Components and Biological Activities of Venom from Lionfishes (Scorpaenidae: Pterois)
Abstract
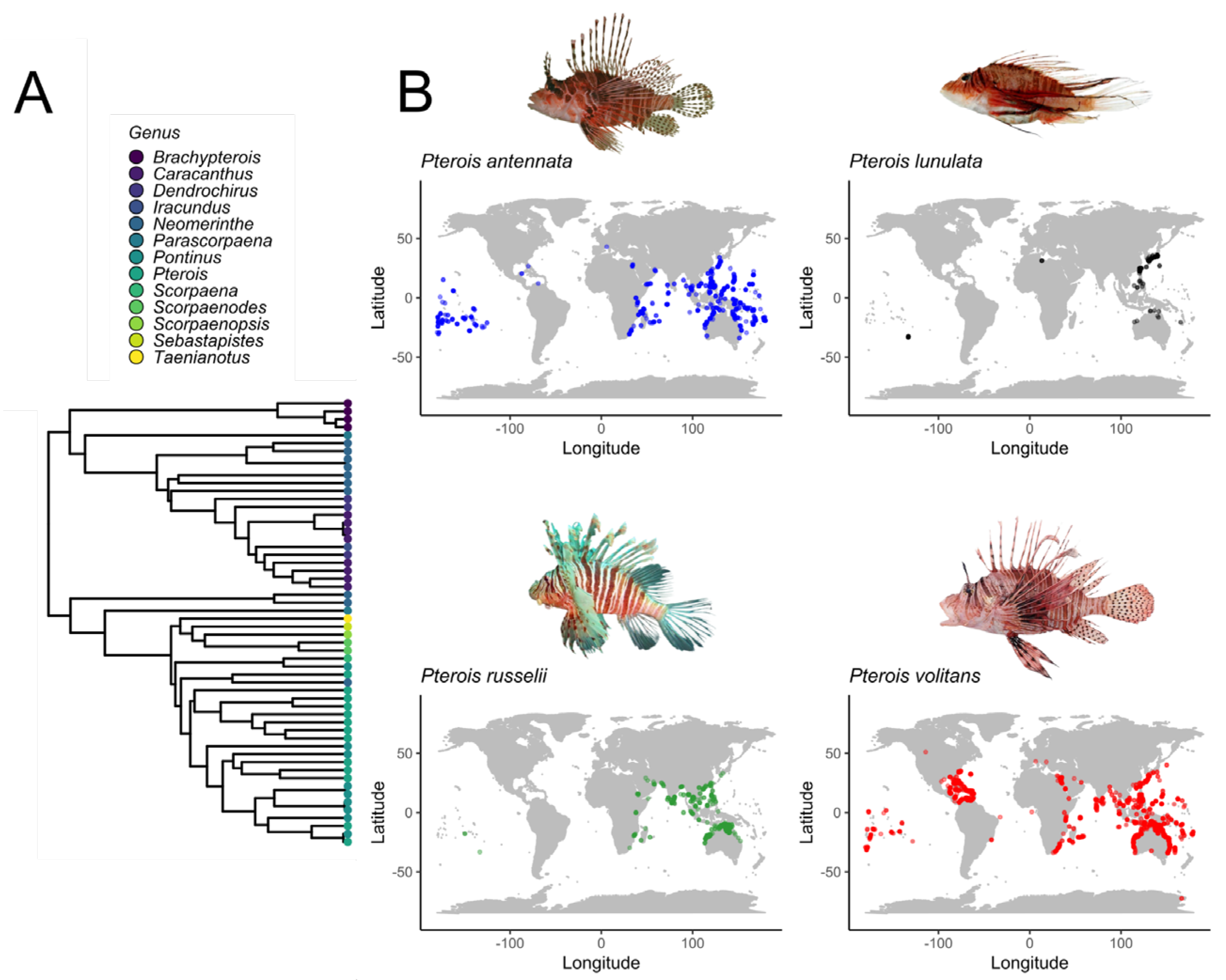
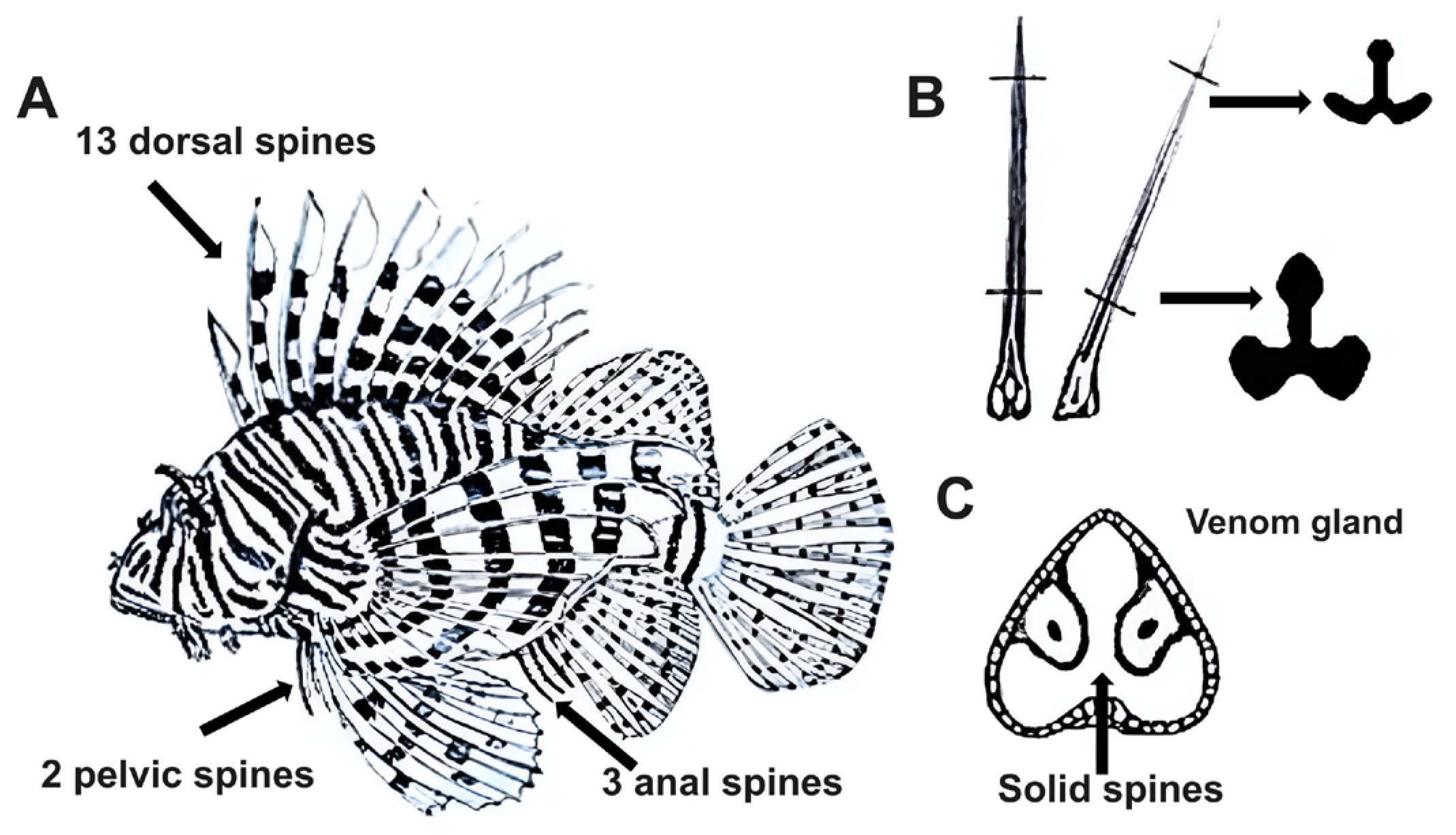
1. Introduction
2. Crude Preparation, Fractionation, and Chemical Components from Pterois Venom
2.1. Peptides
2.2. Enzymes
3. Biological Activities of Pterois Venom
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity
3.2. Anticancer Activity
3.3. Antioxidant Activity
3.4. Antiviral Activity
3.5. Cardiovascular Activity
3.6. Coagulant Activity
3.7. Neurological and Neuromuscular Activity
3.8. Nutraceutical Activity
| MM (kDa) | Identification d | Lionfish | Biological Activity e | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.6 | MS | P. volitans | anticancer | [56] |
| 7.9 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticancer, antioxidant | [34] |
| 14.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticholinergic | [69] |
| 14.2 | SEC | P. volitans | * | [80] |
| 15.7 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticholinergic | [69] |
| 19.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [42] |
| 26.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [27] |
| 29.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticancer, cardioactive | [26] |
| 32.0 | SE | P. volitans | hemorrhagic | [80] |
| 33.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticancer | [56] |
| 35.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | * | [69] |
| 39.2 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticholinergic | [69] |
| 45.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | cardioactive, protease | [26,27] |
| 46.2 | PAGE | P. volitans | antioxidant | [34] |
| 49.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticancer | [56] |
| 52.7 | PAGE | P. volitans | antioxidant | [34] |
| 53.3 a | DNA Cloning | P. antennata, P. volitans | hyaluronidase | [41] |
| 60.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [27] |
| 65.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticancer | [56] |
| 66.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | cardioactive | [26] |
| 73.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [27] |
| 75.0 b | PAGE | P. volitans | hemolytic, hyaluronidase | [27,69,78] |
| 80.0 c | PAGE | P. volitans, P. lunnulata | protease | [27] |
| 85.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | antibiotic, anticancer, antiviral, phospholipase | [32,33,56,61] |
| 90.6 | PAGE | P. volitans | * | [69] |
| 97.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | cardioactive | [26,69] |
| 100.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [27] |
| 110.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | anticancer | [32] |
| 111.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [27] |
| 116.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | cardioactive | [26] |
| 153.5 a | DNA cloning | P. antennata, P. volitans | * | [78] |
| 160.0 | SE | P. lunnulata | hemolytic | [81] |
| 200.0 | PAGE | P. volitans | protease | [27] |
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
5. Recommendations
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holford, M.; Daly, M.; King, G.; Norton, R.S. Venoms to Rescue. Science 2018, 361, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L.; Wheeler, W.C. Venom Evolution Widespread in Fishes: A Phylogenetic Road Map for the Bioprospecting of Piscine Venoms. J. Hered. 2006, 97, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F.A.; Fuentes, T.F.; Alonso, I.P.; Bosch, R.A.; Brunetti, A.E.; Lopes, N.P. A comprehensive of patented antimicrobial peptides from amphibian anurans. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.W.; Stern, J.H.; Girard, M.G.; Davis, M.P. Evolution of Venomous Cartilaginous and Ray-Finned Fishes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jared, C.; Mailho-Fontana, P.L.; Antoniazzi, M.M. Differences between poison and venom: An attempt at an integrative biological approach. Acta Zool. 2021, 102, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelsen, D.R.; Nisani, Z.; Cooper, A.M.; Fox, G.A.; Gren, E.C.K.; Corbit, A.G.; Hayes, W.K. Poisons, Toxungens, and Venoms: Redefining and Classifying Toxic Biological Secretions and the Organisms that Employ Them. Biol. Rev. 2014, 89, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, J.; Díaz-Ferguson, E.; Silliman, B.; Saunders, J.; Buddo, D.; Hunter, M. Range-Wide phylogenetic structure of invasive red Lionfish, Pterois volitans, reveals two regional clusters. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ferguson, E.; Hunter, M. Life history, genetics, range expansion and new frontiers of Pterois volitans (Perciformes: Pteroidae) in Latin America. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 31, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.; Beaver, C.; Johnson, N.; Bors, E.; Mignucci-Giannoni, A.; Buddo, D.; Searl, L.; Díaz-Ferguson, E. Genetic analysis of Red Lionfish (Pterois volitans) from Florida, USA, leads to alternative North Atlantic introduction scenarios. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 675, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, M.; Green, S.; Albins, M.; Akins, J.; Morris, J. Lionfish: A major marine invasion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 558, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabosky, D.L.; Chang, J.; Title, P.O.; Cowman, P.F.; Sallan, L.; Friedman, M.; Kaschner, K.; Garilao, C.; Near, T.J.; Coll, M.; et al. An inverse latitudinal gradient in speciation rate for marine fishes. Nature 2018, 559, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, K.A.; Porter, M.E. Mechanical Properties of the Venomous Spines of Pterois volitans and Morphology among Lionfish Species. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb197905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halstead, B.W.; Chitwood, M.J.; Modglin, F.R. The Anatomy of the Venom Apparatus of the Zebrafish, Pterois volitans (Linnaeus). Anat. Rec. 1955, 122, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prithiviraj, N.; Annadurai, D.; Kumaresan, S. Lenght-weight relationship of lionfish Pterois mombasae (Smith, 1957) and spine used as biomedical agent from Parangipettai coast, Tamilnadu, India. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Resiere, D.; Cerland, L.; De Haro, L.; Valentino, R.; Criquet-Hayot, A.; Chabartier, C.; Kaidomar, S.; Brouste, Y.; Mégarbane, B.; Mehdaoui, H. Envenomation by the Invasive Pterois volitans Species (lionfish) in the French West Indies-a two-Year Prospective Study in Martinique. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 14, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Memar, B.; Jamili, S.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Bagheri, K.P. Description of Histopathological Changes Induced by the Venom of the Persian Gulf Lionfish (Pterois russelli) in a Mouse Model Multiorgan Toxicity. Toxicon 2016, 122, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, C.H.; Yuen, R.; Khoo, H.E.; Chung, M.; Gwee, M.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Purification and Partial Characterization of Stonustoxin (lethal factor) from Synanceja horrida venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Comp. Biochem. 1991, 99, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, K.; Hosaka, M.; Fujita, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Kikuchi, T. Venoms form six species of marine fish: Lethal and hemolytic activities and their neutralization by commercial stonefish antivenom. Mar. Biol. 1989, 103, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrano, S.J.; Lebowitz, J.B.; Marcus, S. Lionfish Envenomation. J. Emerg. Med. 2002, 23, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niznik, L.; Jablonska, K.; Orczyk, M.; Orzechowska, M.; Jasinska, J.; Smoliniec, B.; Hucko, A.; Kosowicz, P.; Klocek, A.; Sloma, P.; et al. Hot-Water Immersion (HWI) or Ice-Pack Treatment (IPT) as First Aid for Human Envenomation by Marine Animals? Review of Literature. Toxins 2024, 16, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadley, E.B.; Hancock, E.W. Strategies for the discovery and advancement of novel cationic antimicrobial peptides. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.S.; Olek, A.J. An Extract of Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Spine Tissue Contains Acetylcholine and a Toxin That Affects Neuromuscular Transmission. Toxicon 1989, 27, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englander, S.W.; Mayne, L.; Krishna, M.M. Protein folding and Misfolding: Mechanism and Principles. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 40, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, P.; Taylor, P.B. Venom of the Lionfish Pterois volitans. Am. J. Physiol. 1959, 197, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choromanski, J.M. Chemical Stabilization and Pharmacological Characterization of the Venom of the Lionfish, Pterois volitans. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Bravo, Á.A. Análisis Preliminar de Los Componentes Proteicos Del Veneno Del Pez León Pterois volitans de La Costa de Santa Marta y Evaluación de Su Actividad Biológica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, P. Protein Purification; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, M.S.R.; Cheung, P.; Leong, I.; Ruggieri, G.D. A Non-Proteinaceous Toxin from the Venomous Spines of the Lionfish Pterois volitans (Linnaeus). Toxicon 1985, 23, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Grimsley, G.R.; Razvi, A.; Scholtz, J.M.; Pace, C.N. Increasing Protein Stability by Improving beta-turns. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2009, 77, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, M.; Signor, G.; Matthews, B.W. Substantial Increase of Protein Stability by Multiple Disulphide Bonds. Nature 1989, 342, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Sari, M.; Ginting, M.J.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. The influence of heating process on anticancer activity of Pterois volitans (Red Lionfish) venom extraction against human cervical carcinoma cell. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2193, 030022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Ramadhan, M.Y.A.; Larasati, R.; Ginting, M.J.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. Extraction of PLA2 and Antibacterial Activity Test of Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Spine Venom. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 462, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Pratiwi, I.; Ginting, M.J.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. The Effects of Heating Process on Protein Isolation of Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Spines Venom Extract to Antioxidant Activity Assay. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2193, 020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Eka, A.K.; Ramadhan, M.Y.A.; Ginting, M.J.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. Protein Isolation and Identification of Pterois volitans Spine Venom Coagulant Activity. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 462, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Larasati, R.; Ginting, M.J.; Pebriani, S.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. Extraction, Antioxidant, and Bioactive Component Assay of Lionfish Venom Pterois volitans. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2193, 030008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houyvet, B.; Bouchon-navaro, Y.; Bouchon, C.; Corre, E.; Zatylny-gaudin, C. Marine Transcriptomics Analysis for the Identification of New Antimicrobial Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houyvet, B.; Bouchon-Navaro, Y.; Bouchon, C.; Goux, D.; Bernay, B.; Corre, E.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C. Identification of a Moronecidin-like Antimicrobial Peptide in the Venomous Fish Pterois volitans: Functional and Structural Study of Pteroicidin-α. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Jia, Y.; Li, R.; He, C.; Chen, H. The Structure-Mechanism Relationship and Mode of Actions of Antimicrobial Peptides: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memar, B.; Jamili, S.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Bagheri, K.P. The First Report on Coagulation and Phospholipase A2 Activities of Persian Gulf Lionfish, Pterois russelli, an Iranian Venomous Fish. Toxicon 2016, 113, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiriake, A.; Madokoro, M.; Shiomi, K. Enzymatic Properties and Primary Structures of Hyaluronidases from Two Species of Lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, A.; Ortiz, N.; Lomonte, B.; Rucavado, A.; Díaz, C. Comparison of Biochemical and Cytotoxic Activities of Extracts Obtained from Dorsal Spines and Caudal Fin of Adult and Juvenile Non Native Caribbean Lion Fish (Pterois volitans/miles). Toxicon 2017, 137, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sri Balasubashini, M.; Karthigayan, S.; Somasundaram, S.T.; Balasubramanian, T.; Viswanathan, P.; Menon, V.P. In Vivo and in Vitro Characterization of the Biochemical and Pathological Changes Induced by Lionfish (Pterios volitans) Venom in Mice. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2006, 16, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, L.; Ros, U.; Valdés, G.; Alonso del Rivero, M.; Lanio, M.E.; Carlos, À. Proteolytic and Hemolytic Activity in the Venom of the Lionfish Pterois volitans, an Invasive Species of Cuban Sea Coasts. Rev. Cuba. Cienc. Biol. 2015, 4, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Tafsili, M.A.B.; Ginting, M.J.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. Utilization of Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Venomous Spines with Effective Purification as an Alternative Antiretroviral HIV/AIDS. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2193, 030016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahyoun, C.; Rima, M.; Mattei, C.; Sabatier, J.M.; Fajloun, Z.; Legros, C. Separation and Analytical Techniques Used in Snake Venomics: A Review Article. Processes 2022, 10, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellard, M. The enzyme as drug: Application of enzymes as pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-de Torre, E.; Rimbault, C.; Jenkins, T.P.; Sorensen, C.V.; Damsbo, A.; Saez, N.J.; Duhoo, Y.; Hackney, C.M.; Ellgaard, L.; Laustsen, A.H. Strategies for Heterologous Expression, Synthesis, and Purification of Animal Venom Toxins. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 811905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Riswandha, F.; Ginting, M.J.; Pebriani, S.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. Protein Isolation of Pterois volitans Venomous with a Heating Process for Antibacterial Activity Assay. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 462, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, G.N.; Navabshan, I.; Unnikrishnan, S.; Ramalingam, K. In Silico Protein-Protein Interaction of Pterois volitans Venom with Cancer Inducers of Helicobacter pylori. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 194, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chen, R.; Wilcox, M.D.P.; Black, D.; Walsh, W.R.; Kumar, N. A New Era of Antibiotics: The Clinical Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-Y.; Li, H.-J.; Li, Q.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C. Application of marine natural products in drug research. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 35, 116058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegman, R.; Alewood, P. Bioactive components in fish venoms. Toxins 2015, 7, 1497–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sri Balasubashini, M.; Karthigayan, S.; Somasundaram, S.T.; Balasubramanian, T.; Viswanathan, V.; Raveendran, P.; Menon, V.P. Fish Venom (Pterios volitans) Peptide Reduces Tumor Burden and Ameliorates Oxidative Stress in Ehrlich’s Ascites Carcinoma Xenografted Mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 6219–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Eka, A.K.; Ginting, M.J.; Pebriani, S.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. The Effect of Ammonium Sulfate Concentration in Protein Isolation of Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Spines Venom Extract for Antitumor Test. In Proceedings of the 4th Biomedical Engineering’s Recent Progress in Biomaterials, Drugs Development, Health, and Medical Devices, Padang, Indonesia, 22–24 July 2019; p. 030009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Balasubashini, M.; Karthigayan, S.; Somasundaram, S.T.; Balasubramanian, T.; Rukkumani, R.; Menon, V.P. FV Peptide Induces Apoptosis in HEp2 and HeLa Cells: An Insight into the Mechanism of Induction. J. Carcinog. 2006, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijanarko, A.; Firdianna, A.; Ginting, M.J.; Lischer, K.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H. Isolation and Anticancer Activity Assay of Stonefish (Synanceia horrida) Bioactive Stonustoxin. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2537, 020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firuzi, O.; Miri, R.; Tavakkoli, M.; Saso, L. Antioxidant therapy: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 3871–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, P. The use of the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) for estimating antioxidant activity. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2004, 26, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Helbig, K.J.; Eyre, N.S.; Yip, E.; Narayana, S.; Li, K.; Fiches, G.; McCartney, E.M.; Jangra, R.K.; Lemon, S.M.; Beard, M.R. The antiviral protein viperin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication via interaction with nonstructural protein 5A. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Muhammad Yusuf Arya, R.; Ginting, M.J.; Pratami, D.K.; Hermansyah, H.; Sahlan, M.; Wijanarko, A. Antiretroviral Activity of Pterois volitans (Red Lionfish) Venom in the Early Development of Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Antiretroviral Alternative Source. Vet. World 2019, 12, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.C.; Borges, B.C.; Oliveira, V.Q.; Carregosa, L.S.; Bastos, L.A.; Santos, I.A.; Jardim, A.C.G.; Melo, F.F.; Freitas, L.M.; Rodrigues, V.M.; et al. Insights into the antiviral activity of phospholipases A2 (PLA2s) from snake venoms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Chlopicki, S. Revisiting pharmacology of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease: Evidence for redox-based therapies. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 157, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. Adrenergic and Cholinergic Activity Contributes to the Cardiovascular Effects of Lion (Pterois volitans) Venom. Toxicon 2002, 40, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.V.; Fiorotti, H.B.; Coitinho, J.B.; Figueiredo, S.G. Fish Cytolysins in All Their Complexity. Toxins 2021, 12, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthra, S.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Sangeshwari, T.; Sivaranjani, G.; Kanchana, S.; Arumugan, M. Characterization and Biological Activity of Stingray Venom (Himantura imbrica). Int. J. Mod. Trends Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Saggiomo, S.L.; Firth, C.; Wilson, D.T.; Seymour, J.; Miles, J.J.; Wong, Y. The geographic distribution, Venom Components, Pathology and Treatments of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Venom. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, T. Neuromuscular blocking drugs: Discovery and development. J. R. Soc. Med. 2002, 95, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Amezcua, M.P.; Hernández-Sámano, A.C.; Puch-Hau, C.; Aguilar, M.B.; Collí-Dulá, R.C. Effect of Pterois volitans (Lionfish) Venom on Cholinergic and Dopaminergic Systems. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 77, 103359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Tae, H.S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Adams, D.J.; Yu, R. Rational Design of Conotoxin RegIIA Analogues Specifically Inhibiting The human α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Through Computational Scanning. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.S.; Brimble, M.A. A Review of Neuroprotective Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadharsini, S.; Manoharan, J.; Varadharajan, D.; Subramaniyan, A. Neuroprotective Effects of Pterois volitans Venom against Alcohol Induced Oxidative Dysfunction in Rats. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Sung, J.M.; Yang-Low, K.S.; Khoo, H.E. Characterization of the Mechanism Underlying Stonustoxin-Mediated Relaxant Response in the Rat Aorta In Vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, J.E.; Moldrich, R.X.; Beart, P.M.; Hodgson, W.C. Modulation of Intracellular Ca2+ Levels by Scorpaenidae Venoms. Toxicon 2003, 41, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, M.; Kreitman, R.J.; Vasmatzis, G.; Lee, B.; Pastan, I. Reduction of the Nonspecific Animal Toxicity of Anti-Tac(Fv)-PE38 by Mutations in the Framework Regions of the Fv which Lower the Isoelectric Point. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6072–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, F.M.; Mero, A. The Impact of PEGylation on Biological Therapies. Drug Dev. 2012, 22, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espín, J.C.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Nutraceuticals: Facts and Fiction. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2986–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiriake, A.; Shiomi, K. Some Properties and CDNA Cloning of Proteinaceous Toxins from Two Species of Lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Toxicon 2011, 58, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavas, L.; Bilgin, Y. Bioactivities from Novel Toxins of Pterois volitans: A Bioinformatics Approach. Gazi University J. Sci. Part A Eng. Innov. 2021, 8, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.; Lomonte, B.; Sáenz, A.; Ortiz, N.; Rucavado, A. Myotoxic and Hemorrhagic Effects of Fractions Obtained from the Venom of Lionfish (Pterois volitans) in Mice and Identification of Potentially Toxic Components. Toxicon 2020, 177, S46–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriake, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Proteinaceous Toxins from Three Species of Scorpaeniform Fish (Lionfish Pterois lunulata, Devil Stinger Inimicus japonicus and Waspfish Hypodytes rubripinnis): Close Similarity in Properties and Primary Structures to Stonefish Toxins. Toxicon 2013, 70, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez, C.; Carrasco, J.; Bruner-Montero, G.; Pires Júnior, O.R.; Gutiérrez, M.; Díaz-Ferguson, E. Components and Biological Activities of Venom from Lionfishes (Scorpaenidae: Pterois). Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020055
Rodriguez C, Carrasco J, Bruner-Montero G, Pires Júnior OR, Gutiérrez M, Díaz-Ferguson E. Components and Biological Activities of Venom from Lionfishes (Scorpaenidae: Pterois). Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(2):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez, Candelario, Jafeth Carrasco, Gaspar Bruner-Montero, Osmindo Rodrigues Pires Júnior, Marcelino Gutiérrez, and Edgardo Díaz-Ferguson. 2025. "Components and Biological Activities of Venom from Lionfishes (Scorpaenidae: Pterois)" Marine Drugs 23, no. 2: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020055
APA StyleRodriguez, C., Carrasco, J., Bruner-Montero, G., Pires Júnior, O. R., Gutiérrez, M., & Díaz-Ferguson, E. (2025). Components and Biological Activities of Venom from Lionfishes (Scorpaenidae: Pterois). Marine Drugs, 23(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020055







