Luteophanol D, New Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp.
Abstract
:Introduction
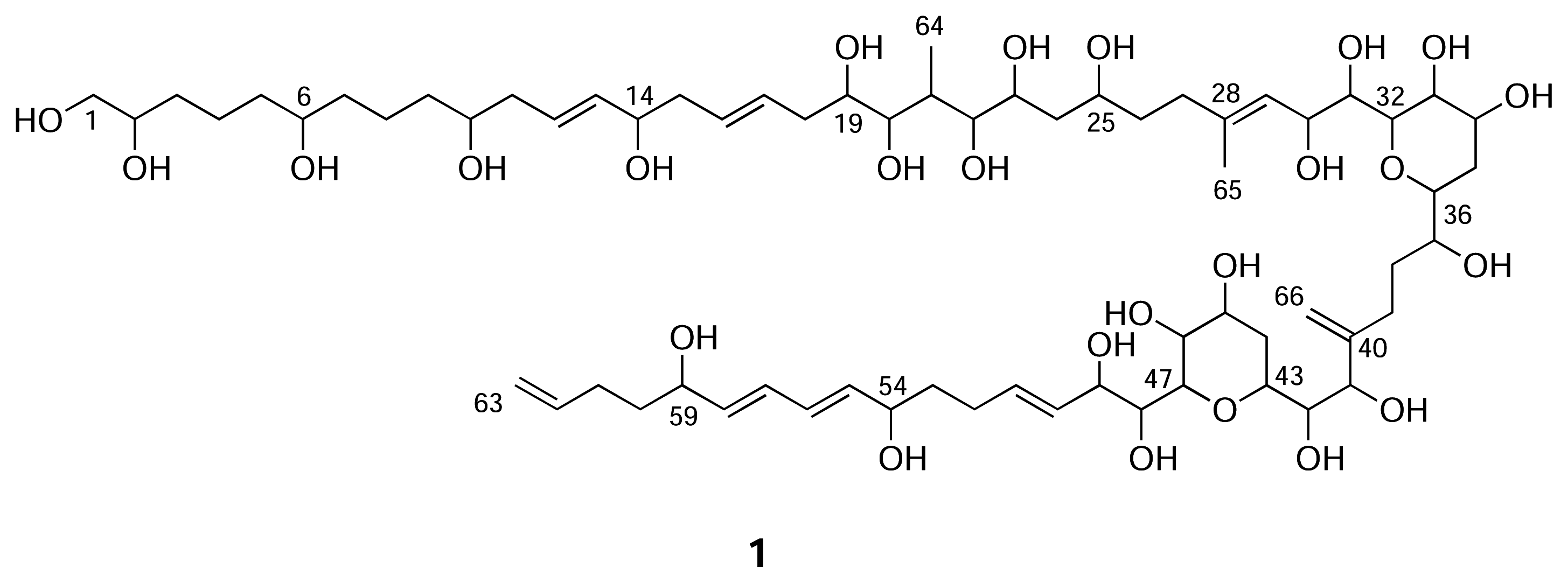
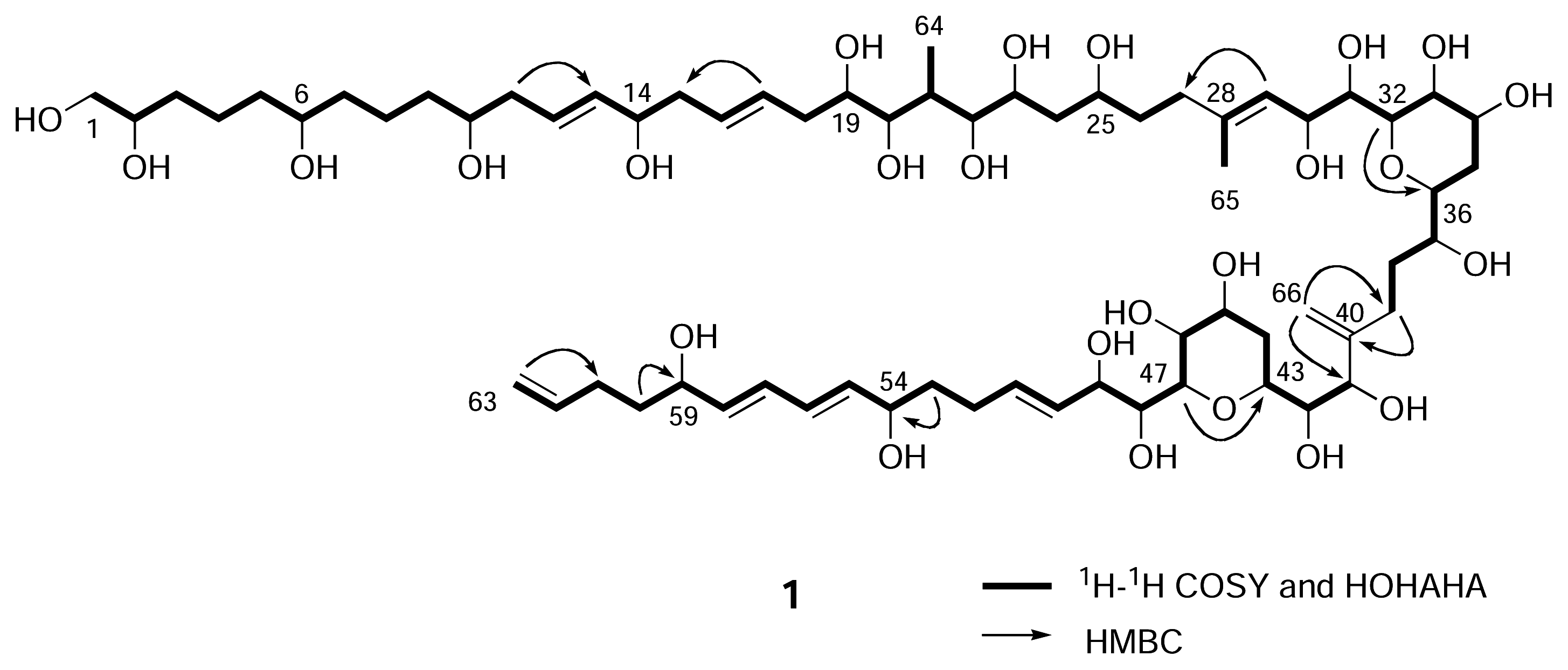
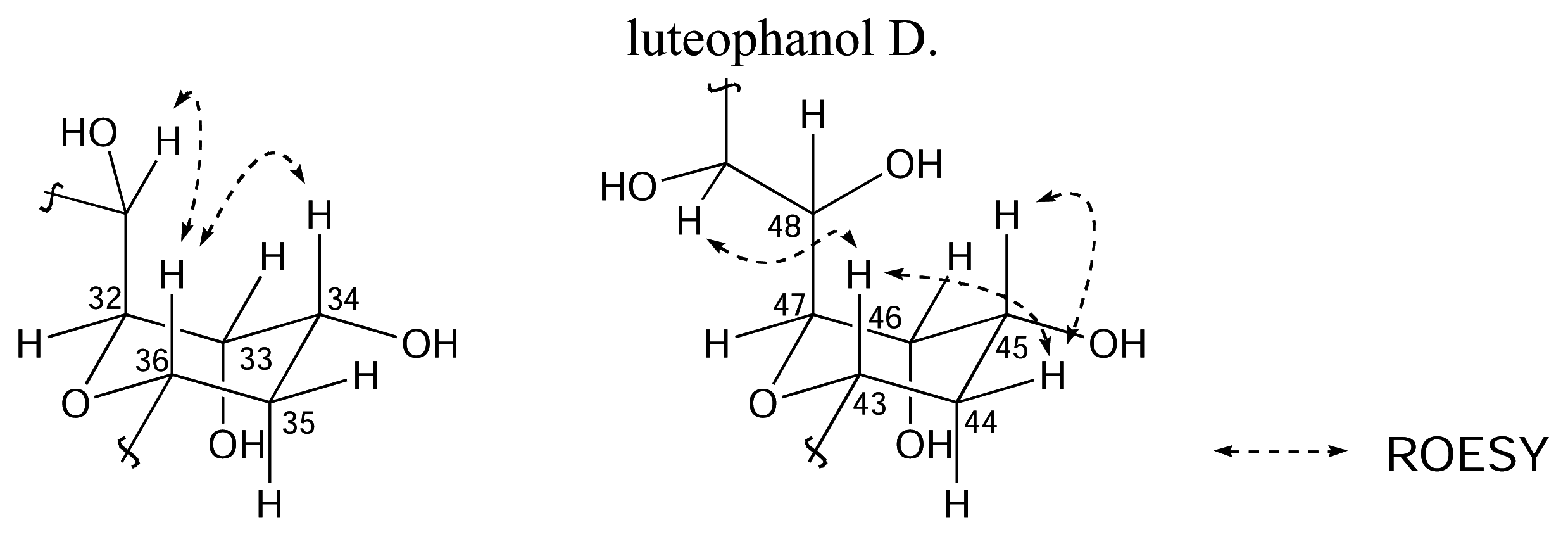
Results and Discussion
Experimental
General
Cultivation and Isolation
Acknowledgments
- Sample availability: Not available.
Reference and Notes
- Kobayashi, J.; Tsuda, M. Amphidinolides, bioactive macrolides from symbiotic marine dinoflagellates. Nat. Prod. Rep 2004, 21, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamichi, H.; Kosaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, J. Luteophanol A, a New Polyhydroxyl Compound from Symbiotic Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem 1997, 62, 3820–3823. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Doi, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Nakamichi, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Kobayashi, J. Luteophanols B and C, New Polyhydroxyl Compounds from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 14455–14464. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Fujta, T.; Naoki, H. Amphidinol, a Polyhydroxypolyene Antifungal Agent with an Unprecedented Structure, from a Marine Dinoflagellate, Amphidnium klebsii. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1991, 113, 9851–9861. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G. K.; Matsumori, N.; Murata, M.; Tachibana, K. Isolation and Chemical Structure of Amphidinol 2, a Potent Hemolytic Compound from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium klebsii. Tetrahedron Lett 1995, 36, 6279–6282. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G. K.; Matsumori, N.; Konoki, K.; Murata, M.; Tachibana, K. Chemical Structures of Amphidinols 5 and 6 Isolated from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium klebsii and Their Cholesterol-dependent Membrane Disruption. J. Mar. Biotechnol 1997, 5, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Echigoya, R.; Rhodes, L.; Oshima, Y.; Satake, M. The Structures of Five New Antifungal and Hemolytic Amphidinol Analogs from Amphidinium carterae Collected in New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, N.; Matsuoka, S.; Houdai, T.; Matsumori, N.; Adachi, S.; Murata, M.; Iwashita, T.; Fujita, T. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of a New Amphidinol with a Truncated Polyhydroxyl Chain from Amphidinium klebsii. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 8606–8610. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, D.; Guo, Y.; Wu, H.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Lin, Y. Lingshuiol, a Novel Polyhydroxyl Compound with Strongly Cytotoxic Activity from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett 2004, 14, 3117–3120. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, D.; Guo, Y.; Wu, H.; Trivellone, E.; Cimino, G. Lingshuiols A and B, Two New Polyhydroxy Compounds from the Chinese Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett 2004, 45, 5501–5504. [Google Scholar]
- Houdai, T.; Matsuoka, S; Murata, M.; Satake, M.; Ota, S.; Oshima, Y.; Rhodes, L. L. Acetate labeling Patterns of Dinoflagellate polyketides, Amphidinols 2, 3 and 4. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 5551–5555. [Google Scholar]
© 2005 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Kubota, T.; Takahashi, A.; Tsuda, M.; Kobayashi, J. Luteophanol D, New Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Mar. Drugs 2005, 3, 113-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/md304113
Kubota T, Takahashi A, Tsuda M, Kobayashi J. Luteophanol D, New Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Marine Drugs. 2005; 3(4):113-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/md304113
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubota, Takaaki, Ayako Takahashi, Masashi Tsuda, and Jun\'ichi Kobayashi. 2005. "Luteophanol D, New Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp." Marine Drugs 3, no. 4: 113-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/md304113
APA StyleKubota, T., Takahashi, A., Tsuda, M., & Kobayashi, J. (2005). Luteophanol D, New Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Marine Drugs, 3(4), 113-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/md304113



