Isolation and Identification of Cis-2,5-Diketopiperazine from a Novel Bacillus Strain and Synthesis of Its Four Stereoisomers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Cyclo-(Phe-Pro)
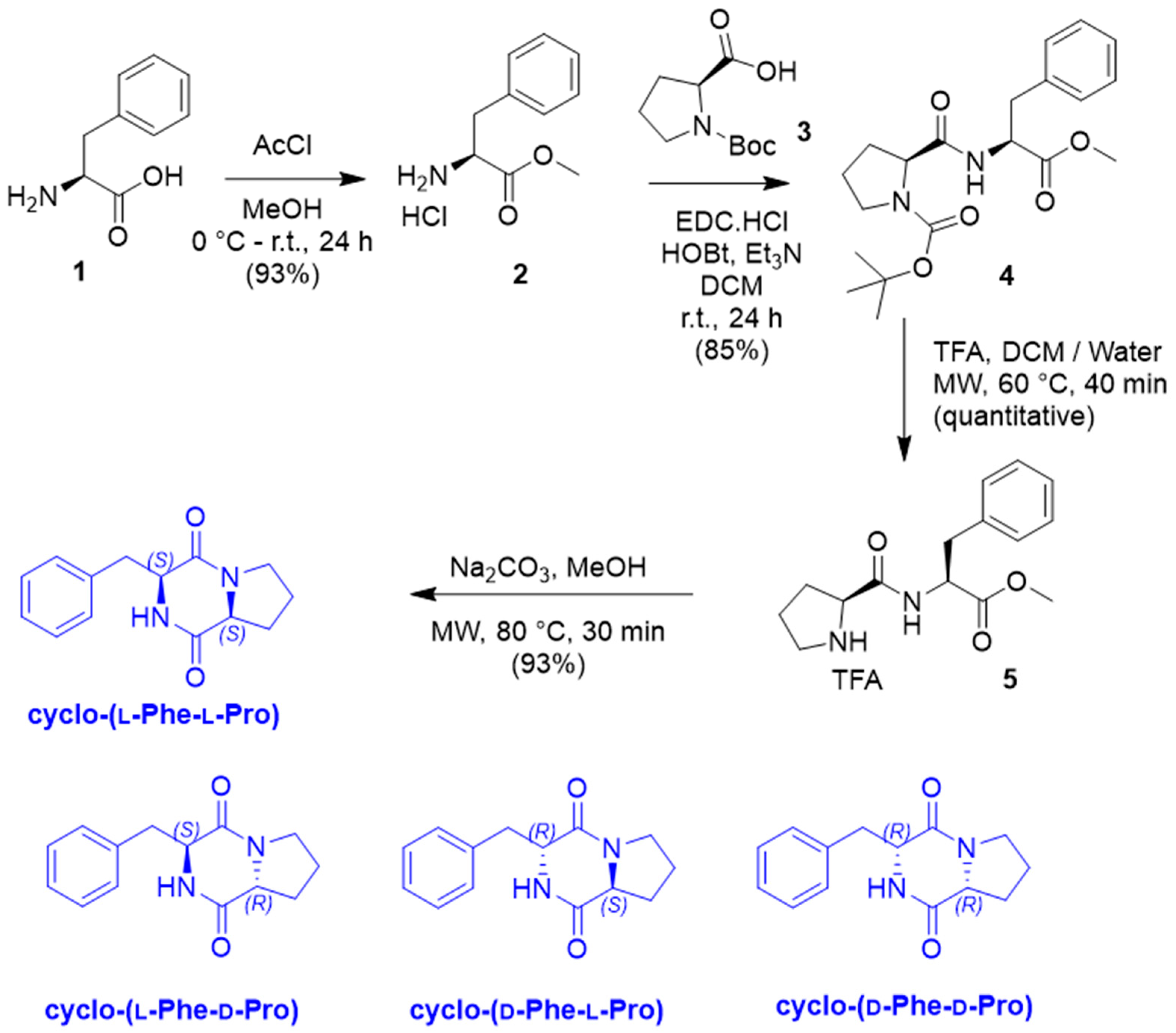
2.2. Chemical Synthesis of Cyclo-(Phe-Pro) Isomers
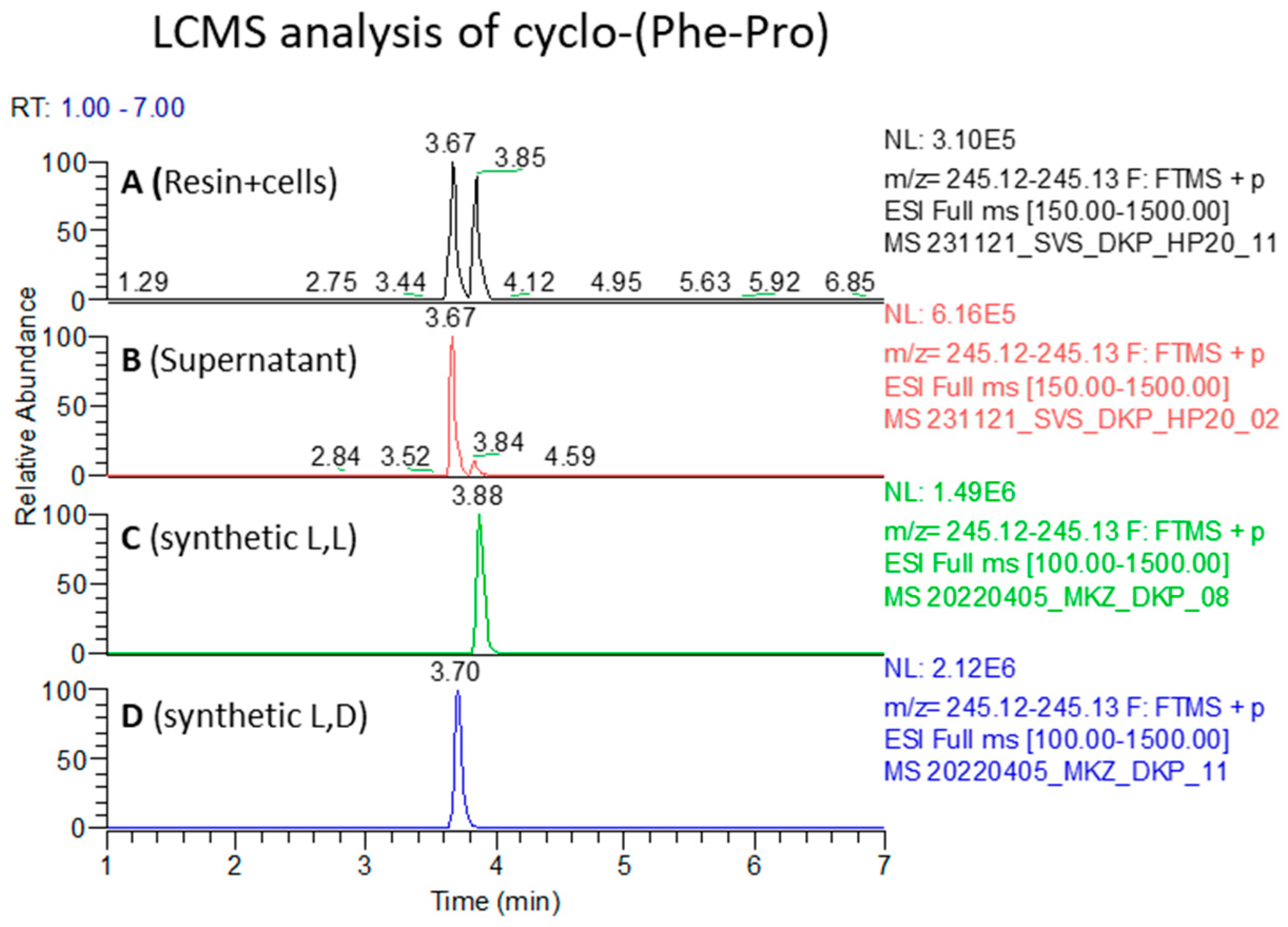
2.3. Establishing the Stereochemistry of Isolated Natural Cyclo-(Phe-Pro)
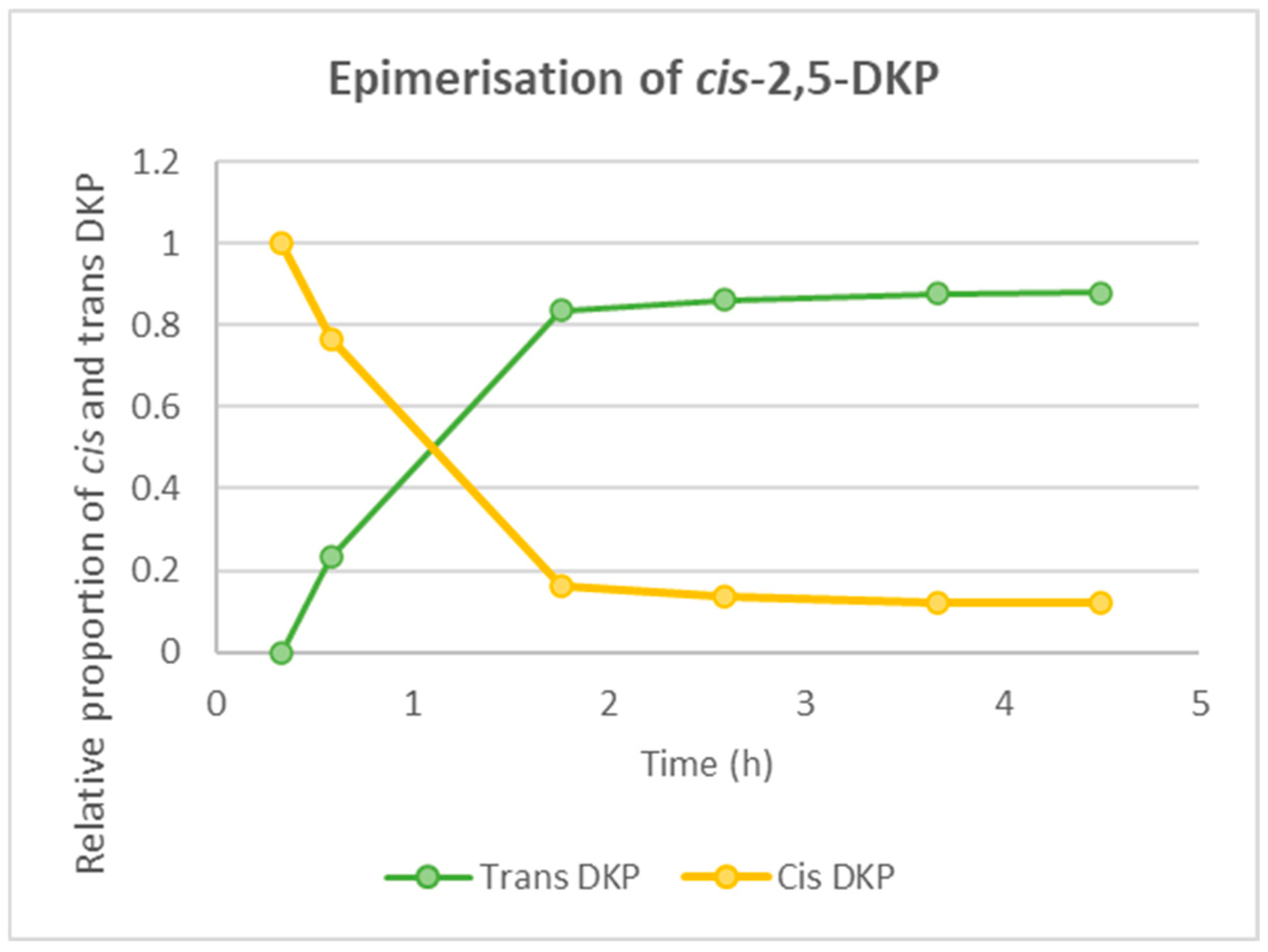
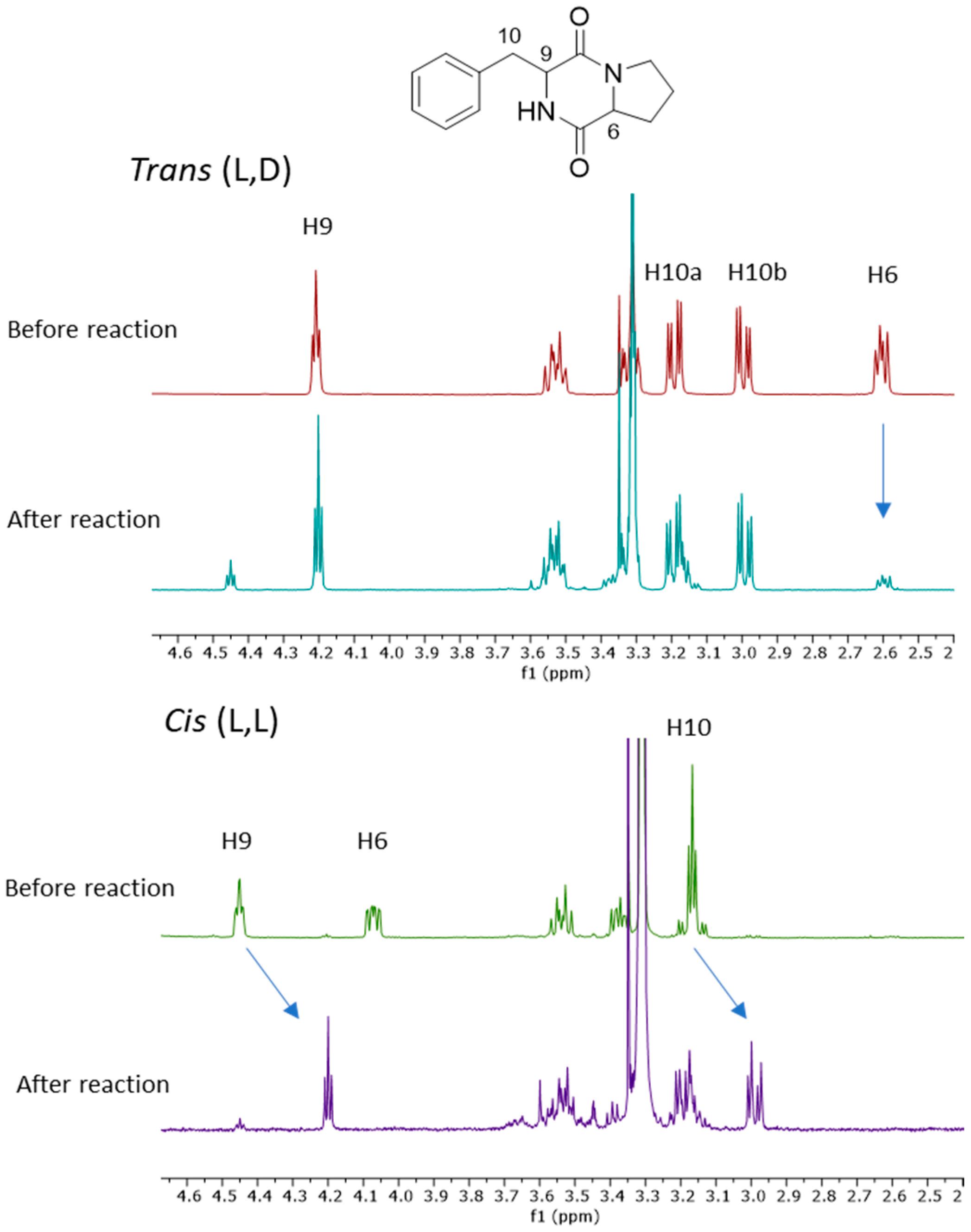
2.4. Probing the Epimerisation of Cyclo-(Phe-Pro)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain Isolation and Culturing
4.2. Fractionation and Isolation of 2,5-DKP
4.3. General Procedure for the Cyclisation of Pro-Phe-OMe to Cyclo-(Phe-Pro)
4.4. Effect of Culturing Conditions and Comparison of Culture Extracts with Synthetic Standards by LCMS
4.5. Synthetic Procedures and Other Methods
4.5.1. Preparation of l-Phenylalanine Methyl Ester Hydrochloride (2)
4.5.2. Preparation of Boc-l-Proline (3)
4.5.3. Peptide Coupling Using Protected Amino Acids
4.5.4. Boc-l-Pro-l-Phe-OMe (4)
4.5.5. Boc-d-Pro-d-Phe-OMe
4.5.6. Boc-l-Pro-d-Phe-OMe
4.5.7. Boc-d-Pro-l-Phe-OMe
4.5.8. Boc Deprotection
4.5.9. l-Pro-l-Phe-OMe·TFA (5)
4.5.10. d-Pro-d-Phe-OMe·TFA
4.5.11. l-Pro-d-Phe-OMe·TFA
4.5.12. d-Pro-l-Phe-OMe·TFA
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borthwick, A.D. 2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, reactions, medicinal chemistry, and bioactive natural products. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3641–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, T.; Miyairi, N.; Aoki, H.; Kosaka, M.; Sakai, H. Bicyclomycin, a new antibiotic. I. Taxonomy, isolation and characterization. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borthwick, A.D.; Da Costa, N.C. 2,5-Diketopiperazines in food and beverages: Taste and bioactivity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 718–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strom, K.; Sjogren, J.; Broberg, A.; Schnurer, J. Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 393 produces the antifungal cyclic dipeptides cyclo(l-Phe-l-Pro) and cyclo(l-Phe-trans-4-OH-l-Pro) and 3-phenyllactic acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4322–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetti, R.; Polizzotto, R.; Vecchione, A.; Borselli, S.; Zulini, L.; D’Ambrosio, M.; di Toppi, L.S.; Pertot, I. Antifungal activity of diketopiperazines extracted from Alternaria alternata against Plasmopara viticola: An ultrastructural study. Micron 2007, 38, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Quan, C. Effect of the environmental factors on diketopiperazine cyclo(Pro-Phe) production and antifungal activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426. Biologia 2021, 76, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.L.; Carrasco, L. Gliotoxin: Inhibitor of poliovirus RNA synthesis that blocks the viral RNA polymerase 3Dpol. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.-K.; Liu, R.; Kwon, J.-O.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, A.H.; Kang, S.-O. Cyclic dipeptides from lactic acid bacteria inhibit proliferation of the influenza A virus. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, B.; Lloyd, G.K.; Miller, B.R.; Palladino, M.A.; Kiso, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Neuteboom, S.T. NPI-2358 is a tubulin-depolymerizing agent: In-vitro evidence for activity as a tumor vascular-disrupting agent. Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, P.J.; Hunt, A.L.; Rostoll, K.; Van Der Walt, J.J.; Graz, C.J.M. The biological activity of selected cyclic dipeptides. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1998, 50, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoh, K.; Kohno, S.; Katada, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Uno, I. Antitumor activity of phenylahistin in vitro and in vivo. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.R.; Lawrence, C.H.; Gray, J.A. Herbicidal properties of the thaxtomin group of phytotoxins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2298–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Yong, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Research progress of the biosynthesis of natural bio-antibacterial agent pulcherriminic acid in Bacillus. Molecules 2020, 25, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.L.; Qi, J.Z.; Lv, Y.; Dong, S.; Cao, C.Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, X. Discovery of 1,3-disubstituted 2,5-diketopiperazine derivatives as potent class I HDACs inhibitors. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, London, 2014. Available online: https://amr-review.org/Publications.html (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Liao, S.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of soluble 2,5-diketopiperazines derivatives as potential antifouling agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51020–51026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dobretsov, S.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Hung, O.; Qian, P.Y. Antifouling diketopiperazines produced by a deep-sea bacterium, Streptomyces fungicidicus. Biofouling 2006, 22, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.M.; Rennison, D.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H.; Hellio, C.; Foulon, V.; Brimble, M.A.; Cahill, P.; Svenson, J. Towards eco-friendly marine antifouling biocides–Nature inspired tetrasubstituted 2,5-diketopiperazines. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaibani, M.M.; Mohamadzin, N.; Jalil, J.; Sidik, N.M.; Ahmad, S.J.; Kamal, N.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Isolation, purification, and characterization of five active diketopiperazine derivatives from endophytic Streptomyces SUK 25 with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities. J. Microb. Biotech. 2017, 27, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, N.Y.; Wen, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Yoon, S.Y.; Jie, H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K.S. Cyclo-(l-Phe-l-Pro), a quorum-sensing signal of Vibrio vulnificus, induces expression of hydroperoxidase through a ToxR-LeuO-HU-RpoS signaling pathway to confer resistance against oxidative stress. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00932-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Dai, S.; Chen, M.; Wu, H.; Xie, L.; Luo, X.; Li, X. Two diketopiperazine cyclo(pro-phe) isomers from marine bacteria Bacillus subtilis sp. 13-2. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2010, 46, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, E.D.; Knuckley, B.; Alqahtani, N.; Porwal, S.; Ban, J.; Karty, J.A.; Viswanathan, R.; Lane, A.L. Two distinct cyclodipeptide synthases from a marine actinomycete catalyze biosynthesis of the same diketopiperazine natural product. ACS Synth. Biol. 2016, 5, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Lin, Q.; Geske, G.D.; Blackwell, H.E. New and unexpected insights into the modulation of LuxR-type quorum sensing by cyclic dipeptides. ACS Chem. Biol. 2009, 4, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Jang, B.R.; Kim, Y.R.; Jung, Y.C.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, K.H. Vibrio vulnificus induces the death of a major bacterial species in the mouse gut via cyclo-Phe-Pro. Microbiome 2021, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, S.D.; Davies, S.G.; Parkin, R.M.; Sánchez-Sancho, F. The biosynthetic origin of diketopiperazines derived from d-Proline. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1998, 15, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauvais, C.; Zirah, S.; Piette, L.; Chaspoul, F.; Domart-Coulon, I.; Chapon, V.; Gallice, P.; Rebuffat, S.; Pérez, T.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. Sponging up metals: Bacteria associated with the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 104, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huy, P.; Neudörfl, J.M.; Schmalz, H.G. A practical synthesis of trans-3-substituted proline derivatives through 1,4-addition. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, A.M.; Zabet-Moghaddam, M.; San Francisco, M. Identification of a novel secreted metabolite cyclo(phenylalanyl-prolyl) from Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and its effect on Galleria mellonella. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budesinsky, M.; Cisarova, I.; Podlaha, J.; Borremans, F.; Martins, J.C.; Waroquier, M.; Pauwels, E. Structures of cyclic dipeptides: An X-ray and computational study of cis- and trans-cyclo(Pip-Phe), cyclo(Pro-Phe) and their N-methyl derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 2010, 66, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, V.; Young, P.E.; Blout, E.R. Cyclic peptides. 14. Conformational energy and circular dichroism of proline-containing cyclic dipeptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 5358–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, T.; Sato, P.; Tsuyama, S.; Nagao, R.; Fujiki, K.; Yamaji, A. Analysis of the isomerization of diketopiperazine consisting of proline and aromatic amino acid residues using nuclear magnetic resonance. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2022, 3, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidukevich, V.A.; Rudenkova, I.V.; Popova, L.A.; Nikolaevich, L.N.; Knizhnikov, V.A. Synthesis of 3-benzylhexahydropyrrolo [1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 54, 1562–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonial, F.; Maia, B.; Gomes-Figueiredo, J.A.; Sobottka, A.M.; Bertol, C.D.; Nepel, A.; Savi, D.C.; Vicente, V.A.; Gomes, R.R.; Glienke, C. Influence of culturing conditions on bioprospecting and the antimicrobial potential of endophytic fungi from Schinus terebinthifolius. Curr. Microbio. 2016, 72, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.Y.; Cho, Y.B.; Kim, O.B.; Kim, K.S. Cyclo(Phe-Pro) produced by Vibrio species passes through biological membranes by simple diffusion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullberg, M.; Grotli, M.; Luthman, K. Efficient synthesis of 2,5-diketopiperazines using microwave assisted heating. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 7484–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, O.R.; Taylor, B.; Higgins, E.M.; Rees, M.; Cobb, S.L.; Simpkins, N.S.; Hayes, C.J.; O’Donoghue, A.C. Unusually high α-proton acidity of prolyl residues in cyclic peptides. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7722–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalker, J.M.; Gunnoo, S.B.; Boutureira, O.; Gerstberger, S.C.; Fernández-González, M.; Bernardes, G.J.L.; Griffin, L.; Hailu, H.; Schofield, C.J.; Davis, B.G. Methods for converting cysteine to dehydroalanine on peptides and proteins. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.K.; Hernández, D.; Lindhardt, A.T.; Skrydstrup, T. Enamides accessed from aminothioesters via a Pd(0)-catalyzed decarbonylative/β-hydride elimination sequence. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4716–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, L.A.; Mansour, E.M.E.; Sadataalaee, D. tert-Butyloxycarbonyl and benzyloxycarbonyl amino-acid fluorides–new, stable rapid-acting acylating agents for peptide-synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 2611–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.B.; Verma, S. Bisection of biotinylated soft spherical structures. Biophys. Chem. 2009, 140, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
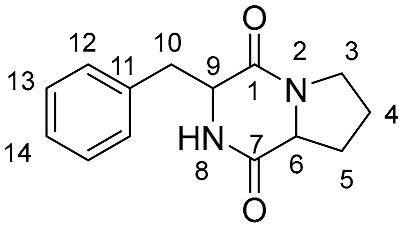
| Position (Group) * | Synthetic Trans (l,d) | Synthetic Cis (l,l) | Natural Isolate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 (CH2) | 3.53 and 3.32 | 3.54 and 3.37 | 3.55 and 3.38 |
| 4 (CH2) | 1.88 and 1.65 | 1.80 | 1.81 |
| 5 (CH2) | 2.03 and 1.65 | 2.10 and 1.20 | 2.11 and 1.22 |
| 6 (CH) | 2.60 | 4.07 | 4.08 |
| 9 (CH) | 4.21 | 4.45 | 4.46 |
| 10 (CH2) | 3.19 and 3.00 | 3.17 | 3.18 |
| 12–14 (Ar-H) | 7.34–7.27 and 7.21–7.16 | 7.31–7.19 | 7.30–7.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obled, A.M.C.; Hamed, R.B.; Spence, E.; Zacharova, M.K.; Sharma, S.V.; Wang, Y.; Lynch, R.; Connaris, H.; Tatheer, A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; et al. Isolation and Identification of Cis-2,5-Diketopiperazine from a Novel Bacillus Strain and Synthesis of Its Four Stereoisomers. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060234
Obled AMC, Hamed RB, Spence E, Zacharova MK, Sharma SV, Wang Y, Lynch R, Connaris H, Tatheer A, Bourguet-Kondracki M-L, et al. Isolation and Identification of Cis-2,5-Diketopiperazine from a Novel Bacillus Strain and Synthesis of Its Four Stereoisomers. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060234
Chicago/Turabian StyleObled, Alan M. C., Refaat B. Hamed, Edward Spence, Marija K. Zacharova, Sunil V. Sharma, Yunpeng Wang, Rosemary Lynch, Helen Connaris, Adina Tatheer, Marie-Lise Bourguet-Kondracki, and et al. 2025. "Isolation and Identification of Cis-2,5-Diketopiperazine from a Novel Bacillus Strain and Synthesis of Its Four Stereoisomers" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060234
APA StyleObled, A. M. C., Hamed, R. B., Spence, E., Zacharova, M. K., Sharma, S. V., Wang, Y., Lynch, R., Connaris, H., Tatheer, A., Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L., Florence, G. J., & Goss, R. J. M. (2025). Isolation and Identification of Cis-2,5-Diketopiperazine from a Novel Bacillus Strain and Synthesis of Its Four Stereoisomers. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060234







