A Broad-Specificity Chitinase from Penicillium oxalicum k10 Exhibits Antifungal Activity and Biodegradation Properties of Chitin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Chitinase-Producing Strains
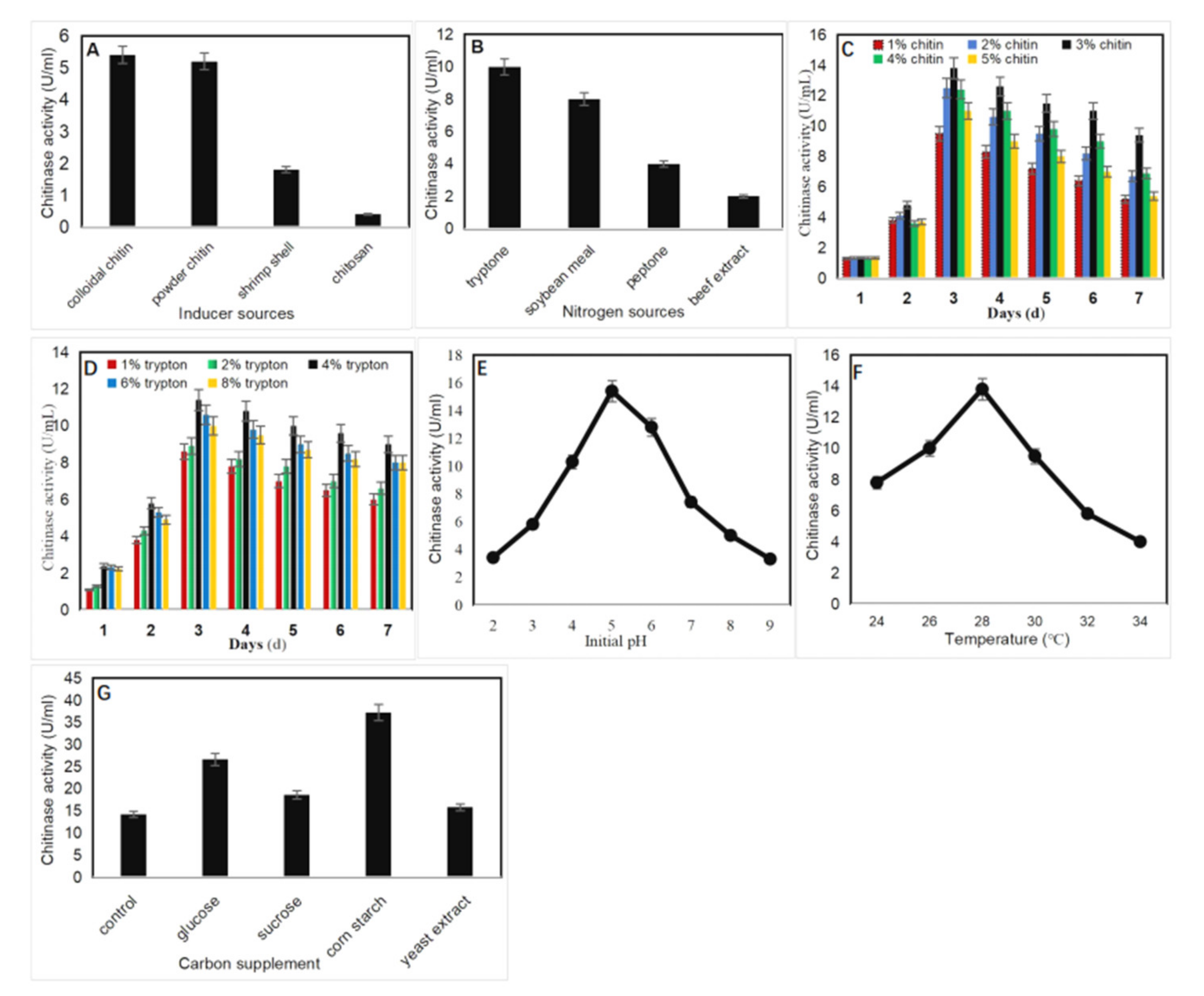
2.2. Optimization of Culture Conditions for Chitinase Production
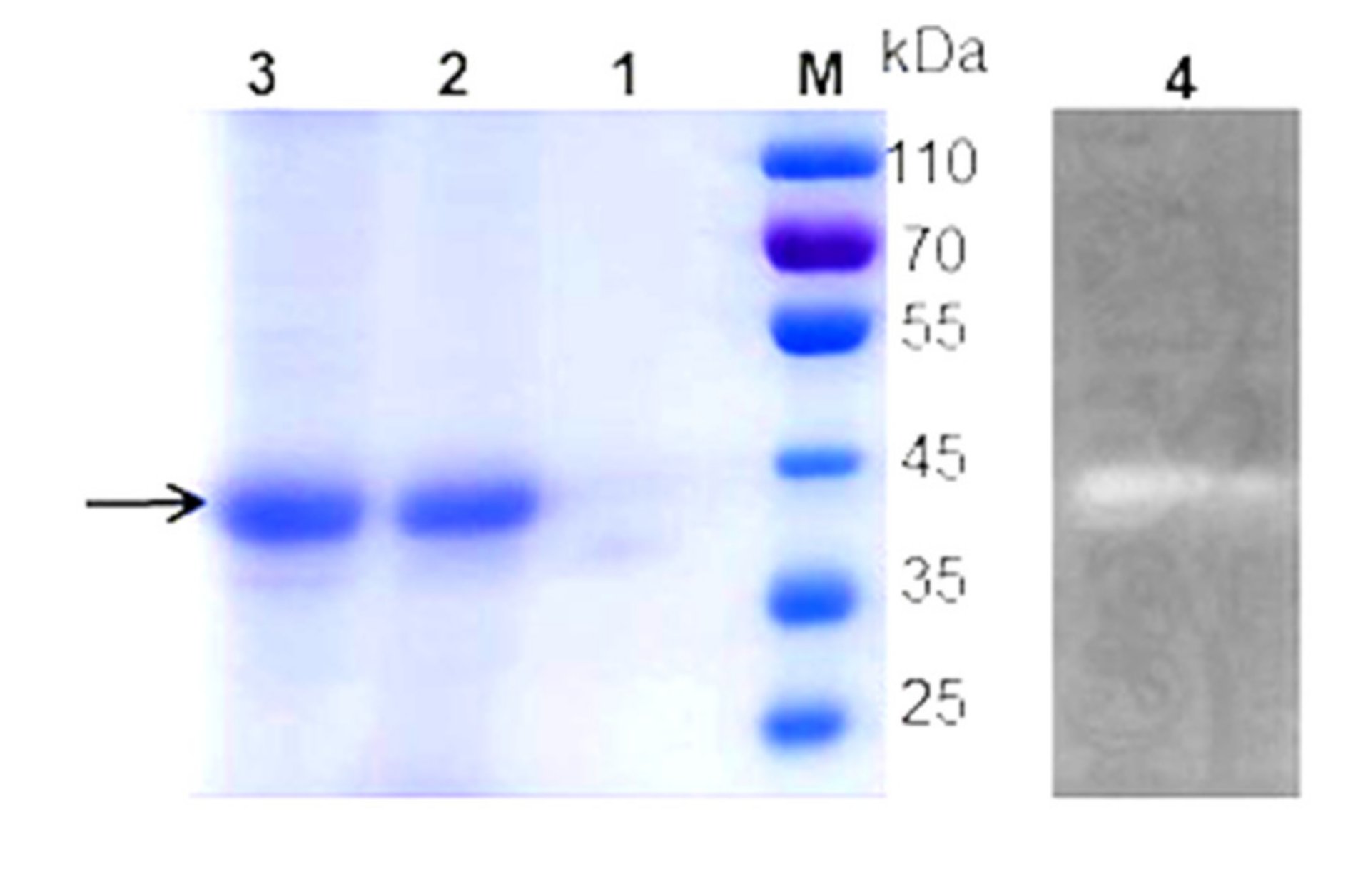
2.3. Chitinase Purification
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Zymography
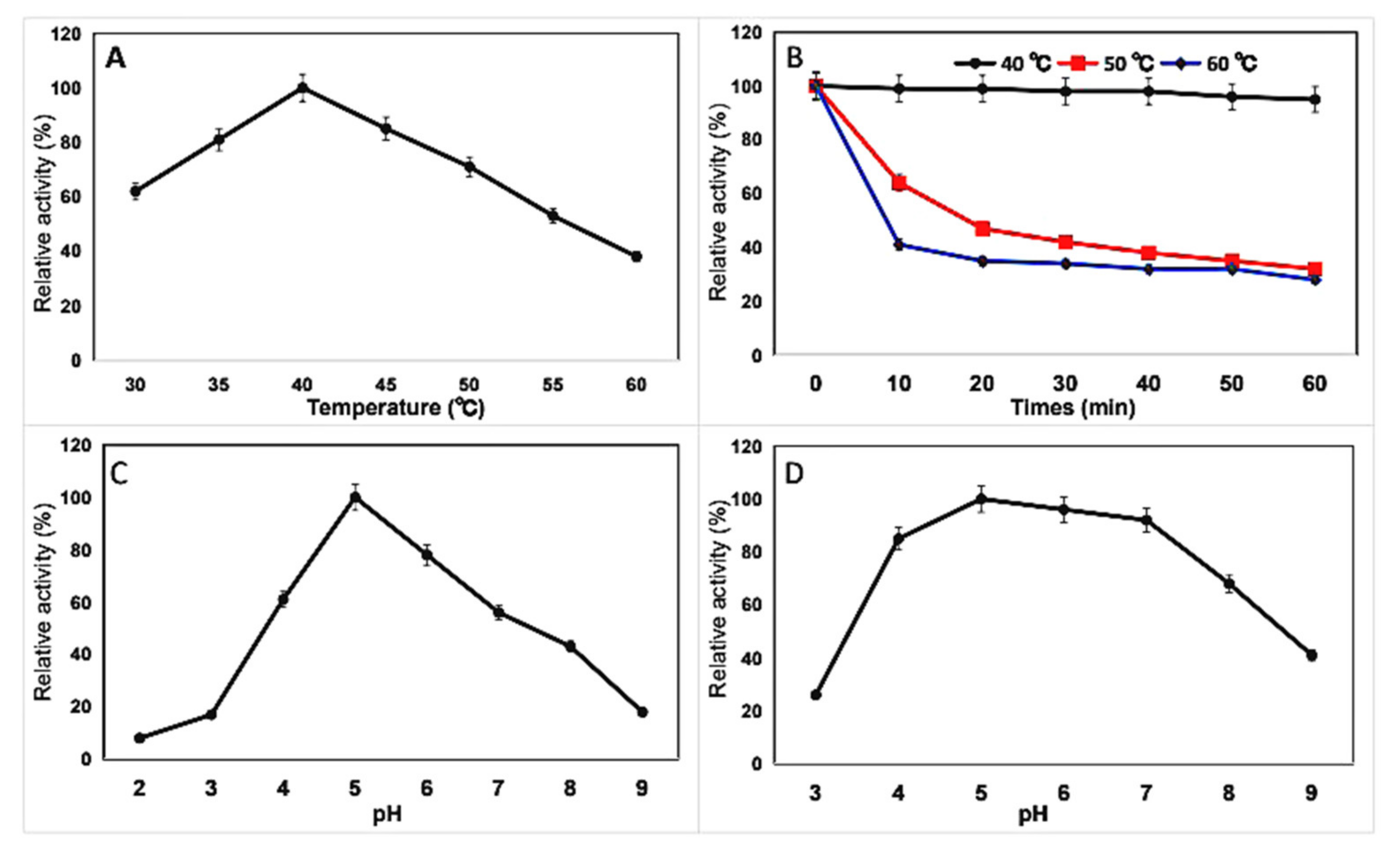
2.5. Effects of Temperature and pH on Chitinase and Kinetic Parameters
2.6. Substrate Specificity of k10 Chitinase
2.7. Effects of Metal Ions and Chemical Reagents on Enzyme Activity
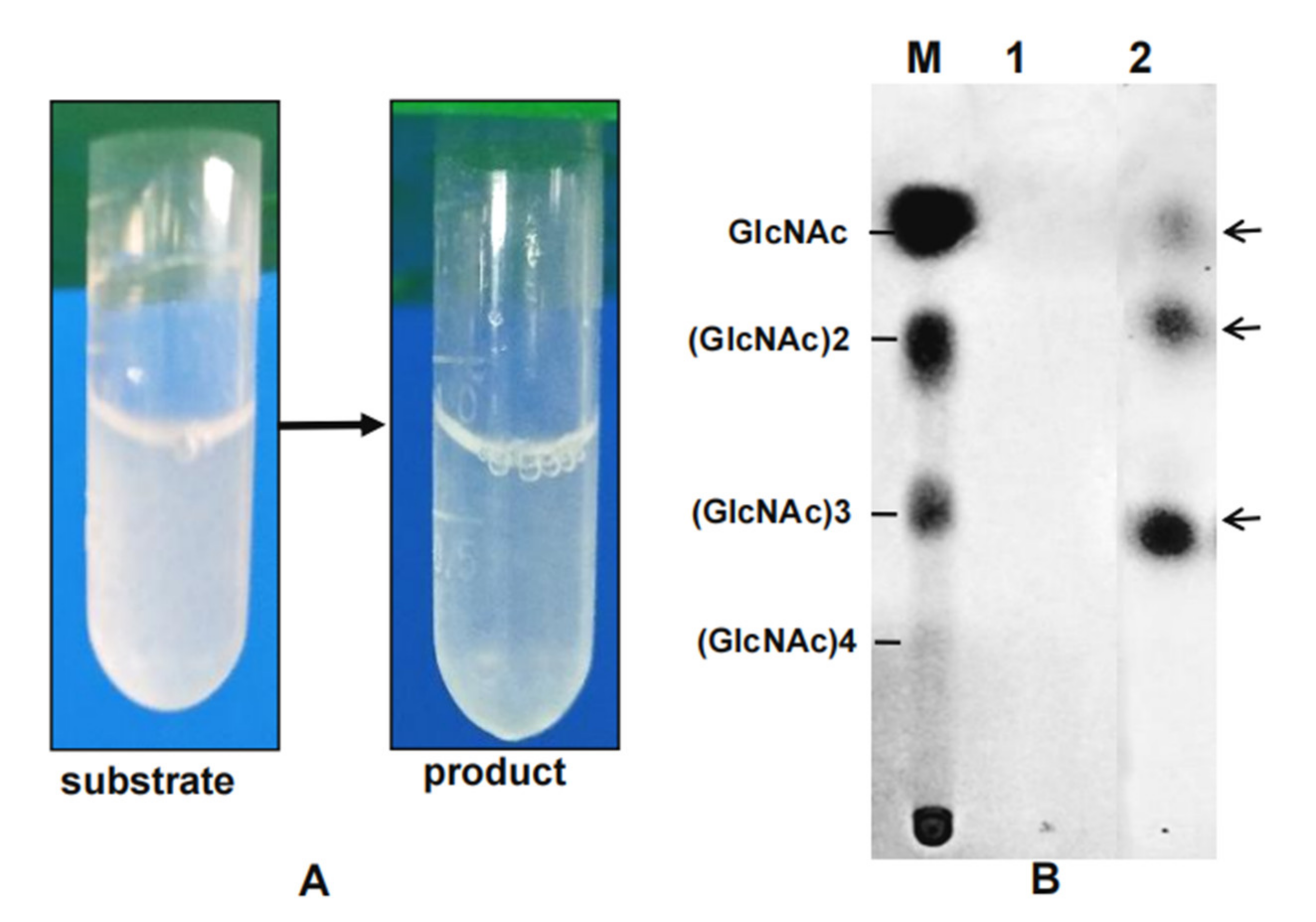
2.8. Chitooligosaccharides (COSs) Preparation and Analysis of End Products
2.9. Antifungal Activity of Chitinase
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Colloidal Chitin and Ultrafine Chitin
3.3. Screening, Cultivation, and Identification of the Microbial Strain
3.4. Antagonistic Activity Evaluation of Strain
3.5. Determination of Chitinase Activity and Oligosaccharide Content
3.6. Optimization of Chitinase Production
3.7. Enzyme Purification
3.8. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Zymography
3.9. Effects of Temperature and pH on Chitinase Activity and Stability
3.10. Kinetic Analysis of k10 Chitinase
3.11. Substrate Specificity Determination
3.12. Effects of Metal Ions and Chemical Reagents on Enzyme Activity
3.13. Preparation of COSs
3.14. Thin Layer Chromatography Analysis of end Products of Hydrolysis
3.15. Assay for Antifungal Activity of Chitinase
3.16. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacombe-Harvey, M.E.; Brzezinski, R.; Beaulieu, C. Chitinolytic functions in actinobacteria: Ecology, enzymes, and evolution. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7219–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.P.; Almeida, B.C.; Colwell, R.R.; Rivera, I.N.G. The importance of chitin in the marine environment. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Kaur, S.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M. Green synthesis approach: Extraction of chitosan from fungus mycelia. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 33, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, Y.K.; Lampe, J.W.; Sung, M.K. Effects of dietary supplementation of glucosamine sulfate on intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of experimental colitis. J. Gastroen. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.K.; Shen, C.R.; Liu, C.L. N-acetylglucosamine: Production and applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2493–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalirfardouei, R.; Karimi, G.; Jamialahmadi, K. Molecular mechanisms and biomedical applications of glucosamine as a potential multifunctional therapeutic agent. Life Sci. 2016, 152, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudan, S.; Eksittikul, T.; Pichyangkura, R.; Park, R.D. Preparation of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and N, N’-acetylchitobiose by enzymatic hydrolysis of chitin with crude chitinases. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.; Baek, K.; Bae, S.S.; Jung, J. Identification and characterization of a marine-derived chitinolytic fungus, Acremonium sp. YS2-2. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; Du, G.; Liu, L. Molecular engineering of chitinase from Bacillus sp. DAU101 for enzymatic production of chitooligosaccharides. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2019, 124, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.A.; Moon, C.; Seo, D.J.; Jung, W.J. Expression and degradation patterns of chitinase purified from Xuehuali (Pyrus bretschneiderilia) pollen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Kumar, M.; Kumari, P.; Mahapatro, G.K.; Sarin, N.B. Novel insecticidal chitinase from the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus nematophila. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, D.; Liu, T.; Yang, Q. Production of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine from mycelial waste by a combination of bacterial chitinases and an insect Nacetyl-D-glucosaminidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6738–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, E.C.; Tuveng, T.R.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G.; Eijsink, V.G.; Gardner, J.G. Systems analysis of the family glycoside hydrolase family 18 enzymes from Cellvibrio japonicus characterizes essential chitin degradation functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3849–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Park, G.C.; Kim, K.S. Antagonistic evaluation of Chromobacterium sp. JH7 for biological control of ginseng root rot caused by Cylindrocarpon destructans. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.J.; Park, R.D. Bioproduction of chitooligosaccharides: Present and perspectives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5328–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, G.J.; Hall, R. Index of plant hosts of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1994, 16, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Lee, M.C.; Harman, G.E. The Biocontrol Activity of Chromobacterium sp. Strain C-61 against Rhizoctonia solani Depends on the Productive Ability of Chitinase. Plant Pathol. J. 2005, 21, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moon, C.; Seo, D.J.; Song, Y.S.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Jung, W.J. Antifungal activity and patterns of N-acetyl-chitooligosaccharide degradation via chitinase produced from Serratia marcescens PRNK-1. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Seo, D.J.; Jung, W.J. Identification, purification, and expression patterns of chitinase from psychrotolerant Pedobacter sp. PR-M6 and antifungal activity in vitro. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeed, Y.; Atrash, F.; Naffaa, W. Partial purification and characterization of chitinase produced by Bacillus licheniformis B307. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc, N.H.; Huy, N.D.; Quang, H.T.; Lan, T.T.; Ha, T.T.T. Characterisation and antifungal activity of extracellular chitinase from a biocontrol fungus, Trichoderma asperellum PQ34. Mycology 2020, 11, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbaz, U.; Yu, X. Cloning, isolation, and characterization of novel chitinase-producing bacterial strain UM01 (Myxococcus fulvus). J. Gen. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K.; Sadaiappan, B.; Aruni, W.; Kumarappan, A.; Thirunavukarasu, R.; Srinivasan, G.P.; Bharathi, S.; Nainangu, P.; Renuga, P.S.; Elamaran, A.; et al. Bioconversion of chitin and concomitant production of chitinase and N-acetylglucosamine by novel Achromobacter xylosoxidans isolated from shrimp waste disposal area. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhat, A.A.-T.; George, S.I. Anticancer and antifungal efficiencies of purified chitinase produced from Trichoderma viride under submerged fermentation. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shivalee, A.; Lingappa, K.; Mahesh, D. Influence of bioprocess variables on the production of extracellular chitinase under submerged fermentation by Streptomyces pratensis strain KLSL55. J. Gen. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouacem, K.; Laribi-Habchi, H.; Mechri, S.; Hacenea, H.; Jaouadi, B.; Bouanane-Darenfed, A. Biochemical characterization of a novel thermostable chitinase from Hydrogenophilus hirschii strain KB-DZ44. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Brar, A.; Vivekanand, V.; Pareek, N. Production of chitinase from thermophilic Humicola grisea and its application in production of bioactive chitooligosaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abassi, S.; Emtiazi, G.; HosseiniAbari, A.; Kim, B.G. Chitooligosaccharides and Thermostable Chitinase against Vulvovaginal Candidiasis and Saprophyte Fungi: LC Mass Studies of Shrimp Shell Fermentation by Bacillus altitudinis. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Wu, P.L. Gene Cloning, Characterization, and Molecular Simulations of a Novel Recombinant Chitinase from Chitinibacter Tainanensis CT01 Appropriate for Chitin Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Polymers 2020, 12, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, A.; Han, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, Q. A potent chitinase from Bacillus subtilis for the efficient bioconversion of chitin-containing wastes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, J.; Secundo, F.; Xin, G.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Cloning, characterization and substrate degradation mode of a novel chitinase from Streptomyces albolongus ATCC 27414. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, A.J.; Silva, C.F.; Sousa, J.S.; Júnior, J.E.M.; Freire, J.E.; Sousa, B.L.; Lobo, M.D.; Monteiro-Moreira, A.C.; Grangeiro, T.B. A thermostable chitinase from the antagonistic Chromobacterium violaceum that inhibits the development of phytopathogenic fungi. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2019, 126, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; Yu, M.; Wu, Y.H.; Ran, L.M.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, X.H. Two Highly Similar Chitinases from Marine Vibrio Species have Different Enzymatic Properties. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.K.; Hu, Y.J.; Ng, T.B.; Guo, B.Q.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Ye, X.Y. Expression and biochemical characterization of a novel chitinase ChiT-7 from the metagenome in the soil of a mangrove tidal flat in China. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Liang, Y.; Yan, R.; Xu, X.; Lin, J. Expression and characterization of a chitinase from Serratia marcescens. Protein Expres. Purif. 2020, 171, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankiewicz, U.; Baranowski, B.; Swiontek Brzezinska, M.; Frak, M. Purifcation, characterization and cloning of a chitinase from Stenotrophomonas rhizophila G22. 3 Biotech. 2020, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.S.; Ghormade, V.; Deshpande, M.V. Chitinolytic enzymes: An exploration. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.N.; Yu, K.; Liu, H.Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Li, D.C. Two novel thermostable chitinase genes from thermophilic fungi: Cloning, expression and characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5546–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.J.; Shi, D.; Mao, H.H.; Li, Z.W.; Liang, S.; Ke, Y.; Luo, X.C. Heterologous expression and characterization of an antifungal chitinase (Chit46) from Trichoderma harzianum GIM 3.442 and its application in colloidal chitin conversion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmani, K.L.; Bouacem, K.; Ouelhadj, A.; Yahiaoui, M.; Bechami, S.; Mechri, S.; Jabeur, F.; Menguellet, K.T.A.; Jaouadi, B. Biochemical and molecular characterization of an acido-thermostable endo-chitinase from Bacillus altitudinis KA15 for industrial degradation of chitinous waste. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 495, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardozo, F.A.; Facchinatto, W.M.; Colnago, L.A.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Pessoa, A. Bioproduction of N-acetyl-glucosamine from colloidal α-chitin using an enzyme cocktail produced by Aeromonas caviae CHZ306. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aounallah, M.A.; Slimene-Debez, I.B.; Djebali, K.; Gharbi, D.; Hammami, M.; Azaiez, S.; Limam, F.; Tabbene, O. Enhancement of Exochitinase Production by Bacillus licheniformis AT6 Strain and Improvement of N-Acetylglucosamine Production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 650–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, T.S.; Madhuprakash, J.; Podile, A.R. Chitinase-E from Chitiniphilus shinanonensis generates chitobiose from chitin flakes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uedaa, M.; Shioyamaa, T.; Nakadoia, K.; Nakazawaa, M.; Sakamotoa, T.; Iwamotob, T.; Sakaguchi, M. Cloning and expression of a chitinase gene from Eisenia fetida. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrzheshch, P. Steady-state kinetics of bifunctional enzymes. Taking into account kinetic hierarchy of fast and slow catalytic cycles in a generalized model. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, M.; Laribi-Habchi, H.; Bouacem, K.; Asmani, K.L.; Mechri, S.; Harir, M.; Bendif, H.; AEl Fertas, R.; Jaouadi, B. Purification and biochemical characterization of a new organic solventtolerant chitinase from Paenibacillus timonensis strain LK-DZ15 isolated from the Djurdjura Mountains in Kabylia, Algeria. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 483, 107747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Wang, N.N.; He, J.; Li, Y.F.; Gao, X.N.; Huang, L.L.; Yan, X. Expression and characterization of a novel chitinase with antifungal activity from a rare actinomycete, Saccharothrix yanglingensis Hhs.015. Protein Expres. Purif. 2018, 143, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.N.; Abd el Aty, A.A.; Darwish, D.A.; Abdel Wahab, W.A.; Mostafa, F.A. Purification, physicochemical and thermodynamic studies of antifungal chitinase with production of bioactive chitosan-oligosaccharide from newly isolated Aspergillus griseoaurantiacus KX010988. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 107, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Song, Y.S.; Seo, D.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Jung, W.J. Antifungal activity and expression patterns of extracellular chitinase and beta-1,3-glucanase in Wickerhamomyces anomalus EG2 treated with chitin and glucan. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishad, K.S.; Rebello, S.; Shabanamol, P.S.; Jisha, M.S. Biocontrol potential of Halotolerant bacterial chitinase from high yielding novel Bacillus Pumilus MCB-7 autochthonous to mangrove ecosystem. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2017, 137, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.K.; Hur, J.Y.; Kim, Y.C. Purification and Characterization of a Major Extracellular Chitinase from a Biocontrol Bacterium, Paenibacillus elgii HOA73. Plant Pathol. J. 2017, 33, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.; Yang, S.H. Characterization of a chitinase from Salinivibrio sp. BAO-1801 as an antifungal activity and a biocatalyst for producing chitobiose. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, B.M.; Dunn, M.F.; Navarro, K.G.; Melendez, F.H.; Ortiz, M.H.; Guevara, S.E.; Palacios, G.H. Antifungal performance of extracellular chitinases and culture supernatants of Streptomyces galilaeus CFFSUR-B12 against Mycosphaerella fijiensis Morelet. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Yang, C.; Liang, X.; Li, L. Identification and characterization of a novel chitinase with antifungal activity from ‘Baozhu’ pear (Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim.). Food Chem. 2016, 196, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhya, C.; Adapa, L.K.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Binod, P.; Szakacs, G.; Pandey, A. Extracellular chitinase production by Trichoderma harzianum in submerged fermentation. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 44, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V.; Agarwal, P.; Saroj, S.; Singh, R.P. Bioconversion to chitosan: A two stage process employing chitin deacetylase from Penicillium oxalicum SAEM-51. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuli, P.E.; Suhartono, M.T.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hwang, J.K.; Pyun, Y.R. Characteristics of thermostable chitinase enzymes from the indonesian Bacillus sp. 13.26. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2004, 35, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.A.; Xiao, X.; Hafeez, F.Y.; Gai, Y.; Wang, F. Molecular characterization of the modular chitin binding protein Cbp50 from Bacillus thuringiensis serovar konkukian. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2011, 100, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Steps | Total Protein (mg) | Total Activity (U) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Purification Fold | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture Supernatant | 265 | 37,000 | 139.62 | 1 | 100 |
| (NH4)2SO4 Precipitate | 220 | 33,750 | 153.41 | 1.1 | 83 |
| Sephadex Column Purified | 190 | 30,800 | 162.1 | 1.16 | 72 |
| Substrates | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Colloidal Chitin | 100.0 ± 1.2 |
| Powder Chitin | 42.6 ± 0.8 |
| Ultrafine Chitin | 58.3 ± 1.4 |
| Shrimp Shell | 15.7 ± 1.0 |
| 90% Deacetylated Chitosan | 11.4 ± 0.6 |
| Cellulose | 0 |
| Additives | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Control | 100.0 ± 1.8 |
| Zinc (Zn2+) | 120.5 ± 3.1 |
| Potassium (K+) | 185.6 ± 4.2 |
| Sodium (Na+) | 101.9 ± 1.8 |
| Calcium (Ca2+) | 95.3 ± 2.7 |
| Magnesium (Mg2+) | 88.8 ± 3.5 |
| Silver (Ag+) | 65.9 ± 2.6 |
| Iron (Fe2+) | 63.9 ± 3.4 |
| Copper (Cu2+) | 40.3 ± 2.3 |
| SDS | 82.7 ± 3.9 |
| EDTA | 78.2 ± 3.6 |
| Carbamide | 49.5 ± 1.8 |
| β-Mercaptoethanol | 75.8 ± 3.0 |
| Chitinase Sources | Phytopathogenic Fungus | References |
|---|---|---|
| P. oxalicum k10 | S. sclerotiorum and M. circinelloides | This study |
| A. griseoaurantiacus | F. solani | [48] |
| T. harzianum | B. cinerea | [39] |
| T. viride | F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici race 3 | [24] |
| W. anomalus EG2 | F. oxysporum KACC 40032 and R. solani KACC 40111 | [49] |
| B. altitudinis | V. Candidiasis and S. Fungi | [28] |
| B. Pumilus MCB-7 | A. flavus, A. niger, A. fumigatus, C. hydrophila, and F. oxysporum | [50] |
| P. elgii HOA73 | Cladosporium, B. cinerea | [51] |
| Salinivibrio sp. BAO-1801 | F. oxysporum and R. solani | [52] |
| S. galilaeus CFFSUR-B12 | M. fijiensis Morelet | [53] |
| P. ussuriensis Maxim | F. oxysporum, F. solani, R. solani, and T. viride | [54] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.-H.; Fu, X.; Yan, X.-Y.; Peng, W.-F.; Kang, L.-X. A Broad-Specificity Chitinase from Penicillium oxalicum k10 Exhibits Antifungal Activity and Biodegradation Properties of Chitin. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070356
Xie X-H, Fu X, Yan X-Y, Peng W-F, Kang L-X. A Broad-Specificity Chitinase from Penicillium oxalicum k10 Exhibits Antifungal Activity and Biodegradation Properties of Chitin. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(7):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070356
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xing-Huan, Xin Fu, Xing-Yu Yan, Wen-Fang Peng, and Li-Xin Kang. 2021. "A Broad-Specificity Chitinase from Penicillium oxalicum k10 Exhibits Antifungal Activity and Biodegradation Properties of Chitin" Marine Drugs 19, no. 7: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070356
APA StyleXie, X.-H., Fu, X., Yan, X.-Y., Peng, W.-F., & Kang, L.-X. (2021). A Broad-Specificity Chitinase from Penicillium oxalicum k10 Exhibits Antifungal Activity and Biodegradation Properties of Chitin. Marine Drugs, 19(7), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070356





