First Confirmed Occurrence of Ciguatera Poisoning in the UK from Imported Pinjalo Snapper (Pinjalo pinjalo)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
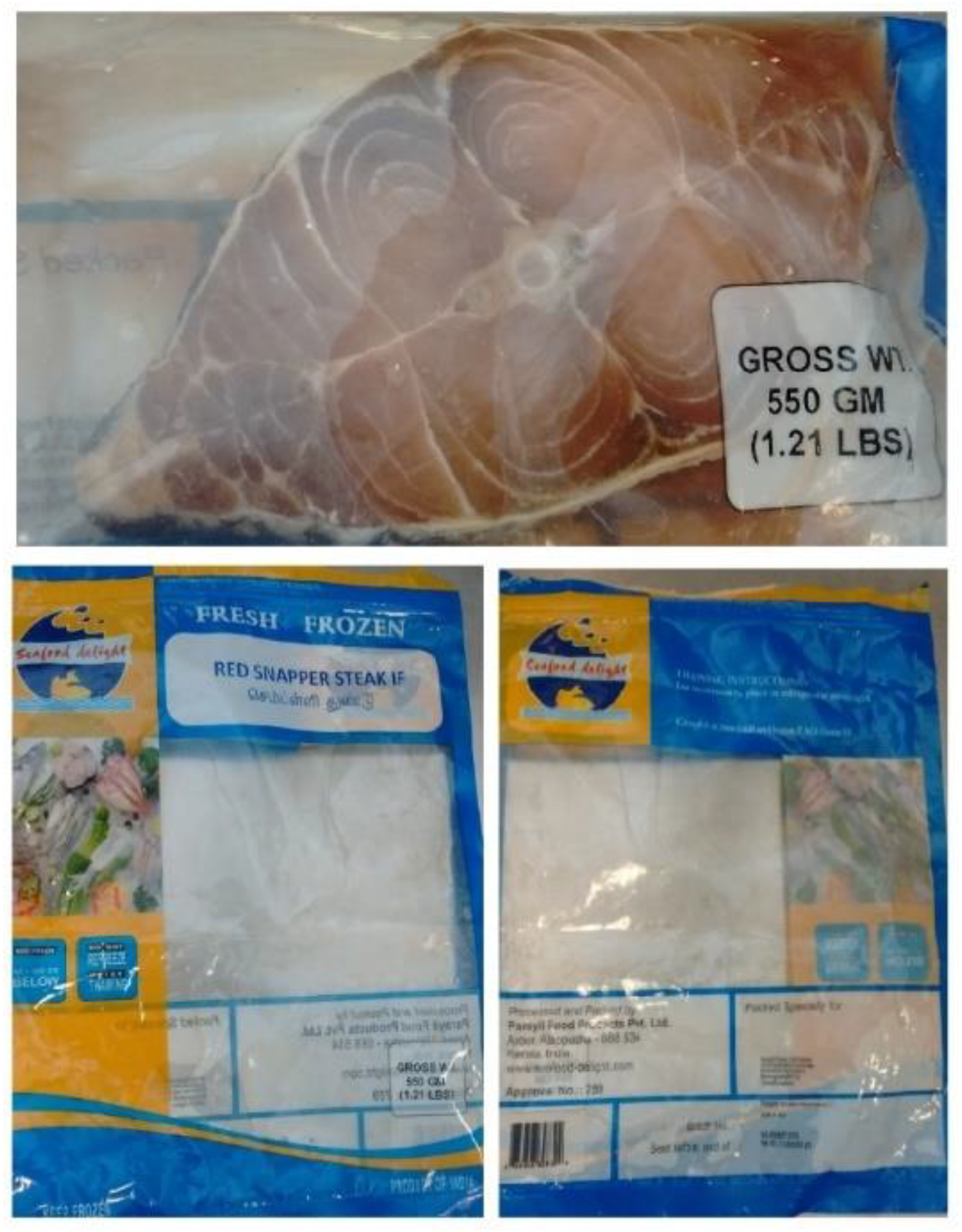
2.1. Fish Speciation
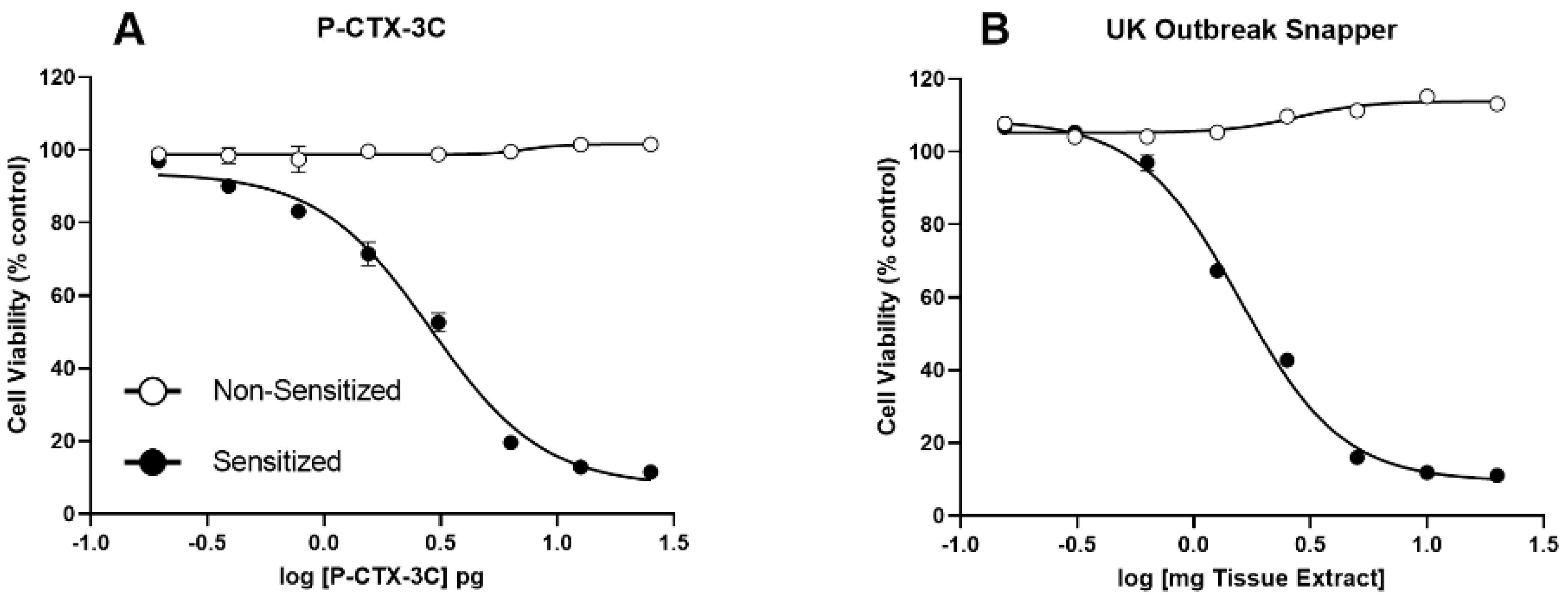
2.2. N2a-MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
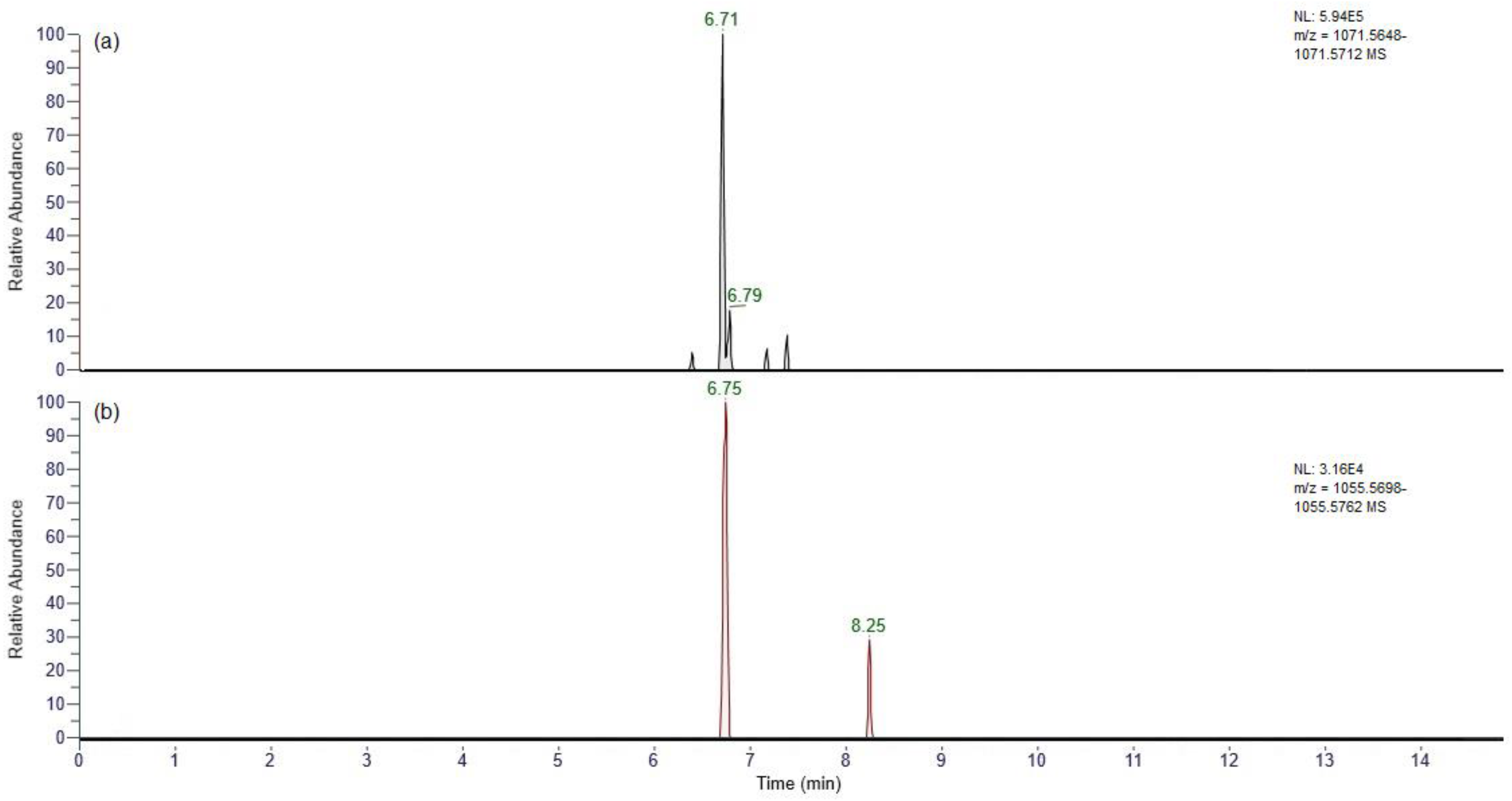
2.3. Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS)
2.3.1. Full Scan
2.3.2. Reaction with Periodate
2.4. Medical Observations
3. Discussion
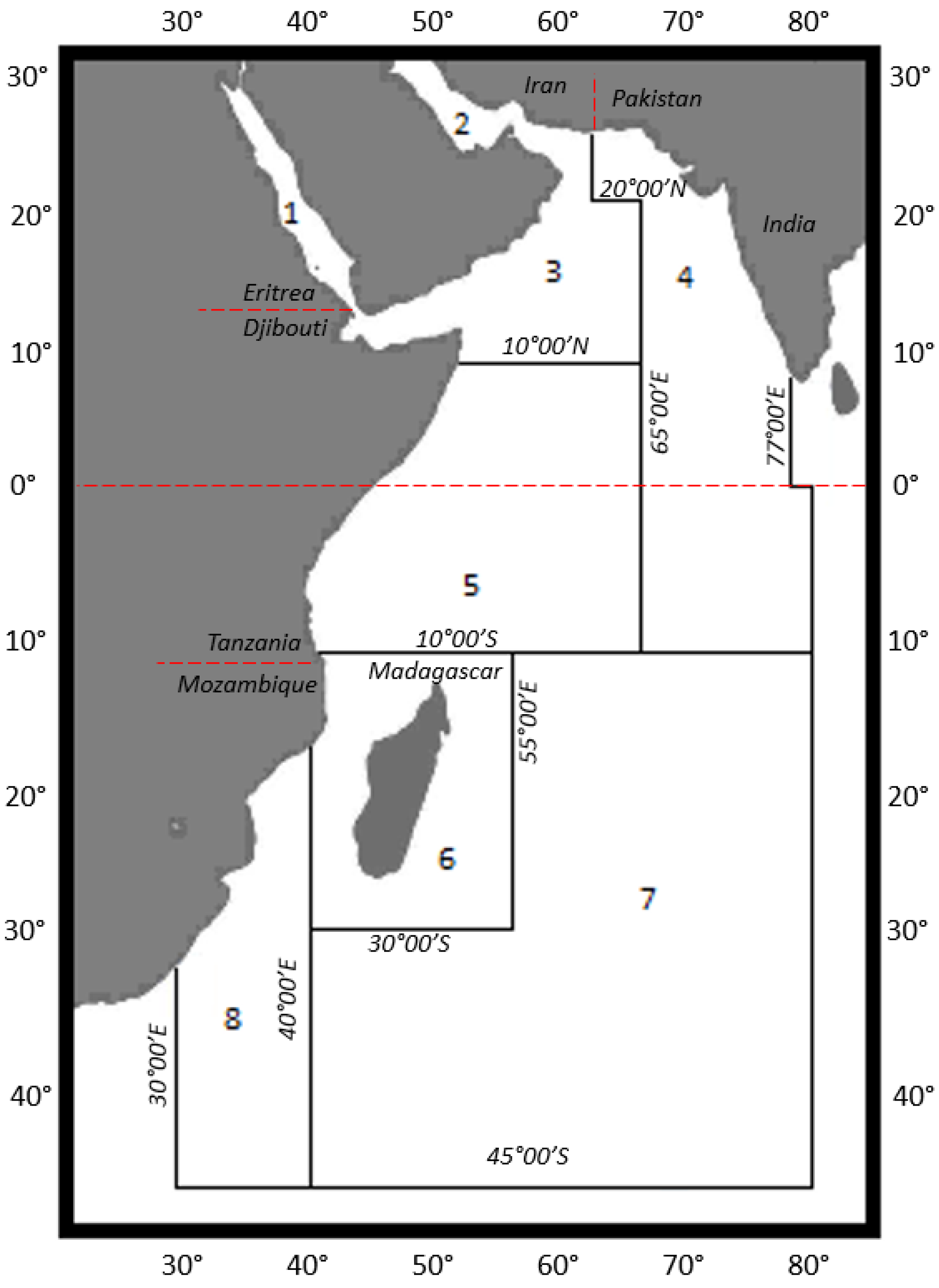
3.1. Location
3.2. Fish Species
3.3. Testing Methods
3.4. Fish Toxicity
3.5. UHPLC-HRMS Analysis
3.6. Symptoms and Overall Assessment
3.7. Legislation and Health Protection
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fish Speciation
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Fish Samples
4.4. Extraction Procedure for Cytotoxicity (N2a-MTT) Assay
4.5. N2a-MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
4.6. Full Scan UHPLC-HRMS
4.7. Periodate Oxidation
4.8. Medical Observations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC (Centre for Disease Control and Prevention). Ciguatera Fish Poisoning—Texas, 1998 and South Carolina, 2004. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. (MMWR) 2006, 55, 935–937. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, L.E.; Broad, K.; Clement, A.; Dewailly, E.; Elmir, S.; Knap, A.; Pomponi, S.A.; Smith, S.; Solo Gabriele, H.; Walsh, P. Oceans and human health: Emerging public health risks in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Darius, H.T.; Quod, J.-P.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning: Rome, 19–23 November 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Nakajima, I.; Bagnis, R.; Adachi, R. Finding of a dinoflagellate as a likely culprit of ciguatera. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1977, 43, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Structures of ciguatoxin and its congoner. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8929–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Fukui, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the moray eel Gymnothorax javanicus and its likely precursor from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Holmes, M.J. Origin and transfer of toxins involved in ciguatera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1993, 106, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.B.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P.; et al. An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: Clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikehara, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Yasumoto, T. Biooxidation of ciguatoxins leads to species-specific toxin profiles. Toxins 2017, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudge, E.M.; Robertson, A.; McCarron, P.; Miles, C.O. Selective and efficient capture and release of vic-diol-containing Pacific and Caribbean ciguatoxins from fish extracts with a boronate affinity polymer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12946–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, E.M.; Miles, C.O.; Ivanova, L.; Uhlig, S.; James, K.S.; Erdner, D.L.; Fæste, C.K.; McCarron, P.; Robertson, A. Algal ciguatoxin identified as source of ciguatera poisoning in the Caribbean. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, A.H.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sasaki, S.; Helfrich, P.; Alender, C.B. Observations on ciguatera-type toxin in fish. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1960, 90, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, A.H.; Helfrich, P.; Piyakarn, T. Retention of ciguatera toxin by red snapper Lutjanus bohar. Copeia 1966, 1966, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, L.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera: Recent advances but the risk remains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, R.W.; Plakas, S.M. Ciguatera: A public health perspective. Toxicon 2010, 56, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Faizuddin, M. Ciguatera in the Indian Ocean with special insights on the Arabian Sea and Adjacent Gulf and Seas: A review. Toxins 2021, 13, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Nagasawa, H.; Nishimura, M.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Ikehara, T.; Tachihara, K.; Yasumoto, T. Analytical studies on ciguateric fish in Okinawa, Japan (II): The Group Variola albimarginata. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roue, M.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z. Ability of giant clams to bioaccumulate ciguatoxins from Gambierdiscus cells. Harmful Algae News 2016, 55, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Mahana iti Gatti, C.; Vanderesa, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Tectus niolticus (Tegulidae, Gastropod) as a novel vector of ciguatera poisoning: Detection of Pacific ciguatoxins in toxic samples from Nuka Hiva Island (French Polynesia). Toxins 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Igarashi, T.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Chinain, M.; Fujita, T.; Naoki, H. Structural elucidation of ciguatoxin congeners by fast-atom bombardment tandem mass spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4988–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Jester EL, E.; Granade, H.R.; Plakas, S.M.; Dickey, R.W. Caribbean ciguatoxin profile in raw and cooked fish implicated in ciguatera. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fleming, L.E.; Fernandez, M.; Bienfang, P.; Schrank, K.; Dickey, R.; Bottein, M.-Y.; Backer, L.; Ayyar, R.; Weisman, R.; et al. Ciguatera fish poisoning: Treatment, prevention and management. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 456–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Tomikawa, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Ishikawa, A.; Toyofuku, H.; Kojima, T.; Asakura, H. LC–MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing the Regional and Species Distinction of Fish in the Tropical Western Pacific. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Tomikawa, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Kimura, K.; Kojima, T.; Yasumoto, T.; Asakura, H. Detection of Ciguatoxins from Fish Introduced into a Wholesale Market in Japan. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. (Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi) 2021, 62, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fouw, J.C.; van Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: A Review; RIVM Report 388802 021; RIVM: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.P.; Lewis, R. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean Islands and Western Atlantic. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 168, 99–141. [Google Scholar]
- Pottier, I.; Hamilton, B.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.P. Identification of slow and fast-acting toxins in a highly ciguatoxic barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and radiolabelled ligand binding. Toxicon 2003, 42, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Hung, P.; Lee, K.L.H.; Kam, K.-M. Study of an outbreak of ciguatera fish poisoning in Hong 272 Kong. Toxicon 2005, 46, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, F.; Bourrat, M.; Pauillac, S. Prevalence, symptoms and chronicity of ciguatera in New Caledonia: Results from an adult population survey conducted in Noumea during 2005. Toxicon 2010, 56, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, A.; de la Iglesia, P.; Darius, H.T.; Pauillac, S.; Aligizaki, K.; Fraga, S.; Chinain, M.; Diogene, J. Update on methodologies available for ciguatoxin determination: Perspectives to confront the onset of ciguatera fish poisoning in Europe. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1838–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Vernoux, J.P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterisation of Indian Ocean ciguatoxin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Multiple ciguatoxins present in Indian Ocean reef fish. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B.; Whittle, N.; Shawc, G.; Eaglesham, G.; Moore, M.R.; Lewis, R.J. Human fatality associated with Pacific ciguatoxin contaminated fish. Toxicon 2010, 56, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucaud-Maitre, D.; Vernoux, J.P.; Pelczar, S.; Daudens-Vaysse, E.; Aubert, L.; Boa, S.; Ferracci, S.; Garnier, R. Incidence and clinical characteristics of ciguatera fish poisoning in Guadeloupe (French West Indies) 275 between 2013 and 2016: A retrospective cases-series. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubaro, A.; Sosa, S.; Hungerford, J. Toxicology and diversity of marine toxins. In: Veterinary Toxicology: Basic and Clinical Principles. Ed: R.C. Gupta, Elsevier. Chp 2012, 69, 896–936. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontisjavanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC regulation no 625/2017 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 March 2017 Amending EC Regulation 854/2004 Laying down Specific Rules for the Organisation of Official Controls on Products of Animal Origin Intended for Human Consumption. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2017/625/oj/eng (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Perez-Arellano, J.L.; Luzardo, O.P.; Brito, A.P.; Cabrera, M.H.; Zumbado, M.; Carranza, C.; Angel-Moreno, A.; Dickey, R.W.; Boada, L.D. Ciguatera fish poisoning, Canary Islands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1981–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Nikolaidis, G. Morphological identification of two tropical dinoflagellates of the genera Gambierdiscus and Sinophysis in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Biol. Res. Thessalon. 2008, 9, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Aligizaki, K.; Nikolaidis, G.; Fraga, S. Is Gambierdiscus expanding to new areas? Harmful Algae News 2008, 36, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Pequeno-Valrierra, A.; Leao, J.M.; Vilarino, O.; Diogene, J.; Gago-Martinez, A. An attempt to characterise the ciguatoxin profile in Seriola fasciata causing ciguatera fish poisoning in Macaronesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Leao, J.M.; Yasumoto, T.; Dickey, R.; Gago-Martinez, A. Implementation of liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of ciguatera fish poisoning in contaminated fish samples from Atlantic coasts. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leao-Martins, J.M.; Costa, P.R.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Hess, P. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for the Confirmation of Caribbean Ciguatoxin-1 as the Main Toxin Responsible for Ciguatera Poisoning Caused by Fish from European Atlantic Coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Prieto, J.O.; Burlingame, A.; Gago-Martinez, A. Characterisation of the ciguatoxin profile in fish samples from the Eastern Atlantic Ocean using Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.R.; Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Soliño, L.; Gouveia, N.; Santos, C.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Leao, J.M.; Gago-Martínez, A. New Insights into the Occurrence and Toxin Profile of Ciguatoxins in Selvagens Islands (Madeira, Portugal). Toxins 2018, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Riobo, P.; Diogene, J.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M. Toxic and potentially toxic benthic dinoflagellates observed in Macaronesia (NE Atlantic Archipelago). In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Cape Town, South Africa, 15–19 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, S.; Rodriguez, F.; Caillaud, A.; Diogene, J.; Raho, N.; Zapata, M. Gambierdiscus exectricus sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a benthic toxic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boada, L.D.; Zumbado, M.; Luzardo, O.R.; Almeida-Gonzalez, M.; Plakas, S.M.; Granade, H.R.; Abraham, A.; Jester, E.L.E.; Dickey, R.W. Ciguatera fish poisoning on the West Africa Coast: An emerging risk in the Canary Islands (Spain). Toxicon 2010, 56, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Pérez, S.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, C.; Rodríguez, P.; Gouveia, N.N.; Gouveia, N.; Delgado, J.; Vale, P.; Hirama, M.; et al. First toxin profile of ciguateric fish in Madeira Arquipelago (Europe). Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6032–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, B.M.; Rawert, B.; Henning, B.; Zidek, W. Ciguatera fish poisoning following travel to the tropics. Z. Fur Gastroenterol. 1997, 35, 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Marine Biotoxins; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004; Volume 80, pp. 1–287. [Google Scholar]
- Mattei, C.; Vetter, I.; Eisenblätter, A.; Krock, B.; Ebbecke, M.; Desel, H.; Zimmermann, K. Ciguatera fish poisoning: A first epidemic in Germany highlights an increasing risk for European countries. Toxicon 2014, 91, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedemann, M. Erster Ciguatera-Ausbruch in Deutschland 2012. Bundesgesundheitsblatt-Gesundheitsforschung-Gesundheitsschutz 2016, 59, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedemann, M. Ciguatera fish poisoning outbreaks from 2012 to 2017 in Germany caused by snappers from India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2019, 14, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Spielmeyer, A.; Friedemann, M.; Kapp, K.; Schwank, U.; Kappenstein, O.; Bodi, D. Food safety risk in Germany from mislabeled imported fish: Ciguatera outbreak trace-back, toxin elucidation, and public health implications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 849857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, H.V.; Uesugi, A.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, R.; Matsushima, R.; Lim, Z.F.; Jipanin, S.J.; Pham, K.X.; Phan, M.-T.; Leaw, C.P.; et al. Identification of fish species and toxins implicated in a snapper food poisoning event in Sabah, Malaysia, 2017. Toxins 2021, 13, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T. Fish poisoning due to toxins of microalgal origins in the Pacific. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turquet, J.; Quod, J.P.; Pannetier, S.; Ramialiharisoa, A.; Ranaivoson, G.; Hurbungs, M.; Jeannoda, V. Manuel Méthodologique. Suivi et Prévention des Intoxications par Consommation d’Animaux Marins dans le Sud-Ouest de l’Océan Indien; Réalisé par ARVAM pour le compte de Commission de l’océan Indien: Quatbon, Mauritius, 2000; 50 p, ISBN 99903-71-01-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gatti, C.; Oelher, E.; Legrand, A.M. Severe seafood poisoning in French Polynesia: A retrospective analysis of 129 medical files. Toxicon 2008, 51, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contamination of Sharks, Especially Tiger and Bull Sharks, by Ciguatoxins: Occurrence, Analytical Methods, Human Cases REPORTED and Ethological Information; ANSES Opinion, Collective Expert Appraisal Report. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296282697 (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Diogene, J.; Reverte, L.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; del Rio, V.; de la Islesia, P.; Campas, M.; Palacios, O.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Ralijaona, C.; et al. Identification of ciguatoins in a shark involved in a fatal food poisoning in the Indian Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8240. [Google Scholar]
- Quod, J.P.; Turqet, J. Ciguatera in Reunion Island (SW Indian Ocean): Epidemiology and clinical patterns. Toxicon 1995, 34, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajisha, R.; Kishore, P.; Panda, S.K.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Kumar, K.A. Confirmation of ciguatoxin fish poisoning in red snapper Lutjanus bohar (Forsskal, 1775) by mouse bioassay. Fish. Technol. 2017, 54, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Karunasagar, I.; Turner, A.D.; Maskrey, B.; Robertson, A.; Shivanagouda Hosagoudar, S.; Rai, P.; Adappa, S.; Hiremath, S.; Kogaluru Shivakumaraswamy, S.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.Y.; et al. Report of a major outbreak of ciguatera fish poisoning in Mangalore, India. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; p. 482. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, R.; Jester, E.; Granade, R.; Mowdy, D.; Moncreiff, C.; Rebarchik, D.; Robl, M.; Musser, S.; Poli, M. Monitoring brevetoxins during a gymnodinium breve red tide: Comparison of sodium channel specific cytotoxicity assay and mouse bioassay for determination of neurotoxic shellfish toxins in shellfish extracts. Nat. Tox. 1999, 7, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Hokama, Y.; Dickey, R.W.; Granade, H.R.; Lewis, R.; Yasumoto, T.; Wekell, M.M. Detection of sodium channel toxins: Directed cytotoxicity assays of purified ciguatoxins, brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and seafood extracts. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechraoui, M.Y.; Tiedeken, J.A.; Persad, R.; Wang, Z.; Granade, H.R.; Dickey, R.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Use of two detection methods to discriminate ciguatoxins from brevetoxins: Application to great barracuda from Florida Keys. Toxicon 2005, 46, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS analysis of ciguatoxins revealing distinct regional and species characteristics in fish and causative alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Sakugawa, S.; Oshiro, N.; Ikehara, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of Toxins Involved in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in the Pacific by LC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USFDA. Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, Fourth Edition. August 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/seafood-guidance-documents-regulatory-information/fish-and-fishery-products-hazards-and-controls-guidance (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Bennett, C.T.; Robertson, A.; Patterson, W.F., III. First record of the non-indigenous Indo-Pacific damselfish, Neopomacentrus cyanomos (Bleeker, 1856) in the northern Gulf of Mexico. BioInvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.M.; Deeds, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hebert, P.D.; Hanner, R.H.; Ormos, A.; Weigt, L.A.; Moore, M.M.; Yancy, H.F. A single-laboratory validated method for the generation of DNA barcodes for the identification of fish for regulatory compliance. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Herbert, P.D.N. Universal primer cocktails for fish DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.; Innes, B.H.; Herbert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. B 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryuchkov, F.; Robertson, A.; Miles, C.O.; Uhlig, S. LC-HRMS and chemical derivatization strategies for the structure elucidation of Caribbean ciguatoxins: Identification of C-CTX-3 and -4. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). FAO Major Fishing Areas, Indian Ocean, Western. FAO, Fisheries and Aquaculture Department. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/area/Area51/en (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Boisier, P.; Ranaivoson, G.; Rosolofonirina, N.; Andriamahefazafy, B.; Roux, J.; Chanteau, S.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Fatal mass poisoning in Madagascar following ingestion of a shark (Carcharhinus leucas): Clinical and epidemiological aspects and isolation of toxins. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D. Observations on fish poisoning in Mauritius. Proc. R. Soc. Arts. Sci. Mauritius 1956, 1, 367–385. [Google Scholar]
- Rajisha, R.; Kishore, P.; Panda, S.K.; Harikrishnan, G.; Ajitha, K.C.; Suresh, M.K.; Chowdhury, L.M.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Ashok Kumar, K. Incidence of ciguatoxin fish poisoning in Trivandrum, India. Indian J. Fish 2017, 64, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajisha, R.; Kishore, P.; Panda, S.K.; Jumar, K.A. Ciguatoxin—An emerging biological hazard among reef fishes of India. Fish. Technol. 2018, 55, 153–167. [Google Scholar]
- RASFF. Ciguatera Poisoning Reports Relating to Fish Originating from India. European Commission RASFF Portal. 2016. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/portal/?event=searchResultList (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Loeffler, C.R.; Tartaglione, L.; Friedemann, M.; Spielmeyer, A.; Kappenstein, O.; Bodi, D. Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmeyer, A.; Loeffler, C.R.; Bodi, D. Extraction and LC-MS/MS analysis of ciguatoxins: A semi-targeted approach designed for fish of unknown origin. Toxins 2021, 13, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.E.; Allen, G.R.; Anderson, W.D., Jr. Revision of the Indo-Pacific lutjanid genus Pinjalo, with description of a new species. Indo-Pac. Fish 1987, 14, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.R.; Erdmann, M.W. Reef fishes of the East Indies; Tropical Reef Research; University of Hawaii Press: Perth, Australia, 2012; Volume I–III. [Google Scholar]
- Assadi, H.; Dehghani, R.P. Atlas of the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman Fishes; Iranian Fisheries Research and Training Organization: Tehran, Iran, 1997; ISBN 964-5513-15-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, C.; Schneider, W.; Poutiers, J.M. FAO species identification field guide for fishery purposes. In The Living Marine Resources of Somalia; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996; 376p, Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/010/v8730e/v8730e00.htm (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Yasumoto, T.; Satake, M.; Fukui, M.; Nagai, H.; Murata, M.; LeGrand, A.-M. A turning point in ciguatera study. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayada, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Ha, D.V.; Uesugi, A.; Uchida, H. Analytical challenges to ciguatoxins. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Satake, M. Chemistry, etiology and determination methods of Ciguatera Toxins. J. Toxicol. Toxins Rev. 1996, 15, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoux, J.P. The mouse ciguatoxin bioassay: Directions for use to control fish for consumption. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 625–629. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Raj, U.; Bagnis, R. Seafood Poisoning in Tropical Regions; Laboratory of Food Hygiene, Faculty of Agriculture, Tohoku University: Miyagi, Japan, 1984; 74p. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Street, R.; Holmes, M.J.; Gillespie, N.C. Excretion of ciguatoxin from moray eel (Muraenidae) of the central Pacific. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Ciguatera Fish Poisoning, La Parguera, Puerto Rico, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 30 April–5 May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lombet, A.; Bidard, J.N.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin and brevetoxins share a common receptor site on the neuronal voltage-dependent Na channel. FEBS Lett. 1987, 219, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, M.; Lewis, R.; Dickey, R.; Musser, S.; Buckner, C.; Carpenter, L. Identification of Caribbean ciguatoxins as the cause of an outbreak of fish poisoning among U.S. soldiers in Haiti. Toxicon 1997, 35, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Wekell, M.M. Tetrazolium-based cell bioassay for neurotoxins active on voltage- sensitive sodium channels: Semiautomated assay for saxitoxin, brevetoxin, and ciguatoxin. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 214, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A.; Vernoux, J.P. HPLC/tandem electrospray mass spectrometry for the determination of sub-ppb levels of Pacific and Caribbean ciguatoxins in crude extracts of fish. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darius, H.T.; Ponton, D.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Ung, A.; Tchou Fouc, M.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera risk assessment in two toxic sites of French Polynesia using the receptor-binding assay. Toxicon 2007, 50, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Yang, A.J.; Jones, A. Rapid extraction combined with LC-tandem mass spectrometry (CREM-LC/MS/MS) for the determination of ciguatoxins in ciguateric fish flesh. Toxicon 2009, 54, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Martinez, A.; Leao, J.M.; Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Barrios, C.; Hess, P.; Sibat, M. Characterisation of ciguatoxins. EFSA external scientific report. EFSA Support. Publ. 2021, 18, 6649E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, R.W. Ciguatera toxins: Chemistry, toxicology, and detection. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 479–500. [Google Scholar]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Sato, T.; Hirama, M.; Fujii, I. Highly sensitive and practical fluorescence sandwich ELISA for ciguatoxins. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7318–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Robertson, A.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Silander, M.C.; Smith, T.B.; Olsen, D. Ciguatoxin prevalence in four commercial fish species along an oceanic gradient in the US Virgin Islands. Env. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.; Garcia, A.C.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Smith, T.B.; Castillo, B.F.; Reale-Munroe, K.; Gulli, J.A.; Olsen, D.A.; Hooe-Rollman, J.I.; Jester, E.L.E.; et al. Invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans): A potential human health threat for ciguatera fish poisoning in tropical waters. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Bogdanoff, A.K.; Morris, J.A.; Quintana, H.A.F.; Loeffler, C.R.; et al. Investigation of ciguatoxins in invasive lionfish from the greater Caribbean region: Implications for fishery development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreiras, G.; Leao, J.M.; Gago-Martinez, A. Design of experiments for the optimisation of electrospray ionisation in the LC-MS/MS analysis of ciguatoxins. J. Mass Spec. 2018, 53, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, N.; Stavinsky, F.; Hoffman, R.; Button, J.; Clark, N.; Martin, S.; Robertson, A.; Hustedt, J. Ciguatera fish poisoning- New York City, 2010-2011. Morb Mort. Wkly Rep. 2013, 62, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, E.G.; Grattan, L.M.; Cook, R.L.; Smith, T.B.; Anderson, D.M.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Ciguatera incidence in the US Virgin Islands has not increased over a 30-year time period despite rising seawater temperatures. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Darius, H.T.; Rou’e, M.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Detection of pacific ciguatoxins using liquid chromatography coupled to either low or high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudó, A.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Flores, C.; Sagristà, N.; Aguayo, P.; Reverte, L.; Campas, M.; Gouveia, N.; Santos, C.; Andree, K.B.; et al. Identification of New CTX Analogues in Fish from the Madeira and Selvagens Archipelagos by Neuro-2a CBA and LC-HRMS. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.Y. Characteristic features and contributory factors in fatal ciguatera fish poisoning-implications for prevention and public education. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Berti, M.; Milandri, A.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G. Marine Biotoxins: Occurrence, Toxicity, Regulatory Limits and Reference Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R.; Kuberski, T.; Laugier, S. Clinical observations on 3009 cases of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in the South Pacific. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, G.M.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatoxins: Cyclic polyether modulators of voltage-gated ion channel function. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 82–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, R.A.; Morgan, S.S. Poisoning, envenomation and trauma from marine creatures. Am. Fam. Physician 2004, 69, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumaran, S.; Balamurgan, N.; Suresh, P.; Thirumalaikolundusubramanian, P. Painful ejaculation, Something fishy. Saudi. Med. J. 2010, 31, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anon. EC regulation no 853/2004 of the European parliament and of the council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific rules for the organisation of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption. Off. J. Eur. Union 2003, L139/55. [Google Scholar]
- USFDA. Guidance for Industry: Purchasing Reef Fish Species Associated with the Hazard of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning; USFDA Guidance; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013.
- Hossen, V.; Solino, L.; Leroy, P.; David, E.; Velge, P.; Dragacci, S.; Krys, S.; Flores Quintana, H.; Diogene, J. Contribution to the risk characterization of ciguatoxins: LOAEL estimated from eight ciguatera fish poisoning events in Guadeloupe (French West Indies). Env. Res. 2015, 143, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmeyer, A.; Loeffler, C.R.; Kappenstein, O. Identical Ciguatoxin-3C group profiles in Lutjanus bohar from the Pacific and Indian Oceans—indicating the need to re-evaluate geographical CTX classifications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 937438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, A.H.; Eckalbar, W.L.; Kreimer, A.; Yosef, N.; Ahituv, N. Use antibiotics in cell culture with caution: Genome-wide identification of antibiotic-induced changes in gene expression and regulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiong, T.; Meng, X.; Yu, D.; Xiao, Z.; Song, L. Different influences on mitochondrial function, oxidative stress and cytotoxicity of antibiotics on primary human neuron and cell lines. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 33, e22277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T. Development of an LC-MS/MS method to simultaneously monitor maitotoxins and selected ciguatoxins in algal cultures and P-CTX-1B in fish. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; Boundy, M.J.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M. Single laboratory validation of a LC-MS/MS method for quantitation of Tetrodotoxins in mussels and oysters. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Fong, S.Y.T.; Hungerford, J.; McNabb, P.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, T. Ultra-high performance hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxin in mussels, oysters, clams, cockles and scallops: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CTX3C Congener | Formula | Ion | Theoretical m/z | Observed m/z | Mass Error (ppm) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,3,51-trihydroxy-CTX-3C | C57H84O19 | [M + H]+ | 1073.5680 | 1073.5663 | −1.58 | 6.84 |
| 2,3,51-trihydroxy-CTX-3C | C57H84O19 | [M + Na]+ | 1095.5499 | 1095.5507 | −0.73 | 6.84 |
| 2,3-dihydroxy-CTX-3C | C57H84O18 | [M + H]+ | 1057.5730 | 1057.5747 | 1.61 | 7.59 |
| 51-hydroxy-CTX-3C | C57H82O17 | [M + H]+ | 1039.5625 | 1039.5602 | −2.21 | 8.61 |
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Admission date | 22 June 2017 | 22 June 2017 | 23 June 2017 |
| Discharge date | 24 June 2017 | 24 June 2017 | Not recorded |
| Sex | Female | Female | Female |
| Year of birth | 1996 | 1972 | 2003 |
| Presenting complaint | Vomiting, myalgia | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, myalgia | Pain in the right shin |
| Allergies | None known | None known | None known |
| Co-morbidities | Asthma | Hypertension | None known |
| post-discharge | Food poisoning: likely/potential ciguatera poisoning | Food poisoning: likely/potential ciguatera poisoning | Ciguatera poisoning: non-specific pains |
| Additional analyses conducted | Full blood count (FBC), urea and electrolytes (U&E), liver function test (LFT) = normal | FBC, U&E, LFT: No apparent disorder | U&E: Urea 2.3 mmol/L, Creatinine 50 µmol/L, Sodium 142 mEq/L, Potassium 3.4 mmol/L |
| Creatinine kinase = normal | Electrocardiogram: No apparent distress | ||
| C-Reactive Protein 8.7 mg/L = mild elevation | |||
| Procedures | Ward based care | Ward based care | Blood taken for analysis. |
| Intravenous fluid infusion | Intravenous fluid infusion | ||
| Post-discharge medications | Paracetamol, codeine | Chlorphenamine, ibuprofen | None |
| Follow up | No | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turner, A.D.; Maskrey, B.H.; Stone, D.; Mudge, E.M.; Robertson, A. First Confirmed Occurrence of Ciguatera Poisoning in the UK from Imported Pinjalo Snapper (Pinjalo pinjalo). Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020067
Turner AD, Maskrey BH, Stone D, Mudge EM, Robertson A. First Confirmed Occurrence of Ciguatera Poisoning in the UK from Imported Pinjalo Snapper (Pinjalo pinjalo). Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(2):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurner, Andrew D., Benjamin H. Maskrey, David Stone, Elizabeth M. Mudge, and Alison Robertson. 2025. "First Confirmed Occurrence of Ciguatera Poisoning in the UK from Imported Pinjalo Snapper (Pinjalo pinjalo)" Marine Drugs 23, no. 2: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020067
APA StyleTurner, A. D., Maskrey, B. H., Stone, D., Mudge, E. M., & Robertson, A. (2025). First Confirmed Occurrence of Ciguatera Poisoning in the UK from Imported Pinjalo Snapper (Pinjalo pinjalo). Marine Drugs, 23(2), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020067






