Effects of Ultrasonic Power on the Structure and Rheological Properties of Skin Collagen from Albacore (Thunnus alalunga)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effect of the Ultrasonic Power on the Collagen Yield
2.2. Amino Acid Composition Analysis
2.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) Analysis
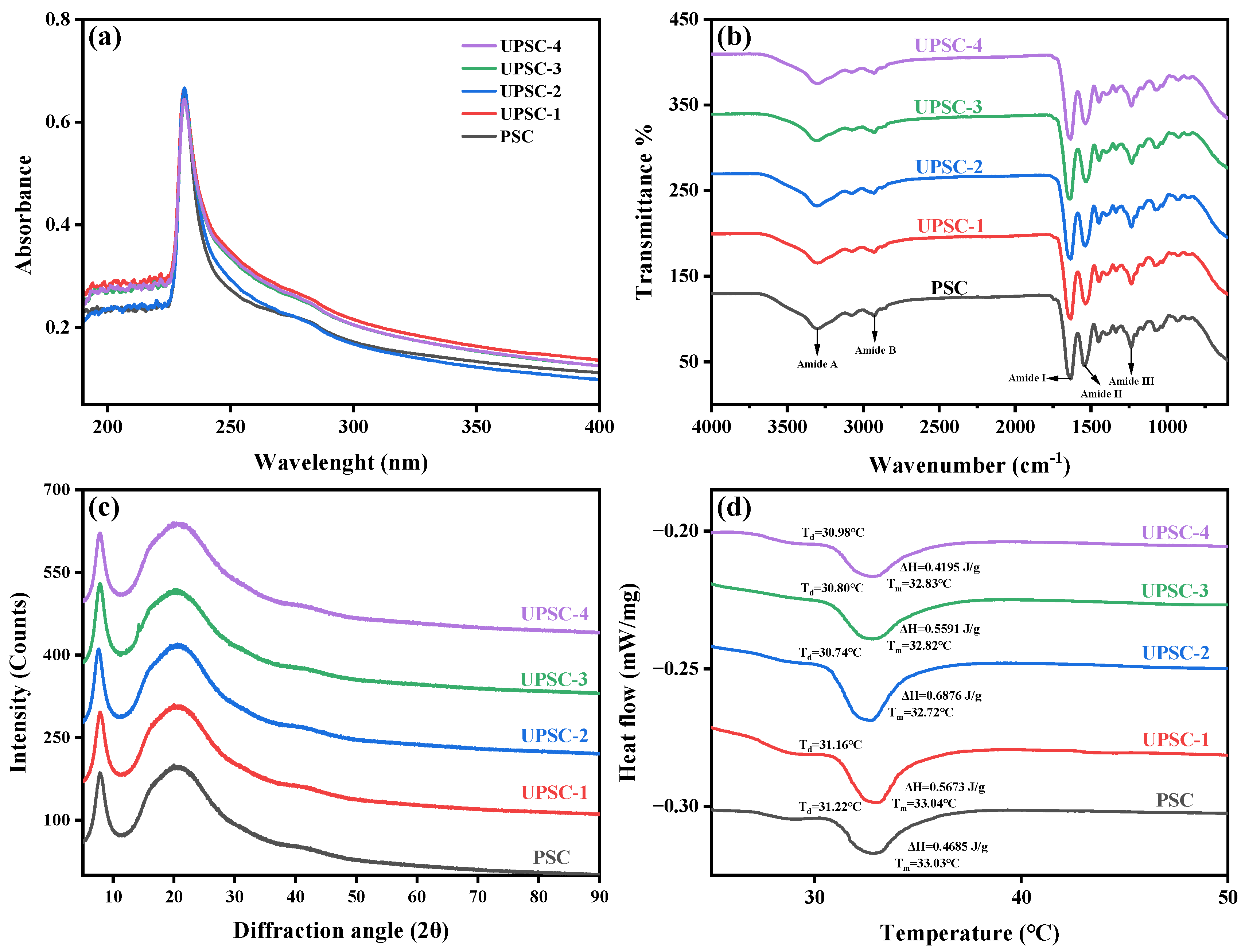
2.4. Ultraviolet Spectrum (UV) Analysis
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.7. Thermal Stability Analysis
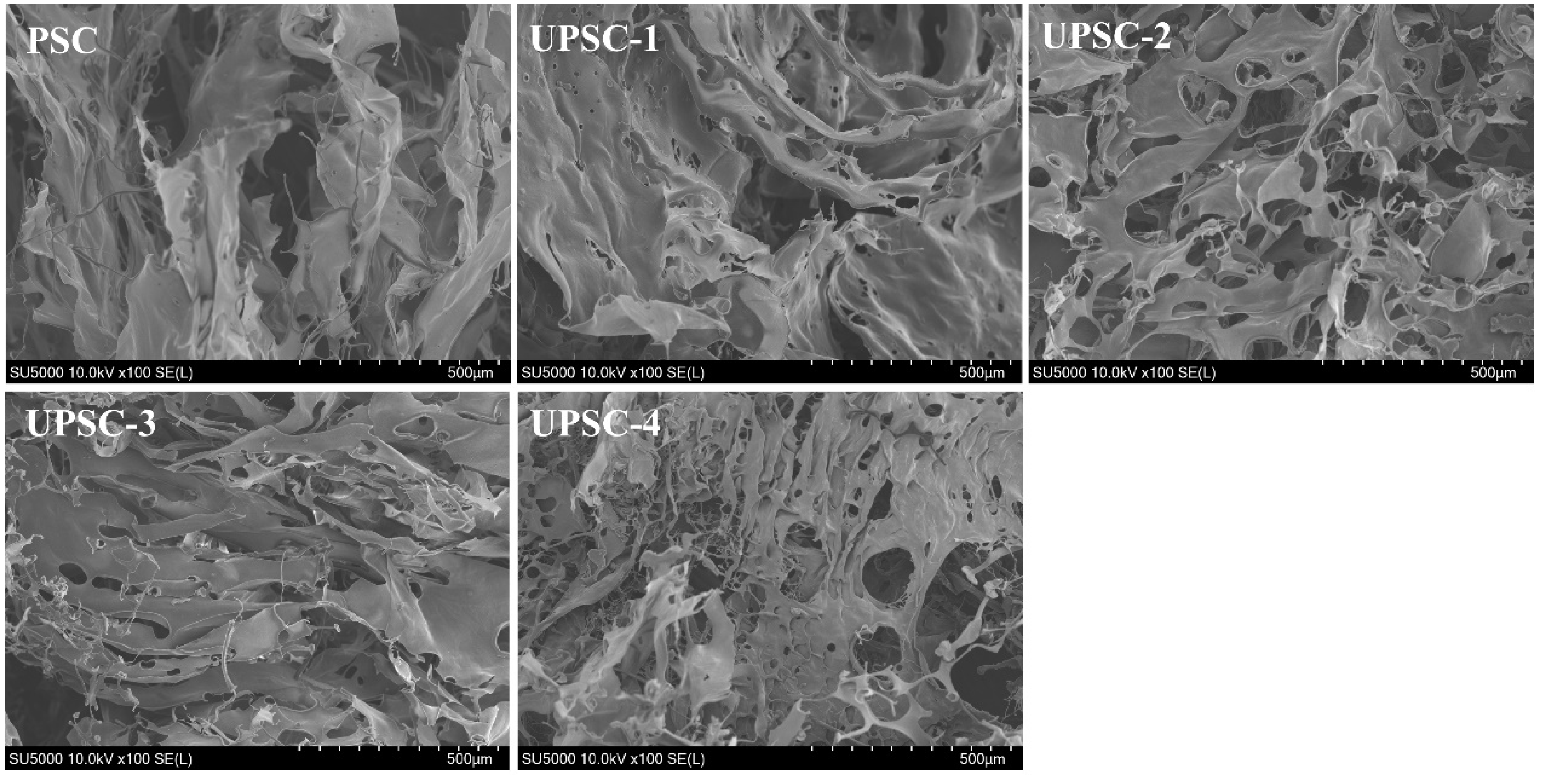
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
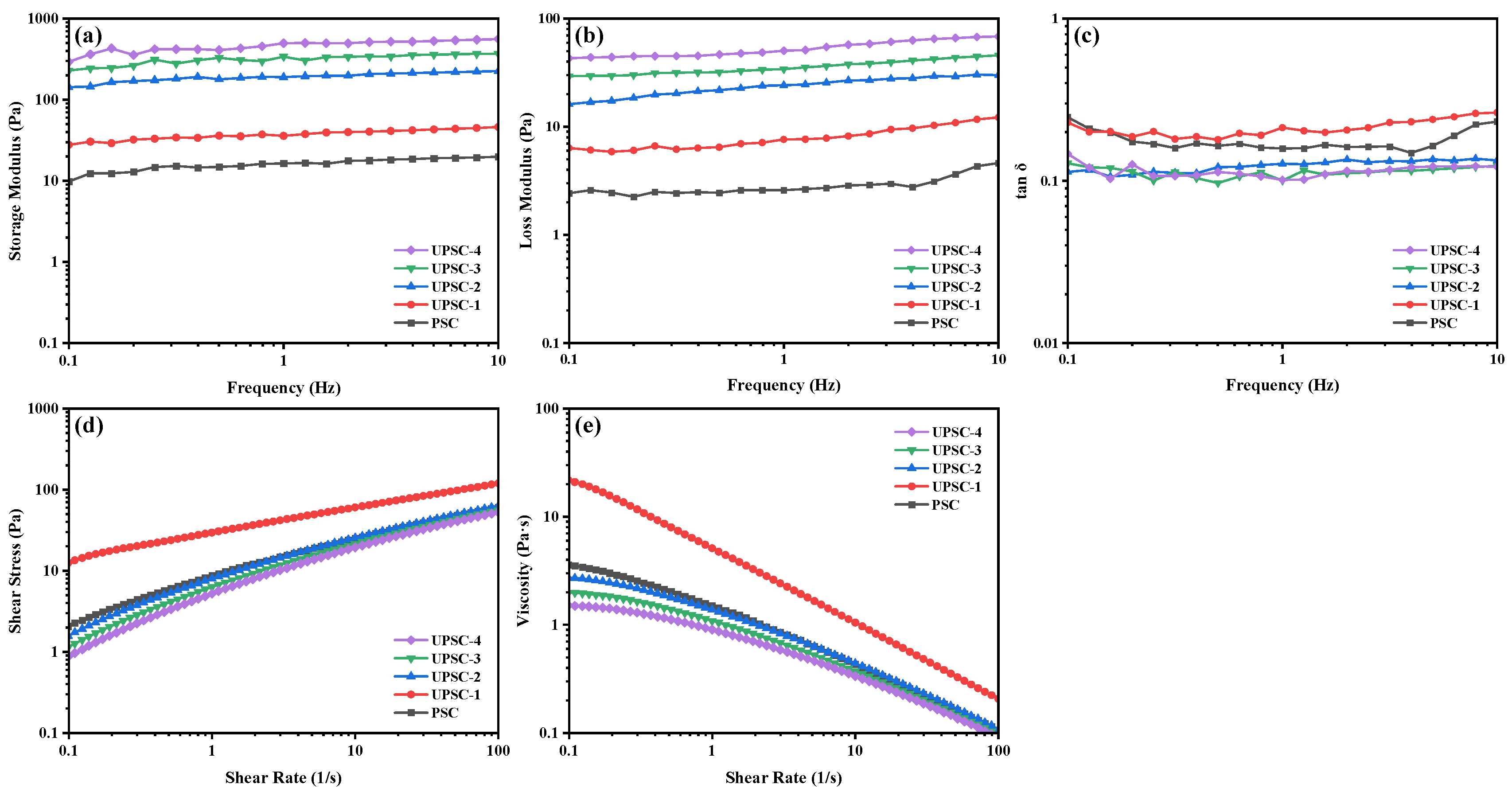
2.9. Rheological Properties
2.9.1. Dynamic Frequency Sweep Tests
2.9.2. Steady Shear Tests
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Extraction of Collagen
3.3. Amino Acid Composition
3.4. SDS-PAGE
3.5. UV
3.6. FTIR
3.7. XRD
3.8. Thermal Stability
3.9. SEM
3.10. Rheological Properties
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bella, J. Collagen structure: New tricks from a very old dog. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 1001–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tu, Z.; Wang, H. Preparation of high content collagen peptides and study of their biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, E.; Sultana, S.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Hossain, M.; Yehya, W.A.; Kader, A.; Bhargava, S.K. Gelatin controversies in food, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products: Authentication methods, current status, and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1495–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, P.G.; Suh, J.H.; Pegg, R.B.; Chen, J.; Mis Solval, K. The emergence of jellyfish collagen: A comprehensive review on research progress, industrial applications, and future opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B. Collagen and its derivatives: From structure and properties to their applications in food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 1132–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezeshk, S.; Rezaei, M.; Abdollahi, M. Impact of ultrasound on extractability of native collagen from tuna by-product and its ultrastructure and physicochemical attributes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 89, 106129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, H.; Ma, H.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, J.; Otu, P.N.Y. Extraction and characterization of chicken feet soluble collagen. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fu, Y.; Huang, S.; Liao, L.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ge, F.; Fang, B. Identification and antioxidant activity of bovine bone collagen-derived novel peptides prepared by recombinant collagenase from Bacillus cereus. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.-G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, B.; Li, F.; Shi, S.; Pan, N.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, X.; et al. The positive contribution of ultrasound technology in muscle food key processing and its mechanism-a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022; 1–22, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Extraction efficiency and characteristics of acid and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin of golden carp (Probarbus Jullieni) as affected by ultrasonication. Process Biochem. 2018, 66, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, N.H. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on collagen extraction from skins of the sea bass Lateolabrax japonicus. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.I.; Chong, J.Y.; Sarbon, N.M. Effect of ultrasound-assisted extraction on the extractability and physicochemical properties of acid and pepsin soluble collagen derived from Sharpnose stingray (Dasyatis zugei) skin. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, P.; Cai, P.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, D. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on the characterization and properties of collagen extracted from soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the scales, skins and swim-bladders of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Biosci. 2015, 9, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Li, C.; Song, W.; Wang, W.; Qian, G. Purification, optimization and physicochemical properties of collagen from soft-shelled turtle calipash. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Structural, functional, rheological, and biological properties of the swim bladder collagen extracted from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hou, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagen extracted from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Nalinanon, S. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of collagen from clown featherback (Chitala ornata) skin: Yield and molecular characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 101, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Getachew, A.T.; Cho, Y.-J.; Chun, B.-S. Application of bacterial collagenolytic proteases for the extraction of type I collagen from the skin of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus). LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Ajithkumar, T.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the outer skin of squid (Doryteuthis singhalensis). Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewbangkerd, K.; Hamzeh, A.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of collagen from broiler chicken trachea and its biochemical characterization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.K.; Nidheesh, T.; Suresh, P.V. Comparative study on characteristics and in vitro fibril formation ability of acid and pepsin soluble collagen from the skin of catla (Catla catla) and rohu (Labeo rohita). Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vate, N.K.; Strachowski, P.; Undeland, I.; Abdollahi, M. Structural and functional properties of collagen isolated from lumpfish and starfish using isoelectric precipitation vs salting out. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Deng, C. Characterization and comparison of collagen extracted from the skin of the Nile tilapia by fermentation and chemical pretreatment. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, B.B.; Bendit, E.G.; Blout, E.R. Infrared spectroscopy of collagen and collagen-like polypeptides. Biopolymers 1975, 14, 937–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewdang, O.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewmanee, T.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of collagens from the swim bladders of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Chem. 2014, 155, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of acid soluble collagen and gelatin from skins and bones of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Xu, N.; Gao, R.; Hong, B. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Yi, R.; Shi, S.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Type I Collagens in Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Skin. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative study on molecular characteristics of acid soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of seabass (Lates calcarifer). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, T. Double-spotted pufferfish (Takifugu bimaculatus) skin collagen: Preparation, structure, cytocompatibility, rheological, and functional properties. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, Z.E.; Scott, D.N.; Buisson, D.H. The role of collagen in the quality and processing of fish. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1984, 20, 301–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yin, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C.; Yang, P.; Wu, W. Structure and characteristics of acid and pepsin-solubilized collagens from the skin of cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Thiansilakul, Y.; Visessanguan, W.; Roytrakul, S.; Kishimura, H.; Prodpran, T.; Meesane, J. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagens from the skin of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenusand and Priacanthus macracanthus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Shiau, C.Y.; Su, Y.C.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, Y.-R. Isolation and characterization of collagens from the skin of giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.R.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Gong, Y.D.; Tang, J.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G.F. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagens and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin and bone of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Suzuki, N. Isolation of collagen from fish waste material–skin, bone and fins. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; An, X.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Q. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the skin of deep-sea redfish (Sebastes mentella). J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E450–E455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinanon, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H.; Osako, K. Type I collagen from the skin of ornate threadfin bream (Nemipterus hexodon): Characteristics and effect of pepsin hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechsle, A.M.; Wittmann, X.; Gibis, M.; Kohlus, R.; Weiss, J. Collagen entanglement influenced by the addition of acids. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 58, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Duan, L.; Tian, Z.H.; Liu, W.T.; Li, G.Y.; Huang, X.P. Rheological behavior of acylated pepsin-solubilized collagen solutions: Effects of concentration. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2015, 27, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, M.; Hellen, L.; Hirvonen, J.; Yliruusi, J. Rheological properties of creams with four different surfactant combinations–effect of storage time and conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Lewandowska, K.; Adamiak, K. The Influence of UV Light on Rheological Properties of Collagen Extracted from Silver Carp Skin. Materials 2020, 13, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, W.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W. High inner phase emulsion of fish oil stabilized with rutin-grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) myofibrillar protein: Application as a fat substitute in surimi gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Amino Acids | PSC | UPSC-1 | UPSC-2 | UPSC-3 | UPSC-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 50.99 ± 2.58 a | 46.32 ± 1.86 b | 50.34 ± 0.53 ab | 47.29 ± 3.29 ab | 46.76 ± 1.78 ab |
| Thr | 31.11 ± 1.58 a | 28.56 ± 1.21 c | 30.71 ± 0.22 ab | 31.20 ± 1.07 a | 28.74 ± 1.05 bc |
| Ser | 34.95 ± 1.76 a | 32.39 ± 1.17 a | 34.49 ± 0.49 a | 30.71 ± 5.70 a | 32.35 ± 1.30 a |
| Glu | 96.34 ± 4.61 a | 87.09 ± 3.81 c | 94.50 ± 0.75 ab | 89.79 ± 4.57 abc | 88.91 ± 2.73 bc |
| Gly | 226.43 ± 9.47 a | 211.84 ± 2.84 bc | 220.78 ± 0.96 ab | 218.61 ± 4.27 ab | 207.61 ± 4.8 c |
| Ala | 102.69 ± 5.05 a | 93.64 ± 2.55 c | 100.25 ± 0.19 ab | 99.11 ± 2.53 ab | 96.35 ± 0.64 bc |
| Val | 23.09 ± 0.91 a | 21.44 ± 0.25 a | 22.88 ± 0.76 a | 23.66 ± 2.23 a | 27.22 ± 7.51 a |
| Met | 6.73 ± 1.35 b | 9.47 ± 2.39 ab | 12.99 ± 0.90 a | 10.17 ± 4.59 ab | 11.66 ± 4.31 ab |
| Ile | 11.06 ± 1.37 a | 13.96 ± 5.36 a | 11.41 ± 1.95 a | 13.38 ± 3.51 a | 14.92 ± 1.32 a |
| Leu | 26.16 ± 1.33 a | 33.01 ± 4.42 a | 26.62 ± 0.84 a | 35.9 ± 12.91 a | 38.51 ± 10.28 a |
| Tyr | 2.10 ± 0.15 b | 8.13 ± 1.44 a | 1.79 ± 0.23 b | 11.92 ± 6.52 a | 10.91 ± 2.22 a |
| Phe | 21.19 ± 0.63 b | 35.34 ± 2.42 a | 21.47 ± 0.67 b | 18.86 ± 2.82 b | 19.91 ± 2.57 b |
| Lys | 35.25 ± 1.56 b | 47.82 ± 1.86 a | 35.60 ± 1.49 b | 32.88 ± 2.93 b | 46.35 ± 6.12 a |
| His | 7.54 ± 0.43 b | 16.75 ± 3.43 ab | 8.08 ± 1.04 b | 20.60 ± 12.64 a | 26.83 ± 5.32 a |
| Arg | 83.15 ± 3.49 a | 74.01 ± 3.39 b | 79.56 ± 1.41 ab | 74.79 ± 4.82 b | 74.00 ± 2.16 b |
| Pro | 105.84 ± 4.82 ab | 106.91 ± 1.17 ab | 109.98 ± 2.54 a | 110.54 ± 1.48 a | 102.84 ± 2.69 b |
| Hyp | 135.39 ± 10.43 ab | 133.3 ± 1.98 ab | 138.56 ± 3.77 a | 130.61 ± 5.68 ab | 126.12 ± 0.93 b |
| Imino acids | 241.23 ± 15.08 ab | 240.22 ± 2.58 ab | 248.54 ± 1.29 a | 241.15 ± 6.32 ab | 228.97 ± 2.08 b |
| Collagen | Ostwald de Waele Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| n | K (Pa·sn) | R2 | |
| PSC | 0.4772 | 1.382929 | 0.9927 |
| UPSC-1 | 0.3134 | 5.035006 | 0.9997 |
| UPSC-2 | 0.5819 | 0.807421 | 0.9759 |
| UPSC-3 | 0.5486 | 0.979941 | 0.9816 |
| UPSC-4 | 0.5184 | 1.241938 | 0.9851 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Ni, J.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, W. Effects of Ultrasonic Power on the Structure and Rheological Properties of Skin Collagen from Albacore (Thunnus alalunga). Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020084
Pan H, Zhang X, Ni J, Liang Q, Jiang X, Zhou Z, Shi W. Effects of Ultrasonic Power on the Structure and Rheological Properties of Skin Collagen from Albacore (Thunnus alalunga). Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020084
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Hao, Xuehua Zhang, Jianbo Ni, Qianqian Liang, Xin Jiang, Zihui Zhou, and Wenzheng Shi. 2024. "Effects of Ultrasonic Power on the Structure and Rheological Properties of Skin Collagen from Albacore (Thunnus alalunga)" Marine Drugs 22, no. 2: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020084
APA StylePan, H., Zhang, X., Ni, J., Liang, Q., Jiang, X., Zhou, Z., & Shi, W. (2024). Effects of Ultrasonic Power on the Structure and Rheological Properties of Skin Collagen from Albacore (Thunnus alalunga). Marine Drugs, 22(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020084




