G. Nodularin in feathers and liver of eiders (Somateria mollissima) caught from the western Gulf of Finland in June–September 2005. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Li, L.; Miyabara, Y.; Park, H. Organ distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave, J.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Bistoni, M.A.; Amé, M.V.; Krause, E.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C. Uptake, tissue distribution and accumulation of microcystin-RR in Corydoras paleatus, Jenynsia multidentata and Odontesthes bonariensis A field and laboratory study. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, T.; Kagalou, I.; Bacopoulos, V.; Leonardos, I.D. Accumulation of microcystins in water and fish tissues: An estimation of risks associated with microcystins in most of the Greek lakes. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 418–427. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, V.F.; Soares, R.M.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Microcystin contamination in fish from the Jacarepaguá Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): Ecological implication and humam health risk. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Haney, J.F. Foodweb transfer, accumulation and depuration of microcystins, a cyanobacterial toxin, in pumpkinmsees sunfish (Lepomis gibbosus). Toxicon 2006, 48, 580–589. [Google Scholar]
- Lance, E. Impact of Toxic Cyanobacteria on Freshwater Gastropods and on Their Role as Vector in Food Web Microcystin Transfer. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sipiä, V.; Kankaanpää, H.; Lahti, K.; Carmichael, W.W.; Meriluoto, J. Detection of nodularin in flounders and cod from the Baltic Sea. Environ. Toxicol. 2000, 16, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kankaanpää, H.; Vuorinen, P.J.; Sipia, V.; Keinanen, M. Acute effects and bioaccumulation of nodularin in sea trout (Salmo trutta L.) exposed orally to Nodularia spumigena under laboratory conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 61, 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, M.; Pääkkönen, J.-P.; Peltonen, H.; Sipiä, V.; Valtonen, T.; Viitasalo, M. Nodularin concentrations in Baltic Sea zooplankton and fish during a cyanobacterial bloom. Mar. Biol. 2008, 155, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, K.-P.; Legrand, C.; Olsson, T. Detection of nodularin in European flounder (Platichthys flesus) in the west coast of Sweden: Evidence of nodularin mediated oxidative stress. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.W. Marine zooplankton can accumulate and retain dinoflagellate toxins and cause fish kills. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, J.E.; Meriluoto, J.A.O.; Lindholm, T. Can Cyanobacterial Toxins Accumulate in Aquatic Food Chains? In Proceeding of the 4th Intternational Symposium of Microbial Ecolology, Ljubljana, Yugoslavia, 24–29 August 1986; pp. 655–658.
- Rodger, H.D.; Turnbull, T.; Edwards, C.; Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) bloom associated pathology in brown trout, Salmo truta L., in Loch Leven, scothland. J. Fish Dis. 1994, 17, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Carmouse, J.P. Une mortalité de poissons dans une lagune tropicale (Brésil) durant une périod de dominance de Cyanophyceae. Rev. Hydrobiol. Trop. 1994, 27, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Malbrouck, C.; Kestemont, P. Effects of microcystins on fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, M.C.M.; Baird, D.J.; Rahmatullah, S.M.; Lawton, L.A.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A. Grazing rates on toxic and nontoxic strains of cyanobacteria by Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Oreochromis niloticus. J. Fish Biol. 1993, 43, 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavanath, P.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Baird, D.J.; Lawton, L.A. The functional grazing response of a phytoplanktivorous fish Oreochromis niloticus to mixtures of toxic and non-toxic strains of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Fish Biol. 1994, 45, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kamjunke, N.; Schimidt, K.; Pflugmacher, S.; Mehner, T. Consumption of cyanobacteria by roach (Rutilus rutilus): Useful or harmful to the fish? Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.H.; Eddy, F.B.; Codd, G.A. Effects of Microcystis cells, cell extracts and lipopolysaccharide on drinking and liver function in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 64, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Marionnet, D.; Chambras, C.; Taysse, L.; Bosgireaud, C.; Deschaux, P. Modulation of drug-metabolizing systems by bacterial endotoxin in carp liver and immune organs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 41, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh, T.; Kokue, E.; Shimoda, M. The suppressive effects of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute phase response on hepatic cytochrome P450-dependent drug metabolism in rabbits. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 22, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardová, B.; Babica, P.; Maršálek, B.; Bláha, L. Isolation and endotoxin activities of lipopolysaccharides from cyanobacterial cultures and complex water blooms and comparison with the effects of heterotrophic bacteria and green alga. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.H.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Eddy, F.B.; Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A. Effects of enteric bacterial and cyanobacterial lipopolysaccharide, and of microcystin-LR, on glutathione S-transferase activities in zebra fish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 60, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, B.; Hoeger, S.J.; O’Brien, E.; Dietrich, D.R. Oral toxicity of the microcystin-containing cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens in European whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, B.; Hoeger, S.J.; O’Brien, E.; Dietrich, D.R. Physiological stress and pathology in European whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus) induced by subchronic exposure to environmentally relevant densities of Planktothrix rubescens. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 82, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kankaanpää, H.; Turunen, A.K.; Karlsson, K.; Bylund, G.; Meriluoto, J.; Sipiä, V. Heterogeneity of nodularin bioaccumulation in northern Baltic Sea flounders in 2002. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Vuorinen, P.J.; Sipiä, V.O.; Karlsson, K.; Keinänen, M.; Furey, A.; Allis, O.; James, K.; Perttilä, U.; Rimaila-Pärnänen, E.; Meriluoto, J.A.O. Accumulation and effects of nodularin from a single and repeated oral doses of cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena on flounder (Platichthys flesus L.). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Oberemm, A.; Beattie, K.A.; Krause, E.; Codd, G.A.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: The first step of detoxication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1425, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, C.; Pflugmacher, S.; Oberemm, A.; Meems, N.; Beattie, K.A.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Codd, G.A. Uptake and effects of microcystin-LR on detoxification enzymes of early life stages of zebra fish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bury, N.R.; Eddy, F.B.; Codd, G.A. The effects of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa, the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR, and ammonia on growth-rate and ionic regulation of brown trout. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 46, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Bury, N.R.; Codd, G.A.; Bonga, S.E.W.; Flik, G. Fatty acids from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa with potent inhibitory effects of fish gill Na+/K+-ATPase activity. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, A.I.; Jos, A.; Pichardo, S.; Moreno, I.; Cameán, A.M. Differential oxidative stress responses to microcystins LR and RR in intraperitoneally exposed tilapia fish (Oreochromis sp.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave, J.; Bistoni, M.A.; Zwirnmann, E.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Wiegand, C. Attenuating effects of natural organic matter on microcystin toxicity in zebra fish (Danio rerio) embryos—benefits and costs of microcystin detoxication. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 21, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Pflugmacher, S.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Comparative study of microcystin-LR-induced behavioral changes of two fish species, Danio rerio and Leucaspius delineatus. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 564–570. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.P.; Gibbs, P.D.L.; Schmale, M.C.; Saker, M.L. Toxicity of cylindrospermopsin, and other apparent metabolites from Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, to the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. Toxicon 2009, 53, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Osswald, T.; Rellán, S.; Carvalho, A.P.; Gago, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Acute effects of an anatoxin-a producing cyanobacterium on juvenile fish—Cyprinus carpio L. Toxicon 2007, 49, 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Osswald, T.; Carvalho, A.P.; Claro, J.; Vasconcelos, V. Effects of cyanobacterial extracts containing anatoxin-a and of pure anatoxin-a on early developmental stages of carp. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 72, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Oberemm, A.; Becker, J.; Codd, G.A.; Steinberg, C. Effects of cyanobacterial toxins and aqueous crude extracts of cyanobacteria on the development of fish and amphibians. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, Z.; Busato, R.H.; Ribeiro, C.A.O.; Cestari, M.M.; Ramsdorf, W.A.; Magalhães, V.F.; Wosiack, A.C.; Assis, H.C.S. Analyses of paralytic shellfish toxins and biomarkers in a southern Brazilian reservoir. Toxicon 2010, 55, 396–406. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.A.; Oba, E.T.; Ramsdorf, W.A.; Magalhães, V.F.; Cestari, M.M.; Ribeiro, C.A.O.; Assis, H.C.S. First report about saxitoxins in freshwater fish Hoplias malabaricus through trophic exposure. Toxicon 2011, 57, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Biggs, D.F. Muscle sensitivity differences in two avian species to anatoxin-a produced by the freshwater cyanophyte Anabaena flos-aquae NRC-44-1. Can. J. Zool. 1978, 56, 510–512. [Google Scholar]
- Skočovská, B.; Hilscherova, K.; Babica, P.; Adamovský, O.; Bandouchová, H.; Horaková, J.; Knotková, Z.; Maršálek, B.; Pašková, V.; Pikula, J. Effects of cyanobacterial biomass on the Japanese quail. Toxicon 2007, 49, 793–803. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuno, M.; Sugaya, Y. Toxicities of Microcystis viridis and the isolated hepatotoxic polypeptides on cladocerans. Verh. Intern. Verein Limnol. 1991, 24, 2622–2626. [Google Scholar]
- Tencalla, F.G.; Dietrich, D.R.; Schlatter, C. Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa peptide toxin to yearling rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus myskiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 1994, 30, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Prepas, E.E.; Kotak, B.G.; Campbell, L.M.; Evans, J.C.; Hrudey, S.E.; Holmes, C.F.B. Accumulation and elimination of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins by the freshwater clam Anodonta grandis simpsoniana. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, W.J.; Dietrich, D.R. Toxicity of the cyanobacterial cyclic heptapepitide toxins microcystin-LR and -RR in early stages of the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis). Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zurawell, R.; Chen, H.; Burke, J.M.; Prepas, E.E. Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: A review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2005, 8, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. Laboratory studies on zooplankton-cyanobacteria interactions. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1987, 21, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Reinikainen, M.; Ketola, M.; Walls, M. Acute toxicity of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa (strain PCC7820) to Daphnia pulex. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. Algol. Stud. 1994, 75, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Reinikainen, M.; Ketola, M.; Walls, M. Effects of the concentrations of toxic Microcystis aeruginisa and an alternative food on the survival of Daphnia pulex. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Laurén-Määttä, C.; Hietala, J.M.; Walls, M. Responses of Daphnia pulex populations to toxic cyanobacteria. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 635–647. [Google Scholar]
- Hietala, J.; Laurén-Määttä, C.; Walls, M. Liffe history responses of Daphnia clones to toxic Microcystis at diferent food levels. J. Plankton Res. 1997, 19, 917–926. [Google Scholar]
- Threlkeld, S.T. Differential temperature sensitivity of two cladoceran species to resource variation during a blue-green algal bloom. Can. J. Zool. 1986, 64, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.J. Effect of temperature on the response of planktonic rotifers to a toxic cyanobacteria. Ecology 1996, 77, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Claska, M.E.; Gilbert, J.J. The effect of temperature on the response of Daphnia to toxic caynobacteria. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 39, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Hietala, J.; Reinikainen, M.; Walls, M. Variation in life history responses of Daphnia to toxic Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Plankton Res. 1995, 17, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Hietala, J.; Laurén-Määttä, C.; Walls, M. Sensitivity of Daphnia to toxic cyanobacteria: Effects of genotype and temperature. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Reinikainen, M.; Hietala, J.M.; Walls, M. Adaptations and resistance of zooplankton to stress: Effects of genetic, environmental, and physiological factors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 40, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Carbis, C.R.; Mitchel, G.F.; Anderson, J.W.; McCauley, I. The effects of microcystins on the serum biochemistry of carp, Cyprinus carpio L., when the toxins are administered by gavage, immersion and intraperitoneal routes. J. Fish Dis. 1996, 19, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Tencalla, F.; Dietrich, D. Biochemical characterization of microcystin toxicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicon 1997, 35, 583–595. [Google Scholar]
- Zimba, P.V.; Khoo, L.; Gaunt, P.S.; Brittain, S.; Carmichael, W.W. Confirmation of catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque), mortality from Microcystis toxins. J. Fish Dis. 2001, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, R.M.; Magalhães, V.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Accumulation and depuration of microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) in Tilapia rendalli (Cichlidae) under laboratory conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xie, P.; Chen, J. In vivo studies on toxin accumulation in liver and ultrastructural changes of hepatocytes of the phytoplanktivorous bighead carp i.p.-injected with extracted microcystins. Toxicon 2005, 46, 533–545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.X. Evaluation of organ distribuition of microcystins in the freshwater phytoplanktivorous fish Hypophytalmincthtys molitrix. J. Zheijang Univ. Sci. B 2007, 8, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, S.S.S.; Nandini, R.; Gulati, R.D. Life history strategies of cladocerans: Comparisons of tropical and temperate taxa. Hydrobiologia 2005, 542, 315–333. [Google Scholar]
- Romanovsky, Y.E. Food limitation and life-history strategies in cladoceran crustaceans. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 1985, 21, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E. Local adaptation of Daphnia pulicaria to toxic cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Hairston, N.G., Jr.; Lampert, W.; Cáceres, C.E.; Holtmeier, C.L.; Weider, L.J.; Gaedke, U.; Fischer, J.M.; Fox, J.A.; Post, D.M. Rapid evolution revealed by dormant eggs. Nature 1999, 401, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Hairston, N.G., Jr.; Holtmeier, C.L.; Lampert, W.; Weider, L.J.; Post, D.M.; Fisher, J.M.; Cáceres, C.E.; Fox, J.A.; Gaedke, U. Natural selection for grazer resistance to toxic cianobactéria: Evolution of phenotypic plasticity? Evolution 2001, 55, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R. Foraging strategies and growth inhibition in five daphnids feeding on mixtures of a toxic cyanobacteria and a green alga. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 42, 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Van Straalen, N.M. Biodiversity of ecotoxicological responses in animals. Neth. J. Zool. 1994, 44, 112–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, D.; Meade, G.; Foley, V.M.; Dowd, C.A. Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: Implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochem. J. 2001, 360, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Connell, L.; Konoki, K.; MacQuarrie, S.P.; Scheuer, T.; Caterrla, W.A.; Trainer, V.L. Sodium channel mutation leading to saxitoxin resistance in clams increases risk of PSP. Nature 2005, 434, 763–767. [Google Scholar]
- Bricelj, V.M.; MacQuarrie, S.P.; Doane, J.A.E.; Connell, L.B. Evidence of selection for resistance to paralytic shellfish toxins during the early life history of soft-shell clam (Mya arenaria) populations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 2463–2475. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.J.; Codd, G.A. Comparative toxicity of four microcystins of different hydrophobicities to the protozoan, Tetrahymena pyriformis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 874–882. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729-2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9122729
Ferrão-Filho AdS, Kozlowsky-Suzuki B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(12):2729-2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9122729
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrão-Filho, Aloysio da S., and Betina Kozlowsky-Suzuki. 2011. "Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals" Marine Drugs 9, no. 12: 2729-2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9122729
APA StyleFerrão-Filho, A. d. S., & Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. (2011). Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals. Marine Drugs, 9(12), 2729-2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9122729





