Meridianins Inhibit GSK3β In Vivo and Improve Behavioral Alterations Induced by Chronic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vivo Inhibition of GSK3β by Meridianins
2.2. Meridianins Modulate Molecular Pathways Involved with GSK3β Signaling
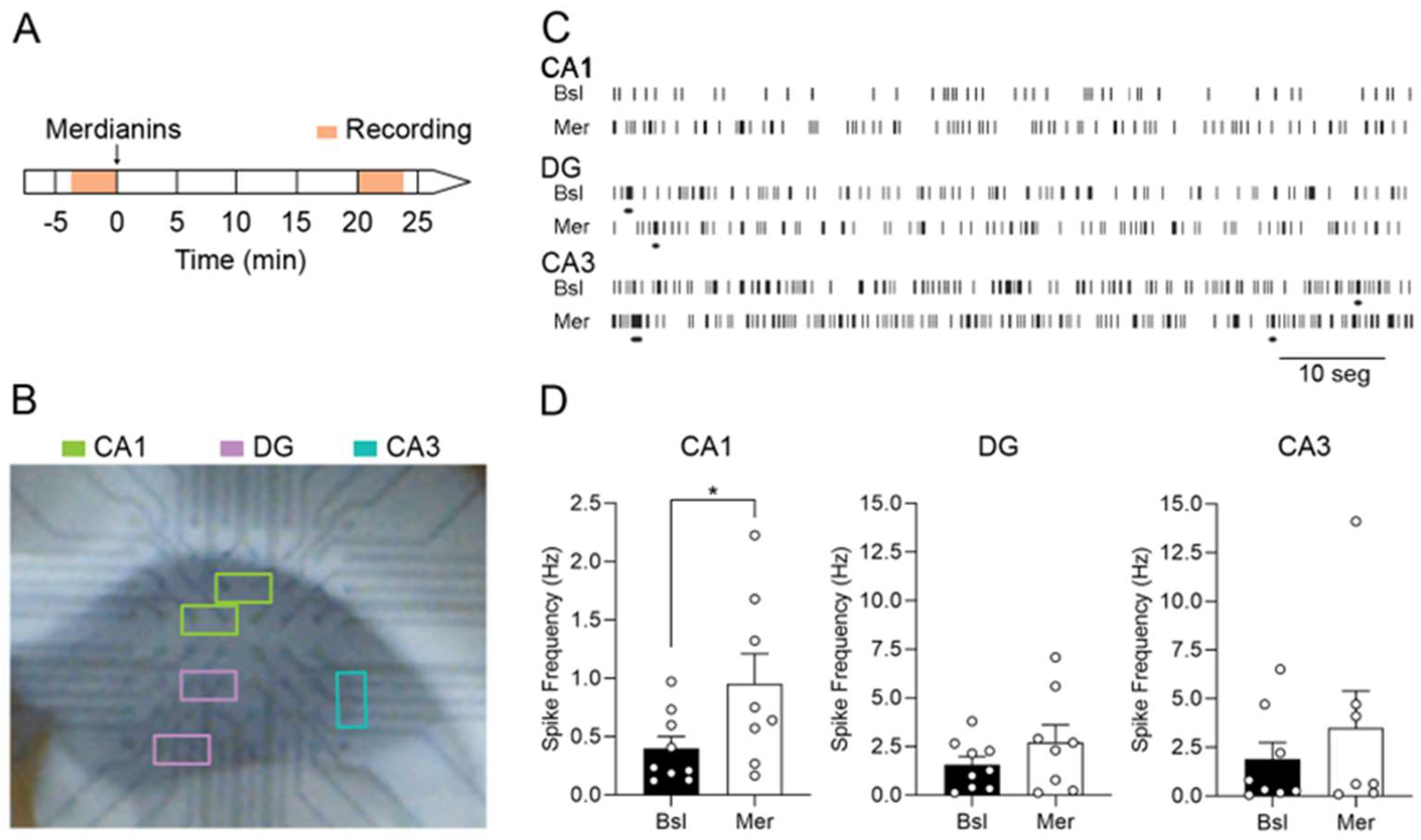
2.3. Meridianins Increase Spontaneous Synaptic Activity in the Hippocampal CA1
2.4. Meridianins Improve Behavioral Deficits Induced by CUMS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Marine Molecules
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Immunoblot Analysis
4.5. Stereotaxic Surgery
4.6. Electrophysiological Field Recordings
4.7. Chronic Stress
4.8. Behavioral Test
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otte, C.; Gold, S.M.; Penninx, B.W.; Pariante, C.M.; Etkin, A.; Fava, M.; Mohr, D.C.; Schatzberg, A.F. Major Depressive Disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D. Prevalence and Clinical Course of Depression: A Review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 31, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabeshima, T.; Kim, H.-C. Involvement of Genetic and Environmental Factors in the Onset of Depression. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter-Levin, G.; Xu, L. How Could Stress Lead to Major Depressive Disorder? IBRO Rep. 2018, 4, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S. Mood Disorders and Allostatic Load. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Protective and Damaging Effects of Stress Mediators: Central Role of the Brain. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Stewart, J.W.; Warden, D.; Niederehe, G.; Thase, M.E.; Lavori, P.W.; Lebowitz, B.D.; et al. Acute and Longer-Term Outcomes in Depressed Outpatients Requiring One or Several Treatment Steps: A STAR*D Report. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jope, R.S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 in the Etiology and Treatment of Mood Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jope, R.S. Is Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 a Central Modulator in Mood Regulation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, Actions, and Diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Voleti, B. Signaling Pathways Underlying the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Depression: Novel Mechanisms for Rapid-Acting Agents. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.; Mesquita, A.R.; Bessa, J.; Sousa, J.C.; Sotiropoulos, I.; Leão, P.; Almeida, O.F.X.; Sousa, N. Lithium Blocks Stress-Induced Changes in Depressive-like Behavior and Hippocampal Cell Fate: The Role of Glycogen-Synthase-Kinase-3β. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.B.; Dias, C.; Magida, J.; Mazei-Robison, M.; Lobo, M.; Kennedy, P.; Dietz, D.; Covington, H.; Russo, S.; Neve, R.; et al. A Novel Role of the WNT-Dishevelled-GSK3β Signaling Cascade in the Mouse Nucleus Accumbens in a Social Defeat Model of Depression. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9084–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceto, G.; Colussi, C.; Leone, L.; Fusco, S.; Rinaudo, M.; Scala, F.; Green, T.A.; Laezza, F.; D’Ascenzo, M.; Grassi, C. Chronic Mild Stress Alters Synaptic Plasticity in the Nucleus Accumbens through GSK3β-Dependent Modulation of Kv4.2 Channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8143–8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karege, F.; Perroud, N.; Burkhardt, S.; Schwald, M.; Ballmann, E.; La Harpe, R.; Malafosse, A. Alteration in Kinase Activity But Not in Protein Levels of Protein Kinase B and Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in Ventral Prefrontal Cortex of Depressed Suicide Victims. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.H.; Park, Y.C.; Kim, S.H. Increased Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β MRNA Level in the Hippocampus of Patients with Major Depression: A Study Using the Stanley Neuropathology Consortium Integrative Database. Psychiatry Investig. 2010, 7, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polter, A.; Beurel, E.; Yang, S.; Garner, R.; Song, L.; Miller, C.A.; Sweatt, J.D.; McMahon, L.; Bartolucci, A.A.; Li, X.; et al. Deficiency in the Inhibitory Serine-Phosphorylation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Increases Sensitivity to Mood Disturbances. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarno, P.; Li, X.; Jope, R.S. Regulation of Akt and Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Phosphorylation by Sodium Valproate and Lithium. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Friedman, A.B.; Zhu, W.; Wang, L.; Boswell, S.; May, R.S.; Davis, L.L.; Jope, R.S. Lithium Regulates Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Implication in the Treatment of Bipolar Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jope, R.; Roh, M.-S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3) in Psychiatric Diseases and Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 7, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Frye, M.A.; Shelton, R.C. Review of Pharmacological Treatment in Mood Disorders and Future Directions for Drug Development. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, N.; Holmes, C.; Mullee, M. Does Lithium Therapy Protect against the Onset of Dementia? Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2005, 19, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Ser, T.; Steinwachs, K.C.; Gertz, H.J.; Andrés, M.V.; Gómez-Carrillo, B.; Medina, M.; Vericat, J.A.; Redondo, P.; Fleet, D.; León, T. Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with the GSK-3 Inhibitor Tideglusib: A Pilot Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.V.; Andersson, U.; Andersson, S.; Knerr, L.; Bauer, U.; Sundgren-Andersson, A.K. The Conundrum of GSK3 Inhibitors: Is It the Dawn of a New Beginning? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, S547–S554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug Development from Marine Natural Products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 1122–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldatou, S.; Baker, B.J. Cold-Water Marine Natural Products, 2006 to 2016. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 585–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Avila, C. Natural Products Mediating Ecological Interactions in Antarctic Benthic Communities: A Mini-Review of the Known Molecules. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1114–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Preckler, C.; De Castro-Fernandez, P.; Martín-Martín, R.; Figuerola, B.; Avila, C. Chemical Ecology in the Southern Ocean. In Life in Extreme Environments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 251–278. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, C.; Angulo-Preckler, C. A Minireview on Biodiscovery in Antarctic Marine Benthic Invertebrates. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 686477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Urgellés, E.; Sancho-Balsells, A.; Chen, W.; López-Molina, L.; Ballasch, I.; del Castillo, I.; Avila, C.; Alberch, J.; Giralt, A. Meridianins Rescue Cognitive Deficits, Spine Density and Neuroinflammation in the 5xFAD Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 791666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldes, A.M.; Brasco, M.F.R.; Franco, L.H.; Palermo, J.A. Identification of Two Meridianins from the Crude Extract of the Tunicate Aplidium meridianum by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gompel, M.; Leost, M.; Bal De Kier Joffe, E.; Puricelli, L.; Hernandez Franco, L.; Palermo, J.; Meijer, L. Meridianins, a New Family of Protein Kinase Inhibitors Isolated from the Ascidian Aplidium meridianum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, L.H.; De Kier Joffé, E.B.; Puricelli, L.; Tatian, M.; Seldes, A.M.; Palermo, J.A. Indole Alkaloids from the Tunicate Aplidium meridianum. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Nieto, R.M.; Avila, C.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J. Mass Spectrometry Detection of Minor New Meridianins from the Antarctic Colonial Ascidians Aplidium falklandicum and Aplidium meridianum. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Carbone, M.; Vázquez, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Nieto, R.M.; Varela, M.M.; Gavagnin, M.; Avila, C. Natural Products from Antarctic Colonial Ascidians of the Genera Aplidium and Synoicum: Variability and Defensive Role. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Forestieri, R.; Nieto, R.M.; Varela, M.; Nappo, M.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C.; Castelluccio, F.; Carbone, M.; Ramos-Espla, A.; et al. Chemical Defenses of Tunicates of the Genus Aplidium from the Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubia, E.; Ortega, M.; Salva, J. Natural Products Chemistry in Marine Ascidians of the Genus Aplidium. Mini. Rev. Org. Chem. 2005, 2, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Dong, B. Marine Drugs Origins and Bioactivities of Natural Compounds Derived from Marine Ascidians and Their Symbionts. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorach-Pares, L.; Nonell-Canals, A.; Avila, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, M. Computer-Aided Drug Design (CADD) to De-Orphanize Marine Molecules: Finding Potential Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative and Cardiovascular Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Huang, S.S.; Hao, Y.N.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.M. Marine-Natural-Products for Biocides Development: First Discovery of Meridianin Alkaloids as Antiviral and Anti-Phytopathogenic-Fungus Agents. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorach-Pares, L.; Nonell-Canals, A.; Avila, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, M. Kororamides, Convolutamines, and Indole Derivatives as Possible Tau and Dual-Specificity Kinase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Computational Study. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhuang, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, F. Structural-Based Optimizations of the Marine-Originated Meridianin C as Glucose Uptake Agents by Inhibiting GSK-3β. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.S.; Park, Y.K.; Ramalingam, M.; Yadav, A.K.; Cho, H.R.; Hong, V.S.; More, K.N.; Bae, J.H.; Bishop-Bailey, D.; Kano, J.; et al. Meridianin C Inhibits the Growth of YD-10B Human Tongue Cancer Cells through Macropinocytosis and the Down-regulation of Dickkopf-related Protein-3. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharate, B.S.; Yadav, R.R.; Battula, S.; Vishwakarma, R.A. Meridianins: Marine-Derived Potent Kinase Inhibitors. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorach-Pares, L.; Nonell-Canals, A.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Avila, C. Computer-Aided Drug Design Applied to Marine Drug Discovery: Meridianins as Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutic Agents. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, K.N.; Jang, H.W.; Hong, V.S.; Lee, J. Pim Kinase Inhibitory and Antiproliferative Activity of a Novel Series of Meridianin C Derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.J.; Goff, D.A.; Lin, N.; Singh, R.; Li, W.; McLaughlin, J.; Baltgalvis, K.A.; Payan, D.G.; Kinsella, T.M. Developing DYRK Inhibitors Derived from the Meridianins as a Means of Increasing Levels of NFAT in the Nucleus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2617–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhou, W.; Zhuang, C.; Chen, F. Structure-Based Design of Marine-Derived Meridianin C Derivatives as Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β Inhibitors with Improved Oral Bioavailability: From Aminopyrimidyl-Indoles to the Sulfonyl Analogues. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 119, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, L.; Qi, L. Metabolite Profiling of Meridianin C in Vivo of Rat by UHPLC/Q-TOF MS. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, W.M.; Barker, W.T.; Baker, J.T.; Hahn, N.A.; Melander, R.J.; Melander, C. Meridianin D Analogues Display Antibiofilm Activity against MRSA and Increase Colistin Efficacy in Gram-Negative Bacteria. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharate, S.B.; Yadav, R.R.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Jacob, M.R.; Khan, I.A.; Vishwakarma, R.A. Meridianin G and Its Analogs as Antimalarial Agents. Med. Chem. Comm. 2013, 4, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Yadav, A.K.; Do, Y.; Heo, M.; Bishop-Bailey, D.; Lee, J.; Jang, B.C. Anti-Survival and pro-Apoptotic Effects of Meridianin C Derivatives on MV4-11 Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorach-Pares, L.; Rodriguez-Urgelles, E.; Nonell-Canals, A.; Alberch, J.; Avila, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Giralt, A. Meridianins and Lignarenone B as Potential GSK3β Inhibitors and Inductors of Structural Neuronal Plasticity. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P. The Chronic Mild Stress (CMS) Model of Depression: History, Evaluation and Usage. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineur, Y.S.; Belzung, C.; Crusio, W.E. Effects of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress on Anxiety and Depression-like Behavior in Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 175, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaal, L.; Veltman, D.J.; van Erp, T.G.M.; Smann, P.G.; Frodl, T.; Jahanshad, N.; Loehrer, E.; Tiemeier, H.; Hofman, A.; Niessen, W.J.; et al. Subcortical Brain Alterations in Major Depressive Disorder: Findings from the ENIGMA Major Depressive Disorder Working Group. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ge, T.; Leng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, R. The Role of Neural Plasticity in Depression: From Hippocampus to Prefrontal Cortex. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pan, J.; Sun, J.; Ding, L.; Ruan, L.; Reed, M.; Yu, X.; Klabnik, J.; Lin, D.; Li, J.; et al. Inhibition of Phosphodiesterase 2 Reverses Impaired Cognition and Neuronal Remodeling Caused by Chronic Stress. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Hui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Teng, G.; Chan, K.C.; Wu, E.X.; Nie, B.; Shan, B.; et al. Learning and Memory Alterations Are Associated with Hippocampal N-Acetylaspartate in a Rat Model of Depression as Measured by 1h-Mrs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, N.; Chiu, C.T.; Moya, P.R.; Leng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hunsberger, J.G.; Leeds, P.; Chuang, D.M. Lentivirally Mediated GSK-3β Silencing in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus Induces Antidepressant-like Effects in Stressed Mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzagalli, D.A.; Roberts, A.C. Prefrontal Cortex and Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, D.B.; Jernigan, C.S.; Chandran, A.; Iyo, A.H.; May, W.L.; Austin, M.C.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Karolewicz, B. Gene Expression Analysis of Novel Genes in the Prefrontal Cortex of Major Depressive Disorder Subjects. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 43, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roddy, D.; Kelly, J.R.; Farrell, C.; Doolin, K.; Roman, E.; Nasa, A.; Frodl, T.; Harkin, A.; O’Mara, S.; O’Hanlon, E.; et al. Amygdala Substructure Volumes in Major Depressive Disorder. Neuroimage 2021, 31, 102781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, Y.; Morris, L.S.; Verma, G.; Rutter, S.B.; Balchandani, P.; Murrough, J.W. Altered Hippocampus and Amygdala Subregion Connectome Hierarchy in Major Depressive Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Han, M.-H.; Mazei-Robison, M.; Iñiguez, S.D.; Ables, J.L.; Vialou, V.; Berton, O.; Ghose, S.; Covington, H.E.; Wiley, M.D.; et al. AKT Signaling within the Ventral Tegmental Area Regulates Cellular and Behavioral Responses to Stressful Stimuli. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Yu, Y.; Lang, X.Y.; Jiang, C.Y.; Lan, R.; Qin, X.Y. 2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-Glucoside Restores BDNF-TrkB and FGF2-Akt Signaling Axis to Attenuate Stress-Induced Depression. Neuroscience 2020, 430, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lee, B.; Liu, R.J.; Banasr, M.; Dwyer, J.M.; Iwata, M.; Li, X.Y.; Aghajanian, G.; Duman, R.S. MTOR-Dependent Synapse Formation Underlies the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of NMDA Antagonists. Science 2010, 329, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira de Assis Lima, I.; Flávia Almeida-Santos, A.; Hélen Ferreira-Vieira, T.; Cristina Aguiar, D.; Mara Ribeiro, F.; Cristina Campos, A.; Carlos Pinheiro de Oliveira, A. Antidepressant-like Effect of Valproic Acid-Possible Involvement of PI3K/Akt/MTOR Pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 329, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, K.W.; O’Brien, R.J.; Mammen, A.L.; Bernhardt, J.; Huganir, R.L. Characterization of Multiple Phosphorylation Sites on the AMPA Receptor GluR1 Subunit. Neuron 1996, 16, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diering, G.H.; Heo, S.; Hussain, N.K.; Liu, B.; Huganir, R.L.; Barria, A.; Roche, K.W. Extensive Phosphorylation of AMPA Receptors in Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 33, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombag, H.S.; Sutton, J.M.; Takamiya, K.; Lee, H.K.; Holland, P.C.; Gallagher, M.; Huganir, R.L. A Necessary Role for GluR1 Serine 831 Phosphorylation in Appetitive Incentive Learning. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 191, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, H.K.; Takamiya, K.; Han, J.S.; Man, H.; Kim, C.H.; Rumbaugh, G.; Yu, S.; Ding, L.; He, C.; Petralia, R.S.; et al. Phosphorylation of the AMPA Receptor GluR1 Subunit Is Required for Synaptic Plasticity and Retention of Spatial Memory. Cell 2003, 112, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneyto, M.; Kristiansen, L.V.; Oni-Orisan, A.; Mccullumsmith, R.E.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. Abnormal Glutamate Receptor Expression in the Medial Temporal Lobe in Schizophrenia and Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.L.N.M.; Guimarães, F.S.; Pearson, R.C.A.; Del Bel, E.A. Effects of Single or Repeated Restraint Stress on GluR1 and GluR2 Flip and Flop MRNA Expression in the Hippocampal Formation. Brain Res. Bull. 2002, 59, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallarackal, A.J.; Kvarta, M.D.; Cammarata, E.; Jaberi, L.; Cai, X.; Bailey, A.M.; Thompson, S.M. Chronic Stress Induces a Selective Decrease in AMPA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Excitation at Hippocampal Temporoammonic-CA1 Synapses. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15669–15674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Hu, W.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Z.C.; Zhang, M.; He, Z.Y. Paeoniflorin Attenuates Impairment of Spatial Learning and Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation in Mice Subjected to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, C.; Janc, O.A.; Kempkes, B.; Callis, C.A.; Flügge, G.; Hülsmann, S.; Müller, M. Restraint Stress Intensifies Interstitial K+ Accumulation during Severe Hypoxia. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ju, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L. Effect of Ketamine on LTP and NMDAR EPSC in Hippocampus of the Chronic Social Defeat Stress Mice Model of Depression. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.R.; Czyz, M.L.; Morris, J.C. Concise Syntheses of Meridianins and Meriolins Using a Catalytic Domino Amino-Palladation Reaction. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.H.; Palermo, J.A. Synthesis of 2-(Pyrimidin-4-Yl)Indoles. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibiletti, F.; Simonetti, M.; Nicholas, K.M.; Palmisano, G.; Parravicini, M.; Imbesi, F.; Tollari, S.; Penoni, A. One-Pot Synthesis of Meridianins and Meridianin Analogues via Indolization of Nitrosoarenes. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1280–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, A.S.; Merkul, E.; Rominger, F.; Müller, T.J.J. Concise Syntheses of Meridianins by Carbonylative Alkynylation and a Four-Component Pyrimidine Synthesis. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6951–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echalier, A.; Bettayeb, K.; Ferandin, Y.; Lozach, O.; Clément, M.; Valette, A.; Liger, F.; Marquet, B.; Morris, J.C.; Endicott, J.A.; et al. Meriolins (3-(Pyrimidin-4-Yl)-7-Azaindoles): Synthesis, Kinase Inhibitory Activity, Cellular Effects, and Structure of a CDK2/Cyclin A/Meriolin Complex. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud, F.; Alves, G.; Debiton, E.; Nauton, L.; Théry, V.; Durieu, E.; Ferandin, Y.; Lozach, O.; Meijer, L.; Anizon, F.; et al. Synthesis, Protein Kinase Inhibitory Potencies, and in Vitro Antiproliferative Activities of Meridianin Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4474–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Salfeena, C.T.F.; Ashitha, K.T.; Krishnan, G.V.; Jesmina, A.R.S.; Varghese, A.M.; Patil, S.A.; Kumar, B.N.S.D.; Sasidhar, B.S. Functionalized Pyrimidines from Alkynes and Nitriles: Application towards the Synthesis of Marine Natural Product Meridianin Analogs. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 6394–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.; Sun, W.-H.; Kruppa, M.; Sommer, G.A.; Müller, T.J.J. Molecules Concise Syntheses of Marine (Bis)Indole Alkaloids Meridianin C, D, F, and G and Scalaridine A via One-Pot Masuda Borylation-Suzuki Coupling Sequence. Molecules 2022, 27, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; García-García, E.; Straccia, M.; Comella-Bolla, A.; Miguez, A.; Masana, M.; Alberch, J.; Canals, J.M.; Rodríguez, M.J. Reduced Fractalkine Levels Lead to Striatal Synaptic Plasticity Deficits in Huntington’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sisqués, L.; Martín-Flores, N.; Masana, M.; Solana-Balaguer, J.; Llobet, A.; Romaní-Aumedes, J.; Canal, M.; Campoy-Campos, G.; García-García, E.; Sánchez-Fernández, N.; et al. RTP801 Regulates Motor Cortex Synaptic Transmission and Learning. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 342, 113755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendy, C.R.; Salcman, M. Bursts and Recurrences of Bursts in the Spike Trains of Spontaneously Active Striate Cortex Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1985, 53, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalban, E.; Al-Massadi, O.; Sancho-Balsells, A.; Brito, V.; de Pins, B.; Alberch, J.; Ginés, S.; Girault, J.A.; Giralt, A. Pyk2 in the Amygdala Modulates Chronic Stress Sequelae via PSD-95-Related Micro-Structural Changes. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sancho-Balsells, A.; García-García, E.; Flotta, F.; Chen, W.; Alberch, J.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Avila, C.; Giralt, A. Meridianins Inhibit GSK3β In Vivo and Improve Behavioral Alterations Induced by Chronic Stress. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100648
Sancho-Balsells A, García-García E, Flotta F, Chen W, Alberch J, Rodríguez MJ, Avila C, Giralt A. Meridianins Inhibit GSK3β In Vivo and Improve Behavioral Alterations Induced by Chronic Stress. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(10):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100648
Chicago/Turabian StyleSancho-Balsells, Anna, Esther García-García, Francesca Flotta, Wanqi Chen, Jordi Alberch, Manuel J. Rodríguez, Conxita Avila, and Albert Giralt. 2022. "Meridianins Inhibit GSK3β In Vivo and Improve Behavioral Alterations Induced by Chronic Stress" Marine Drugs 20, no. 10: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100648
APA StyleSancho-Balsells, A., García-García, E., Flotta, F., Chen, W., Alberch, J., Rodríguez, M. J., Avila, C., & Giralt, A. (2022). Meridianins Inhibit GSK3β In Vivo and Improve Behavioral Alterations Induced by Chronic Stress. Marine Drugs, 20(10), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100648







