Simplified, High Yielding Extraction of Xylan/Xylo-Oligosaccharides from Palmaria palmata: The Importance of the Algae Preservation Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compositional Analysis of P. palmata
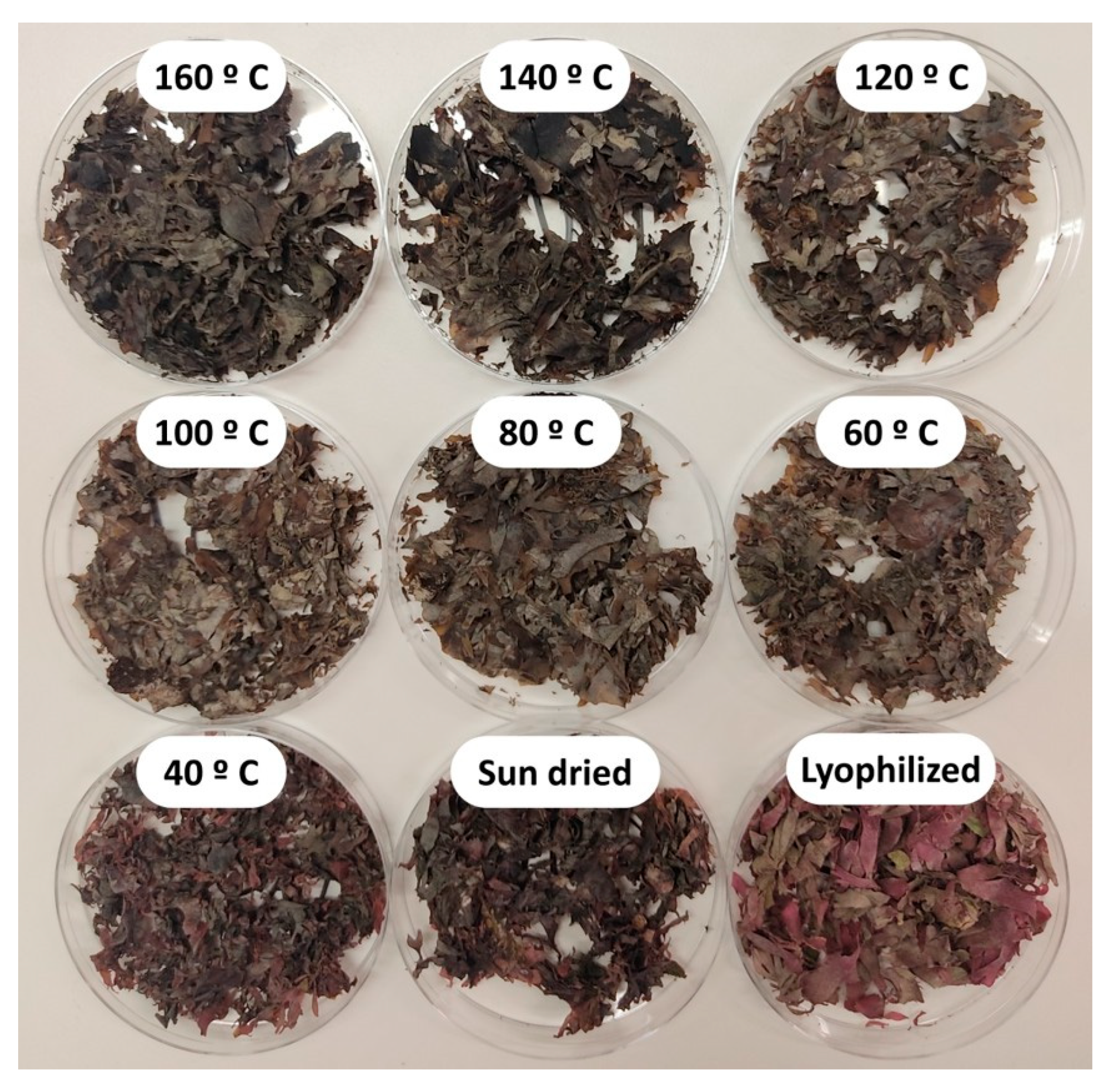
2.2. Algae Preservation: Drying
2.3. Effect of Drying Temperature on P. palmata Colour
2.4. Aqueous Extraction of Xylan
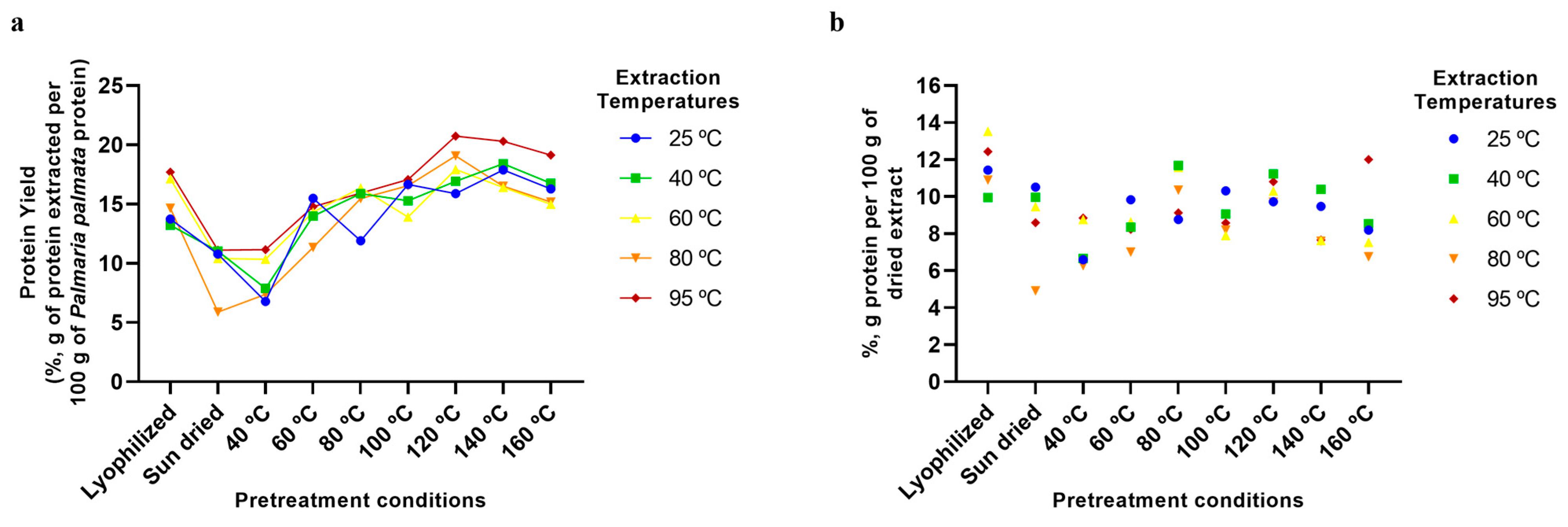
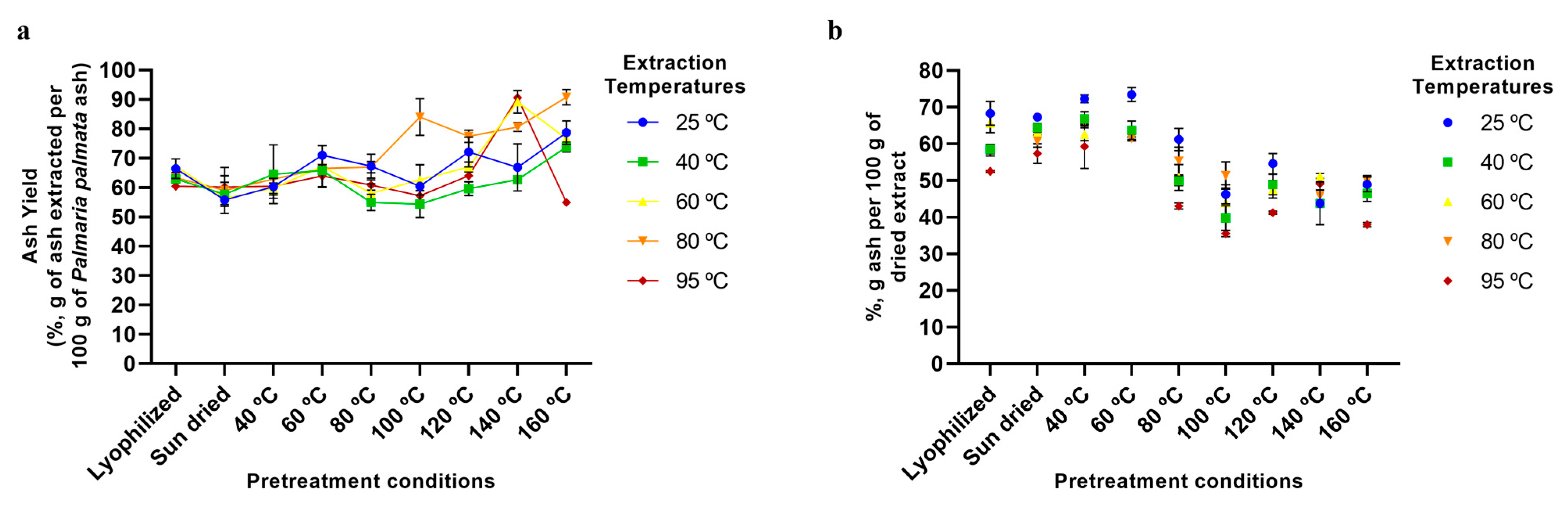
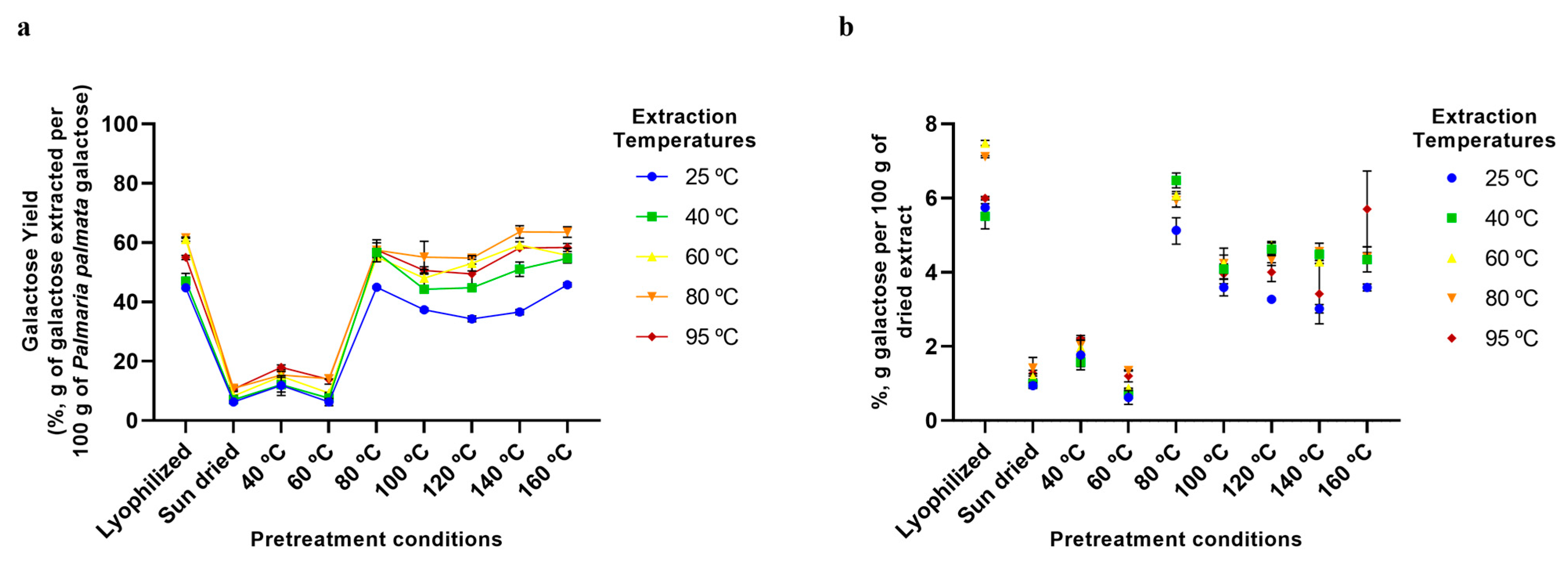
2.5. Aqueous Extraction of P. palmata Components: Protein, Ash, Galactose, and Phenolic Compounds
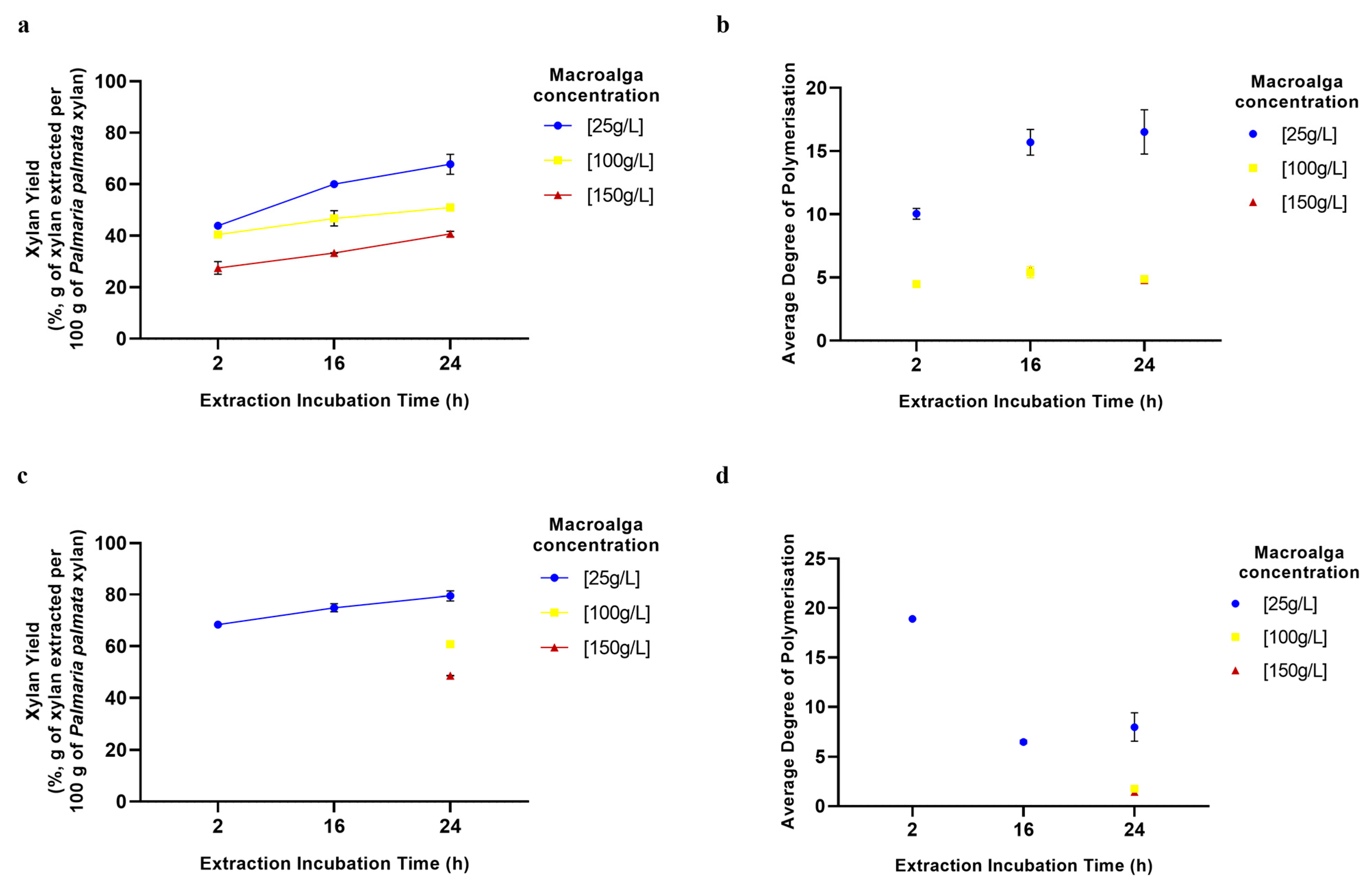
2.6. Effects of Biomass Concentration and Incubation Time on Extraction Process
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. P. palmata Biomass Preparation and Preservation Treatments
3.2. Compositional Analysis of P. palmata
3.3. Aqueous Extraction of Xylan
3.4. Compositional Analysis of the Extracts
3.5. Analysis of the Degree of Polymerisation of Xylan
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNSA | 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid |
| XOS | Xylo-oligosaccharides |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| IMTA | Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture |
| DP | Degree of Polymerisation |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| RI | Refractor Index |
| BSA | Bovin Serum Albumin |
References
- Curry, T.M.; Peña, M.J.; Urbanowicz, B.R. An Update on Xylan Structure, Biosynthesis, and Potential Commercial Applications. Cell Surf. 2023, 9, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Zhang, Z.; Stephens, E.; Dupree, P.; Turner, S.R. Characterization of IRX10 and IRX10-like Reveals an Essential Role in Glucuronoxylan Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 57, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, M.; Barroca, M.; Collins, T. Endo-1,4-β-Xylanase-Containing Glycoside Hydrolase Families: Characteristics, Singularities and Similarities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 65, 108148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.S.Y.; Harris, P.J. Xylans of Red and Green Algae: What Is Known about Their Structures and How They Are Synthesised? Polymers 2019, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Gopikrishna, K.; Nath Tiwari, O.; Bhunia, B.; Muthuraj, M. Algal Carbohydrates: Sources, Biosynthetic Pathway, Production, and Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 413, 131489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biely, P.; Singh, S.; Puchart, V. Towards Enzymatic Breakdown of Complex Plant Xylan Structures: State of the Art. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1260–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.; Gerday, C.; Feller, G. Xylanases, Xylanase Families and Extremophilic Xylanases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, D.S.; Hlangothi, S.P.; John, M.J. Bio-Based Products from Xylan: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.E.; Marcelino, H.R.; Gomes, M.C.S.; Oliveira, E.E.; Nagashima, T., Jr.; Egito, E.S.T.; da Silva, A.E.; Marcelino, H.R.; Gomes, M.C.S.; Oliveira, E.E.; et al. Xylan, a Promising Hemicellulose for Pharmaceutical Use, Products and Applications of Biopolymers. In Products and Application of Biopolymers; Verbeek, J., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, M.M.; Melrose, J. Xylan Prebiotics and the Gut Mcrobiome Promote Health and Wellbeing: Potential Novel Roles for Pentosan Polysulfate. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Pi, Y.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; de Vries, S.; Shang, L.; Tao, S.; Zhang, S.; Han, D.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Xylan Alleviates Dietary Fiber Deprivation-Induced Dysbiosis by Selectively Promoting Bifidobacterium Pseudocatenulatum in Pigs. Microbiome 2021, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, U.P.; Fleming, S.A.; Rasheed, M.S.A.; Jha, R.; Dilger, R.N. The Role of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides of Xylan and Mannan in Gut Health of Monogastric Animals. J. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 9, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, S.; Deshmukh, K.; Khan, T.; Suvarna, V. Recent Advances in Biomedical Applications of Mannans and Xylans. Curr. Drug Targets 2024, 25, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartaxo da Costa Urtiga, S.; Rodrigues Marcelino, H.; Sócrates Tabosa do Egito, E.; Eleamen Oliveira, E. Xylan in Drug Delivery: A Review of Its Engineered Structures and Biomedical Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 151, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.R.; Liang, H.; Dickinson, M.; Botchwey, E.A. Xylan Hemicellulose Improves Chitosan Hydrogel for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, J.; Rajeswari, R.; Shayanti, M.; Sridhar, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Balamurugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Xylan Polysaccharides Fabricated into Nanofibrous Substrate for Myocardial Infarction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Song, T.; Pranovich, A.; Rojas, O.J. Engineering a Semi-Interpenetrating Constructed Xylan-Based Hydrogel with Superior Compressive Strength, Resilience, and Creep Recovery Abilities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaiyang, W.; Huiling, L.; Junli, R.; Chuanfu, L.; Feng, P.; Runcang, S. Preparation of Xylan Citrate—A Potential Adsorbent for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-F.; Liu, B.; Jing, Z.; Wang, H. Preparation and Adsorption Property of Xylan/Poly(Acrylic Acid) Magnetic Nanocomposite Hydrogel Adsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 118, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Vilela, C.; Girão, A.V.; Branco, P.C.; Martins, J.; Freire, M.G.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Wood Inspired Biobased Nanocomposite Films Composed of Xylans, Lignosulfonates and Cellulose Nanofibers for Active Food Packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 337, 122112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, A.O.; Warne, C.M.; Pétremand, H.; König-Mattern, L.; Stöckelmaier, J.; Oostenbrink, C.; Guebitz, G.M.; Luterbacher, J.; Pellis, A. Xylose Acetals—A New Class of Sustainable Solvents and Their Application in Enzymatic Polycondensation. ChemSusChem 2024, 18, e202401877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduri, M.K.R.; Fatehi, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Carboxymethylated Xylan and Its Application as a Dispersant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josey, D.C.; Yadavalli, N.S.; Moore, J.C.; Peña, M.J.; Minko, S.; Urbanowicz, B.R. Valorization of Hemicellulose Waste Streams for Moisture Barrier Coatings and Hydrophobic Films. Biotechnol. Sus. Mater. 2024, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, T.; Meuwis, M.-A.; Stals, I.; Claeyssens, M.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C. A Novel Family 8 Xylanase, Functional and Physicochemical Characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35133–35139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroca, M.; Santos, G.; Johansson, B.; Gillotin, F.; Feller, G.; Collins, T. Deciphering the Factors Defining the pH-Dependence of a Commercial Glycoside Hydrolase Family 8 Enzyme. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2017, 96, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Craeyveld, V.; Swennen, K.; Dornez, E.; Van de Wiele, T.; Marzorati, M.; Verstraete, W.; Delaedt, Y.; Onagbesan, O.; Decuypere, E.; Buyse, J.; et al. Structurally Different Wheat-Derived Arabinoxylooligosaccharides Have Different Prebiotic and Fermentation Properties in Rats. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtin, C.M.; Swennen, K.; Verjans, P.; Delcour, J.A. Heat and PH Stability of Prebiotic Arabinoxylooligosaccharides, Xylooligosaccharides and Fructooligosaccharides. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yun, J.; Gu, Y.; Yan, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, C. Evaluating the in Vitro and in Vivo Prebiotic Effects of Different Xylo-Oligosaccharides Obtained from Bamboo Shoots by Hydrothermal Pretreatment Combined with Endo-Xylanase Hydrolysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsalova, T.; Georgiev, Y.; Moten, D.; Teneva, I.; Dzhambazov, B. Natural Xylooligosaccharides Exert Antitumor Activity via Modulation of Cellular Antioxidant State and TLR4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.M.Z.; Fernández, P.V.; Ciancia, M. Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationship of Xylooligosaccharides Obtained from Carboxyl-Reduced Glucuronoarabinoxylans from Bamboo Shoots. Food Chem. 2024, 455, 139761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Liu, G.; Shen, F.; Wu, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, R.; Che, L.; Feng, B.; Zhuo, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Xylo-Oligosaccharides Enhance Intestinal and Thymic Immunity by Modulating Pyroptosis, Gut Microbiota, and Th17/Treg Immune Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Challenged Piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 103, skaf050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yue, Z.; Liu, E.; Li, X.; Li, C. Assessment of the Bifidogenic and Antibacterial Activities of Xylooligosaccharide. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 858949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, W.H.-H.; Lee, I.-T.; Chen, W.; Chan, Y.-C. Effects of Xylooligosaccharides in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2008, 54, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, N.; Dang, L.; Wang, M.; Tian, H.; Jha, R.; Li, C. Synbiotic Supplementation with Xylooligosaccharide Derived Probiotic Lactobacillus gasseri and Prebiotic Mixture Exerts Antidiabetic Effects via Collaborative Action. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Yoo, S.-H.; Jung, S.; Park, M.-K.; Hong, J.-H. Relative Sweetness, Sweetness Quality, and Temporal Profile of Xylooligosaccharides and Luo Han Guo (Siraitia grosvenorii) Extract. Food. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narisetty, V.; Cox, R.; Bommareddy, R.; Agrawal, D.; Ahmad, E.; Pant, K.K.; Chandel, A.K.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Binod, P.; et al. Valorisation of Xylose to Renewable Fuels and Chemicals, an Essential Step in Augmenting the Commercial Viability of Lignocellulosic Biorefineries. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2022, 6, 29–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Xia, Q.; Mao, Z.; Mu, J.; Peng, F.; Hao, X. Sustainable Bioplastics Build on D-Xylose Cores: From Backup to the Center Stage. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 4464–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, P.; Datta, P.; Baruah, P.K. Conversion of Fructose and Xylose into Platform Chemicals Using Organo-functionalized Mesoporous Material. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 10971–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehuedé, L.; Henríquez, C.; Carú, C.; Córdova, A.; Mendonça, R.T.; Salazar, O. Xylan Extraction from Hardwoods by Alkaline Pretreatment for Xylooligosaccharide Production: A Detailed Fractionation Analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapini, T.; dos Santos, M.S.N.; Bonatto, C.; Wancura, J.H.C.; Mulinari, J.; Camargo, A.F.; Klanovicz, N.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V.; Fongaro, G.; et al. Hydrothermal Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Hemicellulose Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafchahi, M.N.; Acharya, B. Green Extraction of Xylan Hemicellulose from Wheat Straw. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 21229–21243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaire, K.C.; Sharma, K.; Thakur, A.; Moholkar, V.S.; Goyal, A. Extraction and Characterization of Xylan from Sugarcane Tops as a Potential Commercial Substrate. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 131, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Pandey, S.; Bhushan, K. Recent Developments in Extraction, Molecular Characterization, Bioactivity, and Application of Brewers Spent Grain Arabinoxylans. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.; Silvério, S.C.; Prather, K.L.J.; Rodrigues, L.R. From Lignocellulosic Residues to Market: Production and Commercial Potential of Xylooligosaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aachary, A.A.; Prapulla, S.G. Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an Emerging Prebiotic: Microbial Synthesis, Utilization, Structural Characterization, Bioactive Properties, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniaud, E.; Fleurence, J.; Lahaye, M. Interactions of the Mix-Linked Beta-(1,3)/-(1,4)-d-Xylans in the Cell Walls of Palmaria almata (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmedes, P.S. Investigating Hatchery and Cultivation Methods for Improved Cultivation of Palmaria palmata. Ph.D. Thesis, DTU aqua, Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, D.; Melo, T.; Meneses, J.; Abreu, M.H.; Pereira, R.; Domingues, P.; Lillebø, A.I.; Calado, R.; Domingues, M.R. A New Look for the Red Macroalga Palmaria palmata: A Seafood with Polar Lipids Rich in EPA and with Antioxidant Properties. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stévant, P.; Schmedes, P.S.; Le Gall, L.; Wegeberg, S.; Dumay, J.; Rebours, C. Concise Review of the Red Macroalga Dulse, Palmaria palmata (L.) Weber & Mohr. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 523–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafeuille, B.; Tamigneaux, É.; Berger, K.; Provencher, V.; Beaulieu, L. Impact of Harvest Month and Drying Process on the Nutritional and Bioactive Properties of Wild Palmaria palmata from Atlantic Canada. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Singh, G.; Ólafsdóttir, E.S.; Pálsson, S.; Heiðmarsson, S.; de Boer, H.; et al. A Critical Review of the Edible Seaweed Palmaria palmata (L.) Weber & Mohr and Its Bioactive Compounds in the “Omics” Era. Algal Res. 2024, 82, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussan, K.; Huijgen, W.J.J.; de Vrije, T.; van der Wal, H.; Capella, H.; van Doorn, J.; López-Contreras, A.M.; van Hal, J.W. Biorefinery of Red Seaweed Palmaria palmata for Production of Bio-Based Chemicals and Biofuels. Algal Res. 2024, 82, 103608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiener, P.; Zhao, S.; Theodoridou, K.; Carey, M.; Mooney-McAuley, K.; Greenwell, C. The Nutritional Aspects of Biorefined Saccharina latissima, Ascophyllum nodosum and Palmaria palmata. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2017, 7, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, J.; Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Carreira-Casais, A.; Chamorro, F.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Otero, P.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Baamonde, S.; Fernández-Saa, F.; Cao, H.; et al. Nutritional Composition of the Atlantic Seaweeds Ulva rigida, Codium tomentosum, Palmaria palmata and Porphyra purpurea. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødde, R.S.H.; Vårum, K.M.; Larsen, B.A.; Myklestad, S.M. Seasonal and Geographical Variation in the Chemical Composition of the Red Alga Palmaria palmata (L.) Kuntze. Bot. Mar. 2004, 47, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, A.T.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Whelan, S.; Edwards, M.D.; FitzGerald, R.J. Impact of Different Light Conditions on the Nitrogen, Protein, Colour, Total Phenolic Content and Amino Acid Profiles of Cultured Palmaria palmata. Foods 2023, 12, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafeuille, B.; Francezon, N.; Goulet, C.; Perreault, V.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, L. Impact of Temperature and Cooking Time on the Physicochemical Properties and Sensory Potential of Seaweed Water Extracts of Palmaria palmata and Saccharina longicruris. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1731–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, S.L.; Kraan, S. Bioactive Compounds in Seaweed: Functional Food Applications and Legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 543–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.A.; Adams, J.M.M.; Turner, L.B.; Kirby, M.E.; Toop, T.A.; Mirza, M.W.; Theodorou, M.K. Bio-Processing of Macroalgae Palmaria palmata: Metabolite Fractionation from Pressed Fresh Material and Ensiling Considerations for Long-Term Storage. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tello-Ireland, C.; Lemus-Mondaca, R.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; López, J.; Di Scala, K. Influence of Hot-Air Temperature on Drying Kinetics, Functional Properties, Colour, Phycobiliproteins, Antioxidant Capacity, Texture and Agar Yield of Alga Gracilaria chilensis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.R.; Abreu, H.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Effect of Oven-Drying on the Recovery of Valuable Compounds from Ulva rigida, Gracilaria Sp. and Fucus vesiculosus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, H.; Donohoe, P.; Kibblewhite, B. Seaweed and the Applicability of Freeze Drying Techniques. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1386418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Strat, Y.; Mandin, M.; Ruiz, N.; Robiou du Pont, T.; Ragueneau, E.; Barnett, A.; Déléris, P.; Dumay, J. Quantification of Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Activities of Fungal Strains Isolated from Palmaria palmata to Enhance R-Phycoerythrin Extraction of Palmaria palmata: From Seaweed to Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, M.; Jubeau, S.; Wijaya, A.; Morançais, M.; Dumay, J.; Marchal, L.; Jaouen, P.; Fleurence, J. Physicochemical Factors Affecting the Stability of Two Pigments: R-Phycoerythrin of Grateloupia turuturu and B-Phycoerythrin of Porphyridium cruentum. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland-Irmouli, A.V.; Pons, L.; Luçon, M.; Villaume, C.; Mrabet, N.T.; Guéant, J.L.; Fleurence, J. One-Step Purification of R-Phycoerythrin from the Red Macroalga Palmaria palmata Using Preparative Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 739, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Cho, S.-M.; Kim, J.-C.; Kim, H.; Choi, I.-G. Evaluation of Xylooligosaccharides Production for a Specific Degree of Polymerization by Liquid Hot Water Treatment of Tropical Hardwood. Foods 2021, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q. The Hydrophobic Effects: Our Current Understanding. Molecules 2022, 27, 7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kishimura, H.; Kinoshita, Y.; Saburi, W.; Kumagai, Y.; Yasui, H.; Ojima, T. Enzymatic Production of Xylooligosaccharides from Red Alga Dulse (Palmaria Sp.) Wasted in Japan. Process Biochem. 2019, 82, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skriptsova, A.V.; Suzuki, M.; Semenchenko, A.A. Morphological Variation in Northwest Pacific Devaleraea mollis and Description of D. Inkyuleei Sp. Nov. (Palmariaceae, Rhodophyta). Phycologia 2022, 61, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purifcation. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machu, L.; Misurcova, L.; Ambrozova, J.V.; Orsavova, J.; Mlcek, J.; Sochor, J.; Jurikova, T. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity in Algal Food Products. Molecules 2015, 20, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Moreira, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rocha, C.M.R. Tuning the Extraction Methodology Targeting Protein-Enriched Fractions from Red Algae. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, C.; Mortensen, A.M.; Rautenberger, R.; Matsson, S.; Gorzsás, A.; Gentili, F.G. Rapid and Accurate Determination of Protein Content in North Atlantic Seaweed by NIR and FTIR Spectroscopies. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of DNS Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, D.; Costa, D.F.; Barroca, M.; Cunha, S.A.; Pintado, M.M.; Abreu, H.; Martins, M.; Collins, T. Simplified, High Yielding Extraction of Xylan/Xylo-Oligosaccharides from Palmaria palmata: The Importance of the Algae Preservation Treatment. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080302
Coelho D, Costa DF, Barroca M, Cunha SA, Pintado MM, Abreu H, Martins M, Collins T. Simplified, High Yielding Extraction of Xylan/Xylo-Oligosaccharides from Palmaria palmata: The Importance of the Algae Preservation Treatment. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(8):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080302
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, Diogo, Diogo Félix Costa, Mário Barroca, Sara Alexandra Cunha, Maria Manuela Pintado, Helena Abreu, Margarida Martins, and Tony Collins. 2025. "Simplified, High Yielding Extraction of Xylan/Xylo-Oligosaccharides from Palmaria palmata: The Importance of the Algae Preservation Treatment" Marine Drugs 23, no. 8: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080302
APA StyleCoelho, D., Costa, D. F., Barroca, M., Cunha, S. A., Pintado, M. M., Abreu, H., Martins, M., & Collins, T. (2025). Simplified, High Yielding Extraction of Xylan/Xylo-Oligosaccharides from Palmaria palmata: The Importance of the Algae Preservation Treatment. Marine Drugs, 23(8), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080302








