Potential Inhibitors of Human–Naegleria fowleri Interactions: An In Vitro Extracellular Matrix-Based Model
Abstract
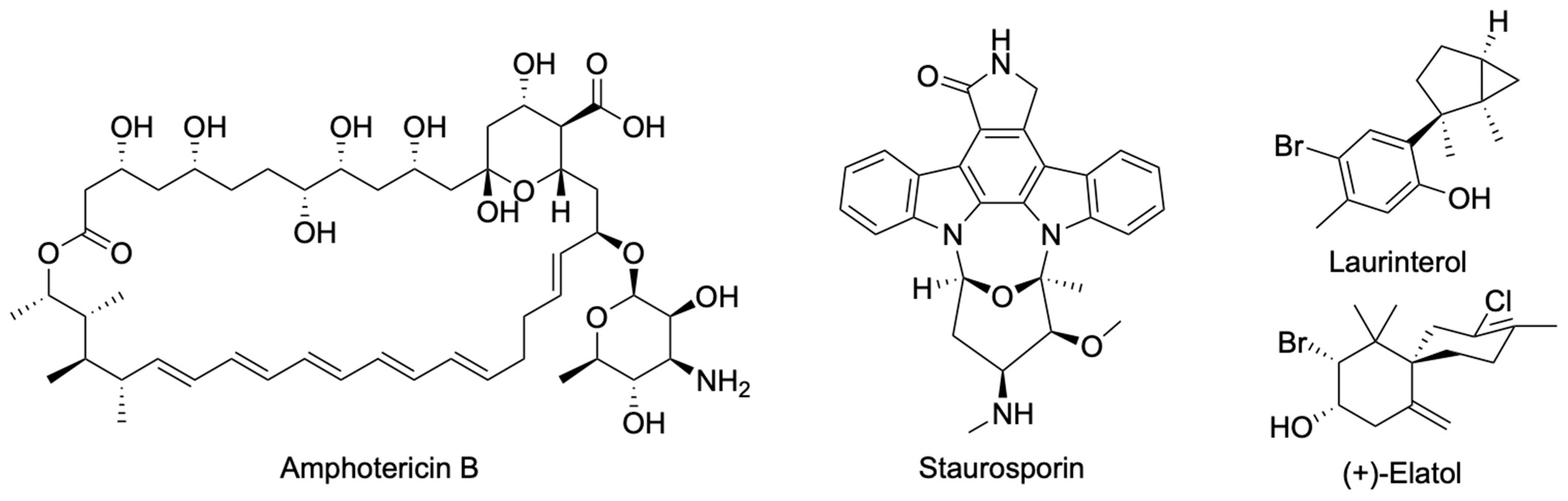
1. Introduction
2. Results
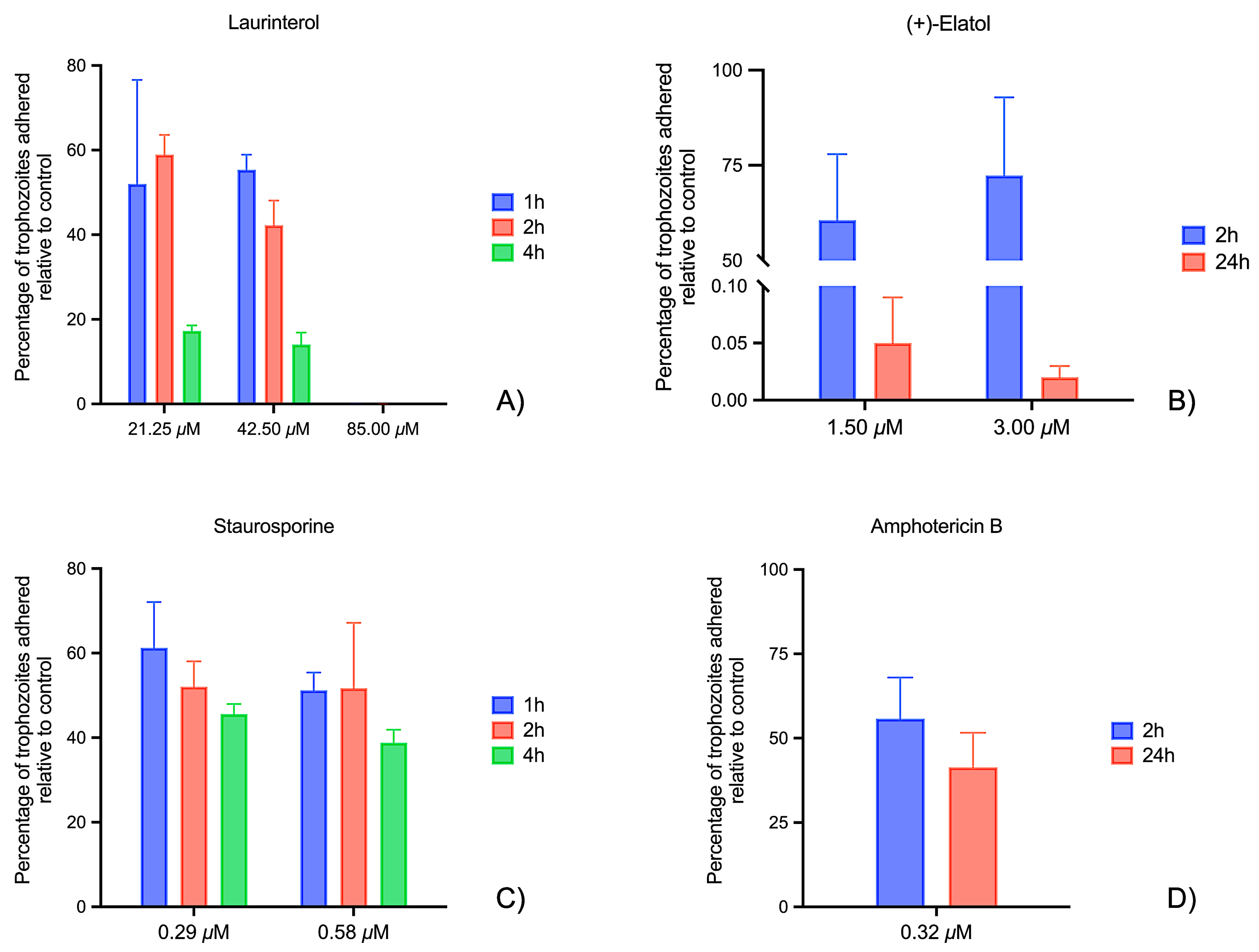
2.1. Laminin Adhesion Assays
2.2. Matrigel® Matrix Adhesion Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Laminin Adhesion Assay Procedure
4.4. ECM Adhesion Assay Procedure
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FLA | Free living amoebae |
| PAM | Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis |
| PCD | Programmed cell death |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Hu, B.; Chen, H.; Pan, J.-R.; Ruan, W.; Yao, L. Identification and Molecular Typing of Naegleria fowleri from a Patient with Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 72, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereeper, A.; Allouch, N.; Guerlais, V.; Garnier, M.; Ma, L.; De Jonckheere, J.F.; Joseph, S.J.; Ali, I.K.M.; Talarmin, A.; Marcelino, I. Naegleria Genus Pangenome Reveals New Structural and Functional Insights into the Versatility of These Free-Living Amoebae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1056418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonckheere, J.F. The Impact of Man on the Occurrence of the Pathogenic Free-Living Amoeboflagellate Naegleria fowleri. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heggie, T.W. Swimming with Death: Naegleria fowleri Infections in Recreational Waters. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2010, 8, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; Serrano-Luna, J.d.J.; García-Latorre, E.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. Characterization of Brain Inflammation during Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heggie, T.W.; Küpper, T. Surviving Naegleria fowleri Infections: A Successful Case Report and Novel Therapeutic Approach. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 16, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, E.; Asbill, S.; Virga, K. Naegleria fowleri: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6677–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Ali, I.K.M.; Cope, J.R.; Khan, N.A. Biology and Pathogenesis of Naegleria fowleri. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.-L.; Lee, H.-J.; Shin, M.; Shin, H.-J.; Im, K.-I.; Park, S.-J. The Involvement of an Integrin-like Protein and Protein Kinase C in Amoebic Adhesion to Fibronectin and Amoebic Cytotoxicity. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 94, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerson, M.; da Rocha-Azevedo, B.; Cabral, G.A.; Marciano-Cabral, F. Pathogenic Naegleria fowleri and Non-Pathogenic Naegleria Lovaniensis Exhibit Differential Adhesion to, and Invasion of, Extracellular Matrix Proteins. Microbiology 2012, 158, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekblom, P.; Lonai, P.; Talts, J.F. Expression and Biological Role of Laminin-1. Matrix Biol. 2003, 22, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Filho, F.C.; Kasai, S.; Nomizu, M.; López, L.B.; Melo-Braga, M.B.; Rocha-Azevedo, B.; Petrópolis, D.B.; Horbach, I.S. How Laminin-1 Can Be Recognized by the Protozoan Parasite Tritrichomonas Foetus: Possible Role Played by the Extracellular Matrix Glycoprotein in Both Cytoadhesion and Cytotoxicity Exerted by the Parasite. Parasitol. Int. 2002, 51, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo, G.A.; Sweeney, S.M.; Körkkö, J.; Ala-Kokko, L.; Antonio, J.D.S. Mapping the Ligand-Binding Sites and Disease-Associated Mutations on the Most Abundant Protein in the Human, Type I Collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4223–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piña-Vázquez, C.; Reyes-López, M.; Ortíz-Estrada, G.; de la Garza, M.; Serrano-Luna, J. Host-Parasite Interaction: Parasite-Derived and -Induced Proteases That Degrade Human Extracellular Matrix. J. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 2012, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W.S.; Midwood, K.S. Plasma and Cellular Fibronectin: Distinct and Independent Functions during Tissue Repair. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungroo, M.R.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R. Naegleria fowleri: Diagnosis, Treatment Options and Pathogenesis. Expert Opin. Orphan Drugs 2019, 7, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, F.Y.; Cortez, C.; Izidoro, M.A.; Juliano, L.; Yoshida, N. Fibronectin-Degrading Activity of Trypanosoma Cruzi Cysteine Proteinase Plays a Role in Host Cell Invasion. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speziale, P.; Arciola, C.R.; Pietrocola, G. Fibronectin and Its Role in Human Infective Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGwire, B.S.; Chang, K.-P.; Engman, D.M. Migration through the Extracellular Matrix by the Parasitic Protozoan Leishmania Is Enhanced by Surface Metalloprotease Gp63. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Fleury, C.; Jalalvand, F.; Riesbeck, K. Human Pathogens Utilize Host Extracellular Matrix Proteins Laminin and Collagen for Adhesion and Invasion of the Host. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 1122–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Teixeira, J.E.; Huston, C.D. Invadosome-Mediated Human Extracellular Matrix Degradation by Entamoeba Histolytica. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, 10.1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arberas-Jiménez, I.; García-Davis, S.; Rizo-Liendo, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Chiboub, O.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Piñero, J.E.; Fernández, J.J.; et al. Laurinterol from Laurencia Johnstonii Eliminates Naegleria fowleri Triggering PCD by Inhibition of ATPases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arberas-Jiménez, I.; Nocchi, N.; Chao-Pellicer, J.; Sifaoui, I.; Soares, A.R.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Fernández, J.J.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Chamigrane-Type Sesquiterpenes from Laurencia Dendroidea as Lead Compounds against Naegleria fowleri. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linam, W.M.; Ahmed, M.; Cope, J.R.; Chu, C.; Visvesvara, G.S.; da Silva, A.J.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Green, J. Successful Treatment of an Adolescent with Naegleria fowleri Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e744–e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Zepeda, J.; Gómez-Alcalá, A.V.; Vázquez-Morales, J.A.; Licea-Amaya, L.; De Jonckheere, J.F.; Lares-Villa, F. Successful Treatment of Naegleria fowleri Meningoencephalitis by Using Intravenous Amphotericin B, Fluconazole and Rifampicin. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo-Liendo, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Cartuche, L.; Arberas-Jiménez, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Piñero, J.E.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Evaluation of Indolocarbazoles from Streptomyces Sanyensis as a Novel Source of Therapeutic Agents against the Brain-Eating Amoeba Naegleria fowleri. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.; Jamerson, M.; Cabral, G.; Carlesso, A.M.; Marciano-Cabral, F. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Naegleria fowleri and Their Role in Invasion of the Central Nervous System. Microbiology 2017, 163, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.R.; Espinoza, M.F.S.; Camacho, N.C.; Cornet-Gomez, A.; Sáenz-Arce, G.; Osuna, A.; Lomonte, B.; Sandí, E.A. Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by a Clinical Isolate of Naegleria fowleri and Identification of Immunogenic Components within Their Protein Cargo. Biology 2022, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, I.K.; Jamerson, M.; Cabral, G.A.; Marciano-Cabral, F. Identification of Peptidases in Highly Pathogenic vs. Weakly Pathogenic Naegleria fowleri Amebae. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2015, 62, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Barragan, A.; Su, C.; Fux, B.; Fentress, S.J.; Tang, K.; Beatty, W.L.; Hajj, H.E.; Jerome, M.; Behnke, M.S.; et al. A Secreted Serine-Threonine Kinase Determines Virulence in the Eukaryotic Pathogen Toxoplasma Gondii. Science 2006, 314, 1776–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Zúñiga, R.; Silva-Olivares, A.; Villalba-Magdaleno, J.D.A.; Sánchez-Monroy, V.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. Amphotericin B Induces Apoptosis-like Programmed Cell Death in Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria Gruberi. Microbiology 2017, 163, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Navarro, C.M.; López-Arencibia, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Cabello-Vílchez, A.M.; Maciver, S.; Valladares, B.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. PrestoBlue® and AlamarBlue® Are Equally Useful as Agents to Determine the Viability of Acanthamoeba Trophozoites. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 145, S69–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kular, J.K.; Basu, S.; Sharma, R.I. The Extracellular Matrix: Structure, Composition, Age-Related Differences, Tools for Analysis and Applications for Tissue Engineering. J. Tissue Eng. 2014, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao-Pellicer, J.; Arberas-Jiménez, I.; Sifaoui, I.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Fernández, J.J.; Jamerson, M.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Potential Inhibitors of Human–Naegleria fowleri Interactions: An In Vitro Extracellular Matrix-Based Model. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080306
Chao-Pellicer J, Arberas-Jiménez I, Sifaoui I, Díaz-Marrero AR, Fernández JJ, Jamerson M, Piñero JE, Lorenzo-Morales J. Potential Inhibitors of Human–Naegleria fowleri Interactions: An In Vitro Extracellular Matrix-Based Model. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(8):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080306
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao-Pellicer, Javier, Iñigo Arberas-Jiménez, Ines Sifaoui, Ana R. Díaz-Marrero, José J. Fernández, Melissa Jamerson, José E. Piñero, and Jacob Lorenzo-Morales. 2025. "Potential Inhibitors of Human–Naegleria fowleri Interactions: An In Vitro Extracellular Matrix-Based Model" Marine Drugs 23, no. 8: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080306
APA StyleChao-Pellicer, J., Arberas-Jiménez, I., Sifaoui, I., Díaz-Marrero, A. R., Fernández, J. J., Jamerson, M., Piñero, J. E., & Lorenzo-Morales, J. (2025). Potential Inhibitors of Human–Naegleria fowleri Interactions: An In Vitro Extracellular Matrix-Based Model. Marine Drugs, 23(8), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080306












