Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Chilean Marine Algae: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Chilean Algae
2.1. Terpenoids
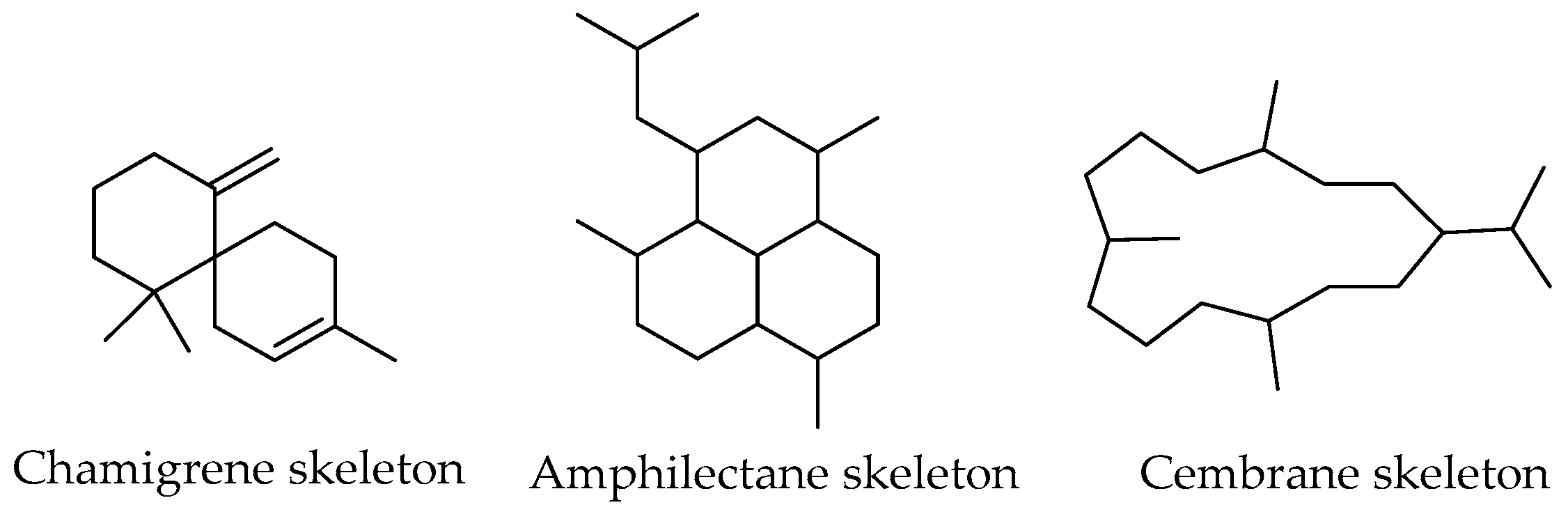
2.1.1. Structural Features of Marine Terpenes
2.1.2. Monoterpenes
Linear Polyhydroxylated Monoterpenes
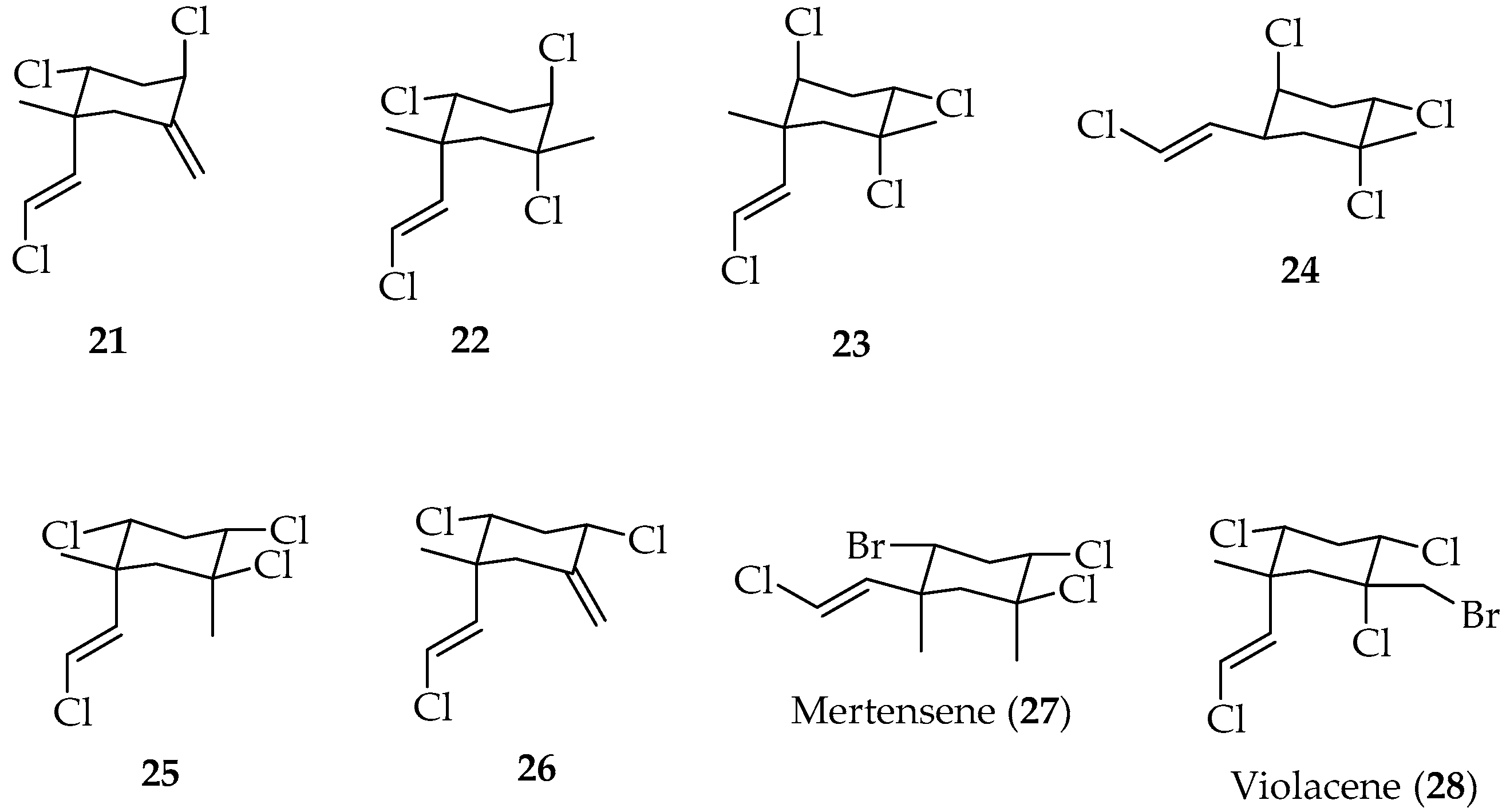
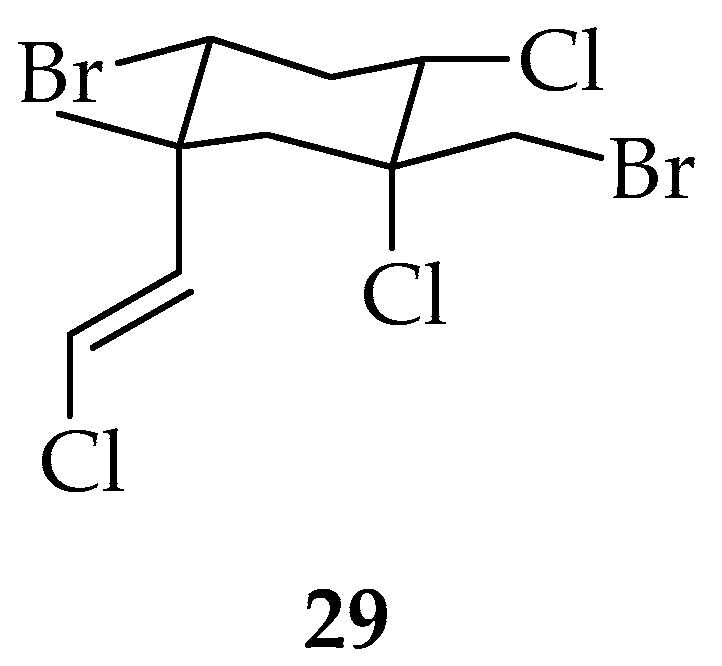
Cyclohexane Polyhalogenated Monocyclic Monoterpenes
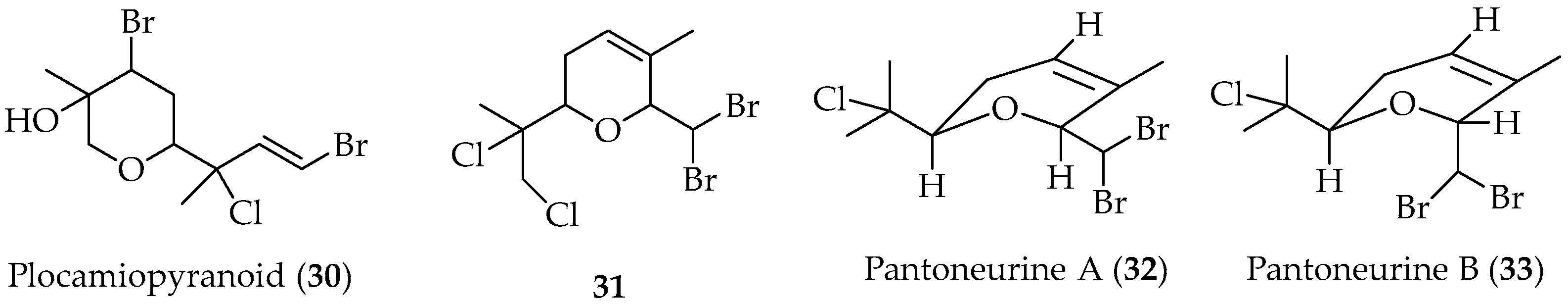
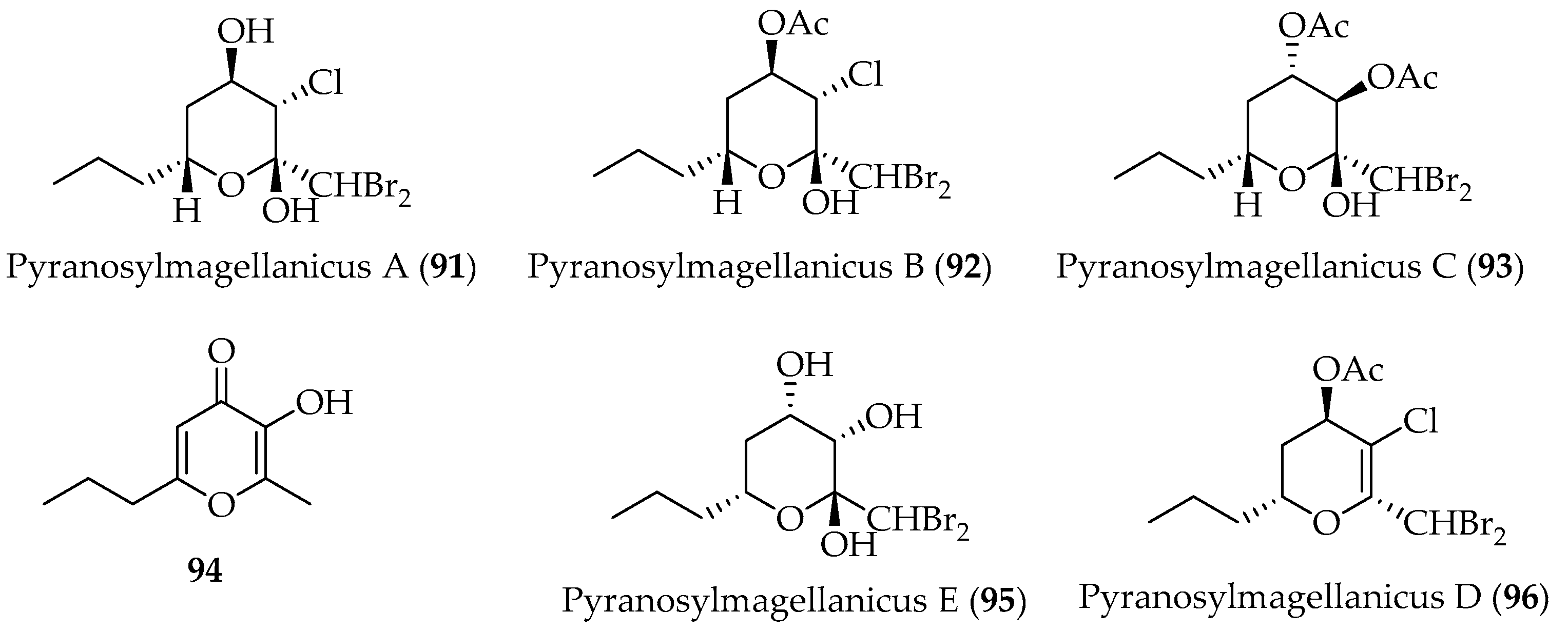
Tetrahydropyran Monoterpenes
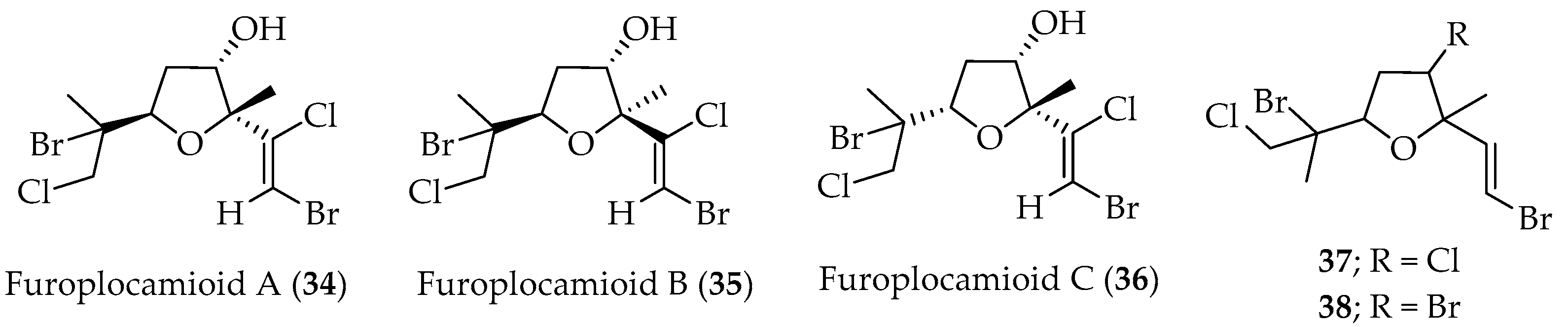
Tetrahydrofuran Monoterpenes
2.1.3. Sesquiterpenes
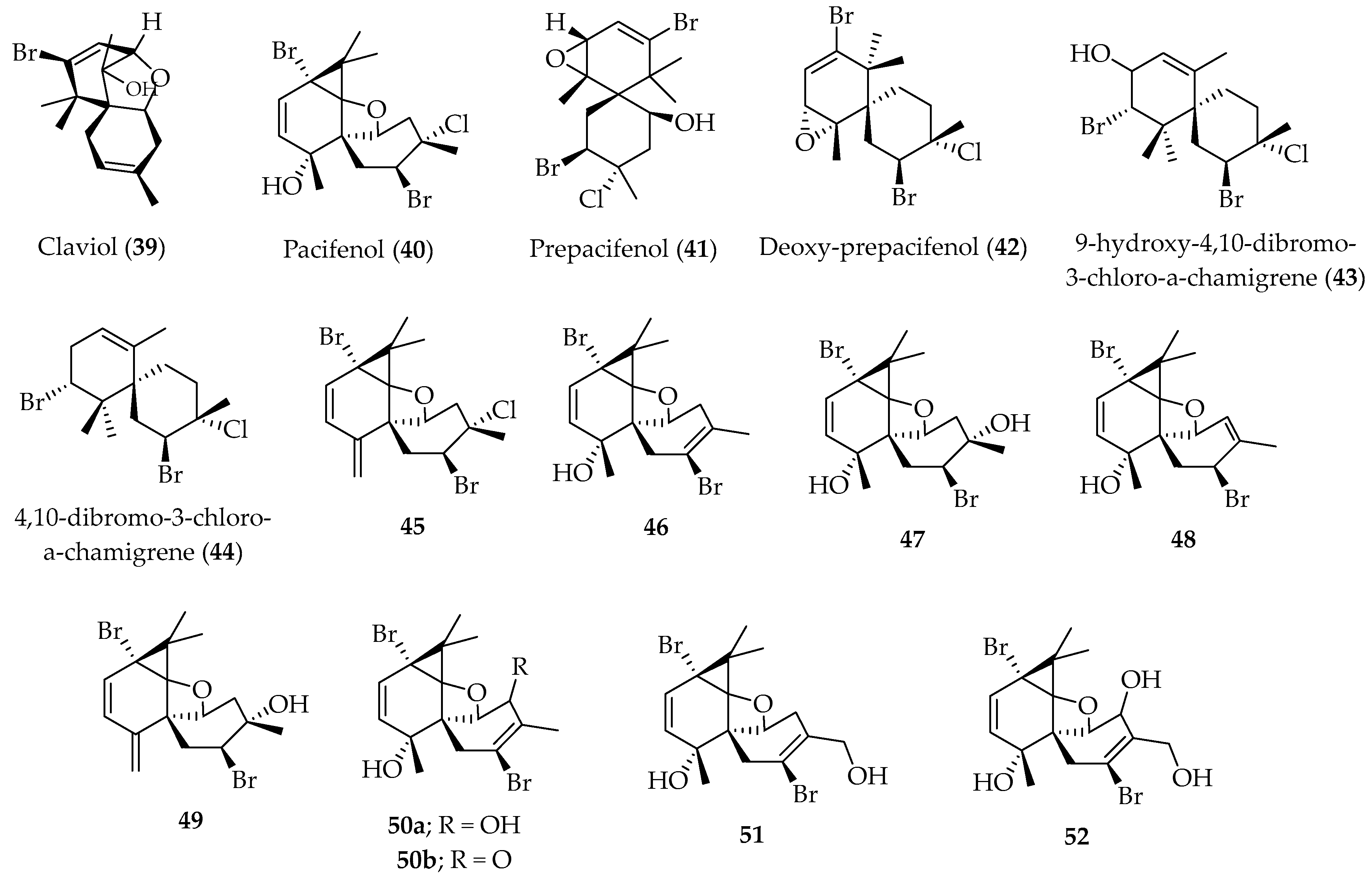
Chamigrene Sesquiterpenes
2.1.4. Diterpenes
Perhydroazulene Diterpenes
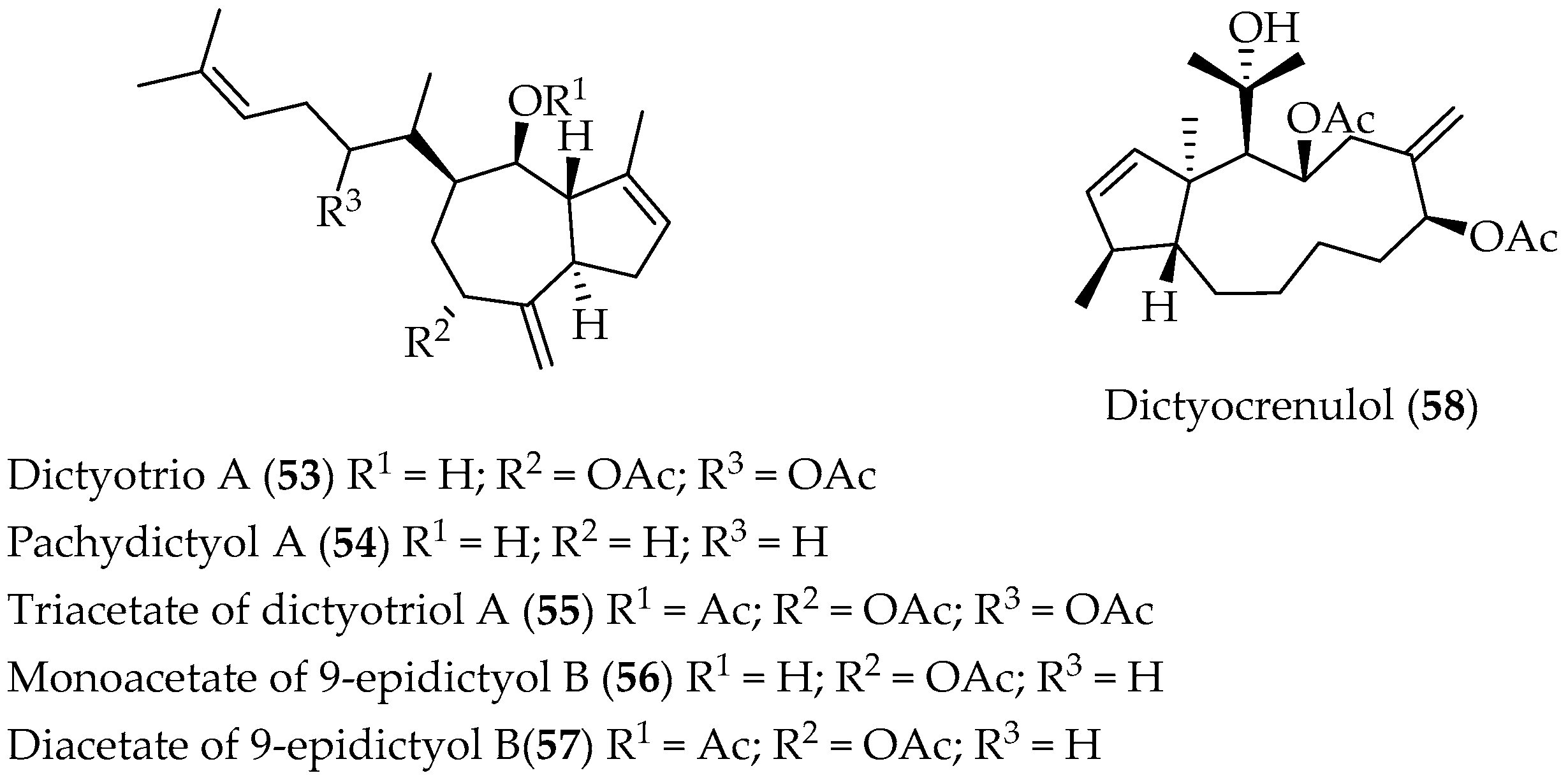
Xenicane Diterpenes
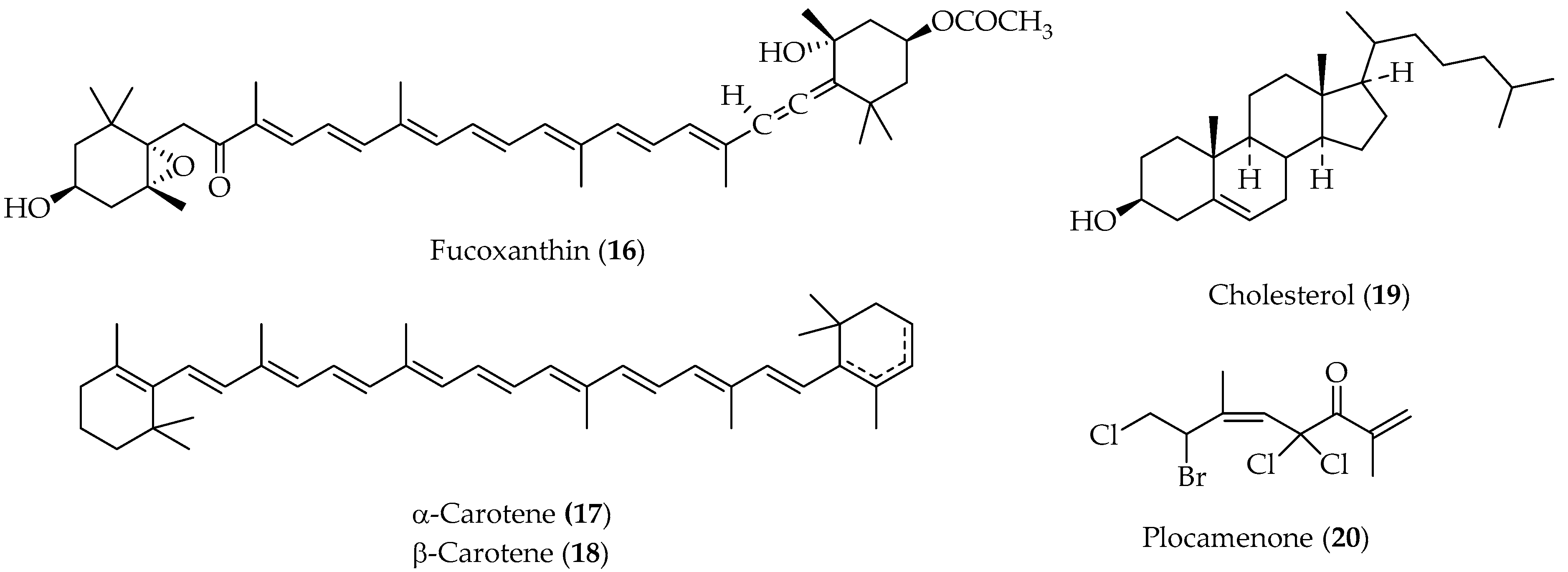
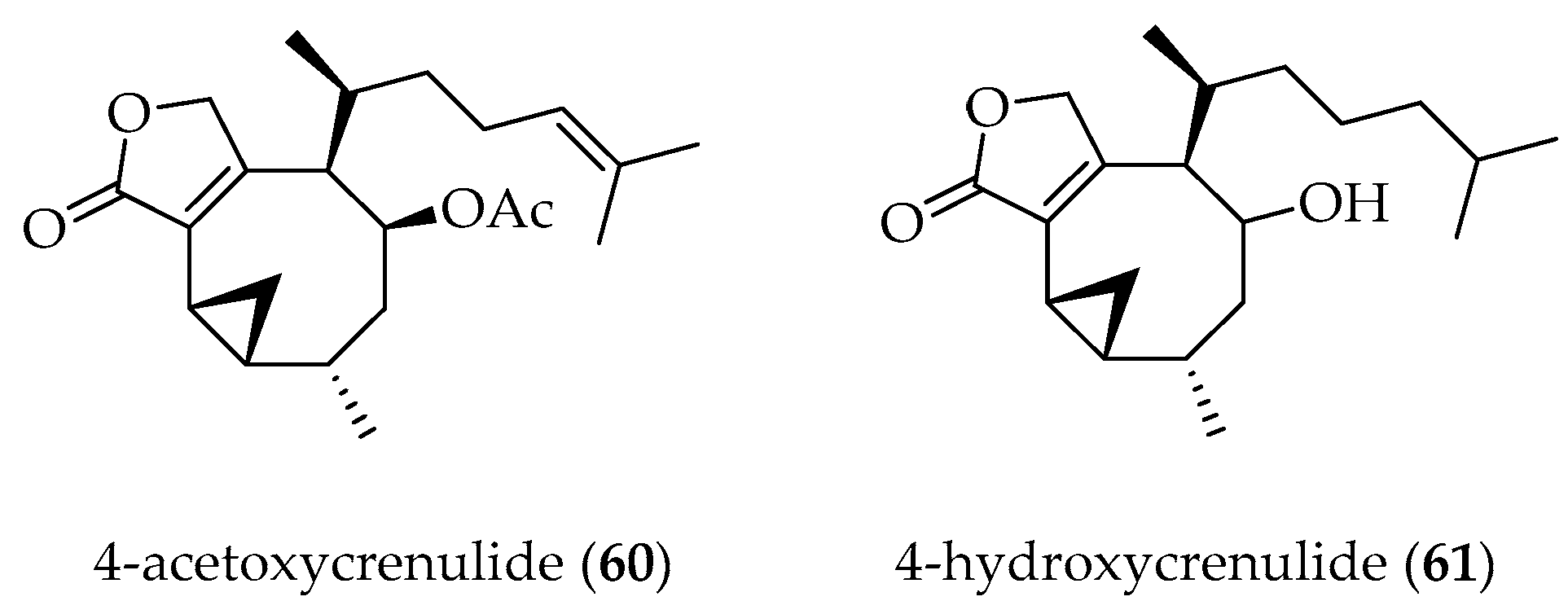
Crenulides Diterpenes
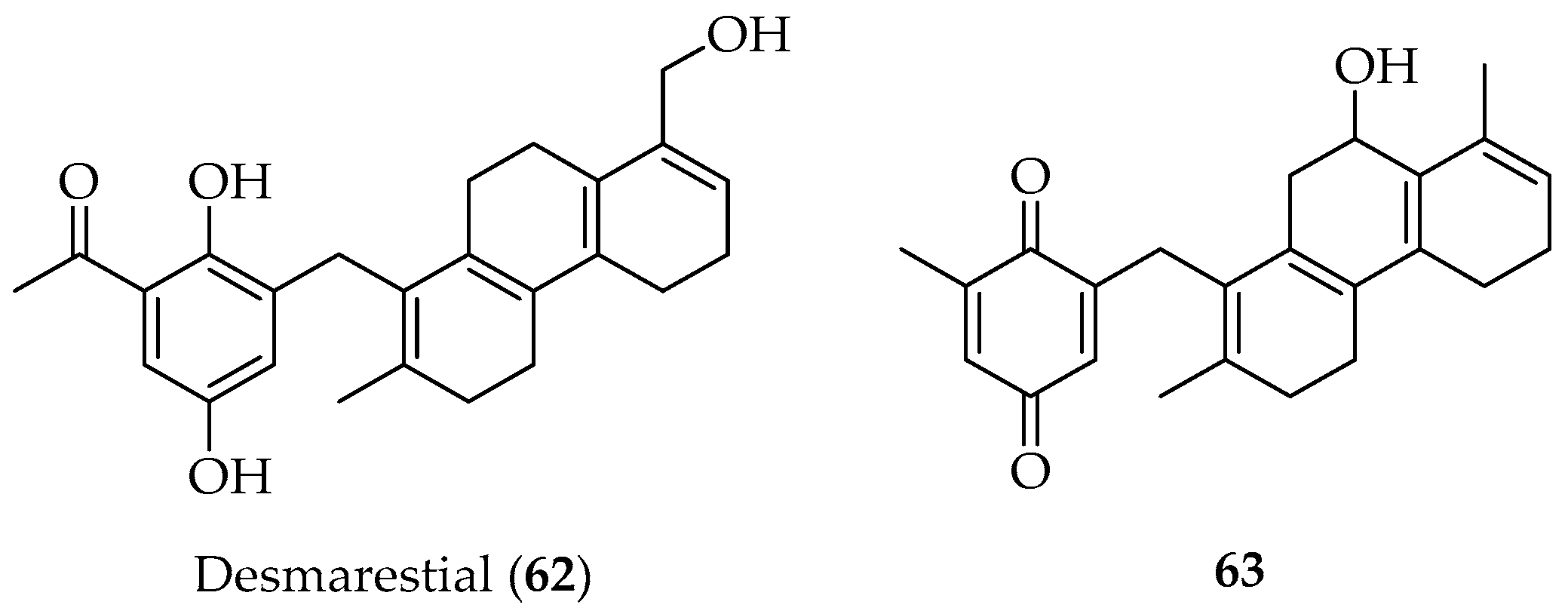
Plastoquinone Diterpenes
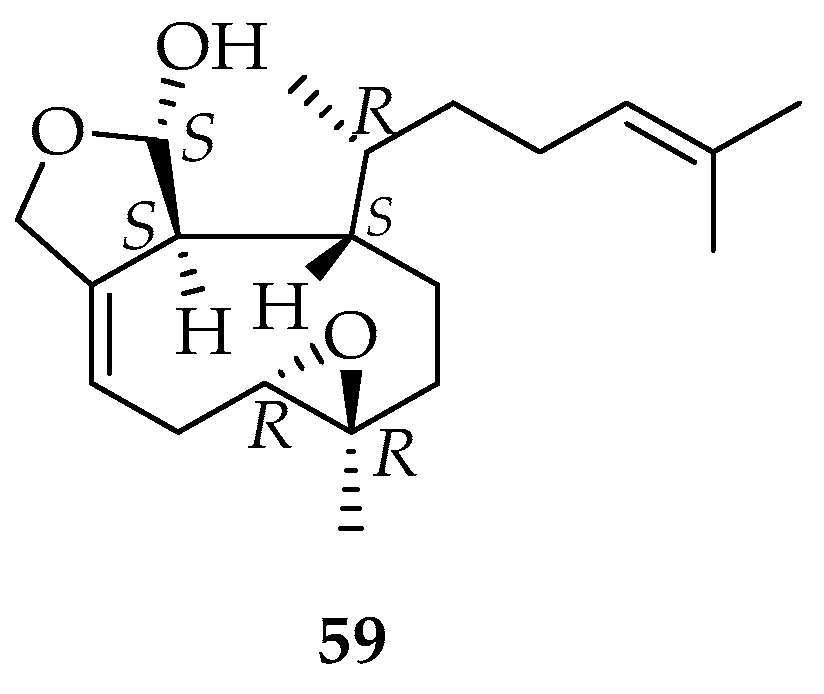
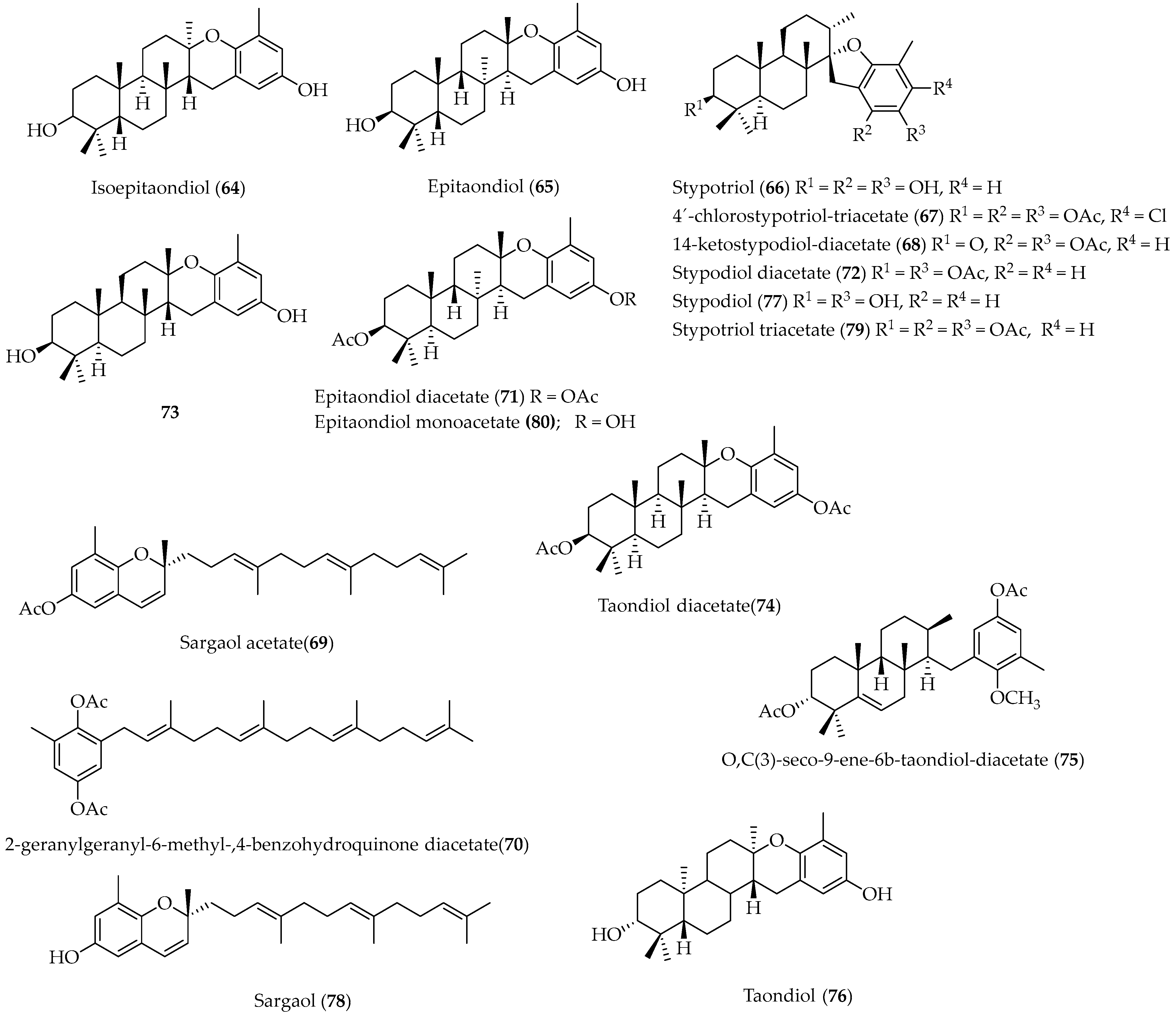
2.1.5. Meroterpenoids
2.2. C15-Acetogenins
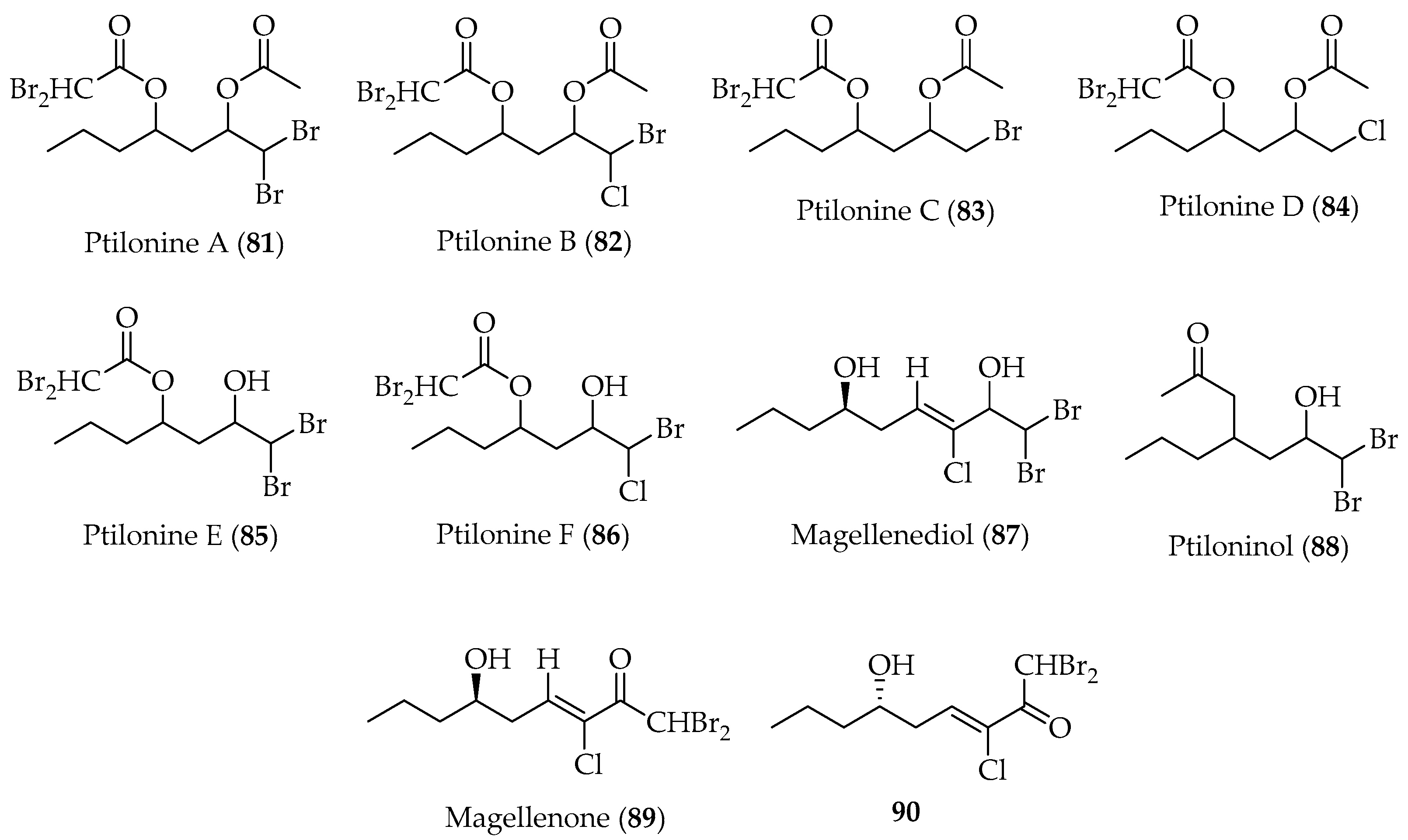
2.2.1. Linear Polyhalogenated C15-Acetogenins
2.2.2. Cyclic Polyhalogenated C15-Acetogenins
2.2.3. Bromoallene C15-Acetogenins
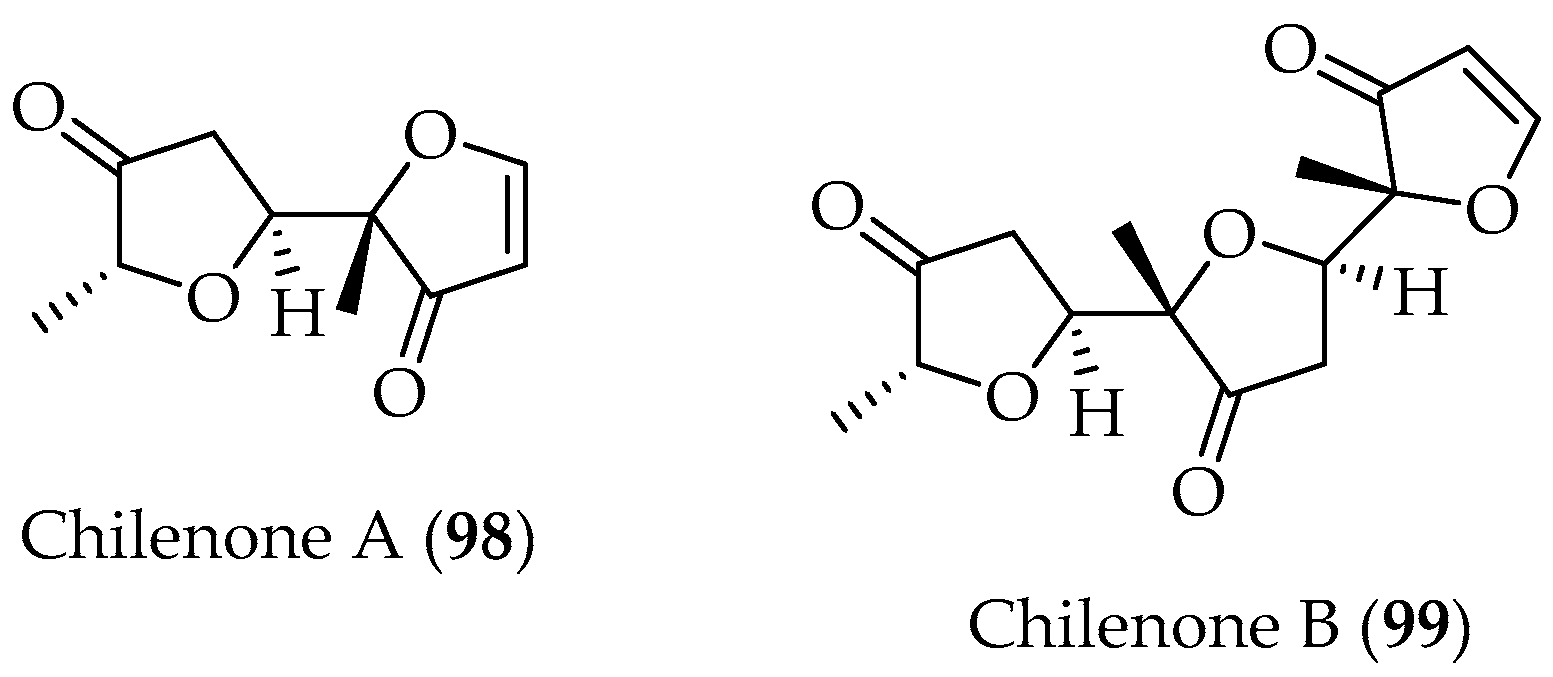
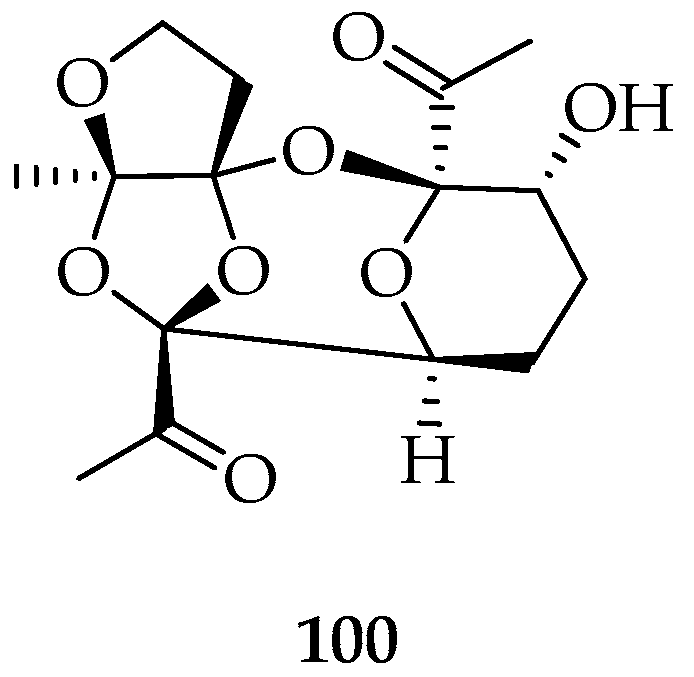
2.3. Furanones
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- San-Martín, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Bacho, M.; Gaete, K.; Ampuero, J. A New Labdane Diterpene from the Limpet Trimusculus Peruvianus. Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plantas. 2012, 11, 520. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Fusetani, N. Marine Pharmacology in 2007–2008: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Anticoagulant, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antimalarial, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous System, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 153, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine Pharmacology in 2012–2013: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 273. [Google Scholar]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Lessons from the Past and Charting the Future of Marine Natural Products Drug Discovery and Chemical Biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022. Advance Article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gamal, A.A. Biological Importance of Marine Algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garson, M.J. Biosynthetic Studies on Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1989, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ścieszka, S.; Klewicka, E. Algae in Food: A General Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lever, J.; Brkljača, R.; Kraft, G.; Urban, S. Natural Products of Marine Macroalgae from South Eastern Australia, with Emphasis on the Port Phillip Bay and Heads Regions of Victoria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for Biodiesel Production and Other Applications: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, F.A.E.; Passalacqua, T.G.; Velásquez, A.M.A.; de Souza, R.A.; Colepicolo, P.; Graminha, M.A.S. New Drugs with Antiprotozoal Activity from Marine Algae: A Review. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Wong, J.H.; Pan, W.L.; Chan, Y.S.; Yin, C.M.; Dan, X.L.; Wang, H.X.; Fang, E.F.; Lam, S.K.; Ngai, P.H.K.; et al. Antifungal and Antiviral Products of Marine Organisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyawali, R.; Ibrahim, S.A. Natural Products as Antimicrobial Agents. Food Control 2014, 46, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Antimicrobial Action of Compounds from Marine Seaweed. Mar. Drugs. 2016, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahms, H.; Dobretsov, S. Antifouling Compounds from Marine Macroalgae. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Silva, S.A.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Gullón, P.; Barroso, M.F.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Macroalgae as a Source of Valuable Antimicrobial Compounds: Extraction and Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine Origin to Therapeutics: The Antitumor Potential of Marine Algae-Derived Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tchokouaha Yamthe, L.; Appiah-Opong, R.; Tsouh Fokou, P.; Tsabang, N.; Fekam Boyom, F.; Nyarko, A.; Wilson, M. Marine Algae as Source of Novel Antileishmanial Drugs: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Nah, J.-W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Potential Anti-Inflammatory Natural Products from Marine Algae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, V.K. Antimicrobial Bioactive Compounds from Marine Algae: A Mini Review. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Cikoš, A.-M.; Jurin, M.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Jokić, S.; Jerković, I. Update on Monoterpenes from Red Macroalgae: Isolation, Analysis, and Bioactivity. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoubaky, G.A.E.; Salem, E.A. Terpenes and Sterols Composition of Marine Brown Algae Padina pavonica (Dictyotales) and Hormophysa triquetra (Fucales). Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2015, 6, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chojnacka, K.; Kim, S.-K. Introduction of Marine Algae Extracts. In Marine Algae Extracts; Kim, S.-K., Chojnacka, K., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine Natural Products and Related Compounds in Clinical and Advanced Preclinical Trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
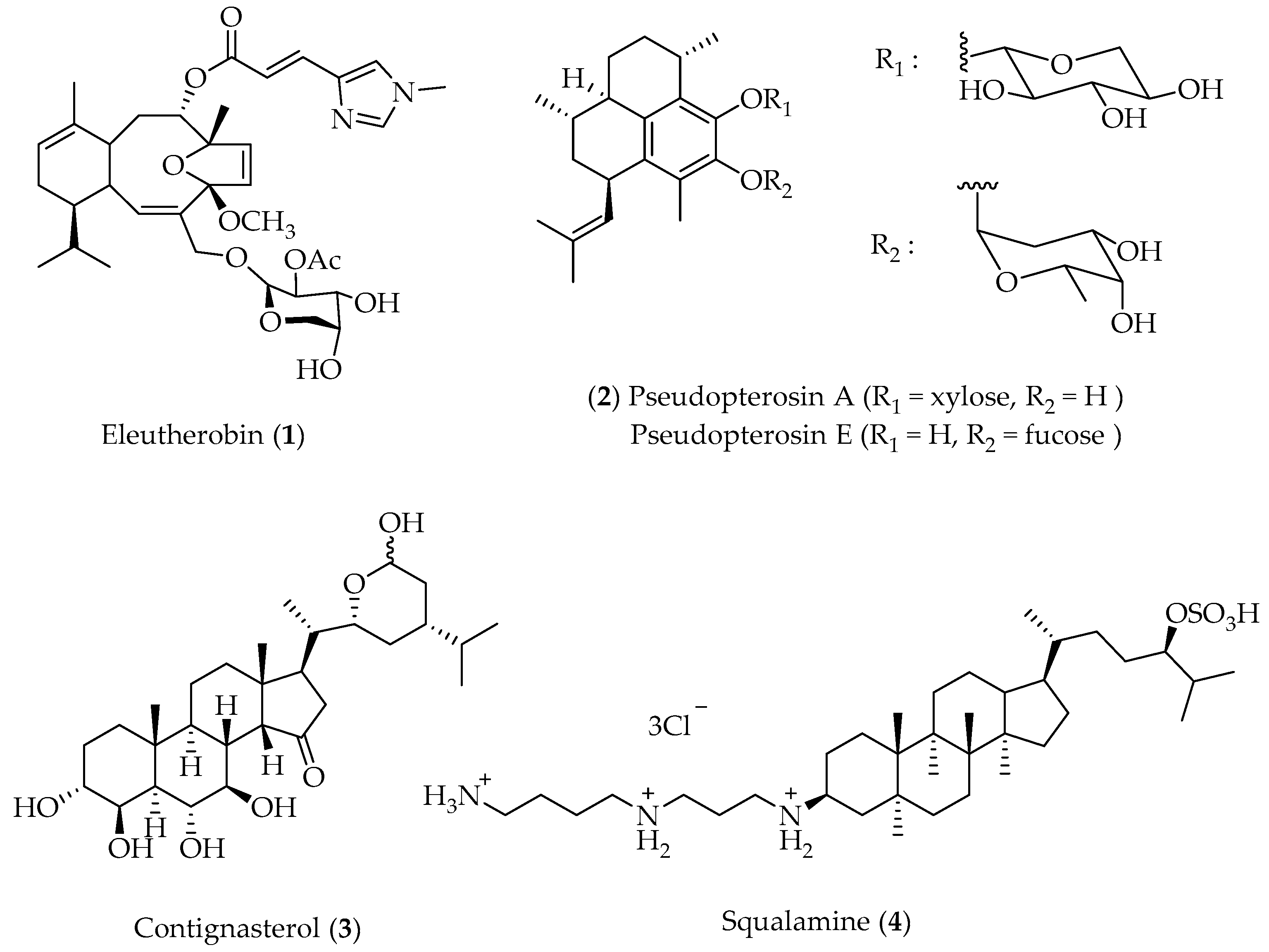
- Lindel, T.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Long, B.H.; Casazza, A.M.; Carboni, J.; Fairchild, C.R. Eleutherobin, a New Cytotoxin That Mimics Paclitaxel (Taxol) by Stabilizing Microtubules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinel, B.; Roberge, M.; Behrisch, H.; van Ofwegen, L.; Castro, C.B.; Andersen, R.J. Antimitotic Diterpenes from Erythropodium caribaeorum Test Pharmacophore Models for Microtubule Stabilization. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Deo-Jangra, U.; Campbell, M.; Roberge, M.; Andersen, R.J. Diterpenoids from Cultured Erythropodium caribaeorum. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.H.; Carboni, J.M.; Wasserman, A.J.; Cornell, L.A.; Casazza, A.M.; Jensen, P.R.; Lindel, T.; Fenica, W.; Fairchild, C.R. Eleutherobin, a Novel Cytotoxic Agent That Induces Tubulin Polymerization, Is Similar to Paclitaxel (Taxol®). Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 11116. [Google Scholar]
- Look, S.A.; Fenical, W.; Matsumoto, G.K.; Clardy, J. The Pseudopterosins: A New Class of Antiinflammatory and Analgesic Diterpene Pentosides from the Marine Sea Whip Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae (Octocorallia). J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerassi, C. Recent Studies in the Marine Sterol Field. Pure Appl. Chem. 1981, 53, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Auria, M.V.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R. Polyoxygenated Steroids of Marine Origin. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Seiki, M.; Itoh, Y. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Two Phosphorylated Sterol Sulfates, MT1-MMP Inhibitors from a Marine Sponge Cribrochalina sp.: Revision of the Structures of Haplosamates A and B. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, A.; Yosief, T.; Loya, S.; Hizi, A.; Schleyer, M.; Kashman, Y. Clathsterol, a Novel Anti-HIV-1 RT Sulfated Sterol from the Sponge Clathria Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J. Sterols in Microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 60, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.S.; Wehrli, S.; Roder, H.; Rogers, M.; Forrest, J.N.; McCrimmon, D.; Zasloff, M. Squalamine: An Aminosterol Antibiotic from the Shark. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wehrli, S.L.; Moore, K.S.; Roder, H.; Durell, S.; Zasloff, M. Structure of the Novel Steroidal Antibiotic Squalamine Determined by Two-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy. Steroids 1993, 58, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, A.K.; Williams, J.I.; Tyler, B.M.; Epstein, D.S.; Sipos, E.P.; Davis, J.D.; McLane, M.P.; Pitchford, S.; Cheshire, K.; Gannon, F.H.; et al. Squalamine Inhibits Angiogenesis and Solid Tumor Growth in Vivo and Perturbs Embryonic Vasculature. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gross, H.; König, G.M. Terpenoids from Marine Organisms: Unique Structures and Their Pharmacological Potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Cox, S.; Rajauria, G.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Growth Inhibition of Common Food Spoilage and Pathogenic Microorganisms in the Presence of Brown Seaweed Extracts. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Recent Developments in the Application of Seaweeds or Seaweed Extracts as a Means for Enhancing the Safety and Quality Attributes of Foods. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Tech. 2011, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio del Medio Ambiente Biodiversidad de Chile, Patrimonio y Desafios, 3rd ed.; Ocho Libros Editores: Santiago, Chile, 2018; Volume I.
- Pacheco, L.V.; Parada, J.; Pérez-Correa, J.R.; Mariotti-Celis, M.S.; Erpel, F.; Zambrano, A.; Palacios, M. Bioactive Polyphenols from Southern Chile Seaweed as Inhibitors of Enzymes for Starch Digestion. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Loyola, A.; Darias, J. Labdane Diterpenes with a New Oxidation Pattern from the Marine Pulmonate Trimusculus Peruvianus. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J.L.; Hernández-Inda, Z.L.; Pérez, P.; García-Grávalos, M.D. A Comparison between Two Brine Shrimp Assays to Detect in Vitro Cytotoxicity in Marine Natural Products. BMC Biotechnol. 2002, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Civitareale, C.; Brambilla, G.; Delupis, G.D.D. Toxicity of Several Important Agricultural Antibiotics to Artemia. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itô, S.; Endo, K.; Yoshida, T.; Yatagai, M.; Kodama, M. Chamigrene, a Sesquiterpene Hydrocarbon of a Novel Carbon Skeleton. Chem. Commun. 1967, 186b. Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/1967/c1/c1967000186b/unauth (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Carbone, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Manzo, E.; Li, X.-L.; Mollo, E.; Mudianta, I.W.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gavagnin, M. Amphilectene Diterpene Isonitriles and Formamido Derivatives from the Hainan Nudibranch Phyllidia Coelestis. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, I.; Miguel, M.; Mnif, W. A Brief Review on New Naturally Occurring Cembranoid Diterpene Derivatives from the Soft Corals of the Genera Sarcophyton, Sinularia, and Lobophytum Since 2016. Molecules 2019, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kladi, M.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Volatile Halogenated Metabolites from Marine Red Algae. Phytochem. Rev. 2004, 3, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guella, G.; Öztunç, A.; Mancini, I.; Pietra, F. Stereochemical Features of Sesquiterpene Metabolites as a Distinctive Trait of Red Seaweeds in the Genus Laurencia. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tori, M.; Nakasklma, K.; Seike, M.; Wrigkt, A.D. Revised Structure of a Brasilane-Type Sesquiterpene Isolated From the Red Alga Laurencia implicata and Its Absolute Configuration. Tetrahedron lett. 1994, 35, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedara, S.R.; Abdel-Halim, O.B.; El-Sharkawy, S.H.; Salama, O.M.; Shier, T.W.; Halim, A.F. Cytotoxic Hydroazulene Diterpenes from the Brown Alga Dictyota Dichotoma. Z. Naturforsch. C 2003, 58, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goez, C.E.; Wright, A.D.; König, G.M.; Sticher, O. Diterpenes from the Brown Alga Dilophus mediterraneus. Phytochem. Anal. 1994, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areche, C.; San-Martín, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Soto-Delgado, J.; Contr Eras, R. An Unusual Halogenated Meroditerpenoid from Stypopodium flabelliforme: Studies by NMR Spectroscopic and Computational Methods. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, B.G.; Pereira, M.V.G.; Da Silva, J.R.P.; Kaisin, M.; Teixeira, V.L.; Kelecom, A. Sterols from Brazilian Marine Brown Algae. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenarska, Z.; Gasic, M.J.; Zlatovic, M.; Rasovic, A.; Sladic, D.; Kljajic, Z.; Stefanov, K.; Seizova, K.; Najdenski, H.; Kujumgiev, A.; et al. Chemical Composition of the Brown Alga Padina pavonia (L.) Gaill. from the Adriatic Sea. Bot. Mar. 2002, 45, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y. Chemical Composition of Seaweeds. In Seaweed Sustainability, 1st ed.; Tiwari, B.K., Troy, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
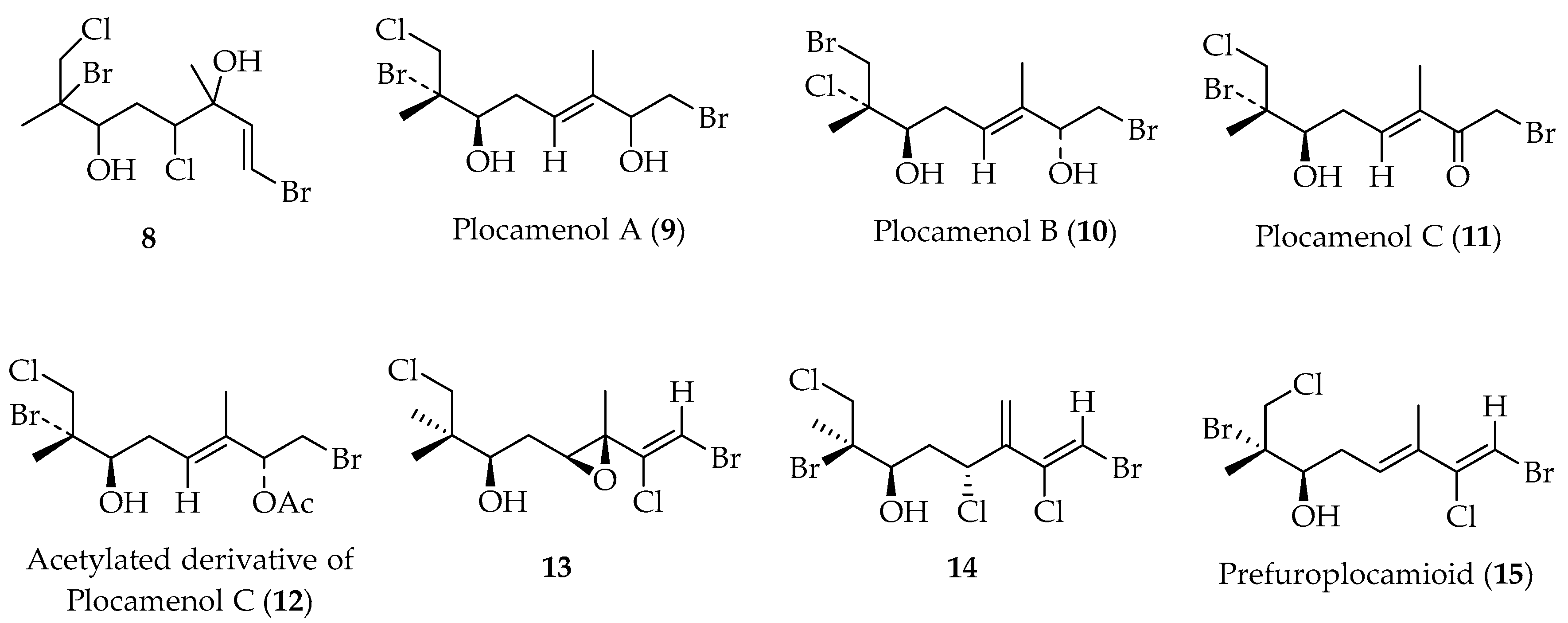
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; Dorta, E.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. New Halogenated Monoterpenes from the Red Alga. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Rovirosa, J.; Darias, J.; San-Martín, A.; Cueto, M. Plocamenols A−C, Novel Linear Polyhalohydroxylated Monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; Dorta, E.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. Geometry and Halogen Regiochemistry Determination of Vicinal Vinyl Dihalides by 1H and 13C NMR. Application to the Structure Elucidation of Prefuroplocamioid, an Unusual Marine Monoterpene. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. Supporting the NMR-Based Empirical Rules to Determine the Stereochemistry and Halogen Regiochemistry of Vicinal Vinyl Dihalides. Naturally Occurring Monoterpenes as Chemical Models. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesternich, V.; Martinez, R.; Gutierrexz, E.; Ballesteros, K.; Mansilla, H. Antibacterial Activity of Some Compounds Isolated from Ceramium rubrum against Gram Negative Bacteria. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quím. 1997, 42, 105. [Google Scholar]
- San-Martin, A.; Rovirosa, J. Variations in the Halogenated Monoterpene Metabolites of Plocamium cartilagineum of the Chilean Coast. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1986, 14, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovirosa, J.; Moena, J.; San-Martín, A. Two Chemical Types of the Red Alga Plocamium cartilagineum from Chile. Biochem. System. Ecol. 1988, 16, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martin, A.; Negrete, R.; Rovirosa, J. Insecticide and Acaricide Activities of Polyhalogenated Monoterpenes from Chilean Plocamium Cart. Phytochem. 1991, 30, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, P.; Astudillo, L.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A. Halogenated Monoterpenes of the Red Alga Shottera. Nicaensis. Biochem. System. Ecol. 1987, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argandoña, V.H.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Riquelme, A.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; Darias, J.; Santana, O.; Guadaño, A.; González-Coloma, A. Antifeedant Effects of Marine Halogenated Monoterpenes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argandoña, V.; Del Pozo, T.; San-Martín, A.; Rovirosa, J. Insecticidal activity of Plocamium cartilagineum monoterpens. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quím. 2000, 45, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Darias, J.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A. Tetrahydropyran Monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum and Pantoneura plocamioides. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darias, J.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A.; Díaz, A.R.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M. Furoplocamioids A−C, Novel Polyhalogenated Furanoid Monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Inés, C.; Argandoña, V.H.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; González-Coloma, A. Cytotoxic Activity of Halogenated Monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum. Z.Naturforsch. C. 2004, 59, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, R.; Edding, M.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Argandoña, V.H. Effect of Photon Flux Density and Temperature on the Production of Halogenated Monoterpenes by Plocamium cartilagineum (Plocamiaceae, Rhodophyta). Z. Naturforsch. C. 2004, 59, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovirosa, J.; Soto, H.; Cueto, M.; Dárias, J.; Herrera, J.; San-Martín, A. Sesquiterpenes from Laurencia claviformis. Phytochemistry 1999, 50, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martin, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Carrasco, A.; Orejarena, S.; Soto-Delgado, J.; Contreras, R.; Chamy, M.C. Microbial Transformation of Marine Halogenated Sesquiterpenes. Nat. Product. Comm. 2010, 5, 1859. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, H.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A.; Argandoña, V.H. Metabolitos secundarios de Dyctiota crenulata. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quim. 1994, 13, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, H.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A. A New Diterpene from Dictyota Crenulata. Z. Naturforsch. B. 2003, 58, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norte, M.; Gonzalez, A.G.; Arroyo, P.; Zarraga, M.; Perez, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Ruiz-Perez, C.; Dorta, L. New xenicane diterpenes from the brown algae of Dictyotaceae. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, P.; Norte, M.; Vazquez, J.T.; Nakanishi, K. Absolute Configuration of Hydroazulenoid Diterpenes Based on Circular Dichroism. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarraga, M.; Amaya, P.; Norte, M. Nuevas crenulidas de algas pardas de la familia Dictyotaceae. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quim. 1997, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, P.; Podestá, F.; Norte, M.; Cataldo, F.; González, A.G. New Plastoquinones from the Brown Alga Desmaresti amenziesii. Can. J. Chem. 1990, 68, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, J.E.; Nagel, J. Biosynthesis of Terpenophenolic Metabolites in Hop and Cannabis. In Recent Advances in Phytochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 40, pp. 179–210. ISBN 978-0-08-045125. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Ferrando, F.; San-Martin, A. Epitaondiol: The First Polycyclic Meroditerpenoid Containing Two Fused Six-Membered Rings Forced into the Twist-Boat Conformation. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovirosa, J.; Sepulveda, M.; Quezada, E.; San-Martin, A. Isoepitaondiol, a Diterpenoid of Stypopodium Flabelliforme and the Insecticidal Activity of Stypotriol, Epitaondiol and Derivatives. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.A.; Areche, C.; San-Martín, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Joseph-Nathan, P. VCD Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Stypotriol. Nat. Product Commun. 2009, 4, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depix, M.S.; Martínez, J.; Santibañez, F.; San-Martín, A.; Maccioni, R.B. The Compound 14-Keto-Stypodiol Diacetate from the Algae Stypopodium flabelliforme Inhibits Microtubules and Cell Proliferation in DU-145 Human Prostatic Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 187, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areche, C.; San-Martín, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Muñoz, M.A.; Hernández-Barragán, A.; Bucio, M.A.; Joseph-Nathan, P. Stereostructure Reassignment and Absolute Configuration of Isoepitaondiol, a Meroditerpenoid from Stypopodium flabelliforme. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph-Nathan, P.; Muñoz, M.A.; Areche, C.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martín, A.; Gordillo-Román, B. Absolute Configuration of the Meroditerpenoids Taondiol and Epitaondiol Diacetates by Vibrational Circular Dichroism. Heterocycles 2012, 85, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areche, C.; Benites, J.; Cornejo, A.; Ruiz, L.; García-Beltrán, O.; Simirgiotis, M.; Sepúlveda, B. Seco-Taondiol, an Unusual Meroterpenoid from the Chilean Seaweed Stypopodium flabelliforme and Its Gastroprotective Effect in Mouse Model. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Areche, C.; San-Martín, A.; Rovinosa, J.; Sepúlveda, B. Gastroprotective Activity of Epitaondiol and Sargaol. Nat. Prod. Comm. 2011, 6, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil, B.; Ferrándiz, M.L.; Sanz, M.J.; Terencio, M.C.; Ubeda, A.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Payá, M. Inhibition of Inflammatory Responses by Epitaondiol and Other Marine Natural Products. Life Sci. 1995, 57, PL25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.M.; Cheel, J.; Areche, C.; San-Martin, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Silva, L.R.; Valentao, P.; Andrade, P.B. Anti-Proliferative Activity of Meroditerpenoids Isolated from the Brown Alga Stypopodium flabelliforme against Several Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, A.B.; Cueto, M.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; de la Rosa, J.M.; Fajardo, V.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. A Set of Biogenetically Interesting Polyhalogenated Acetogenins from Ptilonia magellanica. Phytochemistry 2018, 145, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, M.; Cueto, M.; San-Martín, A.; Fajardo, V.; Darias, J. Pyranosylmagellanicus a Novel Structural Class of Polyhalogenated Acetogenins from Ptilonia magellanica. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnarp, J.; Bielawski, J.; Dahlin, B.-M.; Dahlman, O.; Enzell, C.R.; Pettersson, T.; Edwards, J.V. Tobacco Smoke Chemistry. 5. Alkyl Substituted 3-Hydroxy-4-Pyrones Found in Cigarette Smoke Condensate. Acta Chem. Scand. 1990, 44, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martín, A.; Darias, J.; Soto, H.; Contreras, C.; Herrera, J.S.; Rovirosa, J. A New C15 Acetogenin from the Marine Alga Laurencia claviformis. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1997, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, W. Natural 4-Hydroxy-2,5-Dimethyl-3(2H)-Furanone (Furaneol®). Molecules 2013, 18, 6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmgaard, T.; Persson, T.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M.; Nielsen, J. Synthesis of Furanone-Based Natural Product Analogues with Quorum Sensing Antagonist Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martin, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Muñoz, O.; Chen, M.H.M.; Guneratne, R.D.; Clardy, J. The Isolation and Structure Determination of Chilenone A, a Putative Dimer of 2-Methyl-3(2H)-Furanone from the Marine Alga. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martín, A.; Rovirosa, J.; Xu, C.; Lu, H.S.M.; Clardy, J. Further Structural Studies on the 2-Methyl-3(2H)-Furanone Derived Metabolites of the Marine Alga Laurencia chilensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, M.; Gonzalez, F.; Valdebenito, H.; Silva, M.; Paul, V.J.; Fenical, W.; Chen, M.H.M.; Clardy, J. A Novel Tetracyclic Polyketal from the Marine Red Alga. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arrieche, D.; Carrasco, H.; Olea, A.F.; Espinoza, L.; San-Martín, A.; Taborga, L. Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Chilean Marine Algae: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050337
Arrieche D, Carrasco H, Olea AF, Espinoza L, San-Martín A, Taborga L. Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Chilean Marine Algae: A Review. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050337
Chicago/Turabian StyleArrieche, Dioni, Héctor Carrasco, Andrés F. Olea, Luis Espinoza, Aurelio San-Martín, and Lautaro Taborga. 2022. "Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Chilean Marine Algae: A Review" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050337
APA StyleArrieche, D., Carrasco, H., Olea, A. F., Espinoza, L., San-Martín, A., & Taborga, L. (2022). Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Chilean Marine Algae: A Review. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050337





