In Vitro Biodegradation, Drug Absorption, and Physical Properties of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres Made of Subcritical-Water-Modified Fish Gelatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Changes in Physical Properties of SW-Modified Gelatin Hydrolysates
2.1.1. Color, pH, and Viscosity
2.1.2. MW of SW-Modified Gelatin
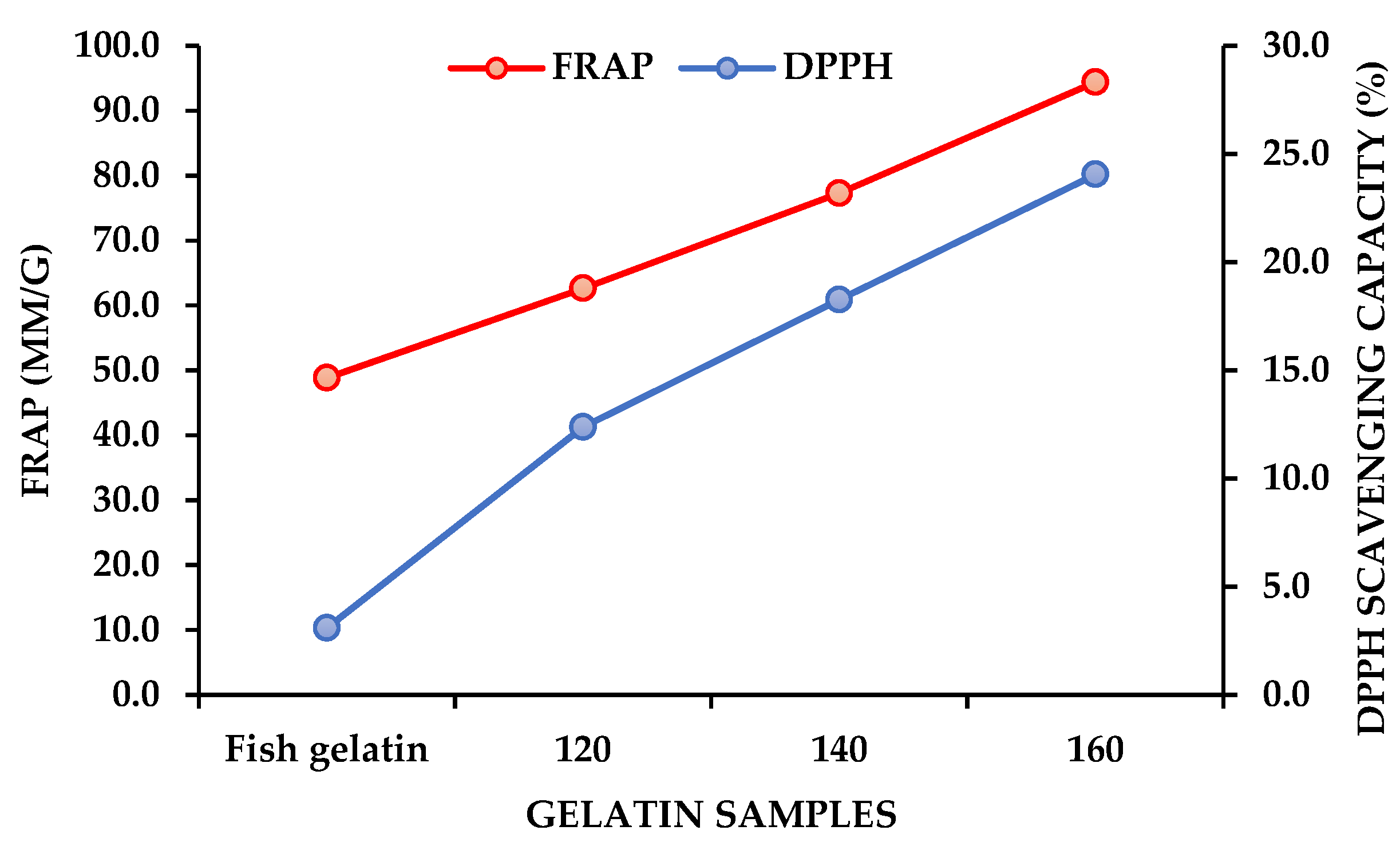
2.2. Antioxidant Activity of Fish Gelatin and SW-Modified Gelatin Hydrolysates
2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
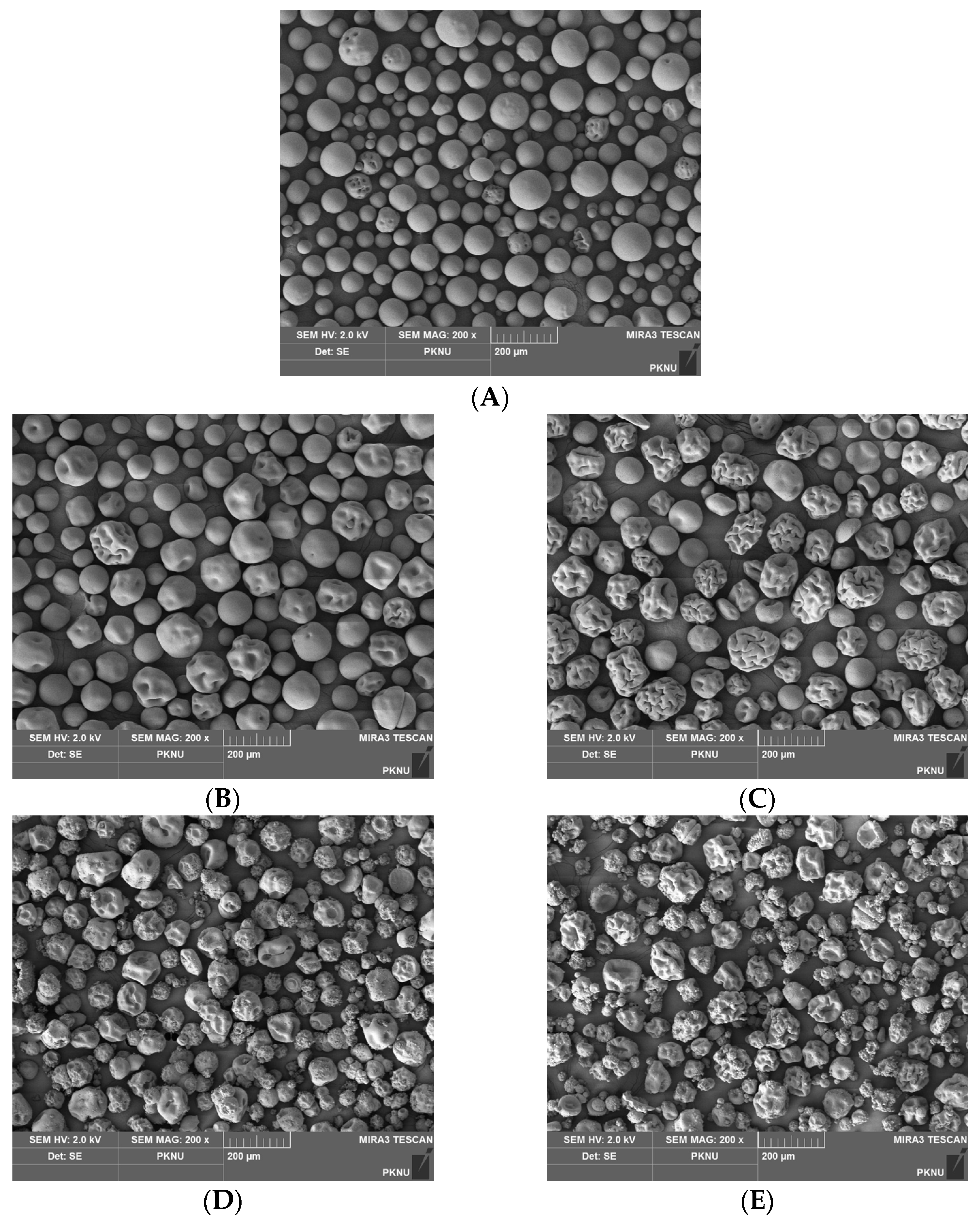
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
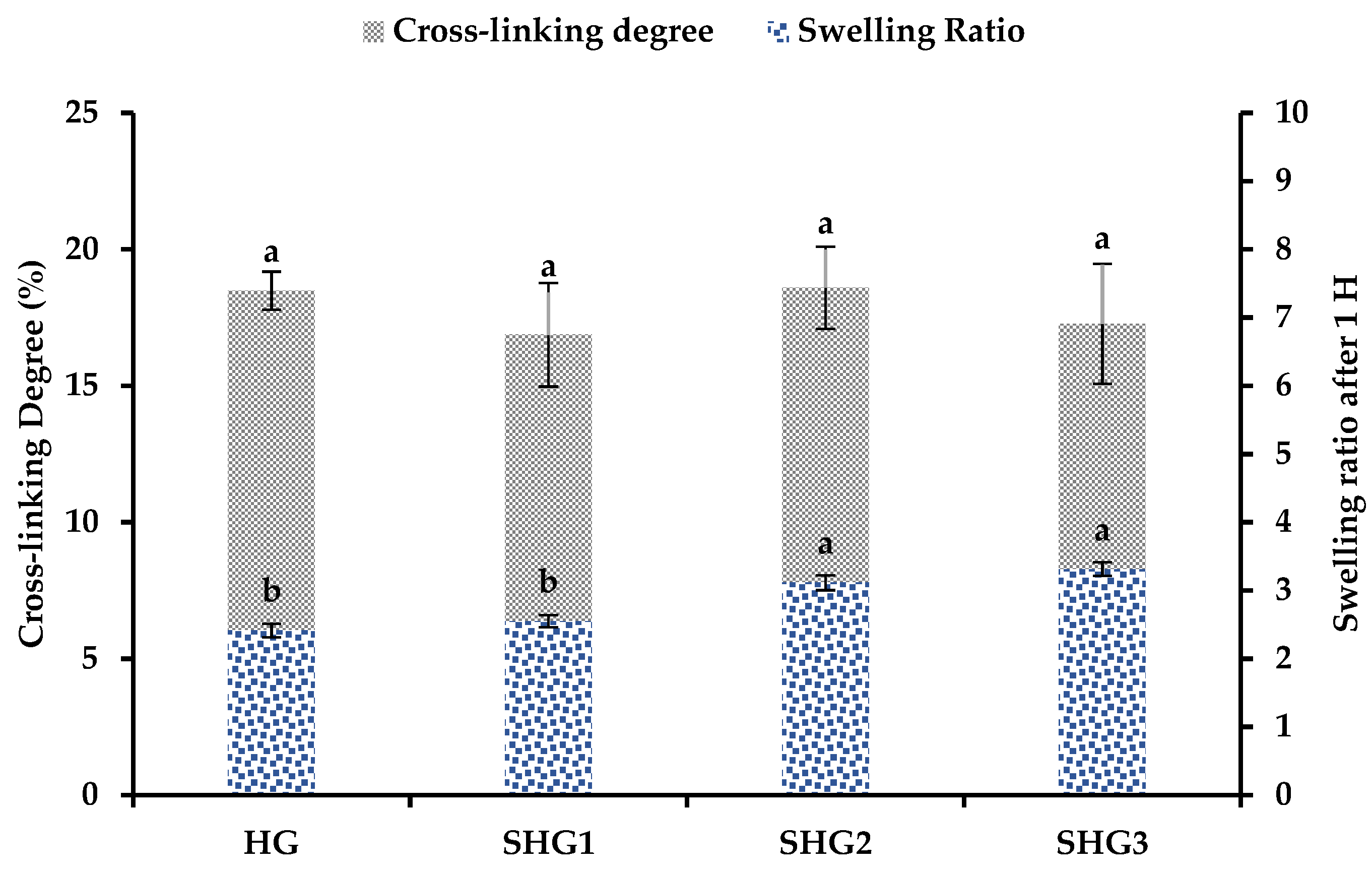
2.5. Cross-Linking Degree of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres
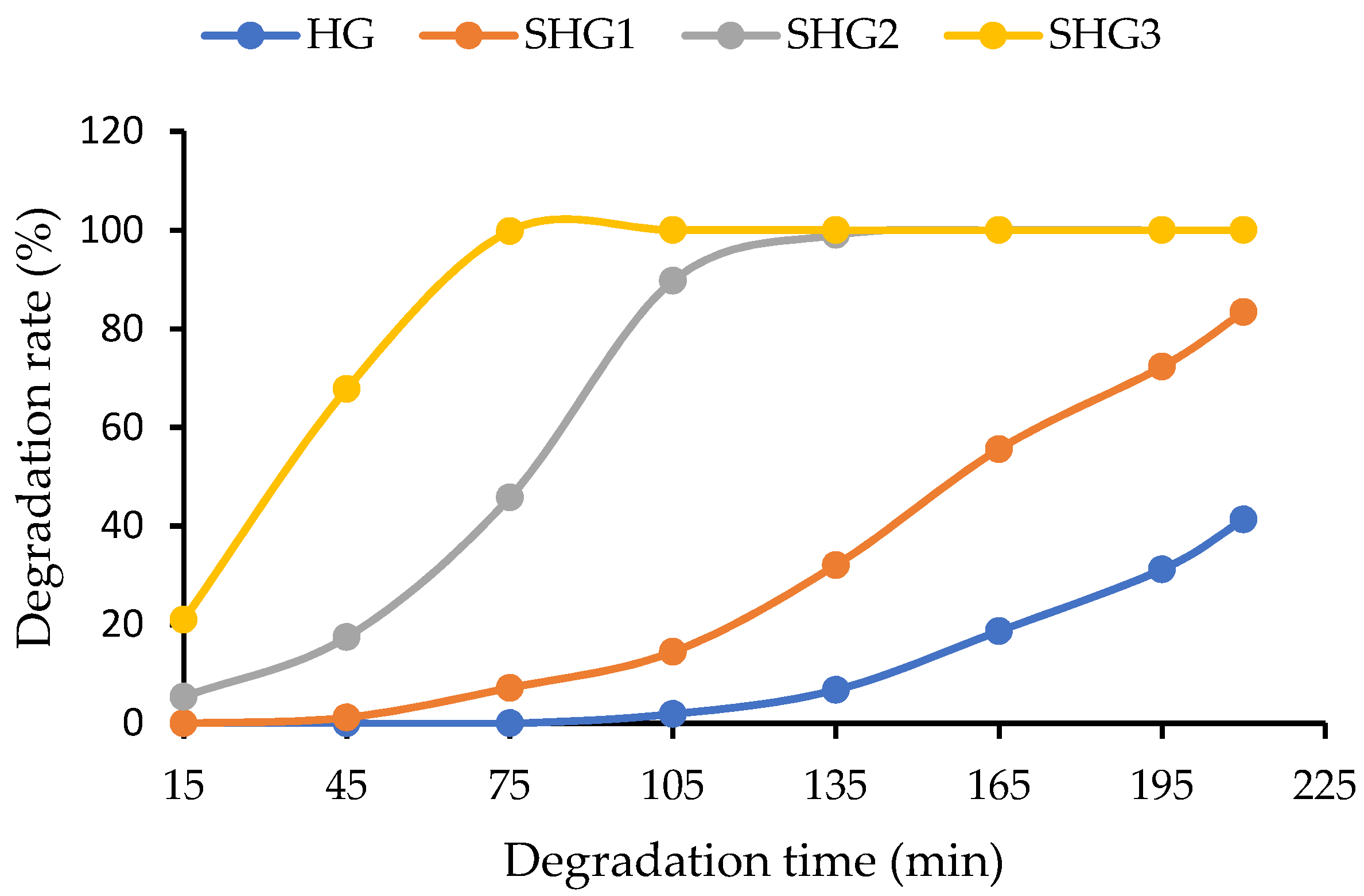
2.6. In Vitro Enzymatic Degradation of Microspheres
2.7. Doxorubicin Absorption Capacity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Subcritical Water Modification of Gelatin
3.3. Viscosity, pH, and Color Measurement
3.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Preparation of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres
3.7. Determination of Crosslinking Degree
3.8. Swelling Property
3.9. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.10. Morphology Analysis (SEM)
3.11. Enzymatic Degradation
3.12. Doxorubicin Absorption
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saralidze, K.; Koole, L.H.; Knetsch, M.L. Polymeric microspheres for medical applications. Materials 2010, 3, 3537–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, M.; Sánchez, P.; Pedraz, J.; Orive, G. Progress of gelatin-based 3D approaches for bone regeneration. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Nagate, T.; Matsuda, H. Acceleration of wound healing by gelatin film dressings with epidermal growth factor. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2005, 67, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, Y.; Yamada, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Nagata, I.; Kikuchi, H.; Aoyama, I.; Tamura, M.; Ikada, Y. Bone regeneration by basic fibroblast growth factor complexed with biodegradable hydrogels. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foox, M.; Zilberman, M. Drug delivery from gelatin-based systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.G.; Lee, M.Y.; Cha, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, Y.-S.; Bae, H. Nanogels Derived from Fish Gelatin: Application to Drug Delivery System. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.-C.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Lu, K.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Mi, F.-L. EGCG/gelatin-doxorubicin gold nanoparticles enhance therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin for prostate cancer treatment. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarasan, S.; Focsan, M.; Potara, M.; Soritau, O.; Florea, A.; Maniu, D.; Astilean, S. Doxorubicin-Incorporated Nanotherapeutic Delivery System Based on Gelatin-Coated Gold Nanoparticles: Formulation, Drug Release, and Multimodal Imaging of Cellular Internalization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22900–22913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C.; Desobry-Banon, S.; Hardy, J. Structure and Technofunctional Properties of Protein-Polysaccharide Complexes: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 689–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Yi, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, W.; Yang, Z. Fabrication and characterization of gelatin/chitosan microspheres for drug release. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2012, 51, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Citkowska, A.; Wróblewska, M.; Winnicka, K. The Impact of Gelatin on the Pharmaceutical Characteristics of Fucoidan Microspheres with Posaconazole. Materials 2021, 14, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, F.; Da Silva, M.A.; Drake, A.F.; Ross-Murphy, S.B.; Dreiss, C.A. Enzymatically cross-linked tilapia gelatin hydrogels: Physical, chemical, and hybrid networks. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-P.; Enomoto, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Aoki, T. Recent advances in phosphorylation of food proteins: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Ho, T.C.; Razack, S.A.; Haq, M.; Roy, V.C.; Park, J.-S.; Kang, H.W.; Chun, B.-S. Oligochitosan recovered from shrimp shells through subcritical water hydrolysis: Molecular size reduction and biological activities. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2023, 196, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizkyana, A.D.; Ho, T.C.; Roy, V.C.; Park, J.-S.; Kiddane, A.T.; Kim, G.-D.; Chun, B.-S. Sulfation and characterization of polysaccharides from Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) extracted using subcritical water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 179, 105412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and Bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Coutinho, A.J.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Bui, N.Q.; Jang, B.; Oh, Y.-O.; Lim, I.G.; Oh, J. Doxorubicin-loaded fucoidan capped gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and photoacoustic imaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, U.T.; Nguyen, K.T.; Vo, T.V.; Duan, W.; Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T. Investigation of fucoidan-oleic acid conjugate for delivery of curcumin and paclitaxel. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents) 2016, 16, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.-Y.; Li, R.; Hsu, C.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Chou, S.-C.; Tsai, M.-L.; Mi, F.-L. Development of a new type of multifunctional fucoidan-based nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, A.; Martín-Sabroso, C.; Gómez-Lázaro, L.; Torres-Suárez, A.I.; Aparicio-Blanco, J. Embolization therapy with microspheres for the treatment of liver cancer: State-of-the-art of clinical translation. Acta Biomater. 2022, 149, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duconseille, A.; Astruc, T.; Quintana, N.; Meersman, F.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Chun, B.-S. Subcritical water hydrolysis for the production of bioactive peptides from tuna skin collagen. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 141, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-T.; Tu, Z.-C.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.-Q.; Fan, L.-L.; Bao, Z.-Y.; Xiao, H. Functional properties and structure changes of soybean protein isolate after subcritical water treatment. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3412–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalinski, T.; Liu, K.; Albrecht, T.; Brunner, G. Hydrolysis kinetics of biopolymers in subcritical water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2008, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, S.; Ichinoi, H.; Zhao, J.; Fujii, T. Degradation of fish gelatin using hot-compressed water and the properties of the degradation products. High Press. Res. 2015, 35, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Roy, V.C.; Ho, T.C.; Park, J.-S.; Jeong, Y.-R.; Lee, S.-C.; Kim, S.-Y.; Chun, B.-S. Amino acid profiles and biopotentiality of hydrolysates obtained from comb penshell (Atrina pectinata) viscera using subcritical water hydrolysis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhirajan, N.; Shanmugasundaram, N.; Babu, M. Gelatin microspheres cross-linked with EDC as a drug delivery system for doxycyline: Development and characterization. J. Microencapsul. 2007, 24, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, K.; Katsumata, H.; Yabuta, T.; Iwanaga, K.; Kakemi, M.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Evaluation of gelatin microspheres for nasal and intramuscular administrations of salmon calcitonin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Ho, T.-C.; Micomyiza, J.-B.; Park, J.-S.; Nkurunziza, D.; Lee, H.-J. Subcritical Water Hydrolysis of Comb Pen Shell (Atrina pectinata) Edible Parts to Produce High-Value Amino Acid Products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.C.; Chun, B.S. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Pseuderanthemum palatiferum (Nees) Radlk. Using Subcritical Water and Conventional Solvents: A Comparison Study. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Temperature (°C) | L * | a * | b * | pH | Viscosity (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original gelatin | - | - | - | - | 7.18 ± 0.11 |
| 120 | 74.87 ± 2.8 | −0.8 ± 0.25 | 2.2 ± 0.24 | 6.36 ± 0.04 | 1.6 ± 0.04 |
| 140 | 72.3 ± 1.62 | −0.9 ± 0.22 | 7.1 ± 0.67 | 6.25 ± 0.02 | 1.0 ± 0.03 |
| 160 | 37.9 ± 1.22 | −0.85 ± 0.1 | 1.46 ± 0.2 | 6.3 ± 0.02 | 0.7 ± 0.07 |
| Samples | Mn (kDa) | Mw (kDa) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish gelatin | 6.6 | 26 | 3.96 |
| 120 | 4.1 | 12.2 | 2.98 |
| 140 | 1.7 | 4.1 | 2.36 |
| 160 | 1.4 | 2.8 | 2.06 |
| Compositions | Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | HG | SHG1 | SHG2 | SHG3 | |
| Fish gelatin (%) | 100 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Subcritical water-modified gelatin at 120 °C (%) | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| Subcritical water-modified gelatin at 140 °C (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| Subcritical water-modified gelatin at 160 °C (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 |
| Fucoidan * (%, w/v) | 0 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, T.C.; Lim, J.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Chun, B.-S. In Vitro Biodegradation, Drug Absorption, and Physical Properties of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres Made of Subcritical-Water-Modified Fish Gelatin. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050287
Ho TC, Lim J-S, Kim S-J, Kim S-Y, Chun B-S. In Vitro Biodegradation, Drug Absorption, and Physical Properties of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres Made of Subcritical-Water-Modified Fish Gelatin. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(5):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050287
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Truc Cong, Ju-Sop Lim, Shin-Jun Kim, Sung-Yeoul Kim, and Byung-Soo Chun. 2023. "In Vitro Biodegradation, Drug Absorption, and Physical Properties of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres Made of Subcritical-Water-Modified Fish Gelatin" Marine Drugs 21, no. 5: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050287
APA StyleHo, T. C., Lim, J.-S., Kim, S.-J., Kim, S.-Y., & Chun, B.-S. (2023). In Vitro Biodegradation, Drug Absorption, and Physical Properties of Gelatin–Fucoidan Microspheres Made of Subcritical-Water-Modified Fish Gelatin. Marine Drugs, 21(5), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050287






