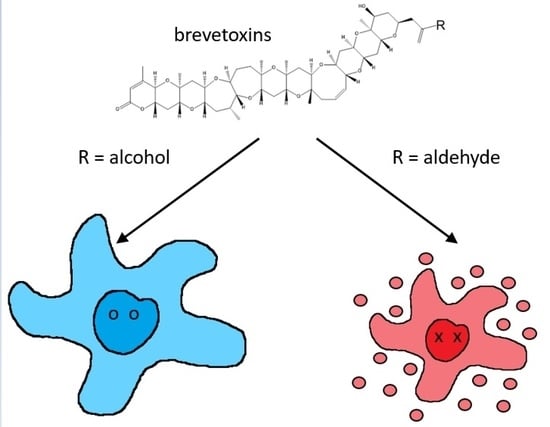
Immune Modulating Brevetoxins: Monocyte Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Activation of M1/M2 Response Elements Is Dependent on Reactive Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Brevetoxin Analog Structures
2.2. Brevetoxin Analog Immunotoxicity Does Not Align with VGSC Receptor Binding
2.3. Inflammatory Activation of THP-1 Monocytes by Brevetoxins
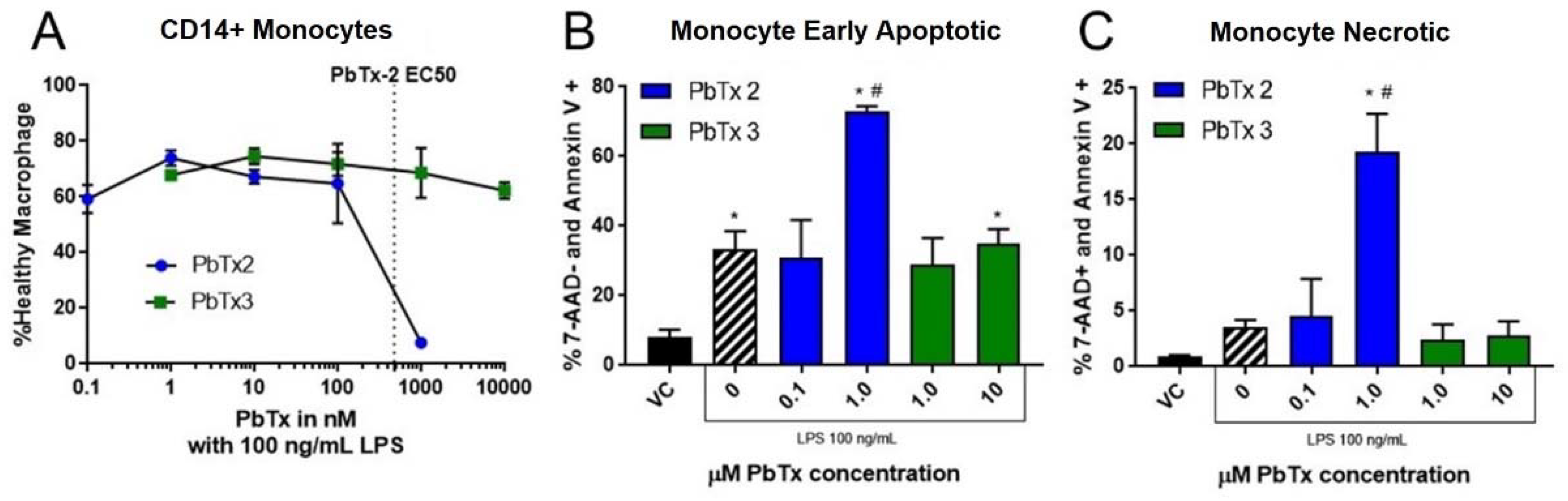
2.4. Apoptosis and Necrosis from Brevetoxin-Treated THP-1 Monocytes
2.5. Apoptosis and Necrosis from Brevetoxin-Treated PBMCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Brevetoxin Extraction and Purification
4.2. Brevetoxin Receptor Binding Assay
4.3. Primary PBMC and THP-1 Cell-Line Culture
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.5. Flow Cytometry Assessment for Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4), Mannose Receptor (CD206), Interleukin 4 Receptor (IL4Ra), and CD80 Receptor Expression
4.6. Quantification of Cytokines by Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assays (ELISAs)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baden, D.G. Brevetoxins: Unique Polyether Dinoflagellate Toxins. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkerson, S.L.; Baden, D.G.; Fieber, L.A. Brevetoxin Modulates Neuronal Sodium Channels in Two Cell Lines Derived from Rat Brain. Neurotoxicology 1999, 20, 909–920. [Google Scholar]
- Jeglitsch, G.; Rein, K.; Baden, D.G.; Adams, D.J. Brevetoxin-3 (PbTx-3) and Its Derivatives Modulate Single Tetrodotoxin-Sensitive Sodium Channels in Rat Sensory Neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baden, D.G.; Adams, D.J. Brevetoxins: Chemistry, Mechanism of Action, and Methods of Detection. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 505–532. [Google Scholar]
- LePage, K.T.; Rainier, J.D.; Johnson, H.W.B.; Baden, D.G.; Murray, T.F. Gambierol Acts as a Functional Antagonist of Neurotoxin Site 5 on Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Cerebellar Granule Neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, E.; Pierce, M.L.; Akasheh, D.; Sellers, S.; Gerwick, W.H.; Baden, D.G.; Murray, T.F. Epicortical Brevetoxin Treatment Promotes Neural Repair and Functional Recovery after Ischemic Stroke. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dravid, S.M.; Baden, D.G.; Murray, T.F. Brevetoxin Augments NMDA Receptor Signaling in Murine Neocortical Neurons. Brain Res. 2005, 1031, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Dravid, S.M.; Prakash, A.; Xie, J.; Peterson, J.; Jabba, S.V.; Baden, D.G.; Murray, T.F. Sodium Channel Activation Augments NMDA Receptor Function and Promotes Neurite Outgrowth in Immature Cerebrocortical Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3288–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Baden, D.G.; Gerwick, W.H.; Murray, T.F. Bidirectional Influence of Sodium Channel Activation on NMDA Receptor-Dependent Cerebrocortical Neuron Structural Plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19840–19845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, R.; Jester, E.; Granade, R.; Mowdy, D.; Moncreiff, C.; Rebarchik, D.; Robl, M.; Musser, S.; Poli, M. Monitoring Brevetoxins during a Gymnodinium Breve Red Tide: Comparison of Sodium Channel Specific Cytotoxicity Assay and Mouse Bioassay for Determination of Neurotoxic Shellfish Toxins in Shellfish Extracts. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, L.C.; Fleming, L.E.; Rowan, A.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Benson, J.; Pierce, R.H.; Zaias, J.; Bean, J.; Bossart, G.D.; Johnson, D.; et al. Recreational Exposure to Aerosolized Brevetoxins during Florida Red Tide Events. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaias, J.; Fleming, L.E.; Baden, D.G.; Abraham, W.M. Repeated Exposure to Aerosolized Brevetoxin-3 Induces Prolonged Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Lung Inflammation in Sheep. Inhal. Toxicol. 2011, 23, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossart, G.D.; Baden, D.G.; Ewing, R.Y.; Roberts, B.; Wright, S.D. Brevetoxicosis in Manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris) from the 1996 Epizootic: Gross, Histologic, and Immunohistochemical Features. Toxicol. Pathol. 1998, 26, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.M.; Hahn, F.F.; March, T.H.; McDonald, J.D.; Sopori, M.L.; Seagrave, J.; Gomez, A.P.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Naar, J.; Zaias, J.; et al. Inhalation Toxicity of Brevetoxin 3 in Rats Exposed for Five Days. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2004, 67, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhard, E.; Levin, M.; Bogomolni, A.; De Guise, S. Immunomodulatory Effects of Brevetoxin (PbTx-3) upon in Vitro Exposure in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Harmful Algae 2015, 44, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, K.M.; Baatz, J.E. Brevetoxin-2 Induces an Inflammatory Response in an Alveolar Macrophage Cell Line. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.M.; Wolf, M.L.; Kajon, A.; Tibbetts, B.M.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G.; March, T.H. Brevetoxin Inhalation Alters the Pulmonary Response to Influenza A in the Male F344 Rat. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2011, 74, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsui, M.; Kumar-Roine, S.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Pacific Ciguatoxin 1B-Induced Modulation of Inflammatory Mediators in a Murine Macrophage Cell Line. Toxicon 2010, 56, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.R.; Jacocks, H.M.; Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J. Development of a Competitive Fluorescence-Based Synaptosome Binding Assay for Brevetoxins. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.F.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Identification of a Rapid Detoxification Mechanism for Brevetoxin in Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 85, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dolah, F.M.; Finley, E.L.; Haynes, B.L.; Doucette, G.J.; Moeller, P.D.; Ramsdell, J.S. Development of Rapid and Sensitive High Throughput Pharmacologic Assays for Marine Phycotoxins. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxins and Brevetoxins, Neurotoxic Polyether Compounds Active on Sodium Channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Hamilton, B.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.P. Identification of Slow and Fast-Acting Toxins in a Highly Ciguatoxic Barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and Radiolabelled Ligand Binding. Toxicon 2003, 42, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Interstate Shellfish Sanitation Conference. Available online: https://www.issc.org/laboratory-method-references (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- McCall, J.R.; Jacocks, H.M.; Niven, S.C.; Poli, M.A.; Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J. Development and Utilization of a Fluorescence-Based Receptor-Binding Assay for the Site 5 Voltage-Sensitive Sodium Channel Ligands Brevetoxin and Ciguatoxin. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Sui, A.; Su, T.; Shen, X.; Xie, B. Identification of Different Macrophage Subpopulations with Distinct Activities in a Mouse Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaguin, M.; Houlbert, N.; Fardel, O.; Lecureur, V. Polarization Profiles of Human M-CSF-Generated Macrophages and Comparison of M1-Markers in Classically Activated Macrophages from GM-CSF and M-CSF Origin. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 281, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelms, K.; Keegan, A.D.; Zamorano, J.; Ryan, J.J.; Paul, W.E. The IL-4 Receptor: Signaling Mechanisms and Biologic Functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 701–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duprez, L.; Wirawan, E.; Berghe, T.V.; Vandenabeele, P. Major Cell Death Pathways at a Glance. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, O.; Misery, L.; Talagas, M.; Le Garrec, R. Immune Effects of the Neurotoxins Ciguatoxins and Brevetoxins. Toxicon 2018, 149, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craner, M.J.; Damarjian, T.G.; Liu, S.; Hains, B.C.; Lo, A.C.; Black, J.A.; Newcombe, J.; Cuzner, M.L.; Waxman, S.G. Sodium Channels Contribute to Microglia/Macrophage Activation and Function in EAE and MS. Glia 2005, 49, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.A.; Newcombe, J.; Waxman, S.G. Nav1.5 Sodium Channels in Macrophages in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. Mult. Scler. 2013, 19, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanschmann, E.-M.; Godoy, J.R.; Berndt, C.; Hudemann, C.; Lillig, C.H. Thioredoxins, Glutaredoxins, and Peroxiredoxins—Molecular Mechanisms and Health Significance: From Cofactors to Antioxidants to Redox Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1539–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tuladhar, A.; Rolle, S.; Lai, Y.; Rodriguez del Rey, F.; Zavala, C.E.; Liu, Y.; Rein, K.S. Brevetoxin-2, Is a Unique Inhibitor of the C-Terminal Redox Center of Mammalian Thioredoxin Reductase-1. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuladhar, A.; Hondal, R.J.; Colon, R.; Hernandez, E.L.; Rein, K.S. Effectors of Thioredoxin Reductase: Brevetoxins and Manumycin-A. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 217, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joardar, N.; Bhattacharya, R.; Halder, S.; Sen, A.; Biswas, S.R.; Jana, K.; Babu, S.P.S. Filarial Thioredoxin Reductase Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects upon Lipopolysaccharide Induced Inflammation in Macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakov, E.; Weisman-Shomer, P.; Benhar, M. Suppression of the Pro-Inflammatory NLRP3/Interleukin-1β Pathway in Macrophages by the Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibitor Auranofin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadri, K.; Mahmood, D.F.D.; Couchie, D.; Jguirim-Souissi, I.; Genze, F.; Diderot, V.; Syrovets, T.; Lunov, O.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. Thioredoxin-1 Promotes Anti-Inflammatory Macrophages of the M2 Phenotype and Antagonizes Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, P.B.; Edes, K.; Nelson, C.C.; Parsawar, K.; Fitzpatrick, F.A.; Moos, P.J. Thioredoxin Reductase Is Required for the Inactivation of Tumor Suppressor P53 and for Apoptosis Induced by Endogenous Electrophiles. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 2538–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.M.; Wright, J.L.C.; Bigwarfe, P.M.; Baden, D.G. A New Polyether Ladder Compound Produced by the Dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Campbell, A.; Van Wagoner, R.M.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.; Baden, D.G.; Wright, J.L.C. Brevisin: An Aberrant Polycyclic Ether Structure from the Dinoflagellate Karenia brevis and Its Implications for Polyether Assembly. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truxal, L.T.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.; Abraham, W.M.; Baden, D.G. Characterization of Tamulamides A and B, Polyethers Isolated from the Marine Dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Brevetoxin | RBA EC50 | XTT EC50 |
|---|---|---|
| PbTx-2 | 9.5 ± 0.74 nM | 2.63 ± 0.9511 µM |
| PbTx-3 | 27.6 ± 7.56 nM | 47.01 ± 1.068 µM |
| PbTx-6 | 584.5 ± 129 nM | 2.09 ± 1.183 µM |
| BTX-B5 | 427.9 ± 123 nM | 57.87 ± 0.4809 µM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McCall, J.R.; Sausman, K.T.; Keeler, D.M.; Brown, A.P.; Turrise, S.L. Immune Modulating Brevetoxins: Monocyte Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Activation of M1/M2 Response Elements Is Dependent on Reactive Groups. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040233
McCall JR, Sausman KT, Keeler DM, Brown AP, Turrise SL. Immune Modulating Brevetoxins: Monocyte Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Activation of M1/M2 Response Elements Is Dependent on Reactive Groups. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040233
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcCall, Jennifer R., Kathryn T. Sausman, Devon M. Keeler, Ariel P. Brown, and Stephanie L. Turrise. 2022. "Immune Modulating Brevetoxins: Monocyte Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Activation of M1/M2 Response Elements Is Dependent on Reactive Groups" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040233
APA StyleMcCall, J. R., Sausman, K. T., Keeler, D. M., Brown, A. P., & Turrise, S. L. (2022). Immune Modulating Brevetoxins: Monocyte Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Activation of M1/M2 Response Elements Is Dependent on Reactive Groups. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040233