Preparation, Identification, Molecular Docking Study and Protective Function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Amino Acid Composition of Skipjack Tuna Muscle
2.2. Preparation of Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle
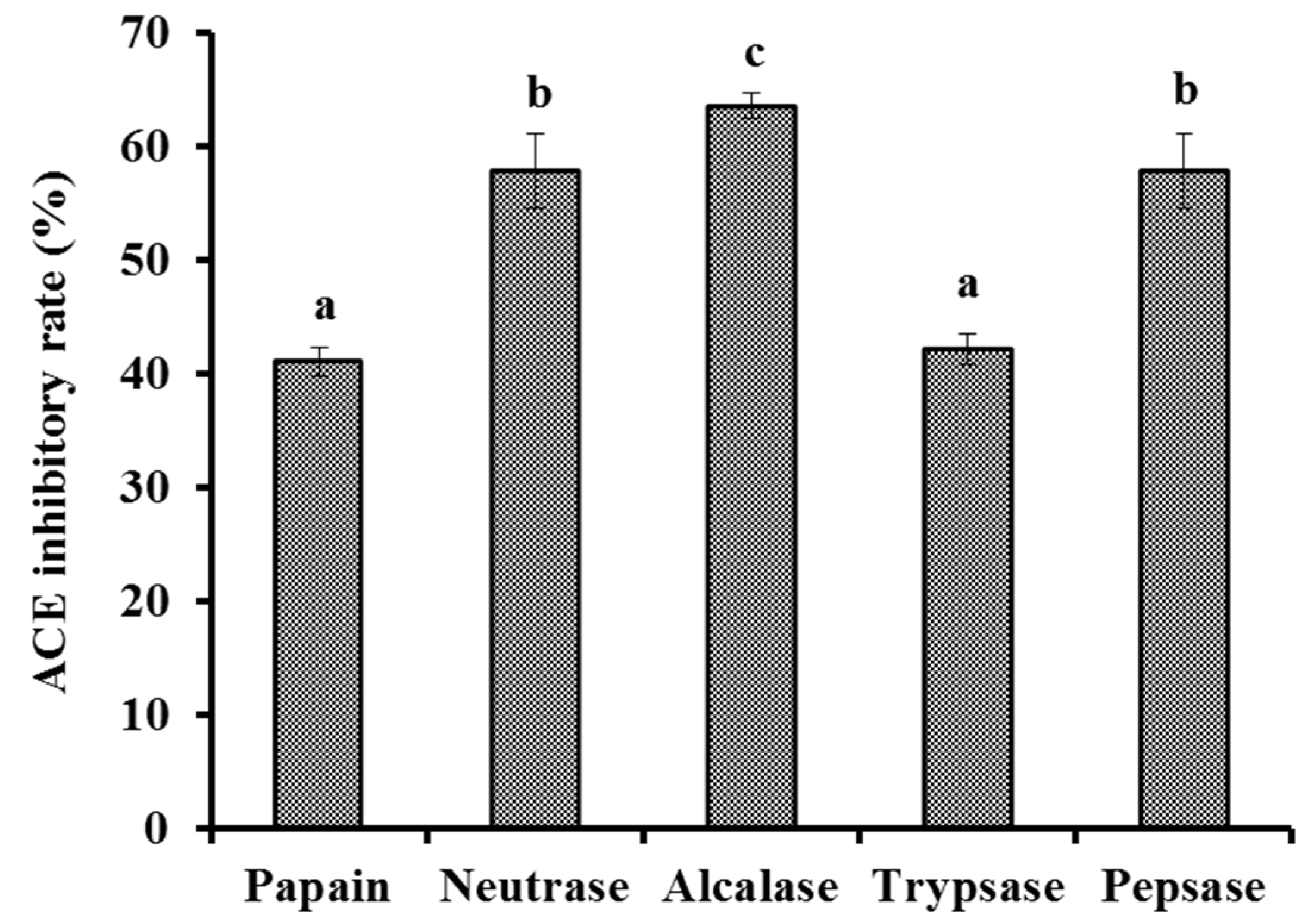
2.2.1. Screening of Protease Species
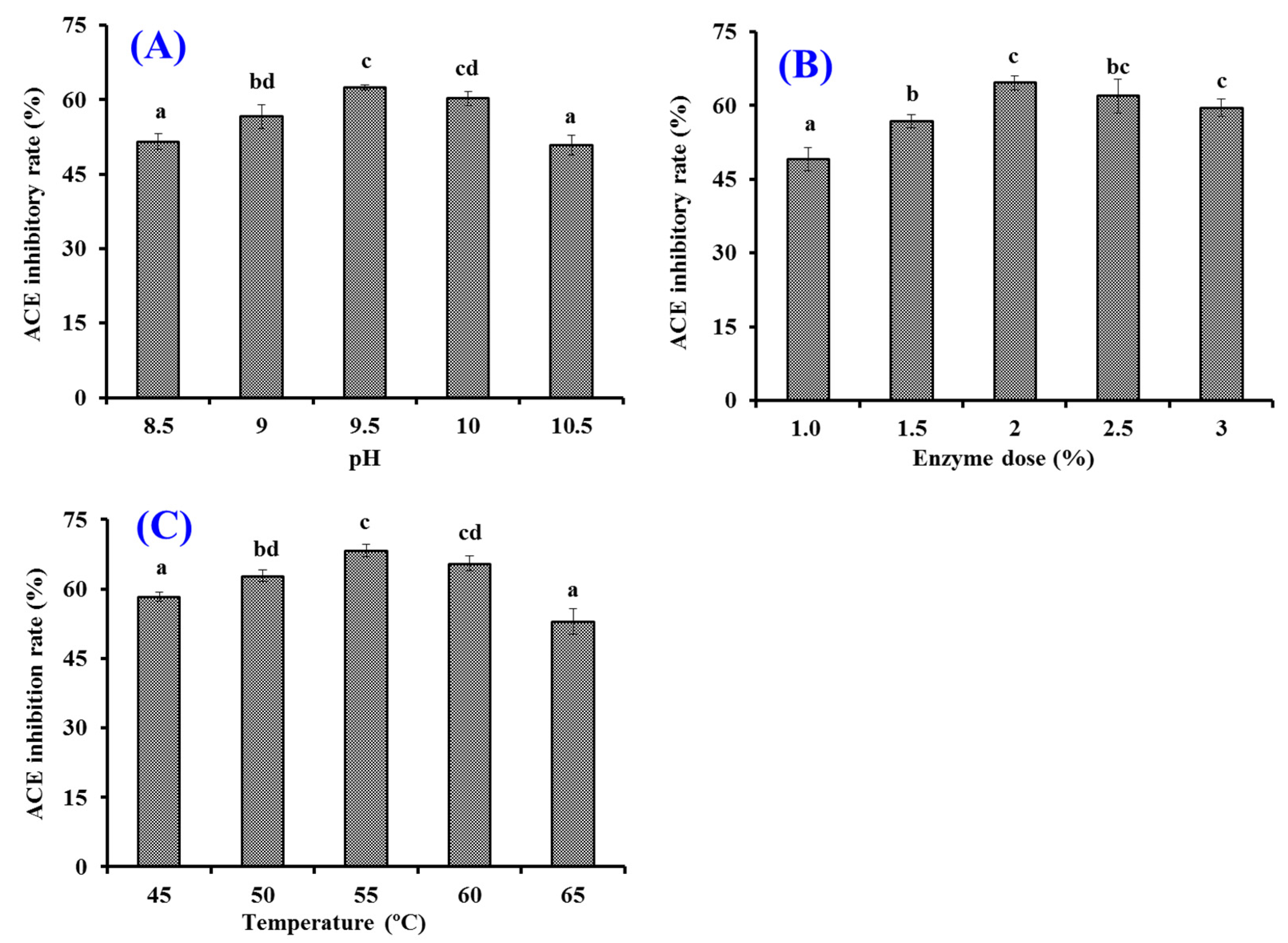
2.2.2. Optimization of the Hydrolysis Conditions of Alcalase Using Single Factor Experiment
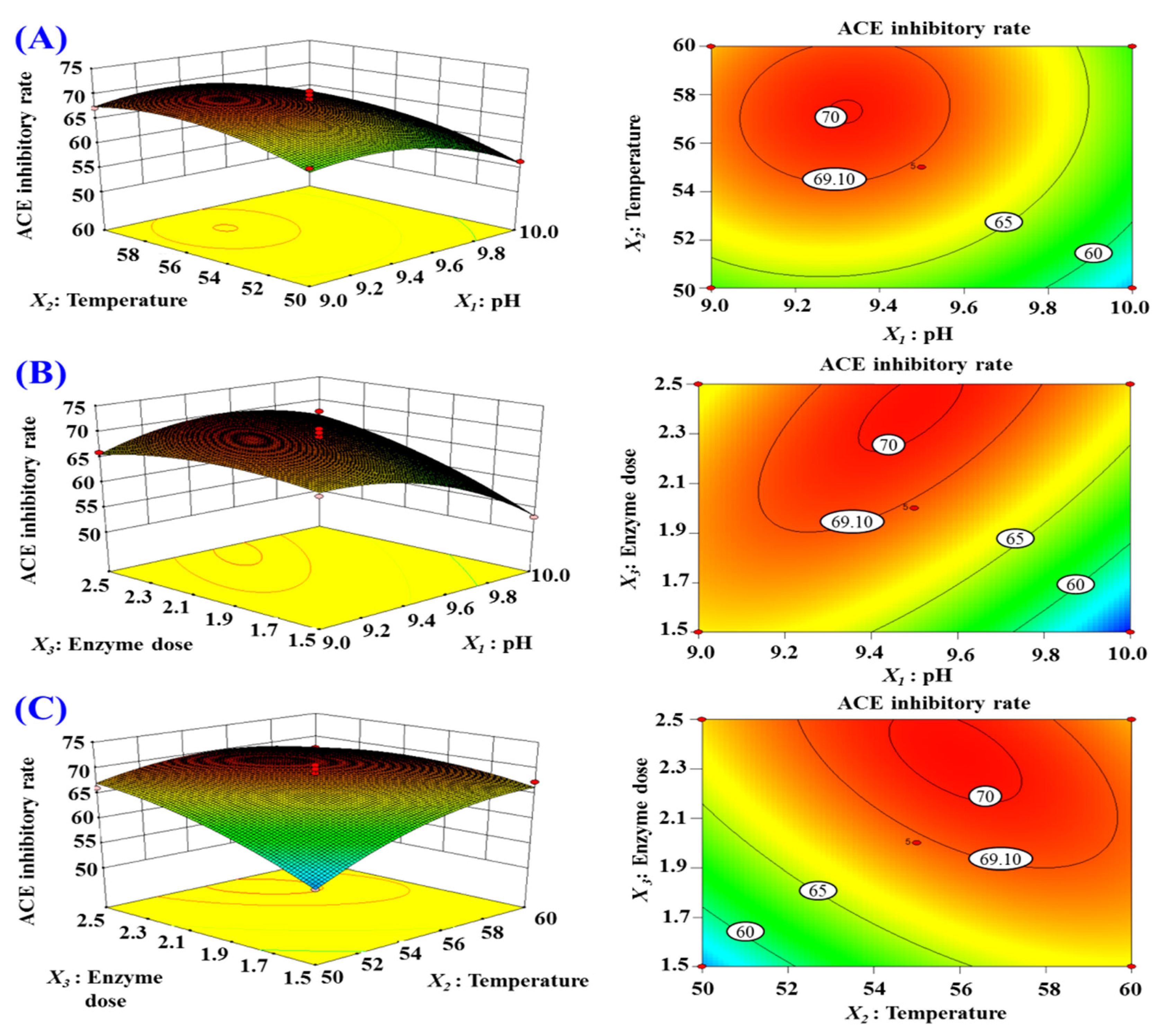
2.2.3. Optimization of the Hydrolysis Conditions of Alcalase by Response Surface Experiment
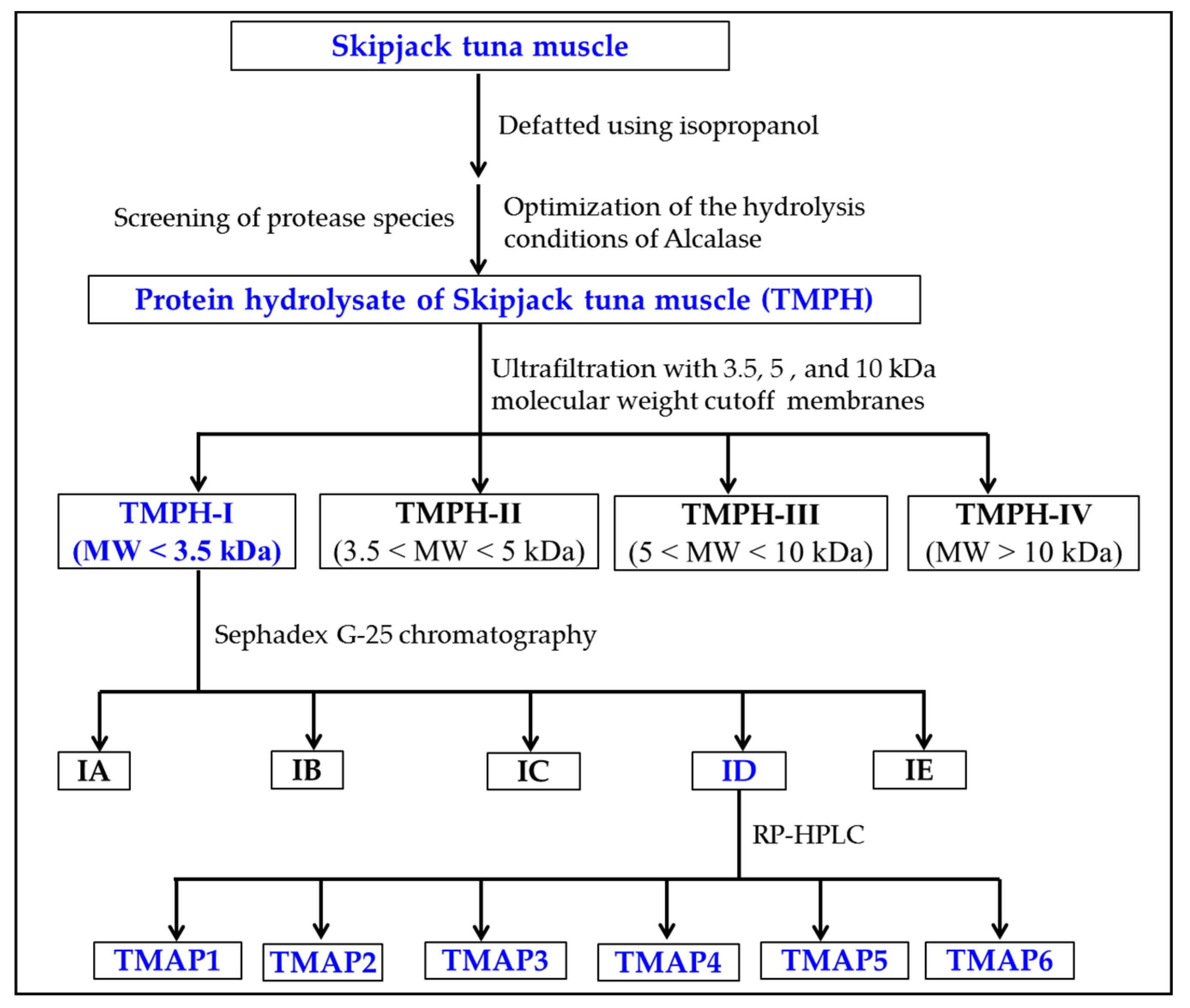
2.3. ACEi Peptides Prepared from TMPH
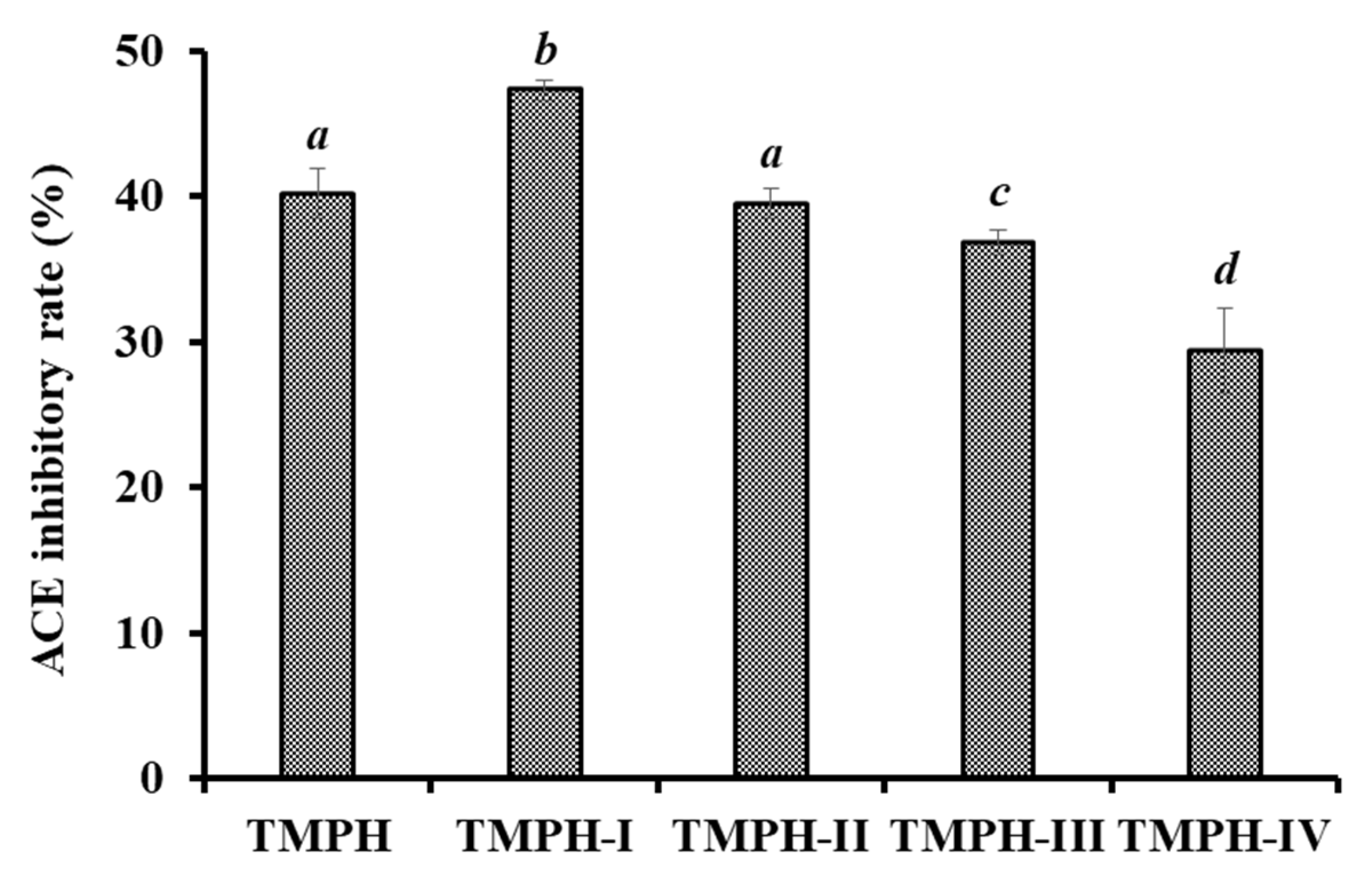
2.3.1. Ultrafiltration of TMPH
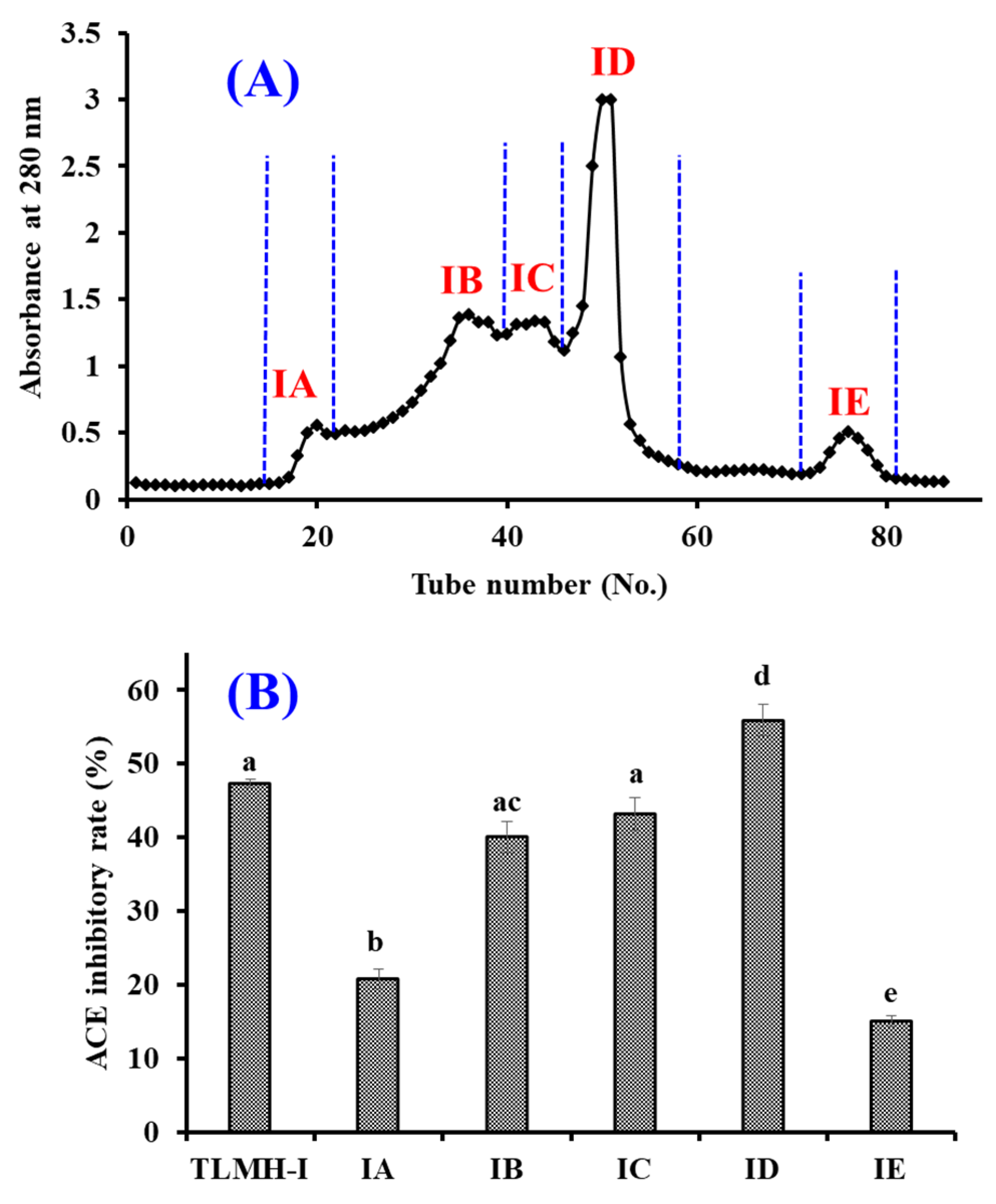
2.3.2. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) of TMPH-I
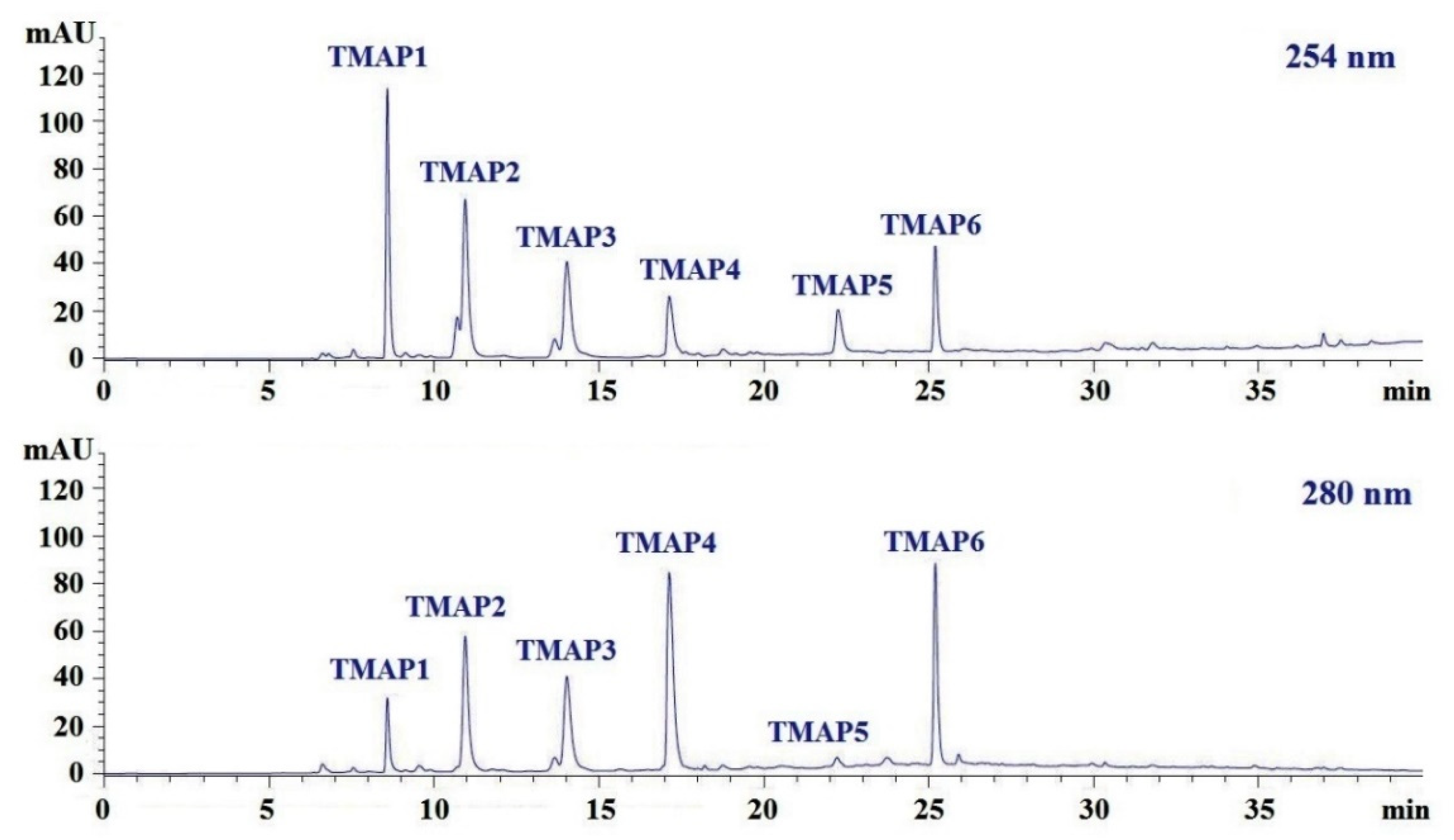
2.3.3. RP-HPLC Purification of TMPH-ID
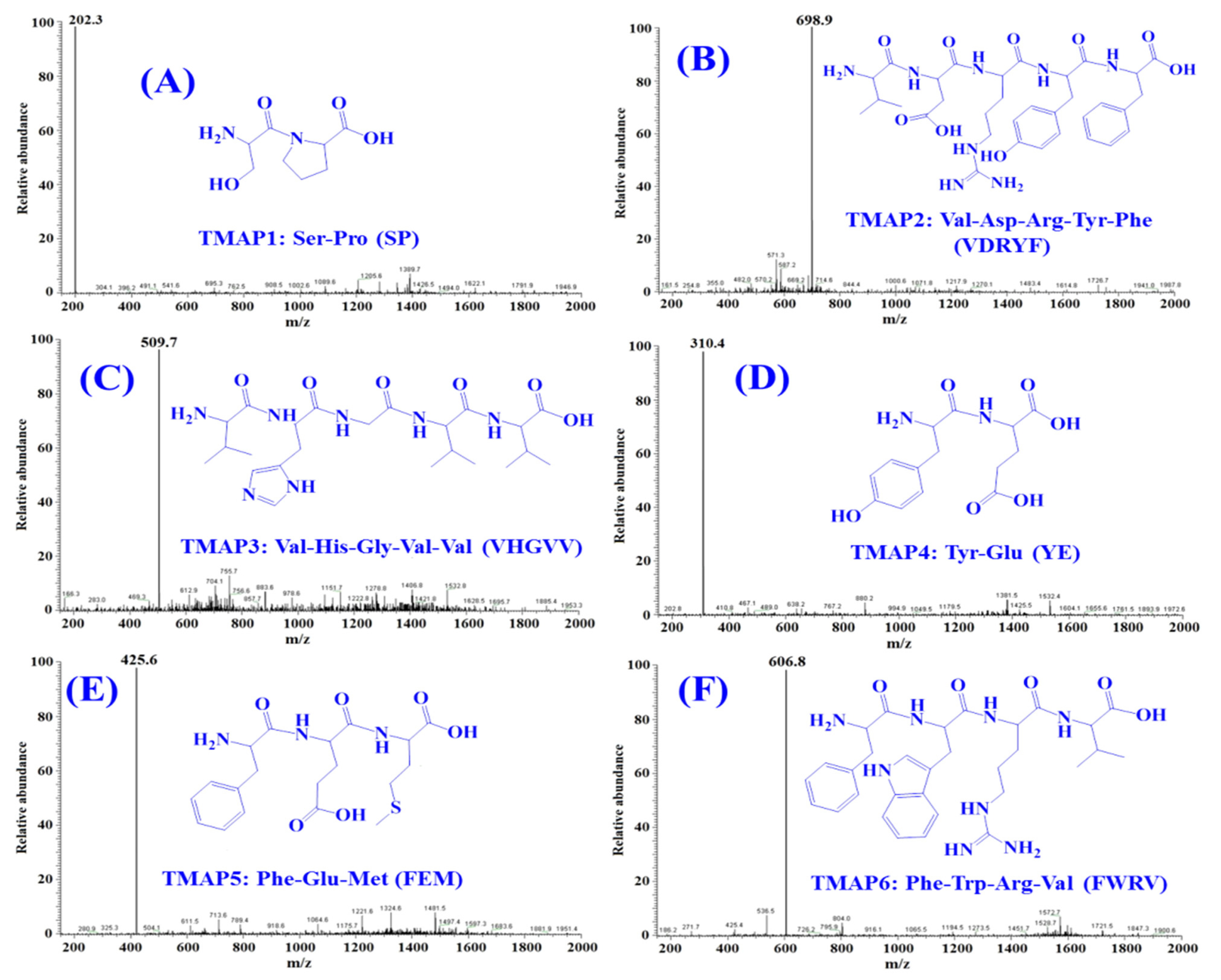
2.4. Peptide Sequences and MWs Determination
2.5. Bioactive Properties of Six ACEi Peptides (TMAP1-TMAP6)
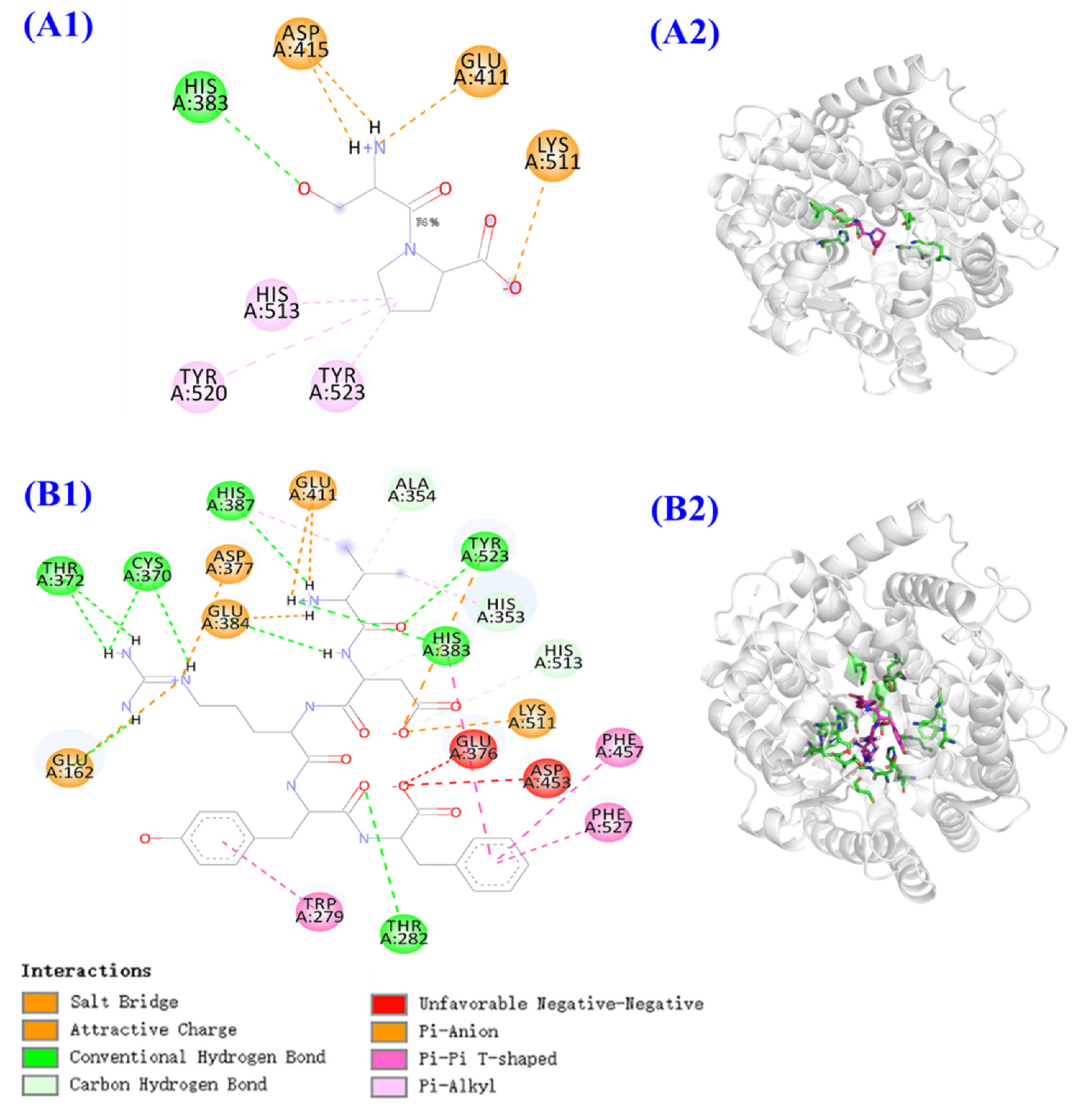
2.5.1. ACEi Activity and Molecular Docking Analysis
2.5.2. Effects of TMAP1 and TMAP2 on HUVECs
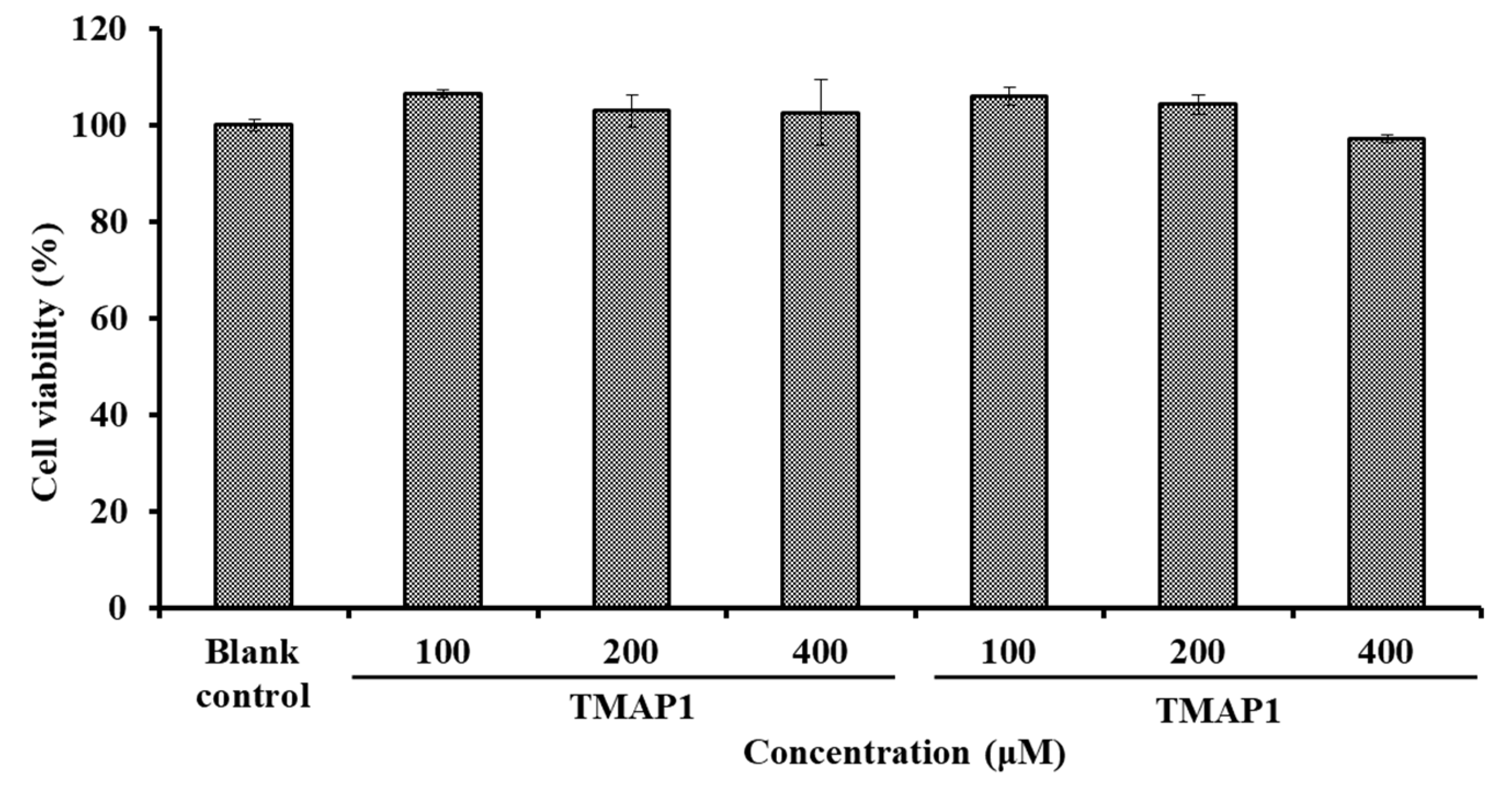
Effects of TMAP1 and TMAP2 on Cell Viability
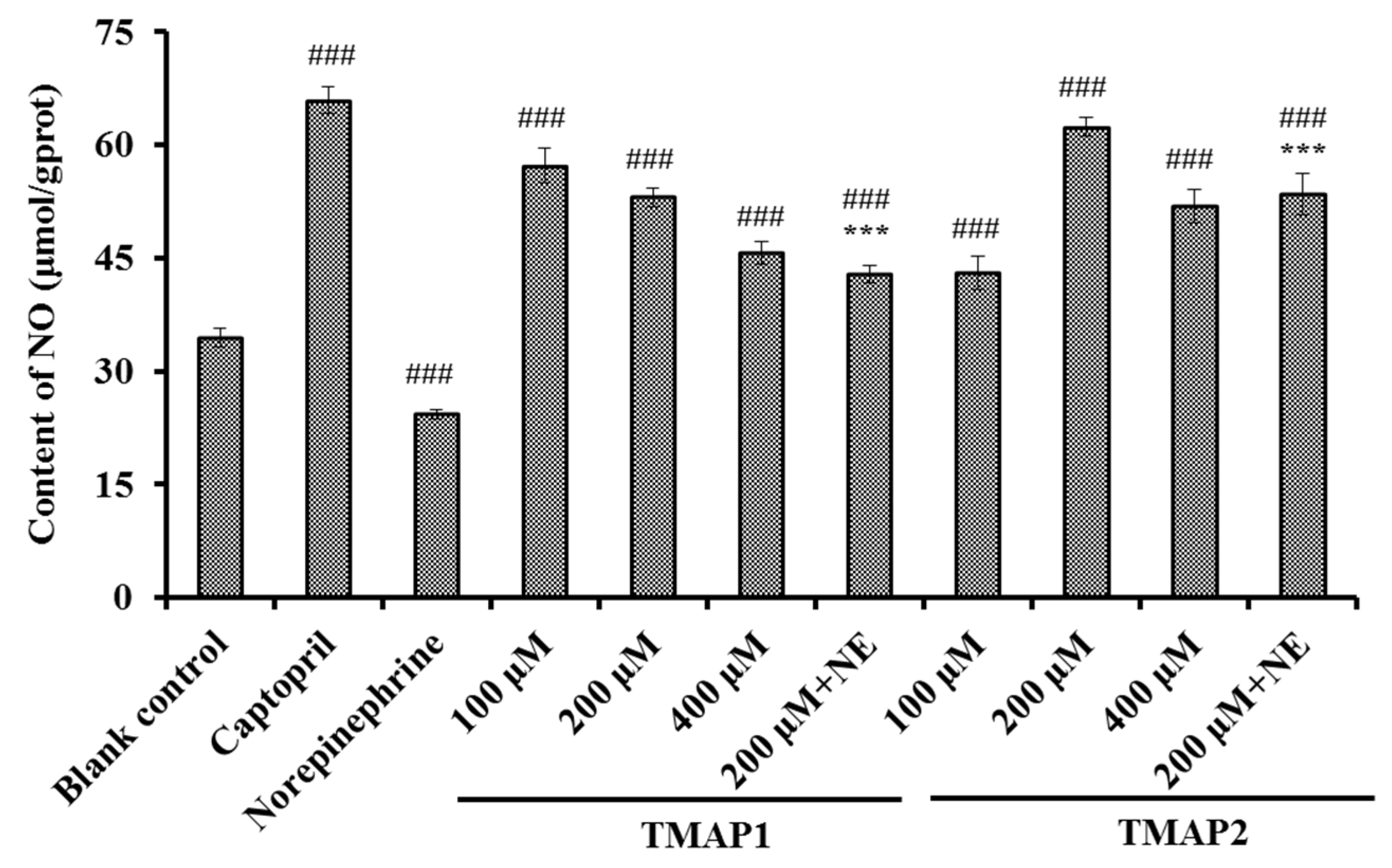
Effects of TMAP1 and TMAP2 on NO Production
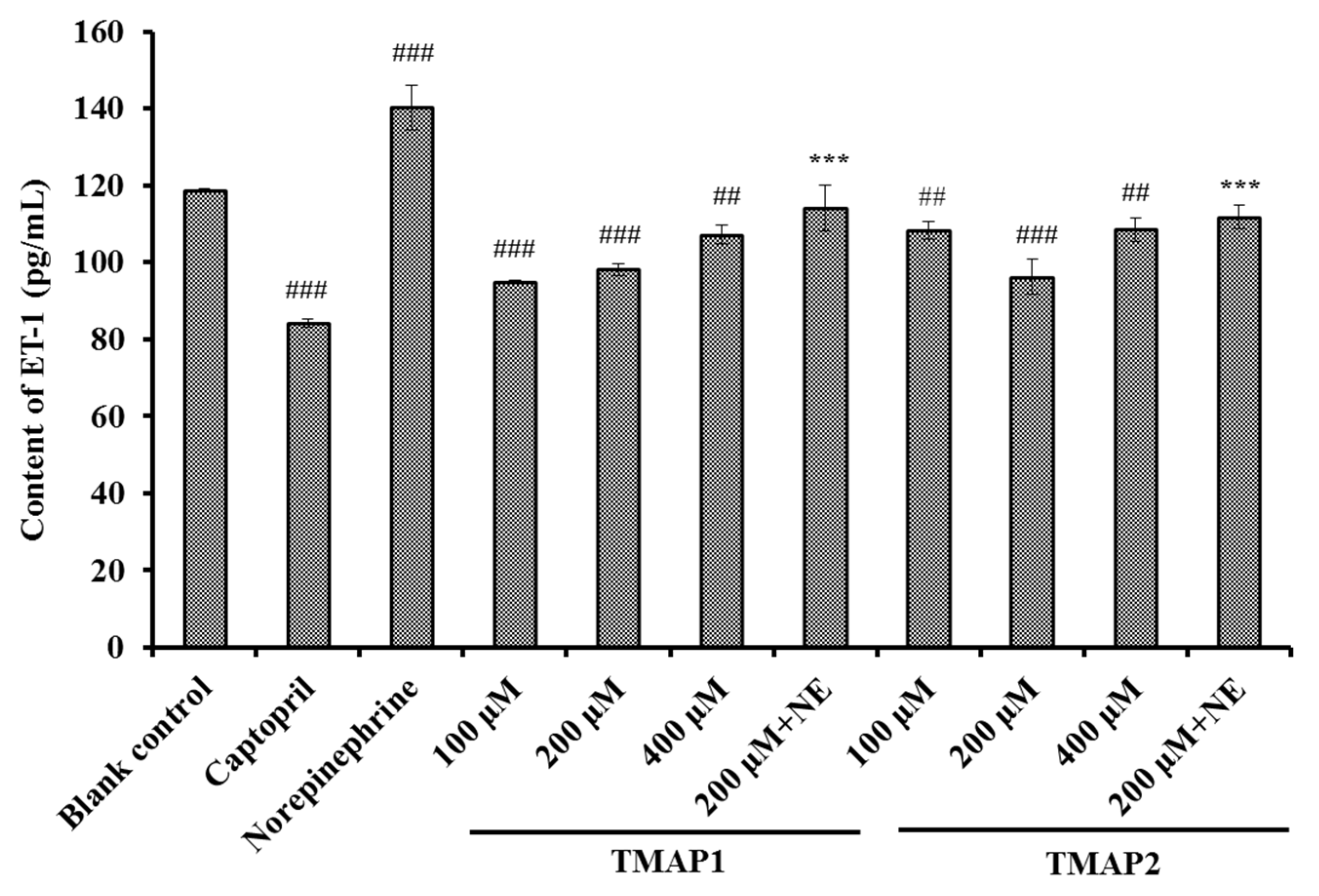
Effects of TMAP1 and TMAP2 on ET-1 Secretion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Determination of Amino Acid Composition and ACEi Activity
3.3. Preparation of Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle
3.3.1. Screening of Protease Species
3.3.2. Optimization of the Hydrolysis Conditions of Alcalase
3.4. Separation Process of ACEi Peptides from TMPH
3.5. Identification of Sequence and MWs of ACEi Peptide
3.6. Molecular Docking Experiment of TMAP1 and TMAP2
3.7. Effects of TMAP1 and TMAP2 on HUVECs
3.7.1. HUVECs Culture and Cell Viability Assessment using MTT Assay
3.7.2. Evaluation of NO and ET-1 Production
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Liu, X.; Li, F.; Zheng, Z.; Li, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T.; Tang, Y.; Qin, W. Association of morning hypertension with chronic kidney disease progression and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease and hypertension. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovas. 2022, 12, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Diamond, J.; Vieco, A.; Chaudhuri, S.; Shinnar, E.; Cromer, S.; Perel, P.; Mensah, G.A.; Narula, J.; Johnson, C.O.; et al. Global atlas of cardiovascular disease 2000–2016: The path to prevention and control. Glob. Heart 2018, 13, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.S.; Ma, J.; Peng, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Li, S.X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Jian, Y.P.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide inhibits atherosclerosis by increasing tetrahydrobiopterin via regulation of GTP-cyclohydrolase 1 and reducing uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. Atherosclerosis 2021, 328, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, M. Basic and recent advances in marine antihypertensive peptides: Production, structure-activity relationship and bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 43–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, D.T.; Kuo, W.W.; Ho, T.J.; Chang, R.L.; Lin, W.T.; Day, C.H.; Viswanadha, V.V.P.; Liao, P.H.; Huang, C.Y. Bioactive peptide VHVV upregulates the long-term memory-related biomarkers in adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Eight antihypertensive peptides from the protein hydrolysate of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): Isolation, identification, and activity evaluation on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimsheena, V.K.; Gowda, L.R. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from Arachin by simulated gastric digestion. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from the protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle: Purification, identification, and cytoprotective function on HepG2 cells damage by H2O2. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-derived bioactive peptides in human health: Challenges and opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Four antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of red stingray (Dasyatis akajei) cartilages: Isolation, identification, and in vitro activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abachi, S.; Bazinet, L.; Beaulieu, L. Antihypertensive and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from fish as potential cardioprotective compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, H.; Liao, W.; Wu, J. Molecular interactions, bioavailability, and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbizo-Reyes, U.; Liceaga, A.M.; Reddivari, L.; Kim, K.H.; Anderson, J.M. Enzyme kinetics, molecular docking, and in silico characterization of canary seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) peptides with ACE and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 88, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, D.; Yang, Z.; Gao, X.; Dang, Y. Angiotensin I-Converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity of umami peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 144, 111265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Ma, Z.; Ramachandran, M.; Souza, C.D.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.W. ACE inhibitory peptide KYIPIQ derived from yak milk casein induces nitric oxide production in HUVECs and diffuses via a transcellular mechanism in Caco-2 monolayers. Process Biochem. 2020, 99, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, L.; Qi, J.; Cao, J.; Tan, Y. Optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cow milk by Lactobacillus bulgaricus LB6. Acta Univ. Cibiniensis Food Technol. 2019, 23, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, T.; Lv, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, G.; Huang, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, M. The protective effects of tripeptides VPP and IPP against small extracellular vesicles from angiotensin II-dnduced vascular smooth muscle cells mediating endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13730–13741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Barrientos, L.M.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; Gonzalez-Cordova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B. Fermentedmilk as antihypertensive functional food. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Ding, G.F.; Li, Z.R. Characterization of acid and pepsin soluble collagens from spine and skull of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis). Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, L.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Twelve antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) roe prepared by Flavourzyme: Purification, sequence identification, and activity evaluation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 813780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, I.H.; Nam, T.J. Peptide derived from desalinated boiled tuna extract inhibits adipogenesis through the down regulation of C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 35, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack tuna milt: Purification, identification, and cytoprotection on H2O2 damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Process Biochem. 2022, 113, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.T.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Preparation and characterization of gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) bone stimulated by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Qian, Z.J.; Kim, S.K. A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tuna frame protein hydrolysate and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, X.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) scales: Preparation, identification and activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, S.; Lu, C.; Wan, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Ming, T.; Jim Wang, Z.; Su, X. The novel peptides ICRD and LCGEC screened from tuna roe show antioxidative activity via Keap1/Nrf2-ARE pathway regulation and gut microbiota modulation. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Batista, I.; Ramos, C.; Montero, P. Enhancement of ACE and prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitory potency of protein hydrolysates from sardine and tuna by-products by simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, G.X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.T.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Identification and active evaluation of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysates of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) head. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, H.; Hosomi, R.; Fukuda, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Fukunaga, K. Dietary tuna dark muscle protein attenuates hepatic steatosis and increases serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in obese type-2 diabetic/obese KK-A(y) mice. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Luo, H.Y. Influence of amino acid compositions and peptide profiles on antioxidant capacities of two protein hydrolysates from skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) dark muscle. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2580–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Jridi, M.; Mora, L.; Oseguera-Toledo, M.E.; Aristoy, M.C.; Amara, I.B.; Toldrá, F.; Nasri, M. In silico analysis and antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysate: Enzyme-peptide interaction study using molecular docking simulation. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Ma, J.H.; Luo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F. Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide derived from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems. A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B. Preparation and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skate (Raja porosa) cartilage. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhao, G.X.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from collagen hydrolysate of redlip croaker (Pseudosciaena polyactis) scales: Preparation, characterization, and cytoprotective effects on H2O2-damaged HepG2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, T.; Ding, G.F. Antioxidant and anticancer peptides from protein hydrolysate of blood clam (Tegillarca granosa) muscle. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Bioactive peptides from cartilage protein hydrolysate of spotless smoothhound and their antioxidant activity in vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, G.X.; Suo, S.K.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Purification, identification, activity evaluation, and stability of antioxidant peptides from Alcalase hydrolysate of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) proteins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, F.; Lan, X.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z.; Liao, D. Separation and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Saurida elongata proteins hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intarasirisawat, R.; Benjakula, S.; Wub, J.; Visessanguanc, W. Isolation of antioxidative and ACE inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack (Katsuwana pelamis) roe. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Kang, K.H.; Ryu, B.; Vo, T.S.; Jung, W.K.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from antihypertensive skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin gelatin hydrolysate in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, A.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Montero, P. Identification of ace-inhibitory peptides from squid skin collagen after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, I.; Qian, Z.J.; Ryu, B.; Ngo, D.H.; Kim, S.K. Purification and identification of antihypertensive peptides from seaweed pipefish (Syngnathus schlegeli) muscle protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. Active peptides from skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin gelatin diminish angiotensin-I converting enzyme activity and intracellular free radical-mediated oxidation. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auwal, S.M.; Abidin, N.Z.; Zarei, M.; Tan, C.P.; Saari, N. Identification, structure-activity relationship and in silico molecular docking analyses of five novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from stone fish (Actinopyga lecanora) hydrolysates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0197644. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, S.; Liu, R.; Hong, B.; Gao, R.; Bai, K. Processing optimization and characterization of angiotensin-Ι-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from lizardfish (Synodus macrops) scale gelatin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; Wei, J. A novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide from rice bran protein: Biochemical characterization and molecular docking study. LWT-Food Sci.Technol. 2017, 75, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, T.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhao, M.; Su, G. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleekayai, T.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Poyarkov, A.A.; CunhaNeves, A.; Suntornsuk, W.; FitzGerald, R.J. Extraction of antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptides from Thai traditional fermented shrimp pastes. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, N. Preparation and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from the marine macroalga Ulva intestinalis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Mora, L.; Jridi, M.; Toldra, F.; Nasri, M. In silico analysis and molecular docking study of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysates fractionated by ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deddish, P.A.; Wang, J.; Michel, B.; Morris, P.W.; Davidson, N.O.; Skidgel, R.A.; Erdös, E.G. Naturally occurring active N-domain of human angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7807–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, R. Purification, characterization, synthesis, in vitro ACE inhibition and in vivo antihypertensive activity of bioactive peptides derived from oil palm kernel glutelin-2 hydrolysates. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 28, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.; Mora, L.; Hussey, K.; Aluko, R.E. Boarfish protein recovery using the pH-shift process and generation of protein hydrolysates with ACE-inhibitory and antihypertensive bioactivities in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2016, 37, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.Y.; Kang, N.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.S.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Jeon, Y.J. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from an enzymatic hydrolysate of flounder fish (Paralichthys olivaceus) muscle as a potent anti-hypertensive agent. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z.; Lan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liao, D. Optimization of hydrolysis conditions for the production of angiotensin-I converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides and isolation of a novel peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) muscle protein hydrolysate. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1066–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Cytoprotective effect of antioxidant pentapeptides from the protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) against H2O2-mediated human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.H.; Luo, Q.B.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, and activity evaluation of ten antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy). J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Hirata, Y.; Adachi, S.; Tanaka, M.; Tsujino, M.; Koike, A.; Nogami, A.; Murumo, F.; Hiroe, M. Endothelin-1 is an autocrine/paracrine factor in the mechanism of angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in cultured rat cardiomyocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.R.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Gong, Y.D.; Tang, J.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G.F. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagens and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin and bone of spanish mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius). Food Hydrocolloid. 2013, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Ten new pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) muscle: Preparation, identification, and antioxidant activity evaluation. LWT-Food Sci.Technol. 2019, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, K.; Tokur, B. Optimization of hydrolysis conditions for the production of protein hydrolysates from fishss wastes using response surface methodology. Food Biosci. 2022, 45, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shahidi, F. Protein hydrolysate from turkey meat and optimization of its antioxidant potential by response surface methodology. Poultry Sci. 2018, 97, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.J.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolyzate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) muscle. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Anticancer activity of a hexapeptide from skate (Raja porosa)cartilage protein hydrolysate in HeLa cells. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.M.; Pan, X.; He, Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Hypolipidemic activities of two pentapeptides (VIAPW and IRWWW) from miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) muscle on lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells through regulation of AMPK pathway. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Amino Acid | Content (g/100g) | |
|---|---|---|
| Undefatted Muscle | Defatted Muscle | |
| Asp | 8.369 | 8.936 |
| Thr | 4.034 | 4.316 |
| Ser | 3.394 | 3.655 |
| Glu | 12.843 | 13.785 |
| Pro | 2.845 | 3.070 |
| Gly | 3.683 | 4.128 |
| Ala | 4.988 | 5.417 |
| Cys | 0.443 | 0.507 |
| Val | 4.540 | 4.835 |
| Met | 2.390 | 2.528 |
| Ile | 4.026 | 4.285 |
| Leu | 7.205 | 7.620 |
| Tyr | 2.970 | 3.234 |
| Phe | 3.952 | 3.944 |
| Lys | 7.851 | 8.189 |
| His | 3.128 | 3.427 |
| Arg | 5.023 | 5.369 |
| WTAA | 81.686 | 87.245 |
| WEAA | 33.998 | 35.717 |
| WEAA/WTAA (100%) | 41.62 | 40.94 |
| WHEAA | 8.15 | 8.80 |
| WNEAA | 39.54 | 42.73 |
| WEAA/WNEAA (100%) | 85.99 | 83.59 |
| Run | Independent Variables a | Dependent Variables b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 (pH) | X2 (temperature/°C) | X3 (enzyme dose/%) | Y (ACEi rate %) | |
| 1 | 9 | 55 | 1.5 | 66.01 |
| 2 | 9 | 60 | 2 | 67.19 |
| 3 | 9.5 | 60 | 2.5 | 67.56 |
| 4 | 10 | 55 | 2.5 | 67.56 |
| 5 | 10 | 55 | 1.5 | 53.06 |
| 6 | 9 | 55 | 2.5 | 66.00 |
| 7 | 10 | 60 | 2 | 61.95 |
| 8 | 9.5 | 55 | 2 | 68.00 |
| 9 | 10 | 50 | 0 | 56.32 |
| 10 | 9.5 | 50 | 1.5 | 55.86 |
| 11 | 9.5 | 55 | 2 | 70.58 |
| 12 | 9 | 50 | 2 | 63.93 |
| 13 | 9.5 | 55 | 2 | 66.82 |
| 14 | 9.5 | 50 | 2.5 | 66.11 |
| 15 | 9.5 | 55 | 2 | 68.39 |
| 16 | 9.5 | 55 | 2 | 67.90 |
| 17 | 9.5 | 60 | 1.5 | 67.31 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 407.86 | 9 | 45.32 | 24.24 | 0.0002 | significant |
| X1-pH | 73.45 | 1 | 73.45 | 39.29 | 0.0004 | |
| X2-Temperature | 59.35 | 1 | 59.35 | 31.75 | 0.0008 | |
| X3-Enzyme dose | 78.06 | 1 | 78.06 | 41.76 | 0.0003 | |
| X1X2 | 1.4 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.75 | 0.4148 | |
| X1X3 | 52.64 | 1 | 52.64 | 28.16 | 0.0011 | |
| X2X3 | 25 | 1 | 25 | 13.37 | 0.0081 | |
| X12 | 60.02 | 1 | 60.02 | 32.11 | 0.0008 | |
| X22 | 31.22 | 1 | 31.22 | 16.7 | 0.0047 | |
| X32 | 15.41 | 1 | 15.41 | 8.24 | 0.024 | |
| Residual | 13.09 | 7 | 1.87 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 4.27 | 3 | 1.42 | 0.65 | 0.6256 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 8.82 | 4 | 2.2 | |||
| Cor Total | 420.95 | 16 |
| Retention Time (min) | Amino Acid Sequence | Observed MW/ Theoretical MW (Da) | IC50 (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMAP1 | 8.590 | Ser-Pro (SP) | 202.3/202.2 | 0.06 ± 0.01 a |
| TMAP2 | 10.950 | Val-Asp-Arg-Tyr-Phe (VDRYF) | 698.9/698.8 | 0.28 ± 0.03 a |
| TMAP3 | 14.032 | Val-His-Gly-Val-Val (VHGVV) | 509.7/509.6 | 0.90 ± 0.16 b |
| TMAP4 | 17.139 | Tyr-Glu (YE) | 310.4/310.3 | 0.80 ± 0.03 b |
| TMAP5 | 22.258 | Phe-Glu-Met (FEM) | 425.6/425.5 | 2.18 ± 0.20 c |
| TMAP6 | 25.209 | Phe-Trp-Arg-Val (FWRV) | 606.8/606.7 | 0.76 ± 0.10 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, S.-L.; Luo, Q.-B.; Suo, S.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Preparation, Identification, Molecular Docking Study and Protective Function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030176
Zheng S-L, Luo Q-B, Suo S-K, Zhao Y-Q, Chi C-F, Wang B. Preparation, Identification, Molecular Docking Study and Protective Function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(3):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030176
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Shuo-Lei, Qian-Bin Luo, Shi-Kun Suo, Yu-Qin Zhao, Chang-Feng Chi, and Bin Wang. 2022. "Preparation, Identification, Molecular Docking Study and Protective Function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle" Marine Drugs 20, no. 3: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030176
APA StyleZheng, S.-L., Luo, Q.-B., Suo, S.-K., Zhao, Y.-Q., Chi, C.-F., & Wang, B. (2022). Preparation, Identification, Molecular Docking Study and Protective Function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle. Marine Drugs, 20(3), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030176








