Marine Collagen from European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Waste for the Development of Chitosan/Collagen Scaffolds in Skin Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
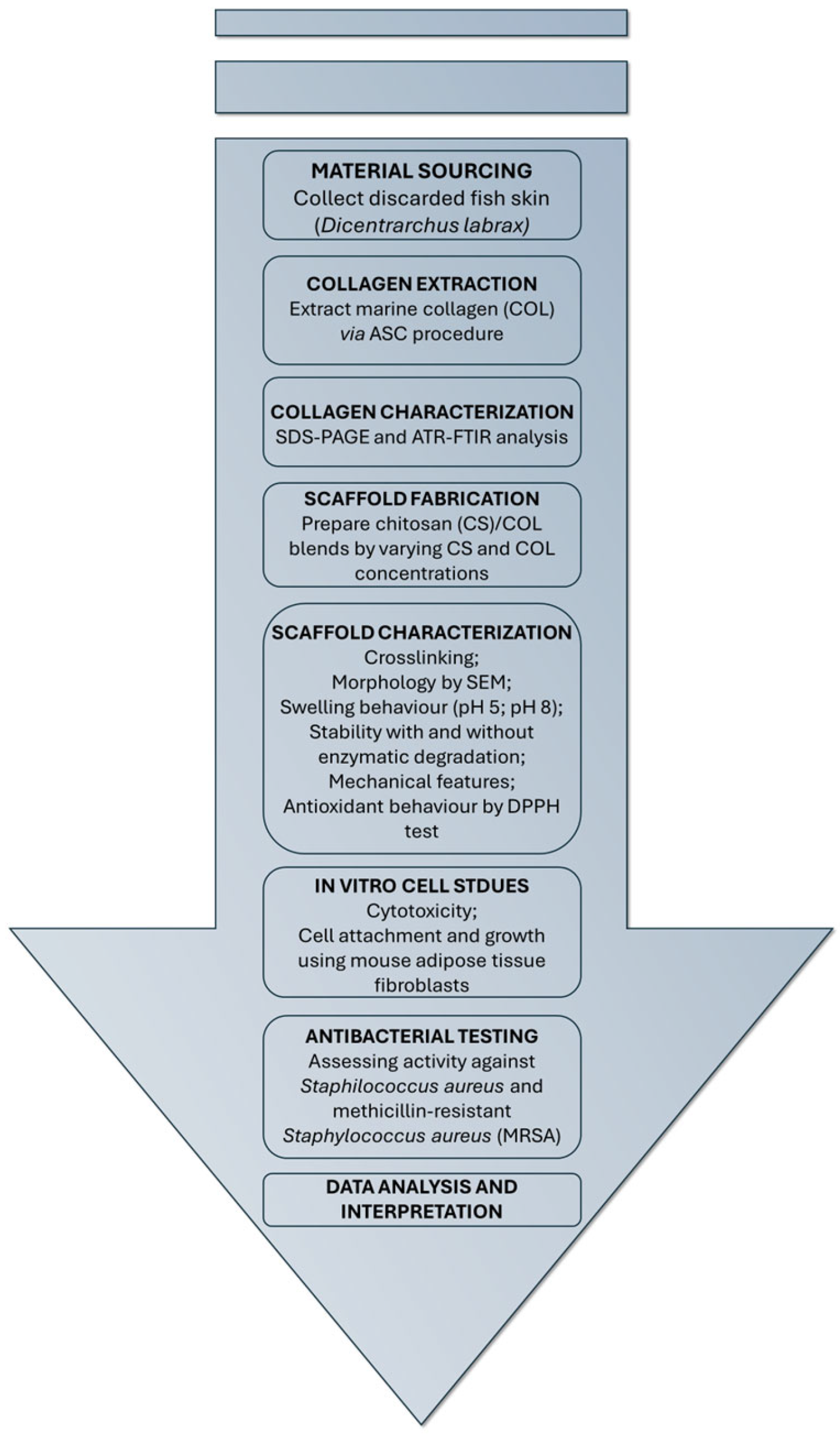
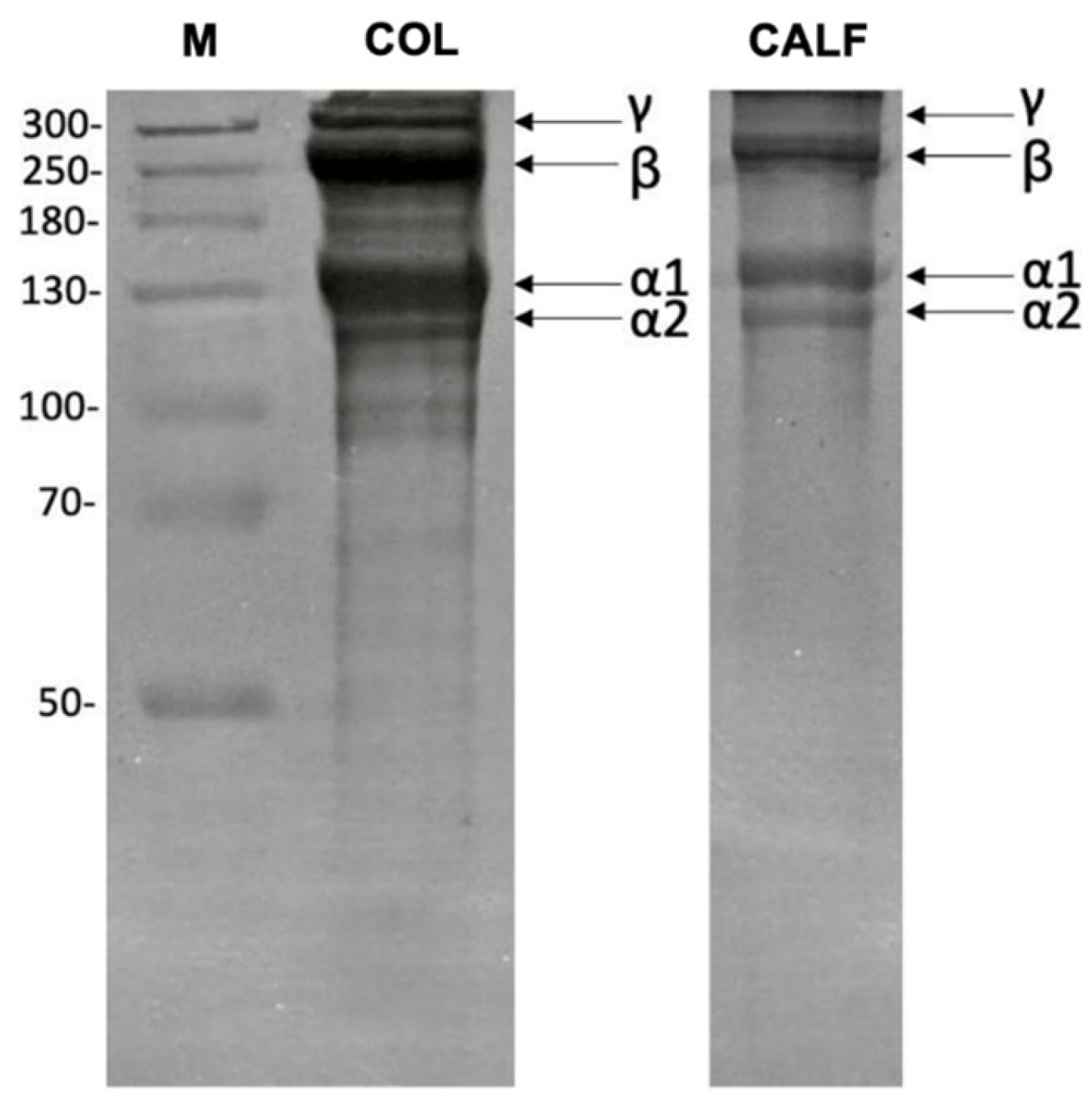
2.1. Collagen Extraction from Sea Bass Skin
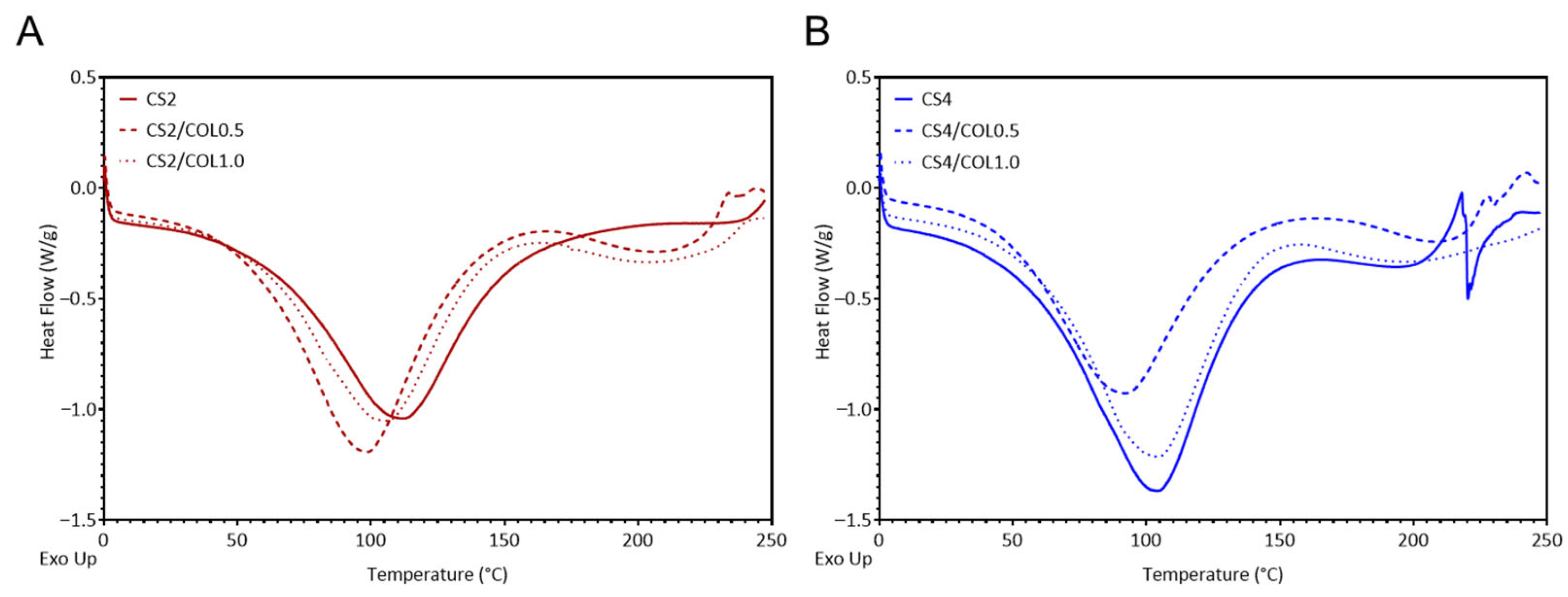
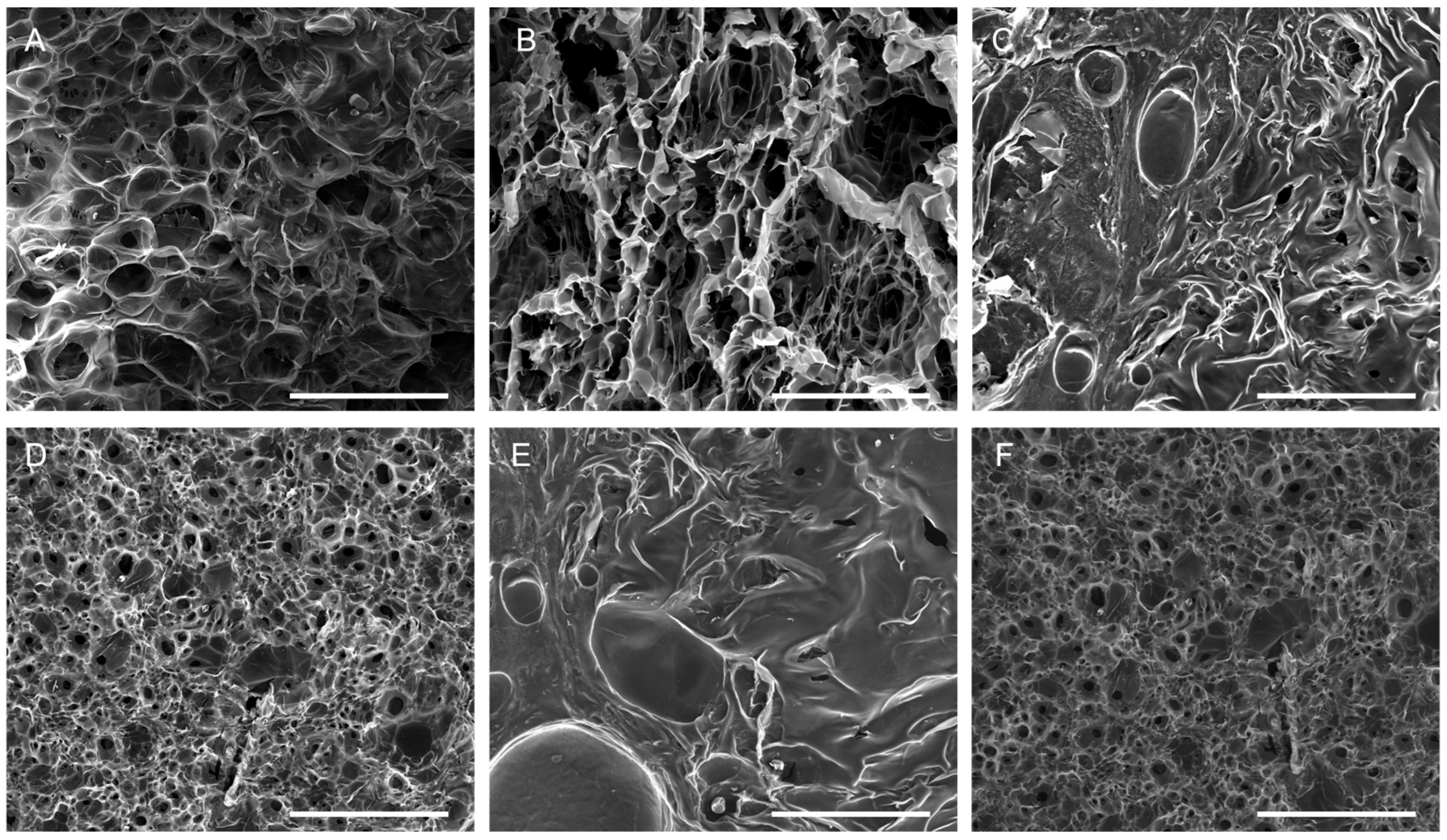
2.2. Scaffolds Preparation and Characterization
2.3. In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Scaffolds
2.4. Antimicrobial Activities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sea Bass Skin Preparation and Acid Soluble Collagen (ASC) Extraction
3.2. SDS-PAGE
3.3. Chitosan/Collagen Scaffold Preparation
3.4. Scaffold Characterization
3.4.1. Physicochemical Analysis
3.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.4.3. Morphological Analysis
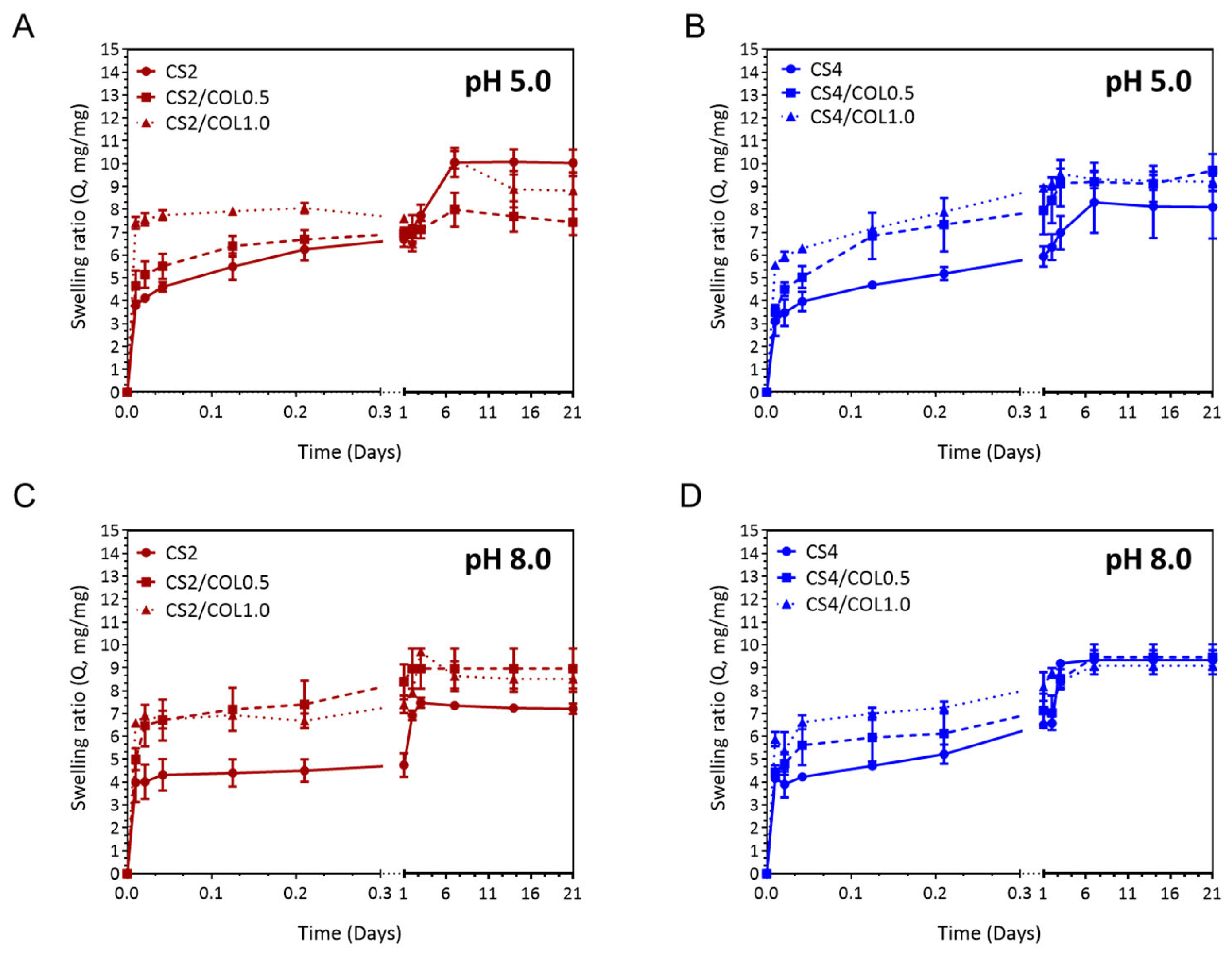
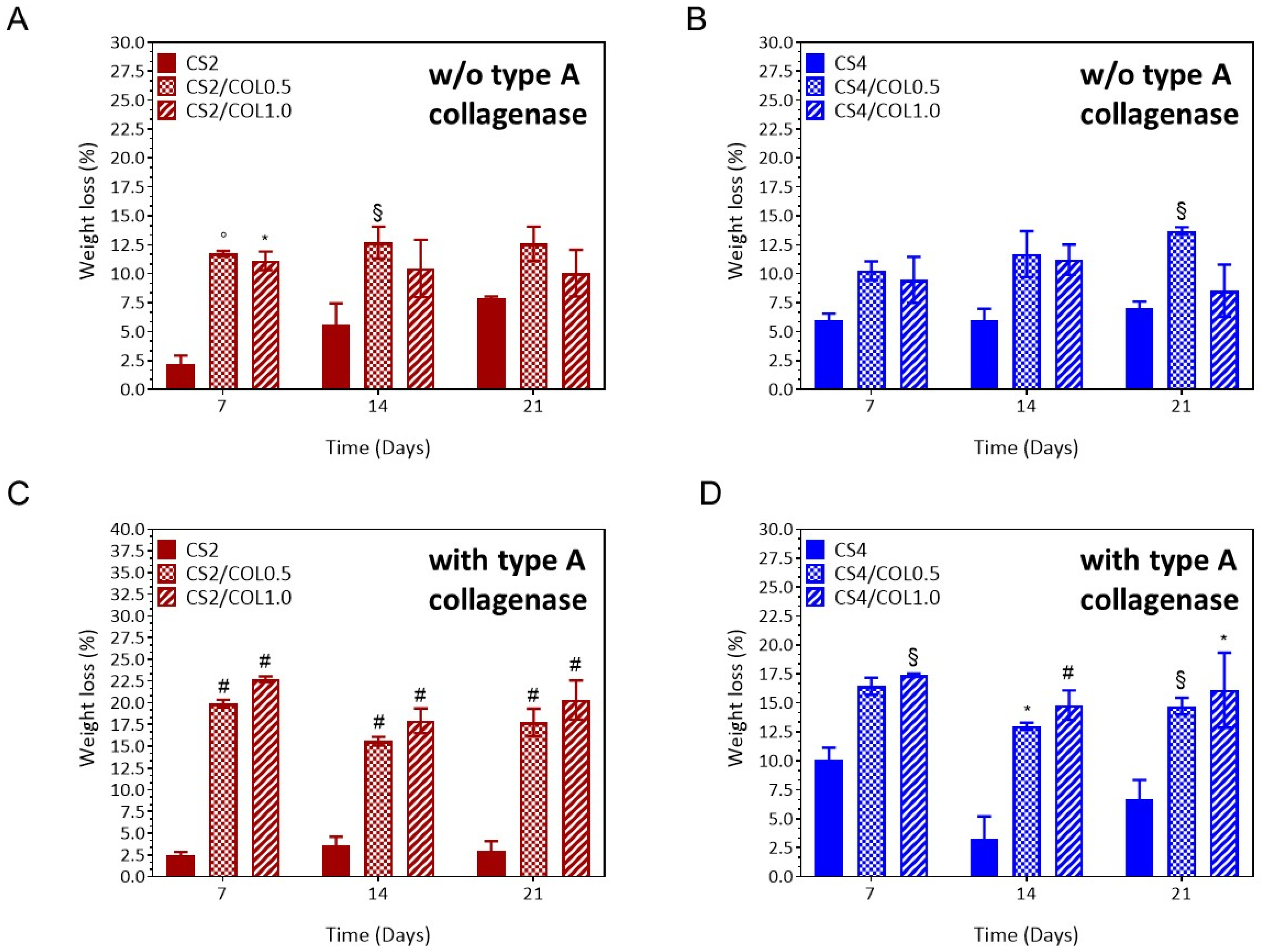
3.4.4. Swelling and Stability Behaviour
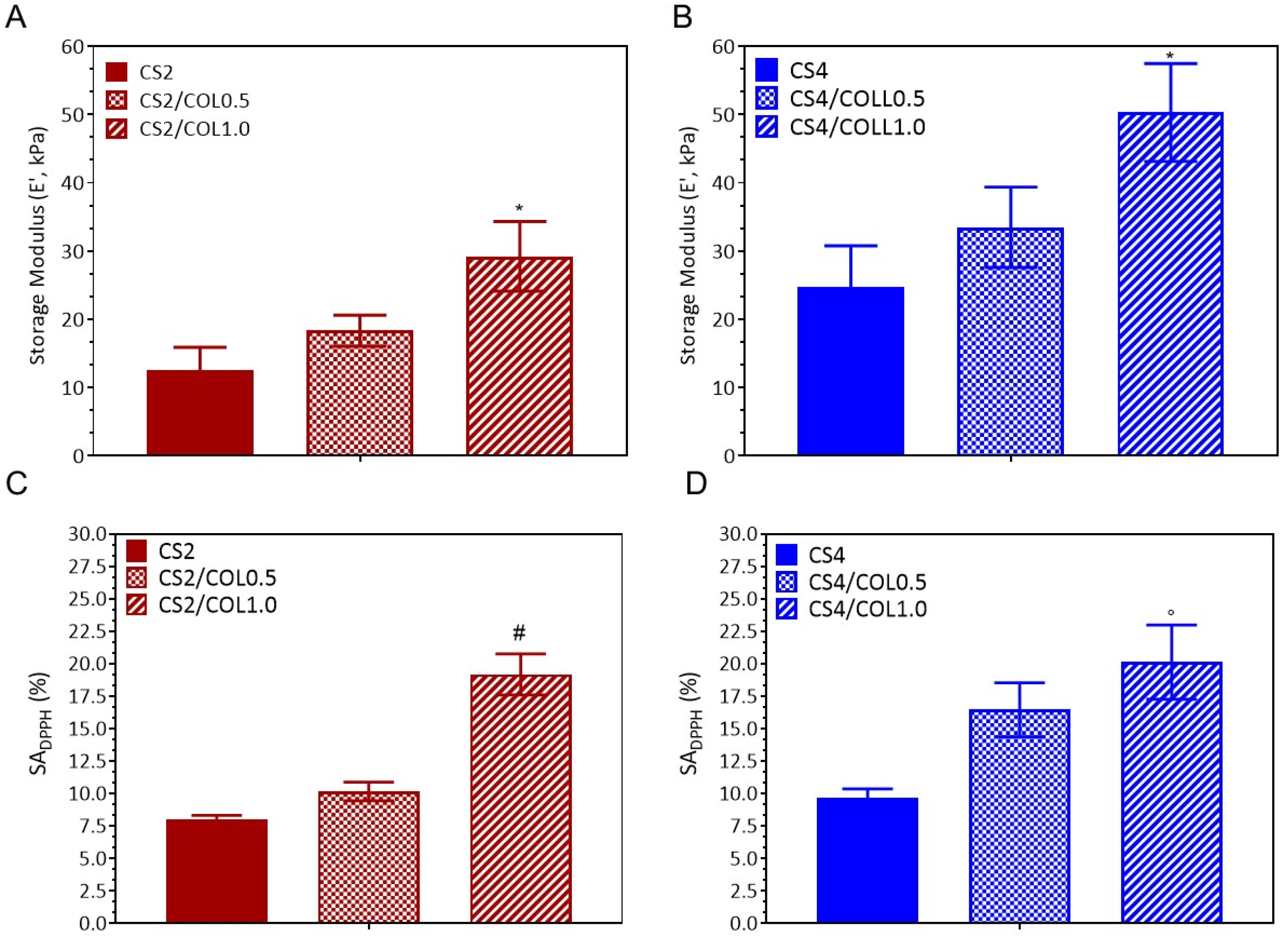
3.4.5. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
3.4.6. Antioxidant Properties
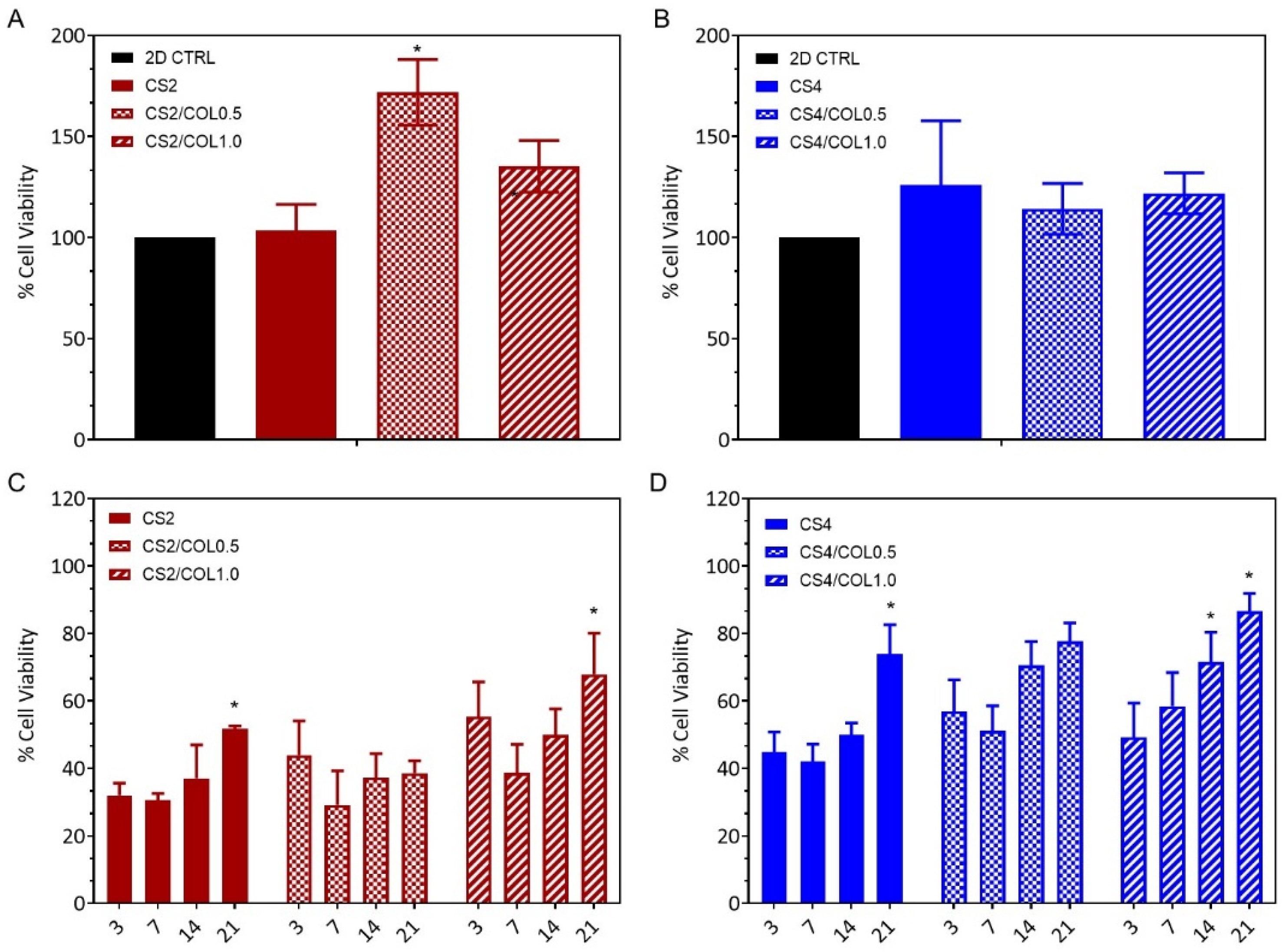
3.5. Cell Viability
3.5.1. In Vitro Indirect Cytotoxic Assay
3.5.2. In Vitro Biocompatibility Assay
3.6. Antimicrobial Assay
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Bielefeld, K.A.; Amini-Nik, S.; Alman, B.A. Cutaneous Wound Healing: Recruiting Developmental Pathways for Regeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2059–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhi, S.; Arno, A.; Jeschke, M.G. The Use of Dermal Substitutes in Burn Surgery: Acute Phase. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.L.; Sullivan, N.; Schoelles, K.M. Skin Substitutes for Treating Chronic Wounds; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, N.R.; Kim, H.-J.; Gouidie, M.J.; Lee, K.; Bandaru, P.; Banton, E.A.; Sarikhani, E.; Sun, W.; Zhang, S.; Cho, H.-J.; et al. Biofabrication of Endothelial Cell, Dermal Fibroblast, and Multilayered Keratinocyte Layers for Skin Tissue Engineering. Biofabrication 2021, 13, 035030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, F.; Campora, S.; Ghersi, G. Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek-Szczepańska, B.; D’Amora, U.; Zasada, L.; Michalska-Sionkowska, M.; Miłek, O.; Łukowicz, K.; Osyczka, A.M. Enhancing Thin Film Properties of Chitosan–Collagen Biocomposites Through Potassium Silicate and Tannic Acid Integration. Polymers 2025, 17, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, Q.; Xu, E.-C.; He, S.-Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, L.-F.; Yang, Z.-L. Fibroblasts/Three-Dimensional Scaffolds Complexes Promote Wound Healing in Rats with Skin Defects. Tissue Barriers 2025, 13, 2334544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The Collagen Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Maroušková, A.; Myšková, K.; Váchal, J.; Vochozka, M.; Žák, J. Techno-Economic Assessment of Collagen Casings Waste Management. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3385–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnaini, N.; Prajaputra, V.; Syafhira, T.; Maryam, S.; Arisa, I.I.; Karina, S.; Agustina, S.; Haridhi, H.A. Recent Update: Collagen Extraction from Marine Resources as a Promising Natural Antiaging. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 87, 03020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Oliviero, M.; Vitale, G.A.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I.; Iannace, S.; de Pascale, D. Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources: Extraction, Processing and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Zou, Y.; Lu, G.; Ronca, A.; D’Amora, U.; Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y. Advanced Application of Collagen-Based Biomaterials in Tissue Repair and Restoration. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Palma Esposito, F.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; de Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Guénette, S.; Pitcher, T.J.; Sumaila, U.R.; Walters, C.J.; Watson, R.; Zeller, D. Towards Sustainability in World Fisheries. Nature 2002, 418, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venslauskas, K.; Navickas, K.; Nappa, M.; Kangas, P.; Mozūraitytė, R.; Šližytė, R.; Župerka, V. Energetic and Economic Evaluation of Zero-Waste Fish Co-Stream Processing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directorate General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries. The EU Fish Market: 2020 Edition. Available online: https://eumofa.eu/documents/20178/415635/EN_The+EU+fish+market_2020.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Li, H.; Chen, R.; Jia, Z.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Xia, H.; Meng, D. Porous Fish Collagen for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 6107–6121. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, G.S.; Marques, C.F.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Pirraco, R.P.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Cell-Laden Biomimetically Mineralized Shark-Skin-Collagen-Based 3D Printed Hydrogels for the Engineering of Hard Tissues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3664–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkasabgy, N.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Shamma, R.N. Determination of Cytocompatibility and Osteogenesis Properties of in Situ Forming Collagen-Based Scaffolds Loaded with Bone Synthesizing Drug for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wu, Q.; Long, H.; Hu, K.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Wei, X.; Suo, J.; et al. Development of Chitosan/Gelatin Hydrogels Incorporation of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, B.; Palaniyandi, K.; Wang, S.; Wenhui, W.; Robinson, J.S. Rheological, Biocompatibility and Osteogenesis Assessment of Fish Collagen Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, G.; Seleenmary Sobhanadhas, L.S.; Sekar Jeyakumar, G.F.; Devi, V.; Sivagnanam, U.T.; Fardim, P. Fabrication of Biohybrid Cellulose Acetate-Collagen Bilayer Matrices as Nanofibrous Spongy Dressing Material for Wound-Healing Application. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2512–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Yang, J. Preparation of Aminated Fish Scale Collagen and Oxidized Sodium Alginate Hybrid Hydrogel for Enhanced Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haijie, C.; Lei, W.; Kai, W.; Guodong, L.; Guolong, L.; Zhongzhen, Y.; Junru, W.; Ying, L.; Xiaorui, J. Fish Collagen Sponge with Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Diabetic Wound Repair in Rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 2025, 240, e31471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Guo, K.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Tang, M. In Situ Sodium Chloride Cross-Linked Fish Skin Collagen Scaffolds for Functional Hemostasis Materials. Small 2024, 20, 2208001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, T.; Latifi, N.; Hivechi, A.; Hosseinpour Sarmadi, V.; Bayat Shahbazi, S.; Amini, N.; Milan, P.B.; Abbaszadeh, A.; Larijani, G.; Fathalian, H.; et al. Sargassum glaucescens Extract/Marine-Derived Collagen Blend Sponge and Their Properties for Wound Healing. Mar. Biotechnol. 2025, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelipcean, A.-M.; Iosageanu, A.; Gaspar-Pintiliescu, A.; Moldovan, L.; Craciunescu, O.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Negreanu-Pirjol, B.; Mitran, R.-A.; Marin, M.; D’Amora, U. Marine and Agro-Industrial By-Products Valorization Intended for Topical Formulations in Wound Healing Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Serra, J.A.; Barat, J.M. Comparison of Wild and Cultured Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Quality. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, Á.; Marcos, C. Ecology and Distribution of Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus 1758): In Biology of European Sea Bass; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 3–33. ISBN 978-1-4665-9945-1. [Google Scholar]
- Levengood, S.K.L.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Based Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3161–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Chemistry, Solubility and Fiber Formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, M.R.; Maia, F.L.M.; Iatecola, A.; Massimino, L.C.; Plepis, A.M.D.G.; Martins, V.D.C.A.; Da Rocha, D.N.; Mariano, E.D.; Hirata, M.C.; Ferreira, J.R.M.; et al. In Vivo Evaluation of Collagen and Chitosan Scaffold, Associated or Not with Stem Cells, in Bone Repair. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Chitin and Chitosan: Prospective Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery, Cancer Treatment, and Wound Healing. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, S.; D’Amora, U.; Piscioneri, A.; Oliviero, M.; Scialla, S.; Coppola, A.; De Pascale, D.; Crocetta, F.; De Santo, M.P.; Davoli, M.; et al. Methacrylated Chitosan/Jellyfish Collagen Membranes as Cell Instructive Platforms for Liver Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, G.K.S.; Sharma, D.; Balakrishnan, R.M.; Ettiyappan, J.B.P. Extraction, Optimization and Characterization of Collagen from Sole Fish Skin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 9, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H. Preparation and Characterisation of Type I and V Collagens from the Skin of Amur Sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Food Chem. 2014, 148, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikel, Ç.; Yanar, Y. Characterization of Acid-Soluble Collagen From By-Product Bones of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, K.; Karsdal, M.A. Type I Collagen. In Biochemistry of Collagens, Laminins and Elastin; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-0-443-15617-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative Study on Molecular Characteristics of Acid Soluble Collagens from Skin and Swim Bladder of Seabass (Lates calcarifer). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkus, O.; Belaney, R.M.; Das, P. Free Radical Scavenging Alleviates the Biomechanical Impairment of Gamma Radiation Sterilized Bone Tissue. J. Orthop. Res. 2005, 23, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, I.; Francolini, I.; Di Lisio, V.; Martinelli, A.; Pietrelli, L.; Scotto d’Abusco, A.; Scoppio, A.; Piozzi, A. Preparation and Characterization of TPP-Chitosan Crosslinked Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.L.; Resende, C.X.; Tavares, D.S.; Soares, G.A.; Castro, L.O.; Granjeiro, J.M. Cytocompatibility of Chitosan and Collagen-Chitosan Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Polímeros 2011, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Tomaz, A.; Sobral De Carvalho, S.M.; Cardoso Barbosa, R.; Silva, S.M.L.; Sabino Gutierrez, M.A.; De Lima, A.G.B.; Fook, M.V.L. Ionically Crosslinked Chitosan Membranes Used as Drug Carriers for Cancer Therapy Application. Materials 2018, 11, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyłek, M.; Bełdowski, P.; Wieland, F.; Cysewski, P.; Sionkowska, A. Collagen Type II—Chitosan Interactions as Dependent on Hydroxylation and Acetylation Inferred from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Molecules 2022, 28, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servín De La Mora-López, D.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; López-Cervantes, J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Soto-Valdez, H.; Madera-Santana, T.J. Bioengineered Chitosan–Collagen–Honey Sponges: Physicochemical, Antibacterial, and In Vitro Healing Properties for Enhanced Wound Healing and Infection Control. Polymers 2025, 17, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongchai, K.; Chuysinuan, P.; Thanyacharoen, T.; Techasakul, S.; Ummartyotin, S. Integration of Collagen into Chitosan Blend Film Composites: Physicochemical Property Aspects for Pharmaceutical Materials. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Krishnaraj, R.; Desai, T.A. Evaluation of Nanostructured Composite Collagen–Chitosan Matrices for Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qian, C.; Zheng, X.; Qi, X.; Bi, J.; Wang, H.; Cao, J. Collagen/Chitosan/Genipin Hydrogel Loaded with Phycocyanin Nanoparticles and ND-336 for Diabetic Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacrory, S.; D’Amora, U.; Longo, A.; Hasanin, M.S.; Soriente, A.; Fasolino, I.; Kamel, S.; Al-Shemy, M.T.; Ambrosio, L.; Scialla, S. Chitosan/Cellulose Nanocrystals/Graphene Oxide Scaffolds as a Potential pH-Responsive Wound Dressing: Tuning Physico-Chemical, pro-Regenerative and Antimicrobial Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyłek, M.; Bełdowski, P. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Affinity of Chitin and Chitosan for Collagen: The Effect of pH and the Presence of Sodium and Calcium Cations. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Its Deriv. 2023, 28, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, F.; Vitale, A.M.; Picone, D.; De Cesare, N.; Swiontek Brzezinska, M.; Kaczmarek-Szczepanska, B.; Ronca, A.; Zavan, B.; Bucchieri, F.; Szychlinska, M.A.; et al. Exploring Methacrylated Gellan Gum 3D Bioprinted Patches Loaded with Tannic Acid or L-Ascorbic Acid as Potential Platform for Wound Dressing Application. Gels 2025, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amora, U.; Scialla, S.; Fasolino, I.; Ronca, A.; Soriente, A.; De Cesare, N.; Manini, P.; Phua, J.W.; Pezzella, A.; Raucci, M.G.; et al. Eumelanin Pigment Release from Photo-Crosslinkable Methacrylated Gelatin-Based Cryogels: Exploring the Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Efficacy in Wound Healing. Biomater. Adv. 2025, 170, 214214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Merkel, A.R.; Sterling, J.A.; Davidson, J.M.; Guelcher, S.A. Substrate Modulus of 3D-Printed Scaffolds Regulates the Regenerative Response in Subcutaneous Implants through the Macrophage Phenotype and Wnt Signaling. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.E.; Downer, M.; Morgan, A.G.; Griffin, M.; Liang, N.E.; Kameni, L.; Laufey Parker, J.B.; Guo, J.; Longaker, M.T.; Wan, D.C. The Effects of Mechanical Force on Fibroblast Behavior in Cutaneous Injury. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1167067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayi, E.; Mudera, V.; Brown, R.A. Close Dependence of Fibroblast Proliferation on Collagen Scaffold Matrix Stiffness. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2009, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Khan, A.U.R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xie, X.; EL-Newehy, M.; EL-Hamshary, H.; Morsi, Y.; Li, J.; Pan, J.; et al. A Multifunctional Nanofiber Reinforced Photo-Crosslinking Hydrogel for Skin Wound Healing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 247, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Mendis, E.; Kim, S.-K. Factors Affecting the Free Radical Scavenging Behavior of Chitosan Sulfate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 36, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasocka, I.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Skibniewski, M.; Skibniewska, E.; Strupinski, W.; Pasternak, I.; Kmieć, H.; Kowalczyk, P. Biocompatibility of Pristine Graphene Monolayer: Scaffold for Fibroblasts. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 48, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakecili, A.G.; Demirtas, T.T.; Satriano, C.; Gümüsderelioglu, M.; Marletta, G. Evaluation of L929 Fibroblast Attachment and Proliferation on Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS)-Immobilized Chitosan in Serum-Containing/Serum-Free Cultures. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2007, 104, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Kim, J.-E.; Kang, H.Y.; Lee, C.; Rajbongshi, L.; Hwang, S.Y.; Oh, S.-O.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, D.; et al. A Marine Collagen-Based 3D Scaffold for In Vitro Modeling of Human Prostate Cancer Niche and Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Discovery. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, G.S.; Permuy, M.; Marques, C.F.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Serra, J.; González, P.; Munõz, F.; Pirraco, R.P.; Reis, R.L.; et al. In Vivo Assessment of Marine vs Bovine Origin Collagen-Based Composite Scaffolds Promoting Bone Regeneration in a New Zealand Rabbit Model. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 159, 213813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnutt, B.M.; Yuan, Y.; Buddington, K.; Haggard, W.O.; Bumgardner, J.D. Composite Chitosan/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Induce Osteocalcin Production by Osteoblasts In Vitro and Support Bone Formation In Vivo. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.N.; Gelinsky, M.; Williams, D.S.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Marine Collagen-Chitosan-Fucoidan/Chondroitin Sulfate Cryo-Biomaterials Loaded with Primary Human Cells Envisaging Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallela, R.; Venkatesan, J.; Janapala, V.R.; Kim, S. Biophysicochemical Evaluation of Chitosan-hydroxyapatite-marine Sponge Collagen Composite for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jin, S.; Tang, Y. Marine Collagen Peptides Promote Cell Proliferation of NIH-3T3 Fibroblasts via NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus Aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-L.; Deng, F.-S.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan. Polymers 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goy, R.C.; Britto, D.D.; Assis, O.B.G. A Review of the Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan. Polímeros 2009, 19, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasaj, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Asghari, B.; Ahmadieh-Yazdi, A.; Asgari, M.; Kabiri-Samani, S.; Sharifi, E.; Arabestani, M. Factors Influencing the Antimicrobial Mechanism of Chitosan Action and Its Derivatives: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Characterisation of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Skin and Bone of Bigeye Snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-5:2009/(R)2014; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. AAMI: Arlington, VA, USA, 2009.
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.; Della Sala, G.; Buonocore, C.; Zannella, C.; Tedesco, P.; Palma Esposito, F.; Ragozzino, C.; Chianese, A.; Morone, M.V.; Mazzella, V.; et al. New Imidazolium Alkaloids with Broad Spectrum of Action from the Marine Bacterium Shewanella aquimarina. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Main Assignment | Contribution from CS | Contribution from COL |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~3300 | O–H and N–H stretching (H-bonding) | –OH and protonated –NH2 groups | Amides (–NH) |
| ~2932 | Aliphatic C–H stretching | CS backbone | Minimal |
| ~1631–1642 (Amide I) | C=O stretching (peptide bond) | Weak (residual acetyl groups) | Strong (peptide bonds) |
| ~1547 (Amide II) | N–H bending + C–N stretching | Weak | Strong |
| ~1236–1237 (Amide III) | C–N stretching + N–H bending | Weak | Strong |
| ~1150 | Asymmetric C–O–C bridge | Strong | – |
| 1070–1030 | C–O stretching (alcohol and C–O–C groups) | Strong | – |
| Sample | Chitosan (CS) (mg/mL) | Collagen (COL) (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| CS2 | 20 | - |
| CS2/COL0.5 | 5 | |
| CS2/COL1.0 | 10 | |
| CS4 | 40 | - |
| CS4/COL0.5 | 5 | |
| CS4/COL1.0 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coppola, A.; Oliviero, M.; De Cesare, N.; Russo, N.; Nappo, N.; Buonocore, C.; Della Sala, G.; Tedesco, P.; Palma Esposito, F.; Galasso, C.; et al. Marine Collagen from European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Waste for the Development of Chitosan/Collagen Scaffolds in Skin Tissue Engineering. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100375
Coppola A, Oliviero M, De Cesare N, Russo N, Nappo N, Buonocore C, Della Sala G, Tedesco P, Palma Esposito F, Galasso C, et al. Marine Collagen from European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Waste for the Development of Chitosan/Collagen Scaffolds in Skin Tissue Engineering. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(10):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100375
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoppola, Alessandro, Maria Oliviero, Noemi De Cesare, Nello Russo, Noemi Nappo, Carmine Buonocore, Gerardo Della Sala, Pietro Tedesco, Fortunato Palma Esposito, Christian Galasso, and et al. 2025. "Marine Collagen from European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Waste for the Development of Chitosan/Collagen Scaffolds in Skin Tissue Engineering" Marine Drugs 23, no. 10: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100375
APA StyleCoppola, A., Oliviero, M., De Cesare, N., Russo, N., Nappo, N., Buonocore, C., Della Sala, G., Tedesco, P., Palma Esposito, F., Galasso, C., de Pascale, D., D’Amora, U., & Coppola, D. (2025). Marine Collagen from European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Waste for the Development of Chitosan/Collagen Scaffolds in Skin Tissue Engineering. Marine Drugs, 23(10), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100375











