Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the cardiovascular effects elicited by Dictyota pulchella, a brown alga, using in vivo and in vitro approaches. In normotensive conscious rats, CH2Cl2/MeOH Extract (CME, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) from Dictyota pulchella produced dose-dependent hypotension (−4 ± 1; −8 ± 2; −53 ± 8 and −63 ± 3 mmHg) and bradycardia (−8 ± 6; −17 ± 11; −257 ± 36 and −285 ± 27 b.p.m.). In addition, CME and Hexane/EtOAc Phase (HEP) (0.01–300 μg/mL) from Dictyota pulchella induced a concentration-dependent relaxation in phenylephrine (Phe, 1 μM)-pre-contracted mesenteric artery rings. The vasorelaxant effect was not modified by the removal of the vascular endothelium or pre-incubation with KCl (20 mM), tetraethylammonium (TEA, 3 mM) or tromboxane A2 agonist U-46619 (100 nM). Furthermore, CME and HEP reversed CaCl2-induced vascular contractions. These results suggest that both CME and HEP act on the voltage-operated calcium channel in order to produce vasorelaxation. In addition, CME induced vasodilatation after the vessels have been pre-contracted with L-type Ca2+ channel agonist (Bay K 8644, 200 nM). Taken together, our data show that CME induces hypotension and bradycardia in vivo and that both CME and HEP induce endothelium-independent vasodilatation in vitro that seems to involve the inhibition of the Ca2+ influx through blockade of voltage-operated calcium channels.
1. Introduction
Marine algae are recognized as rich sources of structurally-diverse-biologically-active compounds with great pharmaceutical and biomedical potentials. Researchers worldwide have demonstrated that marine algae derived compounds exhibit various biological activities such as anticoagulant [1,2], anti-viral [3,4], antioxidant [5,6], anti-allergic [7], anti-cancer [8,9] and as adjuvants for treating cardiopathies [10]. Despite the ascending number of new findings regarding marine algae metabolites possessing biological activity in the last three decades, few products showing real pharmaceutical potential have been identified or developed [11,12].
Marine brown algae have innumerous families, with the Dictyotaceae family being the best studied among them. The genus Dictyota is represented by more than 40 species, thus being the richest genus of the Dictyotaceae family. It is also one of the most abundant seaweeds in tropical marine habitats. The Dictyotaceae family produces a significant number of secondary metabolites, especially diterpenes [13]. Terpenoids constitute the largest family of natural products [14,15] and are classified by the homologous series of number of five carbon isoprene units in their structure: hemiterpenes C5 (1 isoprene unit), monoterpenes C10 (2 isoprene units), sesquiterpenes C15 (3 isoprene units), diterpenes C20 (4 isoprene units), triterpenes C30 (6 isoprene units) [16].
Many reports have extensively shown that several classes of diterpenoids exert significant cardiovascular effects [17–19]. It has also been reported that some classes of diterpenes showed significant systemic hypotensive and coronary vasodilatory effects accompanied by gradual decrease in heart rate [20,21]. The studies pointed at diterpenoids as promising sources for new prototypes in the discovery and development of novel cardiovascular therapeutic agents [19].
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading death cause in developed and developing countries [22], causing a great impact not only on human health, but also in social and economic areas. In an attempt to reduce this impact, several research groups in recent decades have worked extensively to improve the treatment of cardiovascular diseases including the discovery of new therapy strategies and drugs [23,24].
Considering that marine algae constitute great sources of bioactive compounds, the aim of this study was to investigate the mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular effects induced by the brown algae Dictyota pulchella in rats. To reach that goal, we employed in vivo and in vitro approaches.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Dictyota pulchella Elicits Hypotension and Bradycardia in Rats
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were recorded before (baseline) and after intravenous administration of CH2Cl2/MeOH extract from Dictyota pulchella (CME, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg body weight, randomly) in conscious normotensive rats. CME elicited a dose-dependent hypotension (−4 ± 1; −8 ± 2; −53 ± 8 and −63 ± 3 mmHg) and bradycardia (−8 ± 6; −17 ± 11; −257 ± 36 and −285 ± 27 b.p.m.) as illustrated in Figure 1A,B.
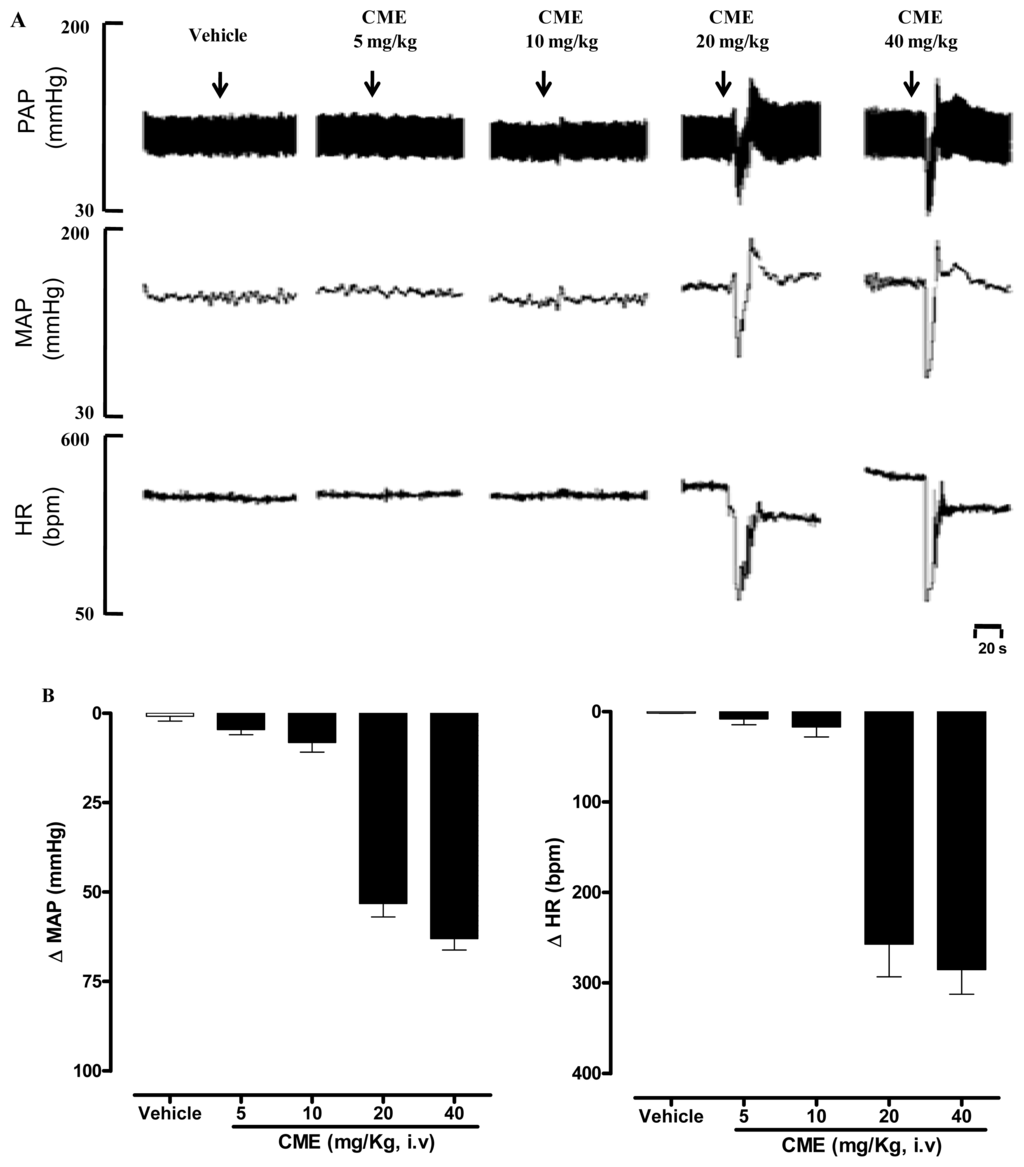
Figure 1.
(A) Representative original tracings showing the changes in pulse arterial pressure (PAP, mmHg), mean arterial pressure (MAP, mmHg), and heart rate (HR, b.p.m.); (B) Changes in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) induced by the acute administration of increasing doses of CME (mg/kg, i.v) and vehicle. Values are expressed by mean ± SEM. (n = 5).
It is well-known that anesthesia modifies the levels of blood pressure and heart rate interfering with central regulatory mechanisms involved in BP regulation, such as the baroreflex, by producing depression of the central nervous system synapses, altering the autonomic responses [25]. In order to avoid the possible influence of anesthesia and surgical stress on cardiovascular parameters [26], our studies were carried out in conscious freely moving rats.
In the present study, the acute administration of CME induced marked hypotension and bradycardia in conscious rats (Figure 1B). It is important to note that reduction in blood pressure due to vasodilation is usually followed by reflex tachycardia. However, under our experimental conditions, in addition to hypotension, CME induced bradycardia, which could be explained, at least in part, by a possible direct effect of the CME on the heart. Although this is an interesting possibility, this hypothesis awaits further investigation.
Although we demonstrated that CME can produce hypotension in normotensive rats, the beneficial effects of this marine algae on experimental hypertension and its clinical relevance still awaits further investigation.
2.2. Dictyota pulchella Elicits Vasorelaxation Mediated by the Blockade of Calcium Influx in Isolated Mesenteric Artery Rings
Based on the reports highlighting that the vascular smooth muscle tone plays an important role in maintaining blood pressure [27], we investigated the possible vasorelaxant effect elicited by Dictyota pulchella in isolated superior mesenteric arteries. An important layer in the regulation of vascular tone is the endothelium. For many years, this layer was considered to be an inert barrier that separated flowing blood from underlying tissue. Over time, it has been established that the endothelium plays an active role in regulating hemostasis, cellular and nutrient trafficking, and vasomotor tone [28]. Endothelial cells are able to produce both vasoconstrictive and vasodilating substances. The main endothelium-derived relaxing factors (EDRF) are nitric oxide, prostacyclin, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF). Among the contracting factors are endothelin-1, thromboxane A2 and reactive oxygen species [29]. To evaluate the possible role played by the endothelium in the hypotension elicited by Dictyota pulchella observed in vivo, mesenteric artery rings were pre-contracted with phenylephrine (1 μM), a α1-adrenoceptors agonist. In the presence of this contracting agent, CME (0.01–500 μg/mL) induced a concentration-dependent relaxation (Maximum Response = 101.4 ± 4.5%; EC50 = 22.35 ± 5.09 μg/mL, n = 6) and this effect was not modified by vascular endothelium removal (Maximum Response = 103.3 ± 8.3%; EC50 = 21.43 ± 8.98 μg/mL, n = 6) (Figure 2A). Similar results were found in the presence of Hexane/EtOAc phase from Dictyota pulchella (HEP) (0.01–500 μg/mL), which induced a concentration-dependent vasodilatation in both intact (Maximum Response = 80.6 ± 5.8%; EC50 = 24.1 ± 8.95 μg/mL, n = 6) or denuded-endothelium (Maximum Response = 95.6 ± 7.5%; EC50 = 23.7 ± 5.65 μg/mL, n = 6) (Figure 2B).
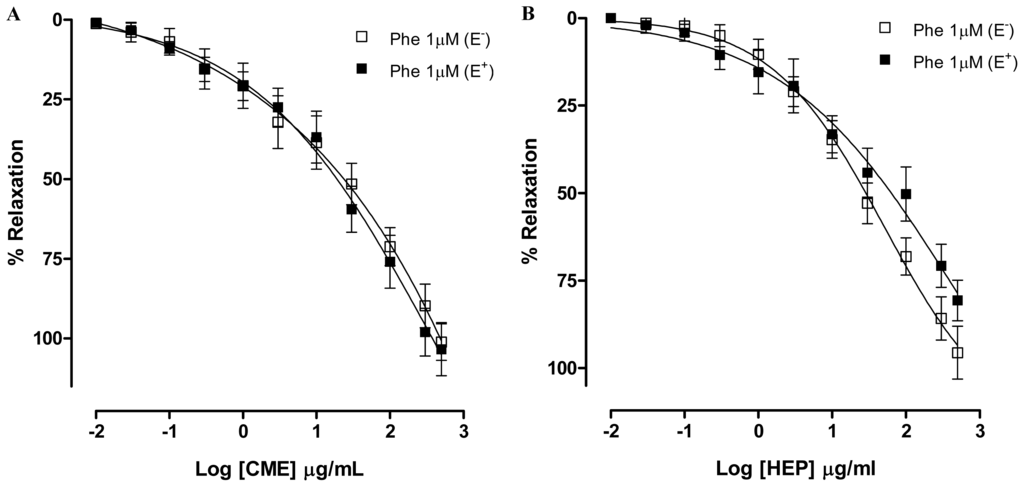
Figure 2.
Concentration–response curves showing the relaxant effect of (A) CME (0.01–500 μg/mL); and (B) Hexane/EtOAc Phase (HEP) (0.01–500 μg/mL) on Phe (1 μM)-pre-contracted mesenteric artery rings with (■, n = 7) and without (□, n = 7) vascular endothelium, respectively. Values are expressed by mean ± SEM.
Potassium channels (K+ channels) appear to play a crucial role in controlling the cellular membrane potential and in the vascular tone. Potassium channel openers exert their biological effects by increasing the probability of opening K+ channels and a number of substances that act on K+ channels have been shown to dilate arteries by causing hyperpolarization in vascular smooth muscle cells [30]. In addition several natural products have been shown to induce vasorelaxant effects through the activation of K+ channels [31–33]. Aiming to investigate involvement of potassium channels (K+) in the vasorelaxant activity elicited by CME, the preparations were pre-incubated with Tyrode’s modified solution containing KCl (20 mM) or with tetraethylammonium (TEA, 3 mM), a non-selective K+ channel blocker. In both preparations, the vasorelaxant activity was not changed (Maximum Response = 102.3 ± 4.8%; EC50 = 25.40 ± 6.05 μg/mL; and Maximum Response = 111.2 ± 5.3%; CE50 = 16.70 ± 3.61 μg/mL; n = 7, respectively) as shown in Figure 3A. These responses were no different from the control curve, suggesting that K+ channels are not involved in the vasorelaxant effect elicited by CME.
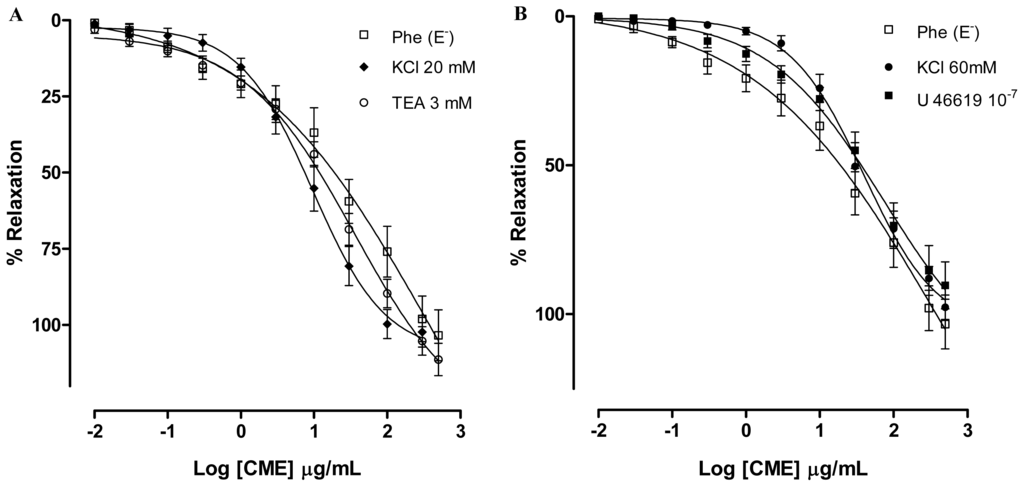
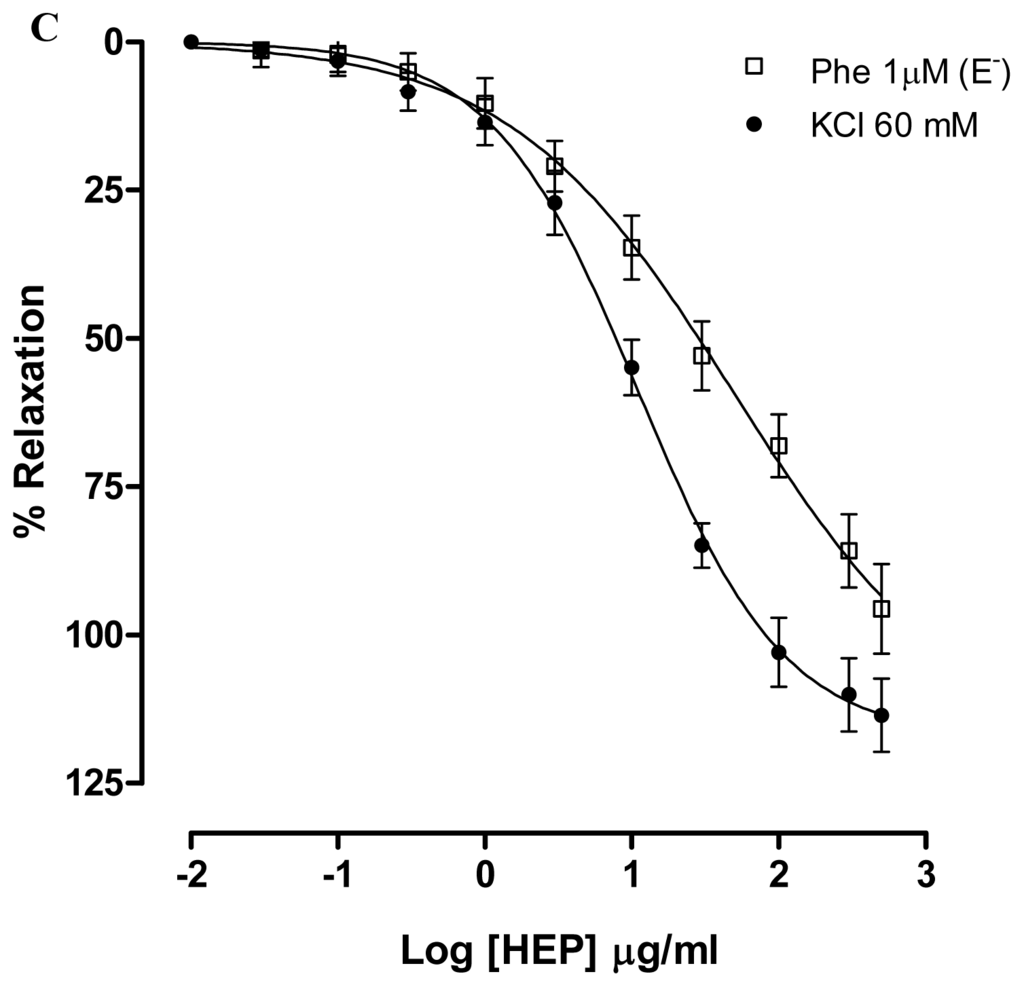
Figure 3.
Concentration–response curves showing the relaxant effect elicited by CME (0.01–500 μg/mL, n = 6) in the presence of (A) KCl (20 mM) (♦) or TEA 3 mM (○); (B) KCl (60 mM) (●) or U-46619; (□) represents phenyephrine pre-contracted mesenteric rings without endothelium; (C) Vasorelaxant effect elicited by HEP (0.01–500 μg/mL) on KCl 60 mM-pre-contracted mesenteric artery rings (●) and Phe (1 μM)-pre-contracted mesenteric rings without endothelium (n = 7). Values are expressed by mean ± SEM.
To test the hypothesis that CME produces vasorelaxant effects independent of the vasoconstrictor agent used in the preparation, mesenteric artery rings were incubated with tromboxane A2 agonist U-46619 (100 nM). In the presence of U-46619, CME induced concentration-dependent vasodilatation (Maximum Response = 90.3 ± 7.8%; EC50 = 24.63 ± 4.04 μg/mL, n = 6) similar to the response found by Phe-contracted mesenteric artery rings (Figure 3B).
In addition, CME produced relaxation in isolated arteries pre-contracted with KCl (60 mM). KCl depolarization elicits contraction by allowing the extracellular Ca2+ influx through voltage-dependent (L- and T-type) Ca2+ channels and subsequent calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Due to the fact that the membrane potential is essentially clamped by the high K+ solution, the mechanism by which relaxation can be produced is through blockade of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels, but not by other mediators that cause hyperpolarization [34]. After exposure to high concentrations of extracellular K+ (KCl, 60 mM), CME induced concentration-dependent vasodilatation (Maximum Response = 97.7 ± 4.0%; EC50 = 34.57 ± 5.11 mg/mL; n = 6). Under the same experimental condition, HEP induced concentration-dependent vasodilatation (Maximum Response = 113.5 ± 6.1%; EC50 = 10.92 ± 2.81 μg/mL; n = 6) (Figure 3C). Furthermore, both CME and HEP relaxed arterial segments pre-contracted with KCl (60 mM) suggesting that CME and HEP block Ca2+ entry through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (Cav).
In order to further investigate the hypothesis that CME and HEP act through the blockade of calcium influx, CME and HEP were tested in the presence of CaCl2-induced contractions in a depolarizing medium without calcium. This protocol was based on the fact that CaCl2-induced contractions are elicited, almost exclusively, through Ca2+ influx, since the depolarization promoted by high concentrations of extracellular K+ induces the opening of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels [35]. Under this experimental condition, CME and HEP (0.03; 0.3; 10; 30 and 100 μg/mL) produced a non-parallel and concentration-dependent rightward shift of the CaCl2 concentration–response curve significantly reducing the maximal response (Maximum Response = 116.1; 122.7; 84; 40.7; 7.6% and 130; 126.2; 46.8; 22.8; 7.3%, respectively) as illustrated in Figure 4A,B.
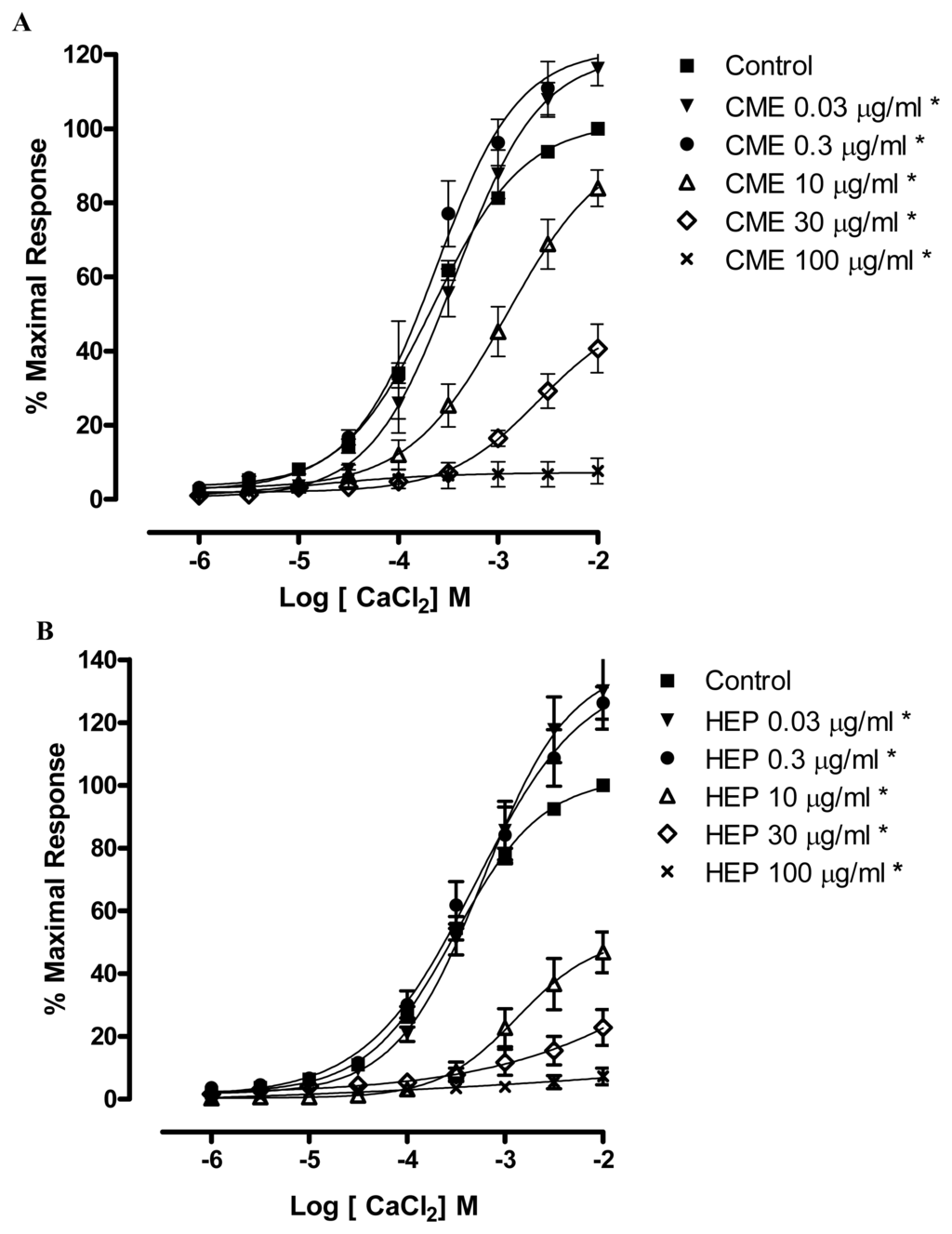
Figure 4.
Effects of (A) CME and (B) HEP on CaCl2-induced contraction in endothelium-denuded mesenteric artery rings. Concentration-response curves for CaCl2 were determined in Ca2+-free solution containing KCl (60 mM). The curves were determined in the absence (control, ■) and after incubation with CME in (A) or HEP in (B) (▾) 0.03; (●) 0.3; (▵) 10; (⋄) 30; (×) 100 μg/mL, n = 7. * Significantly different from control (p < 0.05).
Voltage-dependent calcium channels (Cav) are transmembrane proteins that provide influx of calcium for a variety of intracellular activities in excitable cells. In blood vessels, this calcium entry produces vasoconstriction and blockers of Cav have been used to treat cardiovascular disorders. Voltage-dependent calcium channels consist of different subunits: the α1-subunit, which contains four homologous transmembrane domains encompassing the pore, the voltage sensor and the selectivity filter; and the β, α2δ and γ auxiliary subunits. The α1-subunits have been classified as Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, Cav1.4 (L-type Cav), Cav2.1 (P/Q-type Cav), Cav2.2 (N-type Cav), Cav2.3 (R-type Cav), Cav3.1, Cav3.2 and Cav3.3 (T-type Cav). In the vascular smooth muscle cells two types are expressed: L-type and T-type. The first ones are more expressed in these cells and exert an important role in the regulation of the vascular tone [36,37].
In order to examine which subtype of Cav was involved in the vasorelaxant effect elicited by CME, a contraction with Bay K 8644 (200 nM), a L-type Ca2+ channel agonist, was evoked. CME induced concentration-dependent vasodilatation (Maximum Response = 113.3 ± 6.7%; EC50 = 19.45 ± 6.66 μg/mL, n = 7) and it was similar to the response found under Phe-induced contractions (Figure 5). These data indicate that L-type Cav channels could be involved in the vasorelaxant effect induced by CME.
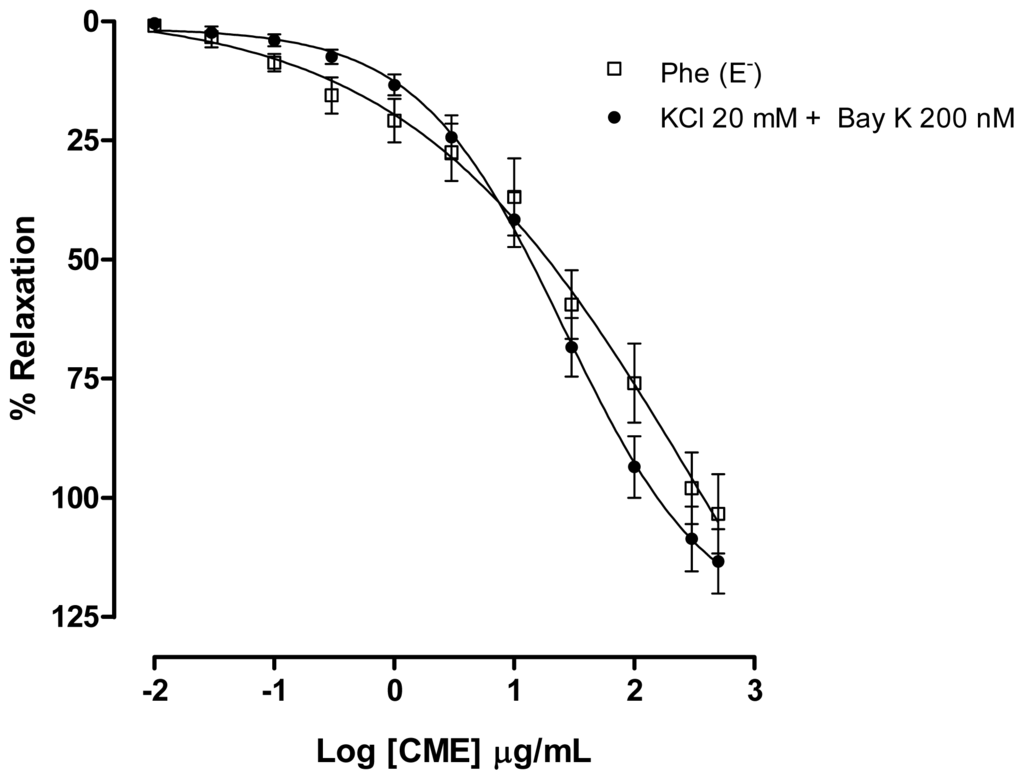
Figure 5.
Effect of increasing concentrations of CME (0.01–500 μg/mL, n = 7) on phenylephrine (Phe, 1 μM) (□) or KCl (20 mM) plus S(−)-BayK 8644 (10−7 M) (▴) induced contractions in isolated mesenteric artery rings without endothelium. Values are expressed by mean ± SEM.
In order to investigate a role for dihydropyridine calcium channels, rings were incubated with nifedipine. In the presence of nifedipine, CME (0.01–500 μg/mL) induced a concentration-dependent relaxation (Maximum Response = 63.6 ± 2.9%; EC50 = 25.4 ± 11.0 μg/mL, n = 6). The maximum response was different to the response found by Phe-contracted mesenteric artery rings (Figure 6A). In addition, in the presence of nifedipine, HEP (0.01–500 μg/mL) induced a concentration-dependent relaxation (Maximum Response = 69.8 ± 1.7%; EC50 = 24.4 ± 10.3 μg/mL, n = 6). The maximum response was different to the response found by Phe-contracted mesenteric artery rings (Figure 6B). Based on these findings, it can be suggested that the endothelium-independent vasodilatation induced by both CME and HEP involves, at least in part, the inhibition of the Ca2+ influx through blockade of calcium channels.
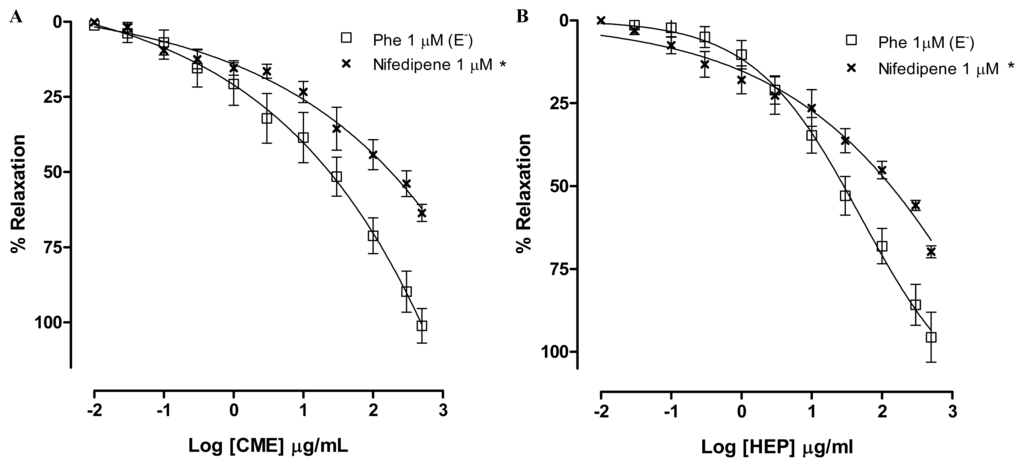
Figure 6.
Concentration–response curves showing the relaxant effect elicited by (A) CME (0.01–500 μg/mL); and (B) HEP (0.01–500 μg/mL) in the presence of nifedipine (×, n = 6); (□) represents phenyephrine pre-contracted mesenteric rings without endothelium. Values are expressed by mean ± SEM. * Significantly different from control (p < 0.05).
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Algal Material and Preparation of CH2Cl2/MeOH Extract (CME) and Hexane/EtOAc Phase (HEP) from Dictyota pulchella
The brown alga Dictyota pulchella Hörnig and Schnetter (Dictyotaceae, Phaeophyceae) was collected at Bessa Beach, João Pessoa, State of Paraíba, Brazil, at coordinates 07°04′01″S and 34°49′35″W in February 2009 at a depth of 1 m and it was identified by George Emmanuel C. de Miranda. A voucher specimen (JPB 41771) is deposited at Lauro Pires Xavier Herbarium of the Federal University of Paraíba.
The freeze-dried material (240 g) was extracted with CH2Cl2/MeOH (2:1) at room temperature. The concentrated extract (10 g) was partitioned by vacuum filtration with silica gel that uses the solvents Hexano/EtOAc (9:1) to give the fraction Hexano/EtOAc (9:1) (850 mg).
The CH2Cl2/MeOH extract (CME) and Hexane/EtOAc phase (HEP) were prepared in a mixture of distilled water (in vitro experiments) or NaCl 0.9 % solution (in vivo experiments) and cremophor (0.013% v/v) and kept at −4° C. The stock solution was diluted to the desired concentrations with distilled water or isotonic saline just before use. The final concentration of cremophor in the bath had no effect when tested in control preparations (data not shown).
3.2. Drugs and Solutions
The following drugs were used: Cremophor EL, l-phenylephrine chloride (Phe), acetylcholine chloride (Ach), tetraethylammonium (TEA), S(−)-Bay K 8644, sodium nitroprusside, Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) and 9,11-Dideoxy-11α,9α-epoxymethanoprostaglandin F2α (U 46619), were purchased from Sigma Chemical (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA). Heparin sodium salt (Roche Brazil, São Paulo, Brazil), sodium thiopental (Cristália, São Paulo, SP, Brazil). The substances were dissolved in distilled water (in vitro experiments) or in NaCl 0.9% solution (in vivo experiments).
The composition of the Tyrode’s solution used to bath isolated rings was (mM): NaCl, 158.3; KCl, 4.0; CaCl2, 2.0; MgCl2, 1.05; NaH2PO4, 0.42; NaHCO3, 10.0 and glucose, 5.6.
3.3. Animals
Male Wistar rats (250–300 g) were used in all experiments. They were housed in conditions of controlled temperature (21 ± 1 °C) and exposed to a 12 h light-dark cycle with free access to food (Labina®, PURINA, Brazil) and tap water. All procedures described in the present study are in agreement with Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Federal University of Paraiba (CEPA/LTF protocol No. 0208/10).
3.4. In Vivo Experiments
Intra-aortic blood pressure was recorded using a technique described by Braga [37] under sodium thiopental anesthesia (45 mg/kg, i.v.), the lower abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava were cannulated via left femoral artery and vein using polyethylene catheters. Thereafter, catheters were filled with heparinized saline solution and tunneled under the skin to emerge between the scapulae. Arterial pressure was measured 24 h after surgery by connecting the arterial catheter to a pre-calibrated pressure transducer (MLT0380/D, ADInstruments, Australia) and connected to a computer (Mikro-tip Blood pressure system, ADInstruments, Australia) running the LabChart software (ADInstruments, Australia). The data were sampled at 2000 Hz. For each pulse pressure, the computer calculated mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR). The venous catheter was used for drug administration.
3.5. In Vitro Experiments
3.5.1. Tissue Preparation
Rats were euthanized by stunning and bleeding. The superior mesenteric artery was removed and cleaned from connective tissue and fat. Rings (1–2 mm) were obtained and placed in physiological Tyrode’s solution, maintained at 37 °C, gassed with carbogenic mixture (95% O2 and 5% CO2), and maintained at pH 7.4. All preparations were stabilized under a resting tension of 0.75 g for 1 h. The solution was replaced every 15 min to prevent the accumulation of metabolites. The force of contraction was isometrically recorded by a force transducer (MLT020, ADInstruments, Australia) connected to a data acquisition system (ML870/P with LabChart version 7.0, ADInstruments, Australia). Endothelium was removed by gently rubbing the intimal surface of the vessels.
The presence of functional endothelium was assessed by the ability of acetylcholine (ACh) (10 μM) to induce more than 90% relaxation of pre-contracted vessels with phenylephrine (10 μM). When the relaxation to ACh was less than 10%, this was taken as evidence that the vessel segments were functionally denuded of endothelium.
3.5.2. Measurement of Vascular Relaxation Elicited by CME or HEP
The ability of extract or phase to cause vascular relaxation was evaluated in both endothelium-intact and endothelium-denuded mesenteric artery rings previously contracted by Phe (1 μM). Under the sustained contraction elicited by Phe the vessels were exposed to cumulative concentrations of CME or HEP (3, 5, 10, 30 and 50 μg/mL).
3.5.3. Effect of CME or HEP on KCl (60 mM) or U-46619 (100 nM)-Induced Contractions in Rings without Endothelium or after KCl (20 mM) and Tetraethylamonium (3 mM) Incubation
Contractions of the vessels were induced with KCl (60 mM) or U-46619 (100 nM) in rings without the endothelium. During the tonic phase of the contraction, CME or HEP (0.01–500 μg/mL) was added to the organ bath. The extent of relaxation was expressed as the percentage of KCl- or U46619-induced contraction. Furthermore, curves for CME were obtained after incubation with KCl (20 mM) or TEA (3 mM), a non-selective K+ channel blocker in rings without the endothelium.
3.5.4. Depolarization Induced by High Extracellular K+ Concentration
In order to access the effects of CME or HEP on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, superior mesenteric artery rings were bathed for 15 min in Ca2+-free Tyrode’s solution, prepared by omitting only CaCl2 and then exposed for an additional 15 min to a high K+ (60 mM) Ca2+-free solution. Under this new experimental condition, cumulative concentration-response curves to CaCl2 (ranging from 1 μM to 3 mM) were obtained. CME and HEP (0.01–500 μg/mL) were added to the preparations for 30 min, and then a new cumulative concentration–response curve for CaCl2 was determined. The maximal contraction obtained with the control concentration–response curve to CaCl2 was taken as 100% and all values were calculated as a percentage of the maximal response. Each preparation was exposed to only one CME or HEP-concentration. All experiments were done using endothelium-denuded superior mesenteric artery rings.
3.5.5. Effect of CME on the Contraction Elicited by S(−)-Bay K 8644 (200 nM) or Nifedipine (1 μM) in Mesenteric Artery Rings without Endothelium
Contractions of the vessels were induced by S(−)-Bay K 8644 (200 nM), an activator of calcium channels sensitive to dihydropyridines, in rings without the endothelium. During the tonic phase of the contraction, CME (0.01–500 μg/mL) was added to the organ bath. The extent of relaxation was expressed as the percentage of S(−)-Bay K 8644 -induced contraction. In addition, in order to intestigate the involvement of calcium channels, nifedipine (1 μM) was used to pre-incubate the preparations prior to CME or HEP administration.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. When appropriate, the significance of differences was determined using one-way ANOVA following Bonferroni’s post test with GraphPad Prism version 5.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Throughout the results, the “maximal relaxation” corresponds to the maximum response of pre-contracted tissues to the highest concentration of drug tested. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
4. Conclusions
Using combined in vivo and in vitro approaches, our data suggest that Dictyota pulchella induces hypotension and bradycardia. In addition, both extract and phase from Dictyota pulchella induce endothelium-independent vasodilatation that involves the inhibition of the Ca2+ influx through blockade of voltage-operated calcium channels. More studies are needed in order to evaluate the effects of this marine alga on experimental models of diseases such as hypertension and heart failure, which will help to advance the field towards clinical trials. Eventually, these data will open new perspectives in the use of these marine brown algae for developing drugs targeting the cardiovascular system.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior (CAPES). We thank José Crispin for his expert care of the animals.
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Matsubara, K; Matsuura, Y; Hori, K; Miyazawa, K. An anticoagulant proteoglycan from the marine green alga, Codium pugniformis. J. Appl. Phycol 2000, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Athukorala, Y; Lee, K; Kim, S; Jeon, Y. Anticoagulant activity of marine green and brown algae collected from Jeju Island in Korea. Bioresour. Technol 2007, 98, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Artan, M; Li, Y; Karadeniz, F; Lee, S; Kim, M; Kim, S. Anti-HIV-1 activity of phloroglucinol derivative, 6,6′-bieckol, from Ecklonia cava. Bioorgan. Med. Chem 2008, 16, 7921–7926. [Google Scholar]
- Huheihel, M; Ishanu, V; Tal, J; Arad, S. Activity of Porphyridium sp. polysaccharide against herpes simplex viruses in vitro and in vivo. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2002, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, SJ; Park, EJ; Lee, KW; Jeon, YJ. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Bioresour. Technol 2005, 96, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y; Qian, Z; Li, Y; Kim, M; Lee, S; Kim, S. Antioxidant effects of phlorotannins isolated from Ishige okamurae in free radical mediated oxidative systems. J. Agric. Food Chem 2008, 56, 7001–7009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y; Lee, S; Le, Q; Kim, M; Kim, S. Anti-allergic effects of phlorotannins on histamine release via binding inhibition between IgE and Fc RI. J. Agric. Food Chem 2008, 56, 12073–12080. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, CS; Kim, JA; Yoon, NY; Kim, SK. Induction of apoptosis by phloroglucinol derivative from Ecklonia cava in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol 2009, 47, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Pangestuti, R; Kim, S-K. Neuroprotective effects of marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 803–818. [Google Scholar]
- Kelecom, A. Secondary metabolites from marine microorganisms. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc 2002, 74, 151–170. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, AJ. Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweeds natural products: a review. J. Appl. Physcol 2004, 16, 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, APA; Torres, MR; Pessoa, C; Moraes, MO; Rocha-Filho, FD; Alves, APNN; Costa-Lotufo, LV. In vivo growth-inhibition of Sarcoma 180 tumor by alginates from brown seaweed Sargassum vulgare. Carbohydr. Polym 2007, 69, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Siamopoulou, P; Bimplakis, A; Iliopoulou, D; Vagias, C; Cos, P; Vanden Berghe, D; Roussis, V. Diterpenes from the brown algae Dictyota dichotoma and Dictyota linearis. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Sacchettini, JC; Poulter, CD. Creating isoprenoid diversity. Science 1997, 277, 1788–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Dewick, PM. The biosynthesis of C5–C25 terpenoid compounds. Nat. Prod. Rep 2002, 19, 181–222. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, VS; Bhalla, R; Luthra, R. An overview of the non-mevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis in plants. J. Biosci 2003, 28, 637–646. [Google Scholar]
- Tirapelli, CR; Ambrosio, SR; da Costa, FB; de Oliveira, AM. Evidence for the mechanisms underlying the effects of pimaradienoic acid isolated from the roots of Viguiera arenaria on rat aorta. Pharmacology 2004, 70, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tirapelli, CR; dos Anjos, MNF; Bonaventura, D; Melo, MC; Ambrosio, SR; de Oliveira, AM; Bendhack, LM; da Costa, FB. Pimaradienoic acid inhibits vascular contraction and induces hypotension in normotensive rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol 2008, 60, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Tirapelli, CR; Ambrosio, SR; de Oliveira, AM; Tostes, RC. Hypotensive action of naturally occurring diterpenes: A therapeutic promise for the treatment of hypertension. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 690–702. [Google Scholar]
- Somova, LI; Shode, FO; Moodley, K; Govender, Y. Cardiovascular and diuretic activity of kaurene derivates of Xylopia aethiopica and Alepidea amatymbica. J. Ethnopharmacol 2001, 77, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, AP; Furtado, FF; Silva, MS; Tavares, JF; Mafra, RA; Araújo, DA; Cruz, JS; Medeiros, IA. Calcium channel blockade as a target for the cardiovascular effects induced by the 8 (17), 12E, 14 labdatrien-18-oic acid (labdane-302). Vasc. Pharmacol 2006, 44, 338–344. [Google Scholar]
- American Heart Association. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2008 update. Circulation 2008, 117, 125–146.
- Lefkowits, RJ; Willerson, J. Prospects for cardiovascular research. JAMA 2001, 285, 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, MRV; Moreira, FV; Fraga, BP; de Souza, DP; Bonjardim, LR; Quintans, LJ, Jr. Cardiovascular effects of monoterpenes: a review. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn 2011, 21, 764–771. [Google Scholar]
- Fluckiger, JP; Sonnay, M; Boillat, N; Atkinson, J. Attenuation of baroreceptor reflex by general anesthetic agent in the normotensive rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1985, 109, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, TL; Hutchins, PM. Anesthetic effects on hemodynamics of spontaneously hypertensive on Wistar-Kyoto rats. Am. J. Physiol 1980, 238, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany, MJ; Aalkjaer, C. Structure and function of small arteries. Physiol. Res 1990, 70, 921–951. [Google Scholar]
- Grover-Páez, F; Zavalza-Gómez, AB. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract 2009, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott, FF; Zawadzki, JV. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 1980, 288, 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Côrtes, SF; Rezende, BA; Corriu, C; Medeiros, IA; Teixeira, MM; Lopes, MJ; Lemos, VS. Pharmacological evidence for the activation of potassium channels as the mechanism involved in the hypotensive and vasorelaxant effect of dioclein in rat small resistance arteries. Br. J. Pharmacol 2001, 133, 849–858. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, JR; Jurgens, TM. A systematic review of mechanisms by which natural products of plant origin evoke vasodilation. Can. J. Phys. Pharmacol 2006, 84, 803–821. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, HY; Oh, H; Li, X; Cho, KW; Kanga, DG; Lee, HS. Ethanol extract of seeds of Oenothera odorata induces vasorelaxation via endothelium dependent NO-cGMP signaling through activation of Akt-eNOS-sGC pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol 2011, 133, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, TP; Porto, DL; Menezes, CP; Antunes, AA; Silva, DF; Sousa, DP; Nakao, LS; Braga, VA; Medeiros, IA. Unravelling the cardiovascular effects induced by α-terpineol: A role for the nitric oxide–cGMP pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Phys 2010, 37, 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo, AP; Somlyo, AV. Signal transduction and regulation in smooth muscle. Nature 1994, 372, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ratz, PH; Berg, KM. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate inhibits KCl-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2006, 541, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, MF; Grayson, TH; Meaney, KR; Cribbs, LL; Hill, CE. Non-L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels control vascular tone of the rat basilar artery. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Phys 2009, 36, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, VA. Dietary salt enhances angiotensin-II-induced superoxide formation in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin 2010, 155, 14–18, Samples Availability: Available from the authors.. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).