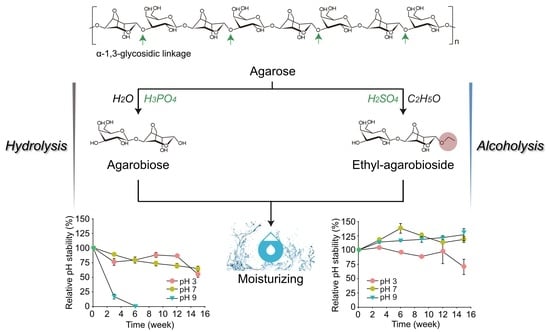
Production of Ethyl-agarobioside, a Novel Skin Moisturizer, by Mimicking the Alcoholysis from the Japanese Sake-Brewing Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Skin-Moisturizing Activity of AB
2.2. Thermal and pH Stabilities of AB
2.3. Production of Ethyl-AB by Acid-Catalyzed Alcoholysis of Agarose
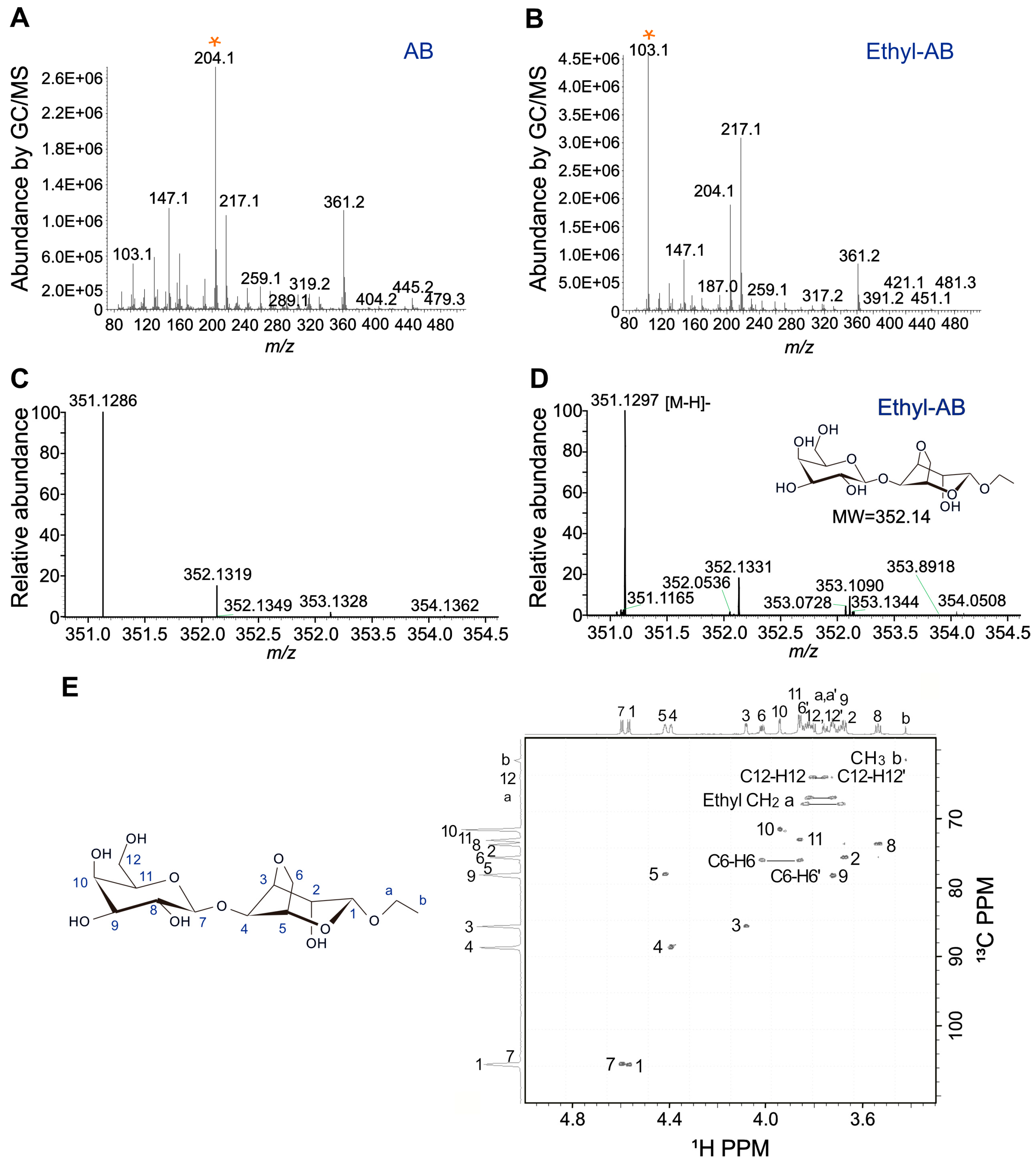
2.4. Identification of Ethyl-AB by MS and NMR Analyses
2.5. Skin-Moisturizing Activity of Ethyl-AB
2.6. Thermal and pH Stabilities of Ethyl-AB
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of AB and Ethyl-AB
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. HPLC Analysis
3.2.2. GC/MS Analysis
3.2.3. LC/MS Analysis
3.2.4. NMR Analysis
3.3. Thermal and pH Stabilities of AB and Ethyl-AB
3.4. In Vitro Skin-Moisturizing Activities of AB and Ethyl-AB
3.4.1. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.4.2. In Vitro Skin-Moisturizing Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, N.; Quarterman, J.; Jin, Y.-S. Marine macroalgae: An untapped resource for producing fuels and chemicals. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.B.A.; Adel, M.; Karimi, P.; Peidayesh, M. Pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, and traditional applications of marine carbohydrates. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 73, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.H.; Ko, S.C.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.J. Screening of marine algae for potential tyrosinase inhibitor: Those inhibitors reduced tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in zebrafish. J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Ravichandran, Y.D.; Khan, S.B.; Kim, Y.T. Prospective of the cosmeceuticals derived from marine organisms. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2008, 13, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takematsu, H.; Seiji, M. Effect of macrophages on elimination of dermal melanin from the dermis. Arch. Dermatol. 1984, 276, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armisen, R.; Galatas, F. Production, properties and uses of agar. In: Production and utilization of products from commercial seaweeds. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 1987, 288, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ridolfi, M.; Paudice, M.; Salvi, S.; Valle, L.; Gualco, M.; Perasole, A.; Anselmi, L.; Fiocca, R.; Mastracci, L.; Grillo, F. Agar pre-embedding of small skin biopsies: Real-life benefits and challenges in high throughput pathology laboratories. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, S.H.; Myslabodski, D.E.; Larsen, B.; Usov, A.I. A modified system of nomenclature for red algal galactans. Bot. Mar. 1994, 37, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, A.I. Structural analysis of red seaweed galactans of agar and carrageenan groups. Food Hydrocoll. 1998, 12, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.J.; Yu, S.; Kim, K.H. Current knowledge on agarolytic enzymes and the industrial potential of agar-derived sugars. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5581–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yu, G.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, G.; Ren, S.; Chai, W. Mechanism of mild acid hydrolysis of galactan polysaccharides with highly ordered disaccharide repeats leading to a complete series of exclusively odd-numbered oligosaccharides. FEBS Lett. 2009, 276, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, E.J.; Seo, N.; Yu, S.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, K.M.; An, H.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, I.-G.; Kim, K.H. Enzymatic liquefaction of agarose above the sol–gel transition temperature using a thermostable endo-type β-agarase, Aga16B. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, E.J.; Yu, S.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, N.J. Different levels of skin whitening activity among 3, 6-anhydro-l-galactose, agarooligosaccharides, and neoagarooligosaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, E.J.; Choi, I.-G.; Kim, K.H. Red macroalgae as a sustainable resource for bio-based products. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Yun, E.J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.H. Novel two-step process utilizing a single enzyme for the production of high-titer 3, 6-anhydro-L-galactose from agarose derived from red macroalgae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12249–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Liu, J.-J.; Lee, J.W.; Pelton, J.G.; Yun, E.J.; Yu, S.; Jin, Y.-S.; Kim, K.H. Biological upgrading of 3, 6-anhydro-l-galactose from agarose to a new platform chemical. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.-T.; Ra, C.H.; Hong, Y.-K.; Kim, J.K.; Kong, I.-S.; Kim, S.-K.; Park, D.-H. Conversion of red-algae Gracilaria verrucosa to sugars, levulinic acid and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Federation of Societies of Cosmetic Chemists (IFSCC). The Fundamentals of Stability Testing (IFSCC Monograph No. 2); Micelle Press Weymouth (UK): New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). [FDA-2000-P-0063]. Guidance for Industry: Labeling for Topically Applied Cosmetic Products Containing Alpha Hydroxy Acids, Updated January 2005, Last Revised November 2018; Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-labeling-cosmetics-containing-alpha-hydroxy-acids (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Kulthanan, K.; Maneeprasopchoke, P.; Varothai, S.; Nuchkull, P. The pH of antiseptic cleansers. Asia Pac. Allergy 2014, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoki, I.; Koji, K. Mammalian hyaluronan synthases. IUBMB Life 2002, 54, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raija, H.T.; Alberto, G.P.; Kirsi, R.; Evgenia, K.; Davide, V.; Makkonen, K.; Markku, I.T. Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of hyaluronan synthesis. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Ozeki, K.; Tsuge, H. Ethyl α-D-glucoside was absorbed in small intestine and excreted in urine as intact form. Nutrition 2005, 21, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaki, T.; Mitani, K.; Oura, Y.; Ozeki, K. Effects of ethyl-α-d- glucoside on human dermal fibroblasts. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Kim, Y.-A.; Yu, S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, N.J. 3,6-Anhydro-l-galactose increases hyaluronic acid production via the EGFR and AMPKα signaling pathway in HaCaT keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 96, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Takisada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kirimura, K.; Usami, S. Neoagarobiose as a novel moisturizer with whitening effect. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Yun, E.J.; Wang, D.; Chung, J.H.; Choi, I.-G.; Kim, K.H. High temperature and low acid pretreatment and agarase treatment of agarose for the production of sugar and ethanol from red seaweed biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Yan, X.-J. Antioxidant activities of agaro-oligosaccharides with different degrees of polymerization in cell-based system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2005, 1722, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.; Okuda, S.; Kudo, Y.; Takashima, F.; Sagawa, H.; Kato, I. Oligosaccharides from agar inhibit pro-inflammatory mediator release by inducing heme oxygenase 1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Park, J.; Na, J.G.; Oh, Y.K.; Chang, Y.K. Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from agarose by using a solid acid catalyst in dimethyl sulfoxide. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47983–47989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Honda, C.; Kobayashi, I.; Katsuta, R.; Matsumura, S.; Wagatsuma, I.; Takehisa, M.; Shindo, H.; Hosaka, M.; Nukada, T. Transglycosylation forms novel glycoside ethyl α-maltoside and ethyl α-isomaltoside in sake during the brewing process by α-glucosidase A of Aspergillus oryzae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Sato, S. Contribution of ethyl α-D-glucoside to flavor construction in sake. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi. 1976, 50, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Iwano, K.; Nunokawa, Y. Formation of ethyl alpha-d-glucoside in Sake brewing. J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1976, 50, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, F.; Uchiyama, H.; Imamura, T. Identification of α-d-glucosylglycerol in sake. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, F.; Uchiyama, H. Synthesis of α-d-glucosylglycerol by α-glucosidase and some of its characteristics. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N.; Zhao, J.; Kurihara, H.; Nakagata, N.; Okajima, K. Effects of topical application of α-D-Glucosylglycerol on dermal levels of insulin-like growth factor-I in mice and on facial skin elasticity in humans. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, N.; Ota, Y.; Haratake, A.; Ikemoto, T.; Tanno, O.; Horikoshi, T. Effects of ethyl α-d-glucoside on skin barrier disruption. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1997, 10, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, K.S.; Deng, F.; Gross, R.A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Swift, G. Ethyl glucoside as a multifunctional initiator for enzyme-catalyzed regioselective lactone ring-opening polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.; Aburada, M.; Ito, H. A simple efficient synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-O-ethylascorbic acid. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1984–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.; Kawasaki, D.; Goto, S.; Gohda, E.; Yamamoto, I. Vitamin C activity in guinea pigs of 6-O-acyl-2-O-α-d-glucopyranosyl-l-ascorbic acids with a branched-acyl chain. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, F.; Sil, B.C.; Moore, D.J.; Lucas, R.A.; Lane, M.E. 3-O-ethyl-l-ascorbic acid: Characterisation and investigation of single solvent systems for delivery to the skin. Int. J. Pharm X 2019, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanari, T.; Tamura, Z. The identification of α-ethyl glucoside and sugar-alcohols in sake. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1971, 35, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Yun, E.J.; Han, N.R.; Jung, I.; Pelton, J.G.; Lee, J.-E.; Kang, N.J.; Jin, Y.-S.; Kim, K.H. Production of Ethyl-agarobioside, a Novel Skin Moisturizer, by Mimicking the Alcoholysis from the Japanese Sake-Brewing Process. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060341
Lee S-H, Yun EJ, Han NR, Jung I, Pelton JG, Lee J-E, Kang NJ, Jin Y-S, Kim KH. Production of Ethyl-agarobioside, a Novel Skin Moisturizer, by Mimicking the Alcoholysis from the Japanese Sake-Brewing Process. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(6):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sun-Hee, Eun Ju Yun, Na Ree Han, Inho Jung, Jeffrey G. Pelton, Jae-Eun Lee, Nam Joo Kang, Yong-Su Jin, and Kyoung Heon Kim. 2023. "Production of Ethyl-agarobioside, a Novel Skin Moisturizer, by Mimicking the Alcoholysis from the Japanese Sake-Brewing Process" Marine Drugs 21, no. 6: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060341
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Yun, E. J., Han, N. R., Jung, I., Pelton, J. G., Lee, J.-E., Kang, N. J., Jin, Y.-S., & Kim, K. H. (2023). Production of Ethyl-agarobioside, a Novel Skin Moisturizer, by Mimicking the Alcoholysis from the Japanese Sake-Brewing Process. Marine Drugs, 21(6), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060341