Abstract
A new oxazole-containing proteasome inhibitor, secomycalolide A, together with known mycalolide A and 30-hydroxymycalolide A, was isolated from a marine sponge of the genus Mycale. They showed proteasome inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 11–45 μg/mL.
Introduction
Mycalolides have been isolated from marine sponges of the genus of Mycale [–] and the hard coral Tubastrea faulkneri [], and their structures are elucidated to be macrocyclic lactones characterized with an unusual tris-oxazole moiety and N-methylformyl terminus. So far, kabiramides [], ulapualides [], halichondramides [], and jaspamides [] are known as structurally related metabolites. Mycalolides A–C exhibited significant cytotoxicity against B-16 melanoma cells [] and potent actin depolymerizing activity []. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway plays a major role in selective protein degradation and regulates various cellular events including cell growth and apoptosis [–]. Ubiquitin, composed of 76 amino acids, attaches to a target protein prior to degradation. The polyubiquitin chains are recognized by the 26S proteasome, an intracellular high-molecular mass protease subunit complex, and the protein portion is degraded by the proteolytic active sites in a cavity in the 26S proteasome [, ]. Several proteasome inhibitors show anti-tumor activity against various tumor cells that are resistant to conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Proteasome inhibitors have been reported to inhibit the degradation of Iκ-B followed by suppression of NF-κB transcriptional activity to induce apoptosis []. To date, synthetic peptides, such as MG132 [] and PS-341 (bortezomib, Velcade®) [], and natural products, including lactacystin [–], epoxomycin [, ], and salinosporamide A [], have been reported to inhibit proteasome activity. Among them, PS-341 has been recently approved by FDA for multiple myeloma treatment []. Interestingly, different classes of proteasome inhibitors can differentially affect the degradation of various proteasome substrates, resulting in diverse cellular responses []. Proteasome inhibitors are now under intensive investigation not only for anti-cancer drugs but also for drugs to treat inflammatory and immune deficiency diseases []. In the course of our search for inhibitors against the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, we succeeded in isolating new agosterol derivatives [] and a pyrone derivative named himeic acid A [] as proteasome inhibitors and a ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) inhibitor, respectively. In addition, we found that girolline, an anti-cancer compound, is the first agent inhibiting the recruitment of polyubiquitinated p53 to the proteasome []. In this paper, we describe the isolation, structure elucidation, and proteasome inhibitory activity of three mycalolides.
Results and Discussion
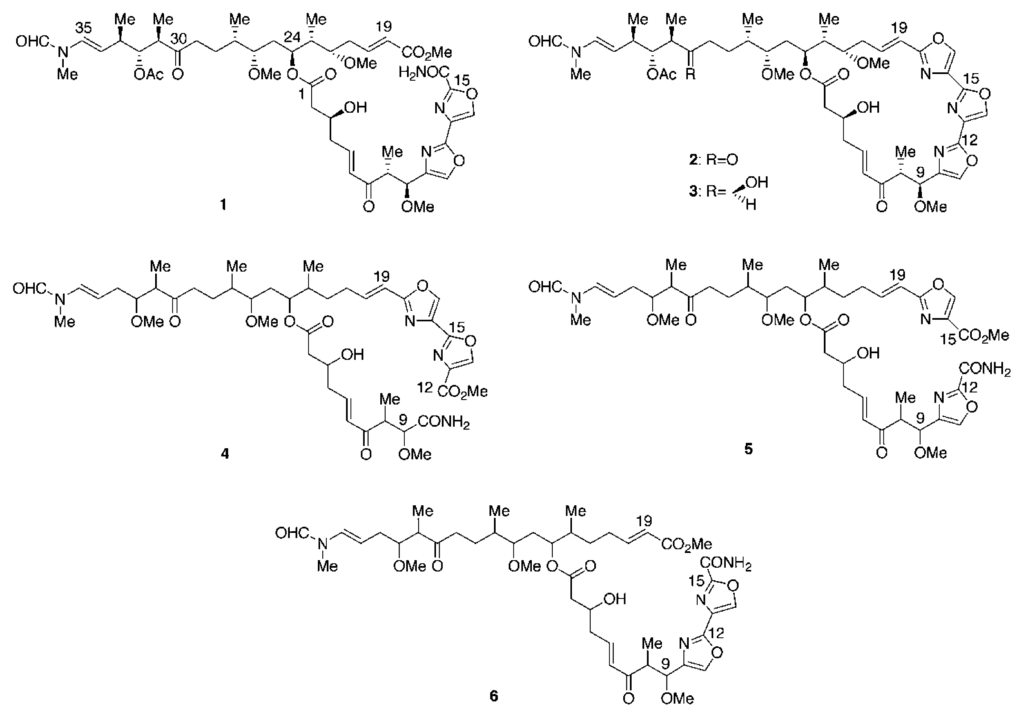
The MeOH extract of a sponge collected from shallow waters off Sugashima Island 130 km southeast of Osaka was subjected to solvent partitioning between EtOAc and water. The active EtOAc fraction was further partitioned between n-hexane and 90% MeOH/H2O, and the latter fraction was purified by ODS chromatography and ODS HPLC to afford a new mycalolide derivative, secomycalolide A (1) together with known mycalolide A (2) [] and 30-hydroxymycalolide A (3) [].
The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 (Table 1) showed two low-field heteroaromatic protons (δ 7.77 and 8.50), a pair of formamides for the major and minor rotational isomers (δ 8.30 and 8.08, intensity 5:3), three E-olefines (δ 5.98/6.84, 6.25/7.00, and 6.50/4.97), six oxygene-bearing protones δ 2.99, 3.58, 4.22, 4.34, 5.16, and 5.22), four O-methyls (δ 3.19, 3.30, 3.45, and 4.05), a pair of N-methyls (δ 3.03 and 3.08), an acetoxy methyl (δ 2.01), and five doublet methyls (δ 0.84, 0.93, 0.94, 1.05, and 1.07). These data readily suggested that 1 was a congener of mycalolide A (2). Comparison of the 1H NMR spectrum of 1 with that of 2 showed the absence of an oxazole proton in the region of δ 7.5–8.6 instead of the presence of an additional O-methyl at δ 4.05. These data indicated that 1 was a seco-oxazole derivative of 2, which was supported by the molecular formula of 1, C47H68N4O16 established by HRFABMS, a H4O2 unit more than 2. So far three seco-oxazole halichondramides were isolated and are known as halishigamides C (4) and D (5) [] and halichondramide ester (6) []. By comparison of their 1H NMR data, the signals for the olefin group at δ 5.98/6.84 (H-19/H-20) in 1 were matched with those in 6 (δ 5.89/6.85). On the contrary, the olefin protons in 4 and 5 were observed at δ 6.37/6.84 (H-19/H-20) and δ 6.31/6.76 (H-19/H-20), respectively. Since H-19 in 1 and 6 corresponded to the α–position in an α,β-unsaturated methyl ester system, they revealed the up-field shift compared to those of 4 and 5, in which H-19 was bonded to an oxazole ring. Thus, the structure of 1 was defined to be a seco-oxazole derivative of mycalolide A as shown [].

Table 1.
1H NMR Data of Secomycalolide A (1) in CDCl3
The proteasome displays multicatalytic activities, e.g. chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like, and peptidylglutamyl-peptide hydrolyzing activities. Inhibitory activities of three mycalolides were tested using a chymotrypsin-like substrate, and the IC50 values of 1, 2, and 3 were found to be 11, 30, and 45 μg/mL, respectively.
Conclusion
We have isolated a new mycalolide derivative secomycalolide A (1) together with known mycalolide A (2) and 30-hydroxymycalolide A (3). They showed moderate inhibitory activities against chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. Among three mycalolides, seco-oxyazole derivative 1 showed the most potent inhibitory activity. So far, cytotoxicity [] and potent actin depolymerizing activity [] of mycalolides have been reported; however, this is the first report of proteasome inhibitory activity of mycalolides.
Experimental
General
NMR spectra were recorded on a JEOL GSX500 in CDCl3. All chemical shifts were reported with respect to the residual solvent peaks (δH 7.26). Mass spectra were measured on a JEOL SX-102 mass spectrometer. The fluorescence intensity (excitation, 360 nm; emission, 460 nm) was measured using a BIO-RAD VersaFluor Fluorometer.
Extraction and Isolation
A marine sponge of the genus Mycale was collected from shallow waters off Sugashima Island 130 km southeast of Osaka. The frozen material (4.2 kg, wet wt) was extracted with MeOH (3 L × 3). The extract was concentrated under reduced pressure and extracted with EtOAc. The EtOAc layer was partitioned between n-hexane and 90% MeOH/H2O. The aqueous MeOH fraction (2.1 g) was subjected to ODS chromatography with MeOH/H2O. The fraction (450 mg) eluted with 80% MeOH/H2O was purified by gel filtration on Sephadex LH-20 with CHCl3/MeOH (1:1) followed by ODS HPLC with 70% MeOH/H2O to afford two active fractions. The first fraction (7.8 mg) was purified by ODS HPLC with 70% CH3CN/H2O to afford mycalolide A (2, 1.51 mg, 3.6 × 10−5%, wet weight) and 30-hydroxymycalolide A (3, 0.54 mg, 1.3 × 10−5%). The second fraction (6.9 mg) was purified by ODS HPLC with 50% CH3CN/H2O to afford secomycalolide A (1, 1.45 mg, 3.5 × 10−5%).
Secomycalolide A (1): 1H NMR (CDCl3), see Table 1; FABMS m/z 967 [M + Na]+; HRFABMS m/z 967.4553 (calcd for C47H68N4O16Na, 967.4528).
Preparation of Proteasome-enriched Fraction
Proteasome used in this study was partially purified from rat liver. The liver was dissected and homogenized in ice-cold lysis buffer consisting of 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 5 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 2 mM ATP, and 10% glycerol at 4 °C for 5 min. The extract was filtered through cheese cloth, and the filtrate was immediately centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was centrifuged at 105,000 × g for 20 min, and the resultant supernatant was further centrifuged at 300,000 × g for 2 h. The precipitates thus obtained were suspended in lysis buffer containing 50% glycerol and used as the crude proteasome-enriched preparation.
Assay for Proteasome Activity
The fluorogenic substrate succinyl-leucyl-leucyl-valyl-tyrosine 4-methylcoumaryl-7-amide (MCA) (Peptide Institute, Inc., Osaka) was used as a substrate for chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. The proteasome-enriched fraction in a mixture (0.1 mL) that contained 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.8, 1 mM dithiothreitol, and 5 mM EDTA was pre-incubated with each inhibitor at 30 °C for 10 min. Then, 0.05 mM substrate was added to the mixture and the mixture was further incubated at 30 °C for 1 h. The reaction was stopped by adding 0.1 mL of 10% SDS and the fluorescence intensity owing to 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) was measured (excitation, 360 nm; emission, 460 nm). The value of IC50, the concentration required for 50% inhibition of proteasome inhibitory activity, was calculated from the data of duplicate measurements.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. H. Yokosawa of the Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University, for his valuable advice on assay for proteasome activity. Thanks are also due to Prof. H. Sawada of the Sugashima Marine Biological Laboratories of the Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, for his help in collection of the sponge. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, Culture, and Technology of Japan and the Ichiro Kanehara Foundation.
- Samples Availability: Not available.
References and Notes
- Fusetani, N.; Yasumuro, K.; Matsunaga, S.; Hashimoto, K. Mycalolides A-C, Hybrid Macrolides of Ulapualides and Halichondramide, from a Sponge of the Genus Mycale. Tetrahedron Lett 1989, 30, 2809–2812. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, S.; Sugawara, T.; Fusetani, N. New Mycalolides from the Marine Sponge Mycale magellanica and Their Interconversion. J. Nat. Prod 1998, 61, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Phuwapraisirisan, P.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R; W. M.; Fusetani, N. Isolation of a New Mycalolide from the Marine Sponge Mycale izuensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 942–943. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M. A.; Gustafson, K. R.; Cardellina, J. H., II; Boyd, M. R. Mycalolides D and E, New Cytotoxic Macrolides from a Collection of the Stony Coral Tubastrea faulkneri. J. Nat. Prod 1995, 58, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Koseki, K.; Noma, M.; Noguchi, H.; Sankawa, U. Further Kabiramides and Halichondramides, Cytotoxic Macrolides Embracing Trisoxazole, from the Hexabranchus Egg Masses. J. Org. Chem 1989, 54, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Roesener, J. A.; Scheuer, P. J. Ulapualide A and B, Extraordinary Antitumor Macrolides from Nudibranch Eggmasses. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1986, 108, 846–847. [Google Scholar]
- Kerman, M. R.; Molinski, T. F.; Faulkner, D. J. Macrocyclic Antifungal Metabolites from the Spanish Dancer Nudibranch Hexabranchus sanguineus and Sponges of the Genus Halichondria. J. Org. Chem 1988, 53, 5014–5020. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Murata, O.; Shigemori, H.; Sasaki, T. Jaspamides A-C, New Cytotoxic Macrolides from the Okinawan Sponge Jaspis sp. J. Nat. Prod 1993, 56, 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, S.; Watabe, S.; Ozaki, H.; Fusetani, N.; Karaki, H. Mycalolide B, a Novel Actin Depolymerizing Agent. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 29710–29714. [Google Scholar]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The Ubiquitin System. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar]
- Voges, D.; Zwickl, P.; Baumeister, W. The 26S Proteasome: A Molecular Machine Designed for Controlled Proteolysis. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1999, 68, 1015–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Pickart, C. M. Mechanisms Underlying Ubiquitination. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2001, 70, 503–533. [Google Scholar]
- Glickman, M. H.; Ciechanover, A. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Proteolytic Pathway: Destruction for the Sake of Construction. Physiol. Rev 2002, 82, 373–428. [Google Scholar]
- Almond, J.B.; Cohen, G.M. The Proteasome: A Novel Target for Cancer Chemotherapy. Leukemia 2002, 16, 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Rock, K.L.; Gramm, C.; Rothstein, L.; Clark, K.; Stein, R.; Dick, L.; Hwang, D.; Goldberg, A. L. Inhibitors of the Proteasome Block the Degradation of Most Cell Proteins and the Generation of Peptides Presented on MHC Class I Molecules. Cell 1994, 78, 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.; Behnke, M.; Chen, S.; Cruickshank, A. A.; Dick, L. R.; Grenier, L.; Klunder, J. M.; Ma, Y.-T.; Plamondon, L.; Stein, R. L. Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Proteasome: Dipeptidyl Boronic Acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 1998, 8, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, S.; Fujimoto, T.; Otoguro, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Moriguchi, R.; Tanaka, H.; Sasaki, Y. Lactacysitin, a Novel Microbial Metabolite, Induces Neuritogenesis of Neuroblastoma Cells. J. Antibiotics 1991, 44, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, S.; Matsuzaki, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Kosuge, K.; Furuya, T.; Fujita, S.; Nakagawa, A. Structure of Lactacystin, a New Microbial Metabolite Which Induces Differentiation of Neuroblastoma Cells. J. Antibiotics 1991, 44, 117–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fenteany, G.; Standaert, R. F.; Reichard, G. A.; Corey, E. J.; Schreiber, S. L. A β-Lactone Related to Lactacystin Induces Neurite Outgrowth in a Neuroblastoma Cell Line and Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression in a Osteosarcoma Cell Line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3358–3362. [Google Scholar]
- Hanada, M.; Sugawara, K.; Kaneta, K.; Toda, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Tomita, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Konishi, M.; Oki, T. Epoxomicin, a New Antitumor Agent of Microbial Origin. J Antibiotics 1992, 45, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Mohan, R.; Kwok, B. H. B.; Elofsson, M.; Sin, N.; Crews, C. M. Epoxomicin, a Potent and Selective Proteasome Inhibitor, Exhibits in vivo Antiinflammatory Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10403–10408. [Google Scholar]
- Feling, R. H.; Buchanan, G. O.; Mincer, T. J.; Kauffman, C. A.; Jensen, P. R.; Fenical, W. Salinosporamide A: A Highly Cytotoxic Proteasome Inhibitor from a Novel Microbial Source, a Marine Bacterium of the New Genus Salinospora. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2003, 42, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, R. C.; Bross, P. F.; Tarrell, A. T.; Pazdur, R. Velcade®: U.S. FDA Approval for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Progressing on Prior Therapy. The Oncologist 2003, 8, 508–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover, A.; Orian, A.; Schwartz, A. L. The Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteolytic Pathway: Mode of Action and Clinical Implications. J. Cell. Biochem. Suppl 2000, 34, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Tatsuno, M.; van Soest, R. W. M.; Yokosawa, H.; Ohta, T. New Polyhydroxy Sterols: Proteasome Inhibitors from a Marine Sponge Acanthodendrorilla sp. J. Nat. Prod 2003, 66, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Hirota, H.; Imachi, M.; Fujimuro, M.; Onuki, H.; Ohta, T.; Yokosawa, H. Himeic Acid A: A New Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme Inhibitor Isolated from a Marine-derived Fungus, Aspergillus sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2005, 15, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Yamashita, K.; Tane, K.; Kizu, R.; Ohta, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Kawahara, H.; Yokosawa, H. Girolline, an Antitumor Compound Isolated from a Sponge, Induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Accumulation of Polyubiquitinated p53. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2004, 27, 699–701. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Tsuda, M.; Fuse, H.; Sasaki, T.; Mikami, Y.; Halishigamides, A-D. New Cytotoxic Oxazole-Containing Metabolites from Okinawan Sponge Halichondria sp. J. Nat. Prod 1997, 60, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Since secomycalolide A (1) decomposed during storage, 13C NMR spectra could not be measured.
© 2005 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.