Revealing the Diversity of Sequences, Structures, and Targets of Peptides from South China Sea Macrodactyla doreensis Based on Transcriptomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptome Sequence Assembly
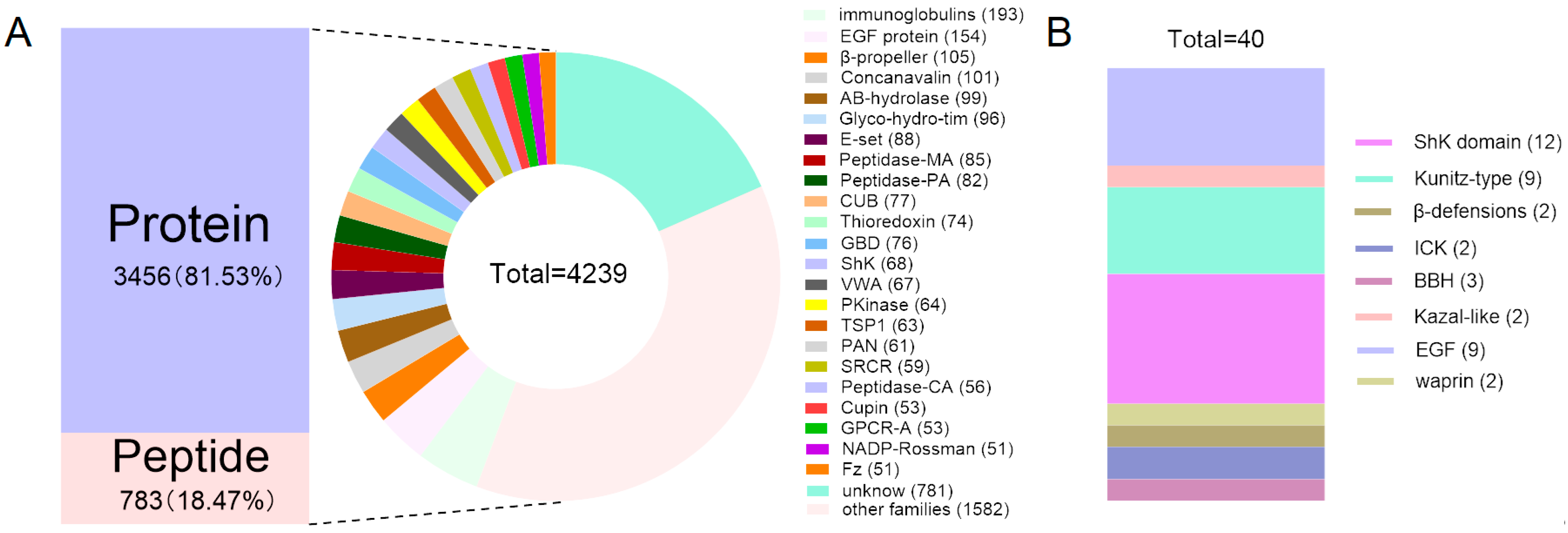
2.2. Family Classification of Putative Proteins and Peptides in the M. doreensis Transcriptome
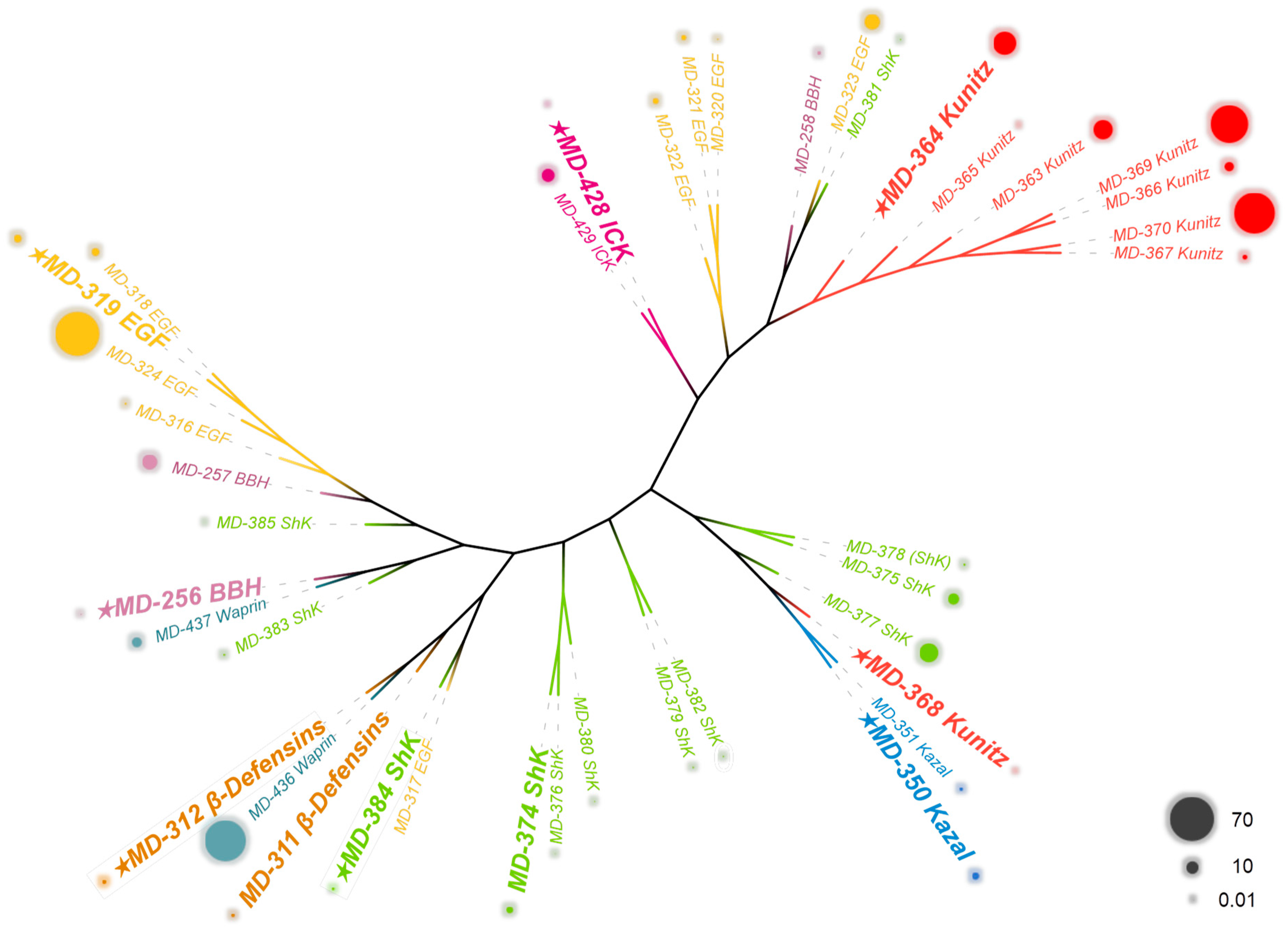
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Putative Proteins and Peptides in Different Tissues of M. doreensis
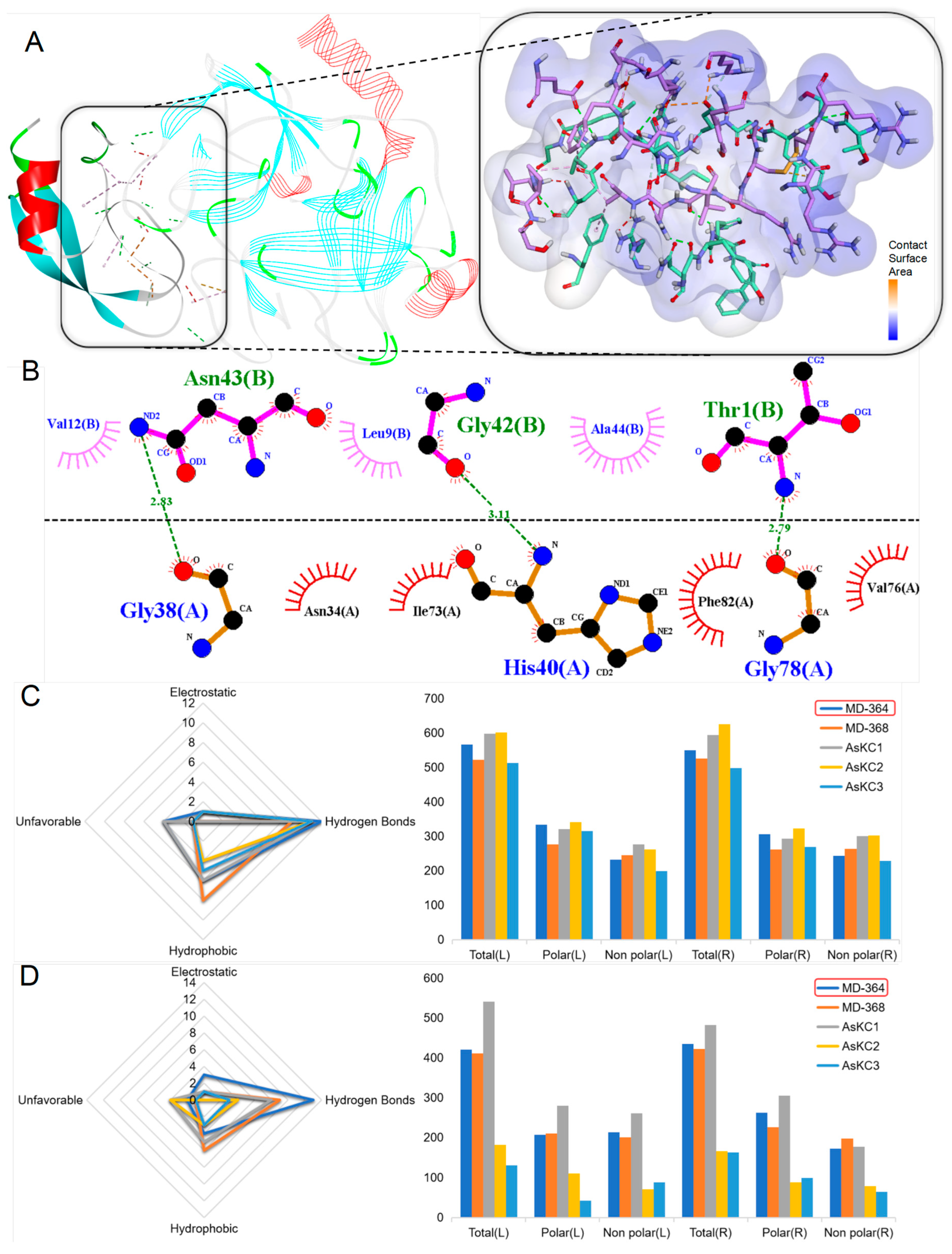
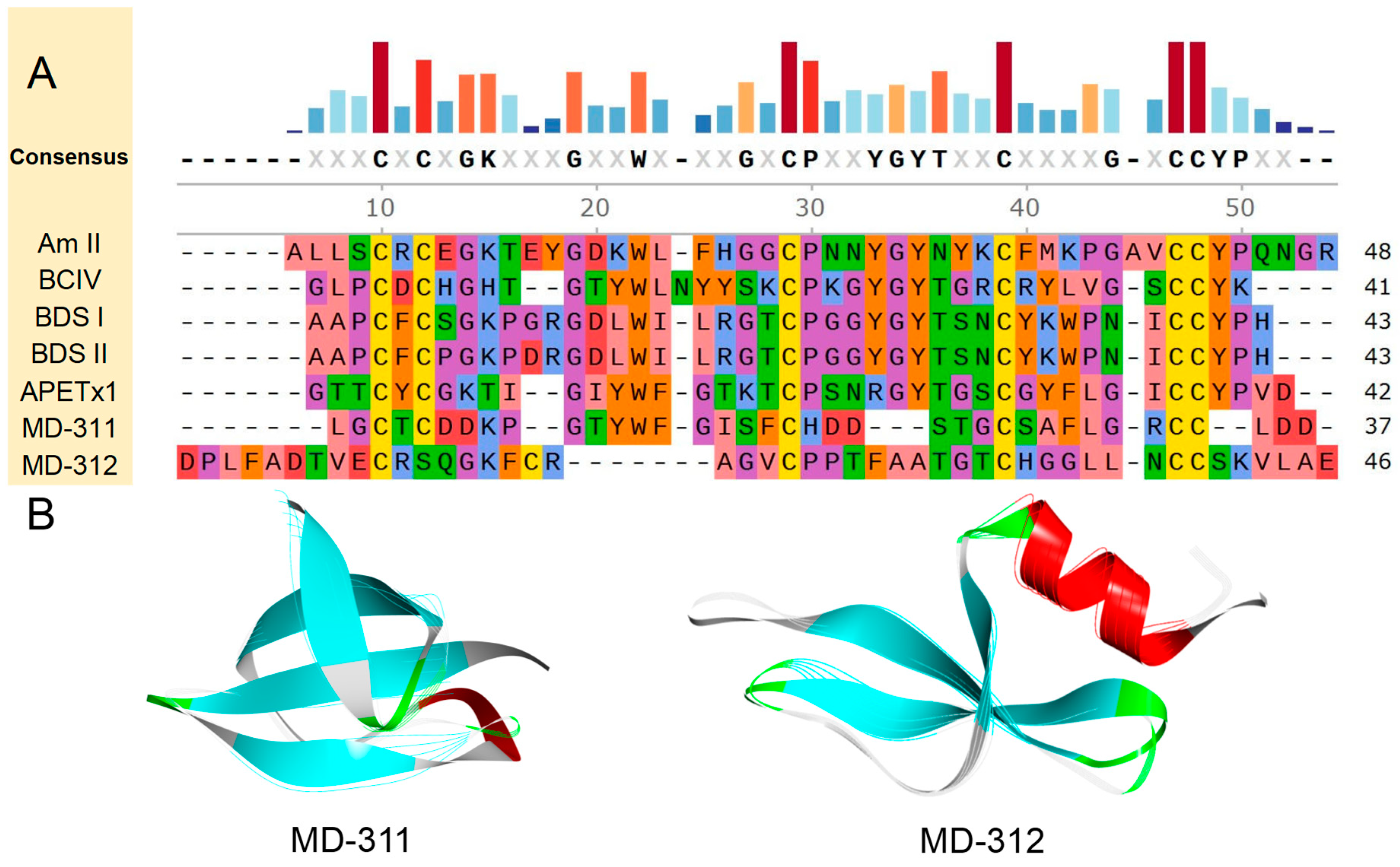
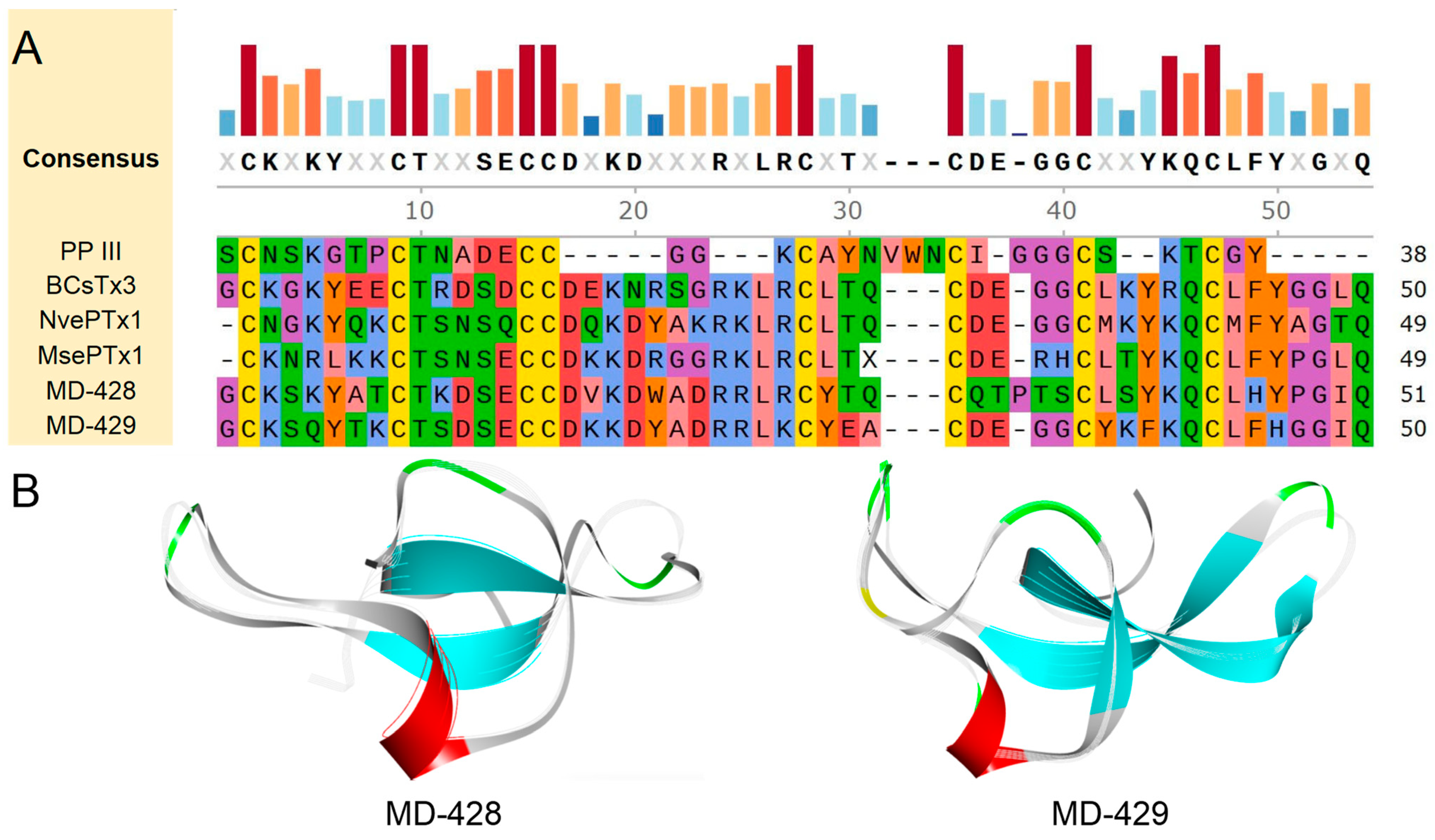
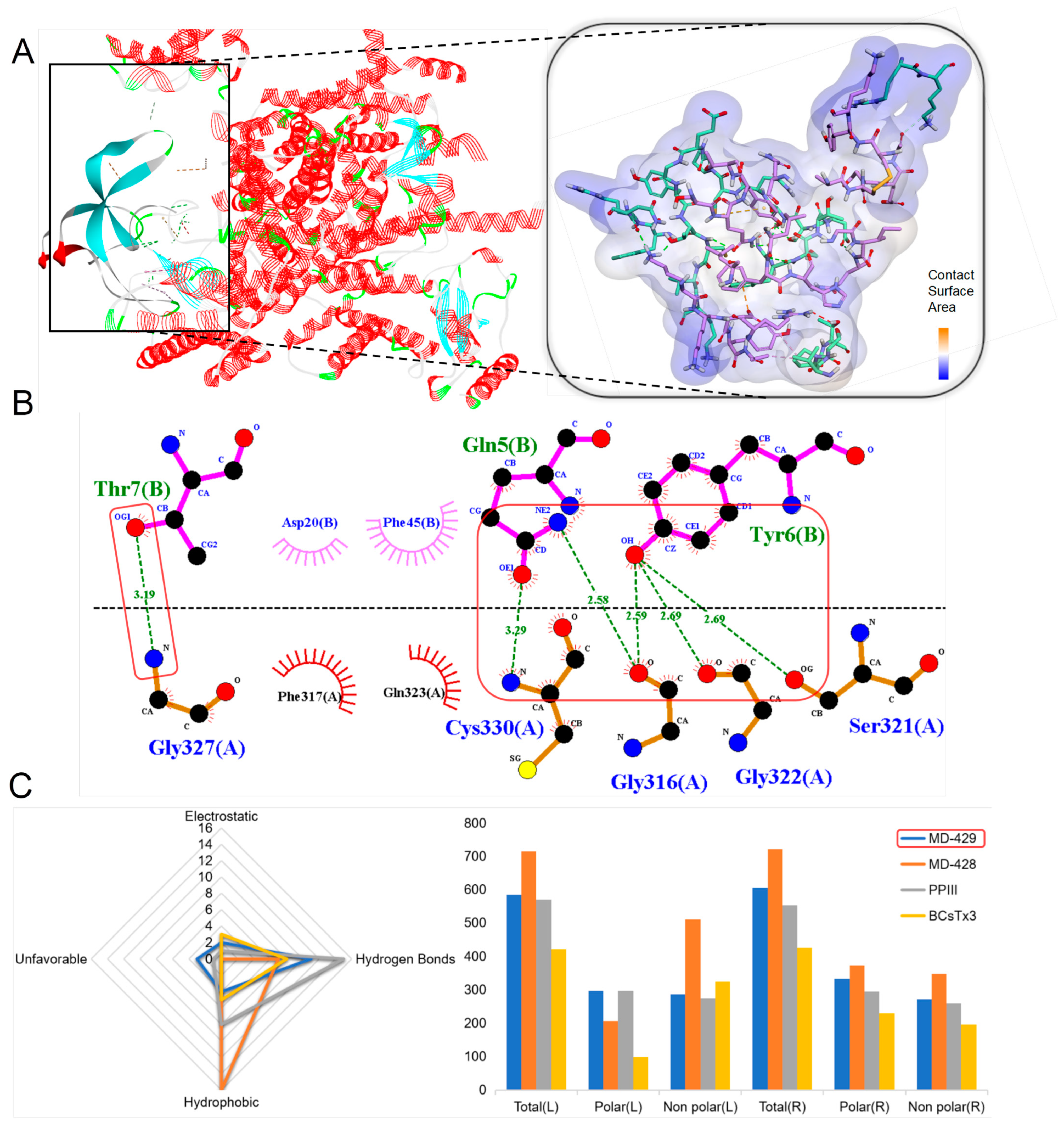
2.4. Sequence Analysis, Structure, and Target Prediction of Typical Putative Peptides
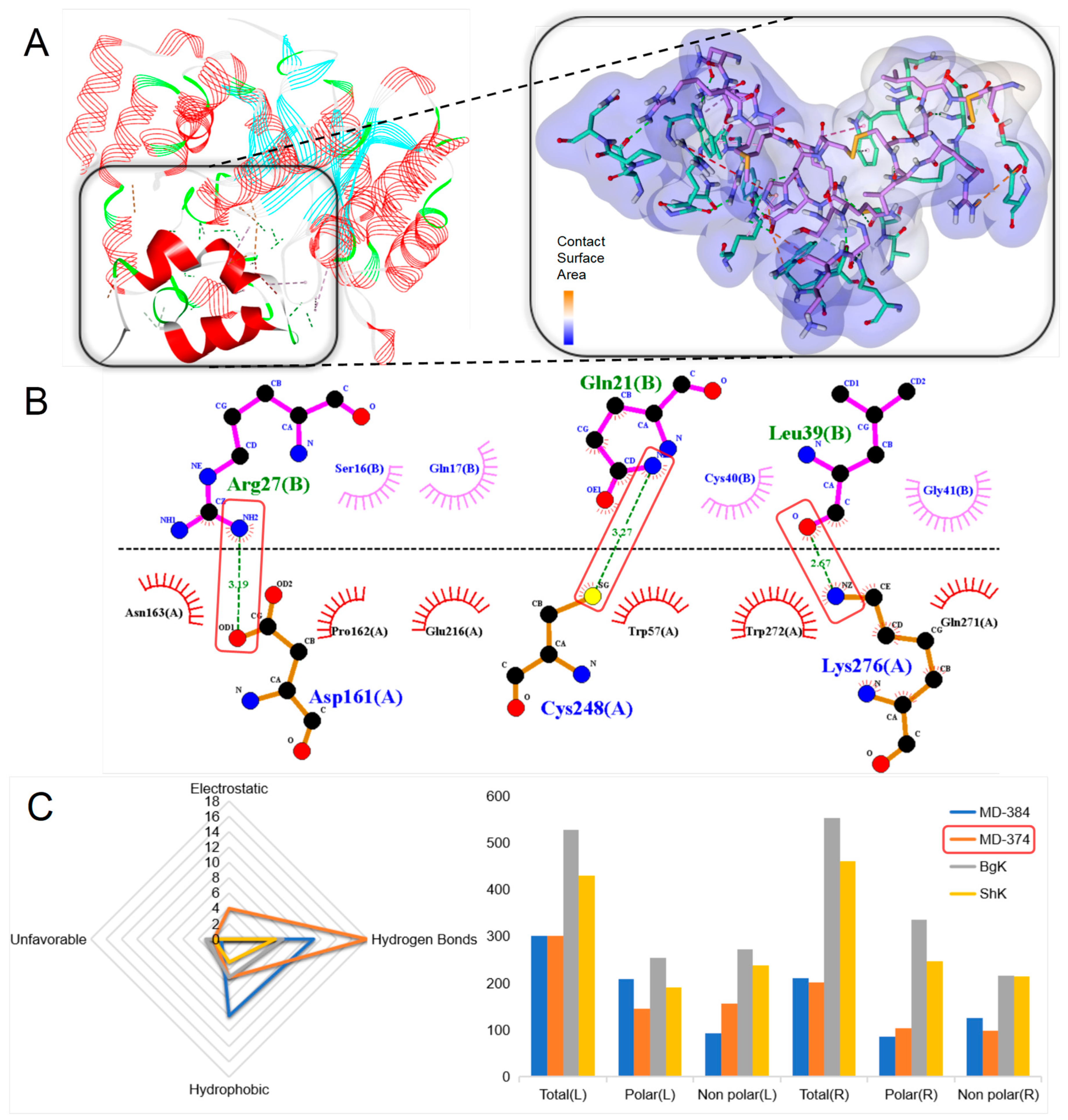
2.4.1. ShK Domain
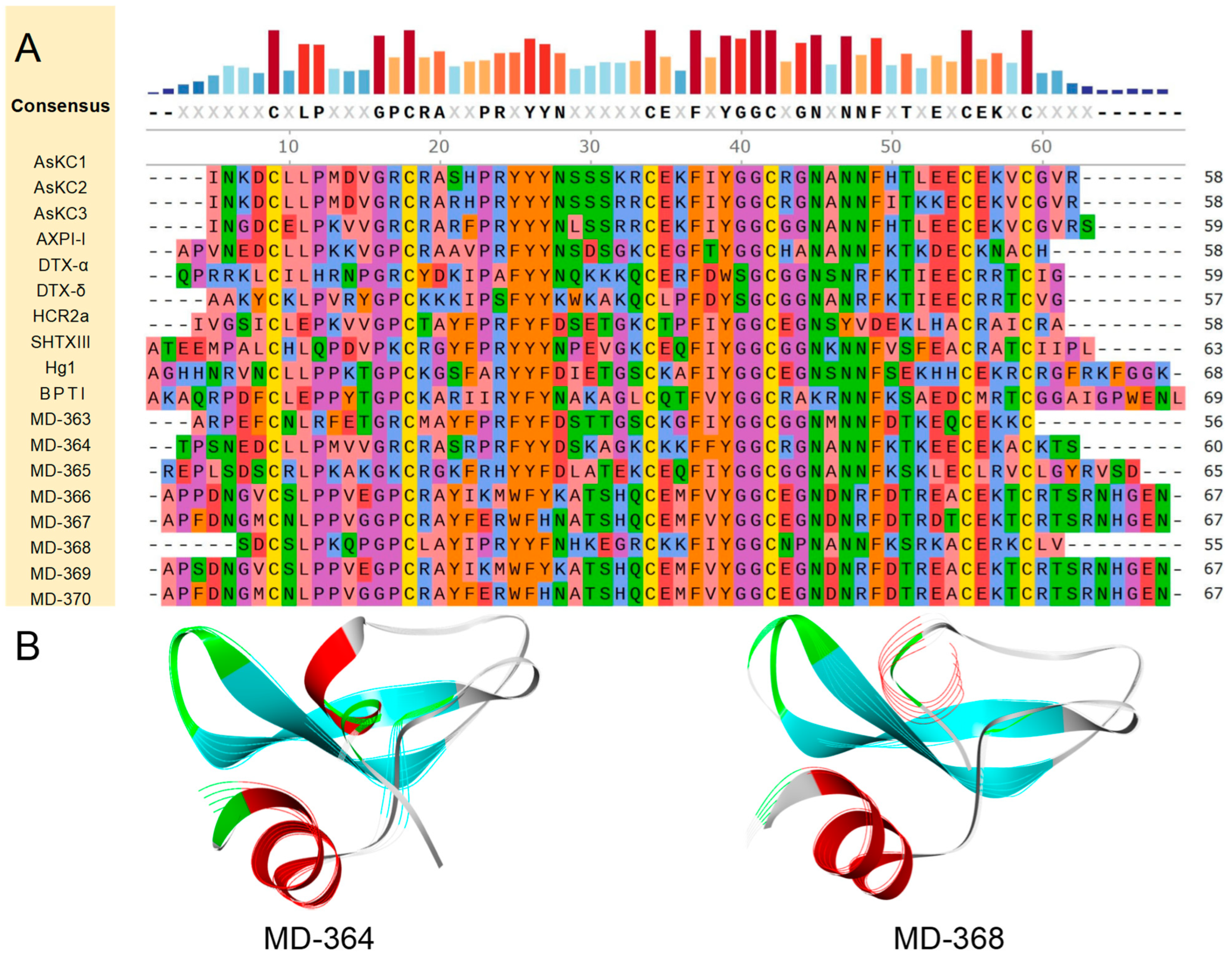
2.4.2. Kunitz-Type
2.4.3. β-Defensins
2.4.4. BBH
2.4.5. ICK
2.4.6. Kazal-like
2.4.7. EGF
2.4.8. Waprin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Specimen Collection
4.2. Transcriptome Construction and Quality Checking
4.3. Gene Annotation
4.4. Classification of Proteins and Peptides of M. doreensis
4.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
4.6. Alignment
4.7. AlphaFold2 Modeling and Model Alignment
4.8. Molecular Docking and Eyelash Diagram
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prentis, P.J.; Pavasovic, A.; Norton, R.S. Sea Anemones: Quiet Achievers in the Field of Peptide Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouiaei, M.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Madio, B.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Fry, B.G. Ancient Venom Systems: A Review on Cnidaria Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garese, A.; Goes Correa, F.; Acuña, F.H.; Stampar, S.N. Cnidom in Ceriantharia (Cnidaria, Anthozoa): New findings in the composition and micrometric variations of cnidocysts. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Corte, C.; Catania, V.; Dara, M.; Parrinello, D.; Staropoli, M.; Trapani, M.R.; Cammarata, M.; Parisi, M.G. Equinins as Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptides Isolated from the Cnidarian Actinia equina (Linnaeus, 1758). Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Pérez, D.; Campos, A.; Alexei Rodríguez, A.; Turkina, M.V.; Ribeiro, T.; Osorio, H.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Proteomic Analyses of the Unexplored Sea Anemone Bunodactis verrucosa. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinzeu, A.; Berthiller, J.; Perreton, N.; Subtil, F.; Gervaise, C.; Luaute, J.; Mertens, P. SPIDOL study protocol for the assessment of intrathecal ziconotide antalgic efficacy for severe refractory neuropathic pain due to spinal cord lesions. Trials 2024, 25, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarcha, E.J.; Olsen, C.M.; Probst, P.; Peckham, D.; Muñoz-Elías, E.J.; Kruger, J.G.; Iadonato, S.P. Safety and pharmacodynamics of dalazatide, a Kv1.3 channel inhibitor, in the treatment of plaque psoriasis: A randomized phase 1b trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.L.; Hossain, M.A.; Lin, F.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Peigneur, S.; Wai, D.C.C.; Delaine, C.; Blyth, A.J.; Forbes, B.E.; Tytgat, J.; et al. Identification, Synthesis, Conformation and Activity of an Insulin-like Peptide from a Sea Anemone. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnahriry, K.A.; Wai, D.C.C.; Ashwood, L.M.; Naseem, M.U.; Szanto, T.G.; Guo, S.; Panyi, G.; Prentis, P.J.; Norton, R.S. Structural and functional characterisation of Tst2, a novel TRPV1 inhibitory peptide from the Australian sea anemone Telmatactis stephensoni. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2024, 1872, 140952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, I.N.; Klimovich, A.A.; Kalina, R.S.; Kozhevnikova, Y.V.; Khasanov, T.A.; Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Andreev, Y.A.; Leychenko, E.V.; et al. Anxiolytic, Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Peptides Hmg 1b-2 and Hmg 1b-4 from the Sea Anemone Heteractis magnifica. Toxins 2023, 15, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackieh, R.; Abou-Nader, R.; Wehbe, R.; Mattei, C.; Legros, C.; Fajloun, Z.; Sabatier, J.M. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: A Prominent Target of Marine Toxins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Qasim, A.; Sophanpanichkul, P.; Dai, H.; Nayak, M.; Sher, I.; Chill, J.; Goldstein, S.A.N. Selective block of human Kv1.1 channels and an epilepsy-associated gain-of-function mutation by AETX-K peptide. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2024, 38, e23381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Junior, W.A.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Kazuma, K.; Picolo, G.; Gutierrez, V.P.; de Freitas, J.C.; Konno, K.; Cury, Y. Peripheral 5-HT3 Receptors Are Involved in the Antinociceptive Effect of Bunodosine 391. Toxins 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalina, R.S.; Gladkikh, I.N.; Klimovich, A.A.; Kozhevnikova, Y.V.; Kvetkina, A.N.; Rogozhin, E.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Kozlov, S.A.; Leychenko, E.V. First Anti-Inflammatory Peptide AnmTX Sco 9a-1 from the Swimming Sea Anemone Stomphia coccinea. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Montoya, C.; Heras-Márquez, D.; Amigot-Sánchez, R.; García-Linares, S.; Martínez-Del-Pozo, Á.; Palacios-Ortega, J. Sticholysin recognition of ceramide-phosphoethanolamine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 742, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Wulff, H.; Singh, S.; Nugent, D.; Crossley, G.; Khaytin, I.; Calabresi, P.A.; Chen, C.Y.; Gutman, G.A.; et al. Targeting effector memory T cells with a selective peptide inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels for therapy of autoimmune diseases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; He, Y.; Peng, C.; Tang, T.; Jin, A.; Liao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Gao, B. Transcriptome Sequencing of the Pale Anemones (Exaiptasia diaphana) Revealed Functional Peptide Gene Resources of Sea Anemone. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 856501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Fu, J.; Yuan, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Yi, B.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B. Diversity analysis of sea anemone peptide toxins in different tissues of Heteractis crispa based on transcriptomics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mao, K.; Huang, M.; Liao, Y.; Fu, J.; Pan, K.; Shi, Q.; Gao, B. Venomics Reveals the Venom Complexity of Sea Anemone Heteractis magnifica. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.; Cabrera-Muñoz, A.; Espinosa, L.A.; Montané, S.; Alvarez-Lajonchere, L.; Mojarena, J.D.; Moya, G.; Lorenzo, J.; González, L.J.; Betzel, C.; et al. CogiTx1: A novel subtilisin A inhibitor isolated from the sea anemone Condylactis gigantea belonging to the defensin 4 protein family. Biochimie 2023, 213, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, K.; Prypoten, V.; Chandy, K.G.; Chalmers, D.K.; Norton, R.S. Interaction of the Inhibitory Peptides ShK and HmK with the Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel K(V)1.3: Role of Conformational Dynamics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 3043–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Go, H.J.; Oh, H.Y.; Lee, T.K.; Park, J.B.; Park, N.G. Defensin-neurotoxin dyad in a basally branching metazoan sea anemone. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3320–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Norton, R.S. Analogs of the sea anemone potassium channel blocker ShK for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2011, 10, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, O.; Sotolongo, V.; Amor, A.M.; Stöcklin, R.; Anderson, A.J.; Harvey, A.L.; Engström, A.; Wernstedt, C.; Karlsson, E. Characterization of a potassium channel toxin from the Caribbean Sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1995, 33, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racapé, J.; Lecoq, A.; Romi-Lebrun, R.; Liu, J.; Kohler, M.; Garcia, M.L.; Ménez, A.; Gasparini, S. Characterization of a novel radiolabeled peptide selective for a subpopulation of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3886–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitz, H.; Bruhn, T.; Guillemare, E.; Moinier, D.; Lancelin, J.M.; Béress, L.; Lazdunski, M. Kalicludines and kaliseptine. Two different classes of sea anemone toxins for voltage sensitive K+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25121–25126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendeh, G.S.; Young, L.C.; de Medeiros, C.L.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Harvey, A.L.; Chung, M.C. A new potassium channel toxin from the sea anemone Heteractis magnifica: Isolation, cDNA cloning, and functional expression. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 11461–11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, S.; Ishida, M.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Primary structure of a potassium channel toxin from the sea anemone Actinia equina. FEBS Lett. 1998, 427, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orts, D.J.; Peigneur, S.; Madio, B.; Cassoli, J.S.; Montandon, G.G.; Pimenta, A.M.; Bicudo, J.E.; Freitas, J.C.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Tytgat, J. Biochemical and electrophysiological characterization of two sea anemone type 1 potassium toxins from a geographically distant population of Bunodosoma caissarum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 655–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Pérez, M.; Capera, J.; Benavente-Garcia, A.; Cassinelli, S.; Colomer-Molera, M.; Felipe, A. Kv1.3 in the spotlight for treating immune diseases. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2024, 28, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M. Evolutionary Aspects of the Structural Convergence and Functional Diversification of Kunitz-Domain Inhibitors. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minagawa, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Ishida, M.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Kunitz-type protease inhibitors from acrorhagi of three species of sea anemones. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 150, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão, C.B.; Schwartz, E.F. Protease inhibitors from marine venomous animals and their counterparts in terrestrial venomous animals. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2069–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imredy, J.P.; MacKinnon, R. Energetic and structural interactions between delta-dendrotoxin and a voltage-gated potassium channel. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, T.; Kawahata, S.; Ishida, M.; Nagai, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Novel peptide toxins from the sea anemone Stichodactyla haddoni. Peptides 2008, 29, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Kessi, M.; Yin, F.; Peng, J. Roles of KCNA2 in Neurological Diseases: From Physiology to Pathology. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharenko, A.J.; Ferreira, W.A., Jr.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Konno, K.; Richardson, M.; Schiavon, E.; Wanke, E.; de Freitas, J.C. Revisiting cangitoxin, a sea anemone peptide: Purification and characterization of cangitoxins II and III from the venom of Bunodosoma cangicum. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 51, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.A.; Garateix, A.; Salceda, E.; Peigneur, S.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Pons, T.; Santos, Y.; Arreguín, R.; Ständker, L.; Forssmann, W.G.; et al. PhcrTx2, a New Crab-Paralyzing Peptide Toxin from the Sea Anemone Phymanthus crucifer. Toxins 2018, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintsova, O.; Gladkikh, I.; Kalinovskii, A.; Zelepuga, E.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Kim, N.; Shevchenko, L.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Kozlovskaya, E.; et al. Magnificamide, a β-Defensin-Like Peptide from the Mucus of the Sea Anemone Heteractis magnifica, Is a Strong Inhibitor of Mammalian α-Amylases. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.Y.; Thompson, D.; Wang, Z.; Fedida, D.; Robertson, B. Modulation of Kv3 subfamily potassium currents by the sea anemone toxin BDS: Significance for CNS and biophysical studies. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8735–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Ferreira, W.A., Jr.; Konno, K.; Shida, C.S.; Richardson, M.; Lúcio, A.D.; Beirão, P.S.; de Freitas, J.C. BcIV, a new paralyzing peptide obtained from the venom of the sea anemone Bunodosoma caissarum. A comparison with the Na+ channel toxin BcIII. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, H.; Castle, N.A.; Pardo, L.A. Voltage-gated potassium channels as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 982–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, K.; Shimomura, T.; Kubo, Y.; Oka, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Imai, S.; Yanase, N.; Akimoto, M.; Fukuda, M.; Yokogawa, M.; et al. Mechanism of hERG inhibition by gating-modifier toxin, APETx1, deduced by functional characterization. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, O.; Harvey, A.L. Discovery and characterization of cnidarian peptide toxins that affect neuronal potassium ion channels. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2009, 54, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, T.; Kudo, T.; Yamane, H.; Ishibashi, F.; Takada, Y.; Honda, S.; Maezawa, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Oyamada, Y. Unique electrophysiological property of a novel Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 sodium channel blocker, ANP-230. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 721, 150126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Kozlov, S.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Sanamyan, N.P.; Sanamyan, K.E.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Mineev, K.S.; et al. Sea anemone peptide with uncommon β-hairpin structure inhibits acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) and reveals analgesic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23116–23127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ishida, M.; Nagai, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Isolation and molecular cloning of novel peptide toxins from the sea anemone Antheopsis maculata. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2005, 45, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharenko, A.J.; Ferreira, W.A., Jr.; Oliveira, J.S.; Richardson, M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Konno, K.; Portaro, F.C.; de Freitas, J.C. Proteomics of the neurotoxic fraction from the sea anemone Bunodosoma cangicum venom: Novel peptides belonging to new classes of toxins. Comp. Biochem. Physiology. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2008, 3, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logashina, Y.A.; Mosharova, I.V.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Kozlov, S.A.; Stensvåg, K.; et al. Peptide from Sea Anemone Metridium senile Affects Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin-repeat 1 (TRPA1) Function and Produces Analgesic Effect. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.B.; Fu, J.X.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, H.F.; Wu, Z.Y.; Chen, D.F. Both gain- and loss-of-function variants of KCNA1 are associated with paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia. J. Genet. Genom. Yi Chuan Xue Bao 2024, 51, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Logashina, Y.A.; Kornilov, F.D.; Lushpa, V.A.; Maleeva, E.E.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S.; et al. Peptides from the Sea Anemone Metridium senile with Modified Inhibitor Cystine Knot (ICK) Fold Inhibit Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2022, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, G.O.; de Resende Lara, P.T.; Scott, L.P.; Braz, A.S.; Chaves-Moreira, D.; Matsubara, F.H.; Soares, E.M.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Gremski, L.H.; Veiga, S.S.; et al. Molecular cloning and in silico characterization of knottin peptide, U2-SCRTX-Lit2, from brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom glands. J. Mol. Model. 2016, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bende, N.S.; Kang, E.; Herzig, V.; Bosmans, F.; Nicholson, G.M.; Mobli, M.; King, G.F. The insecticidal neurotoxin Aps III is an atypical knottin peptide that potently blocks insect voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orts, D.J.; Moran, Y.; Cologna, C.T.; Peigneur, S.; Madio, B.; Praher, D.; Quinton, L.; De Pauw, E.; Bicudo, J.E.; Tytgat, J.; et al. BcsTx3 is a founder of a novel sea anemone toxin family of potassium channel blocker. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4839–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Columbus-Shenkar, Y.Y.; Sachkova, M.Y.; Macrander, J.; Fridrich, A.; Modepalli, V.; Reitzel, A.M.; Sunagar, K.; Moran, Y. Dynamics of venom composition across a complex life cycle. eLife 2018, 7, e35014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Kumazaki, T.; Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, K.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Structural and functional study of an Anemonia elastase inhibitor, a “nonclassical” Kazal-type inhibitor from Anemonia sulcata. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9626–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Zou, X.; Zhou, J.Y.; Sun, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.L.; Wang, R.P. Raddeanin A induces human gastric cancer cells apoptosis and inhibits their invasion in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, S.; Zeng, D.; Zhou, W. Association between polymorphisms and atopic dermatitis susceptibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene 2024, 913, 148397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, E.; Peigneur, S.; Debaveye, S.; Shiomi, K.; Tytgat, J. TRPV1 Channel as New Target for Marine Toxins: Example of Gigantoxin I, a Sea Anemone Toxin Acting Via Modulation of the PLA2 Pathway. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 735–741. [Google Scholar]
- Sampoli Benitez, B.A.; Komives, E.A. Disulfide bond plasticity in epidermal growth factor. Proteins 2000, 40, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga-Córdoba, M.; Clavero-León, C.; Rey-Suarez, P.; Nuñez-Rangel, V.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Solano-González, S.; Alzate, J.F. Unveiling Novel Kunitz- and Waprin-Type Toxins in the Micrurus mipartitus Coral Snake Venom Gland: An In Silico Transcriptome Analysis. Toxins 2024, 16, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.G.; Fry, B.G.; Alewood, P.; Kumar, P.P.; Kini, R.M. Antimicrobial activity of omwaprin, a new member of the waprin family of snake venom proteins. Biochem. J. 2007, 402, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.S. Structures of sea anemone toxins. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2009, 54, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, T.P. Immunoglobulins, Structure, and Function. In Paraproteinemia and Related Disorders; Ragab, G., Quartuccio, L., Goubran, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2022; pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Schmitt, P.; Venier, P.; Rocha, G.; Rosa, R.D.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D. Functional Insights From the Evolutionary Diversification of Big Defensins. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Robertson, B. Dendrotoxins: Structure-activity relationships and effects on potassium ion channels. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlShammari, A.K.; Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Al-Sabi, A. Snake Venom: A Promising Source of Neurotoxins Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Toxins 2023, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biji, C.A.; Balde, A.; Nazeer, R.A. Anti-inflammatory peptide therapeutics and the role of sulphur containing amino acids (cysteine and methionine) in inflammation suppression: A review. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 1203–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banijamali, S.E.; Amininasab, M.; Elmi, M.M. Characterization of a new member of kunitz-type protein family from the venom of Persian false-horned viper, Pseudocerastes persicus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 662, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, K.T.; Rojnuckarin, P. Complementary DNA library of Myanmar Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii siamensis) venom gland. Comparative biochemistry and physiology. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2020, 227, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhu, S. An insect defensin-derived β-hairpin peptide with enhanced antibacterial activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Du, M.; Liu, N.; Shan, Q.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. A Novel β-Hairpin Peptide Z-d14CFR Enhances Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Clearance in a Murine Model of Mastitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Bai, M.; Hou, T.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Guan, P.; Hu, X. Novel photocatalytic carbon dots: Efficiently inhibiting amyloid aggregation and quickly disaggregating amyloid aggregates. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 8074–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, P.; Fernández-Mariño, A.I.; Khanra, N.; He, C.; Paquette, A.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, R.; Smider, V.V.; Rice, W.J.; Swartz, K.J.; et al. Structures of the T cell potassium channel Kv1.3 with immunoglobulin modulators. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladkikh, I.; Peigneur, S.; Sintsova, O.; Lopes Pinheiro-Junior, E.; Klimovich, A.; Menshov, A.; Kalinovsky, A.; Isaeva, M.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Kozlovskaya, E.; et al. Kunitz-Type Peptides from the Sea Anemone Heteractis crispa Demonstrate Potassium Channel Blocking and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvetkina, A.; Leychenko, E.; Chausova, V.; Zelepuga, E.; Chernysheva, N.; Guzev, K.; Pislyagin, E.; Yurchenko, E.; Menchinskaya, E.; Aminin, D.; et al. A new multigene HCIQ subfamily from the sea anemone Heteractis crispa encodes Kunitz-peptides exhibiting neuroprotective activity against 6-hydroxydopamine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintsova, O.; Gladkikh, I.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Tabakmakher, V.; Yurchenko, E.; Menchinskaya, E.; Pislyagin, E.; Andreev, Y.; Kozlov, S.; Peigneur, S.; et al. Sea Anemone Kunitz-Type Peptides Demonstrate Neuroprotective Activity in the 6-Hydroxydopamine Induced Neurotoxicity Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Sarojini, S.; Jayaram, S.; Philip, I.; Umesh, M.; Mascarenhas, R.; Pappuswamy, M.; Balasubramanian, B.; Arokiyaraj, S. Understanding the Role of Antimicrobial Peptides in Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promoting Autoimmune Disorders. Life 2023, 13, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mu, R.; Guo, X. Defensins regulate cell cycle: Insights of defensins on cellular proliferation and division. Life Sci. 2024, 349, 122740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Cui, C.; Hu, Q.; Xu, H.; Yin, B.; Chen, X.; Zhao, D.; et al. Recent advances in small molecule Nav 1.7 inhibitors for cancer pain management. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 150, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, M.; Mercurio, F.A.; Leone, M. Virtual Screening of Peptide Libraries: The Search for Peptide-Based Therapeutics Using Computational Tools. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrander, J.; Brugler, M.R.; Daly, M. A RNA-seq approach to identify putative toxins from acrorhagi in aggressive and non-aggressive Anthopleura elegantissima polyps. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Gong, G.; Poon, T.C.; Ang, I.L.; Lei, K.M.; Siu, S.W.I.; Wong, C.T.T.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis reveals a diversity of venom-related and toxin-like peptides expressed in the mat anemone Zoanthus natalensis (Cnidaria Hexacorallia). Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1745–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungo, F.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I.; Poux, S. The UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Tox-Prot program: A central hub of integrated venom protein data. Toxicon 2012, 60, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Mistry, J.; Tate, J.; Coggill, P.; Heger, A.; Pollington, J.E.; Gavin, O.L.; Gunasekaran, P.; Ceric, G.; Forslund, K.; et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 33, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, M.; Kim, S.S.; Tumescheit, C.; Mirdita, M.; Lee, J.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Z.; Liao, Y.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Lin, L.; Huang, M.; Gao, B. Revealing the Diversity of Sequences, Structures, and Targets of Peptides from South China Sea Macrodactyla doreensis Based on Transcriptomics. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100470
Hua Z, Liao Y, Fu J, Li X, Xu Q, Lin L, Huang M, Gao B. Revealing the Diversity of Sequences, Structures, and Targets of Peptides from South China Sea Macrodactyla doreensis Based on Transcriptomics. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(10):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100470
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Ziqiang, Yanling Liao, Jinxing Fu, Xinru Li, Qianxia Xu, Limin Lin, Meiling Huang, and Bingmiao Gao. 2024. "Revealing the Diversity of Sequences, Structures, and Targets of Peptides from South China Sea Macrodactyla doreensis Based on Transcriptomics" Marine Drugs 22, no. 10: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100470
APA StyleHua, Z., Liao, Y., Fu, J., Li, X., Xu, Q., Lin, L., Huang, M., & Gao, B. (2024). Revealing the Diversity of Sequences, Structures, and Targets of Peptides from South China Sea Macrodactyla doreensis Based on Transcriptomics. Marine Drugs, 22(10), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100470






