Structural Characterization and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of a Novel Sialoglycopeptide from Tuna Eggs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
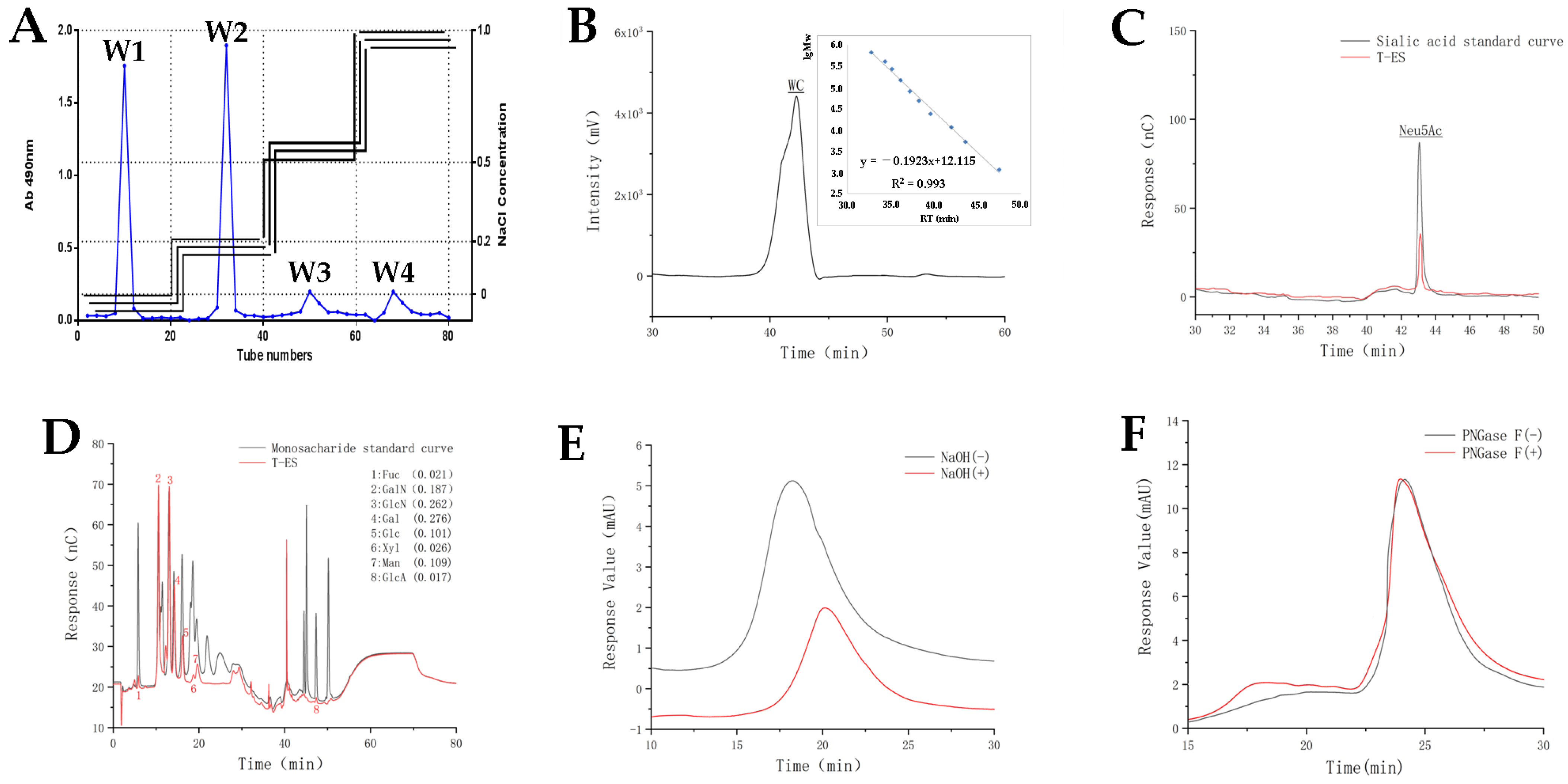
2.1. Isolation and Purification of T-ES and General Property Description
2.2. Chemical Composition of T-ES
2.3. Glycosidic Bond Type of T-ES
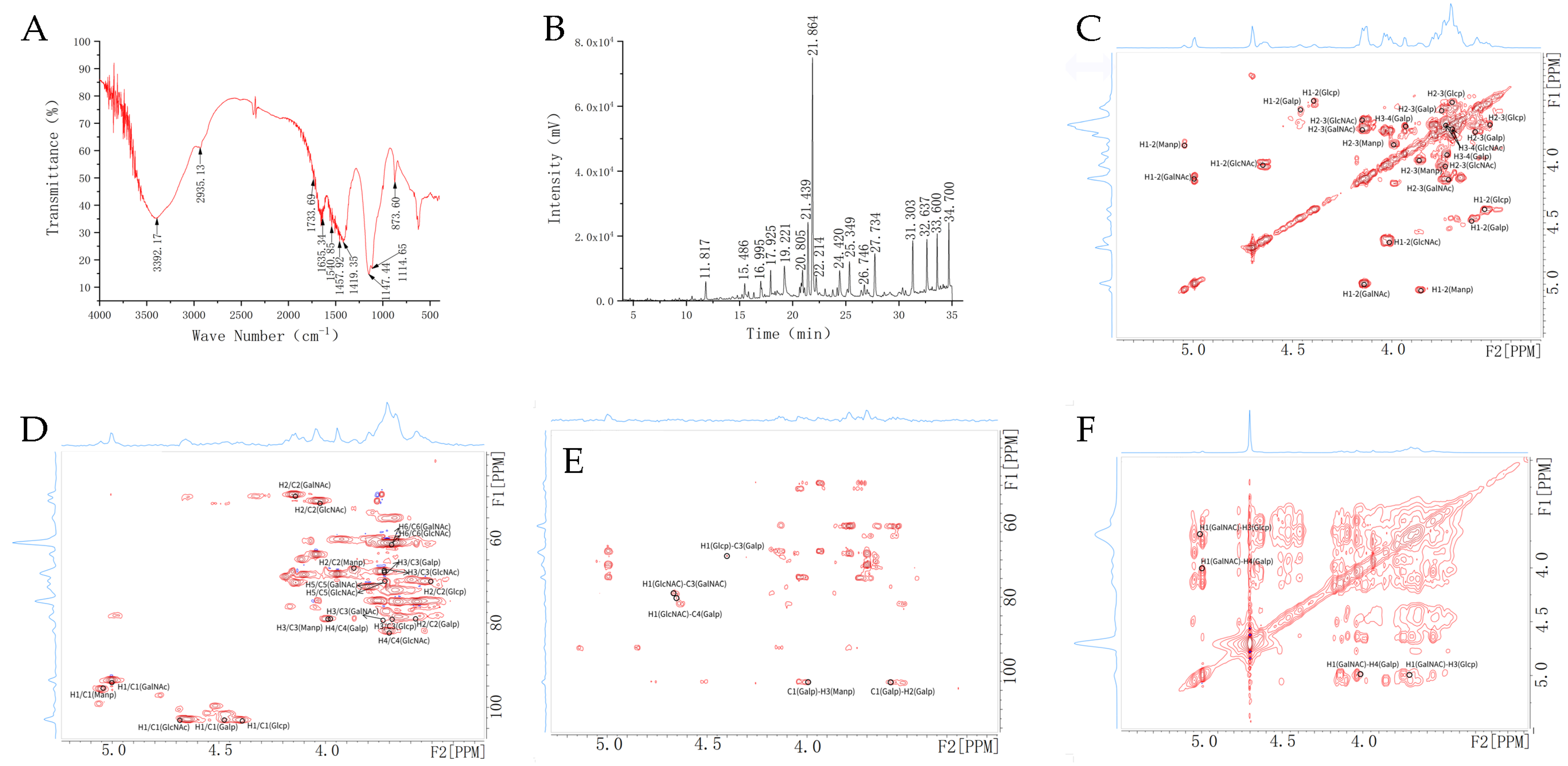
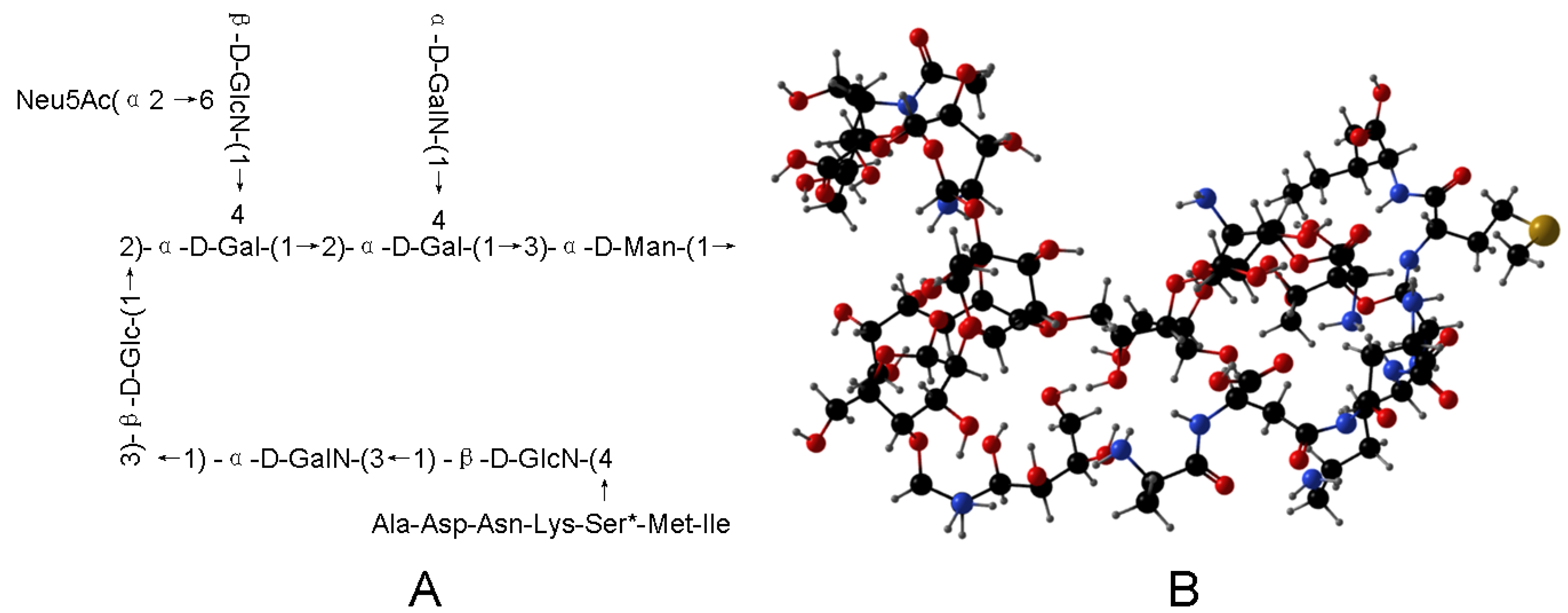
2.4. FT-IR, Methylation and NMR Spectroscopy Analysis for Carbohydrate Chain
2.5. MS Spectrometry for Peptide Chain
2.6. T-ES Increased Bone Density
2.7. T-ES Enhanced Bone Biomechanical Properties
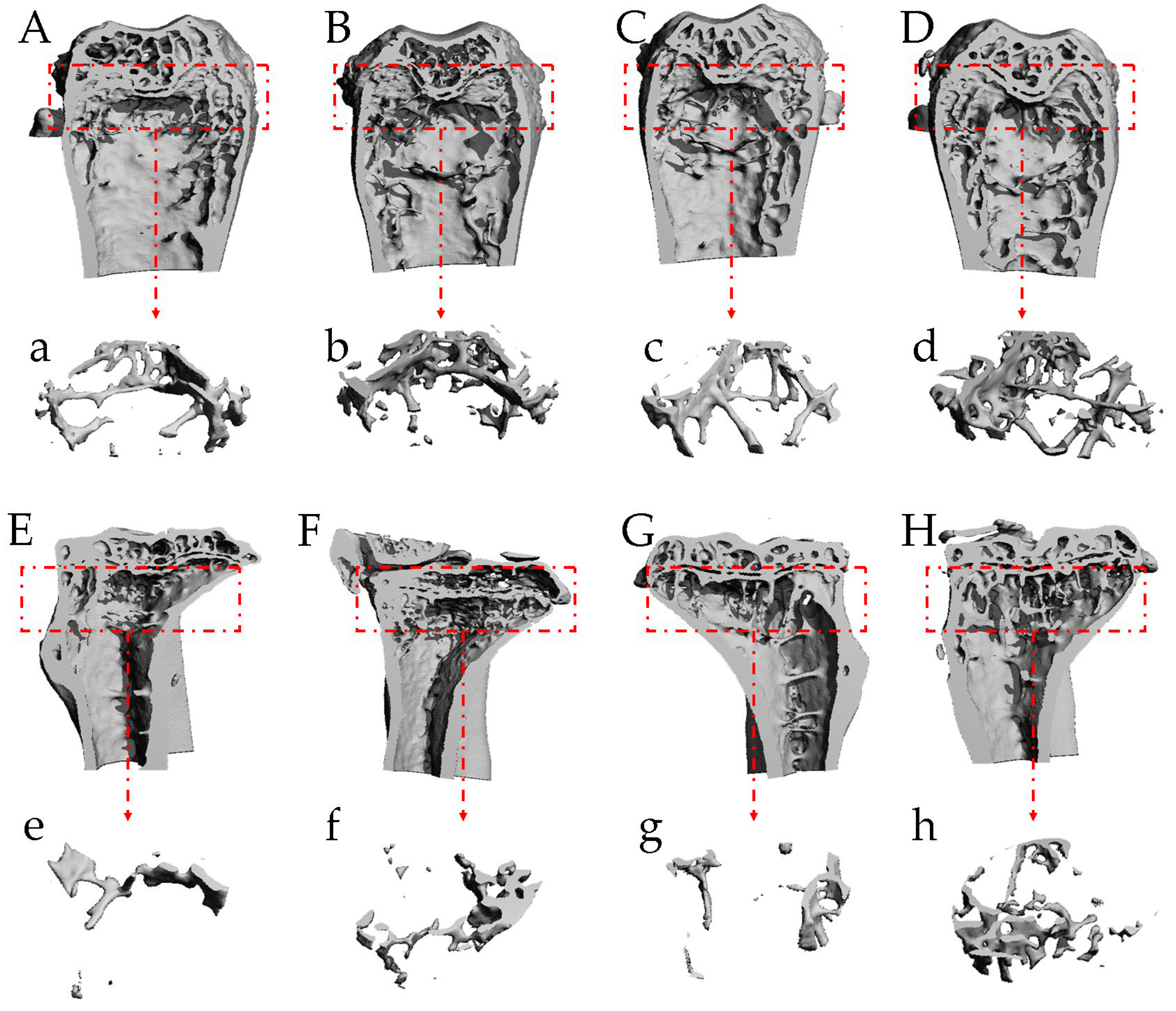
2.8. T-ES Improved Bone Microstructure
2.9. T-ES Elevated Serum Osteogenesis-Related Parameters
2.10. T-ES Reduced Bone Resorption-Related Parameters in Serum and Urine
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Extraction and Purification of the T-ES
3.2. Determination of General Properties
3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.4. Methylation Analysis
3.5. NMR Analysis
3.6. HPLC-MS Spectrometry
3.7. Animals’ Experiments
3.8. Bone Mineral Density Measurement
3.9. Bone Biomechanics Determination
3.10. Bone Microstructure Observation
3.11. Determination of Osteogenesis- and Bone Resorption-Related Markers in Serum and Urine
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, M.; Yu, Q.; Rui, Y. Fecal microbiota transplantation as a promising treatment option for osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 874–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ominsky, M.S.; Villasenor, K.S.; Niu, Q.; Asuncion, F.J.; Xia, X.; Grisanti, M.; Wronski, T.J.; Simonet, W.S.; Ke, H.Z. Sclerostin antibody reverses bone loss by increasing bone formation and decreasing bone resorption in a rat model of male osteoporosis. Endocinology 2018, 159, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compston, J.E.; McClung, M.R.; Leslie, W.D. Osteoporosis. Lancet 2019, 393, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Sialoglycoproteins isolated from the eggs of Carassius auratus prevents osteoporosis by suppressing the activation of osteoclastogenesis related NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J. Funct. Food. 2015, 17, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odén, A.; McCloskey, E.V.; Kanis, J.A.; Harvey, N.C.; Johansson, H. Burden of high fracture probability worldwide: Secular increases 2010–2040. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 2243–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Feng, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Wen, Q.; Hu, R.; Wang, L.; et al. The prevalence of osteoporosis in China, a nationwide, multicenter DXA survey. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Meng, X.; Feng, H.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, T.; Ye, K.; Xing, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhou, F.; et al. Estimation and projection about the standardized prevalence of osteoporosis in mainland China. Arch. Osteoporos. 2020, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seko, A.; Koketsu, M.; Nishizono, M.; Enoki, Y.; Ibrahim, H.R.; Juneja, L.R.; Kim, M.; Yamamoto, T. Occurrence of a sialylglycopeptide and free sialylglycans in hen’s egg yolk. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1335, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Iwasaki, M. Isolation of a novel glycoprotein from the eggs of Rainbow trout: Occurrence of disialosyl groups on all carbohydrate chains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978, 83, 1018–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Kanamori, A.; Kitajima, K.; Inoue, Y. KDN-glycoprotein: A novel deaminated neuraminic acid-rich glycoprotein isolated from vitelline envelope of rainbow trout eggs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 153, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, K.; Inoue, Y.; Inoue, S. Polysialoglycoproteins of Salmonidae fish eggs. Complete structure of 200-kDa polysialoglycoprotein from the unfertilized eggs of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 5262–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, G.; Wang, S.; He, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Anti-osteoporotic activity of sialoglycoproteins isolated from the eggs of Carassius auratus by promoting osteogenesis and increasing OPG/RANKL ratio. J. Funct. Food. 2015, 15, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Yosizawa, Z.; Biochem, J. Sialoglycopeptides isolated from Bovine aorta. J. Biochem. 1975, 77, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Mei, F.; Lu, J.; Xiang, Q.; Xia, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shen, X.; Zhong, Q. Gadus morhua eggs sialoglycoprotein prevent estrogen deficiency-induced high bone turnover by controlling OPG/RANKL/TRAF6 pathway and serum metabolism. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 871521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, S.; Lu, C.; Wan, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Ming, T.; Wang, Z.J.; Su, X. The novel peptides ICRD and LCGEC screened from tuna roe show antioxidative activity via Keap1/Nrf2-ARE pathway regulation and gut microbiota modulation. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, Z.; Zhao, M.; Tian, Y.; Chang, H.; Shen, X.; Xia, G.; Wang, J. Isolation and characterization of a novel sialoglycopeptide promoting osteogenesis from Gadus morhua eggs. Molecules 2020, 25, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsignorio, D.; Perego, L.; Del Giacco, L.; Cotelli, F. Structure and macromolecular composition of the zebrafish egg chorion. Zygote 1996, 4, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Kitajima, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kudo, S. Localization of polysialoglycoprotein as a major glycoprotein component in cortical alveoli of the unfertilized eggs of Salmo gairdneri. Dev. Biol. 1987, 123, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wen, C.; Wang, N.; Yan, C.; Shen, C.; Song, S. Chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharide influence digestibility of whey protein isolate through electrostatic interaction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Olajide, T.M.; Zhai, X.; Qian, J.; Miao, S.; Huang, J. Effects of “nine steaming nine sun-drying” on proximate composition, protein structure and volatile compounds of black soybeans. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandelli, G.; Shan, S.; Campanella, O.H. Effects of alkalinization and addition of pea protein as a co-protein to zein for the development of gluten-free doughs. Food Hydrocol. 2023, 19, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpiri, J.N.; Chermahini, A.N.; Saraji, M.; Shahvar, A. Dehydration of carbohydrates into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over vanadyl pyrophosphate catalysts. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Wilt, T.J. Treatment of low bone density or osteoporosis to prevent fractures. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Bo, Y.; Tian, Y.; Mao, L.; Xue, C.; Dong, P.; Wang, J. Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched phosphatidylcholine exerted superior effects to triglyceride in ameliorating obesity-induced osteoporosis through up-regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13904–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Song, L. Correlation of osteoporosis in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study in Chinese population. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 531904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, J.; Tao, L. Purine metabolism in the development of osteoporosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schini, M.; Vilaca, T.; Gossiel, F.; Salam, S.; Eastell, R. Bone turnover markers:bosic biology to clinical applications. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 417–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Guo, L.; Song, Y.; Miao, J.; Peng, M.; Fang, X.; Bai, M.; Miao, M. Transcriptomic analysis the mechanisms of anti-osteoporosis of desert-living Cistanche herb in ovariectomized rats of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2023, 23, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Tang, X.; Cui, Y.; Hu, W.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Sea cucumber enzymatic hydrolysates relieve osteoporosis through OPG/RANK/RANKL system in ovariectomized rats. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, D.; Wilson, A.; Satgé, F.; Murrell, D.F. Psoriasis and osteoporosis: A literature review. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aenglong, C.; Tang, Q.J.; Tanasawet, S.; Klaypradit, W.; Sukketsiri, W. Osteogenic properties and anti-osteoporosis activity of calcium hydroxyapatite from Katsuwonus pelamis bone and its water-soluble forms. Fish. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suehiro, D.; Moriwaki, Y.; Fukami, K.; Abe-Dohmae, S.; Ohnishi, M. The effect of maltobionic acid on bone metabolism markers in healthy Japanese postmenopausal women: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Weng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, A. An improved phenol-sulfuric acid method for the determination of carbohydrates in the presence of persulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 227, 115332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCraw, A.; Gardner, R.A.; Davies, A.M.; Spencer, D.I.R.; Grandits, M.; Wagner, G.K.; McDonnell, J.M.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Chenoweth, A.; Crescioli, S. Generation and characterization of native and sialic acid-deficient IgE. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgar, D.F.; Hill, J.P.; Holroyd, S.E.; Peddie, G.S. Comparison of analytical methods for measuring protein content of whey protein products and investigation of influences on nitrogen conversion factors. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2020, 73, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, N.; Kumar, A. HPLC in the discovery of plant phenolics as antifungal molecules against Candida infection related biofilms. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galermo, A.G.; Nandita, E.; Castillo, J.J.; Amicucci, M.J.; Lebrilla, C.B. Development of an extensive linkage library for characterization of carbohydrates. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13022–13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievano, E.; Tonoli, M.; Rastrelli, F. NMR quantification of carbohydrates in complex mixtures. A challenge on honey. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13405–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Zhao, W.; Gu, J.; Guo, W.; Li, Y. Screening of specific quantitative peptides of beef by LC–MS/MS coupled with OPLS-DA. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Monosaccharide Composition Proportion % | Mp (Da) | Mw (Da) | Mn (Da) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuc | GalN | GlcN | Gal | Glc | Xyl | Man | GlcA | ||||
| T-ES | 0.021 | 0.187 | 0.262 | 0.276 | 0.101 | 0.026 | 0.109 | 0.017 | 8481 | 9481 | 7221 |
| RT | Methylated Sugar | Mass Fragments (m/z) | MOLAR RATIO | Type of Linkage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.817 | 2,3,4-Me3-Fuc | 43, 59, 72, 89, 101, 115, 117, 131, 175 | 0.027 | Fuc-(1→ |
| 15.486 | 2,3-Me2-Xyl | 43, 71, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 189 | 0.024 | →4)-Xyl-(1→ |
| 16.995 | 2,3,4,6-Me4-Glc | 43, 71, 87, 101, 117, 129, 145, 161, 205 | 0.027 | Glc-(1→ |
| 17.925 | 2,3,4,6-Me4-Man | 43, 71, 87, 101, 117, 129, 145, 161, 205 | 0.030 | Man-(1→ |
| 19.221 | 3,4,6-Me3-D-Glc-2-N | 43, 87, 101, 117, 189, 205 | 0.054 | GlcN-(1→ |
| 20.805 | 3,4,6-Me3-Man | 43, 87, 129, 161, 189 | 0.013 | →2)-Man-(1→ |
| 20.926 | 2,4,6-Me3-Glc | 43, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 173, 233 | 0.032 | →3)-Glc-(1→ |
| 21.439 | 2,3,6-Me3-Glc | 43, 87, 99, 101, 113, 117, 129, 131, 161, 173, 233 | 0.095 | →4)-Glc-(1→ |
| 21.864 | 2,4,6-Me3-Gal | 43, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 173, 233 | 0.299 | →3)-Gal-(1→ |
| 22.214 | 2,3,4-Me3-Glc | 43, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 189, 233 | 0.031 | →6-Glc-(1→ |
| 24.42 | 2,6-Me2-Glc | 43, 87, 97, 117, 159, 185 | 0.041 | →3,4)-Glc-(1→ |
| 25.349 | 2,3-Me2-Man | 43, 71, 85, 87, 99, 101, 117, 127, 159, 161, 201 | 0.045 | →4,6)-Man-(1→ |
| 26.746 | 2,3-Me2-Glc | 43, 71, 85, 87, 99, 101, 117, 127, 159, 161, 201 | 0.017 | →4,6)-Glc-(1→ |
| 27.013 | 2,4-Me2-Glc | 43, 87, 117, 129, 159, 189, 233 | 0.014 | →3,6)-Glc-(1→ |
| 27.734 | 2,3-Me2-Gal | 43, 71, 85, 87, 99, 101, 117, 127, 159, 161, 201, 261 | 0.058 | →4,6)-Gal-(1→ |
| 31.303 | 4,6-Me2-D-Gal-2-N | 45, 73, 87, 99, 117, 129, 173, 189, 233 | 0.060 | →3)-GalN-(1→ |
| 32.637 | 4,6-Me2-D-Glc-2-N | 45, 73, 87, 99, 117, 129, 173, 189, 233 | 0.053 | →3)-GlcN-(1→ |
| 33.600 | 4-Me1-D-Gal-2-N | 43, 74, 116, 129, 143, 158, 233 | 0.039 | →3,6)-GalN-(1→ |
| 34.700 | 4-Me1-D-Glc-2-N | 43, 74, 116, 129, 143, 158, 233 | 0.040 | →3,6)-GlcN-(1→ |
| Tissues | Parameters | Model | ALN | T-ES-L | T-ES-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Femur | Bone density (mg/cm2) | 82.35 ± 9.03 a | 126.54 ± 13.28 b | 90.48 ± 10.07 a | 115.91 ± 11.88 b |
| Max. load (N) | 12.31 ± 0.13 a | 24.52 ± 0.30 b | 15.58 ± 0.22 c | 22.77 ± 0.29 b | |
| Max. deflection (mm) | 0.56 ± 0.04 a | 0.92 ± 0.10 b | 0.63 ± 0.0.07 a | 1.02 ± 0.11 b | |
| Trabecular thickness (µm) | 41.25 ± 3.68 a | 96.42 ± 8.57 b | 60.47 ± 5.40 c | 100.54 ± 9.63 b | |
| Trabecular number (1/mm) | 2.29 ± 0.05 a | 2.91 ± 0.03 b | 2.45 ± 0.07 a | 3.56 ± 0.08 c | |
| Trabecular separation (mm) | 0.42 ± 0.03 a | 0.29 ± 0.02 b | 0.38 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 b | |
| Conectivity density (1/mm3) | 25.44 ± 1.58 a | 37.87 ± 1.85 b | 27.06 ± 2.07 a | 39.29 ± 2.14 b | |
| Structureal model index | 1.87 ± 0.19 a | 0.95 ± 0.09 b | 1.74 ± 0.20 a | 0.81 ± 0.08 b | |
| Cortical bone thickness (mm) | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 b | 0.16 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 b | |
| Tibia | Bone density (mg/cm2) | 51.26 ± 4.89 a | 114.07 ± 12.36 b | 79.40 ± 8.55 c | 109.92 ± 15.48 b |
| Max. load (N) | 10.37 ± 0.10 a | 18.64 ± 0.23 bc | 17.71 ± 0.19 b | 20.45 ± 0.23 cd | |
| Max. deflection (mm) | 0.69 ± 0.08 a | 1.32 ± 0.14 b | 1.04 ± 0.09 c | 1.25 ± 0.11 b | |
| Trabecular thickness (µm) | 58.39 ± 5.26 a | 83.24 ± 9.10 b | 72.61 ± 9.02 ab | 85.90 ± 7.47 b | |
| Trabecular number (1/mm) | 2.11 ± 0.26 a | 3.25 ± 0.27 b | 2.76 ± 0.19 ab | 3.48 ± 0.22 b | |
| Trabecular separation (mm) | 0.60 ± 0.04 a | 0.36 ± 0.04 b | 0.45 ± 0.03 c | 0.31 ± 0.05 bc | |
| Conectivity density (1/mm3) | 9.14 ± 0.88 a | 21.52 ± 4.31 b | 12.39 ± 2.24 a | 23.43 ± 3.16 b | |
| Structureal model index | 3.78 ± 0.42 a | 1.86 ± 0.20 bc | 2.22 ± 0.18 b | 1.55 ± 0.17 c | |
| Cortical bone thickness (mm) | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 b | 0.19 ± 0.01 c | 0.24 ± 0.01 b | |
| Serum | BALP (ng/mL) | 6.39 ± 0.74 a | 8.24 ± 0.78 b | 6.81 ± 0.70 a | 8.83 ± 0.90 b |
| PICP (ng/mL) | 10.68 ± 1.00 a | 15.58 ± 1.34 b | 14.22 ± 1.07 b | 16.21 ± 1.37 b | |
| BGP (ng/mL) | 12.03 ± 1.44 a | 15.62 ± 1.37 b | 16.98 ± 1.45 bc | 17.87 ± 1.69 c | |
| RANKL (pg/mL) | 18.04 ± 1.55 a | 24.87 ± 2.61 b | 21.51 ± 1.88 c | 25.14 ± 2.10 b | |
| OPG (pg/mL) | 13.36 ± 1.07 a | 7.94 ± 0.81 b | 12.68 ± 1.45 a | 7.57 ± 0.67 b | |
| OPG/RANKL | 0.73 ± 0.07 a | 0.32 ± 0.04 b | 0.63 ± 0.09 a | 0.31 ± 0.05 b | |
| Cath-k (ng/mL) | 4.04 ± 0.31 a | 2.83 ± 0.24 b | 3.67 ± 0.24 a | 2.71 ± 0.28 b | |
| MMP-9 (ng/mL) | 42.52 ± 3.16 a | 32.44 ± 2.14 b | 39.51 ± 2.30 c | 31.50 ± 2.59 b | |
| CTX-I (ng/mL) | 18.90 ± 1.73 a | 15.23 ± 1.23 bc | 16.04 ± 0.95 b | 14.34 ± 1.11 c | |
| Urine | DPD (mmol/L) | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 b |
| Ca (mmol/L) | 0.33 ± 0.06 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 0.29 ± 0.03 a | 0.16 ± 0.02 b | |
| P (mmol/L) | 4.77 ± 0.30 a | 2.04 ± 0.18 b | 3.45 ± 0.33 c | 2.26 ± 0.25 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Wan, X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H. Structural Characterization and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of a Novel Sialoglycopeptide from Tuna Eggs. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110573
Hu S, Wan X, Zhu H, Yang H. Structural Characterization and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of a Novel Sialoglycopeptide from Tuna Eggs. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(11):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110573
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shiwei, Xiaofeng Wan, Hongli Zhu, and Huicheng Yang. 2023. "Structural Characterization and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of a Novel Sialoglycopeptide from Tuna Eggs" Marine Drugs 21, no. 11: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110573
APA StyleHu, S., Wan, X., Zhu, H., & Yang, H. (2023). Structural Characterization and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of a Novel Sialoglycopeptide from Tuna Eggs. Marine Drugs, 21(11), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110573






