Abstract
On a global research expedition, over 500 bacterial strains inhibitory towards pathogenic bacteria were isolated. Three hundred of the antibacterial strains were assigned to the Vibrionaceae family. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the phylogeny and bioactivity of five Vibrionaceae strains with pronounced antibacterial activity. These were identified as Vibrio coralliilyticus (two strains), V. neptunius (two strains), and Photobacterium halotolerans (one strain) on the basis of housekeeping gene sequences. The two related V. coralliilyticus and V. neptunius strains were isolated from distant oceanic regions. Chemotyping by LC-UV/MS underlined genetic relationships by showing highly similar metabolite profiles for each of the two V. coralliilyticus and V. neptunius strains, respectively, but a unique profile for P. halotolerans. Bioassay-guided fractionation identified two known antibiotics as being responsible for the antibacterial activity; andrimid (from V. coralliilyticus) and holomycin (from P. halotolerans). Despite the isolation of already known antibiotics, our findings show that marine Vibrionaceae are a resource of antibacterial compounds and may have potential for future natural product discovery.
1. Introduction
Bioactive secondary metabolites are believed to play a key role in microbial interactions by mediating antagonistic activity and intercellular communication [1]. In addition, many microbial natural products have biotechnological potential as antibiotics, biosurfactants, antifungal, or anticancer agents [2]. Sequences of microbial genomes revealed that only a small fraction of the natural product diversity is known, highlighting the potential for finding novel bioactive compounds in environmental microorganisms [3]. The need for novel antimicrobials to combat increasing antibiotic resistances in pathogenic bacteria has stimulated the exploration of other than the traditional sources, such as terrestrial actinomycetes or fungi [4].
The marine environment harbors bacteria with antagonistic traits [5,6], and marine microorganisms are a potential source of novel antimicrobials [7]. Antagonistic marine bacteria have been isolated from surface [8] and deep waters [9], but the majority originated from biotic surfaces such as sponges [10], zooplankton and macroalgae [8,11], corals [12], and bryozoans [13]. Bioactive bacterial strains predominantly belong to Pseudoalteromonas spp. [14], the Roseobacter clade [15], and Actinobacteria [16]. A number of marine-derived antimicrobials have been characterized in greater detail, including halogenated [17] and sulfuric [18] compounds, depsipeptides [19] and lipopeptides [20], glycolipids [21], as well as high molecular weight structures such as amino acid oxidases [22].
Also the Vibrionaceae family, Gram-negative Gammaproteobacteria ubiquitous in marine and brackish environments [23], harbors strains with antagonistic activity [8]. The family comprises eight genera, with Vibrio and Photobacterium constituting the majority of species. To date, Vibrionaceae have primarily been investigated due to their pathogenic potential to humans and aquatic animals, but they also occur in commensal or symbiotic associations with eukaryotic organisms [23]. While the abundance of Vibrionaceae in nutrient-rich microenvironments such as chitinous zooplankton is potentially related to a superior nutrient utilization based on their metabolic versatility [24], antagonism of competing bacteria through production of antimicrobial compounds may also contribute to a selective advantage. Antimicrobials from Vibrio spp. can reduce the number of other microbial community members and influence microscale variations in competing bacterial populations [6]. Antibacterial activities have been described from V. alginolyticus [25], V. parahaemolyticus [26], V. anguillarum [27], and several unidentified Vibrio spp. [28,29]. However, the nature and frequency of antagonism among vibrios is still largely unknown, and only a few antibiotic Vibrio compounds have been structure elucidated to date [30,31].
The present study describes the analysis of bioactive Vibrionaceae strains collected during a global marine expedition [8]. The purpose was to (i) provide phylogenetic and chemical analyses of the strains with strongest antibacterial activity; (ii) characterize their bioactivity depending on culture conditions; and (iii) isolate and elucidate the structure of bioactive metabolites. We report the identification of five Vibrionaceae strains with pronounced antibacterial activity, the use of chemotyping to support genetic identification, and the structures of two antibacterial compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of Strains with Pronounced Antibacterial Activity
Three hundred and one Vibrionaceae strains were isolated during a global marine expedition ( http://www.galathea3.dk/uk) based on their ability to antagonize the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum strain 90-11-287 [8]. After being stored at −80 °C for between six and 12 months, all strains were retested for antibacterial activity against V. anguillarum strain 90-11-287 and the human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus strain 8325 by spotting colony mass on pathogen-seeded agar [8]. Activity was assessed by the formation of clearing zones around spotted colony mass. From 301 strains, only 138 retained antibacterial activity, being a small fraction compared to other antagonistic marine bacteria [32,33]. One hundred strains causing pronounced inhibition (diameter of clearing zones larger than 10 mm) were retested using the same set-up, resulting in a subselection of 39 strains with reproducible strong antibacterial activity when spotted on pathogen-seeded agar. This subselection was inoculated in liquid cultures and extracted with ethyl acetate to determine if antibacterial compounds were extractable with organic solvent. Activity was seen in ethyl acetate extracts from five strains, which were selected for further analyses. The five bioactive strains originated from different surface samples collected in distant oceanic regions (Figure 1).
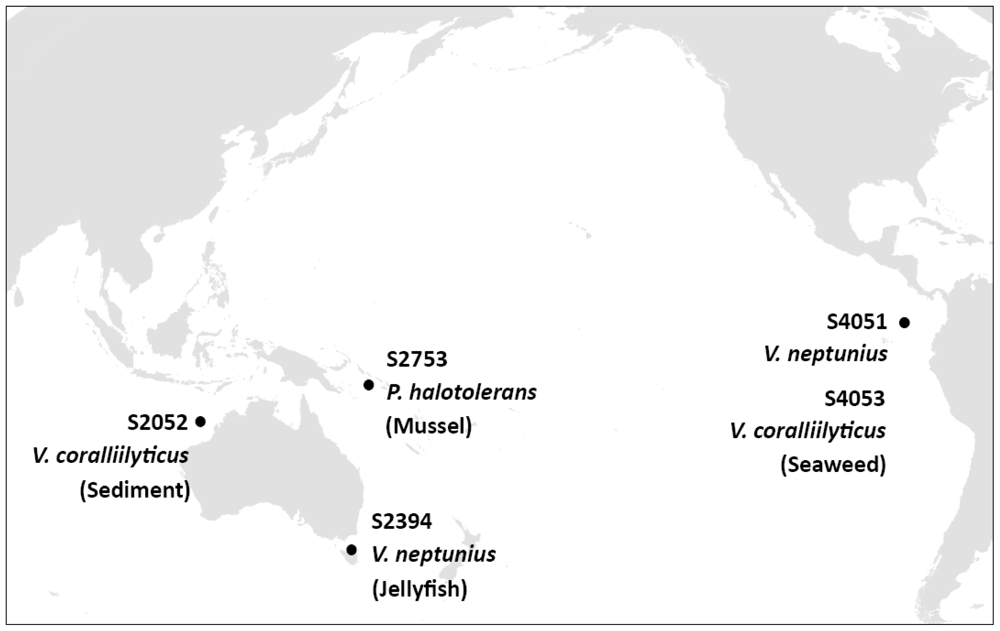
Figure 1.
Site of isolation, source, and species identification of five bioactive marine Vibrionaceae. Strains were identified to the species level by sequence analysis of several housekeeping genes (see below).
2.2. Phylogenetic Identification and Chemotyping of Strains
All strains investigated in the present study had previously been assigned to the Vibrionaceae family based on 16S rRNA gene similarities [8]. However, the 16S rRNA gene is highly conserved among the Vibrionaceae and is not well suited for identification to the species level [34]. Therefore, additional sequence analyses of three housekeeping genes (recA, rpoA, and toxR) were performed. These genes encode constitutively expressed proteins and are suitable for phylogenetic studies of Vibrionaceae [34,35]. On the basis of recA and rpoA sequence similarities, strains S2052 and S4053 were identified as Vibrio coralliilyticus, S2394 and S4051 as Vibrio neptunius, and S2753 as Photobacterium halotolerans (Figure 1). The toxR gene was less suited for general species identification due to its high variability even in closely related vibrios, as well as comparatively few toxR sequence data available in public gene libraries [36]. However, multiple alignments and neighbor-joining analyses of toxR sequences provided the best phylogenetic resolution for determining the relationship between the five strains (Figure 2). The usefulness of toxR for species discrimination was consistent with previous reports [35]. LC-UV/MS metabolite profiles underlined the close relationship between V. coralliilyticus S2052/4053 and V. neptunius S2394/4051, respectively. The evolutionary distance of P. halotolerans S2753 to the other strains was reflected by a unique metabolite profile (Figure 2). All five strains were consistent in their metabolite production in separate cultivations over a one-year interval.
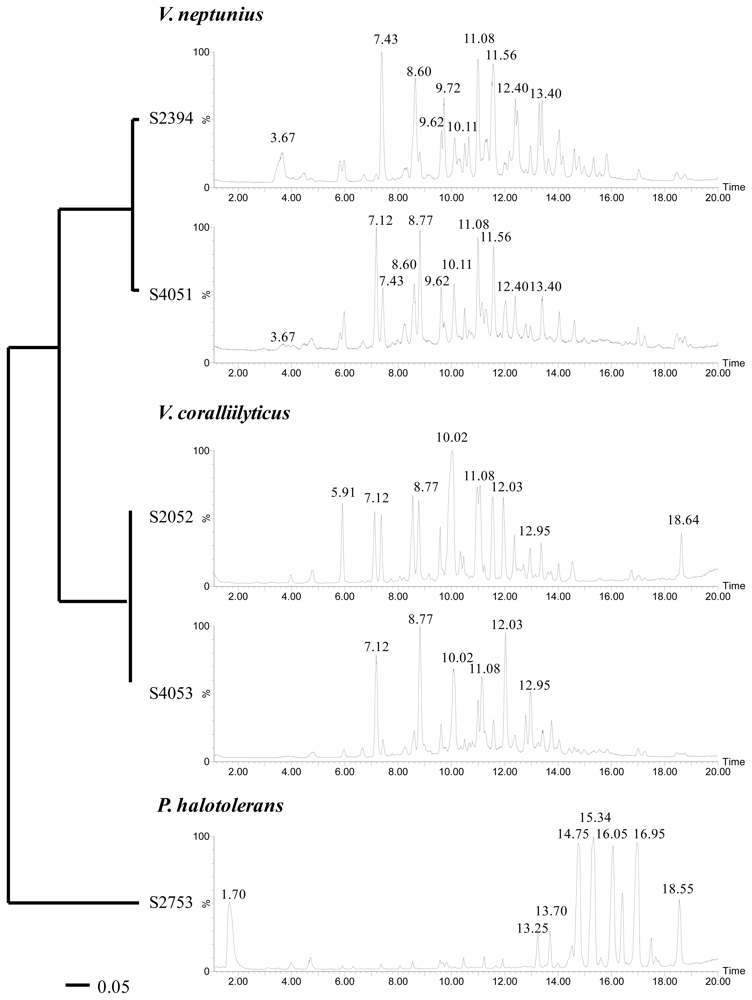
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic and chemical relationship between five bioactive Vibrionaceae based on neighbor-joining analyses of aligned toxR gene sequences and LC-MS Total Ion Chromatograms (TIC). The scale bar relates to the number of base substitutions in toxR gene sequences (as displayed by branch lengths in the phylogenetic tree).
Several metabolites were produced by all V. coralliilyticus and V. neptunius strains, for instance those related to the peaks at retention times Rt = 11.08 and 12.03 min (Figure 2). Although they are different species, V. coralliilyticus and V. neptunius are closely related vibrios with only 2–3% sequence variation in the recA and rpoA genes (data not shown), signifying why biosynthetic pathways are shared between the species. Based on their molecular formulas, UV, and MS characteristics [37], most of the metabolites produced by both species were assigned as smaller peptides (m/z 300–500), a class of molecules commonly produced by marine culturable bacteria [38,39]. Despite the presence of shared metabolites between V. coralliilyticus and V. neptunius, clearly distinguishable peaks were seen as well. For instance, the major peak at retention time Rt = 10.02 min (MW 479 Da) was only seen in the two V. coralliilyticus, and the peak at Rt = 10.11 min (MW 493 Da) only in the two V. neptunius strains.
The metabolites produced by P. halotolerans S2753 comprised a series of larger peptides (m/z 500–900) [40]. The large peak at Rt = 1.70 min (MW 213 Da) displayed a unique UV spectrum characteristic of that of a highly conjugated system. However, this peak could not be ascribed to any known compound or compound class based on LC-UV/MS data alone.
Several metabolites (Rt = 4.70, 7.41, 8.60, 9.60, and 10.50 min) were found in all five strains and assigned as poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid polymers (PHB) of varying lengths (repeating unit n = 86 Da). This was verified by NMR for some of the compounds (data not shown). PHB are common bacterial storage compounds accumulated when growing on an excess carbon source [41].
Chemotyping of prokaryotes has mostly been restricted to analyses of fatty acids and sugars [42], but we show that also the profiling of small molecules can be used for species discrimination. This highlights the usefulness of metabolomics for bacterial classification, adding to recent work of whole-cell laser desorption MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for characterization of vibrios [43] and secondary metabolite profiling to assess the biosynthetic potential of marine Pseudoalteromonas [32]. While our study is limited to the analysis of only three species from the Vibrionaceae family, the isolation of two genetically and chemically closely related “strain siblings” from distant oceanic regions indicated that production of certain secondary metabolites is a preserved trait. Similar secondary metabolite profiles were also shown for marine actinomycetal Salinispora spp. [44] from distant habitats. Also, all Ruegeria mobilis strains from worldwide locations produced the same antibiotic, tropodithietic acid [33].
2.3. Bioassay-Guided Identification of Antibacterial Compounds
V. coralliilyticus (strains S2052 and S4053) and P. halotolerans (S2753) inhibited both V. anguillarum and S. aureus, whereas V. neptunius (strains S2394 and S4051) only inhibited V. anguillarum (Table 1). Antibacterial activity was highest in aerated cultures and detected after one, three, and five days of incubation. No significant difference in activity was seen between the tested culture media.

Table 1.
Inhibition of V. anguillarum strain 90-11-287 and S. aureus strain 8325 by ethyl acetate extracts from five marine Vibrionaceae. Antibacterial activity is displayed by the diameter of clearing zones (–: no activity; +: between 0 and 15 mm; ++: between 15 and 30 mm; +++: over 30 mm).
The finding of bioactivity among marine Vibrionaceae underlined marine microorganisms being a source of antimicrobials. To our knowledge, none of the species investigated here have previously been studied with respect to their secondary metabolome including antibacterial compounds.
To identify the compounds responsible for the observed activity, large-scale cultivations and fractionations were undertaken for V. coralliilyticus S2052 and P. halotolerans S2753, representing two distant Vibrionaceae species with different metabolite profiles. All fractionation steps were guided by activity testing against V. anguillarum strain 90-11-287.
Initial dereplication of S2052 by LC-UV/MS [37] and explorative solid-phase extraction (E-SPE) [45] indicated that andrimid (Rt = 10.02 min; Figure 2) could be responsible for the antibacterial activity. This compound (Figure 3a), a hybrid nonribosomal peptide-polyketide antibiotic, was first described from an insect endosymbiont [46] and later found in other microbial species [47,48] including marine vibrios [29,31]. Pure andrimid was isolated for NMR analysis, and our data was in accordance with literature data [47]. Andrimid acts as an acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor [49], and we extended its broad antibiotic spectrum [50] by showing inhibition of the bacterial pathogens Salmonella Enteritidis, Bacillus cereus, Yersinia enterolitica, Yersinia ruckeri, Vibrio harveyi, and Vibrio vulnificus (data not shown). Production of andrimid was also confirmed for the other isolated V. coralliilyticus strain, S4053. We furthermore speculate whether a recent report of antagonism in the V. coralliilyticus type strain [12] was also attributed to this compound. Previous studies have revealed almost identical andrimid gene clusters and a transposase pseudogene in two producer species, suggesting horizontal gene transfer as the most likely explanation behind the cosmopolitanism of the antibiotic [51]. We hypothesize that such transfer is also the reason for its presence in V. coralliilyticus S2052 and S4053. Our study is the first linking andrimid production to a specific Vibrio species, with production occurring in two strains isolated from very different geographical regions and sources.
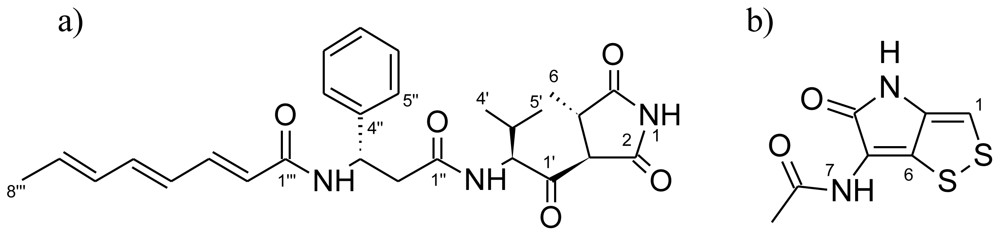
Figure 3.
Structures of andrimid (a) and holomycin (b) isolated from marine Vibrionaceae.
The antibacterial compound of P. halotolerans S2753 was identified as holomycin (Rt = 1.70 min; Figure 2), a compound belonging to the pyrrothine class of antibiotics acting by interference with RNA synthesis [52]. Our NMR data (Figure 3b) was consistent with previous reports [53]. Holomycin has until now only been found in Gram-positive Streptomyces [54,55], and the present study is the first demonstrating production of this antibiotic in a Gram-negative heterotrophic bacterium. While parallel evolution of this trait is possible, horizontal gene transfer is the more likely explanation for its occurrence in both Vibrionaceae and actinomycetes. We extended the broad-spectrum activity of holomycin [52] by showing inhibition of the bacterial pathogens Listeria monocytogenes, Serratia marcescens, S. Enteritidis, B. cereus, Y. enterolitica, Y. ruckeri, V. harveyi, V. vulnificus and V. parahaemolyticus, as well as of several marine strains from the Roseobacter and Pseudoalteromonas groups (data not shown).
Neither andrimid nor holomycin were produced by V. neptunius S2394 and S4051, and further fractionation and purification is needed to identify the compound(s) responsible for their antibacterial activity. Interestingly, V. neptunius S4051 and V. coralliilyticus S4053 were isolated from the same seaweed sample, showing that two antagonistic Vibrio species whose antibacterial activity is based on different compounds co-occur in the same microenvironment. Moreover, the same sample also contained an antibiotic-producing Pseudoalteromonas strain [8].
Two of the antagonistic Vibrionaceae species harbor pathogenic strains, with V. coralliilyticus being pathogenic to corals [56] and V. neptunius being pathogenic to oysters [57]. While we do not know whether V. coralliilyticus S2052 has pathogenic potential, the V. coralliilyticus type strain has both antagonistic and pathogenic traits [12]. Hence, our results suggest that some vibrios possess a dual physiology, being antagonistic against other prokaryotes but pathogenic towards higher organisms. Moreover, the production of antibiotics in several species suggests that these compounds may be of ecological importance [1].
This study highlights one of the challenges in natural product discovery. Despite major screening efforts for novel antimicrobials to be used in pharmaceutical, food, and aquaculture industries, only a limited amount of compounds have been discovered in recent years [58]. While the isolation of culturable bacteria remains a promising approach [42] and the secondary metabolome of marine vibrios has not been extensively studied, we only isolated known compounds despite careful dereplication prior to any compound purification. Dereplication is apparently troubled by the high degree of gene transfer between distantly related bacteria such as Gram-positive actinomycetes and Gram-negative Proteobacteria [3]. Many compounds in natural product databases such as AntiBase [59] have similar masses (<5 ppm difference), so even the combination of UV/VIS spectra, accurate mass data (<5 ppm), and E-SPE [45] is not sufficiently discriminatory for these organisms. To avoid isolation of redundant chemistry, dereplication by NMR [60] or ultra high-resolution mass spectrometry (<1 ppm) with high isotope accuracy ratios for correct elementary composition determination [61] is imperative to exclude previously isolated compounds.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Isolation of Bioactive Marine Vibrionaceae
During a global research expedition ( http://www.galathea3.dk/uk), marine bacterial strains were isolated from environmental samples and screened for antagonistic activity against a pathogenic Vibrio anguillarum, strain 90-11-287. Three hundred and one bioactive strains were identified as Vibrionaceae based on 16S rRNA gene similarities [8]. Pure cultures of strains were stored in cryoprotectant solution at −80 °C until being analyzed in the present study.
3.2. Selection of Strains with Pronounced Antibacterial Activity
All 301 strains were retested for antibacterial activity by spotting colony mass on agar seeded with either V. anguillarum strain 90-11-287 or S. aureus strain 8325. Activity was assessed by the formation of clearing zones around spotted colony mass. Selected active strains were grown both stagnant and aerated (200 rpm) in 30 mL Marine Broth 2216 (Difco 279110) for 3 days at 25 °C in 250 mL glass bottles. Cultures were extracted with an equal volume of HPLC-grade ethyl acetate (EtOAc) for 30 min. The organic phase was transferred to fresh sample vials and evaporated under nitrogen until dryness. Extracts were redissolved in 1 mL of EtOAc and stored at −20 °C until further analysis. EtOAc extracts were tested in a well diffusion agar assay [62] for activity against V. anguillarum strain 90-11-287 and S. aureus strain 8325.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from 1-day cultures using the NucleoSpin Tissue Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR for recA and toxR gene fragments was performed according to [35], and PCR for rpoA gene fragments according to [34]. PCR products were checked by agarose gel electrophoresis and purified using the Wizard PCR Preps DNA Direct Purification System (Promega, Madison, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Obtained nucleotide sequences were edited using Chromas Lite (Technelysium, Australia) and aligned to its closest sequence relative [36]. The phylogenetic relationship between the five isolates was determined by neighbor-joining analyses (1000 bootstrap replicates) of nucleotide and amino acid alignments (translated using EMBOSS Transeq, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/emboss/transeq/) done in ClustalX. Gene sequences have been deposited at GenBank under the accession numbers HQ452614–452618 (toxR), HQ452619–452623 (recA), and HQ452624–452628 (rpoA).
3.4. Influence of Culture Conditions on Bioactivity
The five strains with strongest antibacterial activity (S2052, S2394, S2753, S4051, and S4053) were grown both stagnant and aerated (200 rpm) at 25 °C in either Marine Broth (MB) or Marine Minimal Medium [63] containing 0.4% glucose and 0.3% casamino acids (MMM). Per strain and culture condition, three bottles were inoculated with 30 mL of medium each, of which each one was sampled after 1, 3, and 5 days of incubation. In addition, strains were grown in 30 mL sea salt solution (Sigma S9883; 40 g L−1) with 0.4% glucose and 0.3% casamino acids for 3 days (200 rpm) at 25 °C. EtOAc extracts were prepared as described above, and tested in a well diffusion agar assay [62] for activity against V. anguillarum strain 90-11-287 and S. aureus strain 8325.
3.5. Chemotyping
Liquid chromatography-diode array/mass spectrometry (LC-UV/MS) analyses were performed on dried EtOAc extracts redissolved in methanol (MeOH) from all tested culture conditions to visualize the array of produced molecules. In addition, 3-day MMM cultures were extracted and analyzed in biological triplicate. LC-UV/MS was performed on an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatograph with a diode array detector (Agilent, Waldbronn, Germany) coupled to an LCT TOF mass spectrometer (Micromass, Manchester, UK) using a Z-spray ESI source. The separation was done on a Luna II C18 column (50 mm × 2 mm, 3 μm) (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA) fitted with a security guard system using a linear gradient starting from 15% acetonitrile (MeCN) in water (H2O) to 100% MeCN over 20 min at a flow rate of 300 μL min−1. Both MeCN (HPLC grade) and H2O were buffered with 20 mM HPLC-grade formic acid (FA).
3.6. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Antibacterial Compounds
Strains S2052 and S2753 were grown in 20 L sea salt solution (Sigma S9883; 40 g L−1) with 0.4% glucose and 0.3% casamino acids for 3 days (100 rpm) at 25 °C. On day 3, sterile Dianion HP20SS resin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) was added to the broth (12 g of resin L−1). After 24 h, the resin was filtered off and washed with H2O (2 × 1 L), followed by extraction with MeCN/H2O (80/20 v/v; 2 × 1500 mL).
For S2052, all organic extracts were pooled, absorbed onto 90 g Sepra ZT C18 (Phenomenex), and dried before packing into a 100 g SNAP column (Biotage, Uppsala, Sweden) with pure resin (10 g) in the base. Using an Isolera flash purification system (Biotage), the extract was subjected to a crude fractionation using a MeCN/H2O gradient (flow rate 30 mL min−1) starting with 10% MeCN (10 min, isocratic), increasing to 100% MeCN (25 min) before washing with 100% MeCN (15 min). Fractions were automatically collected using UV detection (210 and 320 nm). The fraction with antibacterial activity (185 mg) was subjected to further purification on a Luna II C18 column (250 × 10 mm, 5 μm) (Phenomenex) using a 45–70% MeCN/H2O gradient (buffered with 20 mM FA, flow rate 5 mL min−1) over 20 minutes on a Gilson 322 liquid chromatograph with a 215 liquid handler/injector (BioLab, Risskov, Denmark). This yielded 7.6 mg of pure andrimid.
For S2753, the MeCN/H2O extract from Dianion HP20SS extraction was evaporated until dryness on a rotary evaporator. The extract was redissolved in EtOAc, absorbed onto 5 g Isolute diol (Biotage), and added to a glass column with pure diol (95 g). A total of 12 fractions were collected from the diol column (100 g, 20 × 350 mm) ranging from heptane, dichloromethane, EtOAc to pure MeOH, running under gravity. The fraction with antibacterial activity (172 mg, 100% EtOAc) was further separated on the Isolera flash purification system, on Sepra ZT C18 (10 g SNAP) using a MeCN/H2O gradient (flow rate 12 mL min−1) starting with 5% MeCN increasing to 30% MeCN (12 min), quickly increasing to 100% MeCN (10 min). Fractions were automatically collected using UV detection (210 and 380 nm). Pure holomycin (4.3 mg) was obtained after final purification on a Luna II C18 column (250 × 10 mm, 5 μm) (Phenomenex) using a MeCN/H2O (buffered with 20 mM FA) gradient from 7–37% MeCN over 17 min.
NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 800 MHz spectrometer with a 5 mm TCI Cryoprobe at the Danish Instrument Center for NMR Spectroscopy of Biological Macromolecules, using standard pulse sequences. The NMR data used for the structural assignment of andrimid and holomycin were acquired in DMSO-d6 (δH 2.49 and δC 39.5 ppm).
Optical rotation was measured on a Perkin Elmer Model 341 polarimeter (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA) (αD at 589 nm).
Andrimid
orange-yellow amorphous solid; UV (MeCN/H2O) λmax 200 (100%), 280 (40%) nm; [α]D20 −62.9° (c 0.24, MeOH); 1H NMR δH ppm: 0.75 (3H, d, 6.7 Hz, H-4′), 0.80 (3H, d, 6.7 Hz, H-5′), 1.07 (d, 7.2 Hz, 1H, H-6), 1.78 (3H, d, 6.7 Hz, H-8‴), 2.30 (m, 1H, H-3′), 2.65 (1H, dd, 14.6, 6.2 Hz, H-2a″), 2.77 (1H, dd, 14.6, 8.2 Hz, H-2b″), 2.91 (m, 1H, H-4), 3.92 (d, 5.6 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.62 (dd, 8.4, 5.4 Hz, 1H, H-2′), 5.28 (1H, m, H-3″), 5.90 (1H, m, H-7‴), 6.01 (1H, d, 15.2 Hz, H-2‴), 6.18 (1H, m, H-6‴), 6.26 (1H, dd, 14.5, 11.4 Hz, H-4‴), 6.53 (1H, dd, 14.5, 10.0 Hz, H-5‴), 7.00 (1H, dd, 15.2, 11.4 Hz, H-3‴), 7.20 (1H, m, H-7″), 7.29-7.31 (4H, m, H-5″/H-6″), 8.11 (1H, d, 8.4 Hz, NH-2′), 8.42 (1H, d, 8.5 Hz, NH-3″), 11.36 ( s, 1H, NH-1); 13C NMR δC ppm: 14.5 (C-6), 17.2 (C-4′), 18.3 (C-8‴), 19.4 (C-5′), 28.1 (C-3′), 39.0 (C-4), 41.9 (C-2″), 57.8 (C-3), 63.1 (C-2′), 124.2 (C-2‴), 126.4 (C-5″), 126.9 (C-7″), 128.1 (C-4‴), 128.2 (C-6″), 131.5 (C-6‴), 133.4 (C-7‴), 139.0 (C-5‴), 139.4 (C-3‴), 142.9 (C-4″), 164.3 (C-1‴), 169.9 (C-1″), 173.8 (C-2), 180.0 (C-5), 203.9 (C-1′); HRESIMS m/z 479.2435 (calcd for C27H33N3O5, 479.2420).
Holomycin
orange-yellow prisms; UV (MeCN/H2O) λmax 200 (100%), 280 (40%) nm; 1H NMR δH ppm: 2.01 (s, 1H, H-9), 7.04 (s, 1H, H-1), 9.86 (s, 1H, NH-7), 10.69 (s, 1H, NH-3); 13C NMR δC ppm: 22.4 (C9), 110.6 (C-1), 115.4 (C-5), 133.7 (C-2), 133.9 (C-6), 167.9 (C-4), 168.8 (C-8); HRESIMS m/z 213.9860 (calcd for C7H6N2O2S2, 213.9871).
4. Conclusions
The present study adds to the knowledge of Vibrionaceae bioactivity and physiology by showing a worldwide occurrence of marine strains producing antibacterial compounds. In addition, we underlined that chemotyping can support gene-based species identification and help resolving phylogenetic relationships within a genetically homogenous family such as the Vibrionaceae. The discovery of known antibiotics that are also produced by evolutionary distant microbes suggests an involvement of horizontal gene transfer, and indicates that these compounds are fundamental to compete and communicate in the natural habitat. The cosmopolitanism of identical antibiotics has major implications for natural product discovery strategies and stresses the need for careful dereplication in the initial stages of screening. An alternative approach could be the screening for largely untested bioactivities, for instance, interference with quorum sensing or modulation of gene expression.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Danish Instrument Center for NMR Spectroscopy of Biological Macromolecules for NMR time. Thanks to Louise Kjærulff for assisting in the purification of holomycin, and to Kamilla Spanggaard and Anja Sander for help with bioassays. Funding from the Programme Committee for Food, Health and Welfare under the Danish Strategic Research Council is acknowledged. The present work was carried out as part of the Galathea 3 expedition under the auspices of the Danish Expedition foundation. This is Galathea 3 contribution no. P70.
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Hibbing, ME; Fuqua, C; Parsek, MR; Peterson, SB. Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat Rev Microbiol 2010, 8, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Demain, AL; Sanchez, S. Microbial drug discovery: 80 years of progress. J Antibiot 2009, 62, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, MA. Antibiotics from microbes: Converging to kill. Curr Opin Microbiol 2009, 12, 520–527. [Google Scholar]
- Berdy, J. Bioactive Microbial Metabolites. J Antibiot 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, S; Simidu, U. Distribution and Significance of Heterotrophic Marine Bacteria with Antibacterial Activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 1987, 53, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E; Azam, F. Antagonistic Interactions among Marine Pelagic Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 2001, 67, 4975–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, LX; An, R; Wang, JP; Sun, N; Zhang, S; Hu, JC; Kuai, J. Exploring novel bioactive compounds from marine microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 2005, 8, 276–281. [Google Scholar]
- Gram, L; Melchiorsen, J; Bruhn, JB. Antibacterial activity of marine culturable bacteria collected from a global sampling of ocean surface waters and surface swabs of marine organisms.
- Hohmann, C; Schneider, K; Bruntner, C; Irran, E; Nicholson, G; Bull, AT; Jones, AL; Brown, R; Stach, JEM; Goodfellow, M; et al. Caboxamycin, a new antibiotic of the benzoxazole family produced by the deep-sea strain Streptomyces sp. 2009, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, MW; Radax, R; Steger, D; Wagner, M. Sponge-Associated Microorganisms: Evolution, Ecology, and Biotechnological Potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wiese, J; Thiel, V; Nagel, K; Staufenberger, T; Imhoff, JF. Diversity of Antibiotic-Active Bacteria Associated with the Brown Alga Laminaria saccharina from the Baltic Sea. Mar Biotechnol 2009, 11, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Rypien, KL; Ward, JR; Azam, F. Antagonistic interactions among coral-associated bacteria. Environ Microbiol 2010, 12, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Herndl, H; Wiese, J; Thiel, V; Imhoff, JM. Phylogenetic diversity and antimicrobial activities of bryozoan-associated bacteria isolated from Mediterranean and Baltic Sea habitats. Syst Appl Microbiol 2010, 33, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, JP. Bioactive Compound Synthetic Capacity and Ecological Significance of Marine Bacterial Genus Pseudoalteromonas. Mar Drugs 2007, 5, 220–241. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, T; Gram, L; Grossart, HP; Kessler, D; Muller, R; Simon, M; Wenzel, SC; Brinkhoff, T. Bacteria of the Roseobacter clade show potential for secondary metabolite production. Microb Ecol 2007, 54, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, AT; Stach, JEM. Marine actinobacteria: new opportunities for natural product search and discovery. Trends Microbiol 2007, 15, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, RJ; Wolfe, MS; Faulkner, DJ. Autotoxic Antibiotic Production by a Marine Chromobacterium. Mar Biol 1974, 27, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, HF; Bruhn, JB; Nielsen, KF; Gram, L; Belas, R. Genetic dissection of tropodithietic acid biosynthesis by marine roseobacters. Appl Environ Microbiol 2008, 74, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, LA; Uchino, M; Kalinovskaya, NI; Mikhailov, VV. Isolation, phylogenetic analysis and screening of marine mollusc-associated bacteria for antimicrobial, hemolytic and surface activities. Microbiol Res 2008, 163, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P; Mukherjee, S; Sen, R. Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans. J Appl Microbiol 2008, 104, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, GS; Thomas, TA; Selvin, J. Production of a new glycolipid biosurfactant from marine Nocardiopsis lucentensis MSA04 in solid-state cultivation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2010, 78, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, D; Espinosa, E; Bertazzo, M; Lucas-Elio, P; Solano, F; Sanchez-Amat, A. The macromolecule with antimicrobial activity synthesized by Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea strains is an l-amino acid oxidase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2008, 79, 925–930. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, FL; Iida, T; Swings, J. Biodiversity of Vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, J; Hickman-Brenner, F. The Genera Vibrio and Photobacterium. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M, Falkow, S, Rosenberg, E, Schleifer, KK-H, Stackebrandt, E, Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B; Stuckey, LF; Robertson, PAW; Effendi, I; Griffith, DRW. A Probiotic Strain of Vibrio alginolyticus Effective in Reducing Diseases Caused by Aeromonas salmonicida, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio ordalii. J Fish Dis 1995, 18, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Radjasa, OK; Sabdono, A; Zocchi, J; Zocchi, E. Richness of secondary metabolite-producing marine bacteria associated with the sponge Haliclona sp. Int J Pharmacol 2007, 3, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm, M; Riaza, A; Formoso, F; Melchiorsen, J; Gram, L. Seasonal Incidence of Autochthonous Antagonistic Roseobacter spp. and Vibrionaceae Strains in a Turbot Larva (Scophthalmus maximus) Rearing System. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004, 70, 7288–7294. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, D; Pujalte, MJ; Lopez-Cortes, L; Garay, E; Borrego, JJ. Vibrios isolated from the cultured manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum): Numerical taxonomy and antibacterial activities. J Appl Microbiol 2002, 93, 438–447. [Google Scholar]
- Long, RA; Rowley, DC; Zamora, E; Liu, J; Bartlett, DH; Azam, F. Antagonistic Interactions among Marine Bacteria Impede the Proliferation of Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005, 71, 8531–8536. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M; Aoki, S; Gato, K; Matsunami, K; Kurosu, M; Kitagawa, I. Marine Natural Products. XXXIV. Trisindoline, a New Antibiotic Indole Trimer, Produced by a Bacterium of Vibrio sp. Separated from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios altum. Chem Pharm Bull 1994, 42, 2449–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Oclarit, JM; Okada, H; Ohta, S; Kaminura, K; Yamaoka, Y; Iizuka, T; Miyashiro, S; Ikegami, S. Anti-Bacillus Substance in the Marine Sponge, Hyatella Species, Produced by an Associated Vibrio Species Bacterium. Microbios 1994, 78, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Vynne, NG; Mansson, M; Nielsen, KF; Gram, L. Bioactivity, chemical profiling and 16S rRNA based phylogeny of Pseudoalteromonas strains collected on a global research cruise. Mar Biotechnol 2010. submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Gram, L; Porsby, CH; Heilmann, J; Jensen, M; Melchiorsen, J; Nielsen, KF. A cosmopolitan bacterium: Phylogentic and phenotypic homogeneity in a global collection of Ruegeria mobilis of the Roseobacter clade. Appl Environ Microbiol 2010. submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, FL; Gevers, D; Thompson, CC; Dawyndt, P; Naser, S; Hoste, B; Munn, CB; Swings, J. Phylogeny and molecular identification of vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005, 71, 5107–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, J; Macian, MC; Arahal, DR; Garay, E; Pujalte, MJ. Multilocus sequence analysis of the central clade of the genus Vibrio by using 16S rRNA, recA, pyrH, rpoD, gyrB, rctB and toxR genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009, 60, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, SF; Madden, TL; Schaffer, AA; Zhang, JH; Zhang, Z; Miller, W; Lipman, DJ. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, KF; Smedsgaard, J. Fungal metabolite screening: database of 474 mycotoxins and fungal metabolites for dereplication by standardised liquid chromatography-UV-mass spectrometry methodology. J Chromatogr A 2003, 1002, 111–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mitova, M; Popov, S; De Rosa, S. Cyclic peptides from a Ruegeria strain of bacteria associated with the sponge Suberites domuncula. J Nat Prod 2004, 67, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Rungprom, W; Siwu, ERO; Lambert, LK; Dechsakulwatana, C; Barden, MC; Kokpol, U; Blanchfield, JT; Kita, M; Garson, MJ. Cyclic tetrapeptides from marine bacteria associated with the seaweed Diginea sp. and the sponge Halisarca ectofibrosa. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 3147–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Mansson, M; Nielsen, A; Kjaerulff, L; Gotfredsen, CH; Ingmer, H; Wietz, M; Gram, L; Larsen, TO. Inhibition of virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by novel depsipeptides from a marine. Photobacterium 2010. to be submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, CC; Chen, CC; Choi, MH; Kung, SS; Wei, YH. Production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Vibrio spp. isolated from marine environment. J Biotechnol 2007, 132, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, AT. Microbial Diversity and Bioprospecting; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann, R; Strauch, E; Alter, T. Rapid identification and characterization of Vibrio species using whole-cell MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J Appl Microbiol 2010, 109, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, PR; Williams, PG; Oh, DC; Zeigler, L; Fenical, W. Species-Specific Secondary Metabolite Production in Marine Actinomycetes of the Genus Salinispora. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007, 73, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Mansson, M; Phipps, RK; Gram, L; Munro, MHG; Larsen, TO; Nielsen, KF. Explorative Solid-Phase Extraction (E-SPE) for Accelerated Microbial Natural Product Discovery, Dereplication, and Purification. J Nat Prod 2010, 73, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Fredenhagen, A; Tamura, SY; Kenny, PTM; Komura, H; Naya, Y; Nakanishi, K; Nishiyama, K; Sugiura, M; Kita, H. Andrimid, a new peptide antibiotic produced by an intracellular bacterial symbiont isolated from a brown planthopper. J Am Chem Soc 1987, 109, 4409–4411. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, J; Kelly, MT; Ishige, M; Andersen, RJ. Andrimid and moiramides A–C, metabolites produced in culture by a marine isolate of the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens: Structure elucidation and biosynthesis. J Org Chem 1994, 59, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M; Fischbach, MA; Clardy, J. A Biosynthetic Gene Cluster for the Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitor Andrimid. J Am Chem Soc 2006, 128, 10660–10661. [Google Scholar]
- Freiberg, C; Brunner, NA; Schiffer, G; Lampe, T; Pohlmann, J; Brands, M; Raabe, M; Häbich, D; Ziegelbauer, K. Identification and Characterization of the First Class of Potent Bacterial Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitors with Antibacterial Activity. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 26066–26073. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, MP; Mroczenski-Wildey, MJ; Steinberg, DA; Andersen, RJ; Maiese, WM; Greenstein, M. Biological activity and mechanistic studies of andrimid. J Antibiot 1997, 50, 270–273. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, MA; Walsh, CT; Clardy, J. The evolution of gene collectives: How natural selection drives chemical innovation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008, 105, 4601–4608. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva, B; O’Neill, A; Wilson, JM; O’Hanlon, PJ; Chopra, I. Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action of the Pyrrothine Holomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001, 45, 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa, H; Kagasaki, T; Kinoshita, T; Haruyama, H; Domon, H; Utsui, Y; Kodama, K; Takahashi, S. Thiomarinol, A New Hybrid Antimicrobial Antibiotic Produced by A Marine Bacterium. Fermentation, Isolation, Structure, and Antimicrobial Activity. J Antibiot 1993, 46, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Kenig, M; Reading, C. Holomycin and an Antibiotic (Mm-19290) Related to Tunicamycin, Metabolites of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot 1979, 32, 549–554. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, YH; Li, FC; Wang, SJ; Qin, S; Wang, QF. Intergeneric conjugation in holomycin-producing marine Streptomyces sp. strain M095. Microbiol Res 2008, 163, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Haim, Y; Thompson, FL; Thompson, CC; Cnockaert, MC; Hoste, B; Swings, J; Rosenberg, E. Vibrio coralliilyticus sp. nov., a temperature-dependent pathogen of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2003, 53, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, S; Romalde, JL; Montes, J; Barja, JL. Pathogenic bacteria isolated from disease outbreaks in shellfish hatcheries. First description of Vibrio neptunius as an oyster pathogen. Dis Aquat Org 2005, 67, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, JW-H; Vederas, JC. Drug discovery and natural products: End of an era or an endless frontier. Science 2009, 325, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Laatsch, H. Antibase; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. Available online: http://www.users.gwdg.de/~ucoc/laatschAntibase.htm accessed on 1 November 2010.
- Lang, G; Mayhudin, NA; Mitova, MI; Sun, L; van der Sar, S; Blunt, JW; Cole, ALJ; Ellis, G; Laatsch, H; Munro, MHG. Evolving trends in the dereplication of natural product extracts: New methodology for rapid, small-scale investigation of natural product extracts. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Kind, T; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic database annotations via query of elemental compositions: Mass accuracy is insufficient even at less than 1 ppm. BMC Bioinformatics 2006, 7, 234. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm, M; Bergh, I; Riaza, A; Nielsen, J; Melchiorsen, J; Jensen, S; Duncan, H; Ahrens, P; Birkbeck, H; Gram, L. Selection and Identification of Autochthonous Potential Probiotic Bacteria from Turbot Larvae (Scophthalmus maximus) Rearing Units. Syst Appl Microbiol 2004, 27, 360–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ostling, J; Goodman, A; Kjelleberg, S. Behaviour of IncP-1 plasmids and a miniMu transposon in a marine Vibrio sp.: Isolation of starvation inducible lac operon fusions. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1991, 86, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors, licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).