New Marine-Inspired Oxadiazole Derivatives for Use Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
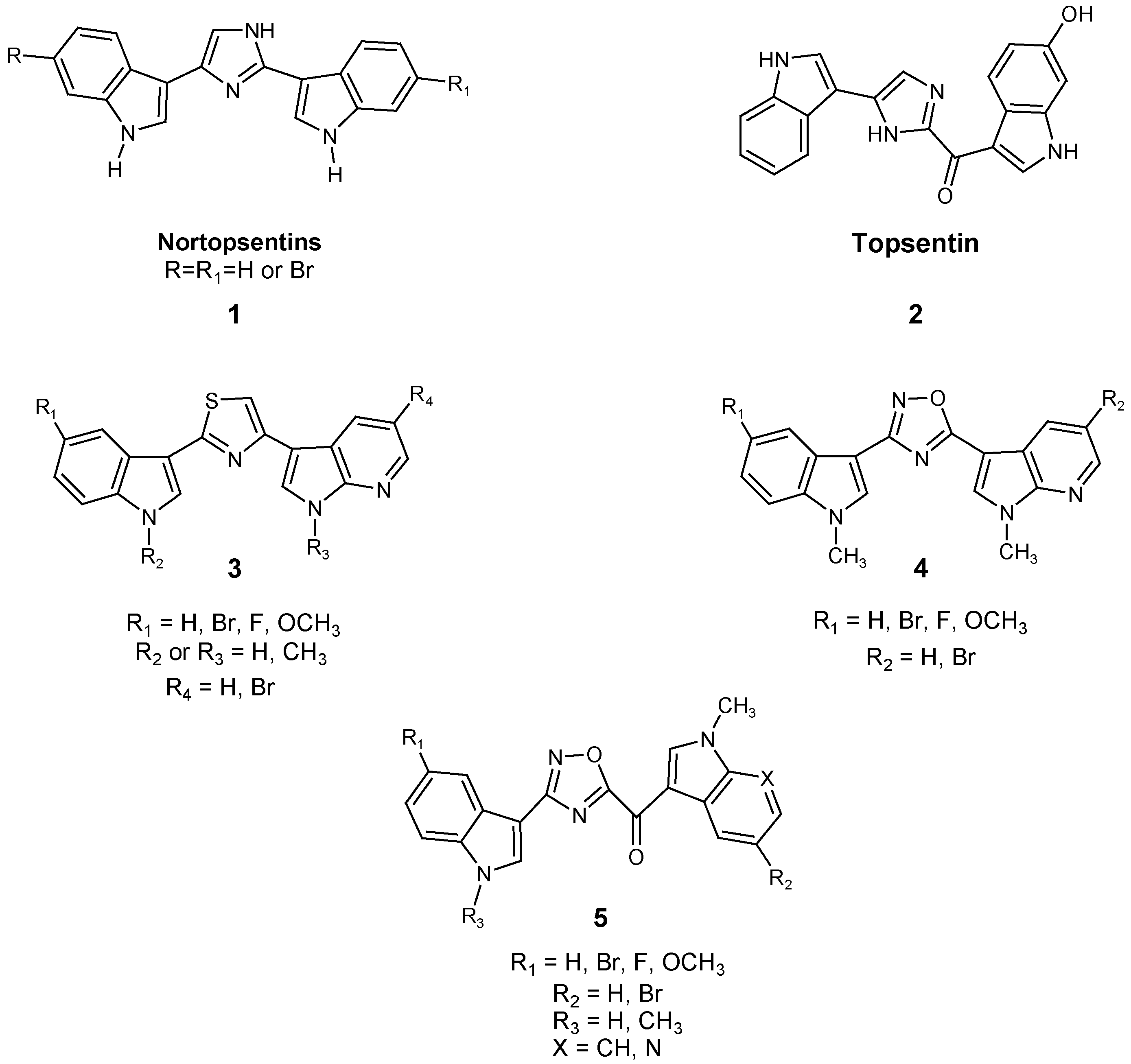
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Studies
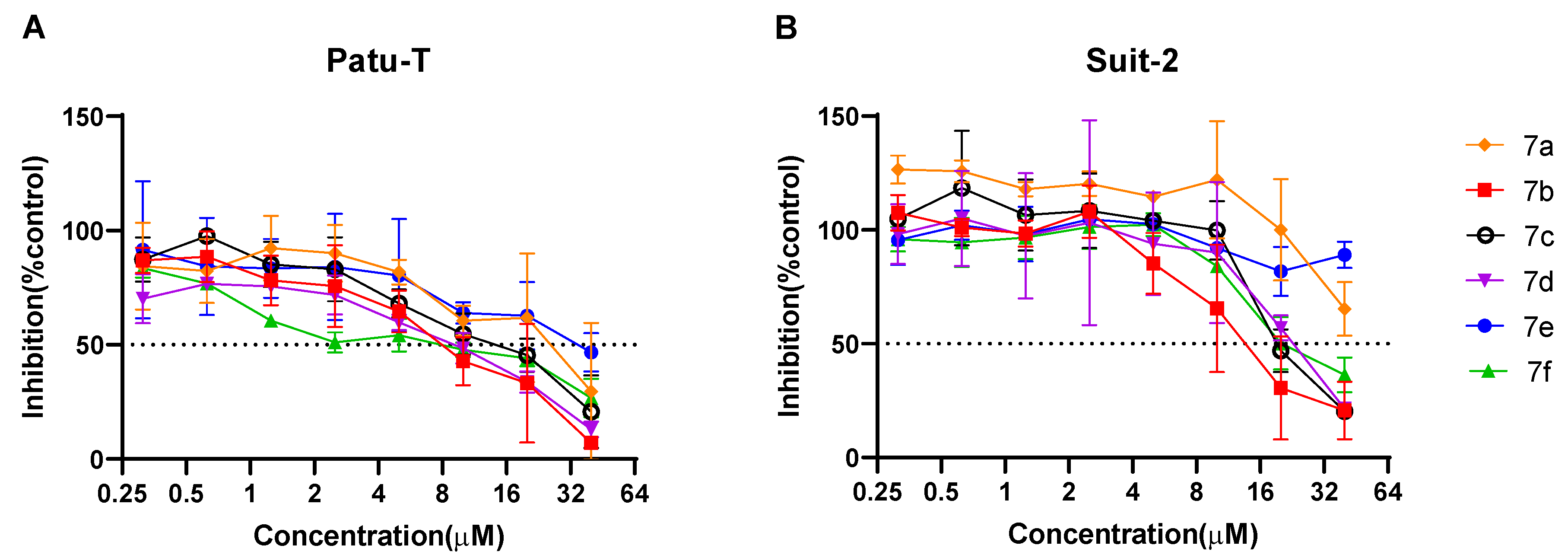
2.2.1. Antiproliferative Activity of the New 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Compounds 6a–e and 7a–h Against PDAC Cells
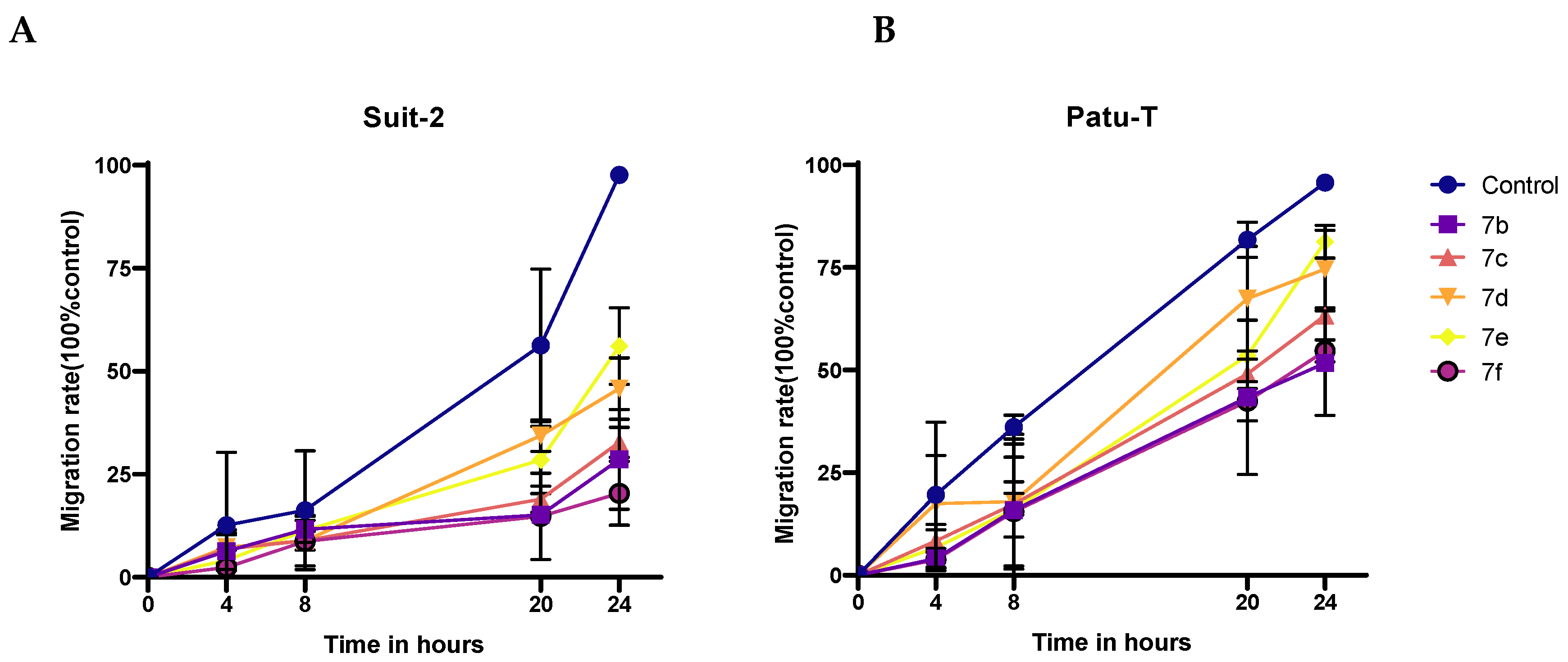
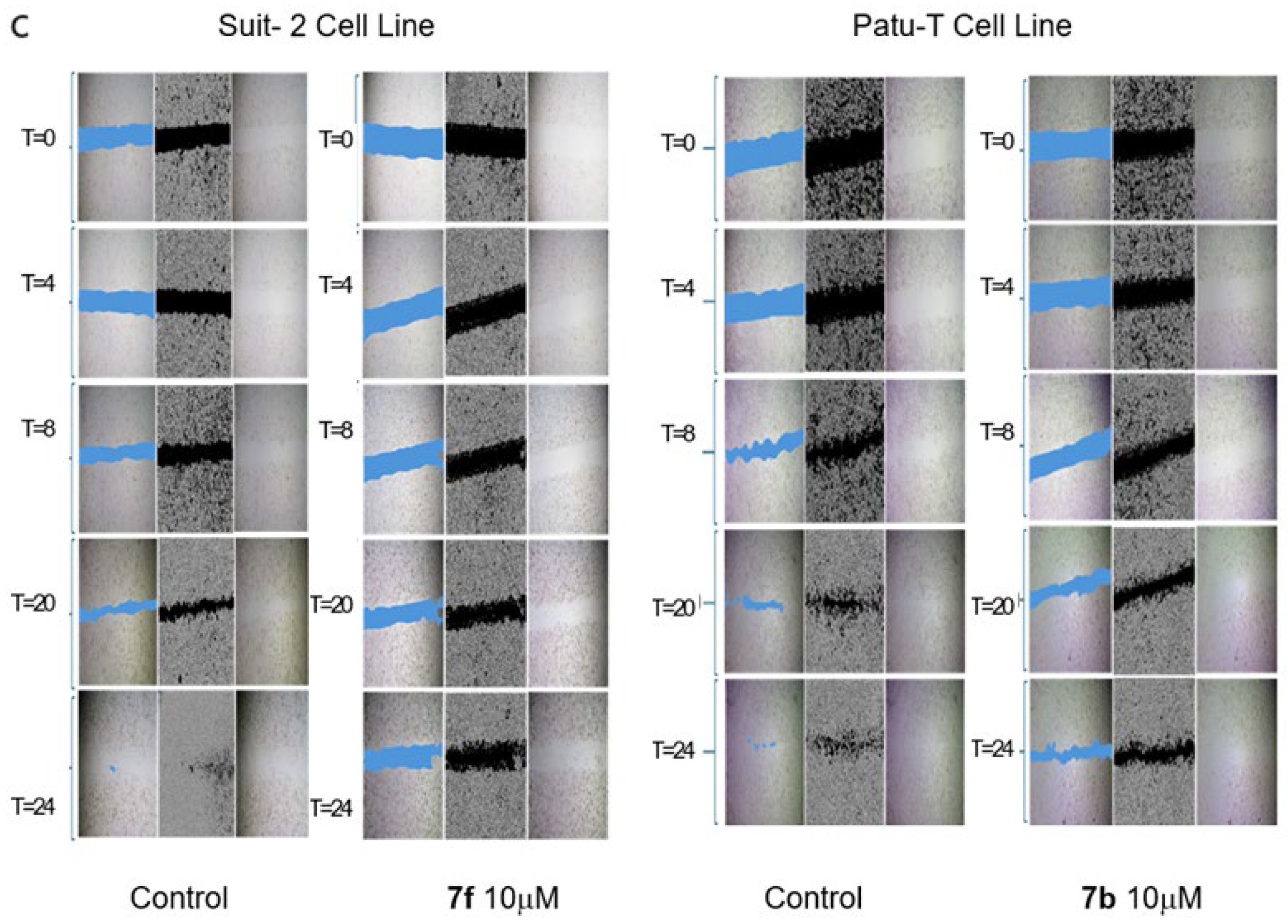
2.2.2. Antimigratory Activity
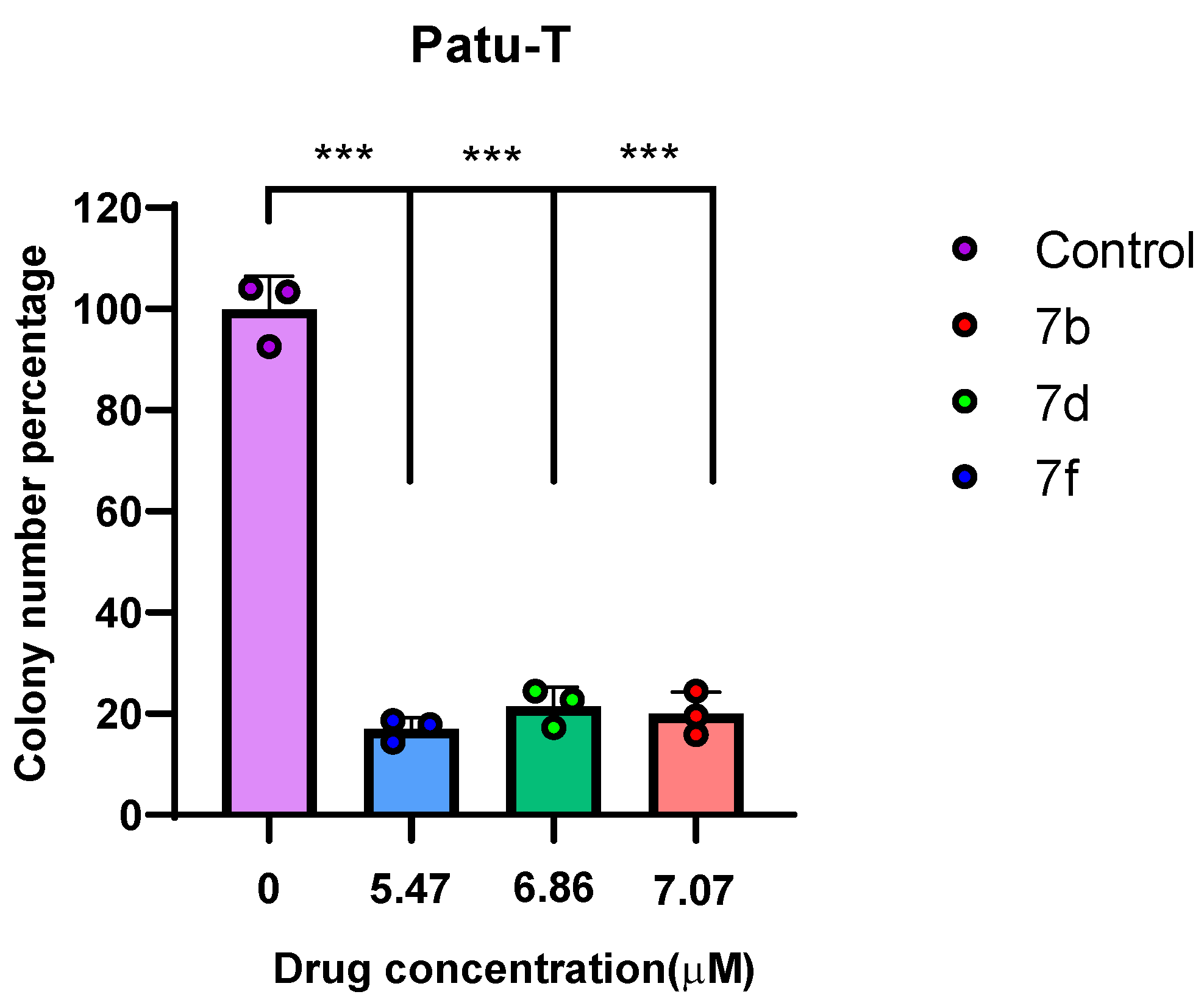
2.2.3. Clonogenic Assay
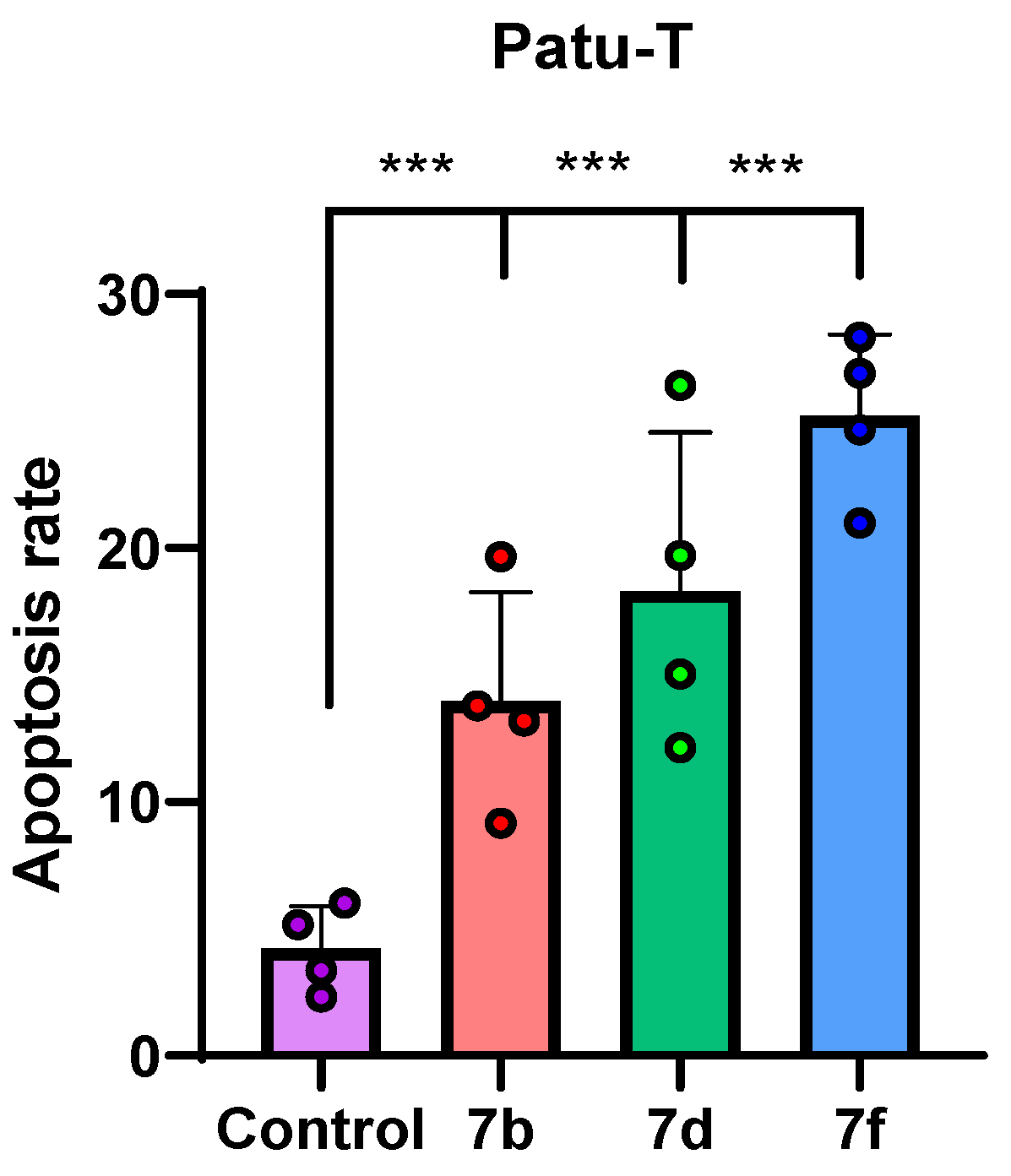
2.2.4. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
2.2.5. ADME Prediction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Thiophene-3-Carbonitrile 10
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N-Hydroxy-Thiophene-3-Carboxamidine 8
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carbonitrile 14
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1-Methyl-1H-Pyrrole-2-Carbonitrile 15
3.1.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N-Hydroxy-1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxamidine (11) or N-Hydroxy-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxamidine (12)
N-Hydroxy-1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxamidine (11)
N-Hydroxy-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxamidine (12)
3.1.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of (1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-oxo-Acetic Acids (16a–e)
(5-Chloro-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-Oxo-Acetic Acid (16e)
3.1.7. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1,2,4-Oxadiazol Based-Topsentins 6a–e and 7a–h
(5-Bromo-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(thiophen-3-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (6a)
(5-Methoxy-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(thiophen-3-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (6b)
(5-Fluoro-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(thiophen-3-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (6c)
(1-Methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(thiophen-3-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (6d)
(5-Chloro-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(thiophen-3-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (6e)
(3-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)(5-fluoro-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (7a)
(3-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)(5-bromo-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (7b)
(3-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)(5-methoxy-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (7c)
(3-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (7d)
(3-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)(5-chloro-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (7e)
(5-Fluoro-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (7f)
(1-Methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (7g)
(5-Methoxy-1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methanone (7h)
3.2. Biology
3.2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
3.2.2. Cell Culture
3.2.3. Viability Assay In Vitro
3.2.4. Wound Healing Assay
3.2.5. Clonogenic Assay
3.2.6. Apoptosis Assay
3.2.7. ADME Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| SRB | Sulforhodamine B |
| BBA | Binding buffer |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Bardeesy, N.; Kalluri, R.; Maitra, A.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2025, 39, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugazia, D.; Al-Najjar, E.; Esmail, A.; Abdelrahim, S.; Abboud, K.; Abdelrahim, A.; Umoru, G.; Rayyan, H.A.; Abudayyeh, A.; Al Moustafa, A.E.; et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: The latest on diagnosis, molecular profiling, and systemic treatments. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1386699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, C.; Konstantinidou, G. Targeted Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer: Overview of Current Treatments and New Opportunities for Personalized Oncology. Cancers 2021, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, G.; Gregori, A.; Toledo, B.; Rebelo, R.; Immordino, B.; Amrutkar, M.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Kocijancic, A.; Pandey, D.P.; Pern, M.; et al. Unravelling the complexities of resistance mechanism in pancreatic cancer: Insights from in vitro and ex-vivo model systems. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 106–107, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakkera, M.; Foote, J.B.; Farran, B.; Nagaraju, G.P. Breaking the stromal barrier in pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2024, 1879, 189065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Pfeiffer, P.; Vilgrain, V.; Lamarca, A.; Seufferlein, T.; O'Reilly, E.M.; Hackert, T.; Golan, T.; Prager, G.; Haustermans, K.; et al. Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbrook, C.J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Pasca di Magliano, M.; Maitra, A. Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Cell 2023, 186, 1729–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, J.M.; Guo, Y.; Goodyear, S.M.; Brody, J.R. Challenges and Opportunities in Targeting the Complex Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment. JCO Oncol. Adv. 2024, 1, e2400050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Castaneda, C.; Cook, S. Targeted Therapies in Pancreatic Cancer: A New Era of Precision Medicine. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Ganguly, K.; Rauth, S.; Sheree, S.S.; Khan, I.; Ganti, A.K.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Kumar, S.; Jain, M.; Batra, S.K. Unveiling the resistance to therapies in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Drug Resist. Updat. 2024, 77, 101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Heterocyclic Compounds: Importance in Anticancer Drug Discovery. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 3196–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.; De Franco, M.; Pecoraro, C.; Bassani, D.; Pavan, M.; Cascioferro, S.; Parrino, B.; Cirrincione, G.; Dall'Acqua, S.; Moro, S.; et al. Discovery of the 3-Amino-1,2,4-triazine-Based Library as Selective PDK1 Inhibitors with Therapeutic Potential in Highly Aggressive Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 24, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.; Pecoraro, C.; Panzeca, G.; Xu, G.; Roeten, M.S.F.; Cascioferro, S.; Giovannetti, E.; Diana, P.; Parrino, B. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole and 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Nortopsentin Derivatives against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Synthesis, Cytotoxic Activity, and Inhibition of CDK1. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasavin, M.; Shetnev, A.; Sharonova, T.; Baykov, S.; Kalinin, S.; Nocentini, A.; Sharoyko, V.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Presnukhina, S.; et al. Continued exploration of 1,2,4-oxadiazole periphery for carbonic anhydrase-targeting primary arene sulfonamides: Discovery of subnanomolar inhibitors of membrane-bound hCA IX isoform that selectively kill cancer cells in hypoxic environment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryzhova, E.A.; Koryakova, A.G.; Bulanova, E.A.; Mikitas, O.V.; Karapetyan, R.N.; Lavrovskii, Y.V.; Ivashchenko, A.V. Synthesis, molecular docking, and biological testing of new selective inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3β. Pharm. Chem. J. 2009, 43, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Mittal, R.K.; Sharma, V.; Kanupriya; Mishra, I. Nitrogen-fused Heterocycles: Empowering Anticancer Drug Discovery. Med. Chem. 2024, 20, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmikeshav, K.; Kumari, P.; Shankaraiah, N. Expedition of sulfur-containing heterocyclic derivatives as cytotoxic agents in medicinal chemistry: A decade update. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 513–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Venugopal, S.; Verma, A.; Sahu, S.K.; Wadhwa, P.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, A. Recent Developments in the Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Indole and Its Derivatives. Curr. Org. Synth. 2023, 20, 376–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcabrini, C.; Catanzaro, E.; Bishayee, A.; Turrini, E.; Fimognari, C. Marine Sponge Natural Products with Anticancer Potential: An Updated Review. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, C.; Terrana, F.; Panzeca, G.; Parrino, B.; Cascioferro, S.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Carbone, D. Nortopsentins as Leads from Marine Organisms for Anticancer and Anti-Inflammatory Agent Development. Molecules 2023, 28, 6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burres, N.S.; Barber, D.A.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Shen, L.L.; Clement, J.J. Antitumor activity and biochemical effects of topsentin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, D.; Vestuto, V.; Ferraro, M.R.; Ciaglia, T.; Pecoraro, C.; Sommella, E.; Cascioferro, S.; Salviati, E.; Novi, S.; Tecce, M.F.; et al. Metabolomics-assisted discovery of a new anticancer GLS-1 inhibitor chemotype from a nortopsentin-inspired library: From phenotype screening to target identification. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 234, 114233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Franco, S.; Parrino, B.; Gaggianesi, M.; Pantina, V.D.; Bianca, P.; Nicotra, A.; Mangiapane, L.R.; Lo Iacono, M.; Ganduscio, G.; Veschi, V.; et al. CHK1 inhibitor sensitizes resistant colorectal cancer stem cells to nortopsentin. iScience 2021, 24, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, C.; Parrino, B.; Cascioferro, S.; Puerta, A.; Avan, A.; Peters, G.J.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Carbone, D. A New Oxadiazole-Based Topsentin Derivative Modulates Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 Expression and Exerts Cytotoxic Effects on Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 27, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meanwell, N.A. The Influence of Bioisosteres in Drug Design: Tactical Applications to Address Developability Problems. Tactics Contemp. Drug Des. 2014, 9, 283–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, G.R.; Shaikh, M.U.; Kale, R.P.; Ghawalkar, A.R.; Gill, C.H. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activities of clubbed [1,2,4]-oxadiazoles with fluorobenzimidazoles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2009, 46, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qunies, A.M.; Spitznagel, B.D.; Du, Y.; David Weaver, C.; Emmitte, K.A. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a novel series of 1,2,4-oxadiazole inhibitors of SLACK potassium channels: Identification of in vitro tool VU0935685. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2023, 95, 117487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.M.; Rompen, I.F.; Franco, J.C.; Swett, B.; Kryschi, M.C.; Habib, J.R.; Diskin, B.; Hewitt, D.B.; Sacks, G.D.; Kaplan, B.; et al. The impact of metastatic sites on survival Rates and predictors of extended survival in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2024, 24, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockrum, P.; Dennen, S.; Brown, A.; Briggs, J.; Paluri, R. Real-world clinical outcomes and economic burden of metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A systematic review. Future Oncol. 2025, 21, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, P.P.; Gregori, A.; Bergonzini, C.; Ali, M.; Mantini, G.; Schmidt, T.; Finamore, F.; Rodrigues, S.M.F.; Frampton, A.E.; McDonnell, L.A.; et al. Differential Sensitivity to Ionizing Radiation in Gemcitabine-Resistant and Paclitaxel-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 118, 1328–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodestijn, S.C.; Miedema, D.M.; Lenos, K.J.; Nijman, L.E.; Belt, S.C.; El Makrini, K.; Lecca, M.C.; Waasdorp, C.; van den Bosch, T.; Bijlsma, M.F.; et al. Marker-free lineage tracing reveals an environment-instructed clonogenic hierarchy in pancreatic cancer. Cell Rep. 2024, 37, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, E.; Burchell, J.M.; Dazzi, F.; Sarker, D.; Beatson, R. Apoptosis in the Pancreatic Cancer Tumor Microenvironment-The Double-Edged Sword of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cells 2021, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
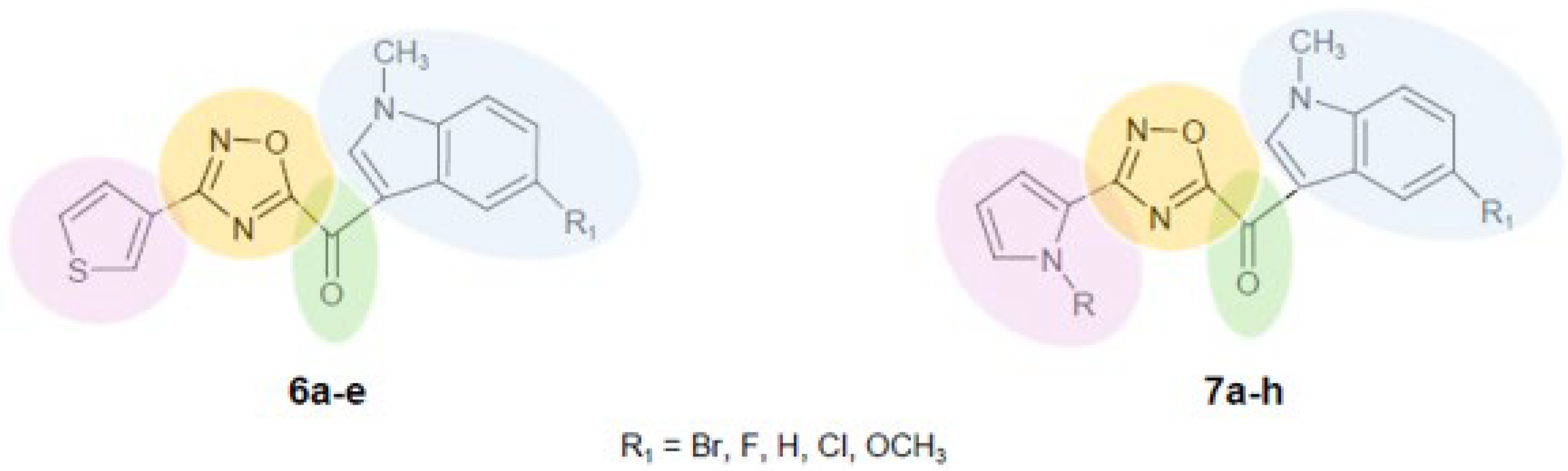
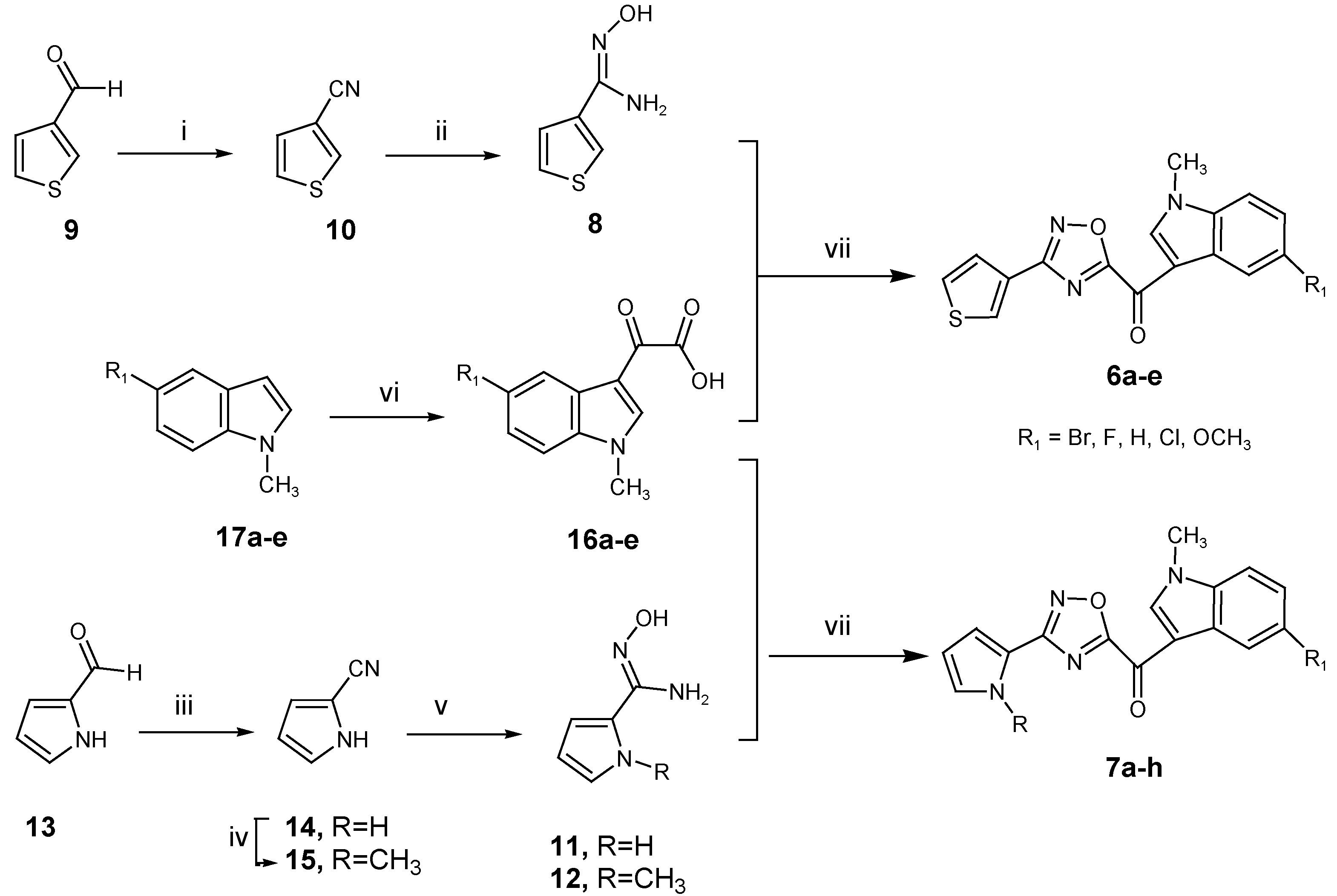

| Compound | R | R1 | Yield% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6a | - | Br | 72 |
| 6b | - | OCH3 | 82 |
| 6c | - | F | 74 |
| 6d | - | H | 81 |
| 6e | - | Cl | 80 |
| 7a | H | F | 76 |
| 7b | H | Br | 78 |
| 7c | H | OCH3 | 83 |
| 7d | H | H | 79 |
| 7e | H | Cl | 80 |
| 7f | CH3 | F | 83 |
| 7g | CH3 | H | 78 |
| 7h | CH3 | OCH3 | 84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pecoraro, C.; Carbone, D.; Al Ostoot, F.H.M.; Vahabi, M.; Lencioni, G.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Parrino, B. New Marine-Inspired Oxadiazole Derivatives for Use Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080327
Pecoraro C, Carbone D, Al Ostoot FHM, Vahabi M, Lencioni G, Diana P, Giovannetti E, Parrino B. New Marine-Inspired Oxadiazole Derivatives for Use Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(8):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080327
Chicago/Turabian StylePecoraro, Camilla, Daniela Carbone, Fares Hezam Mohammed Al Ostoot, Mahrou Vahabi, Giulia Lencioni, Patrizia Diana, Elisa Giovannetti, and Barbara Parrino. 2025. "New Marine-Inspired Oxadiazole Derivatives for Use Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Marine Drugs 23, no. 8: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080327
APA StylePecoraro, C., Carbone, D., Al Ostoot, F. H. M., Vahabi, M., Lencioni, G., Diana, P., Giovannetti, E., & Parrino, B. (2025). New Marine-Inspired Oxadiazole Derivatives for Use Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Marine Drugs, 23(8), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080327










