Influence of a Very High-Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea on Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Relevant Pathomechanisms in Ocular Cell Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Characterization of Fucoidan
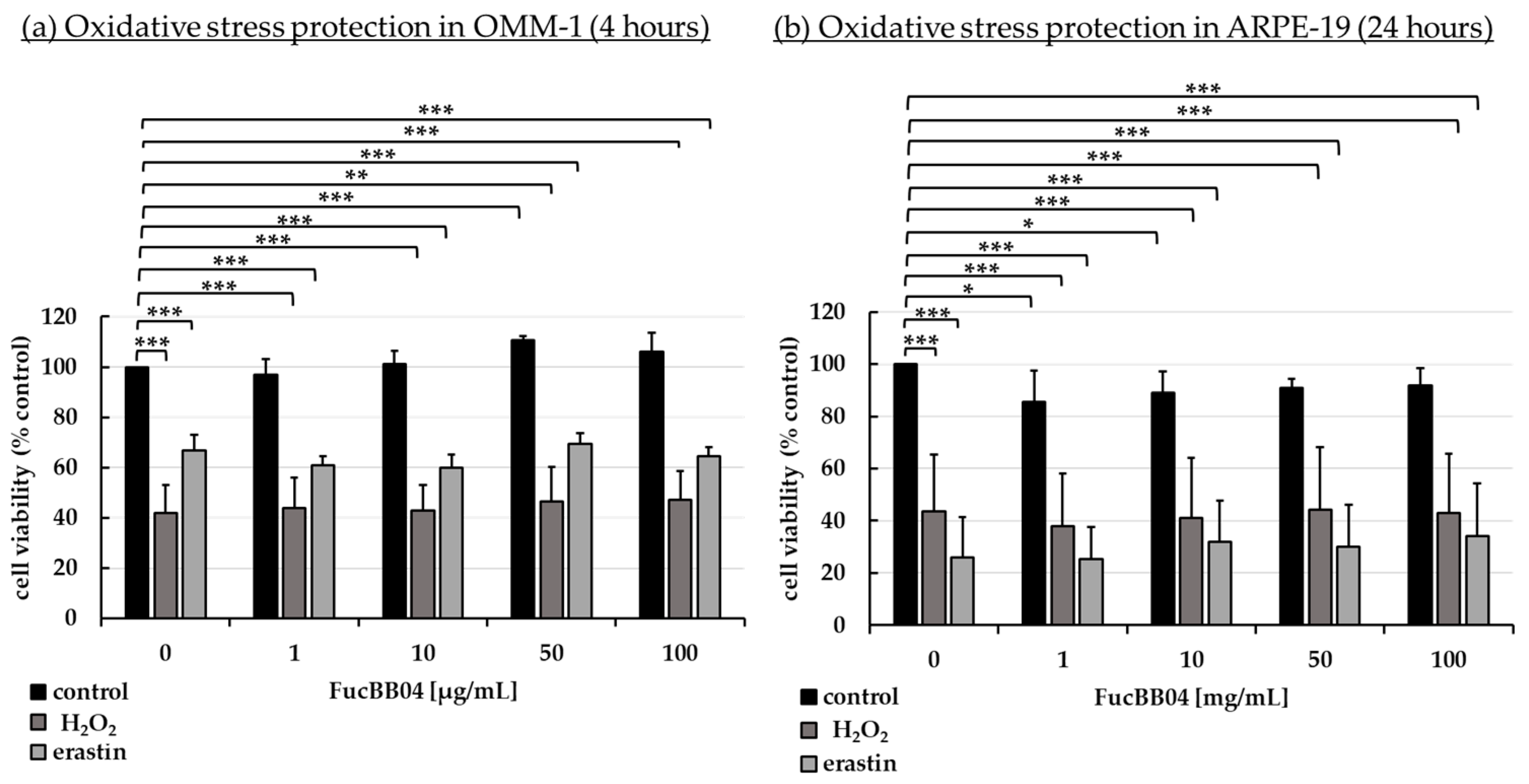
2.2. Oxidative Stress Assays
2.3. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Secretion
2.4. Interleukin Secretion
2.5. Interleukin Gene Expression
2.6. Barrier Measurement
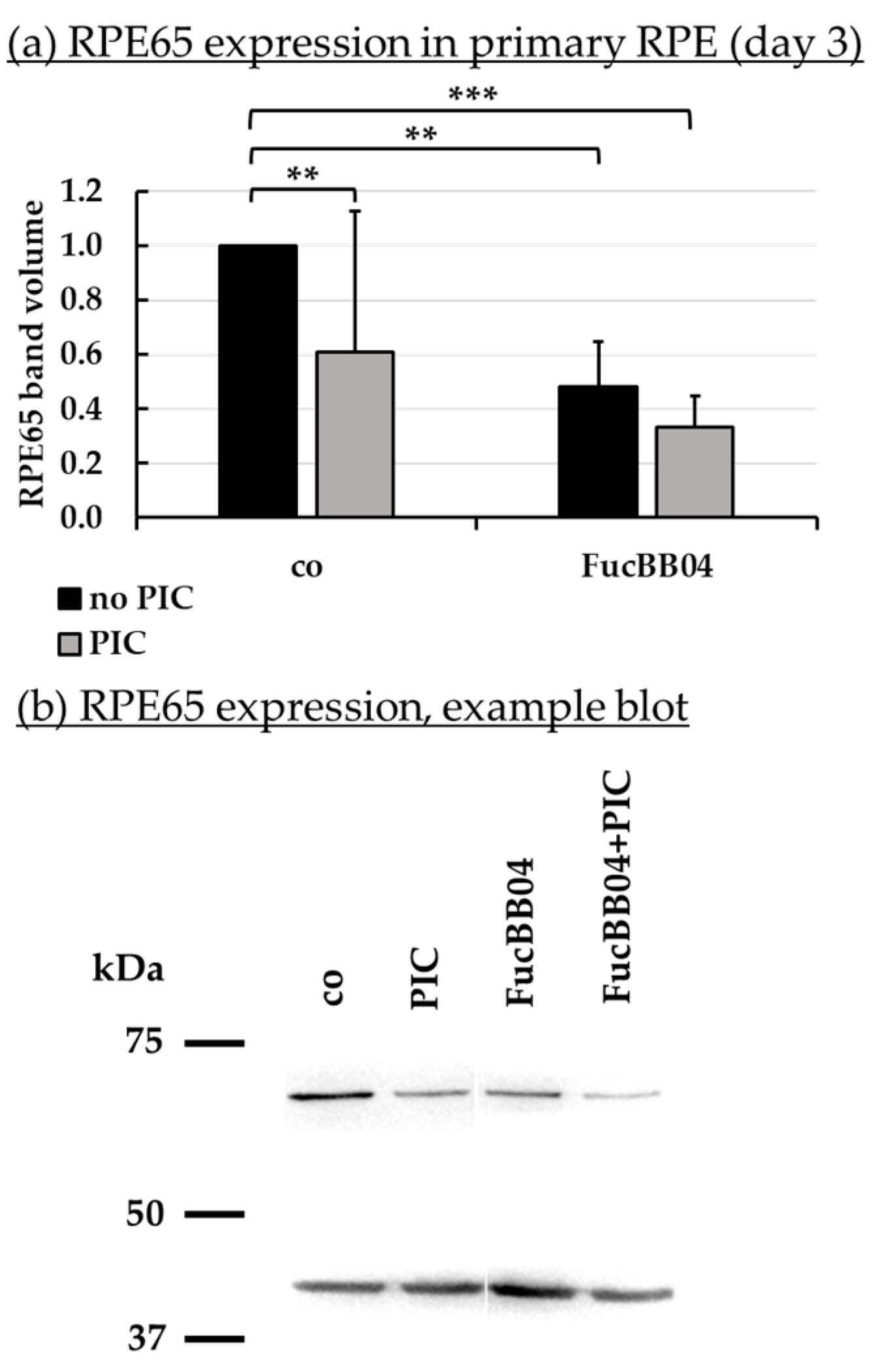
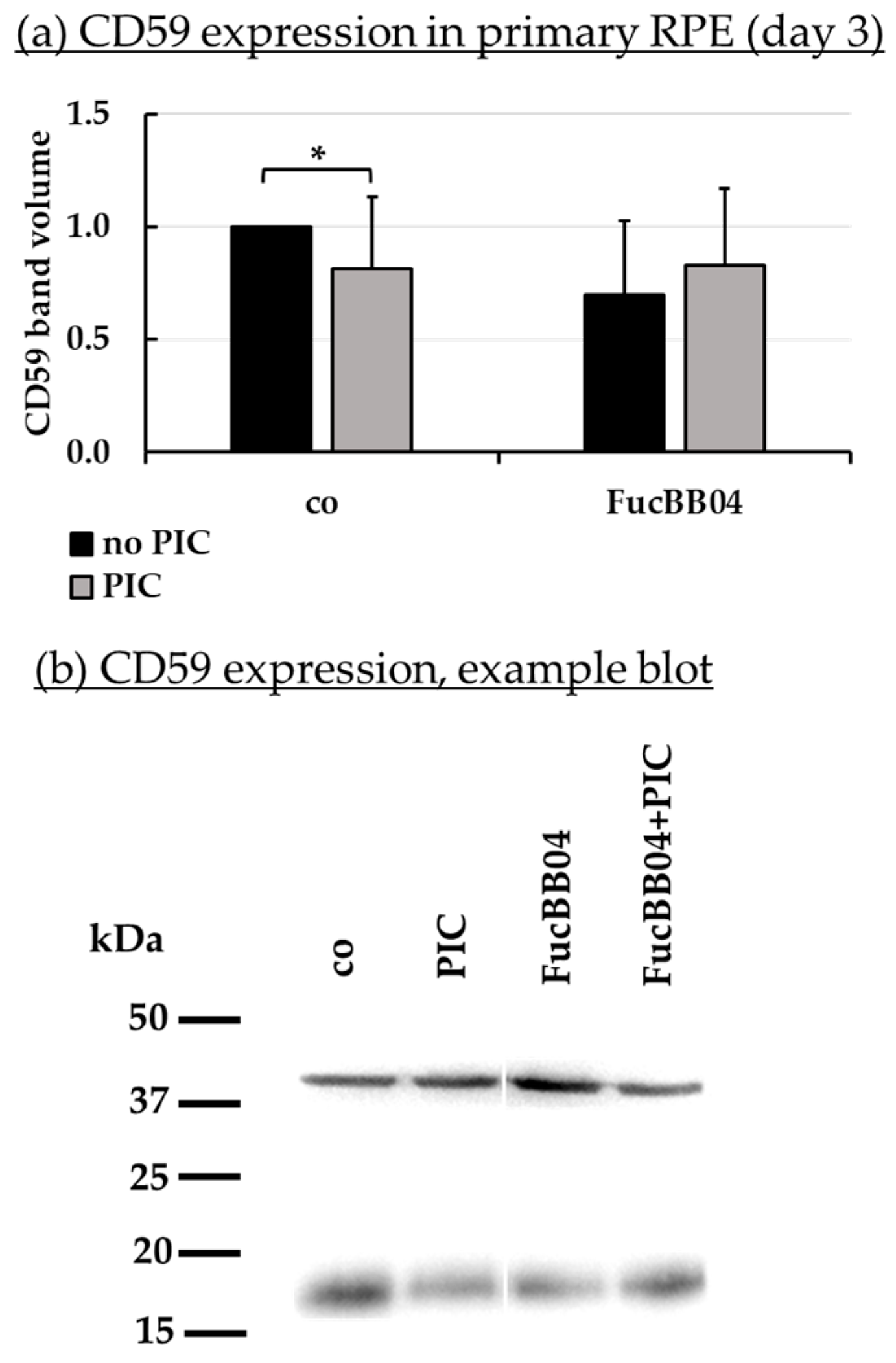
2.7. Protein Expression
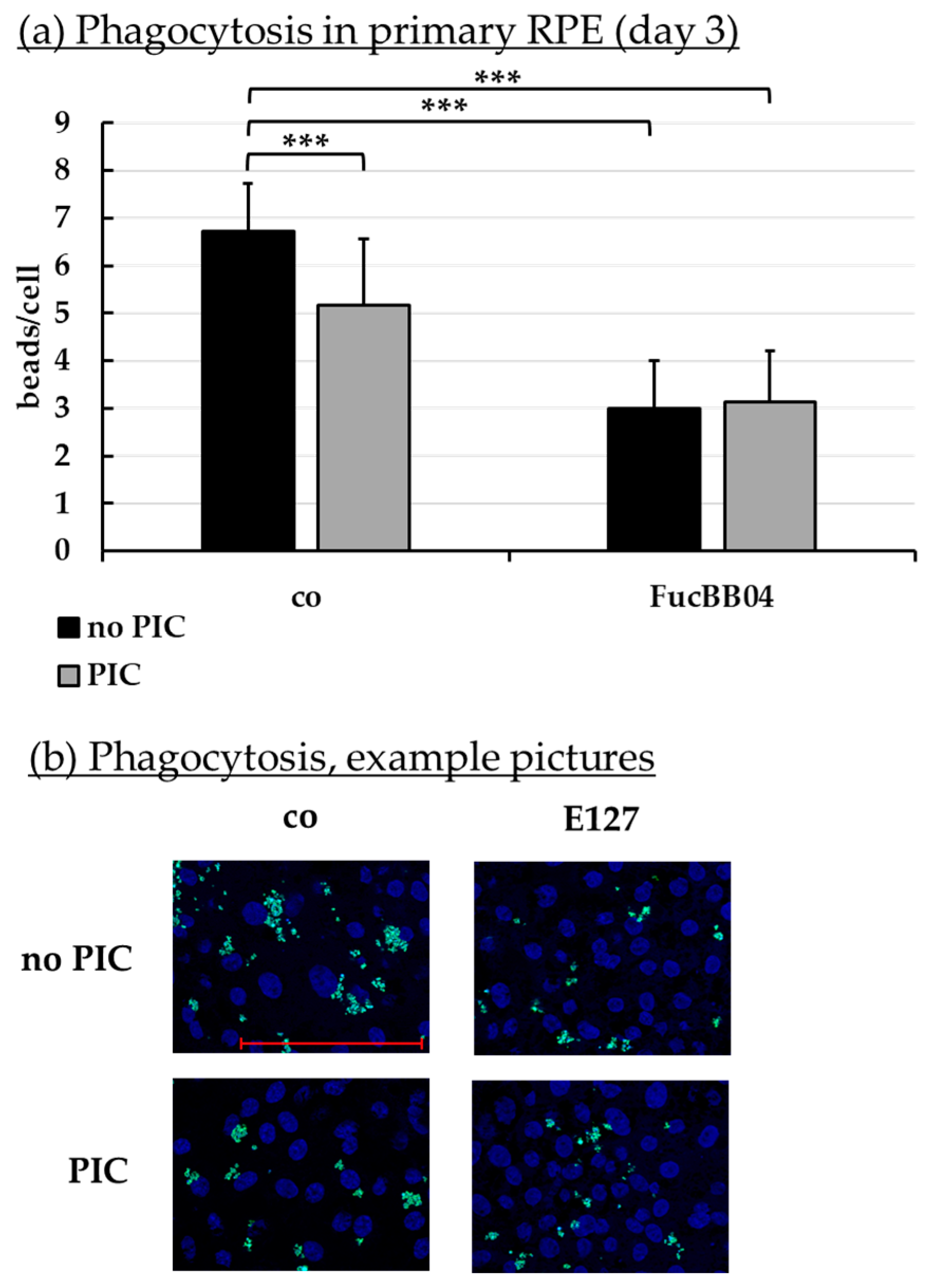
2.8. Phagocytosis Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Algal Material, Fucoidan Extraction and Purification Method
4.2. Molecular Weight Determination
4.3. Sulfate Content
4.4. Total Phenolic Content
4.5. Monosaccharide Analysis
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. Stimulation
4.8. Cell Viability
4.9. Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER)
4.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.11. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.12. Western Blotting
4.13. Phagocytosis Assay
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Cell Viability Data for Section 2.5
| Day 1 | co | LPS | PIC | TNF | Pam | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no FucBB04 | 100 | 105 | 109 | 104 | 103 | Mean |
| 0 | 11 | 14 | 32 | 9 | SD | |
| FucBB04 | 95 | 91 | 94 | 96 | 97 | Mean |
| 3 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 1 | SD | |
| Day 3 | ||||||
| no FucBB04 | 100 | 94 | 96 | 105 | 99 | Mean |
| 0 | 15 | 7 | 9 | 5 | SD | |
| FucBB04 | 98 | 87 | 77 | 95 | 96 | Mean |
| 4 | 16 | 15 | 1 | 1 | SD | |
| Day 7 | ||||||
| no FucBB04 | 100 | 97 | 95 | 93 | 100 | Mean |
| 0 | 13 | 14 | 18 | 12 | SD | |
| FucBB04 | 100 | 81 | 88 | 98 | 91 | Mean |
| 6 | 9 | 5 | 15 | 9 | SD | |
| Day 28 | ||||||
| no FucBB04 | 100 | 90 | 98 | 99 | 81 | Mean |
| 0 | 19 | 26 | 44 | 31 | SD | |
| FucBB04 | 75 | 64 | 78 | 90 | 63 | Mean |
| 16 | 16 | 16 | 13 | 15 | SD |
Appendix A.2. Standard Calibration Curves for ELISA
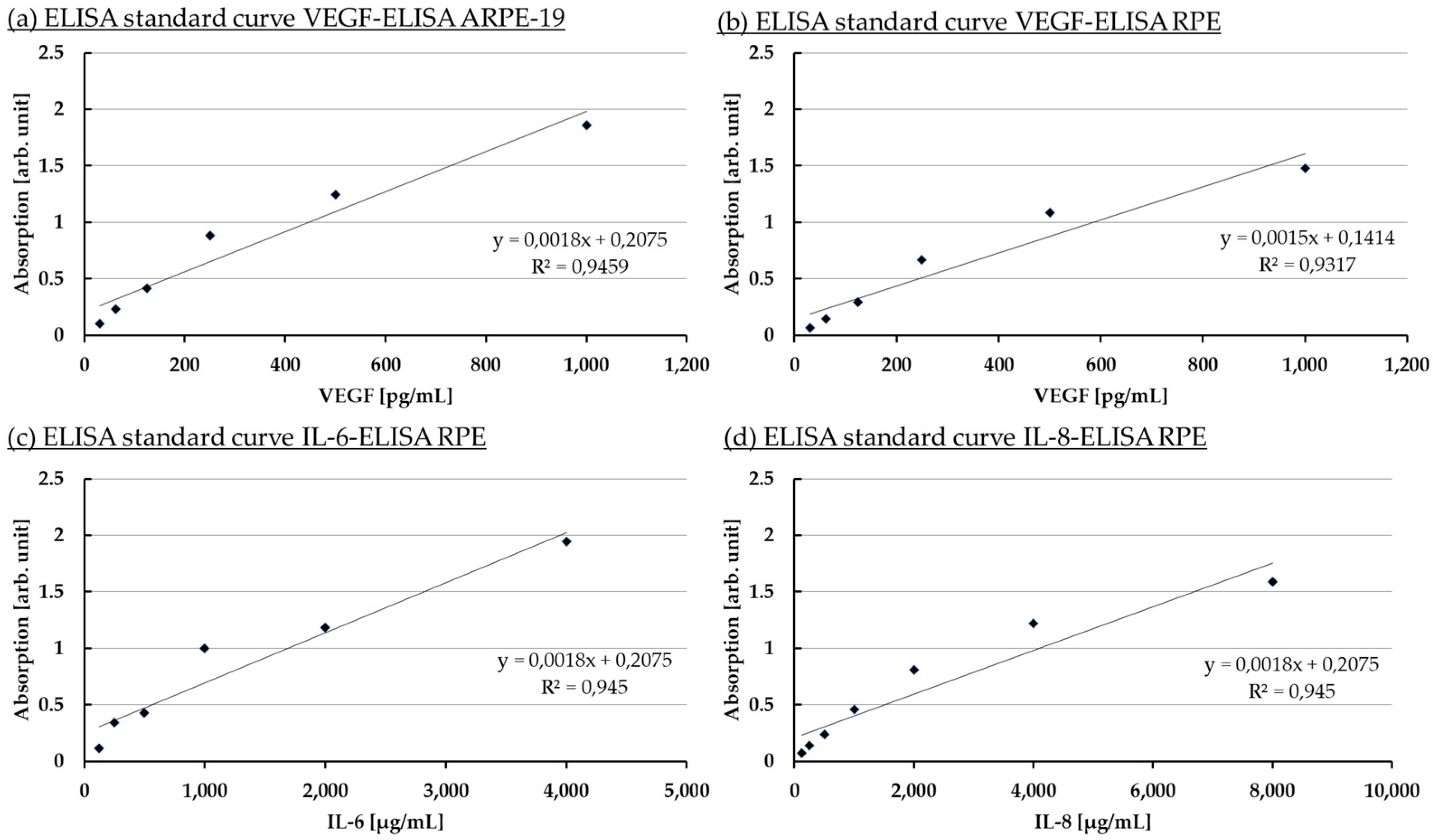
References
- Bourne, R.R.A.; Jonas, J.B.; Bron, A.M.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Friedman, D.S.; Keeffe, J.E.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; et al. Prevalence and causes of vision loss in high-income countries and in Eastern and Central Europe in 2015: Magnitude, temporal trends and projections. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guymer, R.H.; Campbell, T.G. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2023, 401, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutto, I.; Lutty, G. Understanding age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Relationships between the photoreceptor/retinal pigment epithelium/Bruch's membrane/choriocapillaris complex. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 845–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, F.; Safa, H.; Finnemann, S.C. Understanding photoreceptor outer segment phagocytosis: Use and utility of RPE cells in culture. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 126, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yan, B. Ocular immune privilege and retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, 113, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, L.; Lucius, R.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Interaction of inflammatorily activated retinal pigment epithelium with retinal microglia and neuronal cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 199, 108167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klettner, A.; Roider, J. Retinal Pigment Epithelium Expressed Toll-like Receptors and Their Potential Role in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Cano, M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Wang, L.; Handa, J.T. The impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on RPE degeneration in non-neovascular AMD. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 60, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.B.; Halawa, O.A.; Husain, D.; Miller, J.W.; Vavvas, D.G. Dyslipidemia in age-related macular degeneration. Eye 2022, 36, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.W. Beyond VEGF-The Weisenfeld Lecture. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 6911–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klettner, A. Fucoidan as a Potential Therapeutic for Major Blinding Diseases--A Hypothesis. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; Klettner, A. Fucoidans as Potential Therapeutics for Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Current Evidence from In Vitro Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Seeba, C.; Thalenhorst, T.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Anti-inflammatory properties of antiangiogenic fucoidan in retinal pigment epithelium cells. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; Akkurt, H.; Kopplin, G.; Mikkelsen, M.D.; Meyer, A.S.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Establishment of specific age-related macular degeneration relevant gene expression panels using porcine retinal pigment epithelium for assessing fucoidan bioactivity. Exp. Eye Res. 2023, 231, 109469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure, biology, evolution, and medical importance of sulfated fucans and galactans. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Ushakova, N.A.; Usov, A.I.; Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Nifantiev, N.E. Fucoidans: Pro- or antiangiogenic agents? Glycobiology 2014, 24, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgersson, P.S.; Chahal, A.S.; Klau, L.J.; Holte, H.B.; Arlov, Ø.; Aachmann, F.L. Structural characterization and immunomodulating assessment of ultra-purified water extracted fucoidans from Saccharina latissima, Alaria esculenta and Laminaria hyperborea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 343, 122448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoydan, S.; Rustemeyer, T. Investigating the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Various Brown Algae Species. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Kopplin, G.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Effects of Sulfated Fucans from Laminaria hyperborea Regarding VEGF Secretion, Cell Viability, and Oxidative Stress and Correlation with Molecular Weight. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, K.C.; Aotaki-Keen, A.E.; Putkey, F.R.; Hjelmeland, L.M. ARPE-19, a human retinal pigment epithelial cell line with differentiated properties. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 62, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiencke, A.K.; Kiilgaard, J.F.; Nicolini, J.; Bundgaard, M.; Röpke, C.; La Cour, M. Growth of cultured porcine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2003, 81, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyten, G.P.M.; Naus, N.C.; Mooy, C.M.; Hagemeijer, A.; Kan-Mitchell, J.; van Drunen, E.; Vuzevski, V.; de Jong, P.T.V.M.; Luider, T.M. Establishment and characterization of primary and metastatic uveal melanoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnichels, S.; Paquet-Durand, F.; Löscher, M.; Tsai, T.; Hurst, J.; Joachim, S.C.; Klettner, A. Retina in a dish: Cell cultures, retinal explants and animal models for common diseases of the retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 81, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunnikova, N.V.; Maminishkis, A.; Barb, J.J.; Wang, F.; Zhi, C.; Sergeev, Y.; Chen, W.; Edwards, A.O.; Stambolian, D.; Abecasis, G.; et al. Transcriptome analysis and molecular signature of human retinal pigment epithelium. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2468–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; Bittkau, K.S.; Neupane, S.; Roider, J.; Alban, S.; Klettner, A. Effects of Fucoidans from Five Different Brown Algae on Oxidative Stress and VEGF Interference in Ocular Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, P.D. Retinal pigment epithelium 65 kDa protein (RPE65): An update. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022, 88, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabolk, G.; Tomlinson, S.; Rohrer, B. The complement regulatory protein CD59: Insights into attenuation of choroidal neovascularization. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniaud-Bouët, E.; Hardouin, K.; Potin, P.; Kloareg, B.; Hervé, C. A review about brown algal cell walls and fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides: Cell wall context, biomedical properties and key research challenges. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Kadri, N.; Barragan-Montero, V.; Laouer, H.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Fucans from a Tunisian brown seaweed Cystoseira barbata: Structural characteristics and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, B.P.; Vetvicka, V.; Blakemore, W.R. Evaluation of The Immunomodulatory in vivo Activity of Laminaria hyperborea Fucoidan Relative to Commercial (1,3/1,6)-Β-D-Glucans from Yeast and Mushrooms. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2015, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kopplin, G.; Rokstad, A.M.; Mélida, H.; Bulone, V.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Aachmann, F.L. Structural Characterization of Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea: Assessment of Coagulation and Inflammatory Properties and Their Structure-Function Relationship. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Kopplin, G.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Interaction of High-Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea with Natural Functions of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Jiménez-Escrig, A.; Rupérez, P. Molecular weight distribution of polysaccharides from edible seaweeds by high-performance size-exclusion chromatography (HPSEC). Talanta 2012, 93, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, H.R.; Biller, P.; Ross, A.B.; Adams, J. The seasonal variation of fucoidan within three species of brown macroalgae. Algal Res. 2017, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Moe, S.T. Biopolymer Chemistry; Tapir: Trondheim, Norway, 2008; ISBN 978-82-519-2384-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, L.; McClements, D.J.; Xu, X.; Liu, G.; Xue, C. Primary structure and chain conformation of fucoidan extracted from sea cucumber Holothuria tubulosa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podzimek, S. Light Scattering, Size Exclusion Chromatography and Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoai, N.T.; Sasaki, A.; Sasaki, M.; Kaga, H.; Kakuchi, T.; Satoh, T. Synthesis, characterization, and lectin recognition of hyperbranched polysaccharide obtained from 1,6-anhydro-D-hexofuranose. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klettner, A.; Kauppinen, A.; Blasiak, J.; Roider, J.; Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration: From impaired autophagy to neovascularization. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Apitz, S.; Hellige, I.; Neupane, S.; Alban, S.; Kopplin, G.; Ptak, S.; Fretté, X.; Roider, J.; Zille, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Effects of Fucoidans from Fucus Species and Laminaria hyperborea against Oxidative Stress and Iron-Dependent Cell Death. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Thalenhorst, T.; Seeba, C.; Tischhöfer, M.-T.; Neupane, S.; Roider, J.; Alban, S.; Klettner, A. Comparison of Fucoidans from Saccharina latissima Regarding Age-Related Macular Degeneration Relevant Pathomechanisms in Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.; Liew, G.; Gopinath, B.; Wong, T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2018, 392, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, H.; Wang, F. Roles of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance in Mechanisms of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Barrier and Retinal Disorders. Discov. Med. 2022, 34, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shirasawa, M.; Sonoda, S.; Terasaki, H.; Arimura, N.; Otsuka, H.; Yamashita, T.; Uchino, E.; Hisatomi, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Sakamoto, T. TNF-α disrupts morphologic and functional barrier properties of polarized retinal pigment epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 110, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Conley, S.M.; Naash, M.I. RPE65: Role in the visual cycle, human retinal disease, and gene therapy. Ophthalmic Genet. 2009, 30, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Tyrrell, J.; Han, I.; Jaffe, G.J. Expression and modulation of RPE cell membrane complement regulatory proteins. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Rasin, A.B.; Zueva, A.O.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Rubtsov, N.K.; Ermakova, S.P. Discovery of a fucoidan endo-4O-sulfatase: Regioselective 4O-desulfation of fucoidans and its effect on anticancer activity in vitro. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sichert, A.; Corzett, C.H.; Schechter, M.S.; Unfried, F.; Markert, S.; Becher, D.; Fernandez-Guerra, A.; Liebeke, M.; Schweder, T.; Polz, M.F.; et al. Verrucomicrobia use hundreds of enzymes to digest the algal polysaccharide fucoidan. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ai, C.; Wen, C.; Peng, H.; Yang, J.; Cui, Y.; Song, S. Inhibitory effects of fucoidan from Laminaria japonica against some pathogenic bacteria and SARS-CoV-2 depend on its large molecular weight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Kou, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Size-dependent whitening activity of enzyme-degraded fucoidan from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmana Senthil, S. A comprehensive review to assess the potential, health benefits and complications of fucoidan for developing as functional ingredient and nutraceutical. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahrsen, E.; Schoenfeld, A.-K.; Alban, S. Size-dependent pharmacological activities of differently degraded fucoidan fractions from Fucus vesiculosus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.A.R.; Coimbra, M.A. The antioxidant activity of polysaccharides: A structure-function relationship overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 314, 120965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klettner, A. Oxidative stress induced cellular signaling in RPE cells. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Eapen, M.S.; Ishaq, M.; Park, A.Y.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Stringer, D.N.; Sohal, S.S.; Fitton, J.H.; Guven, N.; Caruso, V.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Fucoidan Extracts In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Cong, Q.; Du, Z.; Liao, W.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Ding, K. Sulfated fucoidan FP08S2 inhibits lung cancer cell growth in vivo by disrupting angiogenesis via targeting VEGFR2/VEGF and blocking VEGFR2/Erk/VEGF signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 382, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dithmer, M.; Fuchs, S.; Shi, Y.; Schmidt, H.; Richert, E.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Fucoidan reduces secretion and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in the retinal pigment epithelium and reduces angiogenesis in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klettner, A.; Westhues, D.; Lassen, J.; Bartsch, S.; Roider, J. Regulation of constitutive vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in retinal pigment epithelium/choroid organ cultures: P38, nuclear factor κB, and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase pathway. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klettner, A.; Koinzer, S.; Meyer, T.; Roider, J. Toll-like receptor 3 activation in retinal pigment epithelium cells—Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways of cell death and vascular endothelial growth factor secretion. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013, 91, e211–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaide, R.F.; Vavvas, D.G. Complement Inhibition for Geographic Atrophy: Review of Salient Functional Outcomes and Perspective. Retina 2023, 43, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tang, F.Y.; Chu, W.K.; Young, A.L.; Brelen, M.E.; Pang, C.P.; Chen, L.J. Association of toll-like receptor 3 polymorphism rs3775291 with age-related macular degeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.-L.; Wu, K.-C.; Deng, W.-L.; Lei, X.-L.; Xiang, L.; Zhou, G.-H.; Feng, C.-Y.; Cheng, X.-W.; Zhang, C.-J.; Gu, F.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation Initiates Photoreceptor Cell Death In Vivo and In Vitro. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinman, M.E.; Kaneko, H.; Cho, W.G.; Dridi, S.; Fowler, B.J.; Blandford, A.D.; Albuquerque, R.J.C.; Hirano, Y.; Terasaki, H.; Kondo, M.; et al. Short-interfering RNAs induce retinal degeneration via TLR3 and IRF3. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Cruz, P.M.; Yasumura, D.; Weir, J.; Matthes, M.T.; Abderrahim, H.; LaVail, M.M.; Vollrath, D. Mutation of the receptor tyrosine kinase gene Mertk in the retinal dystrophic RCS rat. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audo, I.; Mohand-Said, S.; Boulanger-Scemama, E.; Zanlonghi, X.; Condroyer, C.; Démontant, V.; Boyard, F.; Antonio, A.; Méjécase, C.; El Shamieh, S.; et al. MERTK mutation update in inherited retinal diseases. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-M.; Ahn, C.; Kang, B.-T.; Kang, J.-H.; Jeung, E.-B.; Yang, M.-P. Fucoidan suppresses excessive phagocytic capacity of porcine peripheral blood polymorphonuclear cells by modulating production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hult, A.; Toss, F.; Malm, C.; Oldenborg, P.-A. In vitro phagocytosis of liquid-stored red blood cells requires serum and can be inhibited with fucoidan and dextran sulphate. Vox Sang. 2020, 115, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Hunger, F.; Schroth, H.; Chen, S.; Kopplin, G.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Effects of Fucoidans on Activated Retinal Microglia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irschick, E.U.; Sgonc, R.; Böck, G.; Wolf, H.; Fuchs, D.; Nussbaumer, W.; Göttinger, W.; Huemer, H.P. Retinal pigment epithelial phagocytosis and metabolism differ from those of macrophages. Ophthalmic Res. 2004, 36, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, K.; Neupane, S.; Bittkau, K.S.; Galarza Pérez, M.; Dörschmann, P.; Roider, J.; Alban, S.; Klettner, A. Effects of Crude Fucus distichus Subspecies evanescens Fucoidan Extract on Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells-Implications for Use in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieffrig, S.A.; Gyimesi, G.; Mao, Y.; Finnemann, S.C. Clearance phagocytosis by the retinal pigment epithelial during photoreceptor outer segment renewal: Molecular mechanisms and relation to retinal inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 319, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, G. Function of the protein RPE65 in the visual cycle. Nutr. Rev. 2005, 63, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miraldi Utz, V.; Coussa, R.G.; Antaki, F.; Traboulsi, E.I. Gene therapy for RPE65-related retinal disease. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekre, M.E.; Holmelid, B.; Underhaug, J.; Pedersen, B.; Kopplin, G.; Jordheim, M. Characterization of high value products in the side-stream of Laminaria hyperborea alginate production—Targeting the phenolic content. Algal Res. 2023, 72, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekre, M.E.; Hellesen Brunvoll, S.; Jordheim, M. Advancing quantification methods for polyphenols in brown seaweeds-applying a selective qNMR method compared with the TPC assay. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klettner, A.; Roider, J. Comparison of bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and pegaptanib in vitro: Efficiency and possible additional pathways. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4523–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Assay Guidance Manual: Cell Viability Assays; Eli Lilly & Co.: Bethesda, ML, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzolo, L.J. Barrier properties of cultured retinal pigment epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 126, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klettner, A.; Möhle, F.; Lucius, R.; Roider, J. Quantifying FITC-labeled latex beads opsonized with photoreceptor outer segment fragments: An easy and inexpensive method of investigating phagocytosis in retinal pigment epithelium cells. Ophthalmic Res. 2011, 46, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sugar | Fuc | Rha | Gal | Xyl | Man | GalA | ManA | GulA | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mol% | 91.59 | 1.32 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.44 | 1.60 | 1.95 | 1.86 | 0.53 |
| SD | 1.40 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.08 | – |
| Fucoidan | DS | Mw [kDa] | Mn [kDa] | PD | DPn | Rz [nm] | dn/dc | B | TPC [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FucBB04 | 0.95 | 3700 | 2500 | 1.48 | 10,300 | 249 | 0.115 | 0.44 | 0.0 |
| Bio Group Name | Target Name | Rq | Rq Min | Rq Max | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | IL6 | 1.649 | 0.305 | 8.916 | 0.661 |
| PIC | IL6 | 1.000 | 0.725 | 1.379 | 1.000 |
| FucBB04 | IL6 | 0.574 | 0.156 | 2.110 | 0.540 |
| FucBB04+PIC | IL6 | 0.603 | 0.157 | 2.321 | 0.586 |
| control | CXCL8 | 0.434 | 0.318 | 0.593 | 0.162 |
| PIC | CXCL8 | 1.000 | 0.498 | 2.007 | 1.000 |
| FucBB04 | CXCL8 | 0.872 | 0.411 | 1.852 | 0.829 |
| FucBB04+PIC | CXCL8 | 1.165 | 0.539 | 2.518 | 0.811 |
| Bio Group Name | Target Name | Rq | Rq Min | Rq Max | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | IL6 | 0.570 | 0.127 | 2.550 | 0.586 |
| PIC | IL6 | 1.000 | 0.694 | 1.442 | 1.000 |
| FucBB04 | IL6 | 1.671 | 1.393 | 2.006 | 0.120 |
| FucBB04+PIC | IL6 | 0.854 | 0.446 | 1.633 | 0.736 |
| control | CXCL8 | 0.270 | 0.242 | 0.301 | 0.134 |
| PIC | CXCL8 | 1.000 | 0.393 | 2.544 | 1.000 |
| FucBB04 | CXCL8 | 0.493 | 0.251 | 0.969 | 0.353 |
| FucBB04+PIC | CXCL8 | 1.847 | 0.326 | 10.475 | 0.627 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dörschmann, P.; Kopplin, G.; Thalenhorst, T.; Seeba, C.; Ullah, S.F.; Srivastava, V.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Influence of a Very High-Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea on Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Relevant Pathomechanisms in Ocular Cell Models. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030101
Dörschmann P, Kopplin G, Thalenhorst T, Seeba C, Ullah SF, Srivastava V, Roider J, Klettner A. Influence of a Very High-Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea on Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Relevant Pathomechanisms in Ocular Cell Models. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(3):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030101
Chicago/Turabian StyleDörschmann, Philipp, Georg Kopplin, Tabea Thalenhorst, Charlotte Seeba, Sadia Fida Ullah, Vaibhav Srivastava, Johann Roider, and Alexa Klettner. 2025. "Influence of a Very High-Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea on Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Relevant Pathomechanisms in Ocular Cell Models" Marine Drugs 23, no. 3: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030101
APA StyleDörschmann, P., Kopplin, G., Thalenhorst, T., Seeba, C., Ullah, S. F., Srivastava, V., Roider, J., & Klettner, A. (2025). Influence of a Very High-Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea on Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Relevant Pathomechanisms in Ocular Cell Models. Marine Drugs, 23(3), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030101









