Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Assessment of Marine Cyanobacteria - Synechocystis and Synechococcus
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
Cyanobacteria biomass
| Strain designation | Genera | Strain | Genera |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEANCYA 1 | Synechocystis sp. | LEANCYA 16 | Synechococcus sp. |
| LEANCYA 5 | Synechocystis sp. | LEANCYA 17 | Synechocystis sp. |
| LEANCYA 7 | Synechococcus sp. | LEANCYA 18 | Synechococcus sp. |
| LEANCYA 10 | Synechococcus sp. | LEANCYA 19 | Synechococcus sp. |
| LEANCYA 11 | Synechococcus sp. | LEANCYA 20 | Synechocystis sp. |
| LEANCYA 13 | Synechocystis sp | LEANCYA 21 | Synechocystis sp. |
| LEANCYA 15 | Synechocystis sp. | LEANCYA 22 | Synechococcus sp. |
Extract preparation
Antimicrobial screening assay
| Bacteria strains | Gram | Temperature (ºC) | Origin of strains |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus | + | 22 | Freshwater srimp |
| Bacillus megaterium DSM 32 | + | 30 | Not specified |
| Cellulomonas uda DSM 20107 | + | 30 | Compost |
| Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. insidiosumDSM 20157 | + | 30 | Not specified |
| Micrococcus luteus ATCC 49732 | + | 37 | Clinical isolate |
| Thiobacillus thioparus DSM 505 | + | 30 | Not specified |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 49134 | + | 37 | Clinical isolate |
| Staphylococcus aureus | + | 22 | Freshwater srimp |
| Streptococcus parauberis | + | 22 | Marine fish |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | - | 22 | Freshwater fish |
| Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida | - | 22 | Freshwater fish |
| Enterobacter cloacae | - | 22 | Freshwater srimp |
| Escherichia coli B | - | 22 | Not specified |
| Halomonas aquamarina NCMB 557 | - | 22 | Seawater |
| Halomonas pacifica ATCC 27122 | - | 22 | Seawater |
| Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida | - | 22 | Marine fish |
| Proteus vulgaris | - | 22 | Freshwater srimp |
| Pseudomonas doudoroff NCMB 1965 | - | 22 | Sea water |
| Vibrio compbelli ATCC 25920 | - | 22 | Sea water |
| Vibrio harveyi | - | 22 | Marine fish |
| Vibrio natriegens ATCC 14048 | - | 22 | Salt marsh mud |
| Vibrio parahemolyticus ATCC 27969 | - | 22 | Blue crab hemolymph |
| Vibrio fluvialis ATCC 33812 | - | 22 | River water |
| Vibrio tubiashii ATCC 19106 | - | 22 | Oyster |
| Vibrio vulnificus ATCC 27562 | - | 22 | Human blood |
| Yersinia ruckeri | - | 22 | River sediment |
Cytotoxic screening assay
Results and Discussion
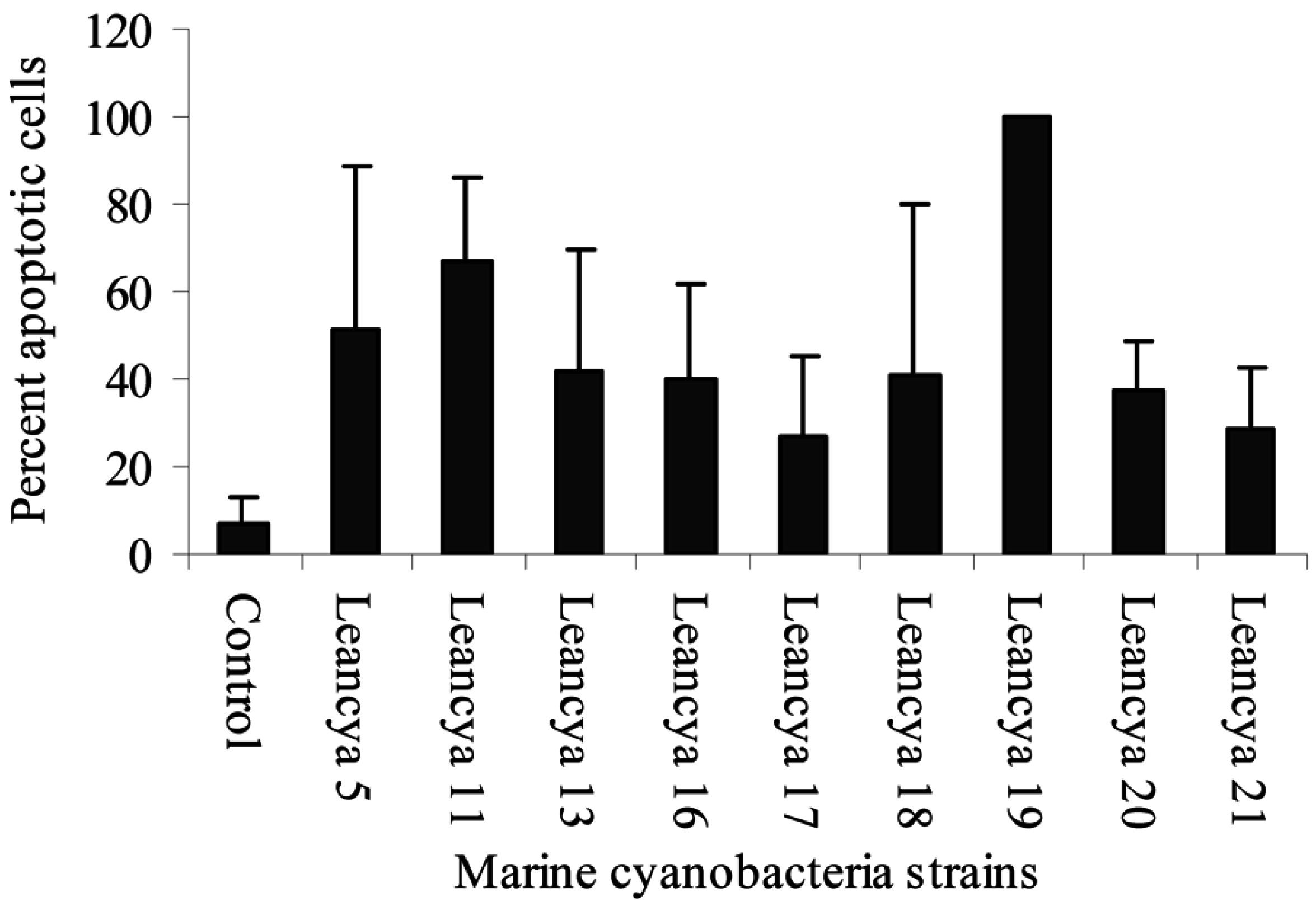
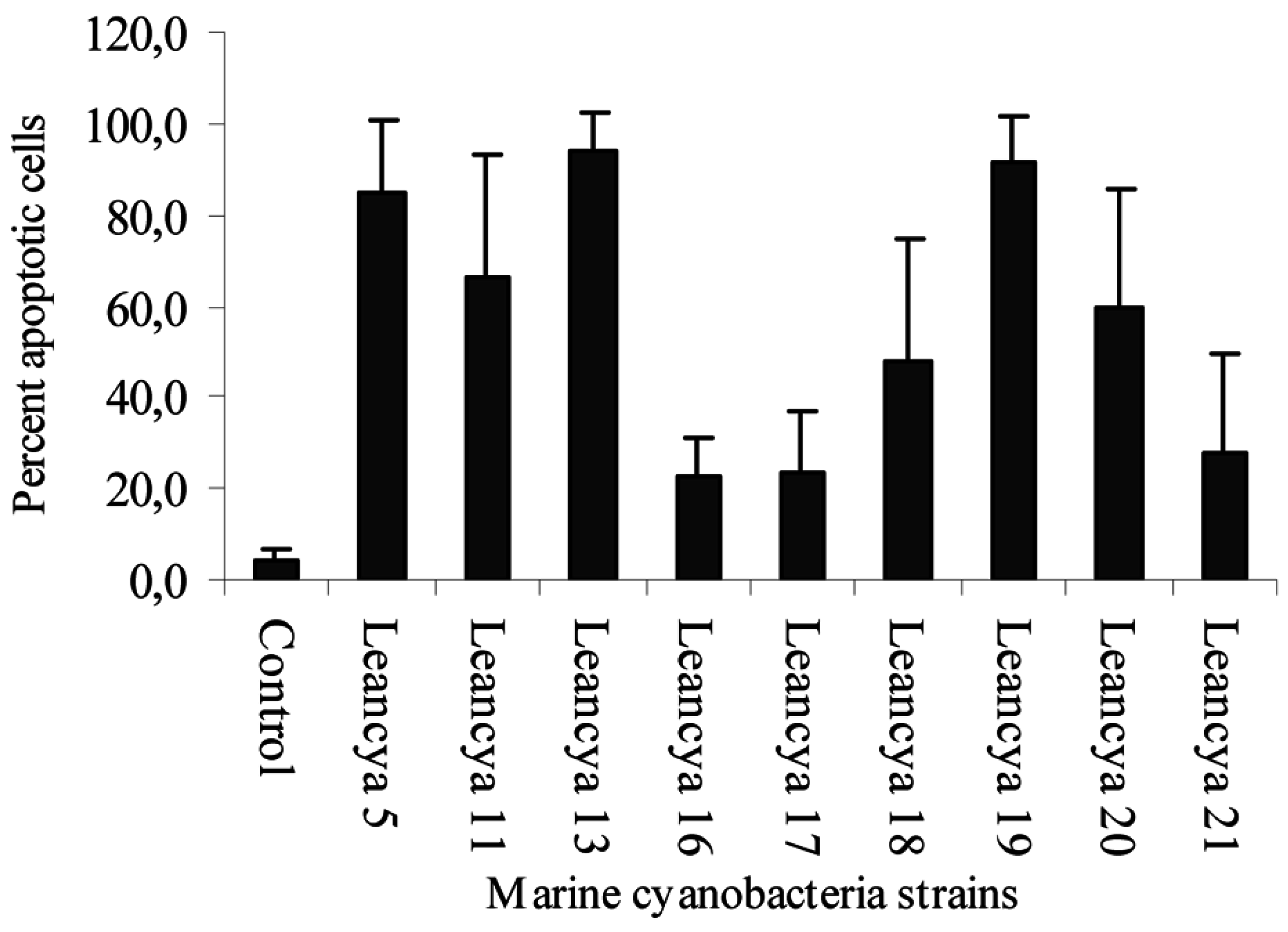

| Cyanobacteria strain | Extract | Gram-positive bacteria | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. insidiosum | Cellulomonas uda | ||
| LEANCYA 5 | Water | - | ++ |
| LEANCYA 7 | Dichloromethane | +++ | - |
| LEANCYA 10 | Methanol | - | +++ |
| Water | +++ | ++ | |
| LEANCYA 11 | Methanol | +++ | ++ |
| LEANCYA 13 | Hexane | ++ | ++ |
| Dichloromethane | ++ | ++ | |
| Methanol | ++ | - | |
| Water | ++ | ++ | |
| LEANCYA 16 | Dichloromethane | +++ | ++ |
| LEANCYA 19 | Hexane | +++ | +++ |
| Dichloromethane | ++ | ++ | |
| Methanol | ++ | ++ | |
| Water | - | +++ | |
| LEANCYA 20 | Hexane | +++ | - |
| Dichloromethane | +++ | - | |
| Water | +++ | - | |
| LEANCYA 22 | Hexane | - | +++ |
| Dichloromethane | - | ++ | |
Acknowledgments
References
- Sponga, F.; Cavaletti, L.; Lazzarini, A.; Borghi, A.; Ciciliato, I.; Losi, D.; Marinelli, F. Biodiversity of potentials of marine-derived microorganisms. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 70, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulberg, O.M. Microalgae as a source of bioactive molecules – experience from cyanophyte research. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, N.; Piccardi, R.; Margheri, M.C.; Rodolfi, L.; Smith, G.D.; Tredici, M.R. Evaluation of Nostoc strain ATCC 53789 as a potential source of natural pesticides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Philippis, R.; Vincenzini, M. Exocellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 22, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, S.; Kreitlow, S.; Nowotny, A.; Effmert, U. Biochemical and pharmacological investigations of selected cyanobacteria. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2001, 203, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.S.V.R. Antimicrobial activity of cyanobacteria. I. J. Mar. Scien. 1994, 23, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, C.M.; Nho, C.W.; Howard, W.; Holton, B. The cyanobacterial toxin, Microcystin-LR, can induce apoptosis in a variety of cell types. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1981–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, A.A. Antibiotic production by the cyanobacteria Oscillatoria angustissima and Calothrix parietina. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1999, 8, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushparaj, B.; Pelosi, E.; Jüttner, F. Toxicological analysis of the marine cyanobacterium Nodularia harveyana. J. Appl. Phycol. 1999, 10, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, I.; Doan, N.T.; Chazal, N.; Smith, G.D. Antibiotic activity of new cyanobacterial isolates from Australia and Asia against green algae and cyanobacteria. J. Appl. Phycol. 1999, 10, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, D.J.; Krylov, V.S. Anti-HIV activity of extracts and compounds from algae and cyanobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 45, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suikkanen, S.; Fistarol, G.O.; Granéli, E. Allelopathic effects of the Baltic Cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and Anabaena lemmermannii on algal monocultures. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 308, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotai, J. Instructions for preparation of modified nutrient solution Z8 for algae; Norwegian Institute for Water Research, B-11769, Blindern, Oslo, 1972.
- Kreitlow, S.; Mundt, S.; Lindequist, U. Cyanobacteria - a potential source of new biologically active substances. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 70, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mellgren, G.; Vintermyr, O.; Døskeland, S.O. Okadaic acid, cAMP, and selected nutrients inhibit hepatocyte proliferation at different stages in G1: modulation of the cAMP effect by phosphatase inhibitors and nutrients. J. Cell Physiol. 1995, 163, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Proteau, P.J.; Nagle, D.G.; Hamel, E.; Blokhin, A.; Slate, D.L. Structure of curacin A, a novel antimitotic, antiproliferative, and brine shrimp toxic natural product from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 1243–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Gustafson, K.R. Marine pharmacology in 2000: antitumor and cytotoxic compounds. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y. Microalgal metabolites. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fladmark, K.E.; Serres, M.H.; Larsen, N.L.; Yasumoto, T.; Aune, T.; Døskeland, S.O. Sensitive detection of apoptogenic toxins in suspension cultures of rat and salmon hepatocytes. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humpage, A.R.; Falconer, I.R. Microcystin-LR and liver tumor promotion: effects on cytokinesis, ploidy, and apoptosis in cultured hepatocytes. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankiewicz, J.; Tarczynska, M.; Fladmark, K.E.; Døskeland, S.O.; Walter, Z.; Zalewski, M. Apoptotic effects of cyanobacterial extract on rat hepatocytes and human lymphocytes. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bironaite, D.; Siegel, D.; Moran, J.L.; Weksler, B.B.; Ross, D. Stimulation of endothelial IL-8 (eIL-8) production and apoptosis by phenolic metabolites of benzene in HL-60 cells and human bone marrow endothelial cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2004, 149, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncet, J. The dolastatins, a family of promising antineoplastic agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 1999, 5, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha, A.B.; Lopes, R.; Schwartsmann, G. Natural products in anticancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2001, 1, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Østensvik, Ø.; Skulberg, O.M.; Underdal, B.; Hormazabal, V. Antibacterial properties of extracts from selected planktonic freshwater cyanobacteria – a comparative study of bacterial bioassays. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.A.; Al-Zazawi, M.; Alderson, G. Permeabilising effects of sub-inhibitory concentrations of microcystin on the growth of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 230, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.E.; Patterson, G.M.L.; Carmichael, W.W. New pharmaceuticals from cultured blue-green algae. In Biomedical importance of marine organisms; Fautin, D.G., Ed.; Mem. Cal. Acad. Sci., 1988; Volume 13, pp. 143-150.
Share and Cite
Martins, R.F.; Ramos, M.F.; Herfindal, L.; Sousa, J.A.; Skærven, K.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Assessment of Marine Cyanobacteria - Synechocystis and Synechococcus. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6010001
Martins RF, Ramos MF, Herfindal L, Sousa JA, Skærven K, Vasconcelos VM. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Assessment of Marine Cyanobacteria - Synechocystis and Synechococcus. Marine Drugs. 2008; 6(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Rosário F., Miguel F. Ramos, Lars Herfindal, José A. Sousa, Kaja Skærven, and Vitor M. Vasconcelos. 2008. "Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Assessment of Marine Cyanobacteria - Synechocystis and Synechococcus" Marine Drugs 6, no. 1: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6010001
APA StyleMartins, R. F., Ramos, M. F., Herfindal, L., Sousa, J. A., Skærven, K., & Vasconcelos, V. M. (2008). Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Assessment of Marine Cyanobacteria - Synechocystis and Synechococcus. Marine Drugs, 6(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/md6010001





